-
 Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Checkpoint Inhibition in Clear Cell Ovarian Carcinoma: Bridging Tumor Biology and Clinical Application in Immunotherapy
Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Checkpoint Inhibition in Clear Cell Ovarian Carcinoma: Bridging Tumor Biology and Clinical Application in Immunotherapy -
 The Central Nervous System Modulatory Activities of N-Acetylcysteine: A Synthesis of Two Decades of Evidence
The Central Nervous System Modulatory Activities of N-Acetylcysteine: A Synthesis of Two Decades of Evidence -
 JUNB and JUND in Urological Cancers: A Literature Review
JUNB and JUND in Urological Cancers: A Literature Review -
 Physical Activity and Metabolic Disorders—What Does Gut Microbiota Have to Do with It?
Physical Activity and Metabolic Disorders—What Does Gut Microbiota Have to Do with It? -
 The Role of miRNAs and Extracellular Vesicles in Adaptation After Resistance Exercise: A Review
The Role of miRNAs and Extracellular Vesicles in Adaptation After Resistance Exercise: A Review
Journal Description
Current Issues in Molecular Biology
Current Issues in Molecular Biology
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal on molecular biology, published monthly online by MDPI (from Volume 43 Issue 1-2021).
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PMC, PubMed, Embase, CAPlus / SciFinder, FSTA, AGRIS, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names are published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
3.0 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.2 (2024)
Latest Articles
Epigenetic Remodeling in Thyroid Cancer: New Dimensions of Targeted Therapy Through lncRNA Modulation
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 863; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100863 (registering DOI) - 18 Oct 2025
Abstract
Thyroid carcinomas are phenotypically heterogeneous malignancies. Advances in molecular and cellular technologies have revealed genetic, epigenetic, and nongenetic factors underlying this heterogeneity. Our study aimed to assess the impact of single and combined treatments with anticancer agents (Carboplatin, Doxorubicin, Paclitaxel, Avastin), natural compounds
[...] Read more.
Thyroid carcinomas are phenotypically heterogeneous malignancies. Advances in molecular and cellular technologies have revealed genetic, epigenetic, and nongenetic factors underlying this heterogeneity. Our study aimed to assess the impact of single and combined treatments with anticancer agents (Carboplatin, Doxorubicin, Paclitaxel, Avastin), natural compounds (Quercetin), and epigenetic modulators (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid and 5-Azacytidine) on the expression of long noncoding RNAs, methylation regulators, and functional features in the human thyroid cancer cell line K1. Methods: Treated and untreated K1 cells were used throughout experiments to evaluate the drug-induced cytotoxicity, apoptosis, cell cycle distribution, cytokine release, gene expression, and global DNA methylation levels. Results: Some single- and combined-drug treatments modulated both cell cycle progression and apoptotic events, demonstrating anti-tumor activity of the tested compounds. Gene expression analysis showed treatment-specific regulation of target genes and lncRNAs, including both upregulation and downregulation across different drug combinations. All treatments resulted in increased global DNA methylation levels compared to the untreated controls. Several combinations significantly upregulated DNMT1 and DNMT3B, while concomitantly decreased EZH2 levels. Conclusions: These coordinated epigenetic changes highlight the therapeutic potential of combining epigenetic modulators with chemotherapeutic agents, suggesting a strategy to prevent or reverse treatment resistance and improve outcomes in thyroid cancer patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Functions of Long Non-Coding RNAs: Implications for Diseases and Therapy)
Open AccessEditorial
Editorial for Special Issue “Mental Disorder: Focus on Pathogenesis to Treatment”
by
Fabrizio Bella, Cecilia Chiarenza and Carmen Concerto
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 862; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100862 (registering DOI) - 18 Oct 2025
Abstract
In recent years, advances in molecular biology have enabled the investigation of previously inaccessible mechanisms at the cellular and immunological levels that underlie the pathogenesis of numerous conditions affecting the central nervous system [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mental Disorder: Focus on Pathogenesis to Treatment)
Open AccessArticle
Contributions of Retinoid Signaling to Autism-like Behaviors Induced by Early Postnatal Lead Exposure in the Mouse Cerebellum
by
Xiaochun Xia, Xulan Zhou, Zihan Ma, Li Liu, Yaqi Wang, Yongli Wu, Ying Zhang and Juan Wang
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 861; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100861 (registering DOI) - 18 Oct 2025
Abstract
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a group of neurodevelopmental dysfunctions characterized by a heterogeneous etiology that involves gene–environment interactions. Early postnatal lead (Pb) exposure has been found to be associated with the etiology of ASD, but the mechanisms remain unclear. The present study
[...] Read more.
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a group of neurodevelopmental dysfunctions characterized by a heterogeneous etiology that involves gene–environment interactions. Early postnatal lead (Pb) exposure has been found to be associated with the etiology of ASD, but the mechanisms remain unclear. The present study aims to investigate the effects of early Pb exposure on the emergence of ASD-like behaviors in offspring and to evaluate its potential relationship with morphological changes and underlying mechanisms in the cerebellum. The study established a mouse model to study early postnatal Pb exposure and examined ASD-like behaviors through the open field test, novel object recognition test, marble burying test, and three-chamber social test. Quantification of Pb levels was performed in cerebellar tissue, examination of Purkinje cell morphology was carried out, and identification of differential protein expression was conducted using TMT-based quantitative proteomics. The study revealed that the offspring of Pb-exposed mice showed significant social deficits, increased repetitive behaviors, and cognitive impairments. The cerebellum showed both elevated Pb levels and a reduction in Purkinje cells. Proteomic analysis identified 45 proteins that were differentially expressed, showing disruption in the retinoid signaling pathway. These findings demonstrate that early postnatal Pb exposure leads to ASD traits and that retinoid signaling may be a key pathway in the cerebellum, at least in part.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Biochemistry, Molecular and Cellular Biology)
►▼
Show Figures
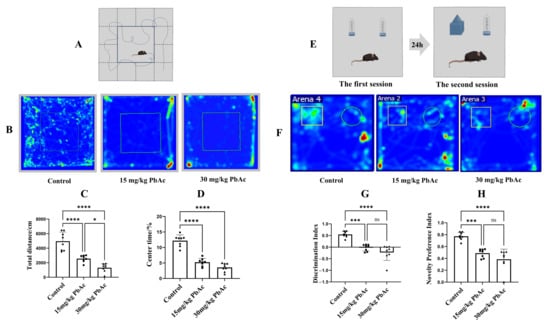
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
In Silico Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Analysis of Rosemary-Derived Compounds as Potential HSP90 Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy
by
Radhia Mazri, Mebarka Ouassaf, Afaf Zekri, Shafi Ullah Khan, Kannan R. R. Rengasamy and Bader Y. Alhatlani
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 860; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100860 (registering DOI) - 18 Oct 2025
Abstract
Cancer remains a major global health challenge, emphasizing the need for new and effective therapies. This study investigates the anticancer potential of bioactive compounds from rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) using an integrative network pharmacology and computational approach. Twelve phytochemicals with favorable pharmacological profiles, optimal
[...] Read more.
Cancer remains a major global health challenge, emphasizing the need for new and effective therapies. This study investigates the anticancer potential of bioactive compounds from rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) using an integrative network pharmacology and computational approach. Twelve phytochemicals with favorable pharmacological profiles, optimal pharmacokinetics, and acceptable toxicological properties were evaluated, revealing 178 putative cancer-related targets. Protein–protein interaction (PPI) analysis highlighted ten key genes—EGFR, ESR1, HIF1A, HSP90AA1, MAPK1, BCL2, STAT3, TP53, CASP3, and SRC—implicated in the progression of various cancers, including breast, colorectal, liver, and lung tumors. Functional enrichment analysis demonstrated their involvement in multiple cancer-associated pathways. Among these, HSP90AA1 emerged as a critical target. Molecular docking revealed Rosmanol, Chlorogenic acid, and Carnosol as the most promising HSP90AA1 binders with strong predicted affinities. ADMET profiling confirmed their excellent drug-likeness and safety profiles, while molecular dynamics simulations validated the stability of the compound–protein complexes, further supporting their potential as HSP90 inhibitors. These findings suggest that rosemary-derived compounds may represent valuable candidates for anticancer drug development, though experimental validation is required to confirm their therapeutic efficacy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Bioinformatics Approaches to Biomedicine)
Open AccessArticle
The Linkage Between Inflammation and the Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
by
Lucy Baldeón-Rojas, Valeria Alulema, Francisco Barrera-Guarderas, Diana Aguirre-Villacís, Cristina Cañadas-Herrera, Ricardo Bedón-Galarza, Francisco Pérez-Tasigchana and Jorge Pérez-Galarza
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 859; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100859 - 17 Oct 2025
Abstract
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) is a chronic metabolic disorder in which inflammation plays a central role in its onset, progression, and complications. Identifying reliable biomarkers is essential to improve risk prediction, disease monitoring, and early intervention. Methods: A total of 169 Ecuadorian
[...] Read more.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) is a chronic metabolic disorder in which inflammation plays a central role in its onset, progression, and complications. Identifying reliable biomarkers is essential to improve risk prediction, disease monitoring, and early intervention. Methods: A total of 169 Ecuadorian participants were stratified into four clinical groups: non-diabetic controls (NDC), controlled T2D (C-T2D), uncontrolled T2D (NC-T2D), and diabetic kidney disease (DKD). Circulating levels of cytokines (IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α), adipokines (leptin, adiponectin), and PBMC-derived microRNAs (miR-146a, miR-155) were quantified. Associations with disease stage were evaluated using ROC curve analysis and logistic regression. Results: Leptin showed the strongest association with T2D (OR = 13.76, 95% CI: 6.47–29.26), followed by IL-8 (OR = 6.73, 95% CI: 3.30–13.70) and IL-6 (OR = 4.43, 95% CI: 2.26–8.97). Adiponectin distinguished NC-T2D from DKD (OR = 4.15, 95% CI: 1.77–9.71), underscoring its potential as an indicator of renal complications. Interestingly, TNF-α levels declined across disease stages, possibly reflecting subclinical inflammation in Ecuadorian NDC with high rates of obesity and dyslipidemia. PBMC-derived miR-146a was upregulated in T2D patients, contrasting with prior serum-based studies and emphasizing the importance of compartment-specific analysis. miR-155 was elevated in C-T2D, suggesting a compensatory immune-regulatory mechanism that diminishes with poor glycemic control and advanced disease. Conclusions: Inflammatory cytokines, adipokines, and microRNAs act in distinct yet complementary ways in T2D. Leptin, IL-6, and IL-8 emerge as strong predictors of disease, while miR-146a and miR-155 provide additional insight into immune-inflammatory regulation. Integrated biomarker panels may enhance patient stratification and support personalized monitoring of T2D progression.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Molecular Medicine)
Open AccessArticle
Pennisetum glaucum (L.) Oral Supplementation Mitigates Multi-Organic Dysfunction Associated with Carcinogenesis in HPV16-Transgenic Mice
by
Paula A. Oliveira, Latifa Hajri, Armando V. Pinto Moreno, Carlos E. Dias Santos, Haissa O. Brito, Margarida M. S. M. Bastos, Rui Medeiros, Soumaya Ghodbane, Mohamed Ammari, Rui M. Gil da Costa and Ana I. Faustino-Rocha
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 858; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100858 - 17 Oct 2025
Abstract
Cancers induced by human papillomavirus are often associated with systemic inflammation and cachexia. This study aimed to determine the interference of Pennisetum glaucum oral supplementation over multi-organic dysfunction in HPV16-transgenic mice. The experimental groups included (1) wildtype (WT) mice with standard diet, (2)
[...] Read more.
Cancers induced by human papillomavirus are often associated with systemic inflammation and cachexia. This study aimed to determine the interference of Pennisetum glaucum oral supplementation over multi-organic dysfunction in HPV16-transgenic mice. The experimental groups included (1) wildtype (WT) mice with standard diet, (2) WT mice with 36% Pennisetum, (3) transgenic mice with standard diet, (4) transgenic mice with 29% Pennisetum, and (5) transgenic mice with 36% Pennisetum. During the 4-week experimental protocol, body weight, food and water intake, and humane endpoints were recorded. At sacrifice, blood and tissue samples were collected for analysis. Oral supplementation with millet was shown to be safe and well tolerated by both WT and transgenic mice, with no adverse effects on behavior, food or water intake, or general animal welfare. In HPV16-transgenic animals, millet supplementation was associated with an improved health status, reduced serum glucose levels, enhanced antioxidant responses, and a notable reduction in the severity of HPV-induced skin and organ lesions. Overall, Pennisetum glaucum was safe under these experimental conditions and is a promising functional food for patients suffering from systemic paraneoplastic syndromes. Longer exposure periods and doses should be evaluated experimentally before proceeding to clinical trials of Pennisetum-containing diets.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Molecular Pharmacology)
►▼
Show Figures
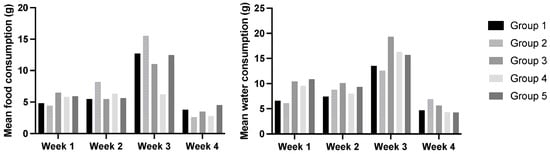
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Biphasic Slc2a4 Gene Expression in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes in Response to Treatment with Low and High Concentrations of Daidzein and Genistein
by
Karen Cristina Rego Gregorio, Caroline Pancera Laurindo, Helayne Soares Freitas, Maristela Mitiko Okamoto, Patricia Monteiro Seraphim and Ubiratan Fabres Machado
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 857; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100857 - 17 Oct 2025
Abstract
Daidzein and genistein are abundant in soy-rich foods, whose supplementation has been proposed to have beneficial effects on several diseases, including diabetes mellitus and obesity. 17β-estradiol (E2) enhances the expression of the Slc2a4 gene and GLUT4 protein in adipose tissue, increasing glucose consumption
[...] Read more.
Daidzein and genistein are abundant in soy-rich foods, whose supplementation has been proposed to have beneficial effects on several diseases, including diabetes mellitus and obesity. 17β-estradiol (E2) enhances the expression of the Slc2a4 gene and GLUT4 protein in adipose tissue, increasing glucose consumption and contributing to glycemic control. We investigated, in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, the effect of low and high doses of daidzein and genistein on Slc2a4/GLUT4 expression and the participation of estrogen receptors 1/2 (ESR1/ESR2) in the regulations observed. Differentiated adipocytes were cultivated, for 24 h, in the presence of 17β-estradiol (E2, 10 nM), daidzein (10 nM–150 μM) and genistein (10 nM–50 μM), with or without ESR1 or ESR2 antagonists. Daidzein/genistein at a low dose (10 nM) increased Slc2a4/GLUT4 expression (50%, p < 0.05), an effect abrogated by an ESR1 antagonist, mimicking the effect of E2. However, maximal doses of daidzein and genistein reduced, in a ESR1-mediated mechanism, the expression of mRNA (by 47% and 60%, p < 0.001) and the protein (by 29% and 36%, p < 0.01), respectively, for daidzein and genistein, as compared to E2. In conclusion, in adipocytes, daidzein and genistein have a biphasic ESR1-mediated effect: while low concentrations increase the expression of Slc2a4/GLUT4, high concentrations decrease it, the former predisposing to an adipogenic effect, the latter to a diabetogenic condition.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Insights into Food-Derived Natural Products and Their Biological Activities—2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
GPX4 Inhibition Enhances the Pro-Oxidant and ER Stress Effects of Tempol in Colon and Gastric Cancer Cell Lines
by
Gorkem Ozdemir and Halil Mahir Kaplan
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 856; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100856 - 16 Oct 2025
Abstract
Tempol, a synthetic nitroxide, exhibits dual antioxidant and pro-oxidant activity, requiring millimolar concentrations to induce oxidative stress, which limits its therapeutic use. Glutathione Peroxidase 4 (GPX4) is a critical lipid peroxidase that prevents ferroptosis, and its inhibition has emerged as a strategy to
[...] Read more.
Tempol, a synthetic nitroxide, exhibits dual antioxidant and pro-oxidant activity, requiring millimolar concentrations to induce oxidative stress, which limits its therapeutic use. Glutathione Peroxidase 4 (GPX4) is a critical lipid peroxidase that prevents ferroptosis, and its inhibition has emerged as a strategy to sensitize cancer cells to oxidative stress. To enhance Tempol’s efficacy, we investigated its interaction with ML210, a GPX4 inhibitor, in human colon (HT29) and gastric (CRL-1739) cancer cell lines. We quantified cell viability, oxidative stress markers (H2O2, Total Oxidant Status (TOS), and Total Antioxidant Status (TAS)) and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress proteins (ATF6, GRP78, and IRE1α) in in vitro assays. Synergy was assessed using Bliss independence analysis. The combination of Tempol (2 mM) and ML210 (0.05 μM) markedly reduced viability in both cell lines. Bliss analysis revealed slight/moderate synergy for cytotoxicity (Δ = +0.15 in HT29; Δ = +0.26 in CRL-1739) and strong synergy for H2O2 accumulation (Δ = +1.92–2.23 across replicates). In contrast, TOS showed moderate-to-strong antagonism across both cell lines, and TAS demonstrated slight synergistic or antagonistic effects. ER stress markers exhibited marker and cell line specific synergy: ATF6 showed strong synergy, IRE1α slight synergy in both lines, and GRP78 activation was highly variable, showing strong synergy in CRL−1739 cells but moderate antagonism in HT29 cells. These findings indicate that the cooperative action of Tempol and ML210 is ROS-pool–specific and pathway-selective in the ER. These findings demonstrate that ML210 potentiates Tempol’s pro-oxidant pressure by targeting GPX4, selectively amplifying H2O2 accumulation and ER stress engagement without collapsing global redox balance. This study provides mechanistic rationale for redox–proteostasis co-targeting in gastric and colon cancers and establishes a foundation for in vivo validation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Biochemistry, Molecular and Cellular Biology)
Open AccessReview
Epigenetic Mechanisms in Fabry Disease: A Thematic Analysis Linking Differential Methylation Profiles and Genetic Modifiers to Disease Phenotype
by
Jatinder Singh, Paramala Santosh and Uma Ramaswami
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 855; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100855 - 16 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Fabry disease is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder. It is characterised by impaired metabolism of glycosphingolipids whose accumulation causes irreversible organ damage and life-threatening complications. Genotype–phenotype correlations have a limited scope in Fabry disease as the disorder presents with wide-ranging
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Fabry disease is an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder. It is characterised by impaired metabolism of glycosphingolipids whose accumulation causes irreversible organ damage and life-threatening complications. Genotype–phenotype correlations have a limited scope in Fabry disease as the disorder presents with wide-ranging clinical variability. In other X-linked disorders, epigenetic profiling has identified methylation patterns and disease modifiers that may explain clinical heterogeneity. In this narrative review and thematic analysis, the role of DNA methylation and epigenetics on the clinical phenotype in Fabry disease was investigated. Methods: Embase, PubMed, and PsycINFO were searched to identify literature on DNA methylation and epigenetics in Fabry disease. Based on the eligibility criteria, 20 articles were identified, and a thematic analysis was performed on the extracted data to identify themes. Results: Three themes emerged: (I) genetic modifiers, (II) methylation profiling, and (III) insights into X chromosome inactivation (XCI). The evidence synthesis revealed that telomere length, especially in early disease stages, bidirectional promoter (BDP) methylation by sphingolipids, epigenetic reader proteins, mitochondrial DNA haplogroups, and DNA methylation of the promoter region of the calcitonin receptor gene are potential genetic modifiers in Fabry disease. Methylation patterns also reveal episignatures in Fabry disease evolution and genes implicated in the maintenance of basement membranes. Studies on XCI further emphasise disease heterogeneity and draw attention to methodological issues in the assessment of XCI. Conclusions: This thematic review shows that DNA methylation and genetic modifiers are key factors modifying clinical variability in Fabry disease. More broadly, it underscores a crucial role for epigenetic processes in driving disease onset, progression, and severity in X-linked disorders.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Latest Review Papers in Molecular Biology 2025)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Pathophysiological Links Between Stroke and Prediabetes: A Systematic Review
by
Yerushka Naicker and Andile Khathi
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 854; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100854 - 16 Oct 2025
Abstract
Prediabetes is an intermediate stage between normoglycaemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), affecting over 425 million people globally and contributing to vascular damage and increased stroke risk. Despite the severity of both conditions, their association remains underexplored. This review examines the literature
[...] Read more.
Prediabetes is an intermediate stage between normoglycaemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), affecting over 425 million people globally and contributing to vascular damage and increased stroke risk. Despite the severity of both conditions, their association remains underexplored. This review examines the literature on stroke-related biomarkers in normoglycaemia, prediabetes and T2DM to identify potential links between prediabetes and stroke. This systematic review followed PRISMA-2020 guidelines. PubMed, Google Scholar, Scopus, Web of Science and Science Direct were searched for studies (2003–2023) on stroke biomarkers in prediabetes. Eligible studies were original human research in English, with defined diagnostic criteria (ADA or WHO) for glycaemic status and reported biomarker associations or stroke risk. Studies with major comorbidities were excluded. Data were extracted and bias was assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale. Meta-analysis was not performed due to limited studies per biomarker. Eight studies (n = 3003) were included. NSE was examined in three studies, all reporting significant elevations in hyperglycaemic individuals. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) was assessed in two studies; one showed a significant increase in diabetes, while the other found a non-significant upward trend. D-dimer and GFAP were each reported in separate single studies, both showing significant elevations in hyperglycaemic individuals with stroke or neurocognitive impairment. S100B was investigated in two studies, with divergent findings: one showed a positive association with glycaemic status, while the other reported lower levels in hyperglycaemia. Findings indicate biomarker alterations in T2DM, suggesting that early changes may occur in prediabetes. Our review suggests that individuals with prediabetes may show alterations in inflammatory (IL-6), coagulation (D-dimer), and neurovascular (S100B, GFAP, NSE) markers, though some findings are inconsistent, reflecting early pathophysiological changes that may increase stroke risk. Further well-designed studies are needed to clarify these associations and establish biomarker-based tools for earlier stroke risk detection and prevention in individuals with prediabetes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Cerebrovascular Diseases: From Pathogenesis to Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Pathogenesis of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) and the Preventive and Therapeutic Effects of Natural Products
by
Yuxin Dong and Yanqing Tong
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 853; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100853 - 16 Oct 2025
Abstract
Chronickidney disease (CKD) poses a major global public health challenge, driven by a complex pathogenesis involving multiple interconnected processes—including metabolic disturbances, chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and ferroptosis—which collectively contribute to progressive and often irreversible loss of renal function. Although current
[...] Read more.
Chronickidney disease (CKD) poses a major global public health challenge, driven by a complex pathogenesis involving multiple interconnected processes—including metabolic disturbances, chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and ferroptosis—which collectively contribute to progressive and often irreversible loss of renal function. Although current standard therapies can ameliorate CKD progression, a substantial number of patients still advance to end-stage renal disease, highlighting the urgent need for innovative treatment strategies. Natural products have shown great promise in the prevention and management of CKD, largely attributable to their multi-target and multi-pathway synergistic effects. This review systematically outlines the core pathogenic mechanisms underlying CKD and elucidates the molecular mechanisms through which bioactive natural compounds exert renoprotective effects. Despite robust preclinical evidence, the clinical translation of these compounds remains hindered by limitations such as poor bioavailability and a lack of large-scale clinical trials. Moving forward, research should prioritize clinical translation of these compounds, aiming to provide novel therapeutic perspectives for CKD management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Applications of Natural and Pseudo-Natural Products in Drug Discovery and Development 2025)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
IL-6 Inhibition Partially Ameliorates Maternal Immune Activation-Induced Autism-Like Behavioral Abnormalities in Mice
by
Xiaoyun Zhang, Weili Luo, Kaiyue He, Yuping Li, Yan Chen, Zhipeng Xu and Zi-Kai Zhou
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 852; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100852 - 16 Oct 2025
Abstract
Prenatal maternal immune activation (MIA) has been implicated in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) pathogenesis, with interleukin-6 (IL-6) identified as a key inflammatory mediator. We investigated the therapeutic potential of IL-6 inhibition in an MIA mouse model induced by Toxoplasma gondii soluble tachyzoite antigen
[...] Read more.
Prenatal maternal immune activation (MIA) has been implicated in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) pathogenesis, with interleukin-6 (IL-6) identified as a key inflammatory mediator. We investigated the therapeutic potential of IL-6 inhibition in an MIA mouse model induced by Toxoplasma gondii soluble tachyzoite antigen (STAg). Adult MIA offspring received systemic administration of the IL-6-neutralizing antibody (MP5-20F3) or isotype control, followed by behavioral assessments one week later. Open field and elevated plus maze tests revealed heightened anxiety-like behaviors in the STAg offspring, which were largely reversed by IL-6 inhibition. Reciprocal social interaction tests showed diminished sociability in the STAg offspring, which was partially restored by IL-6 inhibition. However, core ASD-like features, including impaired social preference and recognition in the three-chamber test, as well as increased repetitive behaviors, remained resistant to IL-6 inhibition. These findings demonstrate that STAg-induced MIA elicits anxiety-like and ASD-like phenotypes in adult offspring, with IL-6 playing an important role in anxiety-like behaviors and social interaction deficits. Systemic IL-6 inhibition partially ameliorates behavioral abnormalities. This study suggests that IL-6-targeted therapies may address a subset of ASD-related symptoms, and comprehensive strategies are needed for broader efficacy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Molecular Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Pro-Angiogenic Bioactive Molecules in Vascular Morphogenesis: Integrating Endothelial Cell Dynamics
by
Claudiu N. Lungu, Gabriela Gurau and Mihaela C. Mehedinti
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 851; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100851 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
During embryonic development, angiogenesis and arteriogenesis are responsible for vast growth and remodeling. These processes have distinct mechanisms, like budding, cord hollowing, cell hollowing, cell wrapping, and intussusception. This review discusses the diversity of morphogenetic mechanisms contributing to vessel assembly and angiogenic sprouting
[...] Read more.
During embryonic development, angiogenesis and arteriogenesis are responsible for vast growth and remodeling. These processes have distinct mechanisms, like budding, cord hollowing, cell hollowing, cell wrapping, and intussusception. This review discusses the diversity of morphogenetic mechanisms contributing to vessel assembly and angiogenic sprouting in blood vessels and how molecular pathways regulate some complex cell behaviors concerning the VEGFR pathway. Also, a particular part is dedicated to the HIF 1α gene. The key components of the VEGFR pathway are VEGF receptors VEGFR1, VEGFR2, and VEGFR3. VEGFR2 plays a central role in vascular morphogenesis. VEGF is the primary ligand involved in angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Various types of VEGF are being studied in terms of their therapeutic use. The ultimate goal of the vascular morphogenesis study is to enable the development of organized vascular tissue that presumably might be used to replace the diseased one. Cellular chirality—the intrinsic “handedness” of cells in movement, structure, and organization—plays a crucial role in angiogenesis, the process by which new blood vessels develop from old ones. This chiral activity is essential for the directed and patterned organization of endothelial cells during vascular formation and remodeling. In angiogenesis, cellular chirality directs endothelial cells to adopt specific orientations and migratory patterns, which are crucial for the formation of functionally organized blood vessels that provide tissues with the necessary nutrients and oxygen. Cellular chirality in this environment is affected by multiple mechanisms, including VEGF/VEGFR signaling, mechanical pressures, interactions with the extracellular matrix (ECM), and cytoskeletal movements. Lately, researchers have focused on the molecular control of blood vessel morphogenesis, the study of signaling circuitry implied in vascular morphogenesis, the emerging mechanism of vascular stabilization, and helical vasculogenesis driven by cell chirality.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Biochemistry, Molecular and Cellular Biology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Significant Association Between Glucokinase Regulatory Protein Variants and Genetic and Metabolic Diseases
by
Ke Xu, Peng Chen, Yujing Su, Yanghui Chen, Xiuli Song, Bo Yu and Hong Wang
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 850; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100850 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
As next-generation sequencing develops, there are significant associations between glucokinase regulatory protein (GCKR) variants and many diseases, especially metabolic diseases. However, there is a lack of solid descriptions and summaries of how GCKR variants lead to diseases and a lack of successful translations
[...] Read more.
As next-generation sequencing develops, there are significant associations between glucokinase regulatory protein (GCKR) variants and many diseases, especially metabolic diseases. However, there is a lack of solid descriptions and summaries of how GCKR variants lead to diseases and a lack of successful translations of drugs targeting this molecular variant. We searched literature datasets, mainly including PubMed and Web of Science, with “GCKR” or “GKRP”, “Variants”, “Hypertriglyceridemia”, “NAFLD”, and “Metabolic diseases” as the search terms. Our review firstly introduces the biological function of the GCKR gene and its encoding protein GKRP and then describes the GCKR variants in different diseases, such as hypertriglyceridemia and NAFLD, revealing that GCKR/GKPR is strongly associated with metabolic diseases. GKPR might be a potential target for T2D and other metabolic diseases. One drug for interfering with the GCK-GKRP complex has been developed and has shown its effectiveness in preclinical studies, with some possible side effects. More and more different-structured drugs should be developed to improve side effects, and more clinical trials should be carried out to determine the best intervention window and timing points to improve prognosis. Taken together, these insights show that GCKR/GKRP is significantly associated with many metabolic diseases via its complex metabolism system and is a potential target in many metabolic diseases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Advances in Hypertension Management and Vascular Health)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Identification and Association of CYP2R1, CYP27B1, and GC Gene Polymorphisms with Vitamin D Deficiency in Apparently Healthy Population and in Silico Analysis of the Binding Pocket of Vitamin D3
by
Saima Manzoor, Asifa Majeed, Palvasha Waheed and Amir Rashid
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 849; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100849 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
Vitamin D deficiency is highly prevalent in Pakistan, but there is limited data on its genetic aspects. This case–control pilot study aimed to determine the association of rs782153744, rs200183599, rs118204011, and rs28934604 with vitamin D deficiency along rs7041 which has been studied in
[...] Read more.
Vitamin D deficiency is highly prevalent in Pakistan, but there is limited data on its genetic aspects. This case–control pilot study aimed to determine the association of rs782153744, rs200183599, rs118204011, and rs28934604 with vitamin D deficiency along rs7041 which has been studied in our population. The DNA of a total of 600 subjects (300 cases and 300 controls) was extracted and genotyped by tetra ARMS PCR, followed by Sanger DNA sequencing of exon 4 of the CYP2R1 and CYP27B1 genes and exon 8 of the GC gene. SNP Stat was employed to analyze the data, while logistic regression was used to calculate the p-values and odds ratios (ORs). The R package version R studio (2025.05.1) Build 513 was used to statistically analyze rs782153744. In silico modeling of wild and mutant CYP2R1 and GC proteins was performed in Swiss-Model, Swiss-Dock, Discovery Studio, and PyMol using 3c6g and IJ78 as templates to perform binding pocket analysis of vitamin D3. The rs782153744 showed a protective association in the additive (OR: 0.15, 95% CI: 0.08–0.27, p-value < 0.001), recessive (OR: 0.19, 95% CI: 0.10–0.33, p-value < 0.001), and dominant (OR: 0.19, CI = 0.10–0.33, p-value < 0.001) models, while GC rs7041 (T > A, T > G) displayed a p-value < 0.0001 across all genetic models. Sanger sequencing yielded insignificant results, and the SNPs rs200183599, rs118204011, and rs28934604 had no significant association with vitamin D deficiency. The molecular pocket analysis of wild and mutant CYP2R1 proteins carrying rs782153744 polymorphisms revealed no changes. GC proteins carrying the rs7041 polymorphism revealed a shift in their 3D and 2D configuration, as well as a change in the amino acid residue of the binding pocket of VD3. The risk-associated rs7041 and protective rs782153744 variants back genetic screening for vitamin D deficiency risk stratification, allowing targeted supplementation in predisposed subjects and assisting in formulating a genotype-specific therapeutic approach.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Bioinformatics Approaches to Biomedicine)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Hydrogen Sulfide and Nitric Oxide Improve Renal Function and α-Adrenergic Responsiveness in Rats with Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
by
Tabinda Fatima, Latifah Al Shammari, Mohamed Ibrahim Lazhari, Waad Alrohily, Tan Yong Chia, Nimer Alsabeelah, Eid Fahad Alanazi, Khalid Abdulrahman Almutairi, Sultan Mujahid Alhabradi, Naif Saleh Alharbi and Ashfaq Ahmad
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 848; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100848 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
In left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), the combined external administration of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and nitric oxide (NO) has been shown to reverse LVH by activating the endothelial nitric oxide synthase pathway (eNOS/NO), independent of the cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE/H2S) pathway.
[...] Read more.
In left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), the combined external administration of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and nitric oxide (NO) has been shown to reverse LVH by activating the endothelial nitric oxide synthase pathway (eNOS/NO), independent of the cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE/H2S) pathway. Individually, both H2S and NO have also been reported to significantly improve RCBP, restore renal excretory performance, and enhance α-adrenergic receptor responsiveness in rats. The induction of LVH was performed over a period of two weeks using drinking water with caffeine and isoprenaline. Five weeks later, the rats were fed with L-arginine (1.25 g/L) as a nitrogen oxide donor. Vascular reactions to methoxamine, phenylephrine, and noradrenaline were assessed in presences and absence of 5-methylurapidil (5-MeU), BMY7378, and chloroethylclonidine (CeC) and α1-adrenoceptor antagonists. In both the Control WKY and LVH-WKY groups, combined H2S+NO therapy significantly (p < 0.05) upregulated the renal mRNA of CSE and eNOS when compared with untreated LVH rats. The treatment also markedly increased RCBP in LVH-H2S+NO rats relative to LVH controls. Furthermore, H2S+NO administration enhanced the activity of α1A, α1B, and α1D adrenergic receptors in mediating renal vasoconstriction. Even under receptor blockade with high doses (HDs) of 5-MeU, CeC, and BMY 7378, renal vasoconstriction responses to adrenergic agonists like NA, PE, and ME in the LVH-H2S+NO group remained comparable to those observed in the counterpart Control-H2S+NO group. The findings of current study suggest that simultaneous exogenous administration of H2S and NO donors improve renal cortical blood flow, support renal function, and augment α1A, α1B, and α1D adrenergic receptor responsiveness to adrenergic agonists like NA, PE, and ME in LVH rats. This effect appears to rely primarily on the eNOS/NO pathway, with partial contribution from the CSE/H2S pathway.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Mechanisms and Pharmacological Underlying Cardiorenal Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Gut Microbiota Changes in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Common Pathogenic Features
by
Giuseppe Guido Maria Scarlata, Domenico Morano, Abdulrahman Ismaiel, Rocco Spagnuolo, Francesco Luzza, Dan Lucian Dumitrascu and Ludovico Abenavoli
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 847; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100847 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
Gut microbiota changes have emerged as central players in the pathogenesis of both metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Although these diseases affect distinct primary organs, they share converging mechanisms driven by dysbiosis, including loss of beneficial short-chain fatty acid-producing taxa
[...] Read more.
Gut microbiota changes have emerged as central players in the pathogenesis of both metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Although these diseases affect distinct primary organs, they share converging mechanisms driven by dysbiosis, including loss of beneficial short-chain fatty acid-producing taxa such as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Roseburia, enrichment of pro-inflammatory Enterobacteriaceae, and disruption of bile acid and tryptophan metabolism. These shifts compromise epithelial barrier integrity, promote the translocation of microbial products such as lipopolysaccharide, and trigger toll-like receptor 4-mediated activation of inflammatory cascades dominated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and transforming growth factor-beta. In MASH, this dysbiotic environment fuels hepatic inflammation, insulin resistance, and fibrogenesis, while in IBD it sustains chronic mucosal immune activation. Shared features include impaired butyrate availability, altered bile acid pools affecting farnesoid X receptor and Takeda G protein-coupled Receptor 5 signaling, and defective aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation, all of which link microbial dysfunction to host metabolic and immune dysregulation. Understanding these overlapping pathways provides a deeper understanding of the role of the gut-liver and gut-immune axes as unifying frameworks in disease progression. This narrative review synthesizes current evidence on gut microbiota in MASH and IBD, underscoring the need for longitudinal, multi-omics studies and microbiome-targeted strategies to guide personalized therapeutic approaches.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Intestinal Inflammation: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Empagliflozin Attenuates Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis in NAFLD: Evidence from Mendelian Randomization and Mouse Experiments
by
Chao Fu, Lijiao Deng, Xiaochan Zhu, Bin Wang, Bin Hu, Huan Xue, Qingxuan Zeng and Yi Zhang
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 846; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100846 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent chronic liver disorder and a major global health challenge, yet effective pharmacological therapies are lacking. Empagliflozin, a sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, has shown systemic metabolic and anti-inflammatory benefits, but its liver-specific molecular mechanisms remain incompletely
[...] Read more.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent chronic liver disorder and a major global health challenge, yet effective pharmacological therapies are lacking. Empagliflozin, a sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor, has shown systemic metabolic and anti-inflammatory benefits, but its liver-specific molecular mechanisms remain incompletely understood. In this study, we evaluated the therapeutic effects of empagliflozin in a diet-induced mouse model of NAFLD, supported by Mendelian randomization analysis. Histological examination, serum biochemistry, and hepatic triglyceride quantification demonstrated that empagliflozin markedly attenuated hepatic steatosis and improved liver injury indices. At the molecular level, empagliflozin suppressed NF-κB-mediated inflammatory signaling and significantly downregulated fibrotic markers including α-SMA and COL1A1, while modulating TIMP-1 and MMP-9 expression. Collectively, these findings reveal that empagliflozin ameliorates NAFLD by inhibiting inflammatory and fibrotic molecular pathways, highlighting its potential as a mechanism-based therapeutic option for NAFLD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Fatty Liver Disease: From Pathogenesis to Treatment, 2nd Edition)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Action of Carnosic Acid Against Melanoma: A Strategy for Selective Radiosensitization with Protection of Non-Tumoral Cells
by
Amparo Olivares, Isabel de la Fuente, Daniel Gyingiri Achel, Ana María Mercado, José Antonio Garcia-Gamuz, María del Rosario Tudela and Miguel Alcaraz
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 845; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100845 - 14 Oct 2025
Abstract
Carnosic acid (CA) is a phenolic diterpene with high antioxidant activity that supports its radioprotective capacity. This study aims to determine whether the radiosensitizing effect of CA established in B16F10 melanoma cells also occurs in other melanin-producing cells. Cell survival analysis, apoptosis, intracellular
[...] Read more.
Carnosic acid (CA) is a phenolic diterpene with high antioxidant activity that supports its radioprotective capacity. This study aims to determine whether the radiosensitizing effect of CA established in B16F10 melanoma cells also occurs in other melanin-producing cells. Cell survival analysis, apoptosis, intracellular glutathione levels, and cell cycle progression were evaluated by comparing radiosensitive cells (PNT2) with radioresistant melanin-producing cells (MELAN A, SK-MEL-1, and B16F10). In PNT2 cells, CA exhibited radioprotective capacity, with 100% cell survival after exposure to 20 Gy of X-rays (p < 0.001), decreasing apoptosis (p < 0.001) and increasing the GSH/GSSG ratio (p < 0.01), without significant modification in cell cycle progression. However, CA administration to irradiated cells failed to exert radioprotection in MELAN A and SK-MEL-1 cells, and even doubled cell death in B16F10 cells (p < 0.001). Specifically, CA did not alter apoptosis or prevent the decrease in GSH/GSSG ratio in MELAN A and SK-MEL-1 cells, while it intensified radiation-induced cell cycle disruptions in all melanin-producing cells. All of these led to a loss of radioprotective capacity in the melanin-producing cells (MELAN A and SK-MEL-1) and even induced a radiosensitizing effect in B16F10 cells. Understanding the mechanisms of action of substances such as CA could promote new applications that protect healthy cells and exclusively damage neoplastic cells when both are present within the same irradiated volume in cancer patients requiring radiotherapy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Insights into Radiation Oncology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Epigenetic Factors in Pathogenesis of Retinoblastoma: DNA Methylation and Histone Acetylation
by
Georgios Kiosis, Kanellos Skourtsidis, Despoina Ioannou, Vasilis-Spyridon Tseriotis, Konstantinos Stergiou, Fani Akritidou, Theodora Papamitsou, Maria Kourti and Sofia Karachrysafi
Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47(10), 844; https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47100844 - 14 Oct 2025
Abstract
(Background) Retinoblastoma is the most common intraocular malignancy in childhood, primarily caused by mutations in the RB1 gene. However, increasing evidence highlights the significant role of epigenetic mechanisms, particularly DNA methylation and histone acetylation, in tumor initiation and progression. This review aims to
[...] Read more.
(Background) Retinoblastoma is the most common intraocular malignancy in childhood, primarily caused by mutations in the RB1 gene. However, increasing evidence highlights the significant role of epigenetic mechanisms, particularly DNA methylation and histone acetylation, in tumor initiation and progression. This review aims to summarize and critically assess recent findings on how DNA methylation and histone acetylation contribute to the pathogenesis of retinoblastoma, and to explore their potential role as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. (Methods) We searched the databases PubMed, Scopus, and ScienceDirect following PRISMA guidelines. Eligible studies were English-language, open-access articles published within the last ten years, including cohort studies, research articles, and case reports. After rigorous screening, 18 studies were included in the final analysis. (Results) Aberrant DNA methylation was found to inactivate tumor suppressor genes (RB1, RASSF1A, p16INK4A, MGMT) and promote oncogenesis through hypermethylation of regulatory elements. Similarly, histone acetylation’s dysregulation contributed to chromatin remodeling and overexpression of oncogenic factors such as SYK, GALNT8, and lincRNA-ROR. Elevated histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity was also linked to tumor cell proliferation, metastasis, and treatment resistance. Epigenetic inhibitors targeting these pathways demonstrated promising therapeutic potential. (Conclusions) DNA methylation and histone acetylation play a crucial role in the epigenetic regulation of genes implicated in retinoblastoma. Their dysregulation promotes tumorigenesis, and targeting these mechanisms represents a promising avenue for novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in pediatric oncology.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Molecular Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal MenuJournal Browser
► ▼ Journal Browser-
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios Current issue - Volumes not published by MDPI
- Vol. 42 (2021)
- Vol. 41 (2021)
- Vol. 40 (2021)
- Vol. 39 (2020)
- Vol. 38 (2020)
- Vol. 37 (2020)
- Vol. 36 (2020)
- Vol. 35 (2020)
- Vol. 34 (2019)
- Vol. 33 (2019)
- Vol. 32 (2019)
- Vol. 31 (2019)
- Vol. 30 (2019)
- Vol. 29 (2018)
- Vol. 28 (2018)
- Vol. 27 (2018)
- Vol. 26 (2018)
- Vol. 25 (2018)
- Vol. 24 (2017)
- Vol. 23 (2017)
- Vol. 22 (2017)
- Vol. 21 (2017)
- Vol. 20 (2016)
- Vol. 19 (2016)
- Vol. 18 (2016)
- Vol. 17 (2015)
- Vol. 16 (2014)
- Vol. 15 (2013)
- Vol. 14 (2012)
- Vol. 13 (2011)
- Vol. 12 (2010)
- Vol. 11 (2009)
- Vol. 10 (2008)
- Vol. 9 (2007)
- Vol. 8 (2006)
- Vol. 7 (2005)
- Vol. 6 (2004)
- Vol. 5 (2003)
- Vol. 4 (2002)
- Vol. 3 (2001)
- Vol. 2 (2000)
- Vol. 1 (1999)
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Brain Sciences, CIMB, Epigenomes, Genes, IJMS, DNA
Genetics and Epigenetics of Substance Use Disorders
Topic Editors: Aleksandra Suchanecka, Anna Maria Grzywacz, Kszysztof ChmielowiecDeadline: 15 November 2025
Topic in
Animals, CIMB, Genes, IJMS, DNA
Advances in Molecular Genetics and Breeding of Cattle, Sheep, and Goats
Topic Editors: Xiukai Cao, Hui Li, Huitong ZhouDeadline: 30 November 2025
Topic in
Biophysica, CIMB, Diagnostics, IJMS, IJTM
Molecular Radiobiology of Protons Compared to Other Low Linear Energy Transfer (LET) Radiation
Topic Editors: Francis Cucinotta, Jacob RaberDeadline: 20 December 2025
Topic in
BioTech, DNA, Genes, IJMS, CIMB
Single-Cell Technologies: From Research to Application
Topic Editors: Ken-Hong Lim, Chung-Der Hsiao, Pei-Ming YangDeadline: 31 December 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
CIMB
Molecular Roles of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Immune Responses and Disease
Guest Editor: Sofía S. JerezDeadline: 30 October 2025
Special Issue in
CIMB
The Molecular Pathways Involved in Atopic Dermatitis: Implications for Targeted Therapy
Guest Editor: Ciro Martins GomesDeadline: 30 October 2025
Special Issue in
CIMB
Natural Products in Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy, 2nd Edition
Guest Editor: Ahmed Ezat El ZowalatyDeadline: 31 October 2025
Special Issue in
CIMB
Challenges and Advances in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
Guest Editor: Haijun GongDeadline: 31 October 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
CIMB
Feature Papers in Current Issues in Molecular BiologyCollection Editor: Madhav Bhatia
Topical Collection in
CIMB
Molecular Mechanisms in Human Diseases
Collection Editor: Roberto Campagna
Topical Collection in
CIMB
Feature Papers Collection in Molecular Microbiology
Collection Editor: Bruce Seal
Topical Collection in
CIMB
Advancements in Molecular Biology and Pharmaceutical Science
Collection Editor: Arun Butreddy







