Cytokine Patterns in COVID-19 Patients: Which Cytokines Predict Mortality and Which Protect Against?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Luminex-Based Multiplex Assay for Serum Cytokine Concentration
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Ethics
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Patients
3.2. Association between Inflammatory Cytokine Levels and Mortality in COVID-19 Patients
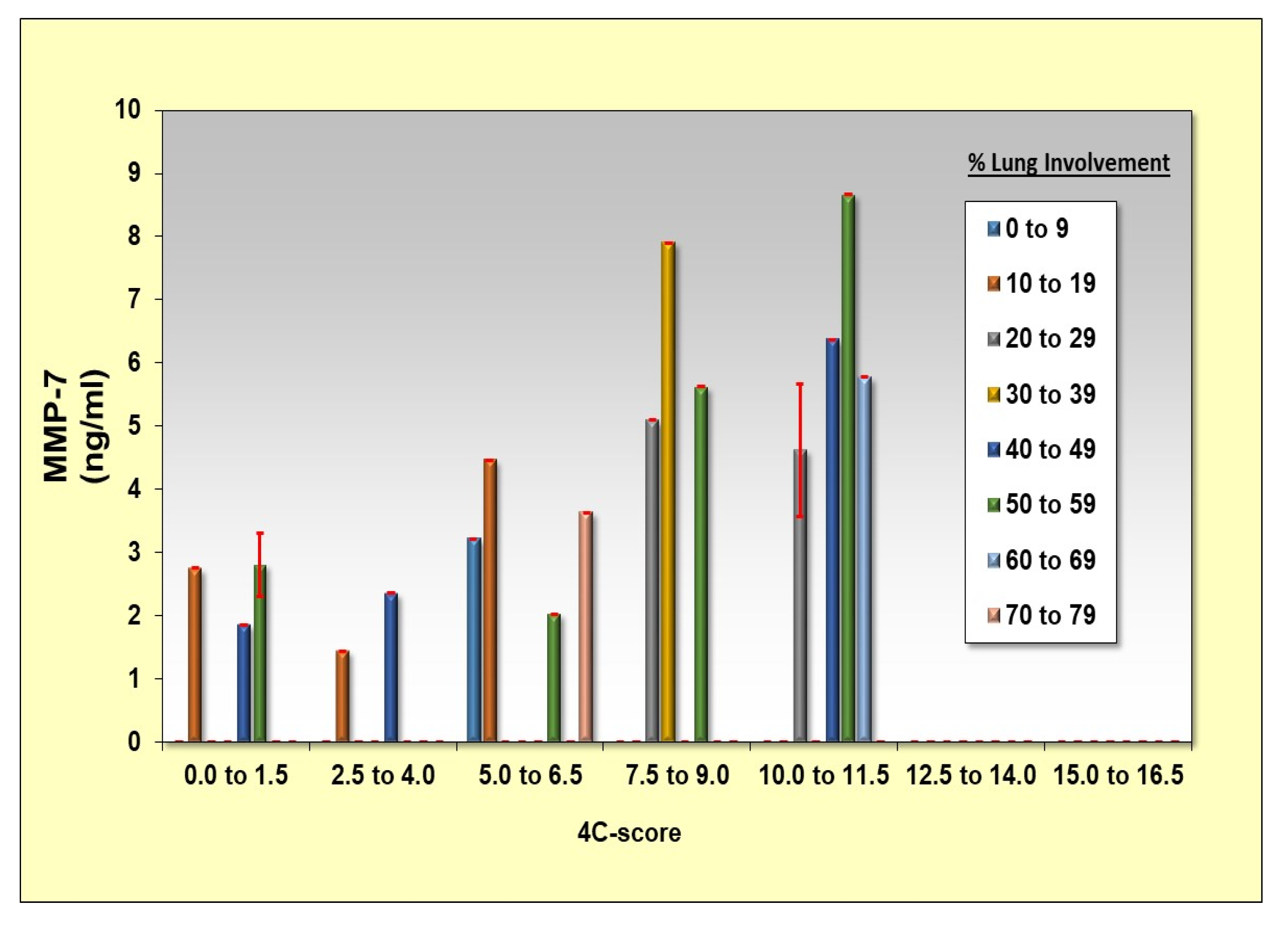
3.3. MMP-7 Correlates with Cytokine Storm and 4-C Score Levels
3.4. Association between Inflammatory Cytokine Levels and Lung Involvement (% of Consolidation) in COVID-19 Patients
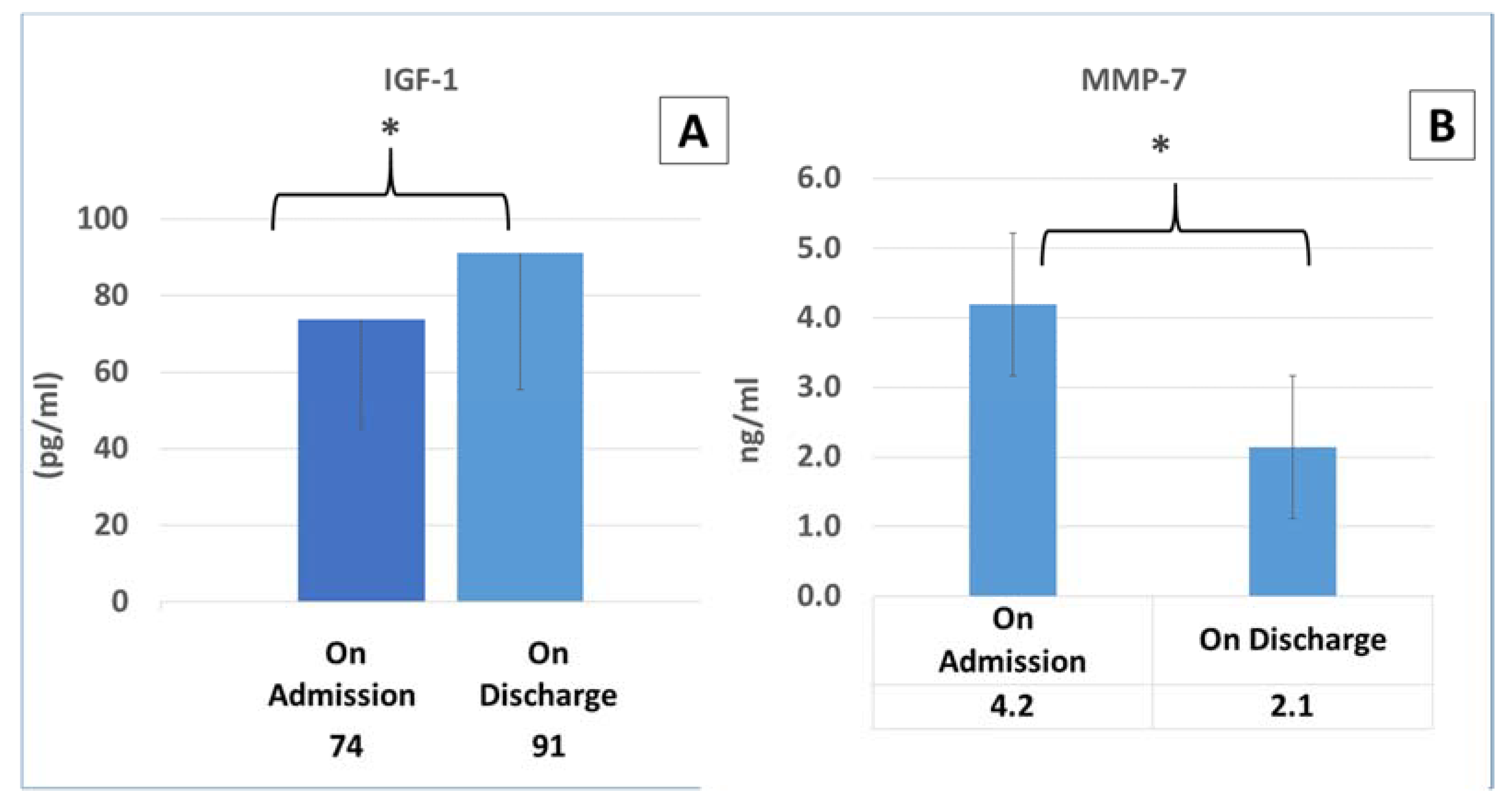
3.5. The Dynamics in the Cytokine Concentrations in COVID-19 Patients upon Admission and Discharge
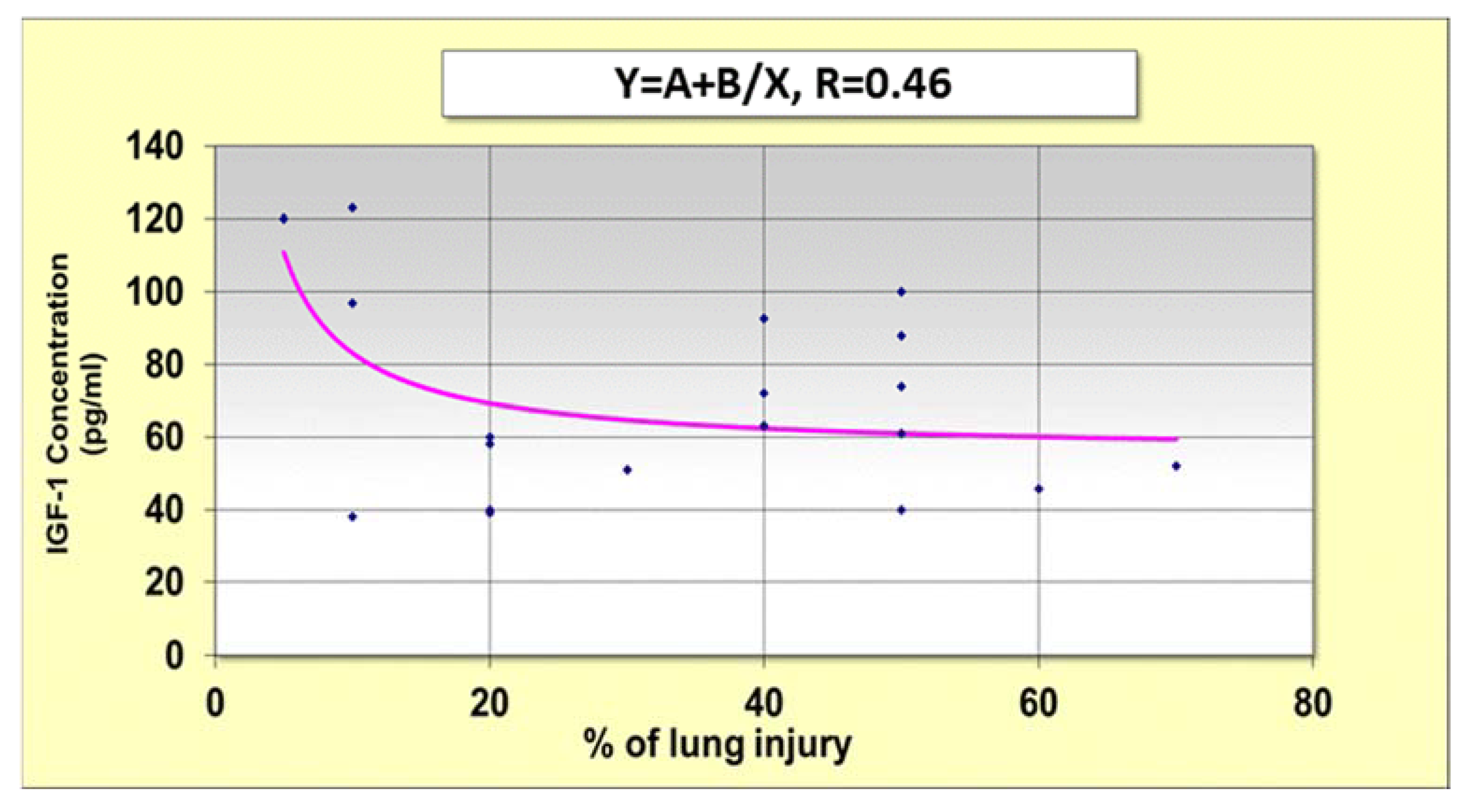
3.6. Correlation between IGF-1 Concentrations in Admission and Lung Injury
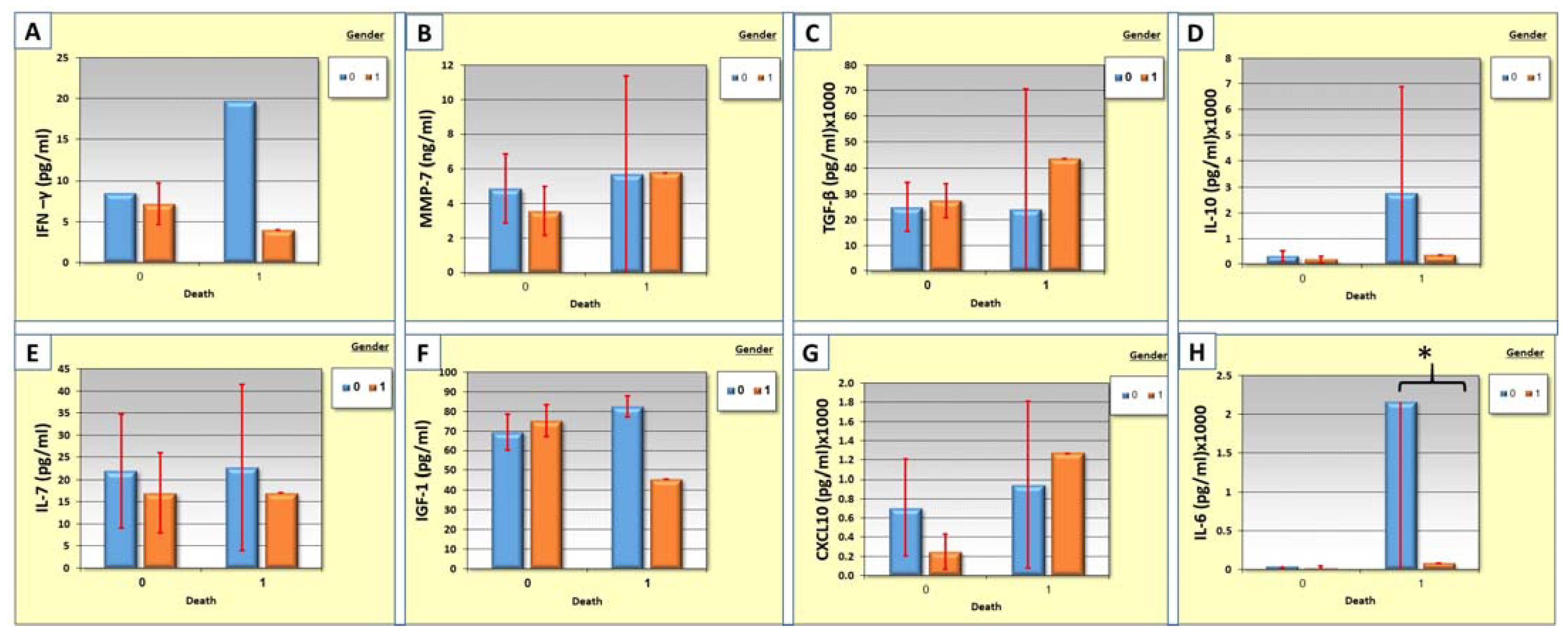
3.7. Correlation between Cytokine Levels, Gender, and Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richardson, S.; Hirsch, J.S.; Narasimhan, M.; Crawford, J.M.; McGinn, T.; Davidson, K.W.; Barnaby, D.P.; Becker, L.B.; Chelico, J.C.; Cohen, S.L.; et al. Presenting characteristics, comorbidities and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area. JAMA 2020, 323, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Liu, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Yu, T.; Qu, J.; Zhou, M.; Chen, L.; Meng, S.; Hu, Y.; et al. Effectiveness of convalescent plasma therapy in severe COVID-19 patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9490–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.K.; Mainbourg, S.; Friggeri, A.; Bertoletti, L.; Douplat, M.; Dargaud, Y.; Grange, C.; Lobbes, H.; Provencher, S.; Lega, J.-C. Arterial and venous thromboembolism in COVID-19: A studylevel meta-analysis. Thorax 2021, 76, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, V.; Tan, B.K.; Mainbourg, S.; Potus, F.; Cucherat, M.; Lega, J.-C.; Provencher, S. Venous thromboembolism in COVID-19 compared to nonCOVID-19 cohorts: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2021, 2, 106882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miró, Ò.; Jiménez, S.; Mebazaa, A.; Freund, Y.; Putze, G.; Martin, A.; Martin-Sanchez, F.J.; Garcia, E.J.; Alquezar-Arbe, A.; Jacob, J.; et al. Pulmonary embolism in patients with COVID-19: Incidence, risk factors, clinical characteristics, and outcome. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 24, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.P.; Blet, A.; Smyth, D.; Li, H. The science underlying COVID-19: Implications for the cardiovascular system. Circulation 2020, 142, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendren, N.S.; Drazner, M.H.; Bozkurt, B.; Cooper, L.T., Jr. Description and proposed management of the acute COVID-19 cardiovascular syndrome. Circulation 2020, 141, 1903–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, L.T. Healing after COVID-19: Are Survivors at Risk for Pulmonary Fibrosis? Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2021, 320, L257–L265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shen, C.; Wang, L.; Majumder, S.; Zhang, D.; Deen, M.J.; Li, Y.; Qing, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; et al. Pulmonary fibrosis and its related factors in discharged patients with new corona virus pneumonia: A cohort study. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Li, S.-Q. Pulmonary Fibrosis in Critically Ill Patients with Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia during the Convalescent Stage and a Proposal for Early Intervention. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1376–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, R.M.M.; Ghonimy, M.B.I. Post-COVID-19 pneumonia lung fibrosis: A worrisome sequelae in surviving patients. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2021, 52, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, R.; Zhan, Q.; Ni, F.; Fang, S.; Lu, Y.; Ding, X.; et al. 3-month, 6-month, 9-month, and 12-month respiratory outcomes in patients following COVID-19-related hospitalisation: A prospective study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarenac, T.; Trapecar, M.; Gradisnik, L.; Rupnik, M.S.; Pahor, D. Single-cell analysis reveals IGF-1 potentiation of inhibition of the TGF-β/Smad pathway of fibrosis in human keratocytes in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheer, M.; Saad, E.; Hagai, R.; Assy, N. Clinical Predictors of Mortality and Critical Illness in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. Metabolites 2021, 11, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caricchio, R.; Gallucci, M.; Dass, C.; Zhang, X.; Gallucci, S.; Fleece, D.; Bromberg, M.; Criner, G.J.; Temple University COVID-19 Research Group. Preliminary predictive criteria for COVID-19 cytokine storm. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, S.R.; Ho, A.; Pius, R.; Buchan, I.; Carson, G.; Drake, T.M.; Dunning, J.; Fairfield, C.J.; Gamble, C.; Green, C.A.; et al. Stratification of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterization Protocol: Development and validation of the 4-C Mortality Score. BMJ 2020, 370, m3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, K.; Sivashanmugam, K.; Kandasamy, M.; Subbiah, R.; Ravikumar, V. Repurposing of histone deacetylase inhibitors: A promising strategy to combat pulmonary fibrosis promoted by TGF-β signalling in COVID-19 survivors. Life Sci. 2021, 266, 118883. [Google Scholar]
- Abbul, K.A.; Andrew, H.; Lichtman, S.P. Imunologia Celular e Molecular, 8th ed.; Elsevier: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Walton, K.L.; Johnson, K.E.; Harrison, C.A. Targeting TGF-β Mediated SMAD Signaling for the Prevention of Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheer, M.; Saad, E.; Assy, N. The Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: The Strongest Link to Morbidity and Mortality in the Current Epidemic. COVID 2022, 2, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costela-Ruiz, V.J.; Illescas-Montes, R.; Puerta-Puerta, J.M.; Ruiz, C.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L. SARS-CoV-2 infection: The role of cytokines in COVID-19 disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 54, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, A.; Kishimoto, T. Il-6: Regulator of Treg/Th17 Balance. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 1830–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. Immunotherapeutic Implications of IL-6 Blockade for Cytokine Storm. Immunotherapy 2016, 8, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letizia, A.; Eller, M.A.; Polyak, C.; Eller, L.A.; Creegan, M.; Dawson, P.; Bryant, C.D.K.; Crowell, T.A.; Lombardi, K.; Rono, E.; et al. Biomarkers of inflammation correlate with clinical scoring indices in Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Kenyans. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, H.J.; Coutavas, E.; Pine, A.B.; Lee, A.I.; Yu, V.L.; Shallow, M.K.; Giovacchini, C.X.; Mathews, A.M.; Stephenson, B.; Que, L.G.; et al. Immuno-fibrotic drivers of impaired lung function in post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Immuno-fibrotic drivers of impaired lung function in post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2. JCI Insights 2021, 6, e148476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, A.; McAuley, D.F.; O’Kane, C.M. Matrix metalloproteinases in acute lung injury: Mediators of injury and drivers of repair. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, A.; Cabrera, S.; Maldonado, M.; Selman, M. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buendía-Roldán, I.; Fernandez, R.; Mejía, M.; Juarez, F.; Ramirez-Martinez, G.; Montes, E.; Pruneda, A.K.S.; Martinez-Espinosa, K.; Alarcon-Dionet, A.; Herrera, I.; et al. Risk factors associated with the development of interstitial lung abnormalities. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 14, 2003005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safont, B.; Tarraso, J.; Rodriguez-Borja, E.; Fernandez-Fabrellas, E.; Sancho-Chust, J.; Molina, V. Lung function, radiological findings and biomarkers of fibrogenesis in a Cohort of COVID-19 patients six months after hospital discharge. Arch. Bronchoneumol. 2022, 58, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Galan, L.; Ruiz, A.; Martinez-Espinosa, K.; Aguilar-Duran, H.; Torres, M.; Falfan-Valencia, R.; Perez-Rubio, G.; Selman, M.; Buendia-Roldan, I. Circulating Levels of PD-L1, TIM-3 and MMP-7 Are Promising Biomarkers to Differentiate COVID-19 Patients That Require Invasive Mechanical Ventilation. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coperchini, F.; Chiovato, L.; Ricci, G.; Croce, L.; Magri, F.; Rotondi, M. The Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: Further Advances in Our Understanding the Role of Specific Chemokines Involved. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 58, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Han, Y.; Nilsson-Payant, B.E.; Gupta, V.; Wang, P.; Duan, X.; Tang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, Z.; Jaffre, F.; et al. A Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Based Platform to Study SARS-CoV-2 Tropism and Model Virus Infection in Human Cells and Organoids. Cell Stem Cell. 2020, 27, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Melo, D.; Nilsson-Payant, B.E.; Liu, W.C.; Uhl, S.; Hoagland, D.; Møller, R.; Jordan, T.X.; Oishi, K.; Panis, M.; Sachs, D.; et al. Imbalanced Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Drives Development of COVID-19. Cell 2020, 181, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altara, R.; Manca, M.; Brandão, R.D.; Zeidan, A.; Booz, G.W.; Zouein, F.A. Emerging Importance of Chemokine Receptor CXCR3 and its Ligands in Cardiovascular Diseases. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhou, C.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, S.; Liu, J.; Luo, W.; Tao, C.; Qin, Q.; Deng, P. Characterization of Cytokine/Chemokine Profiles of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenez, E.; Albert, E.; Torres, I. SARS-CoV-2-reactive interferon-gamma-producing CD8+ T cells in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 93, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.E.; Garcia-Sastre, A. The virus battles: IFN induction of the antiviral state and mechanisms of viral evasion. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001, 12, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Gribbin, E.; Wang, H. Interferon-gamma inhibition attenuates lethality after cecal ligation and puncture in rats: Implication of high mobility group box-1. Shock 2005, 24, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wu, D.; Guo, W. Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2620–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackall, C.L.; Fry, T.J.; Gress, R.E. Harnessing the biology of IL-7 for therapeutic application. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, J.T.; Durum, S.K.; Seddon, B. Flip the coin: IL-7 and IL-7R in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1584–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francois, B.; Jeannet, R.; Daix, T.; Walton, A.H.; Shotwell, M.S.; Unsinger, J.; Monmeret, G.; Rimmele, T.; Blood, T.; Morre, M.; et al. Interleukin-7 restores lymphocytes in septic shock: The IRIS-7 randomized clinical trial. JCI Insights 2018, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laterre, P.F.; François, B.; Collienne, C.; Hantson, P.; Jeannet, R.; Jenneth, E.R.; Hotchkiss, R.S. Association of Interleukin 7 Immunotherapy with Lymphocyte Counts Among Patients with Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2016485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monneret, G.; de Marignan, D.; Coudereau, R.; Bernet, C.; Ader, F.; Frobert, E.; Gossez, M.; Viel, S.; Venet, F.; Wallet, F. Immune monitoring of interleukin-7 compassionate use in a critically ill COVID-19 patient. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 1001–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Balzano-Nogueira, L.; Lleo, A.; Conesa, A. Transcriptional Differences for COVID-19 Disease Map Genes between Males and Females Indicate a Different Basal Immunophenotype Relevant to the Disease. Genes 2020, 11, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| VARIABLE | |
|---|---|
| Total | N = 40 |
| Age | 63 ± 18 |
| Male (%) | 56% |
| BMI | 29.4 ± 6 |
| Comorbidities % | |
| Diabetes (%) | 42 |
| Hypertension (%) | 53 |
| Lung disease (%) | 7 |
| Hemodialysis (%) | 0 |
| Aspirin use (%) | 50 |
| Symptom’s duration before admission to hospitals (days) | 6 ± 4 |
| Symptoms before admission (% of total) | |
| Fever % | 61 |
| Diarrhea % | 0 |
| Dyspnea % | 58 |
| Clinical severity upon admission % | 23 |
| Lab Findings upon admission | |
| Hemoglobin (mg/dL) | 12.5 ± 1.5 |
| Absolute neutrophil count (×103/µL) | 4.4 ± 2.6 |
| Absolute lymphocyte count (×103/µL) | 1.07 ± 0.7 |
| Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) | 5.7 ± 4.7 |
| Platelet (×103/µL) | 190 ± 92 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 17.5 ± 8.8 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.01 ± 1.0 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 140 ± 57 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 28 ± 10 |
| C-reactive protein (CRP) (mg/dL) | 99 ± 86 |
| Ferritin (µg/L | 466 ± 325 |
| D-dimer (ng/mL) | 1080 ± 813 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dl) | 677 ± 165 |
| ALT (U/L) | 24 ± 16 |
| 4-C score | 7.0 ± 4.5 |
| O2 supplement upon admission % | 11 |
| High flow use (% of total) | 11 |
| Survival (% of total) | 85 |
| A. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | 95% Conf. (±) | Std. Error | T | p-Value | |
| Constant | |||||
| MMP-7 | −0.02 | 0.05 | 0.02 | −0.81 | 0.44 |
| TGF-β | 2.4 | 0.0001 | 7.19 | 3.34 | 0.01 |
| CCL2 | 0.0002 | 0.0005 | 0.00002 | −1.06 | 0.32 |
| CCL3 | 0.01 | 0.018 | 0.007 | 1.9 | 0.1 |
| CXCL-10 | 0.000 | 0.00 | 0.0001 | 3.81 | 0.008 |
| G-CSF | 0.002 | 0.05 | 0.002 | 1.22 | 0.26 |
| IFN gamma | −1.85 | 1.95 | 0.79 | −2.32 | 0.049 |
| IL-10 | −0.008 | 0.001 | 0.0005 | −1.64 | 0.15 |
| IL-2 | -0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | −0.761 | 0.47 |
| IL-4 | 5.67 | 5.89 | 2.4 | 2.35 | 0.056 |
| IL-6 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.99 | 0.358 |
| IL-7 | −0.02 | 0.02 | 0.008 | −2.44 | 0.04 |
| TNF-α | −0.005 | 0.01 | 0.007 | −0.67 | 0.52 |
| IL-6 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 1.7 | 0.13 |
| IGF-1 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.688 | 0.51 |
| B. | |||||
| Coefficient | 95% Conf. (±) | Std. Error | T | p-Value | |
| Constant | |||||
| IFN gamma | 0.07 | 0.048 | 0.023 | −2.98 | 0.007 |
| IL-10 | 0.0005 | 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 3.87 | 0.001 |
| C. | |||||
| Actual Count | 0 | 1 | |||
| Died patients | 3 | 3 | 0 | ||
| Survived patients | 22 | 1 | 21 | ||
| A. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | 95% Conf. (±) | Std. Error | T | p-Value | |
| Constant | |||||
| MMP-7 | 0.097 | 0.084 | 0.04 | 2.42 | 0.025 |
| B. | |||||
| Coefficient | 95% Conf. (±) | Std. Error | T | p-Value | |
| Constant | |||||
| MMP-7 | 1.48 | 0.56 | 0.27 | 5.44 | 0.00002 |
| Coefficient | 95% Conf. (±) | Std. Error | T | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | |||||
| MMP-7 | −18.027 | 8.5 | 0.38 | −4.7 | 0.0008 |
| TGF-β | 0.001 | 0.0008 | 0.0003 | 2.7 | 0.022 |
| IL-10 | −0.04 | 0.042 | 0.019 | −2.45 | 0.033 |
| IL-7 | 1.5 | 0.93 | 0.41 | 3.56 | 0.005 |
| TNF-α | 2.01 | 1.52 | 0.686 | 2.9 | 0.014 |
| IL-6 | 0.97 | 0.44 | 0.199 | 4.8 | 0.0006 |
| Protectors | Predictors |
|---|---|
| IFN-γ | TGF-β |
| IL-7 | CXCL-10 |
| MMP-7 | IL-10 |
| IGF-1 | IL-6 |
| TNF-α |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basheer, M.; Saad, E.; Kananeh, M.; Asad, L.; Khayat, O.; Badarne, A.; Abdo, Z.; Arraf, N.; Milhem, F.; Bassal, T.; et al. Cytokine Patterns in COVID-19 Patients: Which Cytokines Predict Mortality and Which Protect Against? Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 4735-4747. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44100323
Basheer M, Saad E, Kananeh M, Asad L, Khayat O, Badarne A, Abdo Z, Arraf N, Milhem F, Bassal T, et al. Cytokine Patterns in COVID-19 Patients: Which Cytokines Predict Mortality and Which Protect Against? Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2022; 44(10):4735-4747. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44100323
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasheer, Maamoun, Elias Saad, Majd Kananeh, Layyous Asad, Osama Khayat, Anan Badarne, Zaki Abdo, Nada Arraf, Faris Milhem, Tamara Bassal, and et al. 2022. "Cytokine Patterns in COVID-19 Patients: Which Cytokines Predict Mortality and Which Protect Against?" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 44, no. 10: 4735-4747. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44100323
APA StyleBasheer, M., Saad, E., Kananeh, M., Asad, L., Khayat, O., Badarne, A., Abdo, Z., Arraf, N., Milhem, F., Bassal, T., Boulos, M., & Assy, N. (2022). Cytokine Patterns in COVID-19 Patients: Which Cytokines Predict Mortality and Which Protect Against? Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 44(10), 4735-4747. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44100323







