RIP140-Mediated NF-κB Inflammatory Pathway Promotes Metabolic Dysregulation in Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Recombinant Adenovirus Preparation
2.3. Adenovirus Infection and siRNA Interference
2.4. Mitochondrial Activity Assay
2.5. Western Blotting Assay
2.6. Cytoplasmic Glycogen Concentration Assay
2.7. Isolation of Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Proteins
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.9. ELISA for TNF-α and IL-1β, IL-6 Measurement
2.10. Animals
2.11. Subretinal Injection
2.12. Electroretinogram (ERG)
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. RIP140 Regulates the Key Metabolic Genes and Lipid Processing Genes in ARPE-19 Cells
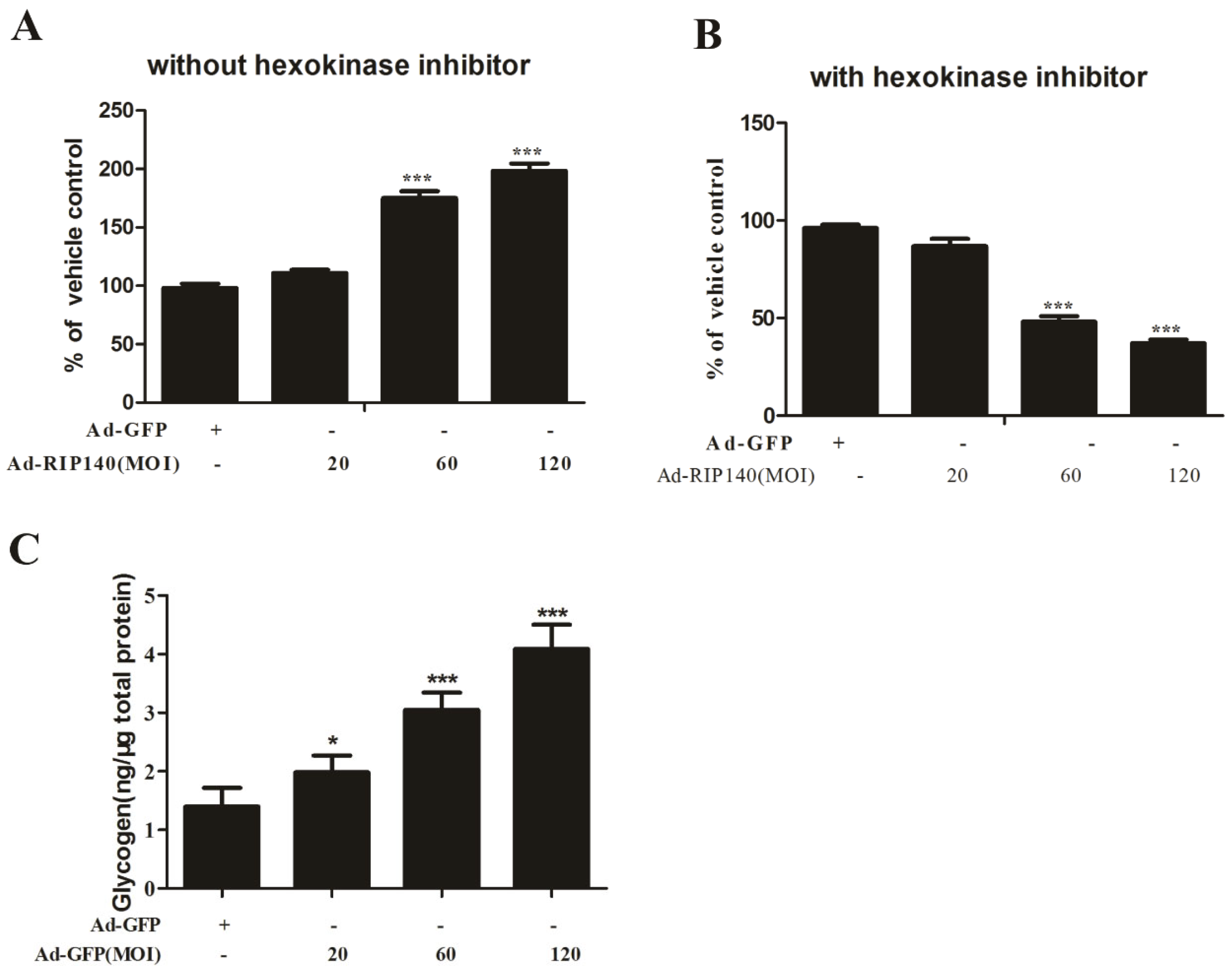
3.2. RIP140 Overexpression Induced Functional Impairments in ARPE-19 Cells
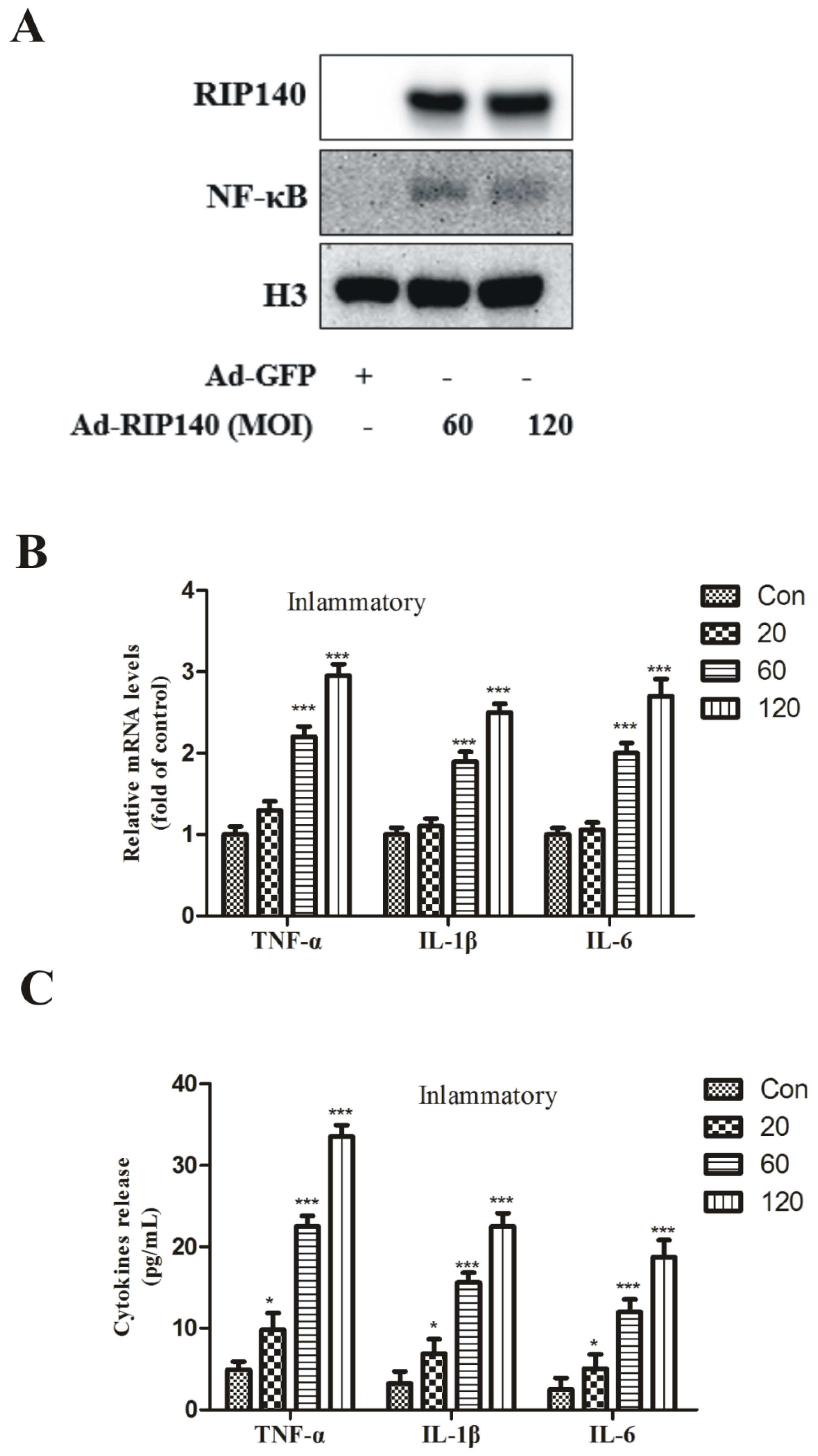
3.3. RIP140 Overexpression Upregulated NF-κB Translocation, Subsequent Proinflammatory Gene Expression and Cytokines Release in ARPE-19 Cells
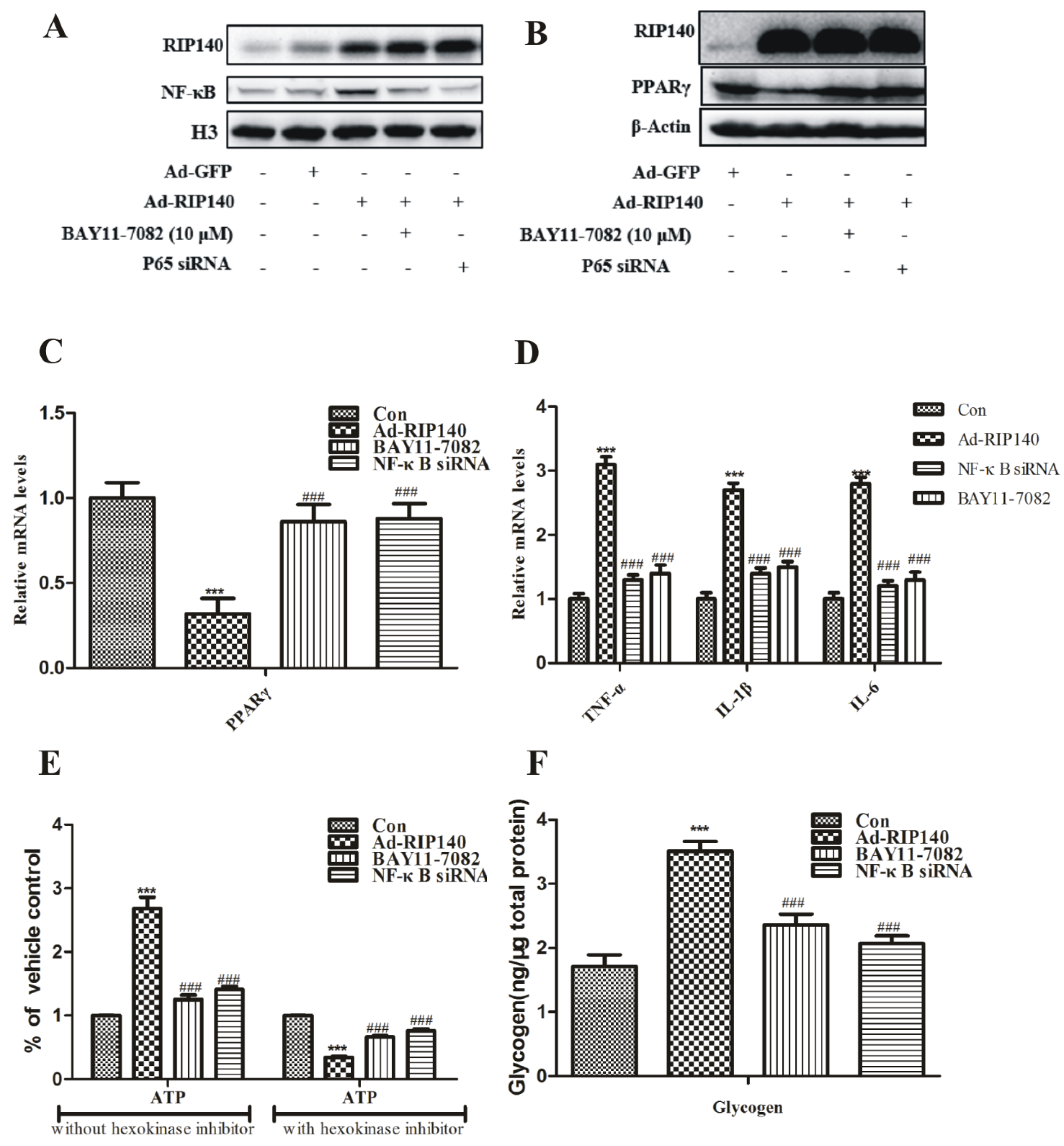
3.4. NF-κB Was Involved in RIP140-Induced Metabolic Dysfunction in ARPE-19 Cells
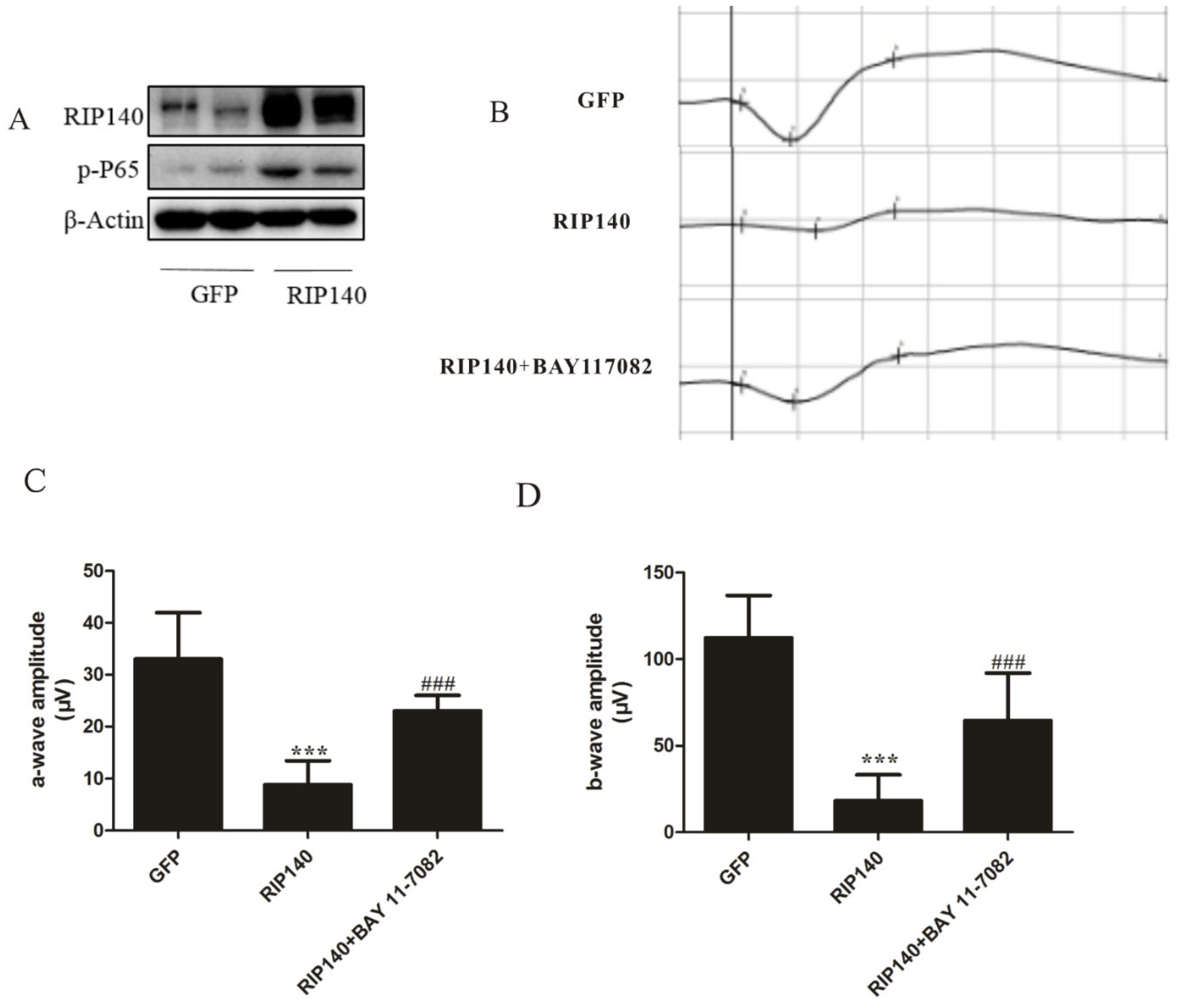
3.5. RIP140-Mediated NF-κB Inflammatory Pathway Involved in Photoreceptor Functional Impairments
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, W.L.; Su, X.; Li, X.; Cheung, C.M.; Klein, R.; Cheng, C.Y.; Wong, T.Y. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2014, 2, e106–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalik, L.; Desvergne, B.; Wahli, W. Peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptors and cancers: Complex stories. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okawa, H.; Sampath, A.P.; Laughlin, S.B.; Fain, G.L. ATP consumption by mammalian rod photoreceptors in darkness and in light. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 1917–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.N.; Green, B.D.; Thompson, R.B.; den Hollander, A.I.; Lengyel, I.; EYE-RISK Consortium. Metabolomics and Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Metabolites 2018, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Kini, A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Chen, Y.; Vukmanic, E.; Emery, D.; Liu, Y.; Lu, X.; Jin, L.; et al. Metabolic Deregulation of the Blood-Outer Retinal Barrier in Retinitis Pigmentosa. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 1323–1334.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasiak, J.; Petrovski, G.; Vereb, Z.; Facsko, A.; Kaarniranta, K. Oxidative stress, hypoxia, and autophagy in the neovascular processes of age-related macular degeneration. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 768026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrington, D.A.; Ebeling, M.C.; Kapphahn, R.J.; Terluk, M.R.; Fisher, C.R.; Polanco, J.R.; Roehrich, H.; Leary, M.M.; Geng, Z.; Dutton, J.R.; et al. Altered bioenergetics and enhanced resistance to oxidative stress in human retinal pigment epithelial cells from donors with age-related macular degeneration. Redox Biol. 2017, 13, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambati, J.; Atkinson, J.P.; Gelfand, B.D. Immunology of age-related macular degeneration. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovelli, J.; Rowe, G.C.; Khadka, A.; Diaz-Aguilar, D.; Spencer, C.; Arany, Z.; Saint-Geniez, M. PGC-1α Induces Human RPE Oxidative Metabolism and Antioxidant Capacity. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1038–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, M.A.B.; Shu, D.Y.; Iacovelli, J.; Saint-Geniez, M. Loss of PGC-1α in RPE induces mesenchymal transition and promotes retinal degeneration. Life Sci. Alliance 2019, 2, e201800212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golestaneh, N.; Chu, Y.; Cheng, S.K.; Cao, H.; Poliakov, E.; Berinstein, D.M. Repressed SIRT1/PGC-1α pathway and mitochondrial disintegration in iPSC-derived RPE disease model of age-related macular degeneration. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nautiyal, J.; Christian, M.; Parker, M.G. Distinct functions for RIP140 in development, inflammation, and metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Yue, Z.; He, Y.; Zou, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; et al. The p65 subunit of NF-kappaB involves in RIP140-mediated inflammatory and metabolic dysregulation in cardiomyocytes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 554, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zschiedrich, I.; Hardeland, U.; Krones-Herzig, A.; Berriel Diaz, M.; Vegiopoulos, A.; Muggenburg, J.; Sombroek, D.; Hofmann, T.G.; Zawatzky, R.; Yu, X.; et al. Coactivator function of RIP140 for NFkappaB/RelA-dependent cytokine gene expression. Blood 2008, 112, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storti, F.; Raphael, G.; Griesser, V.; Klee, K.; Drawnel, F.; Willburger, C.; Scholz, R.; Langmann, T.; von Eckardstein, A.; Fingerle, J.; et al. Regulated efflux of photoreceptor outer segment-derived cholesterol by human RPE cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 165, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.M.; Presley, J.B.; Zhang, X.; Dashti, N.; Chung, B.H.; Medeiros, N.E.; Guidry, C.; Curcio, C.A. Retina expresses microsomal triglyceride transfer protein: Implications for age-related maculopathy. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Skiba, N.P.; Tewkesbury, G.M.; Treboschi, V.M.; Baciu, P.; Jaffe, G.J. Complement-Mediated Regulation of Apolipoprotein E in Cultured Human RPE Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 3073–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Ding, J.D.; Qi, X.; Boulton, M.E.; Yao, P.L.; Peters, J.M.; Malek, G. PPARβ/δ selectively regulates phenotypic features of age-related macular degeneration. Aging 2016, 8, 1952–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, T.; Maegdefrau, U.; Hartmann, A.; Agaimy, A.; Marienhagen, J.; Weiss, T.S.; Stoeltzing, O.; Warnecke, C.; Scholmerich, J.; Oefner, P.J.; et al. GLUT1 expression is increased in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes tumorigenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 1544–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson, A.; Hamark, B.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T. Glucose transporter isoform 4 is expressed in the syncytiotrophoblast of first trimester human placenta. Hum. Reprod. 2005, 20, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Tian, J.; Yang, Y.; Cutler, R.G.; Wu, T.; Telljohann, R.S.; Mattson, M.P.; Handa, J.T. Oxidized low density lipoproteins induce a pathologic response by retinal pigmented epithelial cells. J. Neurochem. 2008, 105, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.; Millar, J.C.; Wang, W.H.; Silverman, S.M.; Liu, Y.; Wordinger, R.J.; Rubin, J.S.; Pang, I.H.; Clark, A.F. Existence of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway in the human trabecular meshwork. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 7043–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.; Okuwaki, T.; Ushikubo, H.; Mori, A.; Nakahara, T.; Ishii, K. Activation inhibitors of nuclear factor kappa B protect neurons against the NMDA-induced damage in the rat retina. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 135, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Yu, W.; Zheng, S.; Shi, H.; Li, M.; Sun, J.; Wang, D.; Hou, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; et al. RIP140/PGC-1α axis involved in vitamin A-induced neural differentiation by increasing mitochondrial function. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzo, A.; Manco, R.; Bonfiglio, F.; Cali, G.; De Cristofaro, T.; Patergnani, S.; Cicatiello, R.; Scrima, R.; Zannini, M.; Pinton, P.; et al. NRIP1/RIP140 siRNA-mediated attenuation counteracts mitochondrial dysfunction in Down syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 4406–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, C.A.; Johnson, M.; Huang, J.D.; Rudolf, M. Apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in retinal aging and age-related macular degeneration. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H.; Tan, J.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Deng, S.; Gao, S.; Li, H.; et al. Distinct cardiac energy metabolism and oxidative stress adaptations between obese and non-obese type 2 diabetes mellitus. Theranostics 2020, 10, 2675–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondrath, K.; Steel, J.H.; Katsouri, L.; Ries, M.; Parker, M.G.; Christian, M.; Sastre, M. The nuclear cofactor receptor interacting protein-140 (RIP140) regulates the expression of genes involved in Abeta generation. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 47, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, M.; Jones, M.C.; Parker, M.G. Role of nuclear receptor corepressor RIP140 in metabolic syndrome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponferrada, A.; Caso, J.R.; Alou, L.; Colon, A.; Sevillano, D.; Moro, M.A.; Lizasoain, I.; Menchen, P.; Gomez-Lus, M.L.; Lorenzo, P.; et al. The role of PPARgamma on restoration of colonic homeostasis after experimental stress-induced inflammation and dysfunction. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1791–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Ward, W.F. PGC-1α: A key regulator of energy metabolism. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2006, 30, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.; Morganstein, D.; Christian, M.; Seth, A.; Herzog, B.; Parker, M.G. Role of RIP140 in metabolic tissues: Connections to disease. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.; Datta, S.; Wang, L.; Pegany, R.; Cano, M.; Handa, J.T. The impact of lipids, lipid oxidation, and inflammation on AMD, and the potential role of miRNAs on lipid metabolism in the RPE. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 181, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curcio, C.A.; Johnson, M.; Rudolf, M.; Huang, J.D. The oil spill in ageing Bruch membrane. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 95, 1638–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurihara, T.; Westenskow, P.D.; Gantner, M.L.; Usui, Y.; Schultz, A.; Bravo, S.; Aguilar, E.; Wittgrove, C.; Friedlander, M.; Paris, L.P.; et al. Hypoxia-induced metabolic stress in retinal pigment epithelial cells is sufficient to induce photoreceptor degeneration. eLife 2016, 5, e14319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Cano, M.; Ebrahimi, K.; Wang, L.; Handa, J.T. The impact of oxidative stress and inflammation on RPE degeneration in non-neovascular AMD. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2017, 60, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Peterson, K.; Yin, L.; Berger, A.; Fan, J.; Wistow, G. Accumulation of cholesterol and increased demand for zinc in serum-deprived RPE cells. Mol. Vis. 2016, 22, 1387–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Curcio, C.A. Soft Drusen in Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Biology and Targeting Via the Oil Spill Strategies. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, AMD160–AMD181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrer, B.; Bandyopadhyay, M.; Beeson, C. Reduced Metabolic Capacity in Aged Primary Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) is Correlated with Increased Susceptibility to Oxidative Stress. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 854, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaarniranta, K.; Uusitalo, H.; Blasiak, J.; Felszeghy, S.; Kannan, R.; Kauppinen, A.; Salminen, A.; Sinha, D.; Ferrington, D. Mechanisms of mitochondrial dysfunction and their impact on age-related macular degeneration. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2020, 79, 100858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppinen, A.; Paterno, J.J.; Blasiak, J.; Salminen, A.; Kaarniranta, K. Inflammation and its role in age-related macular degeneration. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1765–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, G.; Hu, P.; Wielgus, A.; Dwyer, M.; Cousins, S. PPAR nuclear receptors and altered RPE lipid metabolism in age-related macular degeneration. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 664, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzlich, A.A.; Tuo, J.; Chan, C.C. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor and age-related macular degeneration. PPAR Res. 2008, 2008, 389507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanow, M.A.; Giarmarco, M.M.; Jankowski, C.S.; Tsantilas, K.; Engel, A.L.; Du, J.; Linton, J.D.; Farnsworth, C.C.; Sloat, S.R.; Rountree, A.; et al. Biochemical adaptations of the retina and retinal pigment epithelium support a metabolic ecosystem in the vertebrate eye. eLife 2017, 6, e28899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Groppe, M.; Salvetti, A.P.; MacLaren, R.E. Technique of retinal gene therapy: Delivery of viral vector into the subretinal space. Eye 2017, 31, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, G.; Busik, J.; Grant, M.B.; Choudhary, M. Models of retinal diseases and their applicability in drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2018, 13, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creel, D.J. Electroretinograms. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 160, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.; Yan, F.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, H.; Qiu, K.; Xu, J.; Zheng, W. Insulin-like growth factor-1 activates PI3K/Akt signalling to protect human retinal pigment epithelial cells from amiodarone-induced oxidative injury. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerth, C. The role of the ERG in the diagnosis and treatment of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2009, 118, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhong, J.; Li, Z.; Guo, Q.; Yao, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W. RIP140-Mediated NF-κB Inflammatory Pathway Promotes Metabolic Dysregulation in Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 5788-5801. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44110393
Guo Z, Shen Y, Zhong J, Li Z, Guo Q, Yao X, Wang Y, Wu W. RIP140-Mediated NF-κB Inflammatory Pathway Promotes Metabolic Dysregulation in Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2022; 44(11):5788-5801. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44110393
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Zeli, Yuli Shen, Jianwen Zhong, Zhuoyun Li, Qi Guo, Xiangchao Yao, Yandong Wang, and Wenyu Wu. 2022. "RIP140-Mediated NF-κB Inflammatory Pathway Promotes Metabolic Dysregulation in Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 44, no. 11: 5788-5801. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44110393
APA StyleGuo, Z., Shen, Y., Zhong, J., Li, Z., Guo, Q., Yao, X., Wang, Y., & Wu, W. (2022). RIP140-Mediated NF-κB Inflammatory Pathway Promotes Metabolic Dysregulation in Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 44(11), 5788-5801. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44110393






