Artemisiae argyi Water Extract Alleviates Obesity-Induced Metabolic Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extract Preparation
2.2. Experimental Animals and Diet
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Plasma and Hepatic Lipid Profile
2.5. White Adipose Tissue (WAT) and Hepatic Morphology
2.6. Plasma Adipokine Content
2.7. Fasting Blood Glucose Level, Intraperitoneal Glucose Tolerance Test, and Homeostatic Index of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR)
2.8. mRNA Expression Analysis
2.9. Enzyme Activities in the Liver and Epididymal WAT
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
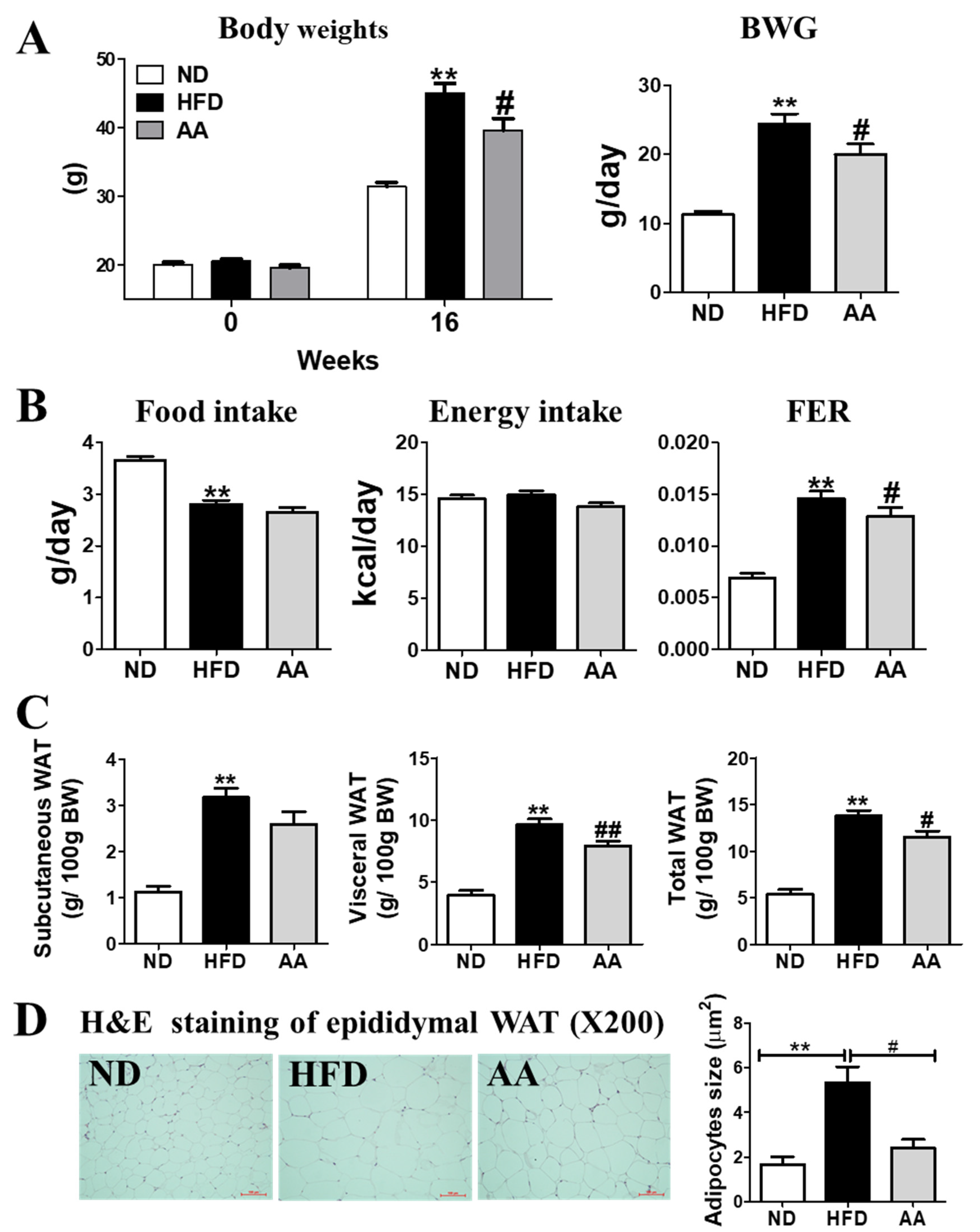
3.1. A. argyi Water Extract Supplementation Reduces Body Weight and Body Fat Mass
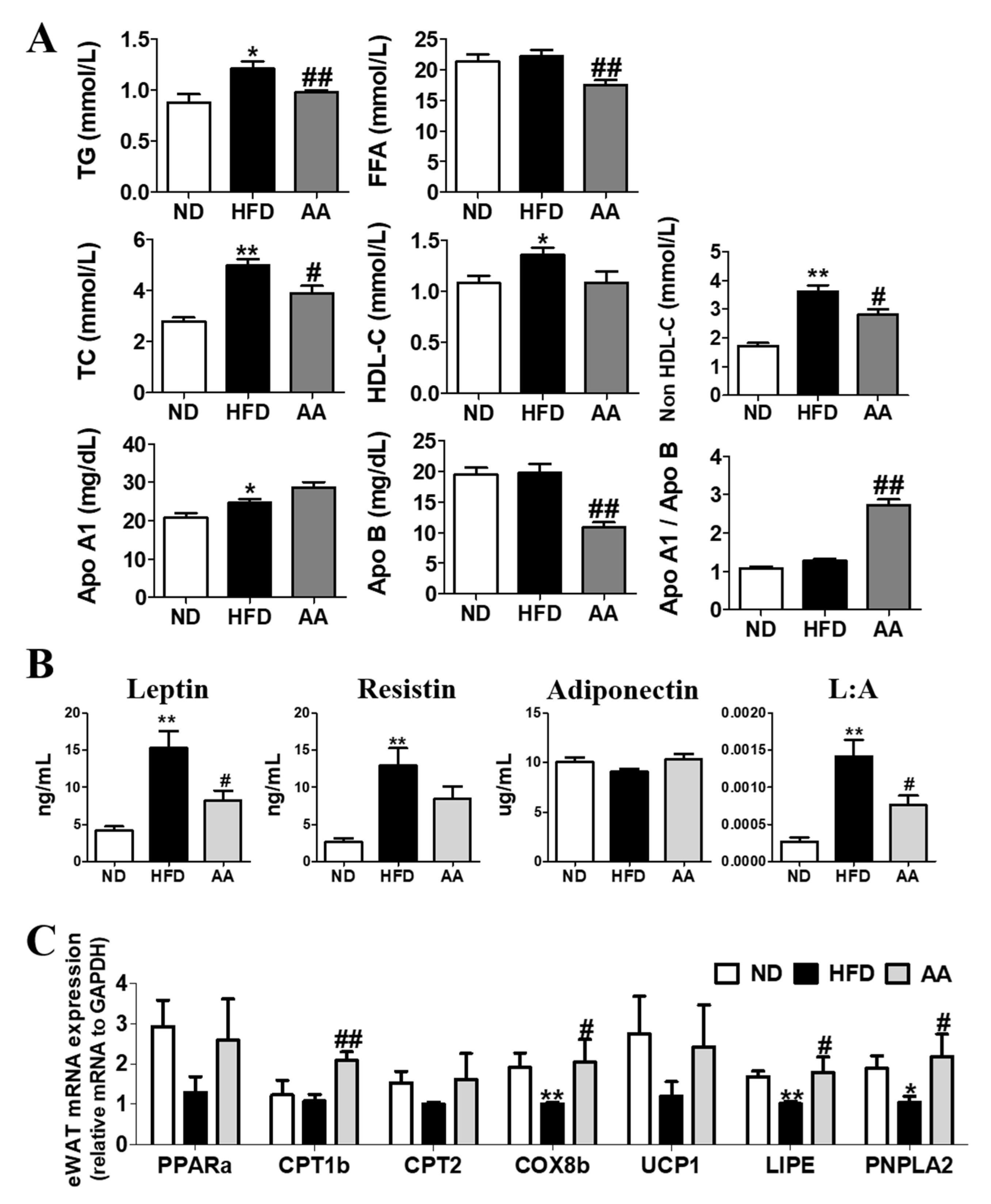
3.2. A. argyi Water Extract Supplementation Improves Plasma Lipid Profiles and Adipokine Levels by Regulating the Adipocyte mRNA Expression involved in Fatty Acid Oxidation
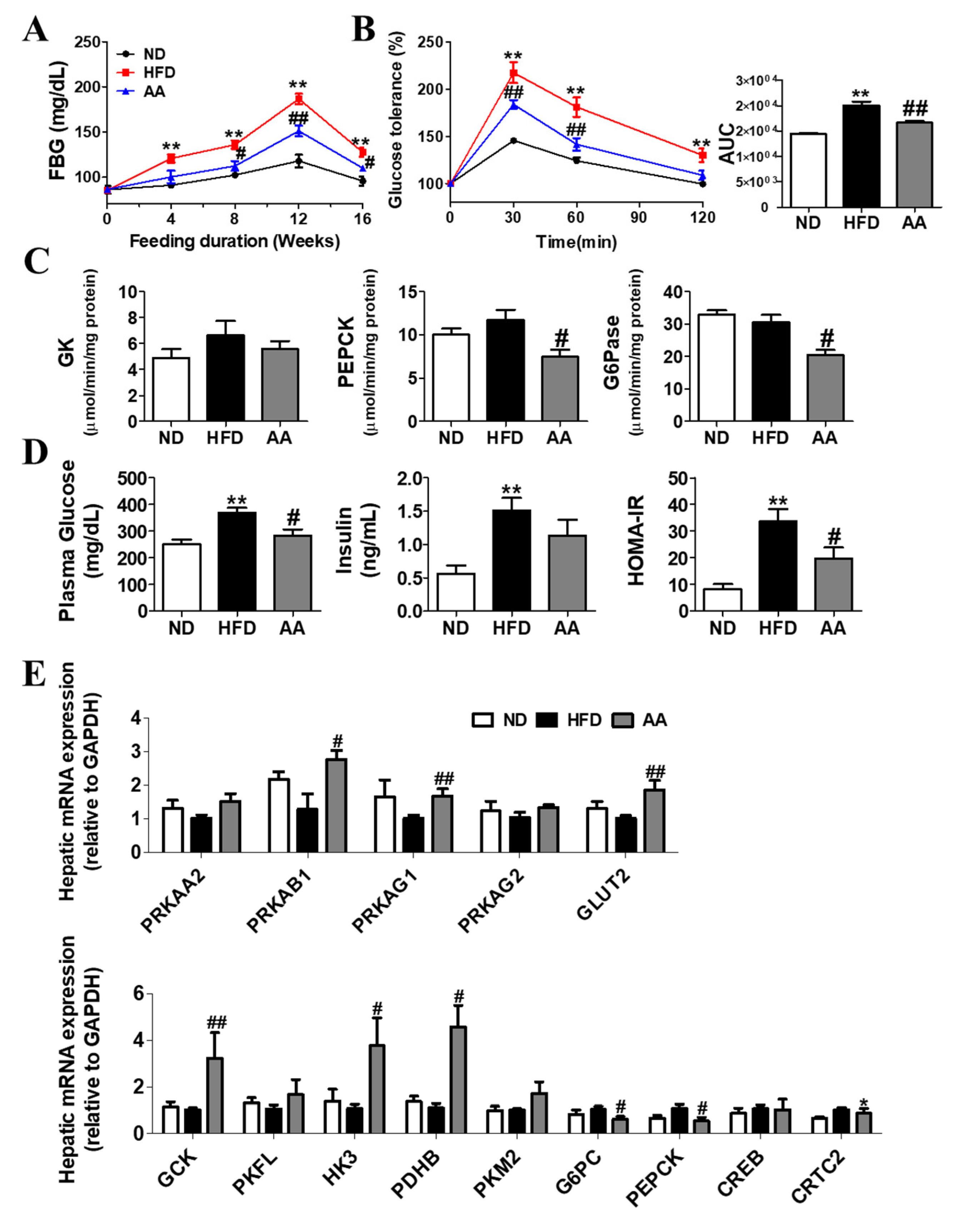
3.3. A. argyi Water Extract Supplementation Alleviates Impaired Glucose Metabolism-Related Obesity
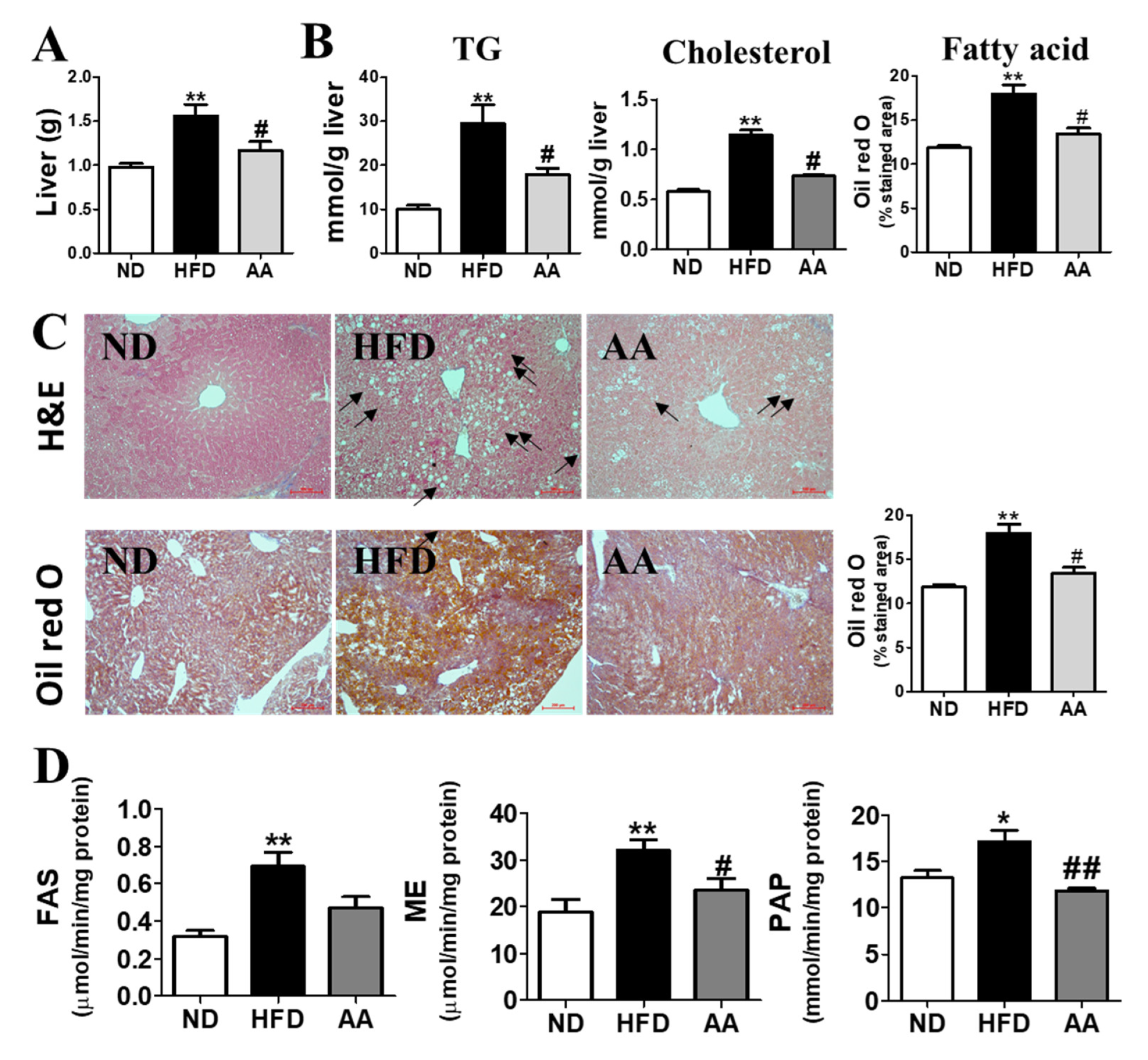
3.4. A. argyi Water Extract Supplementation Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis
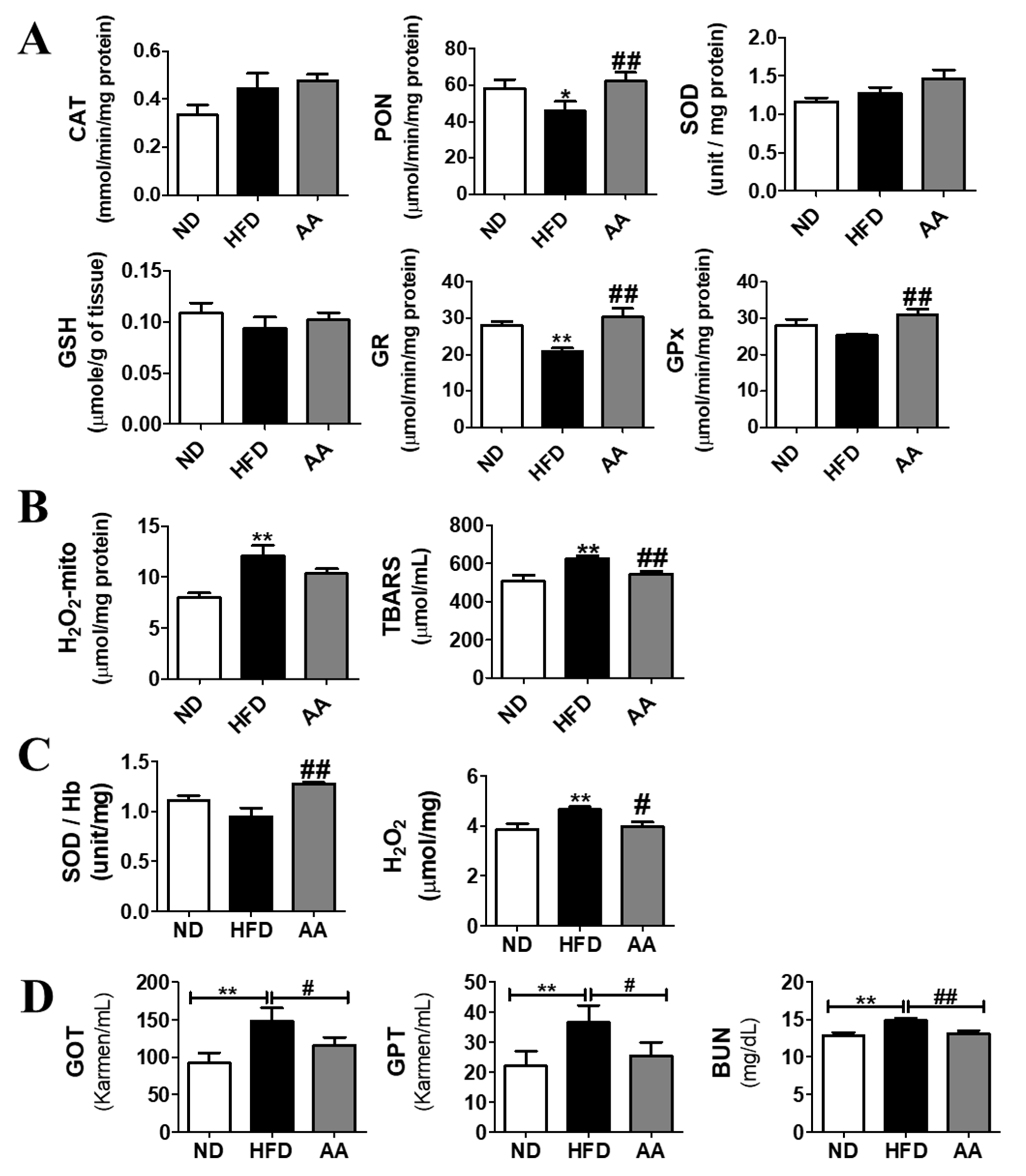
3.5. A. argyi Water Extract Supplementation Ameliorates Oxidative Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scherer, F.M. The pharmaceutical industry. Handb. Health Econ. 2000, 1, 1297–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Parganiha, R.; Tripathi, A.K.; Prathyusha, S.; Baghel, P.; Lanjhiyana, S.; Lanjhiyana, S.; Katiyar, D.; Tyagi, S.; Sharma, P.P.; Sarkar, D. A Review of Plants for Hepatic Disorders. J. Complement. Med. Res. 2022, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, Y.; Veerapur, V.P.; Nagappa, A.N.; Unnikrishnan, M. Perspectives in efficacy, safety and clinical evaluation of bioactive natural products. In Compendium of Bioactive Natural Products, M/S; Studium Press LLC: Huston, Texas, USA, 2009; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, A.R.; Abdullah, M.R. The effect of active compounds and trace elements extracted from Artemisia fruit on some liver enzymes in humans. Arch. Razi Inst. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wen, X.; He, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, S.; Wang, M. Phytochemical components and biological activities of Artemisia argyi. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 52, 648–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, Y.Q.; Jin, X.; Yan, S.M.; Shi, B.L. Effects of Artemisia argyi flavonoids on growth performance and immune function in broilers challenged with lipopolysaccharide. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Shi, B.; Li, T.; Xu, Y.; Jin, X.; Guo, X.; Yan, S. Immunomodulatory effect of Artemisia argyi polysaccharide on peripheral blood leucocyte of broiler chickens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.; Jung, Y.; Chun, W.; Yang, B.; Ryu, J.; Lim, C.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Cho, S.-I. Anti-inflammatory effects of Artemisia leaf extract in mice with contact dermatitis in vitro and in vivo. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 8027537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, M.S.; Baek, J.M.; Park, J.; Youn, B.-S.; Oh, J. Massive elimination of multinucleated osteoclasts by eupatilin is due to dual inhibition of transcription and cytoskeletal rearrangement. Bone Rep. 2015, 3, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Shin, E.-C.; Lim, H.-J.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, C.R.; Suh, S.H.; Kim, C.-J.; Park, G.G.; Park, C.-S.; Kim, H.K. Characterization of nutritional composition, antioxidative capacity, and sensory attributes of Seomae mugwort, a native Korean variety of Artemisia argyi H. Lev. & Vaniot. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2015, 2015, 916346. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, K.-W.; Wang, S.; Dong, X.; Jiang, Y.; Tu, P.-F. Sesquiterpene dimer (DSF-52) from Artemisia argyi inhibits microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via suppression of NF-κB, JNK/p38 MAPKs and Jak2/Stat3 signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama, P.; Vignesh, A.; Lakshmanan, G.; Murugesan, K. In vitro antioxidant activity of Achyranthes aspera Linn. Int. J. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 3, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, H.; Wang, S.Y. Correlation of antioxidant capacities to oxygen radical scavenging enzyme activities in blackberry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 5672–5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, J.; He, K.; Zhang, X.; Chang, L.; Xiang, G. Determination of Eupatilin in Folium artemisiae Argyi and its inhibitory effect on hepatoma cells. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2018, 14, 129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhou, S.; Yang, W.; Meng, D. Gastro-protective effect of edible plant Artemisia argyi in ethanol-induced rats via normalizing inflammatory responses and oxidative stress. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 214, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, N.-R.; Ryu, H.-W.; Ko, J.-W.; Park, S.-H.; Yuk, H.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, J.-C.; Jeong, S.-H.; Shin, I.-S. Artemisia argyi attenuates airway inflammation in ovalbumin-induced asthmatic animals. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 209, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.-R.; Park, S.-H.; Ko, J.-W.; Ryu, H.-W.; Jeong, S.-H.; Kim, J.-C.; Shin, D.-H.; Lee, H.-S.; Shin, I.-S. Artemisia argyi attenuates airway inflammation in lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury model. Lab. Anim. Res. 2017, 33, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, A.H.; Jacobson, K.A.; Rose, J.; Zeller, R. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2008, 2008, pdb.prot4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Zacarias, J.; Castro-Munozledo, F.; Kuri-Harcuch, W. Quantitation of adipose conversion and triglycerides by staining intracytoplasmic lipids with Oil red O. Histochemistry 1992, 97, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Yu, J.; Cui, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Guo, W.; Zhao, C.; Chen, X.; Meng, M.; Li, Y. Combination usage of adipocount and image-pro plus/imagej software for quantification of adipocyte sizes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 642000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehlem, A.; Hagberg, C.E.; Muhl, L.; Eriksson, U.; Falkevall, A. Imaging of neutral lipids by oil red O for analyzing the metabolic status in health and disease. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.; Rudenski, A.; Naylor, B.; Treacher, D.; Turner, R. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yoon, J.; Choi, M.S. Tracing the Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism/Triggers of d-Allulose: A Profile Study of Microbiome Composition and mRNA Expression in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 1900982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulcher, F.H.; Oleson, W.H. Simplified spectrophotometric assay for microsomal 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase by measurement of coenzyme A. J. Lipid Res. 1973, 14, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepokroeff, C.M.; Lakshmanan, M.; Porter, J.W. Fatty acid synthase from rat liver. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975; Volume 35, pp. 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Rudack, D.; Chisholm, E.M.; Holten, D. Rat liver glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase: Regulation by carbohydrate diet and insulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, S. Malic enzyme: Malic enzymes from pigeon and wheat germ. Methods Enzymol. 1955, 1, 323–326. [Google Scholar]
- Markwell, M.A.K.; McGroarty, E.J.; Bieber, L.L.; Tolbert, N. The subcellular distribution of carnitine acyltransferases in mammalian liver and kidney: A new peroxisomal enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1973, 248, 3426–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarow, P.B. [19] Assay of peroxisomal β-oxidation of fatty acids. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981; Volume 72, pp. 315–319. [Google Scholar]
- Drewnowski, A.; Specter, S.E. Poverty and obesity: The role of energy density and energy costs. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccurello, R.; Romano, A.; Giacovazzo, G.; Tempesta, B.; Fiore, M.; Giudetti, A.M.; Marrocco, I.; Altieri, F.; Moles, A.; Gaetani, S. Increased intake of energy-dense diet and negative energy balance in a mouse model of chronic psychosocial defeat. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaswal, J.S.; Keung, W.; Wang, W.; Ussher, J.R.; Lopaschuk, G.D. Targeting fatty acid and carbohydrate oxidation—A novel therapeutic intervention in the ischemic and failing heart. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 1333–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubkowska, A.; Radecka, A.; Bryczkowska, I.; Rotter, I.; Laszczyńska, M.; Dudzińska, W. Serum adiponectin and leptin concentrations in relation to body fat distribution, hematological indices and lipid profile in humans. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 11528–11548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, D.B.; Petersen, K.F.; Shulman, G.I. Disordered lipid metabolism and the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, M.D.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Postic, C.; Previs, S.F.; Shulman, G.I.; Magnuson, M.A.; Kahn, C.R. Loss of insulin signaling in hepatocytes leads to severe insulin resistance and progressive hepatic dysfunction. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaboration, E.R.F. Diabetes mellitus, fasting glucose, and risk of cause-specific death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellentani, S.; Marino, M. Epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Ann. Hepatol. 2009, 8, S4–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Park, H.; Choi, B.-R.; Ji, Y.; Kwon, E.-Y.; Choi, M.-S. Alteration of microbiome profile by d-allulose in amelioration of high-fat-diet-induced obesity in mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.X.; Pandey, S.K.; Booten, S.L.; Murray, S.F.; Monia, B.P.; Bhanot, S. Reduced adiposity and improved insulin sensitivity in obese mice with antisense suppression of 4E-BP2 expression. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 294, E530–E539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hatting, M.; Tavares, C.D.; Sharabi, K.; Rines, A.K.; Puigserver, P. Insulin regulation of gluconeogenesis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1411, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lontchi-Yimagou, E.; Sobngwi, E.; Matsha, T.E.; Kengne, A.P. Diabetes mellitus and inflammation. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2013, 13, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, F.; Bai, J.; Tan, X.; Chen, T.; Yang, W.; He, F. Antimicrobial activities and mechanism of the essential oil from Artemisia argyi Levl. et Van. var. argyi cv. Qiai. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 125, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-C.; Wang, H.-F.; Yih, K.-H.; Chang, L.-Z.; Chang, T.-M. Dual bioactivities of essential oil extracted from the leaves of Artemisia argyi as an antimelanogenic versus antioxidant agent and chemical composition analysis by GC/MS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 14679–14697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Wei, Y.; Meng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, G. Effects of Water Extract from Artemisia argyi Leaves on LPS-Induced Mastitis in Mice. Animals 2022, 12, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucena, M.I.; Salmerón, J.; Planas, R.; de Catalunya, G.; Andrade, R.J. Liver injury induced by “natural remedies”: An analysis of cases submitted to the Spanish Liver Toxicity Registry. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2008, 100, 688–695. [Google Scholar]
- López-Gil, S.; Nuño-Lámbarri, N.; Chávez-Tapia, N.; Uribe, M.; Barbero-Becerra, V.J. Liver toxicity mechanisms of herbs commonly used in Latin America. Drug Metab. Rev. 2017, 49, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasugi, T.; Nakashima, M.; Komai, K. Antimutagens in Gaiyou (Artemisia a rgyi Levl. et Vant.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3256–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, S.-W.; Kim, N.-J.; Baek, N.-I.; Kim, D.-H. Inhibitory effect of eupatilin and jaceosidin isolated from Artemisia princeps on carrageenan-induced inflammation in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 125, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.C.; Park, S.Y.; Nam, Y.; Nguyen, T.T.; Sohn, U.D. The protective effect of eupatilin against hydrogen peroxide-induced injury involving 5-lipoxygenase in feline esophageal epithelial cells. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 16, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, S.G.; Min, K.; Kwon, T.K.; Kim, H.-J.; Nam, J.-O. Eupatilin inhibits adipogenesis through suppression of PPARγ activity in 3T3-L1 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Jiao, Q.; Zhang, D.; Liu, A.-P.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, Y.-G. Quality evaluation of Artemisiae Argyi Folium based on fingerprint analysis and quantitative analysis of multicomponents. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi/Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi/China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2018, 43, 977–984. [Google Scholar]
| Amount | |
|---|---|
| Total polyphenolic content | 143.94 ± 1.20 (GAE)/g |
| Total flavonoid content | 23.42 ± 0.01 (QE)/g |
| Eupatilin content | 0.82 ± 0.01 (mg eupatilin/g) |
| Ingredient (g) | ND (AIN-93G) | HFD (60 kcal% Fat) | AA (0.1% A. argyi) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Casein | 200 | 267 | 267 |
| Corn starch | 397.486 | 63.381 | 63.381 |
| Sucrose | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Dextrose | 132 | 176 | 176 |
| Cellulose | 50 | 67 | 67 |
| Soybean oil | 70 | 33 | 33 |
| Lard | 0 | 327 | 327 |
| Mineral mixture 1 | 35 | 47 | 47 |
| Vitamin mixture 2 | 10 | 13 | 13 |
| TBHQ, antioxidant | 0.014 | 0.019 | 0.019 |
| L-cystine | 3 | 4 | 4 |
| Choline bitartrate | 2.5 | 3 | 3 |
| Artemisiae argyi | - | - | 1 |
| Total (g) | 1000.00 | 1000.00 | 1001.00 |
| Calorie (kcal/g) | 4000 | 5332.62 | 5332.62 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Park, H.-J.; Hong, M.-K.; Shin, M.-R.; Roh, S.-S.; Kwon, E.-Y. Artemisiae argyi Water Extract Alleviates Obesity-Induced Metabolic Disorder. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 6158-6171. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44120420
Han Y, Park H-J, Hong M-K, Shin M-R, Roh S-S, Kwon E-Y. Artemisiae argyi Water Extract Alleviates Obesity-Induced Metabolic Disorder. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2022; 44(12):6158-6171. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44120420
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Youngji, Hae-Jin Park, Min-Kyeong Hong, Mi-Rae Shin, Seong-Soo Roh, and Eun-Young Kwon. 2022. "Artemisiae argyi Water Extract Alleviates Obesity-Induced Metabolic Disorder" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 44, no. 12: 6158-6171. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44120420
APA StyleHan, Y., Park, H.-J., Hong, M.-K., Shin, M.-R., Roh, S.-S., & Kwon, E.-Y. (2022). Artemisiae argyi Water Extract Alleviates Obesity-Induced Metabolic Disorder. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 44(12), 6158-6171. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44120420







