Developmental Cues and Molecular Drivers in Myelinogenesis: Revisiting Early Life to Re-Evaluate the Integrity of CNS Myelin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Myelinogenesis and Myelin Development: A Spatiotemporal Coordination
2.1. Primordium Regions of OPCs
2.2. Molecular Signals Driving Myelinogenesis
2.2.1. Formation of OPCs
2.2.2. Migration
2.2.3. Proliferation
2.2.4. Differentiation
2.2.5. Ensheathment
2.2.6. Myelin Sheath Growth and Preservation
2.3. Myelin Formation after Infancy
3. Myelinogenesis in Disease and Beyond
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OPCs | Oligodendrocyte precursor cells |
| OLs | Oligodendrocytes |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| NSCs | Neural stem cells |
| aOPCs | Adult oligodendrocyte precursor cells |
| E | Embryonic day |
| GW | Gestational week |
| VZ | Ventricular zone |
| SVZ | Subventricular zone |
| RG | Radial glia |
| oSVZ | Outer subventricular zone |
| MGE | Medial ganglionic eminence |
| MS | Multiple sclerosis |
| ABCD1 | Adenosine triphosphate binding cassette subfamily D member 1 |
| ASCL1 | Achaete-scute family basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor 1 |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| BMP4 | Bone morphogenetic protein 4 |
| BMP7 | Bone morphogenetic protein 7 |
| CADM1b | Cell adhesion molecule 1b |
| CADM2 | Cell adhesion molecule 2 |
| CADM3 | Cell adhesion molecule 3 |
| CADM4 | Cell adhesion molecule 4 |
| CASPR | Contactin-associated protein |
| CASPR2 | Contactin-associated protein-like 2 |
| CGT | Ceramide galactosyl transferase |
| CHD7 | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 7 |
| CHD8 | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 8 |
| CLDN1 | Claudin 1 |
| OSP | Oligodendrocyte specific protein |
| CLDN3 | Claudin 3 |
| CNPase | 2′,3′-cyclic nucleotide 3′ phosphodiesterase |
| CNTN1 | Contactin 1 |
| CST | Ceramide sulfotransferase |
| CX32 | Connexin 32 |
| CX47 | Connexin 47 |
| CXCL1 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 1 |
| CXCL12 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 |
| CXCR2 | C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 2 |
| CXCR4 | C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4 |
| DLX1 | Distal-less homeobox 1 |
| DLX2 | Distal-less homeobox 2 |
| EphA4 | Ephrin receptor A4 |
| EphB1 | Ephrin receptor B1 |
| EphB2 | Ephrin receptor B2 |
| ET-1 | Endothelin 1 |
| FGF2 | Fibroblast growth factor 2 |
| FGFR1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 |
| FGFR2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 |
| GAL-4 | Galectin-4 |
| GALC | Galactosylceramidase |
| GLI2 | Glioma-associated oncogene family zinc finger 2 |
| HDAC1 | Histone deacetylase 1 |
| HDAC2 | Histone deacetylase 2 |
| HDAC3 | Histone deacetylase 3 |
| HES5 | Hairy and enhancer of split family basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor 5 |
| HGF | Hepatocyte growth factor |
| ID2 | Inhibitor of DNA binding 2 |
| ID4 | Inhibitor of DNA binding 4 |
| JAG1 | Jagged canonical Notch ligand 1 |
| LINGO-1 | Leucine-rich repeat and Ig-like domain-containing Nogo receptor interacting protein 1 |
| MAG | Myelin-associated glycoprotein |
| MAP2 | Microtubule-associated protein 2 |
| MAPT | Microtubule-associated protein tau |
| MBP | Myelin basic protein |
| MYRF | Myelin regulatory factor |
| MYT1 | Myelin transcription factor 1 |
| NCAD | N-cadherin |
| NCAM | Neural cell adhesion molecule |
| NKX2-2 | NK2 homeobox 2 |
| NKX2-6 | NK2 homeobox 6 |
| NKX6-2 | NK6 homeobox 2 |
| NRG1 | Neuregulin 1 |
| NT-3 | Neurotrophin 3 |
| OAP-1 | Oligodendrocyte specific protein–associated protein |
| OLIG1 | Oligodendrocyte transcription factor 1 |
| OLIG2 | Oligodendrocyte transcription factor 2 |
| OMgp | Oligodendrocyte myelin glycoprotein |
| PAX6 | Paired box 6 |
| PDGFA | Platelet-derived growth factor subunit A |
| PDGFRα | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha |
| PLP | Myelin proteolipid protein |
| QKI | Quaking homolog, KH domain RNA binding |
| S1PR1 | Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 |
| S1PR2 | Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 |
| S1PR3 | Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3 |
| S1PR5 | Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 5 |
| SHH | Sonic hedgehog signaling molecule |
| BRG1 | Brahma-Related Gene-1 |
| SOD1 | Superoxide dismutase 1 |
| SOX1 | Sex-determining region Y-box transcription factor 1 |
| SOX10 | Sex-determining region Y-box transcription factor 10 |
| SOX11 | Sex-determining region Y-box transcription factor 11 |
| SOX2 | Sex-determining region Y-box transcription factor 2 |
| SOX3 | Sex-determining region Y-box transcription factor 3 |
| SOX5 | Sex-determining region Y-box transcription factor 5 |
| SOX6 | Sex-determining region Y-box transcription factor 6 |
| SOX8 | Sex-determining region Y-box transcription factor 8 |
| SOX9 | Sex-determining region Y-box transcription factor 9 |
| SREBF2 | Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 2 |
| TRα | Thyroid hormone receptor alpha |
| TRβ1 | Thyroid hormone receptor isoform beta 1 |
| TDP-43 | Transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 |
| TMEM10 | Transmembrane Protein 10 |
| TMEM98 | Transmembrane protein 98 |
| TPPP | Tubulin polymerization promoting protein |
| VEGF-A | Vascular endothelial growth factor A |
| VEGFR2 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 |
| αvβ1 integrin | Integrin subunit beta 1 |
| αvβ3 integrin | Integrin subunit beta 3 |
Appendix A
| Gene * | Chromosomal Locus * | Protein * | Biological Role | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABCD1 | Xq28 | ATP binding cassette subfamily D member 1 | Differentiation | [163,164] |
| ADGRG1 | 16q21 | Adhesion G protein-coupled receptor G1 | Proliferation | [239] |
| ANOS1 | Xp22.31 | Anosmin 1 | Migration | [240] |
| ASCL1 | 12q23.2 | Achaete-scute family bHLH transcription factor 1 | Specification; Proliferation; Differentiation | [93,108,139,241] |
| BCAS1 | 20q13.2 | Brain enriched myelin-associated protein 1 | Differentiation | [156,157,242] |
| BDNF | 11p14.1 | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor | Proliferation; Differentiation | [75,128] |
| BMP2 | 20p12.3 | Bone morphogenetic protein 2 | Specification; Differentiation | [27,105] |
| BMP4 | 14q22.2 | Bone morphogenetic protein 4 | Specification; Migration; Differentiation | [28,65,105] |
| BMP7 | 20q13.31 | Bone morphogenetic protein 7 | Migration | [65] |
| CDH2 | 18q12.1 | Cadherin 2 | Migration | [57] |
| CDKN1B | 12p13.1 | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B | Proliferation | [85] |
| CHD7 | 8q12.2 | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 7 | Proliferation; Differentiation | [80,243] |
| CHD8 | 14q11.2 | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 8 | Specification; Proliferation; Differentiation | [80,81] |
| CLDN1 | 3q28 | Claudin 1 | Migration; Proliferation; Differentiation | [70] |
| CLDN3 | 7q11.23 | Claudin 3 | Migration; Proliferation; Differentiation | [70] |
| CLDN11 | 3q26.2 | Claudin 11 | Migration; Proliferation | [56] |
| CNP | 17q21.2 | 2′,3′-cyclic nucleotide 3′ phosphodiesterase | Migration; Differentiation | [52,153] |
| CNTF | 11q12.1 | Ciliary neurotrophic factor | Proliferation; Differentiation | [148,244] |
| CNTFR | 9p13.3 | Ciliary neurotrophic factor receptor | Proliferation | [244] |
| CNTN1 | 12q12 | Contactin 1 | Differentiation | [141] |
| CREB3L2 | 7q33 | CAMP responsive element binding protein 3 like 2 | Differentiation | [243] |
| CSPG4 | 15q24.2 | Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 | Proliferation | [245] |
| CXCL1 | 4q13.3 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 1 | Migration; Proliferation | [67,72] |
| CXCL12 | 10q11.21 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 | Migration; Proliferation | [68,73] |
| CXCR2 | 2q35 | C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 2 | Migration; Proliferation | [67,72] |
| CXCR4 | 2q22.1 | C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4 | Migration; Proliferation | [68,73] |
| DLX1 | 2q31.1 | Distal-less homeobox 1 | Specification | [246] |
| DLX2 | 2q31.1 | Distal-less homeobox 2 | Specification | [246] |
| DUSP15 | 20q11.21 | Dual specificity phosphatase 15 | Differentiation | [247] |
| EDN1 | 6p24.1 | Endothelin 1 | Migration; Proliferation | [60,98] |
| EDNRB | 13q22.3 | Endothelin receptor type B | Proliferation | [98] |
| EFNB2 | 13q33.3 | Ephrin B2 | Migration; Proliferation | [46,248] |
| EFNB3 | 17p13.1 | Ephrin B3 | Migration | [46] |
| EGF | 4q25 | Epidermal growth factor | Proliferation | [76] |
| EGR1 | 5q31.2 | Early growth response 1 | Differentiation | [116] |
| ENPP6 | 4q35.1 | Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 6 | Differentiation | [135] |
| EPHB2 | 1p36.12 | Ephrin receptor B2 | Migration; Proliferation | [46,248] |
| FEZ1 | 11q24.2 | Fasciculation and elongation protein zeta 1 | Differentiation | [152] |
| FGF2 | 4q28.1 | Fibroblast growth factor 2 | Specification; Migration; Proliferation | [240,249] |
| FGFR1 | 8p11.23 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Migration; Proliferation | [240,249] |
| FGFR2 | 10q26.13 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Specification | [31,249] |
| FGFR3 | 4p16.3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Proliferation | [249] |
| FLT1 | 13q12.3 | Fms related receptor tyrosine kinase 1 | Proliferation | [250] |
| FN1 | 2q35 | Fibronectin 1 | Migration; Proliferation | [59,96] |
| GAB1 | 4q31.21 | GRB2-associated binding protein 1 | Differentiation | [132] |
| GALC | 14q31.3 | Galactosylceramidase | Differentiation | [144] |
| GDPD2 | Xq13.1 | Glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase domain containing 2 | Proliferation | [244] |
| GJC2 | 1q42.13 | Gap junction protein gamma 2 | Differentiation | [160,161,162,251] |
| GLI2 | 2q14.2 | GLI family zinc finger 2 | Specification; Differentiation | [38] |
| GPR17 | 2q14.3 | G protein-coupled receptor 17 | Differentiation | [113] |
| GPR37 | 7q31.33 | G protein-coupled receptor 37 | Differentiation | [252] |
| GSX1 | 13q12.2 | GS homeobox 1 | Proliferation | [99] |
| GSX2 | 4q12 | GS homeobox 2 | Specification; Proliferation | [99,253] |
| HDAC1 | 1p35.2-p35.1 | Histone deacetylase 1 | Specification | [254,255] |
| HDAC2 | 6q21 | Histone deacetylase 2 | Specification | [254] |
| HES1 | 3q29 | Hes family bHLH transcription factor 1 | Specification | [256] |
| HES5 | 1p36.32 | Hes family bHLH transcription factor 5 | Differentiation | [139] |
| HEY1 | 8q21.13 | Hes related family bHLH transcription factor with YRPW motif 1 | Differentiation | [257] |
| HGF | 7q21.11 | Hepatocyte growth factor | Migration; Proliferation | [54] |
| ID2 | 2p25.1 | Inhibitor of DNA binding 2 | Proliferation; Differentiation | [89,113,115] |
| ID4 | 6p22.3 | Inhibitor of DNA binding 4, HLH protein | Proliferation; Differentiation | [88,113,114,115] |
| IGF1 | 12q23.2 | Insulin-like growth factor 1 | Proliferation; Differentiation | [74,131] |
| IRX3 | 16q12.2 | Iroquois homeobox 3 | Specification | [37] |
| ITGB1 | 10p11.22 | Integrin subunit beta 1 | Migration; Proliferation; Differentiation | [56,58,258] |
| ITGB3 | 17q21.32 | Integrin subunit beta 3 | Proliferation | [69,97] |
| JAG1 | 20p12.2 | Jagged canonical Notch ligand 1 | Proliferation; Differentiation | [79] |
| JUN | 1p32.1 | Jun proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit | Proliferation | [259,260] |
| KCNJ10 | 1q23.2 | Potassium inwardly rectifying channel subfamily J member 10 | Differentiation | [149] |
| KDR | 4q12 | Kinase insert domain receptor | Migration; Proliferation | [64,250] |
| KLF6 | 10p15.2 | Kruppel-like factor 6 | Differentiation | [127] |
| LAMA2 | 6q22.33 | Laminin subunit alpha 2 | Migration; Proliferation | [96,261] |
| LAMA4 | 6q21 | Laminin subunit alpha 4 | Migration; Proliferation | [96,261] |
| LAMA5 | 20q13.33 | Laminin subunit alpha 5 | Migration; Proliferation | [96,261] |
| LGALS4 | 19q13.2 | Galectin-4 | Proliferation; Differentiation | [100] |
| LINGO1 | 15q24.3 | Leucine rich repeat and Ig domain containing 1 | Differentiation | [143] |
| MAG | 19q13.12 | Myelin-associated glycoprotein | Differentiation | [147] |
| MAP2 | 2q34 | Microtubule-associated protein 2 | Differentiation | [151] |
| MAPT | 17q21.31 | Microtubule-associated protein tau | Differentiation | [151] |
| MBP | 18q23 | Myelin basic protein | Differentiation | [159] |
| MOBP | 3p22.1 | Myelin associated oligodendrocyte basic protein | Differentiation | [190] |
| MYOC | 1q24.3 | Myocilin | Differentiation | [262] |
| MYRF | 11q12.2 | Myelin regulatory factor | Differentiation | [117] |
| MYT1 | 20q13.33 | Myelin transcription factor 1 | Specification; Proliferation | [39,83] |
| NCAM1 | 11q23.2 | Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 | Migration; Proliferation | [47,48,84,142] |
| NES | 1q23.1 | Nestin | Migration; Proliferation | [49,263] |
| NEUROG1 | 5q31.1 | Neurogenin 1 | Specification | [37,264,265] |
| NEUROG2 | 4q25 | Neurogenin 2 | Specification | [37,264,265] |
| NFIA | 1p31.3 | Nuclear factor I A | Specification | [37,266] |
| NGF | 1p13.2 | Nerve growth factor | Proliferation | [92,267] |
| NKX2-2 | 20p11.22 | NK2 homeobox 2 | Specification; Proliferation; Differentiation | [37,108,123,124,268] |
| NKX2-6 | 8p21.2 | NK2 homeobox 6 | Specification; Differentiation | [40] |
| NKX6-1 | 4q21.23 | NK6 homeobox 1 | Specification | [26] |
| NKX6-2 | 10q26.3 | NK6 homeobox 2 | Specification | [26] |
| NOG | 17q22 | Noggin | Proliferation; Differentiation | [91,106,107] |
| NOTCH1 | 9q34.3 | Notch receptor 1 | Proliferation; Differentiation | [79,140] |
| NRG1 | 8p12 | Neuregulin 1 | Migration; Proliferation; Differentiation | [101,103,269] |
| NTF3 | 12p13.31 | Neurotrophin 3 | Proliferation; Differentiation | [92,129,130] |
| NTF4 | 19q13.33 | Neurotrophin 4 | Proliferation | [90] |
| NTN1 | 17p13.1 | Netrin 1 | Migration | [61,62,63] |
| NTRK2 | 9q21.33 | Neurotrophic receptor tyrosine kinase 2 | Proliferation; Differentiation | [75,270] |
| OLIG1 | 21q22.11 | Oligodendrocyte transcription factor 1 | Migration; Differentiation | [50,51,104,271] |
| OLIG2 | 21q22.11 | Oligodendrocyte transcription factor 2 | Specification; Migration; Differentiation | [51,53,271] |
| OMG | 17q11.2 | Oligodendrocyte myelin glycoprotein | Proliferation; Differentiation | [155] |
| OPALIN | 10q24.1 | Oligodendrocytic myelin paranodal and inner loop protein | Differentiation | [272,273] |
| PAK1 | 11q13.5-q14.1 | P21 (RAC1) activated kinase 1 | Differentiation | [146] |
| PAX6 | 11p13 | Paired box 6 | Specification; Proliferation | [94,274,275] |
| PDE5 | 4q26 | Phosphodiesterase 5A | Differentiation | [276] |
| PDGFA | 7p22.3 | Platelet-derived growth factor subunit A | Migration; Proliferation; Differentiation | [42,277] |
| PDGFRA | 4q12 | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Migration; Proliferation; Differentiation | [42,47,71,277] |
| PLP1 | Xq22.2 | Proteolipid protein 1 | Differentiation | [158] |
| PRMT5 | 14q11.2 | Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 | Differentiation | [278] |
| PROM1 | 4p15.32 | Prominin 1 | Differentiation | [145] |
| QKI | 6q26 | QKI, KH domain containing RNA binding | Differentiation | [133,279] |
| RTN4 | 2p16.1 | Reticulon 4 | Migration | [280] |
| S1PR1 | 1p21.2 | Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 | Migration | [66] |
| S1PR2 | 19p13.2 | Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 | Migration | [66] |
| S1PR3 | 9q22.1 | Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3 | Migration | [66] |
| S1PR5 | 19p13.2 | Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 5 | Migration | [66] |
| SEMA3A | 7q21.11 | Semaphorin 3A | Migration | [61] |
| SEMA3F | 3p21.31 | Semaphorin 3F | Migration; Proliferation | [61] |
| SETDB1 | 1q21.3 | SET domain bifurcated histone lysine methyltransferase 1 | Differentiation | [112] |
| SHH | 7q36.3 | Sonic hedgehog signaling molecule | Specification; Migration; Proliferation | [27,28,29,30,32,41] |
| SIRT1 | 10q21.3 | Sirtuin 1 | Differentiation | [126] |
| SIRT2 | 19q13.2 | Sirtuin 2 | Differentiation | [125] |
| SMARCA4 | 19p13.2 | SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily a, member 4 | Specification; Differentiation | [109,243] |
| SOD1 | 21q22.11 | Superoxide dismutase 1 | Proliferation; Differentiation | [95] |
| SOX1 | 13q34 | SRY-box transcription factor 1 | Specification | [33] |
| SOX2 | 3q26.33 | SRY-box transcription factor 2 | Specification; Proliferation; Differentiation | [33,102,119] |
| SOX3 | Xq27.1 | SRY-box transcription factor 3 | Specification; Differentiation | [33,119] |
| SOX5 | 12p12.1 | SRY-box transcription factor 5 | Migration; Proliferation; Differentiation | [44] |
| SOX6 | 11p15.2 | SRY-box transcription factor 6 | Migration; Proliferation; Differentiation | [44] |
| SOX8 | 16p13.3 | SRY-box transcription factor 8 | Specification; Differentiation | [34,35,36,120] |
| SOX9 | 17q24.3 | SRY-box transcription factor 9 | Specification; Migration; Proliferation; Differentiation | [36,44,82] |
| SOX10 | 22q13.1 | SRY-box transcription factor 10 | Specification; Migration; Differentiation | [43,44,122,281] |
| SOX11 | 2p25.2 | SRY-box transcription factor 11 | Differentiation | [116] |
| SP7 | 12q13.13 | Sp7 transcription factor | Differentiation | [243] |
| SREBF2 | 22q13.2 | Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 2 | Differentiation | [133] |
| STAT3 | 17q21.2 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 | Differentiation | [282] |
| SULF1 | 8q13.2-q13.3 | Sulfatase 1 | Specification | [30] |
| TARDBP | 1p36.22 | TAR DNA binding protein | Differentiation | [134] |
| TCF4 | 18q21.2 | Transcription factor 4 | Differentiation | [110] |
| TCF7L2 | 10q25.2-q25.3 | Transcription factor 7 like 2 | Differentiation | [111] |
| THBS1 | 15q14 | Thrombospondin 1 | Migration | [55] |
| THRA | 17q21.1 | Thyroid hormone receptor alpha | Differentiation | [136,137,138] |
| TMEM98 | 17q11.2 | Transmembrane protein 98 | Differentiation | [195] |
| TNC | 9q33.1 | Tenascin C | Migration; Proliferation | [59,69] |
| TPPP | 5p15.33 | Tubulin polymerization promoting protein | Proliferation; Differentiation | [87] |
| TSPAN3 | 15q24.3 | Tetraspanin 3 | Migration; Proliferation | [56] |
| VEGFA | 6p21.1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor A | Migration; Proliferation | [64,250] |
| WDR1 | 4p16.1 | WD repeat domain 1 | Differentiation | [279] |
| YY1 | 14q32.2 | YY1 transcription factor | Differentiation | [283] |
| ZBTB33 | Xq24 | Zinc finger and BTB domain containing 33 | Differentiation | [111] |
| ZDHHC5 | 11q12.1 | Zinc finger DHHC-type palmitoyltransferase 5 | Differentiation | [282] |
| ZEB2 | 2q22.3 | Zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 | Differentiation | [284] |
| ZNF24 | 18q12.2 | Zinc finger protein 24 | Differentiation | [150] |
| Gene * | Chromosomal Locus * | Protein * | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CADM1 | 11q23.3 | Cell adhesion molecule 1 | [174] |
| CADM2 | 3p12.1 | Cell adhesion molecule 2 | [173,174] |
| CADM3 | 1q23.2 | Cell adhesion molecule 3 | [173] |
| CADM4 | 19q13.31 | Cell adhesion molecule 4 | [173] |
| CDH2 | 18q12.1 | Cadherin 2 | [165] |
| CNTN1 | 12q12 | Contactin 1 | [167,168,169,171] |
| CNTN2 | 1q32.1 | Contactin 2 | [172] |
| CNTNAP1 | 17q21.2 | Contactin-associated protein 1 | [167,168,169,170] |
| CNTNAP2 | 7q35–q36.1 | Contactin-associated protein 2 | [172] |
| EFNA1 | 1q22 | Ephrin A1 | [177] |
| EFNB2 | 13q33.3 | Ephrin B2 | [178] |
| EPHA4 | 2q36.1 | Ephrin receptor A4 | [177,178] |
| EPHB1 | 3q22.2 | Ephrin receptor B1 | [178] |
| JAM2 | 21q21.3 | Junctional adhesion molecule 2 | [181] |
| L1CAM | Xq28 | L1 cell adhesion molecule | [166] |
| LGALS4 | 19q13.2 | Galectin-4 | [182] |
| LINGO1 | 15q24.3 | Leucine rich repeat and Ig domain containing 1 | [143,179] |
| MAG | 19q13.12 | Myelin-associated glycoprotein | [176] |
| NCAM1 | 11q23.2 | Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 | [180] |
| NFASC | 1q32.1 | Neurofascin | [167,168,169,170] |
| NRG1 | 8p12 | Neuregulin 1 | [286,287] |
| OLIG1 | 21q22.11 | Oligodendrocyte transcription factor 1 | [183] |
| ST3GAL2 | 16q22.1 | ST3 beta-galactoside alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 2 | [175,176] |
| ST3GAL3 | 1p34.1 | ST3 beta-galactoside alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 3 | [175,176] |
| WASL | 7q31.32 | WASP-like actin nucleation promoting factor | [288,289] |
| Gene * | Chromosomal Locus * | Protein * | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABCD1 | Xq28 | ATP binding cassette subfamily D member 1 | [164,203] |
| AGPS | 2q31.2 | Alkylglycerone phosphate synthase | [24,290] |
| CA2 | 8q21.2 | Carbonic anhydrase 2 | [291] |
| CLDN1 | 3q28 | Claudin 1 | [70] |
| CLDN3 | 7q11.23 | Claudin 3 | [70] |
| CLDN11 | 3q26.2 | Claudin 11 | [185] |
| CNP | 17q21.2 | 2′,3′-cyclic nucleotide 3′ phosphodiesterase | [52,189] |
| DUSP15 | 20q11.21 | Dual specificity phosphatase 15 | [247] |
| FGF1 | 5q31.3 | Fibroblast growth factor 1 | [198] |
| FGF2 | 4q28.1 | Fibroblast growth factor 2 | [198] |
| FGFR1 | 8p11.23 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | [197,198] |
| FGFR2 | 10q26.13 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | [197,198] |
| GAL3ST1 | 22q12.2 | Galactose-3-O-sulfotransferase 1 | [200] |
| GALC | 14q31.3 | Galactosylceramidase | [200,201] |
| GFAP | 17q21.31 | Glial fibrillary acidic protein | [292] |
| GJB1 | Xq13.1 | Gap junction protein beta 1 | [161] |
| GJC2 | 1q42.13 | Gap junction protein gamma 2 | [161] |
| GNPAT | 1q42.2 | Glyceronephosphate O-acyltransferase | [290] |
| HDAC3 | 5q31.3 | Histone deacetylase 3 | [199] |
| ID4 | 6p22.3 | Inhibitor of DNA binding 4, HLH protein | [114] |
| MAG | 19q13.12 | Myelin-associated glycoprotein | [147,186] |
| MAL | 2q11.1 | Mal, T cell differentiation protein | [293] |
| MAP2 | 2q34 | Microtubule-associated protein 2 | [151] |
| MAPT | 17q21.31 | Microtubule-associated protein tau | [151] |
| MBP | 18q23 | Myelin basic protein | [52] |
| MOBP | 3p22.1 | Myelin-associated oligodendrocyte basic protein | [190] |
| MOG | 6p22.1 | Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein | [187,188] |
| MYRF | 11q12.2 | Myelin regulatory factor | [193] |
| NCAM1 | 11q23.2 | Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 | [294] |
| NKX2-2 | 20p11.22 | NK2 homeobox 2 | [194] |
| NKX2-6 | 8p21.2 | NK2 homeobox 6 | [194] |
| NPC1 | 18q11.2 | NPC intracellular cholesterol transporter 1 | [295] |
| OLIG1 | 21q22.11 | Oligodendrocyte transcription factor 1 | [183,196] |
| OLIG2 | 21q22.11 | Oligodendrocyte transcription factor 2 | [112,196] |
| OMG | 17q11.2 | Oligodendrocyte myelin glycoprotein | [86,191,192] |
| OPALIN | 10q24.1 | Oligodendrocytic myelin paranodal and inner loop protein | [204] |
| PEX5 | 12p13.31 | Peroxisomal biogenesis factor 5 | [202] |
| PLP1 | Xq22.2 | Proteolipid protein 1 | [184,185] |
| PROM1 | 4p15.32 | Prominin 1 | [296] |
| QKI | 6q26 | QKI, KH domain containing RNA binding | [133] |
| SETDB1 | 1q21.3 | SET domain bifurcated histone lysine methyltransferase 1 | [112] |
| SOX8 | 16p13.3 | SRY-box transcription factor 8 | [35] |
| SOX10 | 22q13.1 | SRY-box transcription factor 10 | [35,122] |
| SREBF2 | 22q13.2 | Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 2 | [133] |
| TMEM98 | 17q11.2 | Transmembrane protein 98 | [195] |
| TPPP | 5p15.33 | Tubulin polymerization promoting protein | [297] |
| UGT8 | 4q26 | UDP glycosyltransferase 8 | [200,201] |
References
- Allen, N.J.; Barres, B.A. Glia—More than Just Brain Glue. Nature 2009, 457, 675–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, M.; Nave, K.-A. Oligodendrocytes: Myelination and Axonal Support. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a020479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herculano-Houzel, S. The Glia/Neuron Ratio: How It Varies Uniformly across Brain Structures and Species and What That Means for Brain Physiology and Evolution: The Glia/Neuron Ratio. Glia 2014, 62, 1377–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bercury, K.K.; Macklin, W.B. Dynamics and Mechanisms of CNS Myelination. Dev. Cell 2015, 32, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nave, K.-A.; Werner, H.B. Myelination of the Nervous System: Mechanisms and Functions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 503–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boullerne, A.I. The History of Myelin. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 283, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, J.M.; McGowan, E.; Chapple, K.J.; Möbius, W.; Lemgruber, L.; Insall, R.H.; Nave, K.; Boullerne, A. Río-Hortega’s Drawings Revisited with Fluorescent Protein Defines a Cytoplasm-filled Channel System of CNS Myelin. J. Anat. 2021, 239, 1241–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cerdá, F.; Sánchez-Gómez, M.V.; Matute, C. Pío Del Río Hortega and the Discovery of the Oligodendrocytes. Front. Neuroanat. 2015, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Cerdeño, V.; Noctor, S.C. Neural Progenitor Cell Terminology. Front. Neuroanat. 2018, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tilborg, E.; de Theije, C.G.M.; van Hal, M.; Wagenaar, N.; de Vries, L.S.; Benders, M.J.; Rowitch, D.H.; Nijboer, C.H. Origin and Dynamics of Oligodendrocytes in the Developing Brain: Implications for Perinatal White Matter Injury. Glia 2018, 66, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, A.; Shimizu, T.; Sherafat, A.; Richardson, W.D. Life-Long Oligodendrocyte Development and Plasticity. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 116, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scantlebury, N.; Cunningham, T.; Dockstader, C.; Laughlin, S.; Gaetz, W.; Rockel, C.; Dickson, J.; Mabbott, D. Relations between White Matter Maturation and Reaction Time in Childhood. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2014, 20, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabbott, D.J.; Noseworthy, M.; Bouffet, E.; Laughlin, S.; Rockel, C. White Matter Growth as a Mechanism of Cognitive Development in Children. NeuroImage 2006, 33, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.M.; Psachoulia, K.; Tripathi, R.B.; Dunn, S.-J.; Cossell, L.; Attwell, D.; Tohyama, K.; Richardson, W.D. Oligodendrocyte Dynamics in the Healthy Adult CNS: Evidence for Myelin Remodeling. Neuron 2013, 77, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sams, E.C. Oligodendrocytes in the Aging Brain. Neuronal Signal. 2021, 5, NS20210008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinney, H.C.; Volpe, J.J. Chapter 8—Myelination Events. In Volpe’s Neurology of the Newborn, 6th ed.; Volpe, J.J., Inder, T.E., Darras, B.T., de Vries, L.S., du Plessis, A.J., Neil, J.J., Perlman, J.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 176–188. ISBN 978-0-323-42876-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, E.G.; Orthmann-Murphy, J.L.; Langseth, A.J.; Bergles, D.E. Myelin Remodeling through Experience-Dependent Oligodendrogenesis in the Adult Somatosensory Cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabel, L. Developmental Origin of Neural Stem Cells: The Glial Cell That Could. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2012, 8, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.L.; Makowiecki, K.; Cullen, C.L.; Young, K.M. Oligodendrogenesis and Myelination Regulate Cortical Development, Plasticity and Circuit Function. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 118, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergles, D.E.; Richardson, W.D. Oligodendrocyte Development and Plasticity. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 8, a020453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Bhaduri, A.; Velmeshev, D.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Rottkamp, C.A.; Alvarez-Buylla, A.; Rowitch, D.H.; Kriegstein, A.R. Origins and Proliferative States of Human Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells. Cell 2020, 182, 594–608.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessaris, N.; Fogarty, M.; Iannarelli, P.; Grist, M.; Wegner, M.; Richardson, W.D. Competing Waves of Oligodendrocytes in the Forebrain and Postnatal Elimination of an Embryonic Lineage. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradl, M.; Lassmann, H. Oligodendrocytes: Biology and Pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumann, N.; Pham-Dinh, D. Biology of Oligodendrocyte and Myelin in the Mammalian Central Nervous System. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 871–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, R.B.; Clarke, L.E.; Burzomato, V.; Kessaris, N.; Anderson, P.N.; Attwell, D.; Richardson, W.D. Dorsally and Ventrally Derived Oligodendrocytes Have Similar Electrical Properties but Myelinate Preferred Tracts. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 6809–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, J.; Qi, Y.; Hu, X.; Tan, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Sander, M.; Qiu, M. Generation of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells from Mouse Dorsal Spinal Cord Independent of Nkx6 Regulation and Shh Signaling. Neuron 2005, 45, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.; Mehler, M.F.; Zhao, J.; Yu Yung, S.; Kessler, J.A. Sonic Hedgehog and BMP2 Exert Opposing Actions on Proliferation and Differentiation of Embryonic Neural Progenitor Cells. Dev. Biol. 1999, 215, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomes, W.A.; Mehler, M.F.; Kessler, J.A. Transgenic Overexpression of BMP4 Increases Astroglial and Decreases Oligodendroglial Lineage Commitment. Dev. Biol. 2003, 255, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orentas, D.M.; Hayes, J.E.; Dyer, K.L.; Miller, R.H. Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Is Required during the Appearance of Spinal Cord Oligodendrocyte Precursors. Dev. Camb. Engl. 1999, 126, 2419–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesin, C.; Agius, E.; Escalas, N.; Ai, X.; Emerson, C.; Cochard, P.; Soula, C. Ventral Neural Progenitors Switch toward an Oligodendroglial Fate in Response to Increased Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) Activity: Involvement of Sulfatase 1 in Modulating Shh Signaling in the Ventral Spinal Cord. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 5037–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farreny, M.-A.; Agius, E.; Bel-Vialar, S.; Escalas, N.; Khouri-Farah, N.; Soukkarieh, C.; Danesin, C.; Pituello, F.; Cochard, P.; Soula, C. FGF Signaling Controls Shh-Dependent Oligodendroglial Fate Specification in the Ventral Spinal Cord. Neural Develop. 2018, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, C.A.; Walker, M.; Ravanelli, A.M.; Scott, K.; Arzbecker, M.R.; Appel, B. Zebrafish Spinal Cord Oligodendrocyte Formation Requires Boc Function. Genetics 2021, 218, iyab082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bylund, M.; Andersson, E.; Novitch, B.G.; Muhr, J. Vertebrate Neurogenesis Is Counteracted by Sox1–3 Activity. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolt, C.C.; Schmitt, S.; Lommes, P.; Sock, E.; Wegner, M. Impact of Transcription Factor Sox8 on Oligodendrocyte Specification in the Mouse Embryonic Spinal Cord. Dev. Biol. 2005, 281, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turnescu, T.; Arter, J.; Reiprich, S.; Tamm, E.R.; Waisman, A.; Wegner, M. Sox8 and Sox10 Jointly Maintain Myelin Gene Expression in Oligodendrocytes. Glia 2018, 66, 279–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozniak, C.D.; Langseth, A.J.; Dijkgraaf, G.J.P.; Choe, Y.; Werb, Z.; Pleasure, S.J. Sox10 Directs Neural Stem Cells toward the Oligodendrocyte Lineage by Decreasing Suppressor of Fused Expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21795–21800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wegner, M. Specification of Oligodendrocytes. In Patterning and Cell Type Specification in the Developing CNS and PNS; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 847–866. ISBN 978-0-12-814405-3. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Tan, M.; Hui, C.-C.; Qiu, M. Gli2 Is Required for Normal Shh Signaling and Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, L.D.; Romm, E.; Berndt, J.A.; Nielsen, J.A. A Tool for Examining the Role of the Zinc Finger Myelin Transcription Factor 1 (Myt1) in Neural Development: Myt1 Knock-in Mice. Transgenic Res. 2011, 20, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miron, V.E.; Kuhlmann, T.; Antel, J.P. Cells of the Oligodendroglial Lineage, Myelination, and Remyelination. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Mol. Basis Dis. 2011, 1812, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merchán, P.; Bribián, A.; Sánchez-Camacho, C.; Lezameta, M.; Bovolenta, P.; de Castro, F. Sonic Hedgehog Promotes the Migration and Proliferation of Optic Nerve Oligodendrocyte Precursors. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2007, 36, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, E.E.; Zhou, Z.; Krasnesky, K.; Armstrong, R.C. Initiation of Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cell Migration by a PDGF-A Activated Extracellular Regulated Kinase (ERK) Signaling Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2009, 34, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finzsch, M.; Stolt, C.C.; Lommes, P.; Wegner, M. Sox9 and Sox10 Influence Survival and Migration of Oligodendrocyte Precursors in the Spinal Cord by Regulating PDGF Receptor Aexpression. Development 2008, 135, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baroti, T.; Zimmermann, Y.; Schillinger, A.; Liu, L.; Lommes, P.; Wegner, M.; Stolt, C.C. Transcription Factors Sox5 and Sox6 Exert Direct and Indirect Influences on Oligodendroglial Migration in Spinal Cord and Forebrain: SoxD Proteins in Oligodendrocyte Progenitors. Glia 2016, 64, 122–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biname, F.; Sakry, D.; Dimou, L.; Jolivel, V.; Trotter, J. NG2 Regulates Directional Migration of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells via Rho GTPases and Polarity Complex Proteins. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 10858–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prestoz, L.; Chatzopoulou, E.; Lemkine, G.; Spassky, N.; Lebras, B.; Kagawa, T.; Ikenaka, K.; Zalc, B.; Thomas, J.-L. Control of Axonophilic Migration of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells by Eph–Ephrin Interaction. Neuron Glia Biol. 2004, 1, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinspan, J.B.; Franceschini, B. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Is a Survival Factor for PSA-NCAM+ Oligodendrocyte Pre-Progenitor Cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 1995, 41, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, L.; Avellana-Adalid, V.; Nait-Oumesmar, B.; Durbec, P.; Baron-Van Evercooren, A. Oligodendrocyte Precursor Migration and Differentiation: Combined Effects of PSA Residues, Growth Factors, and Substrates. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2000, 16, 422–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, V.; Armstrong, R. Developmental and Growth Factor-Induced Regulation of Nestin in Oligodendrocyte Lineage Cells. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motizuki, M.; Isogaya, K.; Miyake, K.; Ikushima, H.; Kubota, T.; Miyazono, K.; Saitoh, M.; Miyazawa, K. Oligodendrocyte Transcription Factor 1 (Olig1) Is a Smad Cofactor Involved in Cell Motility Induced by Transforming Growth Factor-β. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 18911–18922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Q.; Anderson, D.J. The BHLH Transcription Factors OLIG2 and OLIG1 Couple Neuronal and Glial Subtype Specification. Cell 2002, 109, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, X.; Peterson, J.; Gravel, M.; Braun, P.E.; Trapp, B.D. CNP Overexpression Induces Aberrant Oligodendrocyte Membranes and Inhibits MBP Accumulation and Myelin Compaction. J. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 50, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegener, A.; Deboux, C.; Bachelin, C.; Frah, M.; Kerninon, C.; Seilhean, D.; Weider, M.; Wegner, M.; Nait-Oumesmar, B. Gain of Olig2 Function in Oligodendrocyte Progenitors Promotes Remyelination. Brain 2015, 138, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Rivkees, S.A. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Stimulates the Proliferation and Migration of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 69, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott-Drew, S.; ffrench-Constant, C. Expression and Function of Thrombospondin-1 in Myelinating Glial Cells of the Central Nervous System. J. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 50, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari-Woodruff, S.K.; Buznikov, A.G.; Vu, T.Q.; Micevych, P.E.; Chen, K.; Kornblum, H.I.; Bronstein, J.M. OSP/Claudin-11 Forms a Complex with a Novel Member of the Tetraspanin Super Family and Beta1 Integrin and Regulates Proliferation and Migration of Oligodendrocytes. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Payne, H.R.; Hemperly, J.J.; Lemmon, V. N-Cadherin Expression and Function in Cultured Oligodendrocytes. Dev. Brain Res. 1996, 97, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, R.; Edwards, G.; Streuli, C.; Ffrench-Constant, C. A Role in Migration for the Alpha V Beta 1 Integrin Expressed on Oligodendrocyte Precursors. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 7240–7252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frost, E.; Kiernan, B.W.; Faissner, A.; ffrench-Constant, C. Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Migration by Extracellular Matrix: Evidence for Substrate-Specific Inhibition of Migration by Tenascin-C. Dev. Neurosci. 1996, 18, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadea, A.; Aguirre, A.; Haydar, T.F.; Gallo, V. Endothelin-1 Regulates Oligodendrocyte Development. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 10047–10062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spassky, N.; de Castro, F.; Le Bras, B.; Heydon, K.; Quéraud-LeSaux, F.; Bloch-Gallego, E.; Chédotal, A.; Zalc, B.; Thomas, J.-L. Directional Guidance of Oligodendroglial Migration by Class 3 Semaphorins and Netrin-1. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 5992–6004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarjour, A.A.; Manitt, C.; Moore, S.W.; Thompson, K.M.; Yuh, S.-J.; Kennedy, T.E. Netrin-1 Is a Chemorepellent for Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells in the Embryonic Spinal Cord. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 3735–3744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, H.-H.; Tessier-Lavigne, M.; Miller, R.H. Netrin 1 Mediates Spinal Cord Oligodendrocyte Precursor Dispersal. Development 2003, 130, 2095–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Vutskits, L.; Pepper, M.S.; Kiss, J.Z. VEGF Is a Chemoattractant for FGF-2–Stimulated Neural Progenitors. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 163, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choe, Y.; Huynh, T.; Pleasure, S.J. Migration of Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells Is Controlled by Transforming Growth Factor Family Proteins during Corticogenesis. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 14973–14983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novgorodov, A.S.; El-Awani, M.; Bielawski, J.; Obeid, L.M.; Gudz, T.I. Activation of Sphingosine-1-phosphate Receptor S1P5 Inhibits Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Migration. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-H.; Frost, E.; To, V.; Robinson, S.; Ffrench-Constant, C.; Geertman, R.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Miller, R.H. The Chemokine Receptor CXCR2 Controls Positioning of Oligodendrocyte Precursors in Developing Spinal Cord by Arresting Their Migration. Cell 2002, 110, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dziembowska, M.; Tham, T.N.; Lau, P.; Vitry, S.; Lazarini, F.; Dubois-Dalcq, M. A Role for CXCR4 Signaling in Survival and Migration of Neural and Oligodendrocyte Precursors. Glia 2005, 50, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcion, E.; Faissner, A.; ffrench-Constant, C. Knockout Mice Reveal a Contribution of the Extracellular Matrix Molecule Tenascin-C to Neural Precursor Proliferation and Migration. Dev. Camb. Engl. 2001, 128, 2485–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Mei, A.; Huang, H.; Lin, F. Claudin-1 and Claudin-3 as Molecular Regulators of Myelination in Leukoaraiosis Patients. Clinics 2021, 76, e2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calver, A.R.; Hall, A.C.; Yu, W.-P.; Walsh, F.S.; Heath, J.K.; Betsholtz, C.; Richardson, W.D. Oligodendrocyte Population Dynamics and the Role of PDGF In Vivo. Neuron 1998, 20, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, S.; Tani, M.; Strieter, R.M.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Miller, R.H. The Chemokine Growth-Regulated Oncogene-Alpha Promotes Spinal Cord Oligodendrocyte Precursor Proliferation. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 10457–10463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadi, L.; Selvaraju, R.; de Lys, P.; Proudfoot, A.E.I.; Wells, T.N.C.; Boschert, U. Differential Effects of Chemokines on Oligodendrocyte Precursor Proliferation and Myelin Formation in Vitro. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 174, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frederick, T.J.; Min, J.; Altieri, S.C.; Mitchell, N.E.; Wood, T.L. Synergistic Induction of Cyclin D1 in Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells by IGF-I and FGF-2 Requires Differential Stimulation of Multiple Signaling Pathways. Glia 2007, 55, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van’t Veer, A.; Du, Y.; Fischer, T.Z.; Boetig, D.R.; Wood, M.R.; Dreyfus, C.F. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Effects on Oligodendrocyte Progenitors of the Basal Forebrain Are Mediated through TrkB and the MAP Kinase Pathway. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Cheng, X.; Qi, J.; Xie, B.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, M. EGF Enhances Oligodendrogenesis from Glial Progenitor Cells. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pukos, N.; Yoseph, R.; McTigue, D.M. To Be or Not to Be: Environmental Factors That Drive Myelin Formation during Development and after CNS Trauma. Neuroglia 2018, 1, 63–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, R.A.; Patel, K.D.; Medved, J.; Reiss, A.M.; Nishiyama, A. NG2 Cells in White Matter but Not Gray Matter Proliferate in Response to PDGF. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 14558–14566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Sdrulla, A.D.; diSibio, G.; Bush, G.; Nofziger, D.; Hicks, C.; Weinmaster, G.; Barres, B.A. Notch Receptor Activation Inhibits Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. Neuron 1998, 21, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marie, C.; Clavairoly, A.; Frah, M.; Hmidan, H.; Yan, J.; Zhao, C.; Van Steenwinckel, J.; Daveau, R.; Zalc, B.; Hassan, B.; et al. Oligodendrocyte Precursor Survival and Differentiation Requires Chromatin Remodeling by Chd7 and Chd8. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8246–E8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.; Dong, C.; Frah, M.; Deng, Y.; Marie, C.; Zhang, F.; Xu, L.; Ma, Z.; Dong, X.; Lin, Y.; et al. Dual Requirement of CHD8 for Chromatin Landscape Establishment and Histone Methyltransferase Recruitment to Promote CNS Myelination and Repair. Dev. Cell 2018, 45, 753–768.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, R.; Hori, K.; Owa, T.; Miyashita, S.; Dewa, K.; Masuyama, N.; Sakai, K.; Hayase, Y.; Seto, Y.; Inoue, Y.U.; et al. Origins of Oligodendrocytes in the Cerebellum, Whose Development Is Controlled by the Transcription Factor, Sox9. Mech. Dev. 2016, 140, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.A.; Berndt, J.A.; Hudson, L.D.; Armstrong, R.C. Myelin Transcription Factor 1 (Myt1) Modulates the Proliferation and Differentiation of Oligodendrocyte Lineage Cells. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2004, 25, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoureux, M.-C.; Cunningham, B.A.; Edelman, G.M.; Crossin, K.L. N-CAM Binding Inhibits the Proliferation of Hippocampal Progenitor Cells and Promotes Their Differentiation to a Neuronal Phenotype. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 3631–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casaccia-Bonnefil, P.; Hardy, R.J.; Teng, K.K.; Levine, J.M.; Koff, A.; Chao, M.V. Loss of P27Kip1 Function Results in Increased Proliferative Capacity of Oligodendrocyte Progenitors but Unaltered Timing of Differentiation. Development 1999, 126, 4027–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vourc’h, P.; Dessay, S.; Mbarek, O.; Marouillat Védrine, S.; Müh, J.-P.; Andres, C. The Oligodendrocyte-Myelin Glycoprotein Gene Is Highly Expressed during the Late Stages of Myelination in the Rat Central Nervous System. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 2003, 144, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehotzky, A.; Lau, P.; Tokési, N.; Muja, N.; Hudson, L.D.; Ovádi, J. Tubulin Polymerization-Promoting Protein (TPPP/P25) Is Critical for Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. Glia 2010, 58, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kondo, T. The Id4 HLH Protein and the Timing of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Sdrulla, A.; Johnson, J.E.; Yokota, Y.; Barres, B.A. A Role for the Helix-Loop-Helix Protein Id2 in the Control of Oligodendrocyte Development. Neuron 2001, 29, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scarisbrick, I.A.; Asakura, K.; Rodriguez, M. Neurotrophin-4/5 Promotes Proliferation of Oligodendrocyte-Type-2 Astrocytes (O-2A). Dev. Brain Res. 2000, 123, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, T.; Raff, M.C. A Role for Noggin in the Development of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells. Dev. Biol. 2004, 267, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, R.I.; Marmur, R.; Norton, W.T.; Mehler, M.F.; Kessler, J.A. Nerve Growth Factor and Neurotrophin-3 Differentially Regulate the Proliferation and Survival of Developing Rat Brain Oligodendrocytes. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 6433–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro, D.S.; Martynoga, B.; Parras, C.; Ramesh, V.; Pacary, E.; Johnston, C.; Drechsel, D.; Lebel-Potter, M.; Garcia, L.G.; Hunt, C.; et al. A Novel Function of the Proneural Factor Ascl1 in Progenitor Proliferation Identified by Genome-Wide Characterization of Its Targets. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 930–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warren, N.; Price, D.J. Roles of Pax-6 in Murine Diencephalic Development. Dev. Camb. Engl. 1997, 124, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga, S.; Ly, J.; Chan, P.H.; Bresnahan, J.C.; Beattie, M.S. SOD1 Overexpression Improves Features of the Oligodendrocyte Precursor Response in Vitro. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 503, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, J.; Deng, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.-M. Effects of Extracellular Matrix Molecules on the Growth Properties of Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells in Vitro. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 2854–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaschuk, K.L.; Frost, E.E.; ffrench-Constant, C. The Regulation of Proliferation and Differentiation in Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells by AlphaV Integrins. Dev. Camb. Engl. 2000, 127, 1961–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, K.L.; Riparini, G.; Banerjee, P.; Breur, M.; Bugiani, M.; Gallo, V. Endothelin-1 Signaling Maintains Glial Progenitor Proliferation in the Postnatal Subventricular Zone. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, H.; Riesenberg, A.; Ehrman, L.A.; Kohli, V.; Nardini, D.; Nakafuku, M.; Campbell, K.; Waclaw, R.R. Gsx Transcription Factors Control Neuronal versus Glial Specification in Ventricular Zone Progenitors of the Mouse Lateral Ganglionic Eminence. Dev. Biol. 2018, 442, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancic, M.; Slijepcevic, D.; Nomden, A.; Vos, M.J.; de Jonge, J.C.; Sikkema, A.H.; Gabius, H.-J.; Hoekstra, D.; Baron, W. Galectin-4, a Novel Neuronal Regulator of Myelination. Glia 2012, 60, 919–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canoll, P.D.; Musacchio, J.M.; Hardy, R.; Reynolds, R.; Marchionni, M.A.; Salzer, J.L. GGF/Neuregulin Is a Neuronal Signal That Promotes the Proliferation and Survival and Inhibits the Differentiation of Oligodendrocyte Progenitors. Neuron 1996, 17, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, X.; Gui, X.; Croteau, C.; Song, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, A.; Bannerman, P.; Guo, F. Sox2 Is Essential for Oligodendroglial Proliferation and Differentiation during Postnatal Brain Myelination and CNS Remyelination. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 1802–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brinkmann, B.G.; Agarwal, A.; Sereda, M.W.; Garratt, A.N.; Müller, T.; Wende, H.; Stassart, R.M.; Nawaz, S.; Humml, C.; Velanac, V.; et al. Neuregulin-1/ErbB Signaling Serves Distinct Functions in Myelination of the Peripheral and Central Nervous System. Neuron 2008, 59, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, J.; Bercury, K.K.; Ahrendsen, J.T.; Macklin, W.B. Olig1 Function Is Required for Oligodendrocyte Differentiation in the Mouse Brain. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 4386–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- See, J.; Zhang, X.; Eraydin, N.; Mun, S.-B.; Mamontov, P.; Golden, J.A.; Grinspan, J.B. Oligodendrocyte Maturation Is Inhibited by Bone Morphogenetic Protein. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2004, 26, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnisch, K.; Teuber-Hanselmann, S.; Macha, N.; Mairinger, F.; Fritsche, L.; Soub, D.; Meinl, E.; Junker, A. Myelination in Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Is Associated with Regulation of Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4 and Its Antagonist Noggin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izrael, M.; Zhang, P.; Kaufman, R.; Shinder, V.; Ella, R.; Amit, M.; Itskovitz-Eldor, J.; Chebath, J.; Revel, M. Human Oligodendrocytes Derived from Embryonic Stem Cells: Effect of Noggin on Phenotypic Differentiation in vitro and on Myelination in vivo. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2007, 34, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimori, M.; Nagao, M.; Parras, C.M.; Nakatani, H.; Lebel, M.; Guillemot, F.; Nakafuku, M. Ascl1 Is Required for Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord. Dev. Camb. Engl. 2008, 135, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, S.; Banine, F.; Feistel, K.; Foster, S.; Xing, R.; Struve, J.; Sherman, L.S. Brg1 Directly Regulates Olig2 Transcription and Is Required for Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cell Specification. Dev. Biol. 2016, 413, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedel, M.; Fröb, F.; Elsesser, O.; Wittmann, M.-T.; Lie, D.C.; Reis, A.; Wegner, M. Transcription Factor Tcf4 Is the Preferred Heterodimerization Partner for Olig2 in Oligodendrocytes and Required for Differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 4839–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Deng, Y.; Liu, L.; Yu, K.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; He, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, C.; Wu, L.N.; et al. Dual Regulatory Switch through Interactions of Tcf7l2/Tcf4 with Stage-Specific Partners Propels Oligodendroglial Maturation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Chen, S.; Yang, Q.; Guo, S.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Jiang, M.; Li, H.; Hu, J.; et al. The Oligodendrocyte Transcription Factor 2 OLIG2 Regulates Transcriptional Repression during Myelinogenesis in Rodents. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Koito, H.; Li, J.; Ye, F.; Hoang, J.; Escobar, S.S.; Gow, A.; Arnett, H.A.; et al. The Oligodendrocyte-Specific G Protein–Coupled Receptor GPR17 Is a Cell-Intrinsic Timer of Myelination. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marin-Husstege, M.; He, Y.; Li, J.; Kondo, T.; Sablitzky, F.; Casaccia-Bonnefil, P. Multiple Roles of Id4 in Developmental Myelination: Predicted Outcomes and Unexpected Findings. Glia 2006, 54, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Wu, H.; He, W.; Zhou, F.; Yu, X.; Yi, M.; Du, J.; Xie, B.; Qiu, M. Id2 and Id4 Are Not the Major Negative Regulators of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation during Early Central Nervous System Development. Glia 2022, 70, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiss, V.A.; Nguyen, T.; Dugas, J.; Ibrahim, A.; Barres, B.; Androulakis, I.P.; Casaccia, P. Identification of a Gene Regulatory Network Necessary for the Initiation of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bujalka, H.; Koenning, M.; Jackson, S.; Perreau, V.M.; Pope, B.; Hay, C.M.; Mitew, S.; Hill, A.F.; Lu, Q.R.; Wegner, M.; et al. MYRF Is a Membrane-Associated Transcription Factor That Autoproteolytically Cleaves to Directly Activate Myelin Genes. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emery, B.; Agalliu, D.; Cahoy, J.D.; Watkins, T.A.; Dugas, J.C.; Mulinyawe, S.B.; Ibrahim, A.; Ligon, K.L.; Rowitch, D.H.; Barres, B.A. Myelin Gene Regulatory Factor Is a Critical Transcriptional Regulator Required for CNS Myelination. Cell 2009, 138, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, S.A.; Hos, D.; Küspert, M.; Lang, R.A.; Lovell-Badge, R.; Wegner, M.; Reiprich, S. Stem Cell Factor Sox2 and Its Close Relative Sox3 Have Differentiation Functions in Oligodendrocytes. Development 2014, 141, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stolt, C.C.; Lommes, P.; Friedrich, R.P.; Wegner, M. Transcription Factors Sox8 and Sox10 Perform Non-Equivalent Roles during Oligodendrocyte Development despite Functional Redundancy. Development 2004, 131, 2349–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stolt, C.C.; Rehberg, S.; Ader, M.; Lommes, P.; Riethmacher, D.; Schachner, M.; Bartsch, U.; Wegner, M. Terminal Differentiation of Myelin-Forming Oligodendrocytes Depends on the Transcription Factor Sox10. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takada, N.; Kucenas, S.; Appel, B. Sox10 Is Necessary for Oligodendrocyte Survival Following Axon Wrapping. Glia 2010, 58, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, W.; Qiu, M. The Transcription Factor NKX2-2 Regulates Oligodendrocyte Differentiation through Domain-Specific Interactions with Transcriptional Corepressors. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 1879–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Cai, J.; Wu, Y.; Wu, R.; Lee, J.; Fu, H.; Rao, M.; Sussel, L.; Rubenstein, J.; Qiu, M. Control of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation by the Nkx2.2 Homeodomain Transcription Factor. Dev. Camb. Engl. 2001, 128, 2723–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, S.; Doucette, J.R.; Nazarali, A.J. Sirt2 Is a Novel in Vivo Downstream Target of Nkx2.2 and Enhances Oligodendroglial Cell Differentiation. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 3, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisahara, S.; Iwahara, N.; Matsushita, T.; Suzuki, S.; Matsumura, A.; Fujikura, M.; Yokokawa, K.; Saito, T.; Manabe, T.; Kawamata, J.; et al. SIRT1 Decelerates Morphological Processing of Oligodendrocyte Cell Lines and Regulates the Expression of Cytoskeleton-Related Oligodendrocyte Proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 546, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitman, B.M.; Asp, L.; Mariani, J.N.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Sawai, S.; Chapouly, C.; Horng, S.; Kramer, E.G.; Mitiku, N.; et al. The Transcriptional Activator Krüppel-like Factor-6 Is Required for CNS Myelination. PLOS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vondran, M.W.; Clinton-Luke, P.; Honeywell, J.Z.; Dreyfus, C.F. BDNF+/- Mice Exhibit Deficits in Oligodendrocyte Lineage Cells of the Basal Forebrain. Glia 2010, 58, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heinrich, M.; Gorath, M.; Richter-Landsberg, C. Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) Modulates Early Differentiation of Oligodendrocytes in Rat Brain Cortical Cultures. Glia 1999, 28, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Wood, P.M. NT-3 Weakly Stimulates Proliferation of Adult Rat O1(−)O4(+) Oligodendrocyte-Lineage Cells and Increases Oligodendrocyte Myelination in vitro. J. Neurosci. Res. 2000, 62, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMorris, F.A.; Dubois-Dalcq, M. Insulin-like Growth Factor I Promotes Cell Proliferation and Oligodendroglial Commitment in Rat Glial Progenitor Cells Developing in vitro. J. Neurosci. Res. 1988, 21, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Shao, C.-Y.; Xie, Y.-J.; Wang, N.; Xu, S.-M.; Luo, B.-Y.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Ke, Y.H.; Qiu, M.; Shen, Y. Gab1 Mediates PDGF Signaling and Is Essential to Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and CNS Myelination. eLife 2020, 9, e52056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Shin, S.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Rasband, M.N.; Ren, J.; Dai, C.; Zorrilla-Veloz, R.I.; Shingu, T.; Yuan, L.; et al. Qki Regulates Myelinogenesis through Srebp2-Dependent Cholesterol Biosynthesis. eLife 2021, 10, e60467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, W.Y.; Chang, J.-C.; Lim, K.; Cazenave-Gassiot, A.; Nguyen, A.T.; Foo, J.C.; Muralidharan, S.; Viera-Ortiz, A.; Ong, S.J.M.; Hor, J.H.; et al. TDP-43 Mediates SREBF2-Regulated Gene Expression Required for Oligodendrocyte Myelination. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 220, e201910213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, J.; Kano, K.; Kato, K.; Takita, H.; Sakagami, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Mihara, E.; Ueda, H.; Sato, T.; Tokuyama, H.; et al. Structure and Biological Function of ENPP6, a Choline-Specific Glycerophosphodiester-Phosphodiesterase. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baas, D.; Bourbeau, D.; Sarliève, L.L.; Ittel, M.E.; Dussault, J.H.; Puymirat, J. Oligodendrocyte Maturation and Progenitor Cell Proliferation Are Independently Regulated by Thyroid Hormone. Glia 1997, 19, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barres, B.A.; Lazar, M.A.; Raff, M.C. A Novel Role for Thyroid Hormone, Glucocorticoids and Retinoic Acid in Timing Oligodendrocyte Development. Dev. Camb. Engl. 1994, 120, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baas, D.; Fressinaud, C.; Ittel, M.E.; Reeber, A.; Dalençon, D.; Puymirat, J.; Sarliève, L.L. Expression of Thyroid Hormone Receptor Isoforms in Rat Oligodendrocyte Cultures. Effect of 3,5,3′-Triiodo-l-Thyronine. Neurosci. Lett. 1994, 176, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, T.; Raff, M. Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Proteins and the Timing of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. Dev. Camb. Engl. 2000, 127, 2989–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genoud, S.; Lappe-Siefke, C.; Goebbels, S.; Radtke, F.; Aguet, M.; Scherer, S.S.; Suter, U.; Nave, K.-A.; Mantei, N. Notch1 Control of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation in the Spinal Cord. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 158, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.-D.; Ang, B.-T.; Karsak, M.; Hu, W.-P.; Cui, X.-Y.; Duka, T.; Takeda, Y.; Chia, W.; Sankar, N.; Ng, Y.-K.; et al. F3/Contactin Acts as a Functional Ligand for Notch during Oligodendrocyte Maturation. Cell 2003, 115, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emery, B. Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and Myelination. Science 2010, 330, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jepson, S.; Vought, B.; Gross, C.H.; Gan, L.; Austen, D.; Frantz, J.D.; Zwahlen, J.; Lowe, D.; Markland, W.; Krauss, R. LINGO-1, a Transmembrane Signaling Protein, Inhibits Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and Myelination through Intercellular Self-Interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 22184–22195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirahara, Y.; Bansal, R.; Honke, K.; Ikenaka, K.; Wada, Y. Sulfatide Is a Negative Regulator of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation: Development in Sulfatide-Null Mice. Glia 2004, 45, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.-H.; Na, J.E.; Yoon, Y.R.; Rhyu, I.J.; Ko, Y.-G.; Baik, J.-H. Hypomyelination and Cognitive Impairment in Mice Lacking CD133 (Prominin-1). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 502, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.L.; Hashimoto, H.; Finseth, L.T.; Wood, T.L.; Macklin, W.B. PAK1 Positively Regulates Oligodendrocyte Morphology and Myelination. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarles, R.H. Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein (MAG): Past, Present and Beyond. J. Neurochem. 2007, 100, 1431–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankoff, B.; Aigrot, M.-S.; Noël, F.; Wattilliaux, A.; Zalc, B.; Lubetzki, C. Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor (CNTF) Enhances Myelin Formation: A Novel Role for CNTF and CNTF-Related Molecules. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 9221–9227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalsi, A.S.; Greenwood, K.; Wilkin, G.; Butt, A.M. Kir4.1 Expression by Astrocytes and Oligodendrocytes in CNS White Matter: A Developmental Study in the Rat Optic Nerve. J. Anat. 2004, 204, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howng, S.Y.B.; Avila, R.L.; Emery, B.; Traka, M.; Lin, W.; Watkins, T.; Cook, S.; Bronson, R.; Davisson, M.; Barres, B.A.; et al. ZFP191 Is Required by Oligodendrocytes for CNS Myelination. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, R.; Heinrich, M.; Heck, S.; Blohm, D.; Richter-Landsberg, C. Expression of Microtubule-Associated Proteins MAP2 and Tau in Cultured Rat Brain Oligodendrocytes. Cell Tissue Res. 1997, 288, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ku, L.; Mei, R.; Liu, G.; Xu, C.; Wen, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, F.; Xiao, L.; Feng, Y. Novel Schizophrenia Risk Factor Pathways Regulate FEZ1 to Advance Oligodendroglia Development. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Gravel, M.; Zhang, R.; Thibault, P.; Braun, P.E. Process Outgrowth in Oligodendrocytes Is Mediated by CNP, a Novel Microtubule Assembly Myelin Protein. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 170, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monin, A.; Baumann, P.S.; Griffa, A.; Xin, L.; Mekle, R.; Fournier, M.; Butticaz, C.; Klaey, M.; Cabungcal, J.H.; Steullet, P.; et al. Glutathione Deficit Impairs Myelin Maturation: Relevance for White Matter Integrity in Schizophrenia Patients. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shao, Z.; Qiu, M.; Pepinsky, B.; Miller, R.H.; Mi, S. Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and Myelination Defects in OMgp Null Mice. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2011, 46, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaji, S.; Maki, T.; Ueda, J.; Ishimoto, T.; Inoue, Y.; Yasuda, K.; Sawamura, M.; Hikawa, R.; Ayaki, T.; Yamakado, H.; et al. BCAS1-Positive Immature Oligodendrocytes Are Affected by the α-Synuclein-Induced Pathology of Multiple System Atrophy. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fard, M.K.; van der Meer, F.; Sánchez, P.; Cantuti-Castelvetri, L.; Mandad, S.; Jäkel, S.; Fornasiero, E.F.; Schmitt, S.; Ehrlich, M.; Starost, L.; et al. BCAS1 Expression Defines a Population of Early Myelinating Oligodendrocytes in Multiple Sclerosis Lesions. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaam7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikenaka, K.; Kagawa, T.; Mikoshiba, K. Selective Expression of DM-20, an Alternatively Spliced Myelin Proteolipid Protein Gene Product, in Developing Nervous System and in Nonglial Cells. J. Neurochem. 1992, 58, 2248–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiano, M.R.; Andrieux, A.; Deloulme, J.C.; Bosc, C.; Schweitzer, A.; Job, D.; Hallak, M.E. Myelin Basic Protein Functions as a Microtubule Stabilizing Protein in Differentiated Oligodendrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 84, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlenberg, B.; Schuelke, M.; Rüschendorf, F.; Ruf, N.; Kaindl, A.M.; Henneke, M.; Thiele, H.; Stoltenburg-Didinger, G.; Aksu, F.; Topaloğlu, H.; et al. Mutations in the Gene Encoding Gap Junction Protein Alpha 12 (Connexin 46.6) Cause Pelizaeus-Merzbacher-like Disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 75, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menichella, D.M.; Goodenough, D.A.; Sirkowski, E.; Scherer, S.S.; Paul, D.L. Connexins Are Critical for Normal Myelination in the CNS. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 5963–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasseff, S.K.; Scherer, S.S. Cx32 and Cx47 Mediate Oligodendrocyte:Astrocyte and Oligodendrocyte:Oligodendrocyte Gap Junction Coupling. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 42, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosser, J.; Douar, A.M.; Sarde, C.O.; Kioschis, P.; Feil, R.; Moser, H.; Poustka, A.M.; Mandel, J.L.; Aubourg, P. Putative X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy Gene Shares Unexpected Homology with ABC Transporters. Nature 1993, 361, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strachan, L.R.; Stevenson, T.J.; Freshner, B.; Keefe, M.D.; Miranda Bowles, D.; Bonkowsky, J.L. A Zebrafish Model of X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy Recapitulates Key Disease Features and Demonstrates a Developmental Requirement for Abcd1 in Oligodendrocyte Patterning and Myelination. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 3600–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schnädelbach, O.; Ozen, I.; Blaschuk, O.W.; Meyer, R.L.; Fawcett, J.W. N-Cadherin Is Involved in Axon-Oligodendrocyte Contact and Myelination. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2001, 17, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, L.S.; Chan, C.W.; ffrench-Constant, C. An Integrin–Contactin Complex Regulates CNS Myelination by Differential Fyn Phosphorylation. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 9174–9185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charles, P.; Tait, S.; Faivre-Sarrailh, C.; Barbin, G.; Gunn-Moore, F.; Denisenko-Nehrbass, N.; Guennoc, A.-M.; Girault, J.-A.; Brophy, P.J.; Lubetzki, C. Neurofascin Is a Glial Receptor for the Paranodin/Caspr-Contactin Axonal Complex at the Axoglial Junction. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thaxton, C.; Pillai, A.M.; Pribisko, A.L.; Labasque, M.; Dupree, J.L.; Faivre-Sarrailh, C.; Bhat, M.A. In Vivo Deletion of Immunoglobulin Domains 5 and 6 in Neurofascin (Nfasc) Reveals Domain-Specific Requirements in Myelinated Axons. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 4868–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Labasque, M.; Hivert, B.; Nogales-Gadea, G.; Querol, L.; Illa, I.; Faivre-Sarrailh, C. Specific Contactin N-Glycans Are Implicated in Neurofascin Binding and Autoimmune Targeting in Peripheral Neuropathies. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 7907–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klingseisen, A.; Ristoiu, A.-M.; Kegel, L.; Sherman, D.L.; Rubio-Brotons, M.; Almeida, R.G.; Koudelka, S.; Benito-Kwiecinski, S.K.; Poole, R.J.; Brophy, P.J.; et al. Oligodendrocyte Neurofascin Independently Regulates Both Myelin Targeting and Sheath Growth in the CNS. Dev. Cell 2019, 51, 730–744.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Çolakoğlu, G.; Bergstrom-Tyrberg, U.; Berglund, E.O.; Ranscht, B. Contactin-1 Regulates Myelination and Nodal/Paranodal Domain Organization in the Central Nervous System. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E394–E403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Traka, M.; Goutebroze, L.; Denisenko, N.; Bessa, M.; Nifli, A.; Havaki, S.; Iwakura, Y.; Fukamauchi, F.; Watanabe, K.; Soliven, B.; et al. Association of TAG-1 with Caspr2 Is Essential for the Molecular Organization of Juxtaparanodal Regions of Myelinated Fibers. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elazar, N.; Vainshtein, A.; Golan, N.; Vijayaragavan, B.; Schaeren-Wiemers, N.; Eshed-Eisenbach, Y.; Peles, E. Axoglial Adhesion by Cadm4 Regulates CNS Myelination. Neuron 2019, 101, 224–231.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, A.N.; Appel, B. Oligodendrocytes Express Synaptic Proteins That Modulate Myelin Sheath Formation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sturgill, E.R.; Aoki, K.; Lopez, P.H.; Colacurcio, D.; Vajn, K.; Lorenzini, I.; Majić, S.; Yang, W.H.; Heffer, M.; Tiemeyer, M.; et al. Biosynthesis of the Major Brain Gangliosides GD1a and GT1b. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 1289–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schnaar, R.L. Brain Gangliosides in Axon-Myelin Stability and Axon Regeneration. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harboe, M.; Torvund-Jensen, J.; Kjaer-Sorensen, K.; Laursen, L.S. Ephrin-A1-EphA4 Signaling Negatively Regulates Myelination in the Central Nervous System. Glia 2018, 66, 934–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linneberg, C.; Harboe, M.; Laursen, L.S. Axo-Glia Interaction Preceding CNS Myelination Is Regulated by Bidirectional Eph-Ephrin Signaling. ASN Neuro 2015, 7, 175909141560285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.G. The Rules of Attraction in Central Nervous System Myelination. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, P.; Hernandez, M.P.; Stankoff, B.; Aigrot, M.S.; Colin, C.; Rougon, G.; Zalc, B.; Lubetzki, C. Negative Regulation of Central Nervous System Myelination by Polysialylated-Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 7585–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redmond, S.A.; Mei, F.; Eshed-Eisenbach, Y.; Osso, L.A.; Leshkowitz, D.; Shen, Y.-A.A.; Kay, J.N.; Aurrand-Lions, M.; Lyons, D.A.; Peles, E.; et al. Somatodendritic Expression of JAM2 Inhibits Oligodendrocyte Myelination. Neuron 2016, 91, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díez-Revuelta, N.; Higuero, A.M.; Velasco, S.; Peñas-de-la-Iglesia, M.; Gabius, H.-J.; Abad-Rodríguez, J. Neurons Define Non-Myelinated Axon Segments by the Regulation of Galectin-4-Containing Axon Membrane Domains. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, M.; Yue, T.; Ma, Z.; Wu, F.; Gow, A.; Lu, Q.R. Myelinogenesis and Axonal Recognition by Oligodendrocytes in Brain Are Uncoupled in Olig1-Null Mice. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1354–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lüders, K.A.; Nessler, S.; Kusch, K.; Patzig, J.; Jung, R.B.; Möbius, W.; Nave, K.-A.; Werner, H.B. Maintenance of High Proteolipid Protein Level in Adult Central Nervous System Myelin Is Required to Preserve the Integrity of Myelin and Axons. Glia 2019, 67, 634–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, E.; Mottahedeh, J.; Prins, M.; Ridder, W.; Nusinowitz, S.; Bronstein, J.M. Disrupted Compaction of CNS Myelin in an OSP/Claudin-11 and PLP/DM20 Double Knockout Mouse. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2005, 29, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachner, M.; Bartsch, U. Multiple Functions of the Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein MAG (Siglec-4a) in Formation and Maintenance of Myelin. Glia 2000, 29, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, C.S.; Reid, H.H.; Beddoe, T.; Tynan, F.E.; Perugini, M.A.; Johns, T.G.; Bernard, C.C.A.; Rossjohn, J. The Crystal Structure of Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein, a Key Autoantigen in Multiple Sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11059–11064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johns, T.G.; Bernard, C.C.A. The Structure and Function of Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein. J. Neurochem. 1999, 72, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasband, M.N.; Tayler, J.; Kaga, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lappe-Siefke, C.; Nave, K.-A.; Bansal, R. CNP Is Required for Maintenance of Axon-Glia Interactions at Nodes of Ranvier in the CNS. Glia 2005, 50, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, I.; Müller, C.; Luhmann, H.J.; White, R. MOBP Levels Are Regulated by Fyn Kinase and Affect the Morphological Differentiation of Oligodendrocytes. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vourc’h, P.; Andres, C. Oligodendrocyte Myelin Glycoprotein (OMgp): Evolution, Structure and Function. Brain Res. Rev. 2004, 45, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-J.; Susuki, K.; Dours-Zimmermann, M.T.; Zimmermann, D.R.; Rasband, M.N. Oligodendrocyte Myelin Glycoprotein Does Not Influence Node of Ranvier Structure or Assembly. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 14476–14481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koenning, M.; Jackson, S.; Hay, C.M.; Faux, C.; Kilpatrick, T.J.; Willingham, M.; Emery, B. Myelin Gene Regulatory Factor Is Required for Maintenance of Myelin and Mature Oligodendrocyte Identity in the Adult CNS. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 12528–12542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zheng, K.; Li, H.; Qi, Y.; Cao, Q.; Qiu, M. Co-Localization of Nkx6.2 and Nkx2.2 Homeodomain Proteins in Differentiated Myelinating Oligodendrocytes. Glia 2010, 58, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Teng, P.; Du, J.; Meng, J.; Hu, X.; Tang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, Y.B.; Qiu, M. Interactive Repression of MYRF Self-Cleavage and Activity in Oligodendrocyte Differentiation by TMEM98 Protein. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 9829–9839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, A.; Frim, D.M.; Polak, P.; Vujicic, S.; Arnason, B.G.W.; Boullerne, A.I. Olig1 Is Expressed in Human Oligodendrocytes during Maturation and Regeneration. Glia 2011, 59, 914–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, A.; Furusho, M.; Dupree, J.L.; Bansal, R. Role of ERK1/2 MAPK Signaling in the Maintenance of Myelin and Axonal Integrity in the Adult CNS. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 16031–16045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusho, M.; Ishii, A.; Bansal, R. Signaling by FGF Receptor 2, Not FGF Receptor 1, Regulates Myelin Thickness through Activation of ERK1/2–MAPK, Which Promotes MTORC1 Activity in an Akt-Independent Manner. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 2931–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; He, X.; Liu, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhao, C.; Wang, H.; He, D.; Zheng, T.; Zhou, X.; Hassan, A.; et al. Hdac3 Interaction with P300 Histone Acetyltransferase Regulates the Oligodendrocyte and Astrocyte Lineage Fate Switch. Dev. Cell 2016, 36, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marcus, J.; Honigbaum, S.; Shroff, S.; Honke, K.; Rosenbluth, J.; Dupree, J.L. Sulfatide Is Essential for the Maintenance of CNS Myelin and Axon Structure. Glia 2006, 53, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, T.; Dupree, J.L.; Popko, B. Demyelination and Altered Expression of Myelin-Associated Glycoprotein Isoforms in the Central Nervous System of Galactolipid-Deficient Mice. J. Neurosci. Res. 1998, 54, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulshagen, L.; Krysko, O.; Bottelbergs, A.; Huyghe, S.; Klein, R.; Van Veldhoven, P.P.; De Deyn, P.P.; D’Hooge, R.; Hartmann, D.; Baes, M. Absence of Functional Peroxisomes from Mouse CNS Causes Dysmyelination and Axon Degeneration. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 4015–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, M.; Shinbo, S.; Asahi, A.; Imanaka, T. Very Long Chain Fatty Acid β-Oxidation in Astrocytes: Contribution of the ABCD1-Dependent and -Independent Pathways. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1972–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, Y.; Yoshikawa, F.; Sadakata, T.; Shinoda, Y.; Koebis, M.; Furuichi, T. Age-Dependent Redistribution and Hypersialylation of the Central Myelin Paranodal Loop Membrane Protein Opalin in the Mouse Brain. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 581, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xin, W.; Chan, J.R. Myelin Plasticity: Sculpting Circuits in Learning and Memory. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2020, 21, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, R.J.M.; ffrench-Constant, C. Regenerating CNS Myelin—From Mechanisms to Experimental Medicines. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, G.A.; Yoo, S.; Du, T.Y.; Xiao, J. Plasticity in Oligodendrocyte Lineage Progression: An OPC Puzzle on Our Nerves. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 54, 5747–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, R.J.M.; ffrench-Constant, C. Remyelination in the CNS: From Biology to Therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 839–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyon, S.; Dubessy, A.L.; Aigrot, M.S.; Trotter, M.; Huang, J.K.; Dauphinot, L.; Potier, M.C.; Kerninon, C.; Melik Parsadaniantz, S.; Franklin, R.J.M.; et al. Demyelination Causes Adult CNS Progenitors to Revert to an Immature State and Express Immune Cues That Support Their Migration. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ffrench-Constant, C.; Raff, M.C. Proliferating Bipotential Glial Progenitor Cells in Adult Rat Optic Nerve. Nature 1986, 319, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, A.M.; Rivera, A.D.; Fulton, D.; Azim, K. Targeting the Subventricular Zone to Promote Myelin Repair in the Aging Brain. Cells 2022, 11, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawadzka, M.; Rivers, L.E.; Fancy, S.P.J.; Zhao, C.; Tripathi, R.; Jamen, F.; Young, K.; Goncharevich, A.; Pohl, H.; Rizzi, M.; et al. CNS-Resident Glial Progenitor/Stem Cells Produce Schwann Cells as Well as Oligodendrocytes during Repair of CNS Demyelination. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncan, I.D.; Radcliff, A.B.; Heidari, M.; Kidd, G.; August, B.K.; Wierenga, L.A. The Adult Oligodendrocyte Can Participate in Remyelination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11807–E11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sim, F.J.; Zhao, C.; Penderis, J.; Franklin, R.J.M. The Age-Related Decrease in CNS Remyelination Efficiency Is Attributable to an Impairment of Both Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Recruitment and Differentiation. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, A.L.; Ousman, S.S. Astrocytes and Aging. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thelen, K.M.; Falkai, P.; Bayer, T.A.; Lütjohann, D. Cholesterol Synthesis Rate in Human Hippocampus Declines with Aging. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 403, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, K.-H.; Herrup, K. DNA Damage in the Oligodendrocyte Lineage and Its Role in Brain Aging. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2017, 161, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cantuti-Castelvetri, L.; Fitzner, D.; Bosch-Queralt, M.; Weil, M.-T.; Su, M.; Sen, P.; Ruhwedel, T.; Mitkovski, M.; Trendelenburg, G.; Lütjohann, D.; et al. Defective Cholesterol Clearance Limits Remyelination in the Aged Central Nervous System. Science 2018, 359, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Love, S. Demyelinating Diseases. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 59, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seil, F.J. Demyelination. In Advances in Cellular Neurobiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1982; Volume 3, pp. 235–274. ISBN 978-0-12-008303-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.-W.; Wang, D.-X.; Ma, X.-R.; Dong, Z.-J.; Wu, J.-B.; Wang, F.; Wu, Y. Impaired Metabolism of Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells and Axons in Demyelinated Lesion and in the Aged CNS. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2022, 64, 102205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghoff, S.A.; Spieth, L.; Saher, G. Local Cholesterol Metabolism Orchestrates Remyelination. Trends Neurosci. 2022, 45, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hammel, G.; Shi, M.; Cheng, Z.; Zivkovic, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, P.; He, X.; Guo, B.; Ren, Y.; et al. Myelin Debris Stimulates NG2/CSPG4 Expression in Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages in the Injured Spinal Cord. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 651827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotter, M.R. Myelin Impairs CNS Remyelination by Inhibiting Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cell Differentiation. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoli, I.; Neumann, H. Protective Effects of Microglia in Multiple Sclerosis. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 225, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampron, A.; Larochelle, A.; Laflamme, N.; Préfontaine, P.; Plante, M.-M.; Sánchez, M.G.; Yong, V.W.; Stys, P.K.; Tremblay, M.-È.; Rivest, S. Inefficient Clearance of Myelin Debris by Microglia Impairs Remyelinating Processes. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben-Hur, T.; Einstein, O.; Bulte, J.W.M. Stem Cell Therapy for Myelin Diseases. Curr. Drug Targets 2005, 6, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottoboni, L.; Merlini, A.; Martino, G. Neural Stem Cell Plasticity: Advantages in Therapy for the Injured Central Nervous System. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagoshi, N.; Khazaei, M.; Ahlfors, J.-E.; Ahuja, C.S.; Nori, S.; Wang, J.; Shibata, S.; Fehlings, M.G. Human Spinal Oligodendrogenic Neural Progenitor Cells Promote Functional Recovery After Spinal Cord Injury by Axonal Remyelination and Tissue Sparing. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sankavaram, S.R.; Hakim, R.; Covacu, R.; Frostell, A.; Neumann, S.; Svensson, M.; Brundin, L. Adult Neural Progenitor Cells Transplanted into Spinal Cord Injury Differentiate into Oligodendrocytes, Enhance Myelination, and Contribute to Recovery. Stem Cell Rep. 2019, 12, 950–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theotokis, P.; Kesidou, E.; Mitsiadou, D.; Petratos, S.; Damianidou, O.; Boziki, M.; Chatzidimitriou, A.; Grigoriadis, N. Lumbar Spine Intrathecal Transplantation of Neural Precursor Cells Promotes Oligodendrocyte Proliferation in Hot Spots of Chronic Demyelination. Brain Pathol. Zurich Switz. 2021, 32, e13040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theotokis, P.; Kleopa, K.A.; Touloumi, O.; Lagoudaki, R.; Lourbopoulos, A.; Nousiopoulou, E.; Kesidou, E.; Poulatsidou, K.-N.; Dardiotis, E.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.; et al. Connexin43 and Connexin47 Alterations after Neural Precursor Cells Transplantation in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Glia 2015, 63, 1772–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einstein, O.; Grigoriadis, N.; Mizrachi-Kol, R.; Reinhartz, E.; Polyzoidou, E.; Lavon, I.; Milonas, I.; Karussis, D.; Abramsky, O.; Ben-Hur, T. Transplanted Neural Precursor Cells Reduce Brain Inflammation to Attenuate Chronic Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 198, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluchino, S.; Gritti, A.; Blezer, E.; Amadio, S.; Brambilla, E.; Borsellino, G.; Cossetti, C.; Del Carro, U.; Comi, G.; ’t Hart, B.; et al. Human Neural Stem Cells Ameliorate Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis in Non-Human Primates. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, M.S.Y.; Djelloul, M.; Steiner, E.; Bernard, S.; Salehpour, M.; Possnert, G.; Brundin, L.; Frisén, J. Dynamics of Oligodendrocyte Generation in Multiple Sclerosis. Nature 2019, 566, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacmeister, C.M.; Barr, H.J.; McClain, C.R.; Thornton, M.A.; Nettles, D.; Welle, C.G.; Hughes, E.G. Motor Learning Promotes Remyelination via New and Surviving Oligodendrocytes. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neely, S.A.; Williamson, J.M.; Klingseisen, A.; Zoupi, L.; Early, J.J.; Williams, A.; Lyons, D.A. New Oligodendrocytes Exhibit More Abundant and Accurate Myelin Regeneration than Those That Survive Demyelination. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baaklini, C.S.; Rawji, K.S.; Duncan, G.J.; Ho, M.F.S.; Plemel, J.R. Central Nervous System Remyelination: Roles of Glia and Innate Immune Cells. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, B.; Gao, C.; Giera, S.; Folts, C.J.; Kishore, P.; Yu, D.; Oak, H.C.; Jiang, R.; Piao, X. Cell Type-Specific Evaluation of ADGRG1/GPR56 Function in Developmental Central Nervous System Myelination. Glia 2021, 69, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia-Belmonte, V.; Medina-Rodríguez, E.M.; Bribián, A.; de Castro, F.; Esteban, P.F. ERK1/2 Signaling Is Essential for the Chemoattraction Exerted by Human FGF2 and Human Anosmin-1 on Newborn Rat and Mouse OPCs via FGFR1: Chemotactic Effect of Anosmin-1 on OPCs. Glia 2014, 62, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, H.; Martin, E.; Hassani, H.; Clavairoly, A.; Maire, C.L.; Viadieu, A.; Kerninon, C.; Delmasure, A.; Frah, M.; Weber, M.; et al. Ascl1/Mash1 Promotes Brain Oligodendrogenesis during Myelination and Remyelination. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 9752–9768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulloa-Navas, M.J.; Pérez-Borredá, P.; Morales-Gallel, R.; Saurí-Tamarit, A.; García-Tárraga, P.; Gutiérrez-Martín, A.J.; Herranz-Pérez, V.; García-Verdugo, J.M. Ultrastructural Characterization of Human Oligodendrocytes and Their Progenitor Cells by Pre-Embedding Immunogold. Front. Neuroanat. 2021, 15, 696376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Marie, C.; Zhao, C.; Kim, B.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Clavairoly, A.; Frah, M.; Wang, H.; He, X.; et al. Chd7 Cooperates with Sox10 and Regulates the Onset of CNS Myelination and Remyelination. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 678–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobrowolski, M.; Cave, C.; Levy-Myers, R.; Lee, C.; Park, S.; Choi, B.-R.; Xiao, B.; Yang, W.; Sockanathan, S. GDE3 Regulates Oligodendrocyte Precursor Proliferation via Release of Soluble CNTFRα. Dev. Camb. Engl. 2020, 147, dev180695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharova, K.; Stallcup, W.B. The NG2 Proteoglycan Promotes Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Proliferation and Developmental Myelination. Neuroscience 2010, 166, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petryniak, M.A.; Potter, G.B.; Rowitch, D.H.; Rubenstein, J.L.R. Dlx1 and Dlx2 Control Neuronal versus Oligodendroglial Cell Fate Acquisition in the Developing Forebrain. Neuron 2007, 55, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muth, K.N.; Piefke, S.; Weider, M.; Sock, E.; Hermans-Borgmeyer, I.; Wegner, M.; Küspert, M. The Dual-Specificity Phosphatase Dusp15 Is Regulated by Sox10 and Myrf in Myelinating Oligodendrocytes: Dusp15 as a Common Target of Sox10 and Myrf. Glia 2016, 64, 2120–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conover, J.C.; Doetsch, F.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.-M.; Gale, N.W.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Disruption of Eph/Ephrin Signaling Affects Migration and Proliferation in the Adult Subventricular Zone. Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, K.; Raineteau, O.; Butt, A.M. Intraventricular Injection of FGF-2 Promotes Generation of Oligodendrocyte-Lineage Cells in the Postnatal and Adult Forebrain. Glia 2012, 60, 1977–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Pham, L.-D.D.; Som, A.T.; Lee, B.J.; Guo, S.; Lo, E.H.; Arai, K. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Regulates the Migration of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 10666–10670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fasciani, I.; Pluta, P.; González-Nieto, D.; Martínez-Montero, P.; Molano, J.; Paíno, C.L.; Millet, O.; Barrio, L.C. Directional Coupling of Oligodendrocyte Connexin-47 and Astrocyte Connexin-43 Gap Junctions. Glia 2018, 66, 2340–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-J.; Vainshtein, A.; Maik-Rachline, G.; Peles, E. G Protein-Coupled Receptor 37 Is a Negative Regulator of Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and Myelination. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, H.; Waclaw, R.R.; Pei, Z.; Nakafuku, M.; Campbell, K. The Homeobox Gene Gsx2 Controls the Timing of Oligodendroglial Fate Specification in Mouse Lateral Ganglionic Eminence Progenitors. Dev. Camb. Engl. 2013, 140, 2289–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, F.; Chen, Y.; Hoang, T.; Montgomery, R.L.; Zhao, X.; Bu, H.; Hu, T.; Taketo, M.M.; van Es, J.H.; Clevers, H.; et al. HDAC1 and HDAC2 Regulate Oligodendrocyte Differentiation by Disrupting the β-Catenin–TCF Interaction. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cunliffe, V.T.; Casaccia-Bonnefil, P. Histone Deacetylase 1 Is Essential for Oligodendrocyte Specification in the Zebrafish CNS. Mech. Dev. 2006, 123, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Levine, E.M.; Rao, M.S. Hes1 but Not Hes5 Regulates an Astrocyte versus Oligodendrocyte Fate Choice in Glial Restricted Precursors. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2003, 226, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havrda, M.C.; Paolella, B.R.; Ran, C.; Jering, K.S.; Wray, C.M.; Sullivan, J.M.; Nailor, A.; Hitoshi, Y.; Israel, M.A. Id2 Mediates Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cell Maturation Arrest and Is Tumorigenic in a PDGF-Rich Microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malek-Hedayat, S.; Rome, L.H. Expression of a Beta 1-Related Integrin by Oligodendroglia in Primary Culture: Evidence for a Functional Role in Myelination. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 124, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barres, B.A.; Raff, M.C. Control of Oligodendrocyte Number in the Developing Rat Optic Nerve. Neuron 1994, 12, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.H. Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Vertebrate CNS. Prog. Neurobiol. 2002, 67, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Hyodo, M.; Hayashi, C.; Mabuchi, Y.; Sekimoto, K.; Onchi, C.; Sekiguchi, K.; Akazawa, C. Laminin A2, A4, and A5 Chains Positively Regulate Migration and Survival of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.S.; Nakaya, N.; Abu-Asab, M.; Kim, H.S.; Tomarev, S.I. Myocilin Is Involved in NgR1/Lingo-1-Mediated Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and Myelination of the Optic Nerve. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 5539–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almazán, G.; Vela, J.M.; Molina-Holgado, E.; Guaza, C. Re-Evaluation of Nestin as a Marker of Oligodendrocyte Lineage Cells: Nestin in Oligodendroglial Lineage. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2001, 52, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nieto, M.; Schuurmans, C.; Britz, O.; Guillemot, F. Neural BHLH Genes Control the Neuronal versus Glial Fate Decision in Cortical Progenitors. Neuron 2001, 29, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mizuguchi, R.; Sugimori, M.; Takebayashi, H.; Kosako, H.; Nagao, M.; Yoshida, S.; Nabeshima, Y.; Shimamura, K.; Nakafuku, M. Combinatorial Roles of Olig2 and Neurogenin2 in the Coordinated Induction of Pan-Neuronal and Subtype-Specific Properties of Motoneurons. Neuron 2001, 31, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deneen, B.; Ho, R.; Lukaszewicz, A.; Hochstim, C.J.; Gronostajski, R.M.; Anderson, D.J. The Transcription Factor NFIA Controls the Onset of Gliogenesis in the Developing Spinal Cord. Neuron 2006, 52, 953–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Althaus, H.H.; Klöppner, S.; Schmidt-Schultz, T.; Schwartz, P. Nerve Growth Factor Induces Proliferation and Enhances Fiber Regeneration in Oligodendrocytes Isolated from Adult Pig Brain. Neurosci. Lett. 1992, 135, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucenas, S.; Snell, H.; Appel, B. Nkx2.2a Promotes Specification and Differentiation of a Myelinating Subset of Oligodendrocyte Lineage Cells in Zebrafish. Neuron Glia Biol. 2008, 4, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega, M.C.; Bribián, A.; Peregrín, S.; Gil, M.T.; Marín, O.; de Castro, F. Neuregulin-1/ErbB4 Signaling Controls the Migration of Oligodendrocyte Precursor Cells during Development. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 235, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, A.W.; Xiao, J.; Kemper, D.; Kilpatrick, T.J.; Murray, S.S. Oligodendroglial Expression of TrkB Independently Regulates Myelination and Progenitor Cell Proliferation. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 4947–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Long, Z.; Yang, C. The Effects of the Olig Family on the Regulation of Spinal Cord Development and Regeneration. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 2776–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, N.; Adamsky, K.; Kartvelishvily, E.; Brockschnieder, D.; Möbius, W.; Spiegel, I.; Roth, A.D.; Thomson, C.E.; Rechavi, G.; Peles, E. Identification of Tmem10/Opalin as an Oligodendrocyte Enriched Gene Using Expression Profiling Combined with Genetic Cell Ablation. Glia 2008, 56, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Faria, O.; Dhaunchak, A.S.; Kamen, Y.; Roth, A.D.; Kuhlmann, T.; Colman, D.R.; Kennedy, T.E. TMEM10 Promotes Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and Is Expressed by Oligodendrocytes in Human Remyelinating Multiple Sclerosis Plaques. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Pringle, N.P.; Hardy, A.P.; Richardson, W.D.; Smith, H.K. Pax6 Influences the Time and Site of Origin of Glial Precursors in the Ventral Neural Tube. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 1998, 12, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, E.S.; Goldman, J.E. Pax6 Expression Is Sufficient to Induce a Neurogenic Fate in Glial Progenitors of the Neonatal Subventricular Zone. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muñoz-Esquivel, J.; Göttle, P.; Aguirre-Cruz, L.; Flores-Rivera, J.; Corona, T.; Reyes-Terán, G.; Küry, P.; Torres, K.J. Sildenafil Inhibits Myelin Expression and Myelination of Oligodendroglial Precursor Cells. ASN Neuro 2019, 11, 175909141983244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butt, A.M.; Hornby, M.F.; Kirvell, S.; Berry, M. Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Delays Oligodendrocyte Differentiation and Axonal Myelination in Vivo in the Anterior Medullary Velum of the Developing Rat. J. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 48, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaglione, A.; Patzig, J.; Liang, J.; Frawley, R.; Bok, J.; Mela, A.; Yattah, C.; Zhang, J.; Teo, S.X.; Zhou, T.; et al. PRMT5-Mediated Regulation of Developmental Myelination. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doukhanine, E.; Gavino, C.; Haines, J.D.; Almazan, G.; Richard, S. The QKI-6 RNA Binding Protein Regulates Actin-Interacting Protein-1 MRNA Stability during Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 3029–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, S.Y.C.; Rosenberg, S.S.; Fancy, S.P.J.; Zhao, C.; Shen, Y.-A.A.; Hahn, A.T.; McGee, A.W.; Xu, X.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, L.I.; et al. Neurite Outgrowth Inhibitor Nogo-A Establishes Spatial Segregation and Extent of Oligodendrocyte Myelination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hornig, J.; Fröb, F.; Vogl, M.R.; Hermans-Borgmeyer, I.; Tamm, E.R.; Wegner, M. The Transcription Factors Sox10 and Myrf Define an Essential Regulatory Network Module in Differentiating Oligodendrocytes. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Ou, Z.; Qi, C.; Xing, R.; Wang, S.; Han, Y.; Zhao, T.-J.; Chen, Y. DHHC5 Facilitates Oligodendrocyte Development by Palmitoylating and Activating STAT3. Glia 2022, 70, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Dupree, J.; Wang, J.; Sandoval, J.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Shi, Y.; Nave, K.A.; Casaccia-Bonnefil, P. The Transcription Factor Yin Yang1 Is Essential for Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Differentiation. Neuron 2007, 55, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Yang, B.; He, Q.; Shou, W.; Chen, Y.; Higashi, Y.; van den Berghe, V.; et al. Dual-Mode Modulation of Smad Signaling by Smad-Interacting Protein Sip1 Is Required for Myelination in the Central Nervous System. Neuron 2012, 73, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- The Human Protein Atlas. Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- Taveggia, C.; Thaker, P.; Petrylak, A.; Caporaso, G.L.; Toews, A.; Falls, D.L.; Einheber, S.; Salzer, J.L. Type III Neuregulin-1 Promotes Oligodendrocyte Myelination. Glia 2008, 56, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bare, D.J.; Becker-Catania, S.G.; DeVries, G.H. Differential Localization of Neuregulin-1 Type III in the Central and Peripheral Nervous System. Brain Res. 2011, 1369, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katanov, C.; Novak, N.; Vainshtein, A.; Golani, O.; Dupree, J.L.; Peles, E. N-Wasp Regulates Oligodendrocyte Myelination. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 6103–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, C.; Lakics, V.; Machesky, L.; Rumsby, M. N-WASP Regulates Extension of Filopodia and Processes by Oligodendrocyte Progenitors, Oligodendrocytes, and Schwann Cells—Implications for Axon Ensheathment at Myelination. Glia 2007, 55, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malheiro, A.R.; Correia, B.; Ferreira da Silva, T.; Bessa-Neto, D.; Van Veldhoven, P.P.; Brites, P. Leukodystrophy Caused by Plasmalogen Deficiency Rescued by Glyceryl 1-myristyl Ether Treatment. Brain Pathol. 2019, 29, 622–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, E.; Palminiello, S.; Golabek, A.A.; Walus, M.; Wierzba-Bobrowicz, T.; Rabe, A.; Albertini, G.; Wisniewski, K.E. Carbonic Anhydrase II in the Developing and Adult Human Brain. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 65, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liedtke, W.; Edelmann, W.; Bieri, P.L.; Chiu, F.-C.; Cowan, N.J.; Kucherlapati, R.; Raine, C.S. GFAP Is Necessary for the Integrity of CNS White Matter Architecture and Long-Term Maintenance of Myelination. Neuron 1996, 17, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaeren-Wiemers, N.; Bonnet, A.; Erb, M.; Erne, B.; Bartsch, U.; Kern, F.; Mantei, N.; Sherman, D.; Suter, U. The Raft-Associated Protein MAL Is Required for Maintenance of Proper Axon–Glia Interactions in the Central Nervous System. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 166, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fewou, S.N.; Ramakrishnan, H.; Büssow, H.; Gieselmann, V.; Eckhardt, M. Down-Regulation of Polysialic Acid Is Required for Efficient Myelin Formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 16700–16711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, T.; Lieberman, A.P. Npc1 Acting in Neurons and Glia Is Essential for the Formation and Maintenance of CNS Myelin. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corbeil, D.; Joester, A.; Fargeas, C.A.; Jászai, J.; Garwood, J.; Hellwig, A.; Werner, H.B.; Huttner, W.B. Expression of Distinct Splice Variants of the Stem Cell Marker Prominin-1 (CD133) in Glial Cells. Glia 2009, 57, 860–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.-M.; McAlear, T.S.; Nguyen, H.; Oses-Prieto, J.A.; Valenzuela, A.; Shi, R.D.; Perrino, J.J.; Huang, T.-T.; Burlingame, A.L.; Bechstedt, S.; et al. The Golgi Outpost Protein TPPP Nucleates Microtubules and Is Critical for Myelination. Cell 2019, 179, 132–146.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
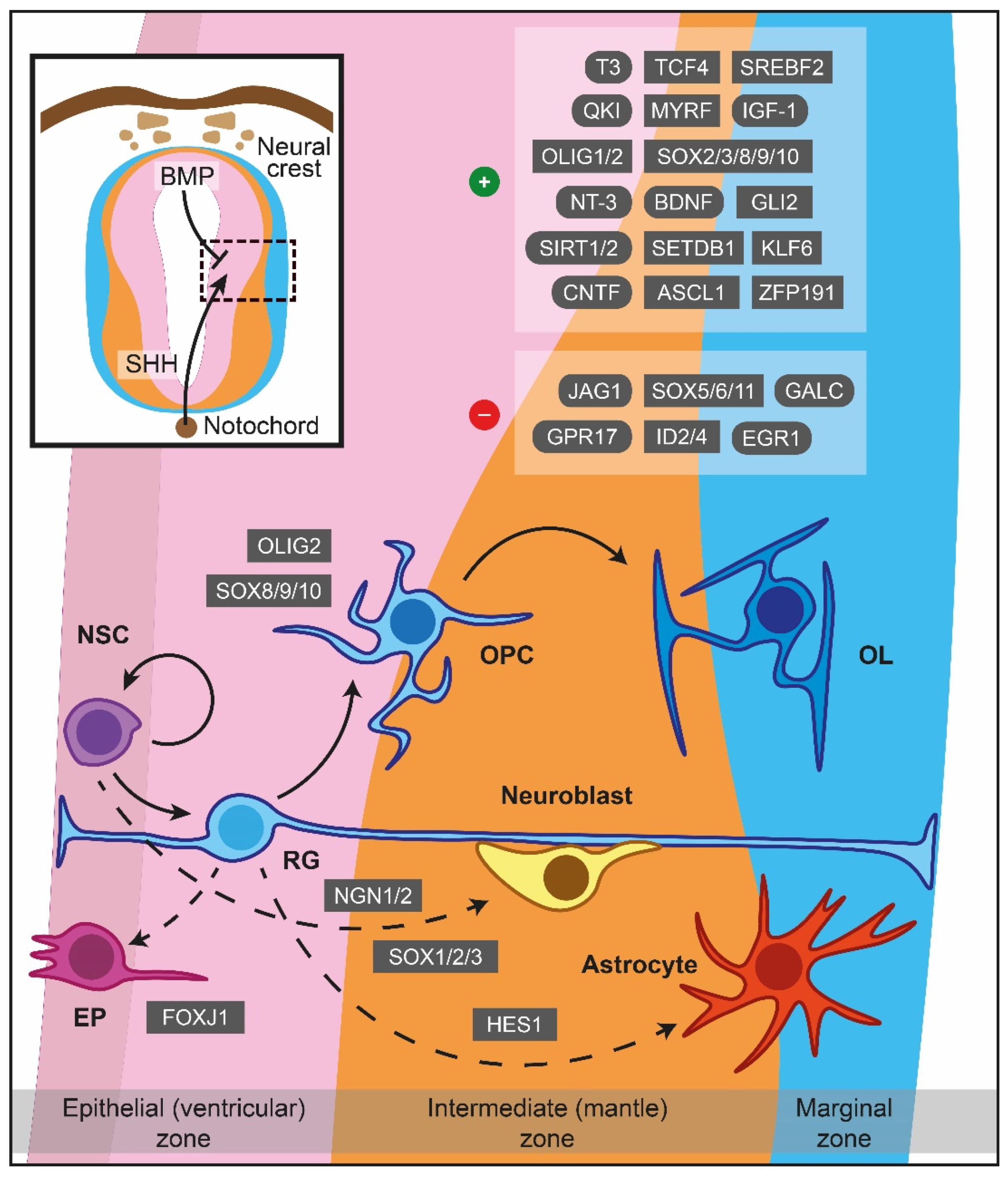
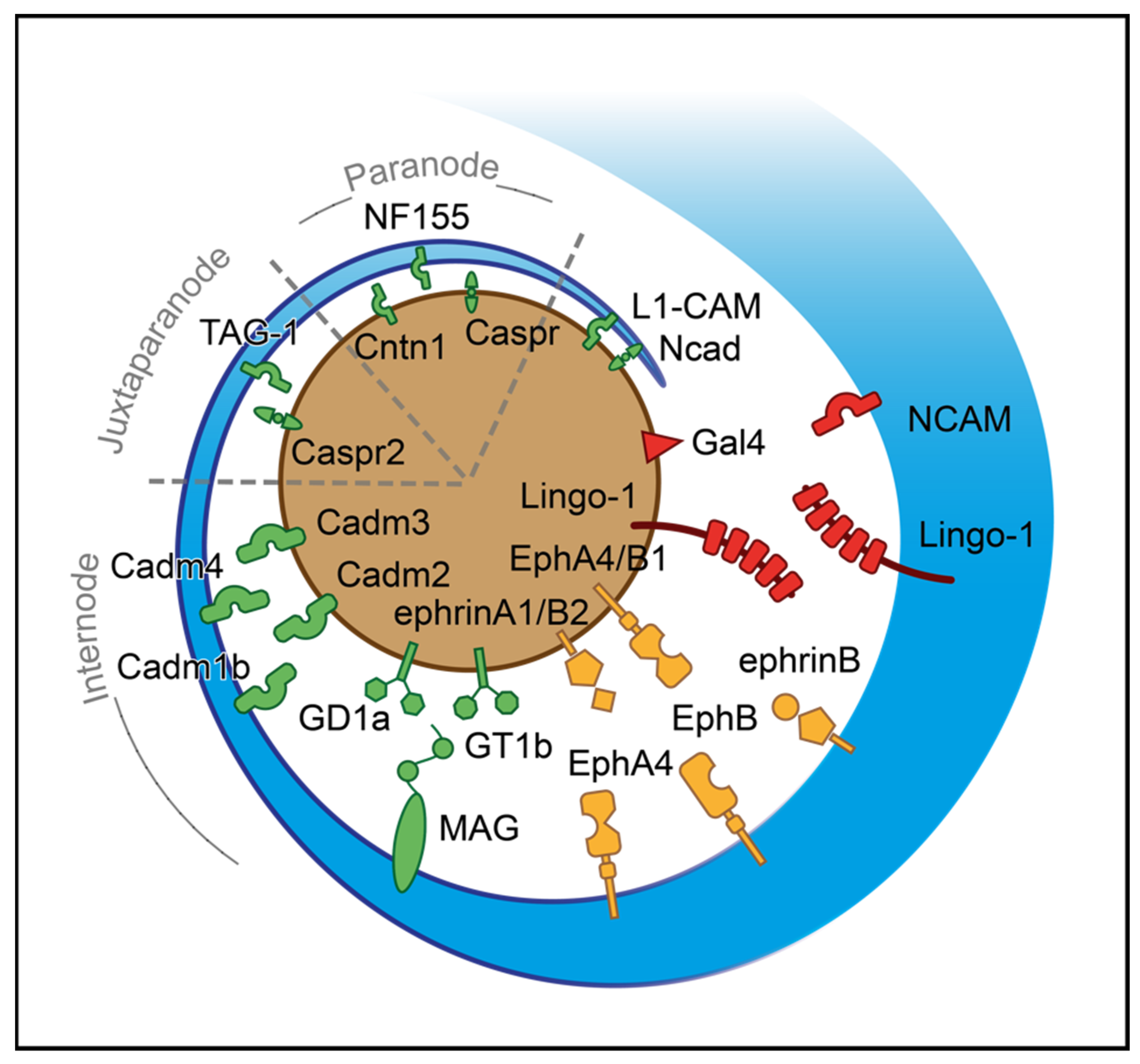
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dermitzakis, I.; Manthou, M.E.; Meditskou, S.; Miliaras, D.; Kesidou, E.; Boziki, M.; Petratos, S.; Grigoriadis, N.; Theotokis, P. Developmental Cues and Molecular Drivers in Myelinogenesis: Revisiting Early Life to Re-Evaluate the Integrity of CNS Myelin. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 3208-3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44070222
Dermitzakis I, Manthou ME, Meditskou S, Miliaras D, Kesidou E, Boziki M, Petratos S, Grigoriadis N, Theotokis P. Developmental Cues and Molecular Drivers in Myelinogenesis: Revisiting Early Life to Re-Evaluate the Integrity of CNS Myelin. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2022; 44(7):3208-3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44070222
Chicago/Turabian StyleDermitzakis, Iasonas, Maria Eleni Manthou, Soultana Meditskou, Dimosthenis Miliaras, Evangelia Kesidou, Marina Boziki, Steven Petratos, Nikolaos Grigoriadis, and Paschalis Theotokis. 2022. "Developmental Cues and Molecular Drivers in Myelinogenesis: Revisiting Early Life to Re-Evaluate the Integrity of CNS Myelin" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 44, no. 7: 3208-3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44070222
APA StyleDermitzakis, I., Manthou, M. E., Meditskou, S., Miliaras, D., Kesidou, E., Boziki, M., Petratos, S., Grigoriadis, N., & Theotokis, P. (2022). Developmental Cues and Molecular Drivers in Myelinogenesis: Revisiting Early Life to Re-Evaluate the Integrity of CNS Myelin. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 44(7), 3208-3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb44070222











