Inhibition of Phagocytosis by Silibinin in Mouse Macrophages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
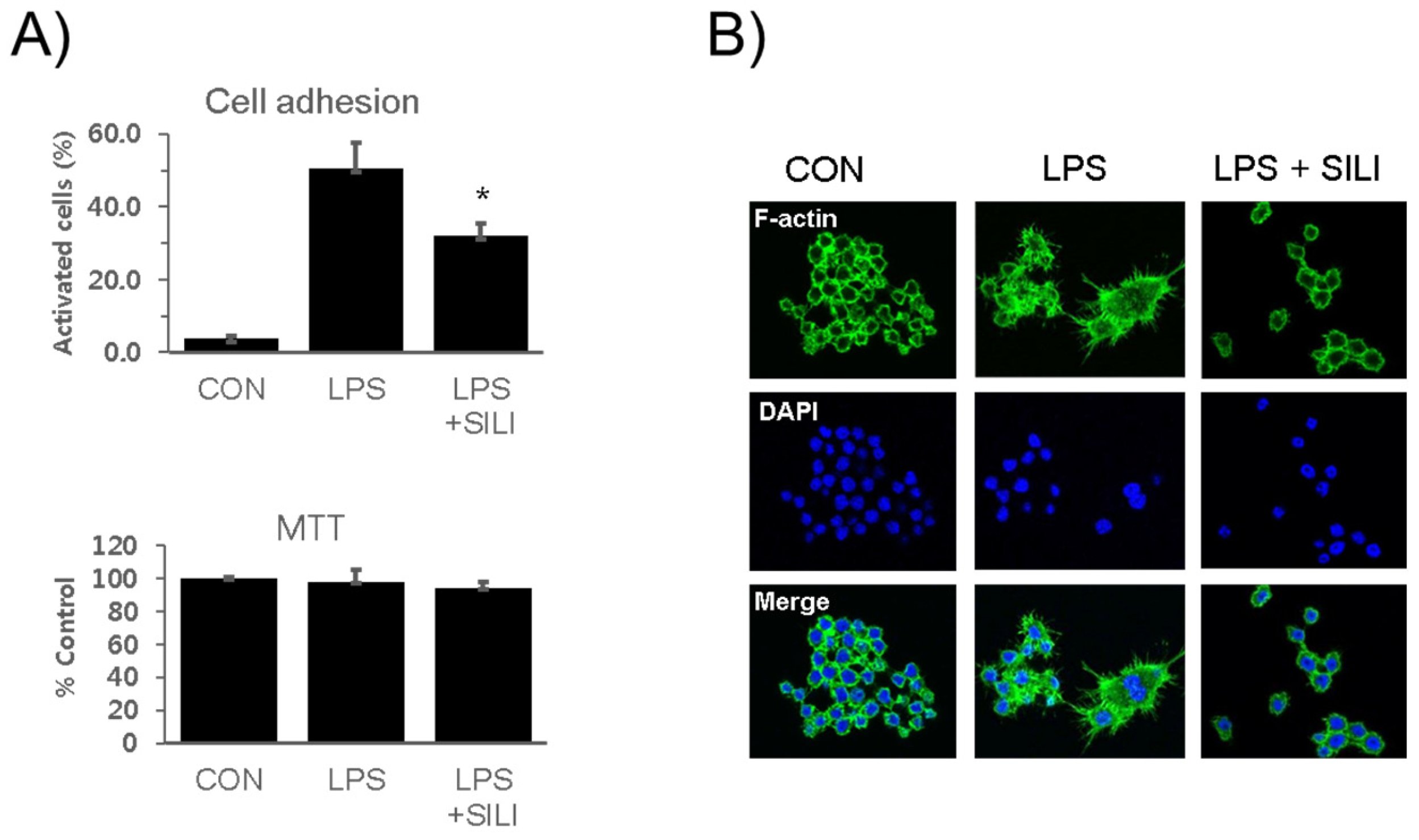
2.2. Cell Culture and Adhesion Assay
2.3. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.5. Phagocytosis Assay
2.6. MAPKs Array
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Inhibition of Macrophage Activation by Silibinin in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells
3.2. Inhibition of Phagocytosis by Silibinin in LPS-Stimulated Macrophages
3.3. Inhibition of MAPKs by Silibinin in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells
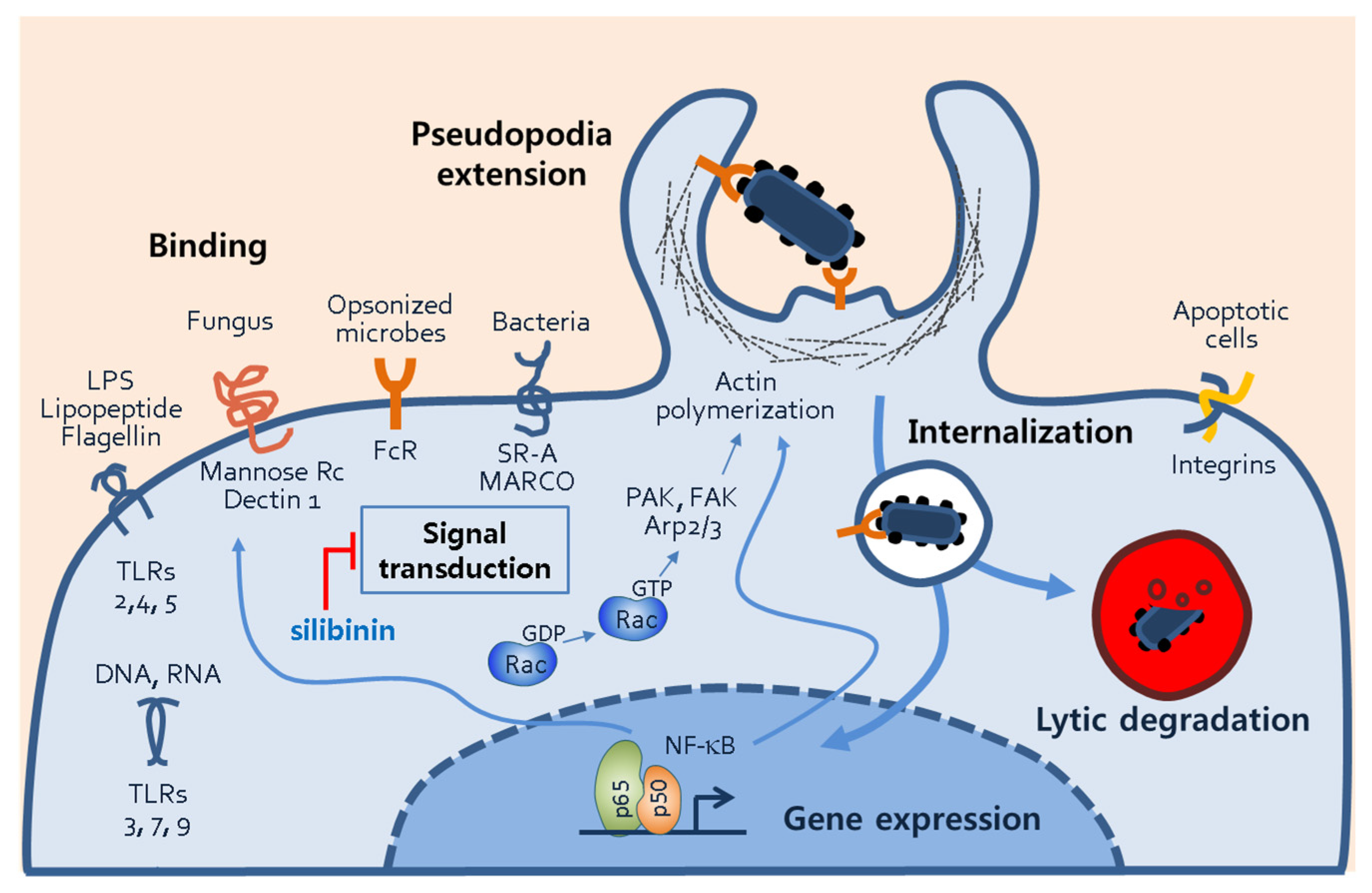
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radjadian, T.; Rezazadeh, S.H.; Huseini, H.F. Analysis of silymarin components in the seed extracts of some milk thistle ecotypes from Iran by Hplc. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Sci. Trans. A 2008, 32, 141–146. [Google Scholar]
- Bektur, N.E.; Sahin, E.; Baycu, C.; Unver, G. Protective effects of silymarin against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in mice. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2016, 32, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mereish, K.A.; Bunner, D.L.; Ragland, D.R.; Creasia, D.A. Protection against microcystin-LR-induced hepatotoxicity by Silymarin: Biochemistry, histopathology, and lethality. Pharm. Res. 1991, 8, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, A.; Garrido, A. Biochemical bases of the pharmacological action of the flavonoid silymarin and of its structural isomer silibinin. Biol. Res. 1994, 27, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Hong, R.; Tian, T. Silymarin’s protective effects and possible mechanisms on alcoholic fatty liver for rats. Biomol. Ther. 2013, 21, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofalo, R.; Bannwart-Castro, C.F.; Magalhães, C.G.; Borges, V.T.; Peraçoli, J.C.; Witkin, S.S.; Peraçoli, M.T. Silibinin attenuates oxidative metabolism and cytokine production by monocytes from preeclamptic women. Free Radic. Res. 2013, 47, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, F.S.; Krishnegowda, N.K.; Mikhailova, M.; Kahlenberg, M.S. Flavonoid, silibinin, inhibits proliferation and promotes cell-cycle arrest of human colon cancer. J. Surg. Res. 2007, 143, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, C.K.; Cho, S.I.; Lee, M.Y.; Jeon, Y.J.; Lee, S.K. Inhibition of ERK1/2 by silymarin in mouse mesangial cells. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 21, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, M.J.; Motamed, N.; Shokrgozar, M.A. Evaluation of silibinin on the viability, migration and adhesion of the human prostate adenocarcinoma (PC-3) cell line. Cell Biol. Int. 2008, 32, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikov, D.A. Macrophages in the embryo and beyond: Much more than just giant phagocytes. Genesis 2008, 46, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y. M1 and M2 polarization of macrophages: A mini-review. Med. Biol. Sci. Eng. 2019, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Greten, F.R.; Karin, M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, X. Tumor-recruited M2 macrophages promote gastric and breast cancer metastasis via M2 macrophage-secreted CHI3L1 protein. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.O.; Gordon, S. The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: Time for reassessment. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, S.; Schaible, U.E.; Schneider, B.E. Interferon gamma activated macrophages kill mycobacteria by nitric oxide induced apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pi, J.; Li, T.; Liu, J.; Su, X.; Wang, R.; Yang, F.; Bai, H.; Jin, H.; Cai, J. Detection of lipopolysaccharide induced inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 macrophages using atomic force microscope. Micron 2014, 65, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machesky, L.M. Lamellipodia and filopodia in metastasis and invasion. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 2102–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, J.V.; Stradal, T.; Vignal, E.; Rottner, K. The lamellipodium: Where motility begins. Trends Cell Biol. 2002, 12, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, H.; Stelzer, E.H.; Holzer, D.; Buss, F.; Griffiths, G.; Rohrbach, A. Filopodia act as phagocytic tentacles and pull with discrete steps and a load-dependent velocity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11633–11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, P.K.; Lappalainen, P. Filopodia: Molecular architecture and cellular functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavsar, P.J.; Vigorito, E.; Turner, M.; Ridley, A.J. Vav GEFs regulate macrophage morphology and adhesion-induced Rac and Rho activation. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 3345–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, A.K.; Hou, Y.Y.; Hirata, H.; Yamauchi, S.; Yip, A.K.; Chiam, K.H.; Tanaka, N.; Sawada, Y.; Kawauchi, K. Loss of p53 enhances NF-κB-dependent lamellipodia formation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, D.; Iida, T.; Nakase, H. The Phagocytic Function of Macrophage-Enforcing Innate Immunity and Tissue Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity 2011, 34, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.L.; Chen, J.T.; Liang, C.M.; Tai, M.C.; Lu, D.W.; Chen, Y.H. Silibinin treatment prevents endotoxin-induced uveitis in rats in vivo and in vitro. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, B.; Cao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D. Silybin attenuates LPS-induced lung injury in mice by inhibiting NF-κB signaling and NLRP3 activation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, C.K.; Park, S.J.; Lee, M.Y.; Cha, M.J.; Kim, O.H.; You, H.J.; Chang, I.Y.; Yoon, S.P.; Jeon, Y.J. Silibinin Inhibits LPS-Induced Macrophage Activation by Blocking p38 MAPK in RAW 264.7 Cells. Biomol. Ther. 2013, 21, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Karin, M. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades and regulation of gene expression. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1996, 8, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.; Jin, H.M.; Song, I.; Youn, B.U.; Lee, J.; Kim, N. Silibinin inhibits osteoclast differentiation mediated by TNF family members. Mol. Cells 2009, 28, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.J.; Jung, S.P.; Han, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.S.; Nam, S.J.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, J.H. Silibinin inhibits TPA-induced cell migration and MMP-9 expression in thyroid and breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choi, J.H.; Lim, H.I.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, W.W.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Choe, J.H.; Yang, J.H.; Nam, S.J.; et al. Silibinin prevents TPA-induced MMP-9 expression and VEGF secretion by inactivation of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Choi, M.G.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, W.W.; Hur, S.M.; Kim, J.H.; Choe, J.H.; Nam, S.J.; et al. Silibinin suppresses TNF-alpha-induced MMP-9 expression in gastric cancer cells through inhibition of the MAPK pathway. Molecules 2009, 14, 4300–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herre, J.; Marshall, A.S.; Caron, E.; Edwards, A.D.; Williams, D.L.; Schweighoffer, E.; Tybulewicz, V.; Reis e Sousa, C.; Gordon, S.; Brown, G.D. Dectin-1 uses novel mechanisms for yeast phagocytosis in macrophages. Blood 2004, 104, 4038–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezekowitz, R.A.; Sastry, K.; Bailly, P.; Warner, A. Molecular characterization of the human macrophage mannose receptor: Demonstration of multiple carbohydrate recognition-like domains and phagocytosis of yeasts in Cos-1 cells. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 172, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Laan, L.J.; Döpp, E.A.; Haworth, R.; Pikkarainen, T.; Kangas, M.; Elomaa, O.; Dijkstra, C.D.; Gordon, S.; Tryggvason, K.; Kraal, G. Regulation and functional involvement of macrophage scavenger receptor MARCO in clearance of bacteria in vivo. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiser, L.; Gough, P.J.; Kodama, T.; Gordon, S. Macrophage classA scavenger receptor-mediated phagocytosis of Escherichia coli: Role of cell heterogeneity, microbial strain, and culture conditions in vitro. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 1953–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.A.; Li, Y.; Kodama, T.; Suzuki, H.; Silverstein, S.C.; El Khoury, J. Protection from lethal gram-positive infection by macrophage scavenger receptor-dependent phagocytosis. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.L.; Shen, L.; Eicher, D.M.; Wewers, M.D.; Gill, J.K. Phagocytosis mediated by three distinct Fc γ receptor classes on human leukocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 171, 1333–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Fcγ receptors as regulators of immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Agarwal, C.; Ichikawa, H.; Singh, R.P.; Aggarwal, B.B. Anticancer potential of silymarin: From bench to bed side. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 4457–4498. [Google Scholar]
- Iademarco, M.F.; McQuillan, J.J.; Rosen, G.D.; Dean, D.C. Characterization of the promoter for vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1). J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 16323–16329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledebur, H.C.; Parks, T.P. Transcriptional regulation of the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 gene by inflammatory cytokines in human endothelial cells. Essential roles of a variant NF-κB site and p65 homodimers. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, J.; Ghersa, P.; Hooft van Huijsduijnen, R.; Gray, J.; Chandra, G.; Talabot, F.; DeLamarter, J.F. An NF kappa B-like factor is essential but not sufficient for cytokine induction of endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 (ELAM-1) gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991, 19, 2645–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchione, G.; Grasselli, E.; Voci, A.; Baldini, F.; Grattagliano, I.; Wang, D.Q.; Portincasa, P.; Vergani, L. Silybin counteracts lipid excess and oxidative stress in cultured steatotic hepatic cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 6016–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, K.-H.; Lee, M.-Y.; Jeon, Y.-J. Inhibition of Phagocytosis by Silibinin in Mouse Macrophages. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 8126-8137. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45100513
Sun K-H, Lee M-Y, Jeon Y-J. Inhibition of Phagocytosis by Silibinin in Mouse Macrophages. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2023; 45(10):8126-8137. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45100513
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Kyung-Hoon, Min-Young Lee, and Young-Jin Jeon. 2023. "Inhibition of Phagocytosis by Silibinin in Mouse Macrophages" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 45, no. 10: 8126-8137. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45100513
APA StyleSun, K. -H., Lee, M. -Y., & Jeon, Y. -J. (2023). Inhibition of Phagocytosis by Silibinin in Mouse Macrophages. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 45(10), 8126-8137. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45100513






