Impact of Hypoxia-Induced miR-210 on Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
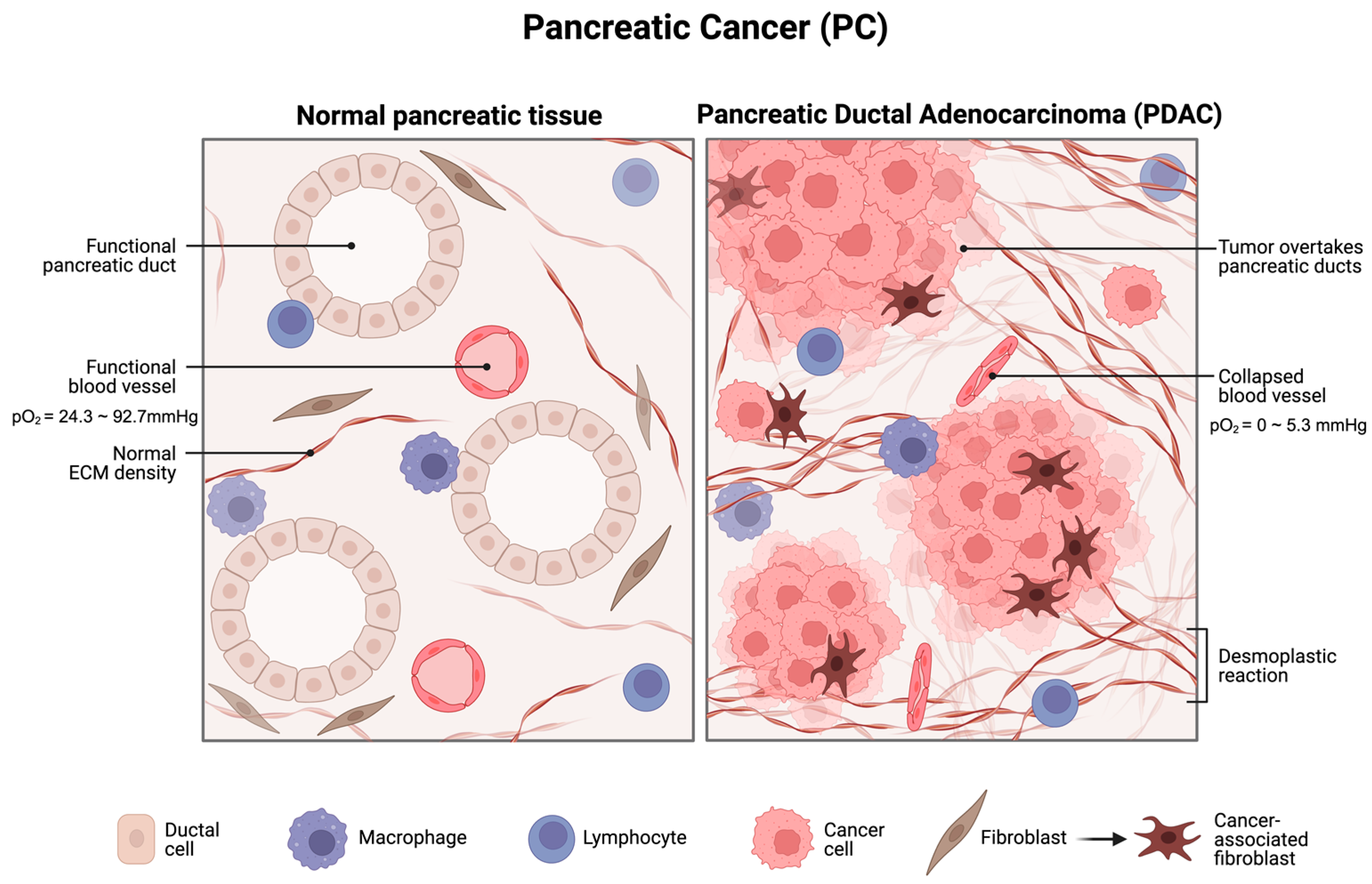
:1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms of Hypoxia-Induced Upregulation of miR-210
2.1. Hypoxia
2.2. Roles of HIFs during Hypoxic Adaptive Response
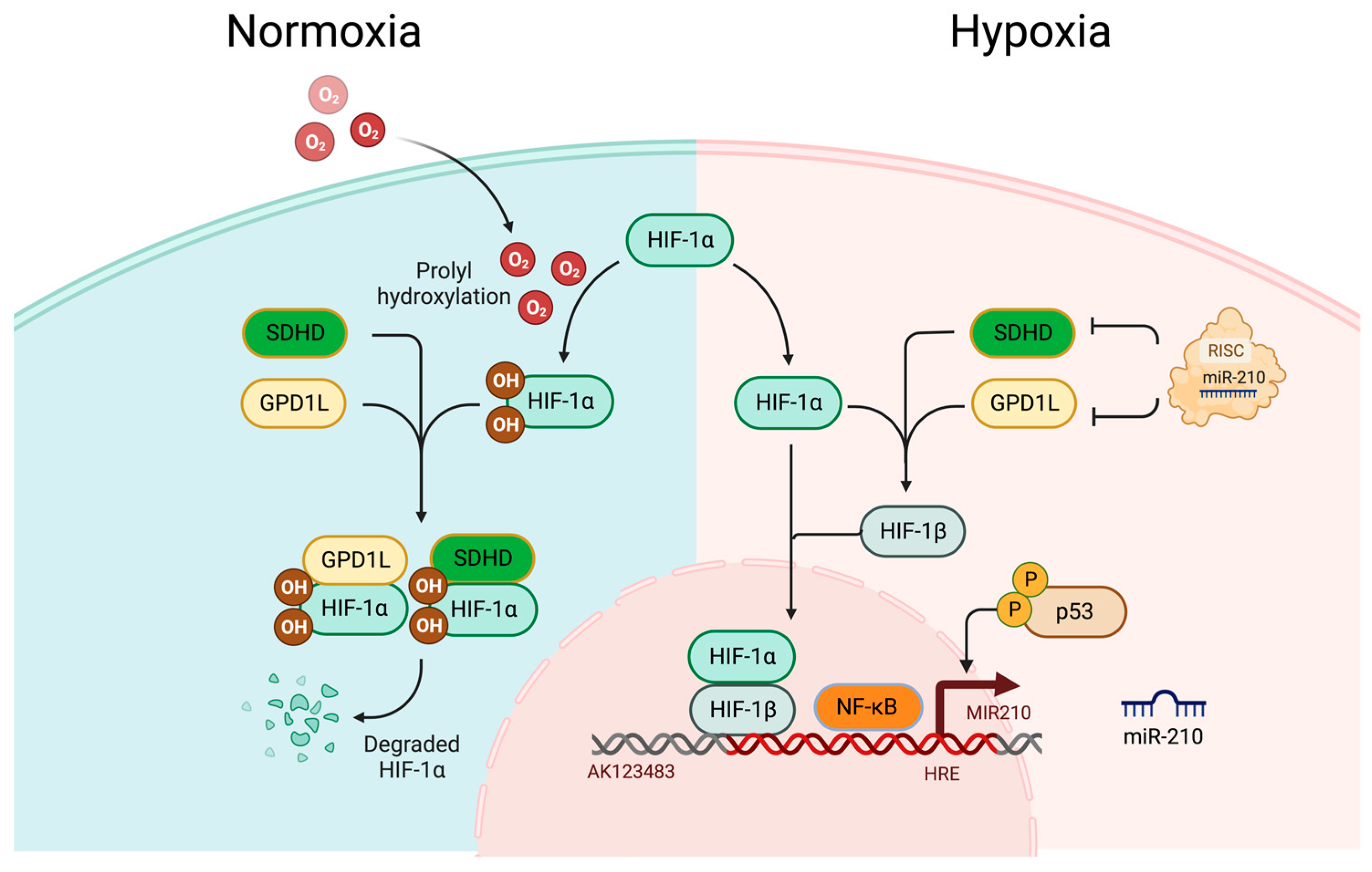
2.3. HIF-Dependent Upregulation of miR-210 during Hypoxia
2.4. HIF-Independent Upregulation of miR-210 during Hypoxia
3. Roles of miR-210 in Pancreatic Cancer
3.1. Hypoxia Induces miR-210 Upregulation in Pancreatic Cancer
3.2. Molecular Targets and Hallmarks of miR-210 Upregulation in Pancreatic Cancer
3.3. Roles of miR-210 in PC Chemoresistance
3.4. miR-210 as a Potential Diagnostic Marker for Pancreatic Cancer Early Detection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daoud, A.Z.; Mulholland, E.J.; Cole, G.; McCarthy, H.O. MicroRNAs in Pancreatic Cancer: Biomarkers, prognostic, and therapeutic modulators. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiella, S.; Sandini, M.; Gianotti, L.; Butturini, G.; Salvia, R.; Bassi, C. The prognostic impact of para-aortic lymph node metastasis in pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 42, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Shang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Bao, J.; Hao, C. Surgical treatment for locally advanced pancreatic cancer localized in the pancreatic body and tail (report of 11 cases). Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 4676–4681. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.; Chapple, A.; Salisbury, H.; Corrie, P.; Ziebland, S. “It can’t be very important because it comes and goes”—Patients’ accounts of intermittent symptoms preceding a pancreatic cancer diagnosis: A qualitative study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e004215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Sanagapalli, S.; Stoita, A. Challenges in diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2047–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, T.; Castan, F.; Lopez, A.; Turpin, A.; Ben Abdelghani, M.; Wei, A.C.; Mitry, E.; Biagi, J.J.; Evesque, L.; Artru, P.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes of FOLFIRINOX vs Gemcitabine as Adjuvant Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnelldorfer, T.; Ware, A.L.; Sarr, M.G.; Smyrk, T.C.; Zhang, L.; Qin, R.; Gullerud, R.E.; Donohue, J.H.; Nagorney, D.M.; Farnell, M.B. Long-term survival after pancreatoduodenectomy for pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Is cure possible? Ann. Surg. 2008, 247, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, J.; Betancourt, M. Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Monogr. Clin. Cytol. 2020, 26, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, T.J.; Hua, K.; Singh, A. Molecular Pathogenesis of Pancreatic Cancer. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2016, 144, 241–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesinmeyer, M.D.; Austin, M.A.; Li, C.I.; De Roos, A.J.; Bowen, D.J. Differences in survival by histologic type of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2005, 14, 1766–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.W.; Lang, B.H.H.; McLeod, D.S.A.; Newbold, K.; Haymart, M.R. Thyroid cancer. Lancet 2023, 401, 1531–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, D.C.; Meyers, G.J.; Hu, J.S. Testicular Cancer: Diagnosis and Treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2018, 97, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Koong, A.C.; Mehta, V.K.; Le, Q.T.; Fisher, G.A.; Terris, D.J.; Brown, J.M.; Bastidas, A.J.; Vierra, M. Pancreatic tumors show high levels of hypoxia. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 48, 919–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Yang, G.; Zhou, W.; Qiu, J.; Chen, G.; Luo, W.; Zhao, F.; You, L.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, T.; et al. Targeting hypoxic tumor microenvironment in pancreatic cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Qin, Y.; Ji, S.; Xu, W.; Liu, W.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, M.; Ni, Q.; Yu, X.; et al. UHRF1 promotes aerobic glycolysis and proliferation via suppression of SIRT4 in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 452, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, J.G.; Wong, S.C.; Sharp, T.V. The hypoxic tumor microenvironment: Driving the tumorigenesis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 2659–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Zhu, W.; Xu, W.; Zhang, B.; Shi, S.; Ji, S.; Liu, J.; Long, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, L.; et al. LSD1 sustains pancreatic cancer growth via maintaining HIF1α-dependent glycolytic process. Cancer Lett. 2014, 347, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, G.; Brkić, J.; Hayder, H.; Peng, C. MicroRNAs in Human Placental Development and Pregnancy Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 5519–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, K.; Myers, K.A. The role of hypoxia-induced miR-210 in cancer progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 6353–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Chua, C.Y.X.; Tian, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chiao, P.J.; Zhang, W. MicroRNA Signaling Pathway Network in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. J. Genet. Genom. 2015, 42, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Azmi, A.S.; Ali, S.; Ahmad, A.; Li, Y.; Banerjee, S.; Kong, D.; Sarkar, F.H. The biological kinship of hypoxia with CSC and EMT and their relationship with deregulated expression of miRNAs and tumor aggressiveness. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1826, 272–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouaib, S.; Umansky, V.; Kieda, C. The role of hypoxia in shaping the recruitment of proangiogenic and immunosuppressive cells in the tumor microenvironment. Contemp. Oncol. 2018, 22, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Perspectives on oxygen sensing. Cell 1999, 98, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.L.; Jiang, B.H.; Rue, E.A.; Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5510–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, V.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, M.; Melino, G.; Amelio, I. The hypoxic tumour microenvironment. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eales, K.L.; Hollinshead, K.E.; Tennant, D.A. Hypoxia and metabolic adaptation of cancer cells. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzuto, A.; Carico, E. Role of HIF-1 in Cancer Progression: Novel Insights. A Review. Curr. Mol. Med. 2018, 18, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulos, O.; Kibel, A.; Gray, S.; Kaelin, W.G., Jr. Tumour suppression by the human von Hippel-Lindau gene product. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 822–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesener, M.S.; Jürgensen, J.S.; Rosenberger, C.; Scholze, C.K.; Hörstrup, J.H.; Warnecke, C.; Mandriota, S.; Bechmann, I.; Frei, U.A.; Pugh, C.W.; et al. Widespread hypoxia-inducible expression of HIF-2alpha in distinct cell populations of different organs. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Du, F.; Shen, G.; Zheng, F.; Xu, B. The role of hypoxia-inducible factor-2 in digestive system cancers. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serocki, M.; Bartoszewska, S.; Janaszak-Jasiecka, A.; Ochocka, R.J.; Collawn, J.F.; Bartoszewski, R. miRNAs regulate the HIF switch during hypoxia: A novel therapeutic target. Angiogenesis 2018, 21, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinowski, L.; Janaszak-Jasiecka, A.; Siekierzycka, A.; Bartoszewska, S.; Woźniak, M.; Lejnowski, D.; Collawn, J.F.; Bartoszewski, R. Posttranscriptional and transcriptional regulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase during hypoxia: The role of microRNAs. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2016, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keith, B.; Johnson, R.S.; Simon, M.C. HIF1α and HIF2α: Sibling rivalry in hypoxic tumour growth and progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 12, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.J.; Wang, L.Y.; Chodosh, L.A.; Keith, B.; Simon, M.C. Differential roles of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) and HIF-2alpha in hypoxic gene regulation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 23, 9361–9374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loboda, A.; Stachurska, A.; Dorosz, J.; Zurawski, M.; Wegrzyn, J.; Kozakowska, M.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. HIF-1 attenuates Ref-1 expression in endothelial cells: Reversal by siRNA and inhibition of geranylgeranylation. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 51, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoud, G.; Li, W. HIF-1α pathway: Role, regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, M.Y.; Powis, G. Passing the baton: The HIF switch. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2012, 37, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolfs, A.; Kvietikova, I.; Gassmann, M.; Wenger, R.H. Oxygen-regulated transferrin expression is mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 20055–20062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentze, M.W.; Muckenthaler, M.U.; Andrews, N.C. Balancing acts: Molecular control of mammalian iron metabolism. Cell 2004, 117, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Wu, C.; Xiong, Z.F.; Fang, X. Progress on hypoxia-inducible factor-3: Its structure, gene regulation and biological function (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 2411–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, S.; Hamada, J.; Kobayashi, C.; Kondo, Y.; Imura, N. Expression and characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-3alpha in human kidney: Suppression of HIF-mediated gene expression by HIF-3alpha. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 287, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.F.; Wang, X.R.; Yang, Y.W.; Lin, H. Hypoxia upregulates hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-3alpha expression in lung epithelial cells: Characterization and comparison with HIF-1alpha. Cell Res. 2006, 16, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalilian, S.; Bijanvand, A.; Abedinlou, H.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. A review on the role of miR-210 in human disorders. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 241, 154244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, C.; Greco, S.; Martelli, F.; Ivan, M. miR-210: More than a silent player in hypoxia. IUBMB Life 2011, 63, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, C.; Buffa, F.M.; Colella, S.; Moore, J.; Sotiriou, C.; Sheldon, H.; Harris, A.L.; Gleadle, J.M.; Ragoussis, J. hsa-miR-210 Is induced by hypoxia and is an independent prognostic factor in breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fei, M.; Xue, G.; Zhou, Q.; Jia, Y.; Li, L.; Xin, H.; Sun, S. Elevated levels of hypoxia-inducible microRNA-210 in pre-eclampsia: New insights into molecular mechanisms for the disease. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallamshetty, S.; Chan, S.Y.; Loscalzo, J. Hypoxia: A master regulator of microRNA biogenesis and activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 64, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corn, P.G. Hypoxic regulation of miR-210: Shrinking targets expand HIF-1’s influence. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Lee, C.Y.; Park, J.H.; Park, M.S.; Maeng, L.S.; Yoon, C.S.; Lee, M.Y.; Hwang, K.C.; Chung, Y.A. Survival of hypoxic human mesenchymal stem cells is enhanced by a positive feedback loop involving miR-210 and hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J. Vet. Sci. 2013, 14, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Shi, M.; Ding, Y.; Sun, H.; Yuan, F.; Zou, Z. Elevated expression of miR-210 predicts poor survival of cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.J.; Souza, A.L.; Clish, C.B.; Puigserver, P. A hypoxia-induced positive feedback loop promotes hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha stability through miR-210 suppression of glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 1-like. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 31, 2696–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorospe, M.; Tominaga, K.; Wu, X.; Fähling, M.; Ivan, M. Post-Transcriptional Control of the Hypoxic Response by RNA-Binding Proteins and MicroRNAs. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutharasan, R.K.; Nagpal, V.; Ichikawa, Y.; Ardehali, H. microRNA-210 is upregulated in hypoxic cardiomyocytes through Akt- and p53-dependent pathways and exerts cytoprotective effects. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 301, H1519–H1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, E.P.; Taylor, C.T. Hypoxia-responsive transcription factors. Pflug. Arch. 2005, 450, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Q.; Furong, W.; Baosheng, L. Multiple functions of hypoxia-regulated miR-210 in cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 33, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.Y.; Liu, W.J.; Zhao, Y.P.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, T.P.; Chen, G.; Shu, H. Induction, modulation and potential targets of miR-210 in pancreatic cancer cells. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2012, 11, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaconstantinou, I.G.; Manta, A.; Gazouli, M.; Lyberopoulou, A.; Lykoudis, P.M.; Polymeneas, G.; Voros, D. Expression of microRNAs in patients with pancreatic cancer and its prognostic significance. Pancreas 2013, 42, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.S.; Huang, X.; Cao, H.; Christman-Skieller, C.; Bennewith, K.; Le, Q.T.; Koong, A.C. Circulating miR-210 as a Novel Hypoxia Marker in Pancreatic Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2010, 3, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guz, M.; Jeleniewicz, W.; Cybulski, M.; Kozicka, J.; Kurzepa, J.; Mądro, A. Serum miR-210-3p can be used to differentiate between patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and chronic pancreatitis. Biomed. Rep. 2021, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Peng, L.; Tan, C.; Liu, H.; Chen, P.; Wang, H. Role of HOXA9 in solid tumors: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic potential. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Zhou, S.; Yuan, W.; Cen, F.; Yan, Q. Mechanism of miR-210 involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer cells under hypoxia. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2019, 39, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wu, H.; Xiong, J.; Peng, T. Long Non-coding RNA DLEU2L Targets miR-210-3p to Suppress Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Cancer Cells via BRCA2 Regulation. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 645365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, N.; Cui, J.; Wu, H.; Xiong, J.; Peng, T. Exosomes derived from cancer stem cells of gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells enhance drug resistance by delivering miR-210. Cell. Oncol. 2020, 43, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Ma, C.; Li, P.; Ma, C.; Ping, F.; Li, W.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Q.; Li, Y. Low glucose enhanced metformin’s inhibitory effect on pancreatic cancer cells by suppressing glycolysis and inducing energy stress via up-regulation of miR-210-5p. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 2168–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.B.; Lin, Y.; Li, S.J.; Gao, J.; Han, B.; Zhang, C.S. MiR-210 knockdown promotes the development of pancreatic cancer via upregulating E2F3 expression. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 8640–8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Zhou, G.; Soufan, O.; Xia, J. miRNet 2.0: Network-based visual analytics for miRNA functional analysis and systems biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W244–W251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Feng, B.; Lu, L.; Han, S.; Chu, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, R. MiRNAs and E2F3: A complex network of reciprocal regulations in human cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 60624–60639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.B.; Song, Y.; Lai, Y.T.; Qiu, S.Z.; Hu, A.K.; Li, D.X.; Zheng, N.S.; Zeng, H.Q.; Lin, Q.C. MiR-210-3p enhances intermittent hypoxia-induced tumor progression via inhibition of E2F3. Sleep Breath. 2023; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakakis, A.; Sandaltzopoulos, R.; Greshock, J.; Liang, S.; Huang, J.; Hasegawa, K.; Li, C.; O’Brien-Jenkins, A.; Katsaros, D.; Weber, B.L.; et al. miR-210 links hypoxia with cell cycle regulation and is deleted in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Gao, L.; Yu, Y.; Wang, N.; Chen, H. EFNA3 Is a Prognostic Biomarker Correlated With Immune Cell Infiltration and Immune Checkpoints in Gastric Cancer. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 796592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Li, M.; Cui, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, C.; Si, J.; Lin, K.; Yu, H. Small extracellular vesicles derived from hypoxic mesenchymal stem cells promote vascularized bone regeneration through the miR-210-3p/EFNA3/PI3K pathway. Acta Biomater. 2022, 150, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yin, B.; Wang, B.; Ma, Z.; Liu, W.; Lv, G. MicroRNA-210 promotes proliferation and invasion of peripheral nerve sheath tumor cells targeting EFNA3. Oncol. Res. 2013, 21, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ding, X.; Quan, G.; Xiong, J.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Hypoxia-Induced miR-210 Promotes Endothelial Cell Permeability and Angiogenesis via Exosomes in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Biochem. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 7752277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaño-Pons, J.; Arsenian-Henriksson, M.; León, J. The Multiple Faces of MNT and Its Role as a MYC Modulator. Cancers 2021, 13, 4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y.; Xie, Y.; Deng, M.; Zhu, L.; Wu, X.; Li, G.; Shi, N.X.; Wen, C.; Huang, W.; Duan, Y.; et al. c-Myc-activated intronic miR-210 and lncRNA MIR210HG synergistically promote the metastasis of gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2022, 526, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Tao, X.; Huang, Y. Silencing microRNA-210 in Hypoxia-Induced HUVEC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Inhibits Hemangioma. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 49, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, R.; Puleo, F.; Collignon, J.; Meurisse, N.; Chavez, M.; Seidel, L.; Gast, P.; Polus, M.; Loly, C.; Delvenne, P.; et al. A single center experience in resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: The limitations of the surgery-first approach. Critical review of the literature and proposals for practice update. Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 2017, 80, 451–461. [Google Scholar]
- Burris, H.A., 3rd; Moore, M.J.; Andersen, J.; Green, M.R.; Rothenberg, M.L.; Modiano, M.R.; Cripps, M.C.; Portenoy, R.K.; Storniolo, A.M.; Tarassoff, P.; et al. Improvements in survival and clinical benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 1997, 15, 2403–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Pöttler, M.; Lan, B.; Grützmann, R.; Pilarsky, C.; Yang, H. Chemoresistance in Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Purohit, V.; Mehla, K.; Gunda, V.; Chaika, N.V.; Vernucci, E.; King, R.J.; Abrego, J.; Goode, G.D.; Dasgupta, A.; et al. MUC1 and HIF-1alpha Signaling Crosstalk Induces Anabolic Glucose Metabolism to Impart Gemcitabine Resistance to Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 71–87.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhayat, S.A.; Mardin, W.A.; Seggewiß, J.; Ströse, A.J.; Matuszcak, C.; Hummel, R.; Senninger, N.; Mees, S.T.; Haier, J. MicroRNA Profiling Implies New Markers of Gemcitabine Chemoresistance in Mutant p53 Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abue, M.; Yokoyama, M.; Shibuya, R.; Tamai, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sato, I.; Tanaka, N.; Hamada, S.; Shimosegawa, T.; Sugamura, K.; et al. Circulating miR-483-3p and miR-21 is highly expressed in plasma of pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Shao, C.; Li, A.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; Li, J. Diagnostic Value of Plasma miR-181b, miR-196a, and miR-210 Combination in Pancreatic Cancer. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 6073150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, A.; Kullmann, F.; Kunzmann, V.; Al-Batran, S.E.; Oettle, H.; Plentz, R.; Siveke, J.; Springfeld, C.; Riess, H. Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer and Hyperbilirubinaemia: Review and German Expert Opinion on Treatment with nab-Paclitaxel plus Gemcitabine. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2015, 38, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Raimondo, M.; Guha, S.; Chen, J.; Diao, L.; Dong, X.; Wallace, M.B.; Killary, A.M.; Frazier, M.L.; Woodward, T.A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs in Pancreatic Juice as Candidate Biomarkers of Pancreatic Cancer. J. Cancer 2014, 5, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Xu, C.; Yuan, W.; Wang, C.; Zhao, P.; Chen, L.; Ma, J. Evaluation of Plasma MicroRNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: miR-196a and miR-210 Could Be Negative and Positive Prognostic Markers, Respectively. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6495867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaeel, A.; Fletcher, E.; Miserlis, D.; Wechsler, M.; Papoutsi, E.; Haynatzki, G.; Smith, R.S.; Bohannon, W.T.; Koutakis, P. Skeletal muscle MiR-210 expression is associated with mitochondrial function in peripheral artery disease patients. Transl. Res. 2022, 246, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Cao, H.; Zhuang, J.; Wan, J.; Guan, M.; Yu, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, W. Identification of miR-130a, miR-27b and miR-210 as serum biomarkers for atherosclerosis obliterans. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Sun, Y.; Mao, Q.; Zhou, C.; Chen, Y.; Xue, D. Exosomal miR-4639 and miR-210 in Plasma and Urine as Biomarkers in IgA Nephropathy. Nephron 2022, 146, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Lin, X.; Sun, Y.; Ji, X. Dysregulation of miR-210 is involved in the development of diabetic retinopathy and serves a regulatory role in retinal vascular endothelial cell proliferation. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2020, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zeng, J.; Yuan, J.; Deng, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, P.; Feng, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. MicroRNA-210 overexpression promotes psoriasis-like inflammation by inducing Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2551–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Zhuang, C.; Wang, X.; Ming, L. Serum miR-146a, miR-155, and miR-210 as potential markers of Graves’ disease. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2018, 32, e22266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, S.S.; Li, J.; Tao, S.S.; Wang, M.; Leng, R.X.; Pan, H.F.; Ye, D.Q. miR-210 expression in PBMCs from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 187, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Qiu, Y. MiR-210-5p regulates STAT3 activation by targeting STAT5A in the differentiation of dermal fibroblasts. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwaponanan, P.; Fucharoen, S.; Sirankapracha, P.; Winichagoon, P.; Umemura, T.; Svasti, S. Elevated levels of miR-210 correlate with anemia in β-thalassemia/HbE patients. Int. J. Hematol. 2016, 104, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardiman, J.W.; Thiele, J.; Arber, D.A.; Brunning, R.D.; Borowitz, M.J.; Porwit, A.; Harris, N.L.; Le Beau, M.M.; Hellström-Lindberg, E.; Tefferi, A. Does HbF induction by hydroxycarbamide work through MIR210 in sickle cell anaemia patients? Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 173, 801–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, H.; Karimi, E.; Shekari, M.; Tahmasebi, A.; Nikpoor, A.R.; Negahi, A.A.; Sanadgol, N.; Mousavi, P. Construction of a lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network to determine the key regulators of the Th1/Th2 imbalance in multiple sclerosis. Epigenomics 2021, 13, 1797–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Futami, M.; Carroll, M.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fernandez, M.; Whichard, Z.; Chen, Y.; Kornblau, S.; Shpall, E.J.; et al. Loss of SHIP-1 protein expression in high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes is associated with miR-210 and miR-155. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4085–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballegaard, V.; Ralfkiaer, U.; Pedersen, K.K.; Hove, M.; Koplev, S.; Brændstrup, P.; Ryder, L.P.; Madsen, H.O.; Gerstoft, J.; Grønbæk, K.; et al. MicroRNA-210, MicroRNA-331, and MicroRNA-7 Are Differentially Regulated in Treated HIV-1-Infected Individuals and Are Associated With Markers of Systemic Inflammation. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2017, 74, e104–e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Nasu, K.; Abe, W.; Aoyagi, Y.; Kawano, Y.; Kai, K.; Moriyama, M.; Narahara, H. Enhanced miR-210 expression promotes the pathogenesis of endometriosis through activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 30, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.C.; Gupta, A. MicroRNAs: Potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of different cancers. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 5798–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelista, A.F.; Oliveira, R.J.; VA, O.S.; RA, D.C.V.; Reis, R.M.; MM, C.M. Integrated analysis of mRNA and miRNA profiles revealed the role of miR-193 and miR-210 as potential regulatory biomarkers in different molecular subtypes of breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishita, A.; Fujita, K.; Iwama, H.; Chiyo, T.; Fujihara, S.; Oura, K.; Tadokoro, T.; Mimura, S.; Nomura, T.; Tani, J.; et al. Role of microRNA-210-3p in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 318, G401–G409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.; Yang, Q.; Dai, Y.; Guo, W.; Du, H.; Song, L.; Peng, X. Oncogenic miR-210-3p promotes prostate cancer cell EMT and bone metastasis via NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabry, D.; El-Deek, S.E.M.; Maher, M.; El-Baz, M.A.H.; El-Bader, H.M.; Amer, E.; Hassan, E.A.; Fathy, W.; El-Deek, H.E.M. Role of miRNA-210, miRNA-21 and miRNA-126 as diagnostic biomarkers in colorectal carcinoma: Impact of HIF-1α-VEGF signaling pathway. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2019, 454, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tian, W.; Meng, L.; Qu, L.; Shou, C. PRL-3 promotes gastric cancer migration and invasion through a NF-κB-HIF-1α-miR-210 axis. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 401–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrozza, V.; Costantini, M.; Tito, C.; Giammusso, L.M.; Sorrentino, V.; Cacciotti, J.; Porta, N.; Iaiza, A.; Pastore, A.L.; Di Carlo, A.; et al. Emerging role of secreted miR-210-3p as potential biomarker for clear cell Renal Cell Carcinoma metastasis. Cancer Biomark. 2020, 27, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Li, X.; Xie, K.P. Coupled liquid biopsy and bioinformatics for pancreatic cancer early detection and precision prognostication. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, H.; Sugano, K.; Fukayama, N.; Kyogoku, A.; Nose, H.; Shimada, K.; Ohkura, H.; Ohtsu, A.; Yoshida, S.; Shimosato, Y. Detection of point mutations in the K-ras oncogene at codon 12 in pure pancreatic juice for diagnosis of pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer 1994, 73, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Sadakari, Y.; Shindo, K.; Suenaga, M.; Brant, A.; Almario, J.A.N.; Borges, M.; Barkley, T.; Fesharakizadeh, S.; Ford, M.; et al. Digital next-generation sequencing identifies low-abundance mutations in pancreatic juice samples collected from the duodenum of patients with pancreatic cancer and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Gut 2017, 66, 1677–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Sadakari, Y.; Ohtsuka, T.; Okayama, T.; Nakashima, Y.; Gotoh, Y.; Saeki, K.; Mori, Y.; Nakata, K.; Miyasaka, Y.; et al. Pancreatic Juice Exosomal MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Detection of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| HIFs | Target | Pathways |
|---|---|---|
| HIF-1α | NOS3, MCT4, CA-IX, PFK, LDHA, LDHA, GLUT1/3, HMOX1, BNIP3, IGF2, IGF-BP1, IGF-BP3, c-Myc, VEGFA, GLUT1, EPO | p53, Angiogenesis, Adipogenesis, AP-1 transcription factor network, Survival, Proliferation |
| HIF-2α | VEGFA, GLUT1, EPO, MMP2, MMP13, OCT-3/4 | p53, Angiogenesis, Adipogenesis, AP-1 transcription factor network, Survival, HIF-1α transcription factor network |
| HIF-3α | Inhibits HIF-1α and HIF-2α | PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Hypoxic and oxygen homeostasis by HIF-1α |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lian, M.; Mortoglou, M.; Uysal-Onganer, P. Impact of Hypoxia-Induced miR-210 on Pancreatic Cancer. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 9778-9792. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45120611
Lian M, Mortoglou M, Uysal-Onganer P. Impact of Hypoxia-Induced miR-210 on Pancreatic Cancer. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2023; 45(12):9778-9792. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45120611
Chicago/Turabian StyleLian, Mutian, Maria Mortoglou, and Pinar Uysal-Onganer. 2023. "Impact of Hypoxia-Induced miR-210 on Pancreatic Cancer" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 45, no. 12: 9778-9792. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45120611
APA StyleLian, M., Mortoglou, M., & Uysal-Onganer, P. (2023). Impact of Hypoxia-Induced miR-210 on Pancreatic Cancer. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 45(12), 9778-9792. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45120611






