MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry of High-Grade Gliomas: A Review of Recent Progress and Future Perspective
Abstract
:1. Glioblastoma
1.1. Epidemiology
1.2. Risk Factors
1.3. Protective Factors
2. Metabolomics in Cancer Research
2.1. Mass Spectrometry
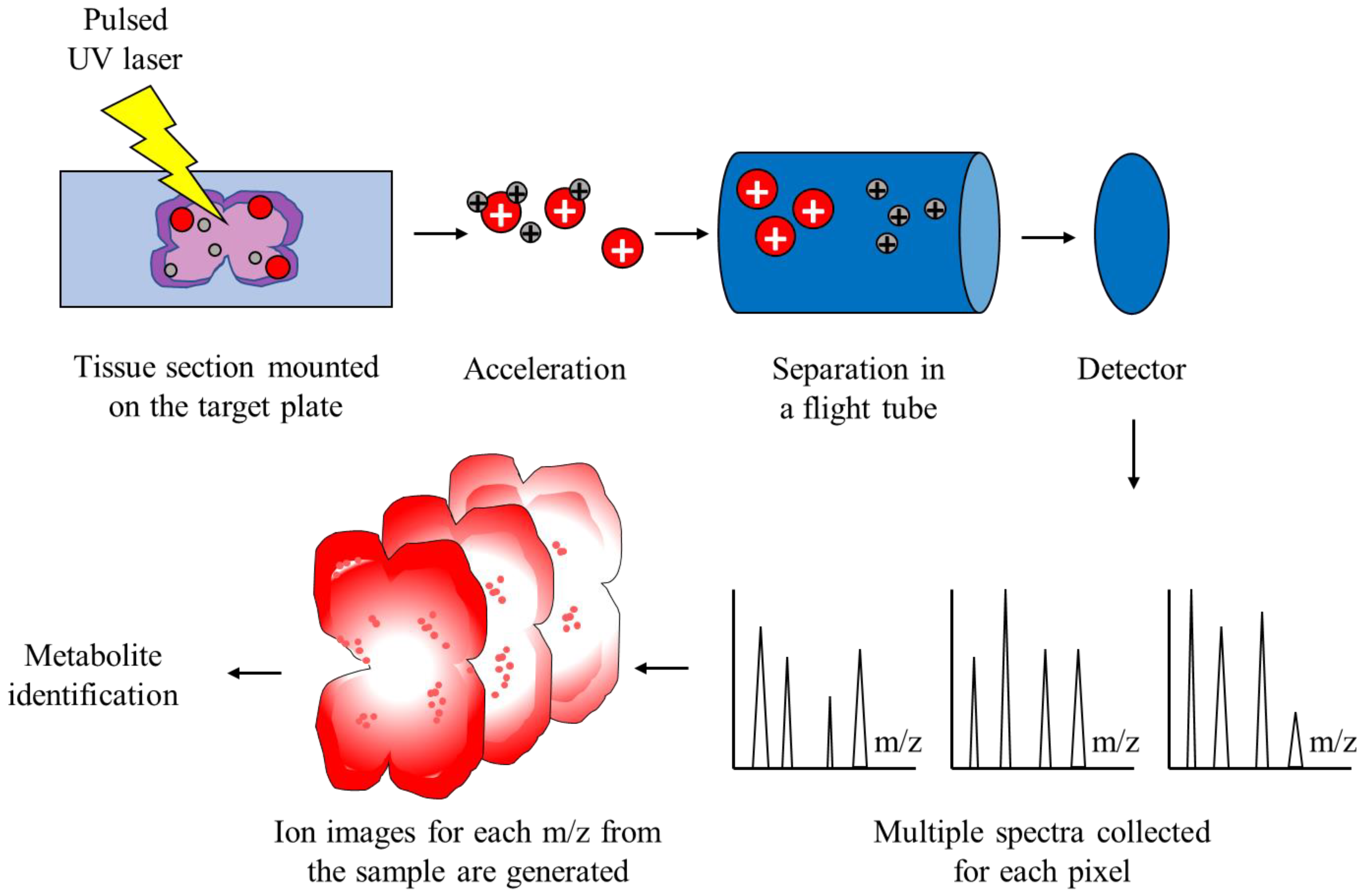
2.2. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry
2.3. MALDI-TOF MS in Cancer Research
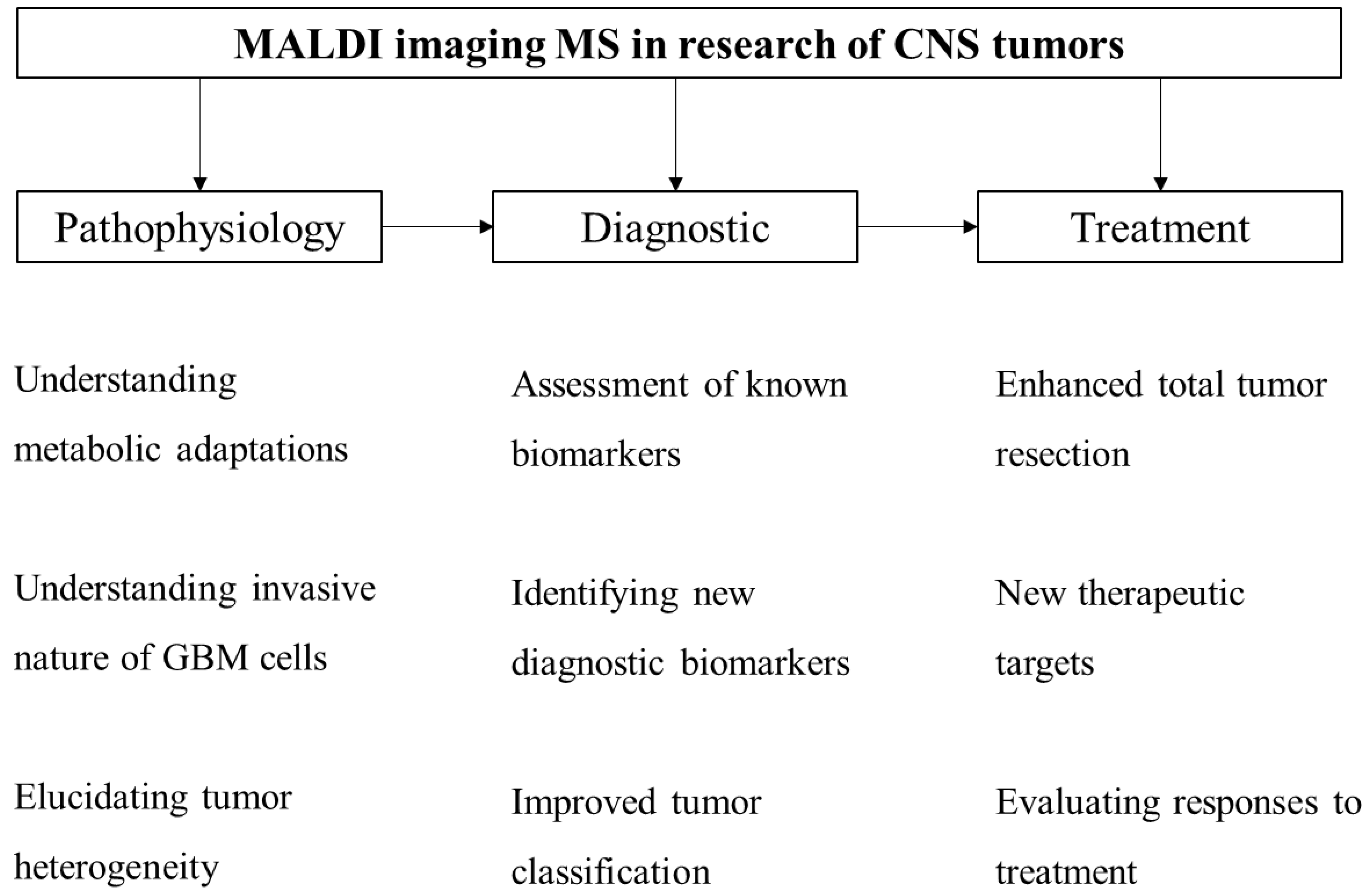
3. MALDI Imaging in CNS Tumor Research
4. Future Perspectives of MALDI-TOF IMS in GBM Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grochans, S.; Cybulska, A.M.; Simińska, D.; Korbecki, J.; Kojder, K.; Chlubek, D.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I. Epidemiology of Glioblastoma Multiforme–Literature Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witthayanuwat, S.; Pesee, M.; Supaadirek, C.; Supakalin, N.; Thamronganantasakul, K.; Krusun, S. Survival Analysis of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2018, 19, 2613–2617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tykocki, T.; Eltayeb, M. Ten-year survival in glioblastoma. A systematic review. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 54, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Fulop, J.; Liu, M.; Blanda, R.; Kromer, C.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2008–2012. Neuro-Oncol. 2015, 17 (Suppl. S4), iv1–iv62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, B.M.; Cloughesy, T.F. Adult Glioblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2402–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.; Costa, A.; Osório, L.; Lago, R.C.; Linhares, P.; Carvalho, B.; Caeiro, C. Current Standards of Care in Glioblastoma Therapy. In Glioblastoma; De Vleeschouwer, S., Ed.; Codon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Colapietro, A.; Yang, P.; Rossetti, A.; Mancini, A.; Vitale, F.; Chakraborty, S.; Martellucci, S.; Marampon, F.; Mattei, V.; Gravina, G.L.; et al. The Botanical Drug PBI-05204, a Supercritical CO2 Extract of Nerium Oleander, Is Synergistic With Radiotherapy in Models of Human Glioblastoma. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 852941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colapietro, A.; Rossetti, A.; Mancini, A.; Martellucci, S.; Ocone, G.; Pulcini, F.; Biordi, L.; Cristiano, L.; Mattei, V.; Delle Monache, S.; et al. Multiple Antitumor Molecular Mechanisms Are Activated by a Fully Synthetic and Stabilized Pharmaceutical Product Delivering the Active Compound Sulforaphane (SFX-01) in Preclinical Model of Human Glioblastoma. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravina, G.L.; Colapietro, A.; Mancini, A.; Rossetti, A.; Martellucci, S.; Ventura, L.; Di Franco, M.; Marampon, F.; Mattei, V.; Biordi, L.A.; et al. ATX-101, a Peptide Targeting PCNA, Has Antitumor Efficacy Alone or in Combination with Radiotherapy in Murine Models of Human Glioblastoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colapietro, A.; Yang, P.; Rossetti, A.; Mancini, A.; Vitale, F.; Martellucci, S.; Conway, T.L.; Chakraborty, S.; Marampon, F.; Mattei, V.; et al. The Botanical Drug PBI-05204, a Supercritical CO2 Extract of Nerium Oleander, Inhibits Growth of Human Glioblastoma, Reduces Akt/mTOR Activities, and Modulates GSC Cell-Renewal Properties. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 552428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Ladomersky, E.; Mozny, A.; Kocherginsky, M.; O’Shea, K.; Reinstein, Z.Z.; Zhai, L.; Bell, A.; Lauing, K.L.; Bollu, L.; et al. Glioblastoma as an age-related neurological disorder in adults. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakkar, J.P.; Dolecek, T.A.; Horbinski, C.; Ostrom, Q.T.; Lightner, D.D.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Villano, J.L. Epidemiologic and molecular prognostic review of glioblastoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 1985–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lah Turnšek, T.; Jiao, X.; Novak, M.; Jammula, S.; Cicero, G.; Ashton, A.W.; Joyce, D.; Pestell, R.G. An Update on Glioblastoma Biology, Genetics, and Current Therapies: Novel Inhibitors of the G Protein-Coupled Receptor CCR5. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, D.J.; Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Duncan, K.R.; CreveCoeur, T.S.; Kruchko, C.; Smith, T.R.; Stampfer, M.J.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. Glioma incidence and survival variations by county-level socioeconomic measures. Cancer 2019, 125, 3390–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, T.; Favereaux, A.; Huang, H.; Shimizu, T.; Yonekawa, Y.; Nakazato, Y.; Ohagki, H. Genetic alterations in primary glioblastomas in Japan. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 65, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, X.; Gong, X.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, W. Height and risk of colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 27, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Lv, G.; Chen, W.; Jiang, J.; Wang, J. Height and kidney cancer risk: A meta-analysis of prospective studies. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.C.; Rajaraman, P.; Dubrow, R.; Darefsky, A.S.; Koebnick, C.; Hollenbeck, A.; Schatzkin, A.; Leitzmann, M.F. Height, Body Mass Index, and Physical Activity in Relation to Glioma Risk. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8349–8355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phillips, L.M.; Zhou, X.; Cogdell, D.E.; Chua, C.Y.; Huisinga, A.; Hess, K.R.; Fuller, G.N.; Zhang, W. Glioma progression is mediated by an addiction to aberrant IGFBP2 expression and can be blocked using anti-IGFBP2 strategies. J. Pathol. 2016, 239, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, R.B.; Madden, M.H.; Thompson, R.C.; Olson, J.J.; LaRocca, R.V.; Pan, E.; Browning, J.E.; Egan, K.M.; Nabors, L.B. Anthropometric factors in relation to risk of glioma. Cancer Causes Control 2013, 24, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanif, F.; Muzaffar, K.; Perveen, K.; Malhi, S.M.; Simjee Sh, U. Glioblastoma Multiforme: A Review of its Epidemiology and Pathogenesis through Clinical Presentation and Treatment. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2017, 18, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bowers, D.C.; Nathan, P.C.; Constine, L.; Woodman, C.; Bhatia, S.; Keller, K.; Bashore, L. Subsequent neoplasms of the CNS among survivors of childhood cancer: A systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, e321–e328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fantuzzi, G. Adipose tissue, adipokines, and inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajetto, A.; Thellung, S.; Dellacasagrande, I.; Pagano, A.; Barbieri, F.; Florio, T. Cross talk between mesenchymal and glioblastoma stem cells: Communication beyond controversies. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2020, 9, 1310–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inskip, P.D.; Mellemkjaer, L.; Gridley, G.; Olsen, J.H. Incidence of intracranial tumors following hospitalization for head injuries (Denmark). Cancer Causes Control CCC 1998, 9, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Park, M.Y.; Kang, M.Y.; Shin, I.S.; An, S.; Kim, H.R. Occupational Lead Exposure and Brain Tumors: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaraman, P.; Stewart, P.A.; Samet, J.M.; Schwartz, B.S.; Linet, M.S.; Zahm, S.H.; Rothman, N.; Yeager, M.; Fine, H.A.; Black, P.; et al. Lead, genetic susceptibility, and risk of adult brain tumors. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 2514–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhatti, P.; Stewart, P.A.; Hutchinson, A.; Rothman, N.; Linet, M.S.; Inskip, P.D.; Rajaraman, P. Lead Exposure, Polymorphisms in Genes Related to Oxidative Stress, and Risk of Adult Brain Tumors. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2009, 18, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caffo, M.; Caruso, G.; Fata, G.L.; Barresi, V.; Visalli, M.; Venza, M.; Venza, I. Heavy metals and epigenetic alterations in brain tumors. Curr. Genom. 2014, 15, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowppli-Bony, A.; Bouvier, G.; Rué, M.; Loiseau, H.; Vital, A.; Lebailly, P.; Fabbro-Peray, P.; Baldi, I. Brain tumors and hormonal factors: Review of the epidemiological literature. Cancer Causes Control CCC 2011, 22, 697–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linos, E.; Raine, T.; Alonso, A.; Michaud, D. Atopy and risk of brain tumors: A meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Bauchet, L.; Davis, F.G.; Deltour, I.; Fisher, J.L.; Langer, C.E.; Pekmezci, M.; Schwartzbaum, J.A.; Turner, M.C.; Walsh, K.M. The epidemiology of glioma in adults: A “state of the science” review. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, 896–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheurer, M.E.; Amirian, E.S.; Davlin, S.L.; Rice, T.; Wrensch, M.; Bondy, M.L. Effects of antihistamine and anti-inflammatory medication use on risk of specific glioma histologies. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferris, J.S.; McCoy, L.; Neugut, A.I.; Wrensch, M.; Lai, R. HMG CoA reductase inhibitors, NSAIDs and risk of glioma. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, E1031–E1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Qiu, J.; Li, Q.; Shi, Z. Prostaglandin E2 Signaling: Alternative Target for Glioblastoma? Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seliger, C.; Schaertl, J.; Gerken, M.; Luber, C.; Proescholdt, M.; Riemenschneider, M.J.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Hau, P.; Klinkhammer-Schalke, M. Use of statins or NSAIDs and survival of patients with high-grade glioma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, S.E.; Moore, S.C.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Inskip, P.D.; Park, Y.; Hollenbeck, A.; Rajaraman, P. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and glioma in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study cohort. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rendon, L.F.; Tewarie, I.A.; Cote, D.J.; Gabriel, A.; Smith, T.R.; Broekman, M.L.D.; Mekary, R.A. Statins and Gliomas: A Systematic Review of the Preclinical Studies and Meta-Analysis of the Clinical Literature. Drugs 2022, 82, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cote, D.J.; Rosner, B.A.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Egan, K.M.; Stampfer, M.J. Statin use, hyperlipidemia, and risk of glioma. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 34, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlehofer, B.; Blettner, M.; Preston-Martin, S.; Niehoff, D.; Wahrendorf, J.; Arslan, A.; Ahlbom, A.; Choi, W.N.; Giles, G.G.; Howe, G.R.; et al. Role of medical history in brain tumour development. Results from the international adult brain tumour study. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 82, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, B.J.; Rankin, K.; Il’yasova, D.; Erdal, S.; Vick, N.; Ali-Osman, F.; Bigner, D.D.; Davis, F. Assessment of Type of Allergy and Antihistamine Use in the Development of Glioma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2011, 20, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheurer, M.E.; El-Zein, R.; Thompson, P.A.; Aldape, K.D.; Levin, V.A.; Gilbert, M.R.; Weinberg, J.S.; Bondy, M.L. Long-term anti-inflammatory and antihistamine medication use and adult glioma risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2008, 17, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glish, G.L.; Vachet, R.W. The basics of mass spectrometry in the twenty-first century. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, H.; Khamis, M.M.; El-Aneed, A. Mass Spectrometry, Review of the Basics: Ionization. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2015, 50, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xu, T.; Peng, C.; Wu, S. Advances in MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging Single Cell and Tissues. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 782432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, T.C.; Han, J.; Borchers, C.H. Recent advancements in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 43, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesl, U. Time-of-flight mass spectrometry: Introduction to the basics. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2017, 36, 86–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, V.; Piras, C.; Pieroni, L.; Ronci, M.; Putignani, L.; Roncada, P.; Urbani, A. Applications of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in clinical proteomics. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2018, 15, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegsmann, J.; Kriegsmann, M.; Casadonte, R. MALDI TOF imaging mass spectrometry in clinical pathology: A valuable tool for cancer diagnostics (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.; Phapale, P.; Chernyavsky, I.; Lavigne, R.; Fay, D.; Tarasov, A.; Kovalev, V.; Fuchser, J.; Nikolenko, S.; Pineau, C.; et al. FDR-controlled metabolite annotation for high-resolution imaging mass spectrometry. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Guo, A.; Oler, E.; Wang, F.; Anjum, A.; Peters, H.; Dizon, R.; Sayeeda, Z.; Tian, S.; Lee, B.L.; et al. HMDB 5.0: The Human Metabolome Database for 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D622–D631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahy, E.; Subramaniam, S.; Murphy, R.C.; Nishijima, M.; Raetz, C.R.; Shimizu, T.; Spener, F.; van Meer, G.; Wakelam, M.J.; Dennis, E.A. Update of the LIPID MAPS comprehensive classification system for lipids. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S9–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Idle, J.R.; Gonzalez, F.J. Metabolomics. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beger, R.D. A Review of Applications of Metabolomics in Cancer. Metabolites 2013, 3, 552–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, J.; Lv, J.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Y.; Qin, N.; Ma, H.; He, Y.Q.; Zhang, R.; Tan, W.; Fan, J.; et al. Identification of risk loci and a polygenic risk score for lung cancer: A large-scale prospective cohort study in Chinese populations. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirchia, S.M.; Faversani, A.; Rovina, D.; Russo, M.V.; Paganini, L.; Savi, F.; Augello, C.; Rosso, L.; Del Gobbo, A.; Tabano, S.; et al. Epigenetic effects of chromatin remodeling agents on organotypic cultures. Epigenomics 2016, 8, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonaparte, E.; Pesenti, C.; Fontana, L.; Falcone, R.; Paganini, L.; Marzorati, A.; Ferrero, S.; Nosotti, M.; Mendogni, P.; Bareggi, C.; et al. Molecular profiling of lung cancer specimens and liquid biopsies using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Diagn. Pathol. 2018, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegsmann, M.; Casadonte, R.; Kriegsmann, J.; Dienemann, H.; Schirmacher, P.; Hendrik Kobarg, J.; Schwamborn, K.; Stenzinger, A.; Warth, A.; Weichert, W.; et al. Reliable Entity Subtyping in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer by Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Imaging Mass Spectrometry on Formalin-fixed Paraffin-embedded Tissue Specimens. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2016, 15, 3081–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambonin, C. MALDI-TOF/MS Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles Released by Cancer Cells. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, M.Y.; Choi, D.-Y.; Lee, J.W.; You, S.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.P. Phospholipids of tumor extracellular vesicles stratify gefitinib-resistant nonsmall cell lung cancer cells from gefitinib-sensitive cells. Proteomics 2015, 15, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, E.-S.; Faruque, H.A.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, K.J.; Choi, J.E.; Kim, B.A.; Kim, B.; Kim, Y.J.; Woo, M.H.; Park, J.Y.; et al. CD5L as an Extracellular Vesicle-Derived Biomarker for Liquid Biopsy of Lung Cancer. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harvey, P.; Basuita, A.; Endersby, D.; Curtis, B.; Iacovidou, A.; Walker, M. A systematic review of the diagnostic accuracy of prostate specific antigen. BMC Urol. 2009, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buszewska-Forajta, M.; Pomastowski, P.; Monedeiro, F.; Król-Górniak, A.; Adamczyk, P.; Markuszewski, M.J.; Buszewski, B. New approach in determination of urinary diagnostic markers for prostate cancer by MALDI-TOF/MS. Talanta 2022, 236, 122843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Nakayama, K.; Goto, T.; Kimura, H.; Akamatsu, S.; Hayashi, Y.; Fujita, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Shimizu, K.; Nonomura, N.; et al. High level of phosphatidylcholines/lysophosphatidylcholine ratio in urine is associated with prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 4292–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.K.; Høiem, T.S.; Claes, B.S.R.; Balluff, B.; Martin-Lorenzo, M.; Richardsen, E.; Krossa, S.; Bertilsson, H.; Heeren, R.M.A.; Rye, M.B.; et al. Spatial differentiation of metabolism in prostate cancer tissue by MALDI-TOF MSI. Cancer Metab. 2021, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momenimovahed, Z.; Salehiniya, H. Epidemiological characteristics of and risk factors for breast cancer in the world. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2019, 11, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iorgulescu, J.B.; Torre, M.; Harary, M.; Smith, T.R.; Aizer, A.A.; Reardon, D.A.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Perry, A. The Misclassification of Diffuse Gliomas: Rates and Outcomes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2656–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loibl, S.; Gianni, L. HER2-positive breast cancer. Lancet 2017, 389, 2415–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauser, S.; Marquardt, C.; Balluff, B.; Deininger, S.O.; Albers, C.; Belau, E.; Hartmer, R.; Suckau, D.; Specht, K.; Ebert, M.P.; et al. Classification of HER2 receptor status in breast cancer tissues by MALDI imaging mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 1854–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meding, S.; Nitsche, U.; Balluff, B.; Elsner, M.; Rauser, S.; Schöne, C.; Nipp, M.; Maak, M.; Feith, M.; Ebert, M.P.; et al. Tumor classification of six common cancer types based on proteomic profiling by MALDI imaging. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 1996–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.Y.; Yeoh, Y.; Omar, N.; Pung, Y.-F.; Lim, L.C.; Low, T.Y. Molecular tissue profiling by MALDI imaging: Recent progress and applications in cancer research. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2021, 58, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, A.; Halbritter, S.; Späth, C.; Feuchtinger, A.; Aichler, M.; Zitzelsberger, H.; Janssen, K.P.; Walch, A. Distribution and quantification of irinotecan and its active metabolite SN-38 in colon cancer murine model systems using MALDI MSI. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 2107–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLendon, R.E.; Rich, J.N. Glioblastoma Stem Cells: A Neuropathologist’s View. J. Oncol. 2011, 2011, 397195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kufe, D.W.; Holland, J.F.; Frei, E. Cancer Medicine 6; BC Decker: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ait-Belkacem, R.; Berenguer, C.; Villard, C.; Ouafik, L.H.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Chinot, O.; Lafitte, D. MALDI imaging and in-source decay for top-down characterization of glioblastoma. Proteomics 2014, 14, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, I.; Delle Monache, S.; Di Francesco, M.; Sanità, P.; D’Ascenzo, S.; Gravina, G.L.; Festuccia, C.; Dolo, V. From glioblastoma to endothelial cells through extracellular vesicles: Messages for angiogenesis. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 12743–12753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunsford, L.D.; Martinez, A.J.; Latchaw, R.E. Magnetic resonance imaging does not define tumor boundaries. Acta Radiol. Suppl. 1986, 369, 154–156. [Google Scholar]
- Calligaris, D.; Norton, I.; Feldman, D.R.; Ide, J.L.; Dunn, I.F.; Eberlin, L.S.; Cooks, R.G.; Jolesz, F.A.; Golby, A.J.; Santagata, S.; et al. Mass spectrometry imaging as a tool for surgical decision-making. J. Mass Spectrom. JMS 2013, 48, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morato, N.M.; Brown, H.M.; Garcia, D.; Middlebrooks, E.H.; Jentoft, M.; Chaichana, K.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A.; Cooks, R.G. High-throughput analysis of tissue microarrays using automated desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccirillo, S.G.M.; Vescovi, A.L. Brain tumour stem cells: Possibilities of new therapeutic strategies. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2007, 7, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattei, V.; Santilli, F.; Martellucci, S.; Delle Monache, S.; Fabrizi, J.; Colapietro, A.; Angelucci, A.; Festuccia, C. The Importance of Tumor Stem Cells in Glioblastoma Resistance to Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montano, N.; D’Alessandris, Q.G.; Izzo, A.; Fernandez, E.; Pallini, R. Biomarkers for glioblastoma multiforme: Status quo. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2016, 2, 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Heimberger, A.B.; Lu, Z.; Wu, X.; Hodges, T.R.; Song, R.; Shen, J. Metabolomics profiling in plasma samples from glioma patients correlates with tumor phenotypes. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20486–20495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ravi, V.M.; Will, P.; Kueckelhaus, J.; Sun, N.; Joseph, K.; Salié, H.; Vollmer, L.; Kuliesiute, U.; von Ehr, J.; Benotmane, J.K.; et al. Spatially resolved multi-omics deciphers bidirectional tumor-host interdependence in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 639–655.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie, S.K.; Shinjo, S.M. Metabolism and brain cancer. Clinics 2011, 66 (Suppl. S1), 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dilillo, M.; Ait-Belkacem, R.; Esteve, C.; Pellegrini, D.; Nicolardi, S.; Costa, M.; Vannini, E.; Graaf, E.L.; Caleo, M.; McDonnell, L.A. Ultra-High Mass Resolution MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry of Proteins and Metabolites in a Mouse Model of Glioblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warburg, O. The Metabolism of Carcinoma Cells1. J. Cancer Res. 1925, 9, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kucharzewska, P.; Christianson, H.C.; Belting, M. Global profiling of metabolic adaptation to hypoxic stress in human glioblastoma cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Lin, J.-M.; Lin, Z.; Li, H.-F. Investigation of the lipidomic changes in differentiated glioblastoma cells after drug treatment using MALDI-MS. Talanta 2021, 233, 122570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimó-Barceló, A.; Martín-Saiz, L.; Fernández, J.A.; Pérez-Romero, K.; Garfias-Arjona, S.; Lara-Almúnia, M.; Piérola-Lopetegui, J.; Bestard-Escalas, J.; Barceló-Coblijn, G. Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid-Enriched Lipid Fingerprint of Glioblastoma Proliferative Regions Is Differentially Regulated According to Glioblastoma Molecular Subtype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Mao, S.; He, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Lin, J.-M.; Lin, Z.-X. Proteomic Distributions in CD34+ Microvascular Niche Patterns of Glioblastoma. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2022, 70, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koruga, N.; Soldo Koruga, A.; Rončević, R.; Turk, T.; Kopačin, V.; Kretić, D.; Rotim, T.; Rončević, A. Telemedicine in Neurosurgical Trauma during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Single-Center Experience. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petre, G.; Durand, H.; Pelletier, L.; Poulenard, M.; Nugue, G.; Ray, P.F.; Rendu, J.; Coutton, C.; Berger, F.; Bidart, M. Rapid Proteomic Profiling by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry for Better Brain Tumor Classification. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2020, 14, 1900116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimura, Y.; Miura, D. MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging for Visualizing In Situ Metabolism of Endogenous Metabolites and Dietary Phytochemicals. Metabolites 2014, 4, 319–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexandrov, T. MALDI imaging mass spectrometry: Statistical data analysis and current computational challenges. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13 (Suppl. S16), S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ovchinnikova, K.; Kovalev, V.; Stuart, L.; Alexandrov, T. OffsampleAI: Artificial intelligence approach to recognize off-sample mass spectrometry images. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seeley, E.H.; Caprioli, R.M. 3D imaging by mass spectrometry: A new frontier. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryabchykov, O.; Popp, J.; Bocklitz, T. Fusion of MALDI Spectrometric Imaging and Raman Spectroscopic Data for the Analysis of Biological Samples. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Adult-type diffuse gliomas |
| Astrocytoma, IDH-mutant |
| Oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant and 1p/19q-codeleted |
| Glioblastoma, IDH-wildtype |
| Pediatric-type diffuse high-grade gliomas |
| Diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27-altered |
| Diffuse hemispheric glioma, H3 G34-mutant |
| Diffuse pediatric-type high-grade glioma, H3-wildtype and IDH-wildtype |
| Infant-type hemispheric glioma |
| Non-Modifiable Risk Factors | Modifiable Risk Factors | Protective Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Exposure to ionizing radiation | Female sex hormones |
| High socioeconomic status | Weight | History of allergies |
| Ethnicity and race | Head trauma | Medications: NSAIDs Statins Antihistamines |
| Tall stature | Exposure to metals (lead) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rončević, A.; Koruga, N.; Soldo Koruga, A.; Debeljak, Ž.; Rončević, R.; Turk, T.; Kretić, D.; Rotim, T.; Krivdić Dupan, Z.; Troha, D.; et al. MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry of High-Grade Gliomas: A Review of Recent Progress and Future Perspective. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 838-851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45020055
Rončević A, Koruga N, Soldo Koruga A, Debeljak Ž, Rončević R, Turk T, Kretić D, Rotim T, Krivdić Dupan Z, Troha D, et al. MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry of High-Grade Gliomas: A Review of Recent Progress and Future Perspective. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2023; 45(2):838-851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45020055
Chicago/Turabian StyleRončević, Alen, Nenad Koruga, Anamarija Soldo Koruga, Željko Debeljak, Robert Rončević, Tajana Turk, Domagoj Kretić, Tatjana Rotim, Zdravka Krivdić Dupan, Damir Troha, and et al. 2023. "MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry of High-Grade Gliomas: A Review of Recent Progress and Future Perspective" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 45, no. 2: 838-851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45020055
APA StyleRončević, A., Koruga, N., Soldo Koruga, A., Debeljak, Ž., Rončević, R., Turk, T., Kretić, D., Rotim, T., Krivdić Dupan, Z., Troha, D., Perić, M., & Šimundić, T. (2023). MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry of High-Grade Gliomas: A Review of Recent Progress and Future Perspective. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 45(2), 838-851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45020055





