Regeneration of Pancreatic Beta Cells by Modulation of Molecular Targets Using Plant-Derived Compounds: Pharmacological Mechanisms and Clinical Potential
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Phytotherapy and Regeneration of Pancreatic Beta Cells
3. Extracellular Signaling Pathways That Mediate Phytochemical Induced Beta-Cell Regeneration
3.1. PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
3.2. Transforming Growth Factor β Pathway
3.3. GLP-1 Signaling and Beta-Cell Regeneration
3.4. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Beta-Cell Regeneration
3.5. JAK2/STAT3 Signaling in Beta-Cell Regeneration
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives: Potential of Phytochemicals as Mediators of Beta-Cell Regeneration
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whiting, D.R.; Guariguata, L.; Weil, C.; Shaw, J. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global Estimates of the Prevalence of Diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 94, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogurtsova, K.; Da, J.D.; Fernandes, R.; Huang, Y.; Linnenkamp, U.; Guariguata, L.; Cho, N.H.; Cavan, D.; Shaw, J.E.; Makaroff, L.E. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global Estimates for the Prevalence of Diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 128, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and Regional Diabetes Prevalence Estimates for 2019 and Projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinclair, A.; Saeedi, P.; Kaundal, A.; Karuranga, S.; Malanda, B.; Williams, R. Diabetes and Global Ageing among 65–99-Year-Old Adults: Findings from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 162, 108078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saeedi, P.; Salpea, P.; Karuranga, S.; Petersohn, I.; Malanda, B.; Gregg, E.W.; Unwin, N.; Wild, S.H.; Williams, R. Mortality Attributable to Diabetes in 20–79 Years Old Adults, 2019 Estimates: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 2017, 108086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aronoff, S.L.; Berkowitz, K.; Shreiner, B.; Want, L. Glucose Metabolism and Regulation: Beyond Insulin and Glucagon. Diabetes Spectr. 2004, 17, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krentz, A.J.; Bailey, C.J. Oral Antidiabetic Agents: Current Role in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Drugs 2005, 65, 385–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwak, L.; Goh, S.-Y.; Hussein, Z.; Malek, R.; Prusty, V.; Khamseh, M.E. Prevalence of Diabetes Complications in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Association with Baseline Characteristics in the Multinational A 1 Chieve Study. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2013, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chala, T.S.; Ali, G.Y. Recent Advance in Diabetes Therapy: Pancreatic Beta Cell Regeneration Approaches. Diabetes Manag. 2016, 6, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez-Bendala, J.; Inverardi, L.; Ricordi, C. Regeneration of Pancreatic Beta-Cell Mass for the Treatment of Diabetes. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2012, 12, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguayo-Mazzucato, C.; Bonner-Weir, S. Pancreatic β Cell Regeneration as a Possible Therapy for Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseini, A.; Shafiee-Nick, R.; Ghorbani, A. Pancreatic Beta Cell Protection/Regeneration with Phytotherapy. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 51, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, H.; Cheng, R.; Yuan, R.; Zhu, X.; Ao, P. Systems Biology Theory Clarification of a Controversy in Pancreatic Beta Cell Regeneration. bioRxiv 2018, 469320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Jiang, Y. Endogenous Pancreatic β Cell Regeneration: A Potential Strategy for the Recovery of β Cell Deficiency in Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, M.; Kanitkar, M.; Bhonde, R.R. Approaches Towards Endogenous Pancreatic Regeneration. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2005, 2, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dor, Y.; Brown, J.; Martinez, O.I.; Melton, D.A. Adult Pancreatic β-Cells Are Formed by Self-Duplication Rather than Stem-Cell Differentiation. Nature 2004, 429, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bentz, J.; O’Connor, M.P.; Bednarczyk, D.; Coleman, J.; Lee, C.; Palm, J.; Pak, Y.A.; Perloff, E.S.; Reyner, E.; Balimane, P.; et al. Variability in P-Glycoprotein Inhibitory Potency (IC 50) Using Various in Vitro Experimental Systems: Implications for Universal Digoxin Drug-Drug Interaction Risk Assessment Decision Criteria. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2013, 41, 1347–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Fiaschi-Taesch, N.M.; Vasavada, R.C.; Scott, D.K.; García-Ocaña, A.; Stewart, A.F. Diabetes Mellitus—Advances and Challenges in Human β-Cell Proliferation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.; Butler, A.; Saisho, Y.; Monchamp, T.; Galasso, R.; Bhushan, A.; Rizza, R.A.; Butler, P.C. β-Cell Replication Is the Primary Mechanism Subserving the Postnatal Expansion of β-Cell Mass in Humans. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1584–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peshavaria, M.; Larmie, B.L.; Lausier, J.; Satish, B.; Habibovic, A.; Roskens, V.; LaRock, K.; Everill, B.; Leahy, J.L.; Jetton, T.L. Regulation of Pancreatic β-Cell Regeneration in the Normoglycemic 60% Partial-Pancreatectomy Mouse. Diabetes 2006, 55, 3289–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rieck, S.; Kaestner, K.H. Expansion of β-Cell Mass in Response to Pregnancy. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 21, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chien, H.-Y.; Bonner-Weir, S. Pancreatic Regeneration After Partial Pancreatectomy in Rodents. In Pancreatic Islet Biology, Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine; Hardikar, A.A., Ed.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwens, L.; Rooman, I. Regulation of Pancreatic Beta-Cell Mass. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 1255–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cinti, F.; Bouchi, R.; Kim-Muller, J.Y.; Ohmura, Y.; Sandoval, P.R.; Masini, M.; Marselli, L.; Suleiman, M.; Ratner, L.E.; Marchetti, P.; et al. Evidence of β-Cell Dedifferentiation in Human Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, S. Molecular Basis of Insulin Resistance: The Role of IRS and Foxo1 in the Control of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2013, 10, e27–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hunter, C.S.; Stein, R.W. Evidence for Loss in Identity, De-Differentiation, and Trans-Differentiation of Islet β-Cells in Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, C.; Li, F.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, P.; Bu, L.; Sheng, H.; Li, H.; Qu, S. Reversibility of β-Cell-Specific Transcript Factors Expression by Long-Term Caloric Restriction in Db/Db Mouse. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 6035046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Dai, C.; Guo, M.; Taylor, B.; Harmon, J.S.; Sander, M.; Robertson, R.P.; Powers, A.C.; Stein, R. Inactivation of Specific β Cell Transcription Factors in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3305–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gribben, C.; Lambert, C.; Messal, H.A.; Hubber, E.L.; Rackham, C.; Evans, I.; Heimberg, H.; Jones, P.; Sancho, R.; Behrens, A. Ductal Ngn3-Expressing Progenitors Contribute to Adult β Cell Neogenesis in the Pancreas. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 2000–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.E.; Cao-Minh, L.; R. Galasso; Rizza, R.A.; Corradin, A.; Cobelli, C.; Butler, P.C. Adaptive Changes in Pancreatic Beta Cell Fractional Area and Beta Cell Turnover in Human Pregnancy. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 2167–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mezza, T.; Muscogiuri, G.; Sorice, G.P.; Clemente, G.; Hu, J.; Pontecorvi, A.; Holst, J.J.; Giaccari, A.; Kulkarni, R.N. Insulin Resistance Alters Islet Morphology in Nondiabetic Humans. Diabetes 2014, 63, 994–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoneda, S.; Uno, S.; Iwahashi, H.; Fujita, Y.; Yoshikawa, A.; Kozawa, J.; Okita, K.; Takiuchi, D.; Eguchi, H.; Nagano, H.; et al. Predominance of β-Cell Neogenesis Rather than Replication in Humans with an Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Newly Diagnosed Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qadir, M.M.F.; Álvarez-Cubela, S.; Klein, D.; van Dijk, J.; Muñiz-Anquela, R.; Moreno-Hernández, Y.B.; Lanzoni, G.; Sadiq, S.; Navarro-Rubio, B.; García, M.T.; et al. Single-Cell Resolution Analysis of the Human Pancreatic Ductal Progenitor Cell Niche. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 10876–10887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huising, M.O.; Lee, S.; van der Meulen, T. Evidence for a Neogenic Niche at the Periphery of Pancreatic Islets. BioEssays 2018, 40, e1800119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Bai, L.; Pan, H.; Feng, H.; Clevers, H.; Zeng, Y.A. Long-Term Expansion of Pancreatic Islet Organoids from Resident Procr+ Progenitors. Cell 2020, 180, 1198–1211.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Jimenez-Gonzalez, M.; Song, W.-J.; Hussain, M.A. The Undoing and Redoing of the Diabetic β-Cell. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2017, 31, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brereton, M.F.; Iberl, M.; Shimomura, K.; Zhang, Q.; Adriaenssens, A.E.; Proks, P.; Spiliotis, I.I.; Dace, W.; Mattis, K.K.; Ramracheya, R.; et al. Reversible Changes in Pancreatic Islet Structure and Function Produced by Elevated Blood Glucose. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; York, N.W.; Nichols, C.G.; Remedi, M.S. Pancreatic β Cell Dedifferentiation in Diabetes and Redifferentiation Following Insulin Therapy. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agwaya, M.; Nandutu, A.; Vuzi, P. Protective Effects of Zanthoxylum Chalybeum in Diabetes-Induced Myocardial Dysfunction in Rats. Eur. J. Med. Plants 2016, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, E.; Akter, K.-M.; Lee, G.-H.; Lee, H.-Y.; Rashid, H.-O.; Choi, M.-K.; Bhattarai, K.R.; Hossain, M.M.M.; Ara, J.; Mazumder, K.; et al. β-Cell Protection and Antidiabetic Activities of Crassocephalum crepidioides (Asteraceae) Benth. S. Moore Extract against Alloxan-Induced Oxidative Stress via Regulation of Apoptosis and Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS). BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramadan, B.K.; Schaalan, M.F.; Tolba, A.M. Hypoglycemic and Pancreatic Protective Effects of Portulaca Oleracea Extract in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soto, C.; Mena, R.; Luna, J.; Cerbón, M.; Larrieta, E.; Vital, P.; Uría, E.; Sánchez, M.; Recoba, R.; Barrón, H.; et al. Silymarin Induces Recovery of Pancreatic Function after Alloxan Damage in Rats. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 2167–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Aziz, M.T.; El-Asmar, M.F.; Rezq, A.M.; Mahfouz, S.M.; Wassef, M.A.; Fouad, H.H.; Ahmed, H.H.; Taha, F.M. The Effect of a Novel Curcumin Derivative on Pancreatic Islet Regeneration in Experimental Type-1 Diabetes in Rats (Long Term Study). Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2013, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajalakshmi, M.; Anita, R. β-Cell Regenerative Efficacy of a Polysaccharide Isolated from Methanolic Extract of Tinospora cordifolia Stem on Streptozotocin -Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 243, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjbari, A.; Azarbayjani, M.A.; Yusof, A.; Mokhtar, A.H.; Akbarzadeh, S.; Ibrahim, M.Y.; Tarverdizadeh, B.; Farzadinia, P.; Hajiaghaee, R.; Dehghan, F. In Vivo and in Vitro Evaluation of the Effects of Urtica Dioica and Swimming Activity on Diabetic Factors and Pancreatic Beta Cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saleh, F.A.; El-Darra, N.; Raafat, K. Hypoglycemic Effects of Prunus cerasus L. Pulp and Seed Extracts on Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Mice with Histopathological Evaluation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadheech, N.; Srivastava, A.; Paranjape, N.; Gupta, S.; Dave, A.; Shah, G.M.; Bhonde, R.R.; Gupta, S. Swertisin an Anti-Diabetic Compound Facilitate Islet Neogenesis from Pancreatic Stem/Progenitor Cells via p-38 MAP Kinase-SMAD Pathway: An In-Vitro and In-Vivo Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mathijs, I.; Da Cunha, D.A.; Himpe, E.; Ladriere, L.; Chellan, N.; Roux, C.R.; Joubert, E.; Muller, C.; Cnop, M.; Louw, J.; et al. Phenylpropenoic Acid Glucoside Augments Pancreatic Beta Cell Mass in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice and Protects Beta Cells from ER Stress-Induced Apoptosis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1980–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.S. Plant-Derived Compounds Targeting Pancreatic Beta Cells for the Treatment of Diabetes. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 629863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghorbani, A.; Rashidi, R.; Shafiee-Nick, R. Flavonoids for Preserving Pancreatic Beta Cell Survival and Function: A Mechanistic Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliaee, D.; Niazkar, H.R.; Abbasnezhad, A.; Ghorbani, M.; Alavi Shahri, P.S.; Saghaee Shahri, S.; Ghanaiyan, K. The Effects of Medicinal Plants on Pancreatic Beta Cells in Diabetes: A Systematic Review of Iranians’ Contributions. Rev. Clin. Med. 2020, 7, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaya, M.K.; Kuo, T.F.; Yang, M.T.; Yang, G.; Hsiao, C.L.; Chang, S.-B.; Lin, Y.; Yang, W.C. Phytochemicals as Modulators of β-Cells and Immunity for the Therapy of Type 1 Diabetes: Recent Discoveries in Pharmacological Mechanisms and Clinical Potential. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 156, 104754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attanayake, A.P.; Jayatilaka, K.A.P.W.; Mudduwa, L.K.B.; Pathirana, C. β-Cell Regenerative Potential of Selected Herbal Extracts in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2018, 16, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Rao, J.M. Diabetes Mellitus and Multiple Therapeutic Approaches of Phytochemicals: Present Status and Future Prospects. Curr. Sci. 2002, 83, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Qi, P.; Bao, J. Agaricus Bisporus Lectins Mediates Islet β-Cell Proliferation through Regulation of Cell Cycle Proteins. Exp. Biol. Med. 2012, 237, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, F.; Tian, W.; Lai, J.; Qian, L.; Hong, W.; Chen, H.; Li, L. Andrographolide Promotes Pancreatic Duct Cells Differentiation into Insulin-Producing Cells by Targeting PDX-1. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 174, 113785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Duan, J.; Chu, J.; Guo, C.; Xi, M.; Li, Y.; Weng, Y.; Wei, G.; Yin, Y.; Wen, A.; et al. Chikusetsu Saponin IVa Protects Pancreatic β Cell against Intermittent High Glucose-Induced Injury by Activating Wnt/β-Catenin/TCF7L2 Pathway. Aging 2020, 12, 1591–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, K.; Hiroki, A.; Kawakami, M.; Naka, H.; Takei, I.; Ogata, T.; Kojima, I.; Koyano, T.; Kowithayakorn, T.; Pang, H.S.; et al. Induction of Insulin Production in Rat Pancreatic Acinar Carcinoma Cells by Conophylline. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2003, 57, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, T.; Li, L.; Yamada, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Takei, I.; Umezawa, K.; Kojima, I. Promotion of Beta-Cell Differentiation by Conophylline in Fetal and Neonatal Rat Pancreas. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2596–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawakami, M.; Hirayama, A.; Tsuchiya, K.; Ohgawara, H.; Nakamura, M.; Umezawa, K. Promotion of β-Cell Differentiation by the Alkaloid Conophylline in Porcine Pancreatic Endocrine Cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2010, 64, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodera, T.; Yamada, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hara, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Seno, M.; Umezawa, K.; Takei, I.; Kojima, I. Administration of Conophylline and Betacellulin-Delta4 Increases the Beta-Cell Mass in Neonatal Streptozotocin-Treated Rats. Endocr. J. 2009, 56, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortsäter, H.; Grankvist, N.; Wolfram, S.; Kuehn, N.; Sjöholm, Å. Diet Supplementation with Green Tea Extract Epigallocatechin Gallate Prevents Progression to Glucose Intolerance in Db/Db Mice. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Choi, J.; Zhao, C.; Ma, Z.A. FTY720 Normalizes Hyperglycemia by Stimulating β-Cell in Vivo Regeneration in Db/Db Mice through Regulation of Cyclin D3 and P57 KIP2. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 5562–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, D.D.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wei, Y.J.; Jia, X.B.; Yin, W.; Shu, L. Geniposide Promotes Beta-Cell Regeneration and Survival through Regulating β-Catenin/TCF7L2 Pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhen, W.; Lum, H.; Nadler, J.; Bassaganya-Riera, J.; Jia, Z.; Wang, Y.; Misra, H.; Liu, D. Genistein Induces Pancreatic β-Cell Proliferation through Activation of Multiple Signaling Pathways and Prevents Insulin-Deficient Diabetes in Mice. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3026–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Ji, H.S.; Kang, J.H.; Shin, D.H.; Park, H.Y.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, I.K.; Yun, B.S.; Jeong, T.S. Soy Leaf Extract Containing Kaempferol Glycosides and Pheophorbides Improves Glucose Homeostasis by Enhancing Pancreatic β-Cell Function and Suppressing Hepatic Lipid Accumulation in Db/Db Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7198–7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, H.; Usami, A.; Shirai, R.; Harada, N.; Ikushiro, S.; Sakaki, T.; Nakano, Y.; Inui, H.; Yamaji, R. S-Equol Activates CAMP Signaling at the Plasma Membrane of INS-1 Pancreatic β-Cells and Protects against Streptozotocin-Induced Hyperglycemia by Increasing β-Cell Function in Male Mice. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, jn250860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, U.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Li, H.; Kang, J.H.; Ji, H.S.; Park, K.H.; Shin, D.H.; Park, H.Y.; Jeong, T.S. Pterocarpan-Enriched Soy Leaf Extract Ameliorates Insulin Sensitivity and Pancreatic β-Cell Proliferation in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Molecules 2014, 19, 18493–18510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Qi, P.; Bao, J. Antihyperglycemic Effect of Ginsenoside Rh2 by Inducing Islet β-Cell Regeneration in Mice. Horm. Metab. Res. 2012, 44, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Hong, S.M.; Sung, S.R.; Lee, J.E.; Kwon, D.Y. Extracts of Rehmanniae Radix, Ginseng Radix and Scutellariae Radix Improve Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion and β-Cell Proliferation through IRS2 Induction. Genes Nutr. 2008, 2, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, E.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, S.U.; Choi, J.E.; Cha, J.Y.; Jun, H.S. Increase in Insulin Secretion Induced by Panax Ginseng Berry Extracts Contributes to the Amelioration of Hyperglycemia in Streptozotocininduced Diabetic Mice. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kannan, P.; Raghunathan, M.; Mohan, T.; Palanivelu, S.; Periandavan, K. Gymnemic Acid Ameliorates Pancreatic β-Cell Dysfunction by Modulating Pdx1 Expression: A Possible Strategy for β-Cell Regeneration. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2022, 19, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, L.; Wen, X.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y.; Peng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Feng, L.; Shu, L. Salidroside, a Natural Antioxidant, Improves β-Cell Survival and Function via Activating AMPK Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dadheech, N.; Soni, S.; Srivastava, A.; Dadheech, S.; Gupta, S.; Gopurappilly, R.; Bhonde, R.R.; Gupta, S. A Small Molecule Swertisin from Enicostemma Littorale Differentiates NIH3T3 Cells into Islet-like Clusters and Restores Normoglycemia upon Transplantation in Diabetic Balb/c Mice. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 280392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, A.; Dadheech, N.; Vakani, M.; Gupta, S. Swertisin Ameliorates Diabetes by Triggering Pancreatic Progenitors for Islet Neogenesis in Streptozotocin Treated BALB/c Mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 100, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, X.; Lei, T.; Liu, Y.; Huai, G.; Sun, M.; Deng, S.; Yang, H.; Tong, R.; Wang, Y. Mangiferin Induces Islet Regeneration in Aged Mice through Regulating P16INK4a. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 3231–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.L.; Li, C.Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.D.; Lu, B.M.; Shi, Z.; An, N.; Zhao, L.K.; Zhang, J.J.; Bao, J.K.; et al. Mangiferin Facilitates Islet Regeneration and β-Cell Proliferation through Upregulation of Cell Cycle and β-Cell Regeneration Regulators. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 9016–9035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ansarullah; Bharucha, B.; Umarani, M.; Dwivedi, M.; Laddha, N.C.; Begum, R.; Hardikar, A.A.; Ramachandran, A.V. Oreocnide Integrifolia Flavonoids Augment Reprogramming for Islet Neogenesis and β-Cell Regeneration in Pancreatectomized BALB/c Mice. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Yao, D.; Yang, H.; Wei, Y.; Peng, Y.; Ding, Y.; Shu, L. Puerarin Protects Pancreatic β-Cells in Obese Diabetic Mice via Activation of GLP-1R Signaling. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 30, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobori, M.; Masumoto, S.; Akimoto, Y.; Takahashi, Y. Dietary Quercetin Alleviates Diabetic Symptoms and Reduces Streptozotocin-Induced Disturbance of Hepatic Gene Expression in Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Sajadimajd, S.; Mahdian, Z.; Hemmati, M.; Malekkhatabi, P.; Bahrami, G.; Mohammadi, B.; Miraghaee, S.; Hatami, R.; Mansouri, K.; et al. Characterization and Anti-Diabetic Effects of the Oligosaccharide Fraction Isolated from Rosa Canina in STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 489, 107927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, C.; Raya, L.; Juárez, J.; Pérez, J.; González, I. Effect of Silymarin in Pdx-1 Expression and the Proliferation of Pancreatic β-Cells in a Pancreatectomy Model. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damame, H.; Rooge, S.; Patil, R.; Garad, C.; Arvindekar, A. In Vitro Differentiation of Human Pancreatic Duct-Derived PANC-1 Cells into β-Cell Phenotype Using Tinospora cordifolia. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2022, 58, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, F. Approaches to Inducing β-Cell Regeneration. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.J.; Peng, Y.C.; Yang, K.M. Cellular Signaling Pathways Regulating β-Cell Proliferation as a Promising Therapeutic Target in the Treatment of Diabetes (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 3275–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baeyens, L.; Bonné, S.; German, M.S.; Ravassard, P.; Heimberg, H.; Bouwens, L. Ngn3 Expression during Postnatal in Vitro Beta Cell Neogenesis Induced by the JAK/STAT Pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 1892–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koblas, T.; Leontovyč, I.; Zacharovová, K.; Berková, Z.; Kříž, J.; Girman, P.; Saudek, F. Activation of the Jak/Stat Signalling Pathway by Leukaemia Inhibitory Factor Stimulates Trans-Differentiation of Human Non-Endocrine Pancreatic Cells into Insulin-Producing Cells. Folia Biol. 2012, 58, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, L.; Zien, K.; Gutjahr, G.; Oberholzer, J.; Pattou, F.; Kerr-Conte, J.; Maedler, K. TCF7L2 Promotes Beta Cell Regeneration in Human and Mouse Pancreas. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 3296–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minami, K.; Okuno, M.; Miyawaki, K.; Okumachi, A.; Ishizaki, K.; Oyama, K.; Kawaguchi, M.; Ishizuka, N.; Iwanaga, T.; Seino, S. Lineage Tracing and Characterization of Insulin-Secreting Cells Generated from Adult Pancreatic Acinar Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15116–15121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghazi, L.; Rachdi, L.; Weiss, A.J.; Cras-Méneur, C.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E. Regulation of β-Cell Mass and Function by the Akt/Protein Kinase B Signalling Pathway. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2007, 9 (Suppl. S2), 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbassov, D.D.; Guertin, D.A.; Ali, S.M.; Sabatini, D.M. Phosphorylation and Regulation of Akt/PKB by the Rictor-MTOR Complex. Science 2005, 307, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woodgett, J.R. Recent Advances in the Protein Kinase B Signaling Pathway. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005, 17, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Tsichlis, P.N. Regulation of the Akt Kinase by Interacting Proteins. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7401–7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguirre, V.; Werner, E.D.; Giraud, J.; Lee, Y.H.; Shoelson, S.E.; White, M.F. Phosphorylation of Ser307 in Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 Blocks Interactions with the Insulin Receptor and Inhibits Insulin Action. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaneto, H.; Matsuoka, T.; Nakatani, Y.; Kawamori, D.; Matsuhisa, M.; Yamasaki, Y. Oxidative Stress and the JNK Pathway in Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2005, 1, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, U.; Cao, Q.; Yilmaz, E.; Lee, A.-H.; Iwakoshi, N.N.; Ozdelen, E.; Tuncman, G.; Gorgun, C.; Glimcher, L.H.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Endoplasm. In Encyclopedia of Parasitology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 306, p. 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanuza-Masdeu, J.; Isabel Arévalo, M.; Vila, C.; Barberà, A.; Gomis, R.; Caelles, C. In Vivo Jnk Activation in Pancreatic β-Cells Leads to Glucose Intolerance Caused by Insulin Resistance in Pancreas. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2308–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Um, S.H.; D’Alessio, D.; Thomas, G. Nutrient Overload, Insulin Resistance, and Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase 1, S6K1. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buteau, J.; Foisy, S.; Joly, E.; Prentki, M. Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Induces Pancreatic β-Cell Proliferation via Transactivation of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Diabetes 2003, 52, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jhala, U.S.; Canettieri, G.; Screaton, R.A.; Kulkarni, R.N.; Krajewski, S.; Reed, J.; Walker, J.; Lin, X.; White, M.; Montminy, M. CAMP Promotes Pancreatic β-Cell Survival via CREB-Mediated Induction of IRS2. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Dong, X.; Fisher, T.L.; Dunn, S.; Omer, A.K.; Weir, G.; White, M.F. Exendin-4 Uses Irs2 Signaling to Mediate Pancreatic β Cell Growth and Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jetton, T.L.; Liu, Y.Q.; Trotman, W.E.; Nevin, P.W.; Sun, X.J.; Leahy, J.L. Enhanced Expression of Insulin Receptor Substrate–2 and Activation of Protein Kinase B/Akt in Regenerating Pancreatic Duct Epithelium of 60%-Partial Pancreatectomy Rats. Diabetologia 2001, 44, 2056–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avruch, J.; Hara, K.; Lin, Y.; Liu, M.; Long, X.; Ortiz-Vega, S.; Yonezawa, K. Insulin and Amino-Acid Regulation of MTOR Signaling and Kinase Activity through the Rheb GTPase. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6361–6372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hay, N.; Sonenberg, N. Upstream and Downstream of MTOR. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 1926–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Dibble, C.C.; Matsuzaki, M.; Manning, B.D. The TSC1-TSC2 Complex Is Required for Proper Activation of MTOR Complex 2. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 4104–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balcazar, N.; Sathyamurthy, A.; Elghazi, L.; Gould, A.; Weiss, A.; Shiojima, I.; Walsh, K.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E. MTORC1 Activation Regulates β-Cell Mass and Proliferation by Modulation of Cyclin D2 Synthesis and Stability. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 7832–7842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, G.; Marshall, C.A.; Pappan, K.L.; Remedi, M.S.; McDaniel, M.L. Signaling Elements Involved in the Metabolic Regulation of MTOR by Nutrients, Incretins, and Growth Factors in Islets. Diabetes 2004, 53 (Suppl. S3), S225–S232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rachdi, L.; Balcazar, N.; Osorio-Duque, F.; Elghazi, L.; Weiss, A.; Gould, A.; Chang-Chen, K.J.; Gambello, M.J.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E. Disruption of Tsc2 in Pancreatic β Cells Induces β Cell Mass Expansion and Improved Glucose Tolerance in a TORC1-Dependent Manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeyama, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Kido, Y.; Hashimoto, N.; Asahara, S.; Matsuda, T.; Takeda, A.; Inoue, T.; Shibutani, Y.; Koyanagi, M.; et al. Biphasic Response of Pancreatic β-Cell Mass to Ablation of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex 2 in Mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dos, D.S.; Ali, S.M.; Kim, D.H.; Guertin, D.A.; Latek, R.R.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Sabatini, D.M. Rictor, a Novel Binding Partner of MTOR, Defines a Rapamycin-Insensitive and Raptor-Independent Pathway That Regulates the Cytoskeleton. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jara, M.A.; Werneck-De-Castro, J.P.; Lubaczeuski, C.; Johnson, J.D.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E. Pancreatic and Duodenal Homeobox-1 (PDX1) Contributes to β-Cell Mass Expansion and Proliferation Induced by Akt/PKB Pathway. Islets 2020, 12, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatrai, S.; Elghazi, L.; Balcazar, N.; Cras-Méneur, C.; Krits, I.; Kiyokawa, H.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E. Akt Induces β-Cell Proliferation by Regulating Cyclin D1, Cyclin D2, and P21 Levels and Cyclin-Dependent Kinase-4 Activity. Diabetes 2006, 55, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blandino-Rosano, M.; Alejandro, E.U.; Sathyamurthy, A.; Scheys, J.O.; Gregg, B.; Chen, A.Y.; Rachdi, L.; Weiss, A.; Barker, D.J.; Gould, A.P.; et al. Enhanced Beta Cell Proliferation in Mice Overexpressing a Constitutively Active Form of Akt and One Allele of P21Cip. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, J.C.; Vo, V.; Gorjala, P.; Fiscus, R.R. Pancreatic-β-Cell Survival and Proliferation Are Promoted by Protein Kinase G Type Iα and Downstream Regulation of AKT/FOXO1. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2017, 14, 434–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.; Laychock, S.G. Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Promotes Pancreatic Islet β-Cell Growth and Akt/Foxo1a/Cyclin D2 Signaling. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 5455–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wrede, C.E.; Dickson, L.M.; Lingohr, M.K.; Briaud, I.; Rhodes, C.J. Protein Kinase B/Akt Prevents Fatty Acid-Induced Apoptosis in Pancreatic β-Cells (INS-1). J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49676–49684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, S.; Ohsugi, M.; Liu, Z.; Fatrai, S.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E.; Permutt, M.A. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis Is Partly Mediated by Reduced Insulin Signaling through Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt and Increased Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β in Mouse Insulinoma Cells. Diabetes 2005, 54, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ammendrup, A.; Maillard, A.; Nielsen, K.; Andersen, A.N.; Serup, P.; Madsen, O.D.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T.; Bonny, C. The C-Jun Amino-Terminal Kinase Pathway Is Preferentially Activated by Interleukin-1 and Controls Apoptosis in Differentiating Pancreatic β-Cells. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Størling, J.; Binzer, J.; Andersson, A.K.; Züllig, R.A.; Tonnesen, M.; Lehmann, R.; Spinas, G.A.; Sandler, S.; Billestrup, N.; Mandrup-Poulsen, T. Nitric Oxide Contributes to Cytokine-Induced Apoptosis in Pancreatic Beta Cells via Potentiation of JNK Activity and Inhibition of Akt. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 2039–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clevers, H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Development and Disease. Cell 2006, 127, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mussmann, R.; Geese, M.; Harder, F.; Kegel, S.; Andag, U.; Lomow, A.; Burk, U.; Onichtchouk, D.; Dohrmann, C.; Austen, M. Inhibition of GSK3 Promotes Replication and Survival of Pancreatic Beta Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 12030–12037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Welters, H.J.; Kulkarni, R.N. Wnt Signaling: Relevance to β-Cell Biology and Diabetes. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 19, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulifson, I.C.; Karnik, S.K.; Heiser, P.W.; Ten Berge, D.; Chen, H.; Gu, X.; Taketo, M.M.; Nusse, R.; Hebrok, M.; Kim, S.K. Wnt Signaling Regulates Pancreatic Beta Cell Proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6247–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiser, P.W.; Lau, J.; Taketo, M.M.; Herrera, P.L.; Hebrok, M. Stabilization of β-Catenin Impacts Pancreas Growth. Development 2006, 133, 2023–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rane, S.G.; Reddy, E.P. Cell Cycle Control of Pancreatic Beta Cell Proliferation. Front. Biosci. 2000, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Badawy, A.; El-Badri, N. The Cell Cycle as a Brake for β-Cell Regeneration from Embryonic Stem Cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohsugi, M.; Gras-Méneur, C.; Zhou, Y.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E.; Johnson, J.D.; Luciani, D.S.; Polonsky, K.S.; Permutt, M.A. Reduced Expression of the Insulin Receptor in Mouse Insulinoma (MIN6) Cells Reveals Multiple Roles of Insulin Signaling in Gene Expression, Proliferation, Insulin Content, and Secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 4992–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanabe, K.; Liu, Z.; Patel, S.; Doble, B.W.; Li, L.; Cras-Méneur, C.; Martinez, S.C.; Welling, C.M.; White, M.F.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E.; et al. Genetic Deficiency of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β Corrects Diabetes in Mouse Models of Insulin Resistance. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, 0307–0318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, M.J.; Selander, L.; Carlsson, L.; Edlund, H. Phosphorylation Marks IPF1/PDX1 Protein for Degradation by Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3-Dependent Mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 6395–6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, F.; Lee, J.T.; Navolanic, P.M.; Steelman, L.S.; Shelton, J.G.; Blalock, W.L.; Franklin, R.A.; McCubrey, J.A. Involvement of PI3K/Akt Pathway in Cell Cycle Progression, Apoptosis, and Neoplastic Transformation: A Target for Cancer Chemotherapy. Leukemia 2003, 17, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, T.; Nakae, J.; Kitamura, Y.; Kido, Y.; Biggs, W.H.; Wright, C.V.E.; White, M.F.; Arden, K.C.; Accili, D. The Forkhead Transcription Factor Foxo1 Links Insulin Signaling to Pdx1 Regulation of Pancreatic β Cell Growth. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, N.; Kido, Y.; Uchida, T.; Asahara, S.I.; Shigeyama, Y.; Matsuda, T.; Takeda, A.; Tsuchihashi, D.; Nishizawa, A.; Ogawa, W.; et al. Ablation of PDK1 in Pancreatic β Cells Induces Diabetes as a Result of Loss of β Cell Mass. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Sakaue, H.; Nishizawa, A.; Matsuki, Y.; Gomi, H.; Watanabe, E.; Hiramatsu, R.; Tamamori-Adachi, M.; Kitajima, S.; Noda, T.; et al. PDK1 Regulates Cell Proliferation and Cell Cycle Progression through Control of Cyclin D1 and P27Kip1 Expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 17702–17711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakae, J.; Oki, M.; Cao, Y. The FoxO Transcription Factors and Metabolic Regulation. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamoto, H.; Hribal, M.L.; Lin, H.V.; Bennett, W.R.; Ward, A.; Accili, D. Role of the Forkhead Protein FoxO1 in β Cell Compensation to Insulin Resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buteau, J.; Spatz, M.L.; Accili, D. Transcription Factor FoxO1 Mediates Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Effects on Pancreatic β-Cell Mass. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez, S.C.; Cras-Méneur, C.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E.; Permutt, M.A. Glucose Regulates Foxo1 through Insulin Receptor Signaling in the Pancreatic Islet β-Cell. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pende, M.; Kozma, S.C.; Jaquet, M.; Oorschot, V.; Burcelin, R.; Le Marchand-Brustel, Y.; Klumperman, J.; Thorens, B.; Thomas, G. Hypoinsulinaemia, Glucose Intolerance and Diminished β-Cell Size in S6K1-Deficient Mice. Nature 2000, 408, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Mizrachi, E.; Wen, W.; Stahlhut, S.; Welling, C.M.; Permutt, M.A. Islet Beta Cell Expression of Constitutively Active Akt1/PKB Alpha Induces Striking Hypertrophy, Hyperplasia, and Hyperinsulinemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, S.G.; Lee, J.H.; Lin, H.M. Transforming Growth Factor-β Pathway: Role in Pancreas Development and Pancreatic Disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006, 17, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gohary, Y.; Tulachan, S.; Guo, P.; Welsh, C.; Wiersch, J.; Prasadan, K.; Paredes, J.; Shiota, C.; Xiao, X.; Wada, Y.; et al. Smad Signaling Pathways Regulate Pancreatic Endocrine Development. Dev. Biol. 2013, 378, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Fischbach, S.; Xiao, X. The Role of the TGFβ Receptor Signaling Pathway in Adult Beta Cell Proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanley, S.; Rosenberg, L. Transforming Growth Factor β Is a Critical Regulator of Adult Human Islet Plasticity. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, X.H.; Derynck, R. Specificity and Versatility in TGF-β Signaling through Smads. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 21, 659–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sjoholm, A.; Hellerstrom, C. TGF-β Stimulates Insulin Secretion and Blocks Mitogenic Response of Pancreatic β-Cells to Glucose. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 1991, 260, C1046–C1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, N.G.; Apelqvist, Å.A.; Gu, X.; Harmon, E.B.; Topper, J.N.; MacDonald, R.J.; Kim, S.K. Conditional Expression of Smad7 in Pancreatic β Cells Disrupts TGF-β Signaling and Induces Reversible Diabetes Mellitus. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toren-Haritan, G.; Efrat, S. TGFβ Pathway Inhibition Redifferentiates Human Pancreatic Islet β Cells Expanded In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, H.; Kudo, T.; Harada, A.; Esaki, R.; Suzuki, H.; Kato, M.; Takahashi, S. Suppression of MafA-Dependent Transcription by Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 364, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.M.; Lee, J.H.; Yadav, H.; Kamaraju, A.K.; Liu, E.; Zhigang, D.; Vieira, A.; Kim, S.J.; Collins, H.; Matschinsky, F.; et al. Transforming Growth Factor-β/Smad3 Signaling Regulates Insulin Gene Transcription and Pancreatic Islet β-Cell Function. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, T.; Dai, P.; Hatakeyama, T.; Harada, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Yoshimura, N.; Takamatsu, T. TGF-β Signaling Regulates Pancreatic β-Cell Proliferation through Control of Cell Cycle Regulator P27 Expression. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2013, 46, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sehrawat, A.; Shiota, C.; Mohamed, N.; DiNicola, J.; Saleh, M.; Kalsi, R.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Prasadan, K.; Gittes, G.K. SMAD7 Enhances Adult β-Cell Proliferation without Significantly Affecting β-Cell Function in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 4858–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokzijl, A.; Dahlqvist, C.; Reissmann, E.; Falk, A.; Moliner, A.; Lendahl, U.; Ibáñez, C.F. Cross-Talk between the Notch and TGF-β Signaling Pathways Mediated by Interaction of the Notch Intracellular Domain with Smad3. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 163, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolome, A.; Zhu, C.; Sussel, L.; Pajvani, U.B. Notch Signaling Dynamically Regulates Adult β Cell Proliferation and Maturity. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Gohary, Y.; Tulachan, S.; Wiersch, J.; Guo, P.; Welsh, C.; Prasadan, K.; Paredes, J.; Shiota, C.; Xiao, X.; Wada, Y.; et al. A Smad Signaling Network Regulates Islet Cell Proliferation. Diabetes 2014, 63, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; Wiersch, J.; El-Gohary, Y.; Guo, P.; Prasadan, K.; Paredes, J.; Welsh, C.; Shiota, C.; Gittes, G.K. TGFβ Receptor Signaling Is Essential for Inflammation-Induced but Not β-Cell Workload-Induced β-Cell Proliferation. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1217–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, X.; Gaffar, I.; Guo, P.; Wiersch, J.; Fischbach, S.; Peirish, L.; Song, Z.; El-Gohary, Y.; Prasadan, K.; Shiota, C.; et al. M2 Macrophages Promote Beta-Cell Proliferation by up-Regulation of SMAD7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, H.L.; Zhang, L.; Becker, T.C.; Haldeman, J.M.; Stephens, S.B.; Arlotto, M.; Moss, L.G.; Newgard, C.B.; Hohmeier, H.E. A Pdx-1-Regulated Soluble Factor Activates Rat and Human Islet Cell Proliferation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 36, 2918–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Karakose, E.; Liu, H.; Swartz, E.; Zlatanic, V.; Wilson, J.; González, B.J.; Takane, K.K.; Ye, L.; Harb, G.; et al. Combined Inhibition of DYRK1A, SMAD and Trithorax Pathways Synergizes to Induce Robust Replication in Adult Human Beta Cells. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drucker, D.J.; Nauck, M.A. The Incretin System: Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetes. Lancet 2006, 368, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buteau, J.; Roduit, R.; Susini, S.; Prentki, M. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Promotes DNA Synthesis, Activates Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase and Increases Transcription Factor Pancreatic and Duodenal Homeobox Gene 1 (PDX-1) DNA Binding Activity in Beta (INS-1)- Cells. Diabetologia 1999, 42, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buteau, J.; Foisy, S.; Rhodes, C.J.; Carpenter, L.; Biden, T.J.; Prentki, M. Protein Kinase Czeta Activation Mediates Glucagon-like Peptide-1-Induced Pancreatic Beta-Cell Proliferation. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, N.; Shirotani, T.; Araki, E.; Kaneko, K.; Todaka, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Tsuruzoe, K.; Motoshima, H.; Yoshizato, K.; Kishikawa, H.; et al. Possible Involvement of Atypical Protein Kinase C (PKC) in Glucose- Sensitive Expression of the Human Insulin Gene: DNA-Binding Activity and Transcriptional Activity of Pancreatic and Duodenal Homeobox Gene-1 (PDX-1) Are Enhanced via Calphostin C-Sensitiv. Endocr. J. 1999, 46, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Xu, E.; Wong, V.; Rhodes, C.; Brubaker, P.L. Glucagon-like Peptitle-1 Regulates Proliferation and Apoptosis via Activation of Protein Kinase B in Pancreatic INS-1 Beta Cells. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Ding, X.; He, Y.; Gu, C.; Zhou, L. Exendin-4 Promotes Beta Cell Proliferation via PI3k/Akt Signalling Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 35, 2223–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoffers, D.A.; Kieffer, T.J.; Hussain, M.A.; Drucker, D.J.; Bonner-Weir, S.; Habener, J.F.; Egan, J.M. Insulinotropic Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Agonists Stimulate Expression of Homeodomain Protein IDX-1 and Increase Islet Size in Mouse Pancreas. Diabetes 2000, 49, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Brubaker, P. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Treatment Delays the Onset of Diabetes in 8 Week-Old Db/Db Mice. Diabetologia 2002, 45, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De León, D.D.; Deng, S.; Madani, R.; Ahima, R.S.; Drucker, D.J.; Stoffers, D.A. Role of Endogenous Glucagon-like Peptide-1 in Islet Regeneration after Partial Pancreatectomy. Diabetes 2003, 52, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.; Stoffers, D.A.; Habener, J.F.; Bonner-Weir, S. Exendin-4 Stimulates Both Beta-Cell Replication and Neogenesis, Resulting in Increased Beta-Cell Mass and Improved Glucose Tolerance in Diabetic Rats. Diabetes 1999, 48, 2270–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourrel, C.; Bailbé, D.; Meile, M.J.; Kergoat, M.; Portha, B. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 and Exendin-4 Stimulate Beta-Cell Neogenesis in Streptozotocin-Treated Newborn Rats Resulting in Persistently Improved Glucose Homeostasis at Adult Age. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaugh, L.C. The What, Where, When and How of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Pancreas Development. Organogenesis 2008, 4, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baek, S.H.; Kioussi, C.; Briata, P.; Wang, D.; Nguyen, H.D.; Ohgi, K.A.; Glass, C.K.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Rose, D.W.; Rosenfeld, M.G. Regulated Subset of G1 Growth-Control Genes in Response to Derepression by the Wnt Pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3245–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briata, P.; Ilengo, C.; Corte, G.; Moroni, C.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Chen, C.-Y.; Gherzi, R. The Wnt/β-Catenin→Pitx2 Pathway Controls the Turnover of Pitx2 and Other Unstable MRNAs. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Habener, J.F. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Activation of TCF7L2-Dependent Wnt Signaling Enhances Pancreatic Beta Cell Proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 8723–8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hino, S.; Tanji, C.; Nakayama, K.I.; Kikuchi, A. Phosphorylation of β-Catenin by Cyclic AMP-Dependent Protein Kinase Stabilizes β-Catenin through Inhibition of Its Ubiquitination. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 9063–9072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heller, C.; Kühn, M.C.; Mülders-Opgenoorth, B.; Schott, M.; Willenberg, H.S.; Scherbaum, W.A.; Schinner, S. Exendin-4 Upregulates the Expression of Wnt-4, a Novel Regulator of Pancreatic β-Cell Proliferation. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 301, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, S.; Yuan, G.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L.; Xue, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.W. Wnt3a Regulates Proliferation, Apoptosis and Function of Pancreatic NIT-1 Beta Cells via Activation of IRS2/PI3K Signaling. J. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 114, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maschio, D.A.; Oliveira, R.B.; Santos, M.R.; Carvalho, C.P.F.; Barbosa-Sampaio, H.C.L.; Collares-Buzato, C.B. Activation of the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Pancreatic Beta Cells during the Compensatory Islet Hyperplasia in Prediabetic Mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 1534–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figeac, F.; Uzan, B.; Faro, M.; Chelali, N.; Portha, B.; Movassat, J. Neonatal Growth and Regeneration of β-Cells Are Regulated by the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Normal and Diabetic Rats. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 298, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukiyama, S.; Matsushita, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Morita, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Tamura, H.; Kamachi, H.; Ozaki, M.; Todo, S. Transduction of Exogenous Constitutively Activated Stat3 into Dispersed Islets Induces Proliferation of Rat Pancreatic β-Cells. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.E.; Darnell, J.E. STATs: Transcriptional Control and Biological Impact. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez, I.A.; Dirice, E.; Gupta, M.K.; Shirakawa, J.; Teo, A.K.K.; Kulkarni, R.N. Proinflammatory Cytokines Induce Endocrine Differentiation in Pancreatic Ductal Cells via STAT3-Dependent NGN3 Activation. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamauchi, A.; Itaya-Hironaka, A.; Sakuramoto-Tsuchida, S.; Takeda, M.; Yoshimoto, K.; Miyaoka, T.; Fujimura, T.; Tsujinaka, H.; Tsuchida, C.; Ota, H.; et al. Synergistic Activations of REG i α and REG i β Promoters by IL-6 and Glucocorticoids through JAK/STAT Pathway in Human Pancreatic β Cells. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miura, M.; Miyatsuka, T.; Katahira, T.; Sasaki, S.; Suzuki, L.; Himuro, M.; Nishida, Y.; Fujitani, Y.; Matsuoka, T.-A.; Watada, H. Suppression of STAT3 Signaling Promotes Cellular Reprogramming into Insulin-Producing Cells Induced by Defined Transcription Factors. EBioMedicine 2018, 36, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baeyens, L.; Lemper, M.; Staels, W.; De Groef, S.; De Leu, N.; Heremans, Y.; German, M.S.; Heimberg, H. (Re)Generating Human Beta Cells: Status, Pitfalls, and Perspectives. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1143–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, G.Y.; Wang, K.W.; Wang, X.Y.; Wu, B. Bioactive Lignans from Zanthoxylum Planispinum with Cytotoxic Potential. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 11, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afelik, S.; Rovira, M. Pancreatic β-Cell Regeneration: Advances in Understanding the Genes and Signaling Pathways Involved. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Domínguez-Bendala, J.; Qadir, M.M.F.; Pastori, R.L. Pancreatic Progenitors: There and Back Again. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nir, T.; Melton, D.A.; Dor, Y. Recovery from Diabetes in Mice by β Cell Regeneration. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2553–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teta, M.; Rankin, M.M.; Long, S.Y.; Stein, G.M.; Kushner, J.A. Growth and Regeneration of Adult Beta Cells Does Not Involve Specialized Progenitors. Dev. Cell 2007, 12, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.S.; De León, D.D.; Kaestner, K.H.; Stoffers, D.A. Regeneration of Pancreatic Islets after Partial Pancreatectomy in Mice Does Not Involve the Reactivation of Neurogenin-3. Diabetes 2006, 55, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorel, F.; Népote, V.; Avril, I.; Kohno, K.; Desgraz, R.; Chera, S.; Herrera, P.L. Conversion of Adult Pancreatic α-Cells to β-Cells after Extreme β-Cell Loss. Nature 2010, 464, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misfeldt, A.A.; Costa, R.H.; Gannon, M. Beta-Cell Proliferation, but Not Neogenesis, Following 60% Partial Pancreatectomy Is Impaired in the Absence of FoxM1. Diabetes 2008, 57, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, K.Y.; Tamaki, H.; Handa, K.; Takahashi, T.; Kakita, A.; Yamashina, S. Differentiation and Proliferation of Endocrine Cells in the Regenerating Rat Pancreas after 90% Pancreatectomy. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 2003, 66, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.C.; Rukstalis, J.M.; Nishimura, W.; Tchipashvili, V.; Habener, J.F.; Sharma, A.; Bonner-Weir, S. Activation of Pancreatic-Duct-Derived Progenitor Cells during Pancreas Regeneration in Adult Rats. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 2792–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonner-Weir, S.; Baxter, L.A.; Schuppin, G.T.; Smith, F.E. A Second Pathway for Regeneration of Adult Exocrine and Endocrine Pancreas: A Possible Recapitulation of Embryonic Development. Diabetes 1993, 42, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, Q.; Qi, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, C.C.; Riggs, A.D.; Zeng, D. Growth Factors and Medium Hyperglycemia Induce Sox9+ Ductal Cell Differentiation into β Cells in Mice with Reversal of Diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, E.P.; Lin, J.-K. Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) and Rutin Suppress the Glucotoxicity through Activating IRS2 and AMPK Signaling in Rat Pancreatic β Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9817–9827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentki, M.; Nolan, C.J. Islet β-Cell Failure in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1802–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eguchi, N.; Vaziri, N.D.; Dafoe, D.C.; Ichii, H. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Pancreatic β Cell Dysfunction in Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böni-Schnetzler, M.; Meier, D.T. Islet Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes. Semin. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanatsuka, A.; Kou, S.; Makino, H. IAPP/Amylin and β-Cell Failure: Implication of the Risk Factors of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetol. Int. 2018, 9, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibowitz, G.; Kaiser, N.; Cerasi, E. β-Cell Failure in Type 2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes Investig. 2011, 2, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernea, S.; Dobreanu, M. Diabetes and Beta Cell Function: From Mechanisms to Evaluation and Clinical Implications. Biochem. Medica 2013, 23, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, G.; Hebrok, M. Islet Formation in Mice and Men: Lessons for the Generation of Functional Insulin-Producing β Cells from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2015, 32, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levetan, C.S.; Pierce, S.M. Distinctions Between the Islets of Mice and Men: Implications for New Therapies for Type 1 and 2 Diabetes. Endocr. Pract. 2013, 19, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
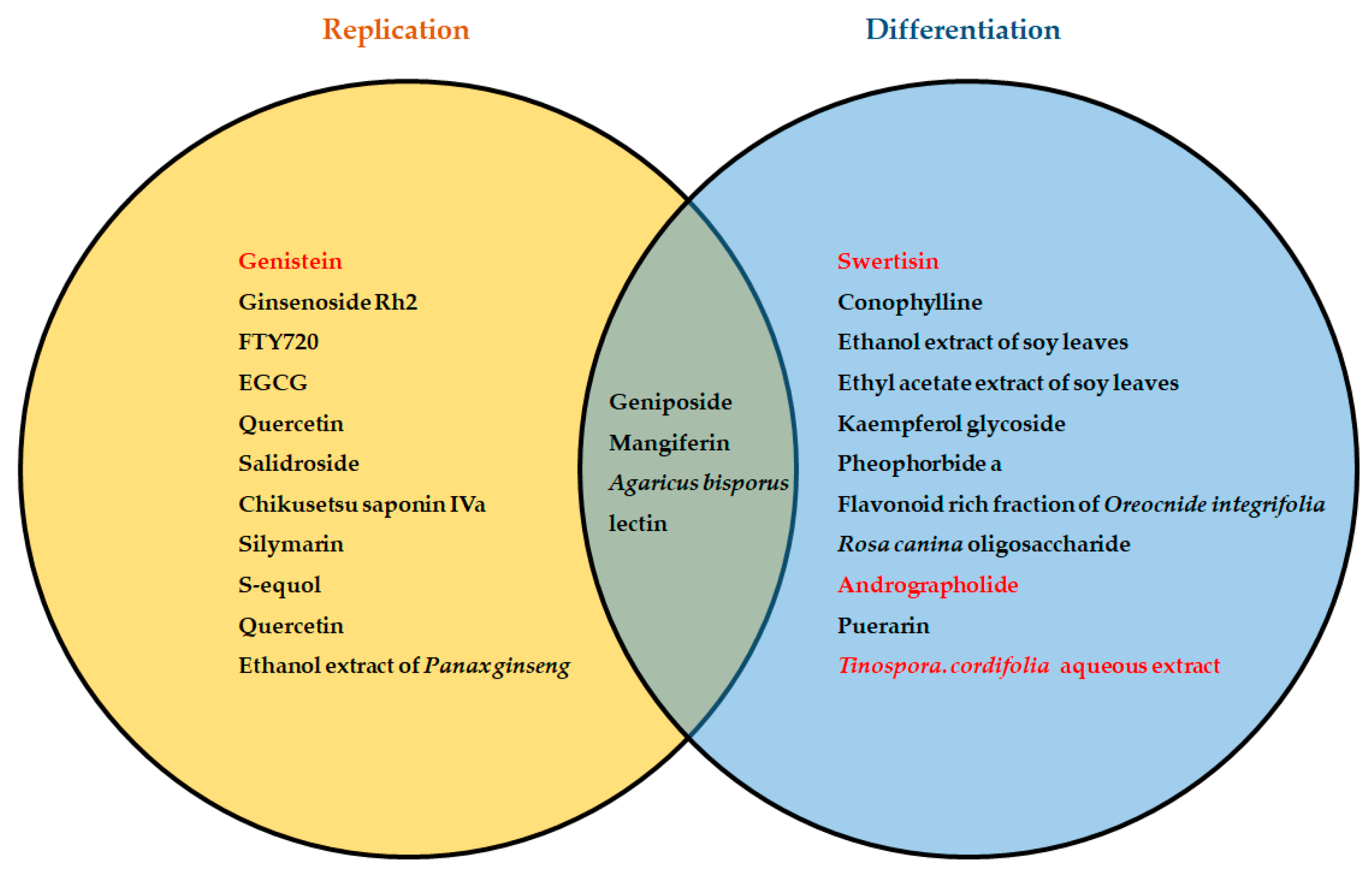


| Plant Source/ Compound | Plant Extract or Compound | Model(s) | Effective Concentration/Dose | Bioactivity | Pathway | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Agaricus bisporus | Agaricus bisporus lectin | 70% pancreatectomized 8-week-old male C57BL/6J mice | 10 mg/kg for 14 days | ↑ proliferation of beta cells and duct cells ↑ beta-cell mass ↑ Cdk4 mRNA and protein ↑ cyclin D1 and D2 ↑ Cdk4 activity ↑ Rb phosphorylation ↑ Pdx-1 and Ngn3 mRNA expression | Not indicated | [55] |
| 2. | Andrographis paniculata | Andrographolide | PANC-1 cells cultured | 1.25, 2.5, 5 μM for 96 h | ↑ differentiation of PANC-1 cells into insulin-producing cells Pdx-1 mRNA and protein levels | Not indicated | [56] |
| 8-week-old 150mg/kg STZ-diabetic male Kunming mice | Transplanted with 200 islets from normal mice or 500 differentiated islet-like cell clusters into the renal capsular for 5 days Or treated with 50 mg/kg daily for 40 days | ↑ Pdx-1 mRNA and protein levels ↑ insulin+ and Pdx-1+ islets Restored islet morphology Pathway not indicated | Not indicated | [56] | |||
| 3. | Aralia taibaiensis | Chikusetsu saponin IVa | βTC3 cell line exposed to high glucose (33.3 mM) | 40 µM for 0, 6, 12, 24, 36 or 48 h | ↑ cell viability and proliferation ↑ TCF7L2, Wnt3a mRNA and protein expression ↑ nuclear β-catenin levels ↑ p-GSK-3β ↑ c-Myc, cyclin D1, skp2 protein levels ↓ p53, p21 and p27 protein levels | Wnt/β-catenin/TCF7L2 | [57] |
| Pancreatic islet cells from male Sprague Dawley rats exposed to high glucose | 40 µM for 24 h | ↑ Wnt3a mRNA and protein ↑ nuclear β-catenin ↑ p-GSK-3β ↑ TCF7L2, c-Myc, cyclin D1, skp2 protein levels ↓ p53, p21 and p27 | Wnt/β-catenin/TCF7L2 | [57] | |||
| β-catenin gene knockout mice (β-catenin−/−) 4-week-old male mice, HFD-fed for 8 weeks then given 50 mg/kg bwt STZ | 120 mg/kg for 30 days | ↑ Wnt3a mRNA and protein ↑ nuclear β-catenin levels ↑ p-GSK-3β ↑ TCF7L2, c-Myc, cyclin D1, skp2 protein levels ↓ p53, p21 and p27 | Wnt/β-catenin/TCF7L2 | [57] | |||
| 4. | Ervatamia microphylla | Conophylline | AR42J-B13 cells | 0.1 μg/mL for 9 or 72 h | Differentiation of AR42J cells into insulin-expressing cells ↑ Ngn3, NeuroD and Nkx2.2 mRNA expression ↑ phosphorylation of p38 | Not indicated | [58] |
| 14.5-day-old embryonic pancreata | 0.1 µg/mL for 72 h or 0.1 µg/mL every 2 days for 10 days | ↑ number of islet-like cell clusters ↑ number of insulin+ cells ↑ β-cell differentiation ↑ insulin+/Pdx-1+ cells around duct-like structures ↑ insulin+/Pdx-1+ area | Not indicated | [59] | |||
| Endocrine cells from neonatal porcine pancreas Islet-like cell clusters from the pancreases of new-born pigs | 0.1 µg/mL conophylline alone or combined with 10 mM nicotinamide treated for 1, 3, 5 or 6 weeks | ↑ number of insulin-producing cells ↑ differentiation of ICC into functional glucose-responsive cells ↑ mRNA levels of Ngn3, Pdx-1, NeuroD in islet-like cell clusters | Not indicated | [60] | |||
| STZ-induced one-day-old male neonatal Wistar rats | 5 µg/g subcutaneously on days 1, 3, 5 and 7 | ↑ relative area for Pdx-1/insulin-positive cells ↑ Pdx-1+ ductal cells ↑ number of islet-like cell clusters ↑ β-cell mass | Not indicated | [59] | |||
| STZ-induced one-day-old male neonatal Wistar rats | 2 μg/g (i.p) conophylline every other day until day 7 or 200 pmol/g betacellulin daily for 7 days with 2 μg/g conophylline every other day for 7 days | ↑ β-cell mass ↑ number and size of islet-like cell clusters ↑ number of insulin+/BrdU+ cells ↑ Pdx-1+/CK-19+ ductal cells | Not indicated | [61] | |||
| 5. | Epigallocatechin gallate, Rutin | Endocrine cells from neonatal porcine pancreas Islet-like cell clusters from the pancreases of new-born pigs | 0.1 µg/mL conophylline alone or combined with 10 mM nicotinamide treated for 1, 3, 5 or 6 weeks | ↑ number of insulin-producing cells ↑ differentiation of ICC into functional glucose-responsive cells ↑ mRNA levels of Ngn3, Pdx-1, NeuroD in islet-like cell clusters | Not indicated | [60] | |
| Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) | 7-week-old male db/db mice | 10 g/kg of diet (EGCG 1% [w/w]) for 10 weeks | ↑ number of islets, islet size, endocrine area ↓ Cdkn1a and Ppp1r15a | Not indicated | [62] | ||
| 6. | FTY720 (Fingolimod) | Five-week-old female db/db mice (BKS.Cg-m+/+Leprdb) | 10 mg/kg of FTY720 daily via oral gavage for 6 weeks | ↑ β-cell mass, islet area ↑ proliferation of beta and duct cells ↑ differentiation of ductal cells to insulin+ cells ↑ expression of Pdx-1, cyclins D1, D2 and D3 ↓ p57KIP2 | PI3K/Akt pathway via Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors | [63] | |
| 7. | Gardenia jasminoides Ellis | Geniposide | MIN6 cells exposed to high glucose (33.3 mM) or a mixture of IL-1β plus IFN-γ | 20 μM for 3 days | ↑ p-Akt, p-GSK-3β, nuclear β-catenin and PKA C-α protein expression | Wnt/β-catenin/TCF7L2 | [64] |
| Primary islets from male C57BL/6J mice exposed to high glucose (33.3 mM) or a mixture of IL-1β plus IFN-γ and exocrine cells from male C57BL/6J mice | 20 µM for 3 days for islets 20 µM for 4 days for exocrine cells | ↑ β-cell proliferation ↑ mRNA expression of Pdx-1, TCF7L2, cyclin D1 ↑ protein expression of TCF7L2 and p-Akt Islet-like clusters from ductal cells Pdx-1+, insulin+, MafA+, ductal cells ↑ Pdx-1 and insulin mRNA in exocrine cells | Wnt/β-catenin/TCF7L2 and JAK2/STAT3 signaling | [64] | |||
| 4-week-old male C57BL/6J mice fed an HFD for 12 weeks 4-week-old male C57Bl/KsJ (BKS) mice and BKS.Cg-Dock7m+/+Leprdb/JNju (db/db) | 100 mg/kg for 4 weeks 100 mg/kg for 35 days | ↑ β-cell mass and proliferation ↑ Pdx-1+ duct cells ↑ Ngn3+ duct cells ↑ islet-like cell clusters within ducts ↑ TCF7L2+ beta and duct cells | Wnt/β-catenin/TCF7L2 and JAK2/STAT3 signaling | [64] | |||
| 8. | Various leguminous plants | Genistein | INS-1 cells | 1 uM genistein for 15 min or 24 h | ↑ β-cell proliferation ↑ cyclin D expression ↑ ERK1/2 phosphorylation | cAMP/PKA and MEK/ERK signaling pathways | [65] |
| Human islet beta cells | 1 µM and 5 µM genistein for 24 h | ↑ β-cell proliferation ↑ cyclin D expression ↑ cAMP levels and activation of PKA in human islets | cAMP/PKA and MEK/ERK signaling pathways | [65] | |||
| High-fat diet + STZ-diabetic 4-week-old male C57BL/6J mice | 0.25 g/kg in the diet for 28 days | ↑ β-cell proliferation | cAMP/PKA and MEK/ERK signaling pathways | [65] | |||
| 9. | Glycine max (Soybean) | G. max leaves compounds (Kaempferol and pheophorbide a) | MIN6 pancreatic β-cells | 50 uM or 100 uM kaempferol for 48 h 0.1 or 1 μM pheophorbide a | Kaempferol - ↑mRNA levels of IRS2 ↑ Akt ↑ FoxO1 phosphorylation ↑ gene expression of Pdx-1, Ngn3 and Pax4 ↑ β-cell proliferation Pheophorbide a - ↑mRNA levels of IRS1 ↑ Ngn3, Pax4 and PKA gene expression ↑ induction of Akt and PKA phosphorylation ↑ β-cell proliferation | For kaempferol -IRS2/PI3K/Akt signaling via FoxO1 Pheophorbide a via IRS1/PI3K/Akt/PKA signaling | [66] |
| S-equol | INS-1 cells exposed to 1 mMol/L streptozotocin | 10 μMol/L for 24 h | ↑ cell proliferation | cAMP/PKA signaling | [67] | ||
| STZ-induced 5-week-old male ICR mice | 20 mg/kg via oral gavage twice daily for 7 days | ↑ β-cell proliferation | cAMP/PKA signaling | [67] | |||
| Ethyl acetate extract of G. max leaves or pinitol | High-fat diet-fed 4-week-old male C57BL/6J mice | 0.56% extract or 0.15% pinitol in the diet for 12 weeks | For extract- ↑ islet size, Ngn3 and MafA mRNA ↓ FoxO1 mRNA For pinitol- ↑ islet size, ↑ Ngn3, Pax4, MafA and IRS1 mRNA | Insulin signaling pathway | [68] | ||
| Ethanol extract of G. max leaves | 5-week-old male C57BLKS/J lar-Leprdb/Leprdb (db/db) and C57BLKS/J lar-m+/Leprdb (db/+) mice | 1% extract for 8 weeks | ↑ gene expression of IRS1, IRS2, Pdx-1, Ngn3, and Pax4 ↓ FoxO1 gene expression ↑ FoxO1 phosphorylation | IRS2/Akt signaling via FoxO1 | [66] | ||
| 10. | Ginseng | Ginsenoside Rh2 (GS-Rh2) | 70% pancreatectomized- 3-month-old male C57BL/6J mice | 1 mg/kg (i.p) for 14 days | ↑ beta-cell proliferation and mass ↑ p-Akt, p-FoxO1, Pdx-1, cyclin D1, cyclin D2 and Cdk4 protein ↑ Pdx-1, cyclin D1, cyclin D2 and Cdk4 mRNA ↑ Cdk4 activity | Akt/FoxO1/Pdx1 signaling | [69] |
| Ginseng | Ethanol extract of G. radix | Isolated pancreatic islets from male rats incubated for 24h in high glucose (20 mM) | 50 μg/mL for 8 h | ↑ IRS2 mRNA ↑ Pdx-1 mRNA | IRS2/IGF-1/Pdx-1 signaling | [70] | |
| Panax ginseng | Ethanol extracts of ripe and unripe ginseng berries | INS-1 rat insulinoma cells STZ-induced -8-week-old male C57BL/6 mice | 5, 10, and 20 µg/mL extract for 24 h 100 or 200 mg/kg extract via oral intubation daily for 10 weeks | ↑ β-cell numbers ↑ cyclin D2, Pdx-1, and IRS2 mRNA ↑ serum insulin | Not indicated | [71] | |
| 11. | Gymnema sylvestre | Gymnemic acid from G. sylvestre leaf | 2-month-old STZ-induced male Wistar rats RIN5-F beta cells exposed to 25 mM high glucose for 48 h | 150 mg/kg b.w; via oral gavage for 30 days. 1 µM for 24 h | ↑ Pdx-1, Ngn3, MafA and NeuroD1 mRNA and protein ↑ E-cadherin, β-catenin, PI3K, AKT, pAKT, Cyclin D1 and CDK4 ↓ FoxO1, GSK-3β and p21cip1 ↑ nuclear localization of Pdx-1 | PI3K/Akt signaling | [72] |
| 12. | Rhodiola rosea | Salidroside | Mouse islets from -10-week-old db/db and -10-week-old C57BL/6 mice exposed to diabetic 33.3 mM glucose, the mixture of 2 ng/mL IL-1 β +1000 U/mL IFN-γ, 0.5 mM palmitic acid or 200 µM H2O2 | 50 µM for 3 days | ↑ β-cell proliferation ↑ nuclear Pdx-1 ↓ nuclear FoxO1 | Akt/FoxO1 signaling | [73] |
| 4-week-old male C57BL/6 mice (HFD-fed) C57Bl/KsJ (BKS) mice BKS.Cg-Dock7m+/+Leprdb/J (db/db) mice | 100 mg/kg/day via oral gavage for 5 weeks | ↑ β-cell mass and proliferation | Akt/FoxO1 signaling | [73] | |||
| 13. | Enicostemma littorale | Swertisin | NIH3T3 cells | 15 µg/mL for 8 days | Initial ↑ gene and protein expression of nestin, Pdx-1, Ngn3, Pax4, Nkx6.1 and Reg-1 later ↓ expression of stem cell markers nestin, vimentin and SMA↑ islet cell differentiation ↓ Smad7 expression ↑ Smad2 expression | SMAD signaling | [74] |
| PANC-1 cells | 15 µg/mL for 8 days | ↑ differentiation into islet-like cell clusters ↑ gene expression of nestin, p38 phosphorylation, unchanged Pdx-1 expression early ↑ and late ↓ Ngn3 expression | MEPK-TKK pathway via p38 phosphorylation SMAD signaling | [47] | |||
| Mouse intra-islet progenitor cells | 15 μg/mL for eight days | ↑ islet differentiation of mouse intra-islet pancreatic progenitor cells into beta cells showing ↑ Ngn3 ↓ Erk1/2 levels ↑ Pax4 expression ↑ n-cadherin ↓ SMAD2/3/7 | MEPK-TKK pathway via p38 phosphorylation SMAD signaling | [47] | |||
| 70% pancreatectomized 3–4-week-old male Balb/c mice | Single injection of swertisin-dose not given | ↓ Pdx-1 ↑ nestin expression ↑ Ngn3 expression ↓ Smad 7 expression ↑ Smad-2/3 phosphorylation ↑ activation of MAP kinase ↑ differentiation of progenitor cells within the acinar and islet tissues | MEPK-TKK pathway SMAD signaling | [47] | |||
| STZ-diabetic 6–8-week-old female Balb/c mice | 2.5 mg/kg for 17 days | ↑ nestin, Pdx-1, Ngn3, MafA and Nkx6.1 protein expression | Not indicated | [75] | |||
| 14. | Mangifera indica | Mangiferin | Islet cells from male adult (age 3 months) and aged (age 12 months) mice | Cells incubated with mangiferin for 24 h (concentration not given) | ↑ Cdk4 activity ↑ inhibition of p16 ↑ expression and phosphorylation of STAT3 | STAT3 signaling | [76] |
| 70% pancreatectomized 8-week-old male C57BL/6J mice | 30 mg/kg or 90 mg/kg for 14 days | ↑ absolute β-cell mass ↑ beta and duct cell proliferation ↑ cyclin D1, cyclin D2 and Cdk4 mRNA and protein expression ↑ Cdk4 activity ↑ Rb phosphorylation ↓ p27 mRNA and protein levels ↑ FoxO1, Pdx-1 and Ngn3 mRNA and protein expression Not indicated | [77] | ||||
| 70% pancreatectomized 12-month-old C57BL/6J mice | 90 mg/kg (i.p.) for 28 days | ↑ proliferation of the islet cells ↑ β-cell volume and mass ↑ transcription and translation of Pdx-1, cyclin D1, D2 and Cdk4 ↓ expression of p16INK4a and p27Kip1 ↑ expression and phosphorylation of STAT3 ↓ phosphorylated Rb ↑ Cdk4 activity | STAT3 signaling | [76] | |||
| 15. | Oreocnide integrifolia | Flavonoid-rich fraction of O. integrifolia | 70% pancreatectomized 7–8-week-old female Balb/c mice | 250 mg/kg for 7, 14, and 21 days | ↑ Pdx-1/insulin co-expressing cells ↑ number of neogenic islet nodes ↑ β-cell density ↑ proliferation of ductal precursor cells ↑ Ngn3, Pdx-1 and Reg- 3α/γ mRNA CK-19/insulin co-expression in ducts | Not indicated | [78] |
| 16. | Radix puerariae | Puerarin | Pancreatic ductal cells from 5-week-old male C57BL/6 mice fed a high-fat diet | 50 µM for 3 days | ↑ Ngn3, Pdx-1, and insulin expression ↑ GLP-1R expression, activation of β-catenin, JAK2 and STAT3 in ductal cells ↑ Pdx-1+/CK19+ staining ↑ ICC formation | GLP-1R/Wnt/STAT signaling | [79] |
| High-fat diet-fed 5-week-old male C57BL/6 mice | 150 or 300 mg/kg per day for 10 or 20 days via oral gavage | ↑ β-cell proliferation ↑ Ngn3+ and Pdx-1+ duct cells ↑ islet-like cell clusters next duct cells | GLP-1R/Wnt/STAT signaling | [79] | |||
| 17. | Commercially sourced | Quercetin | 7-week-old STZ- induced male BALB/c mice | 0.1 or 0.5% (w/w) quercetin in the diet for 2 weeks | ↓ Cdkn1a gene expression | Not indicated | [80] |
| 18. | Rosa canina | Oligosaccharide isolated from Rosa canina (ripe fruits) | STZ-induced 8-week-old male Wistar rats | 8–40 mg/kg of oligosaccharide twice a day for 21 days via oral gavage | ↑ β-cell mass ↑ Ngn3 and Nkx6.1 expression | Not indicated | [81] |
| 19. | Silybum marianum | Silymarin | Alloxan-induced male Wistar rats | 200 mg/kg for 9 weeks | Normalized Pdx-1 protein and pancreas histology | Not indicated | [42] |
| 70% pancreatectomized male Wistar rats | 200 mg/kg (p.o.) for 3, 7, 14, 21, 42 and 63 days | ↑ Pdx-1 gene and protein expression ↑ β-cell proliferation | Not indicated | [82] | |||
| 20. | Tinospora cordifolia | T. cordifolia aqueous extract | PANC-1 cells | 15 μg/mL | ↑ Pdx-1 mRNA expression ↓ Carbonic anhydrase 9 mRNA expression | Not indicated | [83] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kimani, C.N.; Reuter, H.; Kotzé, S.H.; Muller, C.J.F. Regeneration of Pancreatic Beta Cells by Modulation of Molecular Targets Using Plant-Derived Compounds: Pharmacological Mechanisms and Clinical Potential. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 6216-6245. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45080392
Kimani CN, Reuter H, Kotzé SH, Muller CJF. Regeneration of Pancreatic Beta Cells by Modulation of Molecular Targets Using Plant-Derived Compounds: Pharmacological Mechanisms and Clinical Potential. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2023; 45(8):6216-6245. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45080392
Chicago/Turabian StyleKimani, Clare Njoki, Helmuth Reuter, Sanet Henriët Kotzé, and Christo John Fredrick Muller. 2023. "Regeneration of Pancreatic Beta Cells by Modulation of Molecular Targets Using Plant-Derived Compounds: Pharmacological Mechanisms and Clinical Potential" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 45, no. 8: 6216-6245. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45080392
APA StyleKimani, C. N., Reuter, H., Kotzé, S. H., & Muller, C. J. F. (2023). Regeneration of Pancreatic Beta Cells by Modulation of Molecular Targets Using Plant-Derived Compounds: Pharmacological Mechanisms and Clinical Potential. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 45(8), 6216-6245. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb45080392








