Low, but Not High, Pulsating Fluid Shear Stress Affects Matrix Extracellular Phosphoglycoprotein Expression, Mainly via Integrin β Subunits in Pre-Osteoblasts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Low- and High-PFSS Treatment of Cells
2.3. Cell Morphology
2.4. Integrin Structure
2.5. Gene Expression Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cell Morphology Without/with Low or High PFSS
3.2. Integrin Structure in Cells Without/with Low or High PFSS
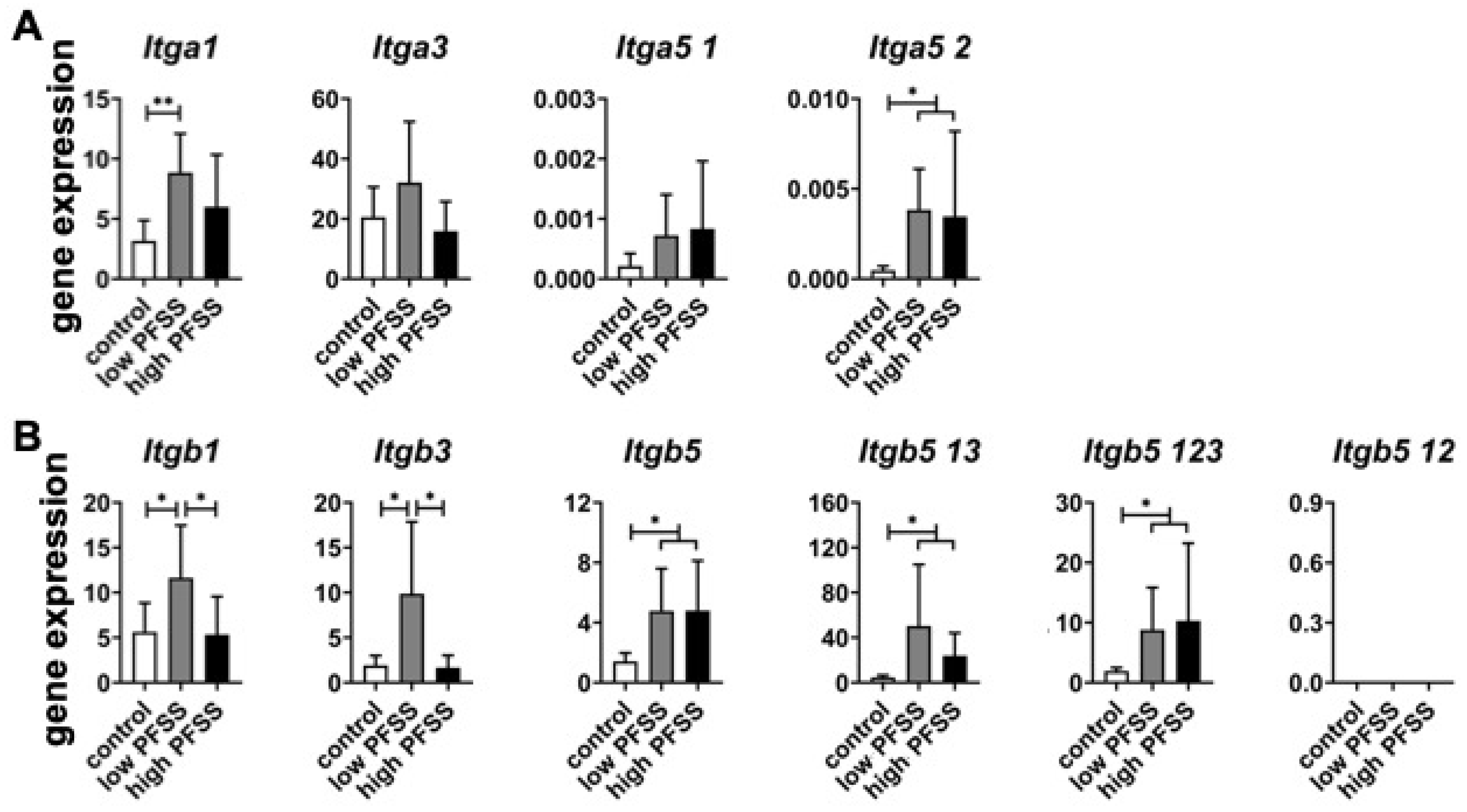
3.3. Integrin α and β Subunit-Related Gene Expression in Cells Without/with Low or High PFSS
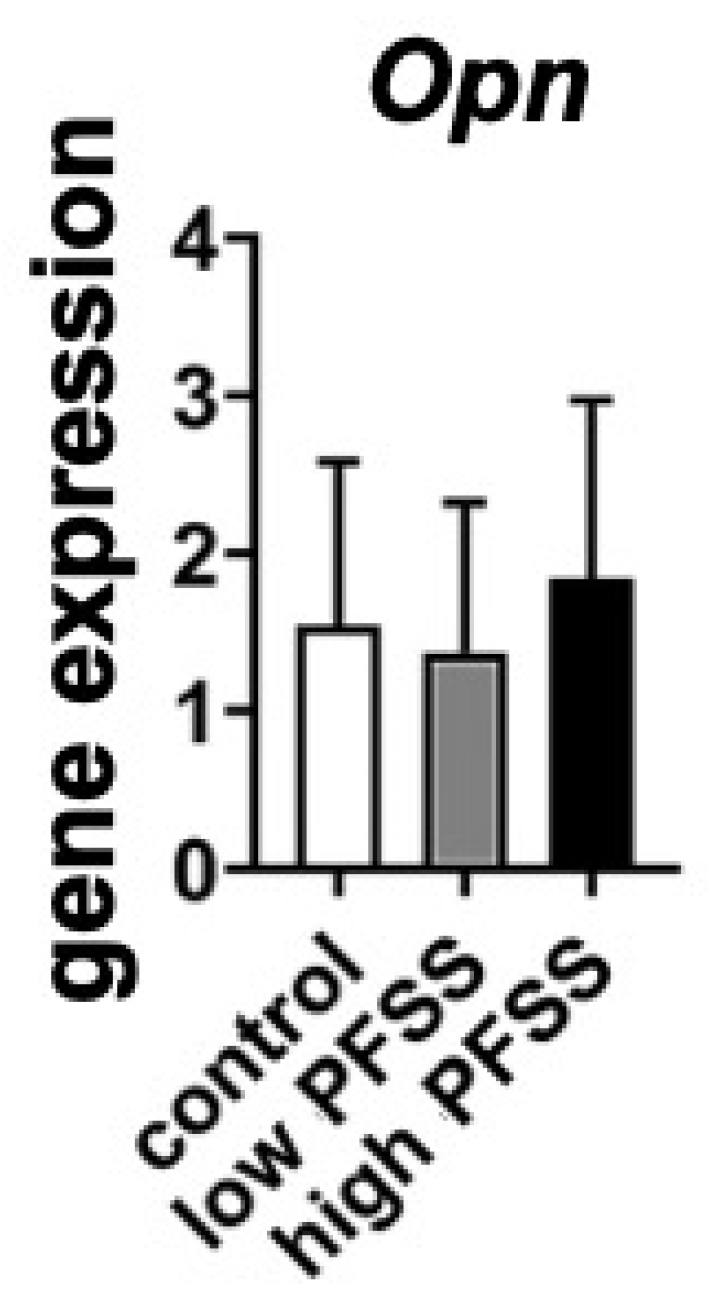
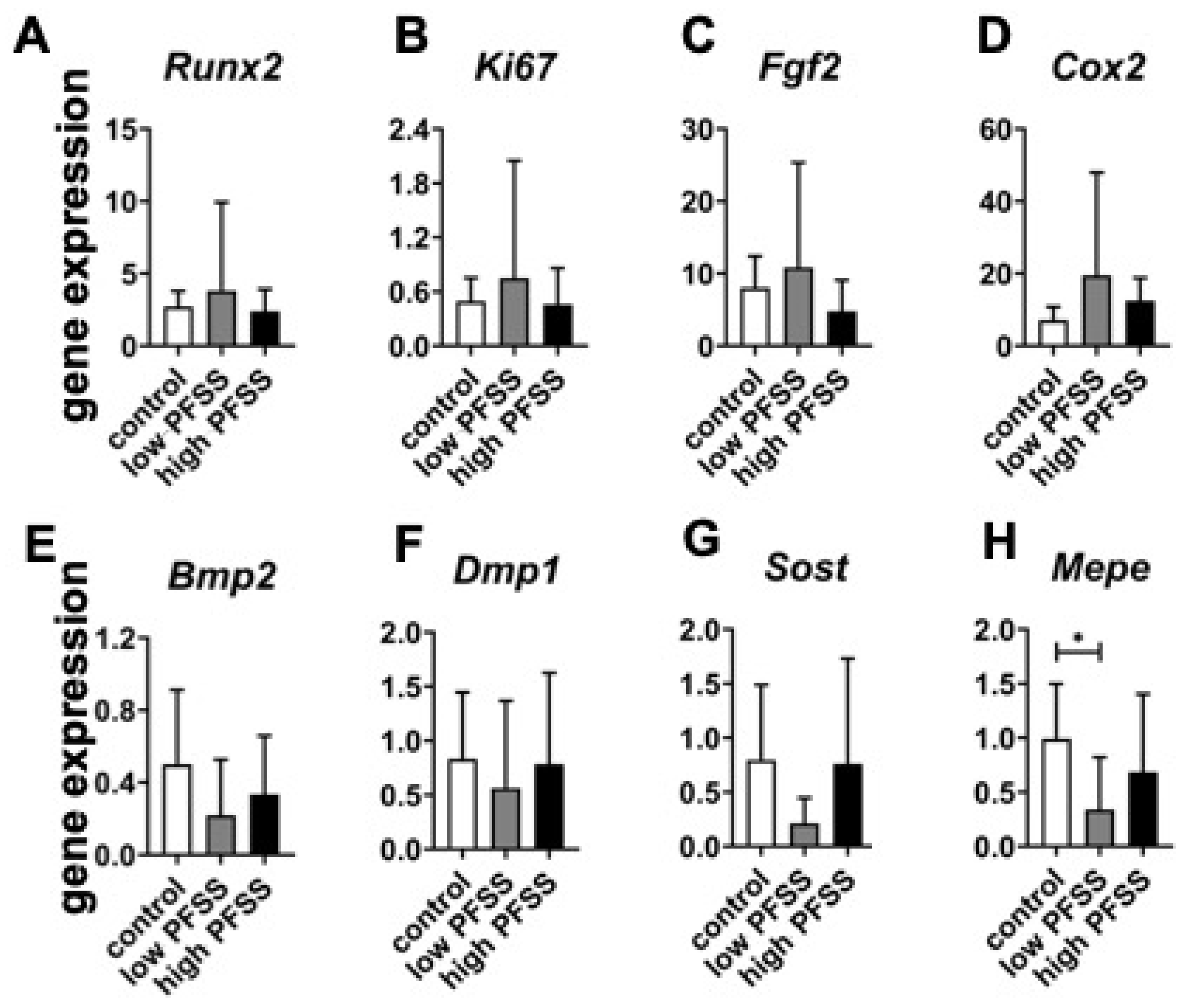
3.4. Osteogenic Differentiation-Related Gene Expression in Cells Without/with Low or High PFSS
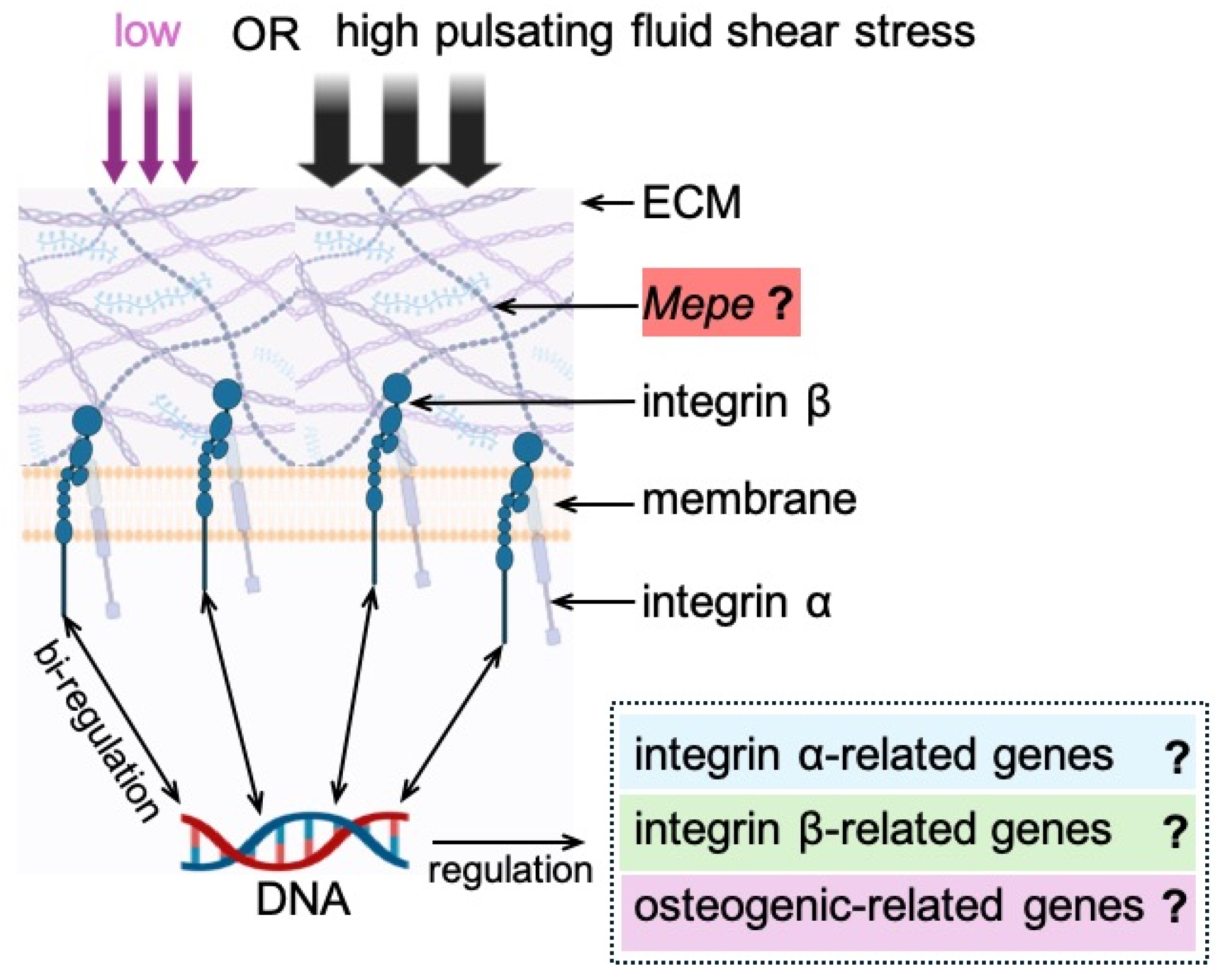
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Klein-Nulend, J.; Bonewald, L.F. The osteocyte. In Principles of Bone Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 133–162. ISBN 9780128148419. [Google Scholar]
- Ozsen, A.; Furman, A.; Guran, T.; Bereket, A.; Turan, S. Fibroblast growth factor-23 and matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein levels in healthy children and, pregnant and puerperal women. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2019, 92, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, T.; Hongo, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Abe, M.; Yoshino, H.; Haraguchi-Kitakamae, M.; Ishizu, H.; Shimizu, T.; Iwasaki, N.; Amizuka, N. Matrix vesicle-mediated mineralization and osteocytic regulation of bone mineralization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, P.S.N.; Kumagai, Y.; Gutierrez, G.; Garrett, I.R.; Blacher, R.; Rosen, D.; Cundy, J.; Navvab, S.; Chen, D.; Drezner, M.K.; et al. MEPE has the properties of an osteoblastic phosphatonin and minhibin. Bone 2004, 34, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.N.; Bakker, A.D.; Everts, V.; Klein-Nulend, J. Inhibition of osteoclastogenesis by mechanically loaded osteocytes: Involvement of MEPE. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2010, 87, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kawashima, N.; Iwata, T.; Xu, J.; Takahashi, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Suda, H. Differentiation of odontoblasts is negatively regulated by MEPE via its C-terminal fragment. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, P.S.N.; Garrett, I.R.; Schwarz, P.M.; Carnes, D.L.; Lafer, E.M.; Mundy, G.R.; Gutierrez, G.E. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) confirms that MEPE binds to PHEX via the MEPE-ASARM motif: A model for impaired mineralization in X-linked rickets (HYP). Bone 2005, 36, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowen, L.C.; Petersen, D.N.; Mansolf, A.L.; Qi, H.; Stock, J.L.; Tkalcevic, G.T.; Simmons, H.A.; Crawford, D.T.; Chidsey-Frink, K.L.; Ke, H.Z.; et al. Targeted disruption of the osteoblast/osteocyte factor 45 gene (Of45) results in increased bone formation and bone mass. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, V.; Martin, A.; Hedge, A.M.; Rowe, P.S.N. Matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein (MEPE) is a new bone renal hormone and vascularization modulator. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 4012–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vordemvenne, T.; Paletta, J.R.; Hartensuer, R.; Pap, T.; Raschke, M.J.; Ochman, S. Cooperative effects in differentiation and proliferation between PDGF-BB and matrix derived synthetic peptides in human osteoblasts. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2011, 12, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashibara, T.; Hiraga, T.; Yi, B.; Nomizu, M.; Kumagai, Y.; Nishimura, R.; Yoneda, T. A synthetic peptide fragment of human MEPE stimulates new bone formation in vitro and in vivo. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2004, 19, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, F.; Ling, J. The effect of matrix extracellular phosphoglycoprotein and its downstream osteogenesis-related gene expression on the proliferation and differentiation of human dental pulp cells. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Six, N.; Septier, D.; Chaussain-Miller, C.; Blachér, R.; DenBésten, P.; Goĺdberg, M. Dentonin, a MEPE fragment initiates pulp-healing response to injury. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nepal, A.K.; van Essen, H.W.; Reijnders, C.M.A.; Lips, P.; Bravenboer, N. Mechanical loading modulates phosphate related genes in rat bone. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282678–e0282689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Chi, S.; Li, Y.; Ling, S.; Tan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, F.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Zhong, G.; et al. The mechanosensitive Piezo1 channel is required for bone formation. eLife 2019, 8, 47454–47478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, D.; Grosse, J.; Wehland, M.; Mann, V.; Reseland, J.E.; Sundaresan, A.; Corydon, T.J. The impact of microgravity on bone in humans. Bone 2016, 87, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vico, L.; Hargens, A. Skeletal changes during and after spaceflight. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, L.; Ge, L.; Pathak, J.L. Osteocyte-mediated translation of mechanical stimuli to cellular signaling and its role in bone and non-bone-related clinical complications. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2020, 18, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlgren, A.; Bratengeier, C.; Semeins, C.M.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Bakker, A.D. Supraphysiological loading induces osteocyte-mediated osteoclastogenesis in a novel in vitro model for bone implant loosening. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, J.L.; Bravenboer, N.; Luyten, F.P.; Verschueren, P.; Lems, W.F.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Bakker, A.D. Mechanical loading reduces inflammation-induced human osteocyte-to-osteoclast communication. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 97, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebben, W.P.; Fauth, M.L.; Kaufmann, C.E.; Petushek, E.J. Magnitude and rate of mechanical loading of a variety of exercise modes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyn-St James, M.; Carroll, S. Meta-analysis of walking for preservation of bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. Bone 2008, 43, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snow-Harter, C.; Bouxsein, M.L.; Lewis, B.T.; Carter, D.R.; Marcus, R. Effects of resistance and endurance exercise on bone mineral status of young women: A randomized exercise intervention trial. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1992, 7, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Bryan, S.J.; Giuliano, C.; Woessner, M.N.; Vogrin, S.; Smith, C.; Duque, G.; Levinger, I. Progressive resistance training for concomitant increases in muscle strength and bone mineral density in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sport. Med. 2022, 52, 1939–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Tu, J.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Z. Effects of mechanical stress stimulation on function and expression mechanism of osteoblasts. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 830722–830734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Seddiqi, H.; Bakker, A.D.; Wu, G.; Verstappen, J.F.M.; Haroon, M.; Korfage, J.A.M.; Zandieh-Doulabi, B.; Werner, A.; Klein-Nulend, J.; et al. Pulsating fluid flow affects pre-osteoblast behavior and osteogenic differentiation through production of soluble factors. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14917–e14934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Chen, Y.; Huang, C.; Song, L.; Liang, Z.; Wei, B. Perception and response of skeleton to mechanical stress. Phys. Life Rev. 2024, 49, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskratsch, T.; Wolfenson, H.; Sheetz, M.P. Appreciating force and shape-the rise of mechanotransduction in cell biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Yao, M.; Cox, C.D. PIEZO1 channels as regulators of integrin-mediated focal adhesions in cardiac fibroblasts. Biophys. J. 2024, 123, 68a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Wang, J.; Yao, M.; Cox, C.D. Joining forces: Crosstalk between mechanosensitive PIEZO1 ion channels and integrin-mediated focal adhesions. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2023, 51, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommerenke, H.; Schmidt, C.; Dürr, F.; Nebe, B.; Lüthen, F.; Müller, P.; Rychly, J. The mode of mechanical integrin stressing controls intracellular signaling in osteoblasts. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2002, 17, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, H.; Yang, C.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Meng, S.; Liu, R.; Huang, L.; Yang, K. Research progress on the regulatory mechanism of integrin-mediated mechanical stress in cells involved in bone metabolism. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18183–e18199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; He, T.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Z.; Lin, S.; Gao, H.; et al. Osteocyte β1 integrin loss causes low bone mass and impairs bone mechanotransduction in mice. J. Orthop. Transl. 2022, 34, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, J.D.; Byron, A.; Humphries, M.J. Integrin ligands at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 3901–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; He, X.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xie, R.; Liu, Z.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, N.; Xiang, Q.; Cui, Y. Targeting integrin pathways: Mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, s41392–s41433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, J.; Petre, B.M.; Walz, T.; Springer, T.A. Global conformational rearrangements in integrin extracellular domains in outside-in and inside-out signaling. Cell 2002, 110, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchanawong, P.; Calderwood, D.A. Organization, dynamics and mechanoregulation of integrin-mediated cell–ECM adhesions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, A.D.; Soejima, K.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Burger, E.H. The production of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 by primary bone cells is shear stress dependent. J. Biomech. 2001, 34, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacabac, R.G.; Smit, T.H.; Mullender, M.G.; Dijcks, S.J.; Van Loon, J.J.W.; Klein-Nulend, J. Nitric oxide production by bone cells is fluid shear stress rate dependent. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 315, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacabac, R.G.; Smit, T.H.; Cowin, S.C.; Van Loon, J.J.W.A.; Nieuwstadt, F.T.M.; Heethaar, R.; Klein-Nulend, J. Dynamic shear stress in parallel-plate flow chambers. J. Biomech. 2005, 38, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Jaspers, R.T.; Wu, G.; Korfage, J.A.M.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Bakker, A.D. Shear stress modulates osteoblast cell and nucleus morphology and volume. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezval, M.; Biblis, M.; Sehmisch, S.; Schmelz, U.; Kolios, L.; Rack, T.; Stuermer, K.M.; Stuermer, E.K. Improvement of femoral bone quality after low-magnitude, high-frequency mechanical stimulation in the ovariectomized rat as an osteopenia model. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2011, 88, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardinier, J.D.; Majumdar, S.; Duncan, R.L.; Wang, L. Cyclic hydraulic pressure and fluid flow differentially modulate cytoskeleton re-organization in MC3T3 osteoblasts. Cell Mol. Bioeng. 2009, 2, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarry, J.G.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Prendergast, P.J. The effect of cytoskeletal disruption on pulsatile fluid flow-induced nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 release in osteocytes and osteoblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 330, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroon, M.; Boers, H.E.; Bakker, A.D.; Bloks, N.G.C.; Hoogaars, W.M.H.; Giordani, L.; Musters, R.J.P.; Deldicque, L.; Koppo, K.; Le Grand, F.; et al. Reduced growth rate of aged muscle stem cells is associated with impaired mechanosensitivity. Aging 2022, 14, 28–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Guo, S.S.; Fässler, R. Integrin-mediated mechanotransduction. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 215, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, H.B.; Fässler, R. Mechanosensitivity and compositional dynamics of cell–matrix adhesions. EMBO Rep. 2013, 14, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.D.; de Vries, T.J.; Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M.; Semeins, C.M.; Everts, V.; Klein-Nulend, J. Osteocytes subjected to fluid flow inhibit osteoclast formation and bone resorption. Bone 2007, 41, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezu-Ndubuisi, O.J.; Maheshwari, A. The role of integrins in inflammation and angiogenesis. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, E.M.; Brahme, N.N.; Calderwood, D.A. Integrin cytoplasmic tail interactions. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Hua, R.; Riquelme, M.A.; Cheng, H.; Guda, T.; Xu, H.; Gu, S.; Jiang, J.X. Osteocytes regulate bone anabolic response to mechanical loading in male mice via activation of integrin α5. Bone Res. 2022, 10, s41413–s41425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, J.H.; Cook, A.A.; Hynes, R.O. An interaction between αvβ8 integrin and Band 4.1B via a highly conserved region of the Band 4.1 C-terminal domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13479–13483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins. Cell 2002, 110, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Leftheris, K. Insights into protein–ligand interactions in integrin complexes: Advances in structure determinations. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 5675–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaib, A.; Motan, D.; Bhattacharya, P.; McNabb, A.; Skerry, T.M.; Lacroix, D. Heterogeneity in the mechanical properties of integrins determines mechanotransduction dynamics in bone osteoblasts. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13113–13126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurakawa, T.; Kakutani, K.; Morita, Y.; Kato, Y.; Yurube, T.; Hirata, H.; Miyazaki, S.; Terashima, Y.; Maeno, K.; Takada, T.; et al. Functional impact of integrin α5β1 on the homeostasis of intervertebral discs: A study of mechanotransduction pathways using a novel dynamic loading organ culture system. Spine J. 2015, 15, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Chen, W.; Masson, A.; Li, Y.-P. Cell signaling and transcriptional regulation of osteoblast lineage commitment, differentiation, bone formation, and homeostasis. Cell Discov. 2024, 10, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, W.N.; Masica, D.L.; Gray, J.J.; McKee, M.D. Phosphorylation-dependent inhibition of mineralization by osteopontin ASARM peptides is regulated by PHEX cleavage. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2010, 25, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Weimer, D.A.; Agans, S.C.; Bain, S.D.; Gross, T.S. Low-magnitude mechanical loading becomes osteogenic when rest is inserted between each load cycle. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2002, 17, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, J.; Zandieh-Doulabi, B. Low, but Not High, Pulsating Fluid Shear Stress Affects Matrix Extracellular Phosphoglycoprotein Expression, Mainly via Integrin β Subunits in Pre-Osteoblasts. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 12428-12441. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46110738
Jin J, Zandieh-Doulabi B. Low, but Not High, Pulsating Fluid Shear Stress Affects Matrix Extracellular Phosphoglycoprotein Expression, Mainly via Integrin β Subunits in Pre-Osteoblasts. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(11):12428-12441. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46110738
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Jianfeng, and Behrouz Zandieh-Doulabi. 2024. "Low, but Not High, Pulsating Fluid Shear Stress Affects Matrix Extracellular Phosphoglycoprotein Expression, Mainly via Integrin β Subunits in Pre-Osteoblasts" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 11: 12428-12441. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46110738
APA StyleJin, J., & Zandieh-Doulabi, B. (2024). Low, but Not High, Pulsating Fluid Shear Stress Affects Matrix Extracellular Phosphoglycoprotein Expression, Mainly via Integrin β Subunits in Pre-Osteoblasts. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(11), 12428-12441. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46110738






