Endocrine and Transcriptome Changes Associated with Testicular Growth and Differentiation in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Fish Material and Rearing Conditions
2.3. Sampling
2.4. Testis Histology and Blood Steroid Hormones
2.5. Microarray
2.6. Calculations
3. Results
3.1. Biometrics, Morphology, and Testis Histology
3.2. Serum Hormones and Pituitary Gene Expression
3.3. Testis Transcriptome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schulz, R.W.; de França, L.R.; Lareyre, J.J.; Le Gac, F.; Chiarini-Garcia, H.; Nobrega, R.H.; Miura, T. Spermatogenesis in fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 390–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safian, D.; Bogerd, J.; Schulz, R.W. Regulation of spermatogonial development by Fsh: The complementary roles of locally produced Igf and Wnt signaling molecules in adult zebrafish testis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 284, 113244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, T.; Tanaka, M. Gonadal development in fish. Sex. Dev. 2014, 8, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe, M.C.; Grier, H.J.; Mejía-Roa, V. Comparative testicular structure and spermatogenesis in bony fishes. Spermatogenesis 2014, 4, e983400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Shen, Q.; Wong, F.M.; Xu, H.; Hong, N.; Zeng, L.; Liu, L.; Wei, Q.; Hong, Y. Germ cell sex prior to meiosis in the rainbow trout. Protein Cell 2011, 2, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okutsu, T.; Suzuki, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Yoshizaki, G. Testicular germ cells can colonize sexually undifferentiated embryonic gonad and produce functional eggs in fish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dziewulska, K.; Domagała, J. Histology of salmonid testes during maturation. Reprod. Biol. 2003, 3, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ytrestøyl, T.; Hjelle, E.; Kolarevic, J.; Takle, H.; Rebl, A.; Afanasyev, S.; Krasnov, A.; Brunsvik, P.; Terjesen, B.F. Photoperiod in recirculation aquaculture systems and timing of seawater transfer affect seawater growth performance of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J. World Aquac. Soc. 2022, 54, 73–95. [Google Scholar]
- Fjelldal, P.G.; Hansen, T.; Huang, T.-S. Continuous light and elevated temperature can trigger maturation both during and immediately after smoltification in male Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 2011, 321, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kadri, S.; Mitchell, D.F.; Metcalfe, N.B.; Huntingford, F.A.; Thorpe, J.E. Differential patterns of feeding and resource accumulation in maturing and immature Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar. Aquaculture 1996, 142, 245–257. [Google Scholar]
- Aksnes, A.; Gjerde, B.; Roald, S.O. Biological, chemical and organoleptic changes during maturation of farmed Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar. Aquaculture 1986, 53, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utter, F.M.; Johnson, O.W.; Thorgaard, G.H.; Rabinovitch, P.S. Measurement and potential applications of induced triploidy in Pacific salmon. Aquaculture 1983, 35, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, D.; O’Donovan, V.; O’Maoiléidigh, N.; Rogan, G.; Roche, N.; Wilkins, N. An evaluation of the use of triploid Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) in minimising the impact of escaped farmed salmon on wild populations. Aquaculture 2000, 186, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, E.; Schulz, R.W.; Almeida, F.; Kleppe, L.; Skaftnesmo, K.O.; Kjærner-Semb, E.; Crespo, D.; Fjelldal, P.G.; Hansen, T.J.; Norberg, B.; et al. Loss of Fshr Prevents Testicular Maturation in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). Endocrinology 2024, 165, bqae013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleppe, L.; Edvardsen, R.B.; Furmanek, T.; Andersson, E.; Skaftnesmo, K.O.; Segafredo, F.T.; Wargelius, A. Transcriptomic analysis of dead end knockout testis reveals germ cell and gonadal somatic factors in Atlantic salmon. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tveiten, H.; Karlsen, K.; Thesslund, T.; Johansson, G.S.; Thiyagarajan, D.B.; Andersen, Ø. Impact of germ cell ablation on the activation of the brain-pituitary-gonadal axis in precocious Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) males. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2022, 89, 471–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleppe, L.; Edvardsen, R.B.; Furmanek, T.; Andersson, E.; Juanchich, A.; Wargelius, A. bmp15l, figla, smc1bl, and larp6l are preferentially expressed in germ cells in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2017, 84, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, F.L.; Skaftnesmo, K.O.; Andersson, E.; Kleppe, L.; Edvardsen, R.B.; Norberg, B.; Fjelldal, P.G.; Hansen, T.J.; Schulz, R.W.; Wargelius, A. The Piwil1 N domain is required for germ cell survival in Atlantic salmon. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 977779. [Google Scholar]
- Yano, A.; von Schalburg, K.; Cooper, G.; Koop, B.F.; Yoshizaki, G. Identification of a molecular marker for type A spermatogonia by microarray analysis using gonadal cells from pvasa-GFP transgenic rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2009, 76, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, D.; Bogerd, J.; Sambroni, E.; LeGac, F.; Andersson, E.; Edvardsen, R.B.; Bergman, E.J.; Björnsson, B.T.; Taranger, G.L.; Schulz, R.W. The initiation of puberty in Atlantic salmon brings about large changes in testicular gene expression that are modulated by the energy status. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M.; Sato, M.; Iwasaki, Y.; Terasawa, M.; Tashiro, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Katayama, N.; Sadaie, S.; Miwa, M.; Yoshizaki, G. Combining next-generation sequencing with microarray for transcriptome analysis in rainbow trout gonads. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2012, 79, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolland, A.D.; Lardenois, A.; Goupil, A.-S.; Lareyre, J.-J.; Houlgatte, R.; Chalmel, F.; Le Gac, F. Profiling of androgen response in rainbow trout pubertal testis: Relevance to male gonad development and spermatogenesis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambroni, E.; Rolland, A.D.; Lareyre, J.-J.; Le Gac, F. FSH and LH have common and distinct effects on gene expression in rainbow trout testis. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 50, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kortner, T.M.; Afanasyev, S.; Koppang, E.O.; Bjørgen, H.; Krogdahl, Å.; Krasnov, A. A comprehensive transcriptional body map of Atlantic salmon unveils the vital role of the intestine in the immune system and highlights functional specialization within its compartments. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024, 146, 109422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skjold, V.; Rørvik, K.-A.; Sveen, L.; Burgerhout, E.; Mota, V.C.; Weihe, R.; Ytrestøyl, T.; Bou, M.; Jacobsen, H.J.; Allaoui, G.; et al. Gradually decreasing daylength after smoltification induced by “winter signal “reduced sexual maturation in male Atlantic salmon. Front. Aquac. 2024, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnov, A.; Timmerhaus, G.; Afanasyev, S.; Jørgensen, S.M. Development and assessment of oligonucleotide microarrays for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2011, 6, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugars, G.; Schmitz, M. Expression of gonadotropin and gonadotropin receptor genes during early sexual maturation in male Atlantic salmon parr. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2008, 75, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, U.; Harris, R.M.; Jameson, J.L. Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in subjects with DAX1 mutations. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 346, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, E.; Borg, B.; Lambert, J.G. Aromatase activity in brain and pituitary of immature and mature Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) parr. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1988, 72, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazeto, Y.; Ijiri, S.; Matsubara, H.; Adachi, S.; Yamauchi, K. Molecular cloning and characterization of 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/Delta5-Delta4 isomerase cDNAs from Japanese eel ovary. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 85, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rand-Weaver, M.; Swanson, P.; Kawauchi, H.; Dickhoff, W.W. Somatolactin, a novel pituitary protein: Purification and plasma levels during reproductive maturation of coho salmon. J. Endocrinol. 1992, 133, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorson, J.F.; Heidorn, N.L.; Ryu, V.; Czaja, K.; Nonneman, D.J.; Barb, C.R.; Hausman, G.J.; Rohrer, G.A.; Prezotto, L.D.; McCosh, R.B.; et al. Relationship of neuropeptide FF receptors with pubertal maturation of gilts. Biol. Reprod. 2017, 96, 617–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajareddy, S.; Reddy, P.; Du, C.; Liu, L.; Jagarlamudi, K.; Tang, W.; Shen, Y.; Berthet, C.; Peng, S.L.; Kaldis, P.; et al. p27kip1 (cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B) controls ovarian development by suppressing follicle endowment and activation and promoting follicle atresia in mice. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 2189–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamin, A.; Wiebe, M.S. Barrier to Autointegration Factor (BANF1): Interwoven roles in nuclear structure, genome integrity, innate immunity, stress responses and progeria. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 34, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, X.-S.; Ouyang, Y.-C.; Hou, Y.; Schatten, H.; Sun, Q.-Y. RNA-associated protein LSM family member 14 controls oocyte meiotic maturation through regulating mRNA pools. J. Reprod. Dev. 2017, 63, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, L. Egg white proteins. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 1991, 100, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöcker, W.; Karmilin, K.; Hildebrand, A.; Westphal, H.; Yiallouros, I.; Weiskirchen, R.; Dietzel, E.; Floehr, J.; Jahnen-Dechent, W. Mammalian gamete fusion depends on the inhibition of ovastacin by fetuin-B. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloch, A.R.; Franěk, R.; Saito, T.; Pšenička, M. Dead-end (dnd) protein in fish-a review. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 47, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, D.; Heisenberg, C.P. Zebrafish gastrulation: Putting fate in motion. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2020, 136, 343–375. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Cui, Z.; Shao, C.; Chen, S. Expression analysis and characterization of zglp1 in the Chinese tongue sole (Cynoglossus semilaevis). Gene 2019, 683, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, F.; King, M.L. Repressive translational control in germ cells. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2013, 80, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellaiche, J.; Lareyre, J.-J.; Cauty, C.; Yano, A.; Allemand, I.; Le Gac, F. Spermatogonial stem cell quest: nanos2, marker of a subpopulation of undifferentiated A spermatogonia in trout testis. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 90, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benayoun, B.A.; Dipietromaria, A.; Bazin, C.; Veitia, R.A. FOXL2: At the crossroads of female sex determination and ovarian function. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 665, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cocquet, J.; De Baere, E.; Gareil, M.; Pannetier, M.; Xia, X.; Fellous, M.; Veitia, R. Structure, evolution and expression of the FOXL2 transcription unit. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2003, 101, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasala, C.; Carré-Eusèbe, D.; Picard, J.Y.; Rey, R. Subcellular and molecular mechanisms regulating anti-Müllerian hormone gene expression in mammalian and nonmammalian species. DNA Cell Biol. 2004, 23, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfennig, F.; Standke, A.; Gutzeit, H.O. The role of Amh signaling in teleost fish—Multiple functions not restricted to the gonads. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 223, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, R.S.; Strüssmann, C.A.; Fernandino, J.I.; Somoza, G.M. Genotypic sex determination in teleosts: Insights from the testis-determining amhy gene. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 192, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Guan, G.J.; Hong, Y.H. Insights of sex determination and differentiation from medaka as a teleost model. Yi Chuan 2017, 39, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yano, A.; Guyomard, R.; Nicol, B.; Jouanno, E.; Quillet, E.; Klopp, C.; Cabau, C.; Bouchez, O.; Fostier, A.; Guiguen, Y. An immune-related gene evolved into the master sex-determining gene in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, T.; Endo, M.; Hirono, I.; Takashima, F.; Aoki, T. Differential expression and cellular localization of activin and inhibin mRNA in the rainbow trout ovary and testis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2002, 125, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudo, S.; Kuwabara, Y.; Park, J.I.; Hsu, S.Y.; Hsueh, A.J. Heterodimeric fly glycoprotein hormone-alpha2 (GPA2) and glycoprotein hormone-beta5 (GPB5) activate fly leucine-rich repeat-containing G protein-coupled receptor-1 (DLGR1) and stimulation of human thyrotropin receptors by chimeric fly GPA2 and human GPB5. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3596–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Cueto, J.A.; Zmora, N.; Paullada-Salmerón, J.A.; Marvel, M.; Mañanos, E.; Zohar, Y. The gonadotropin-releasing hormones: Lessons from fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2020, 291, 113422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielian, P.S.; Hess, R.A.; Lees, J.A. E2f4 and E2f5 are essential for the development of the male reproductive system. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Bonasio, R.; Strino, F.; Kluger, Y.; Holloway, J.K.; Modzelewski, A.J.; Cohen, P.E.; Reinberg, D. SFMBT1 functions with LSD1 to regulate expression of canonical histone genes and chromatin-related factors. Genes. Dev. 2013, 27, 749–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Fu, K.; Yin, H.; Cui, Y.; Yue, Q.; Li, W.; Cheng, L.; Tan, H.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; et al. Sox30 initiates transcription of haploid genes during late meiosis and spermiogenesis in mouse testes. Development 2018, 145, dev164855, Erratum in Development 2019, 146, dev179978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Ki, B.S.; Hong, K.-H.; Park, S.-P.; Ko, J.-J.; Choi, Y. Tudor Domain Containing Protein TDRD12 Expresses at the Acrosome of Spermatids in Mouse Testis. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 29, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajakumar, A.; Senthilkumaran, B. Steroidogenesis and its regulation in teleost—A review. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 46, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.T.; Ham, S.; Jeon, S.; Kim, Y.; Oh, S.; Cho, C. Expression of uncharacterized male germ cell-specific genes and discovery of novel sperm-tail proteins in mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajaddini Mahani, S.; Behnam, B.; Abbassi, M.; Asgari, H.; Nazmara, Z.; Shirinbayan, P.; Joghataei, M.; Koruji, M. Tsga10 expression correlates with sperm profiles in the adult formalin-exposed mice. Andrologia 2016, 48, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churcher, A.M.; Pujolar, J.M.; Milan, M.; Hubbard, P.C.; Martins, R.S.; Saraiva, J.L.; Huertas, M.; Bargelloni, L.; Patarnello, T.; Marino, I.A.; et al. Changes in the gene expression profiles of the brains of male European eels (Anguilla anguilla) during sexual maturation. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciani, E.; von Krogh, K.; Nourizadeh-Lillabadi, R.; Mayer, I.; Fontaine, R.; Weltzien, F.-A. Sexual maturation in Atlantic salmon male parr may be triggered both in late summer and early spring under standard farming conditions. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 737086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, C.D.; Kidd, K.A.; Sumpter, J.P.; Leatherland, J.; Woo, P. Chemically induced alterations to gonadal differentiation in fish. Fish Dis. Disord. Non-Infect. Disord. 2010, 2, 144–165. [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone, R.; Simpson, T.; Youngson, A. Sex reversal in salmonid culture. Aquaculture 1978, 13, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
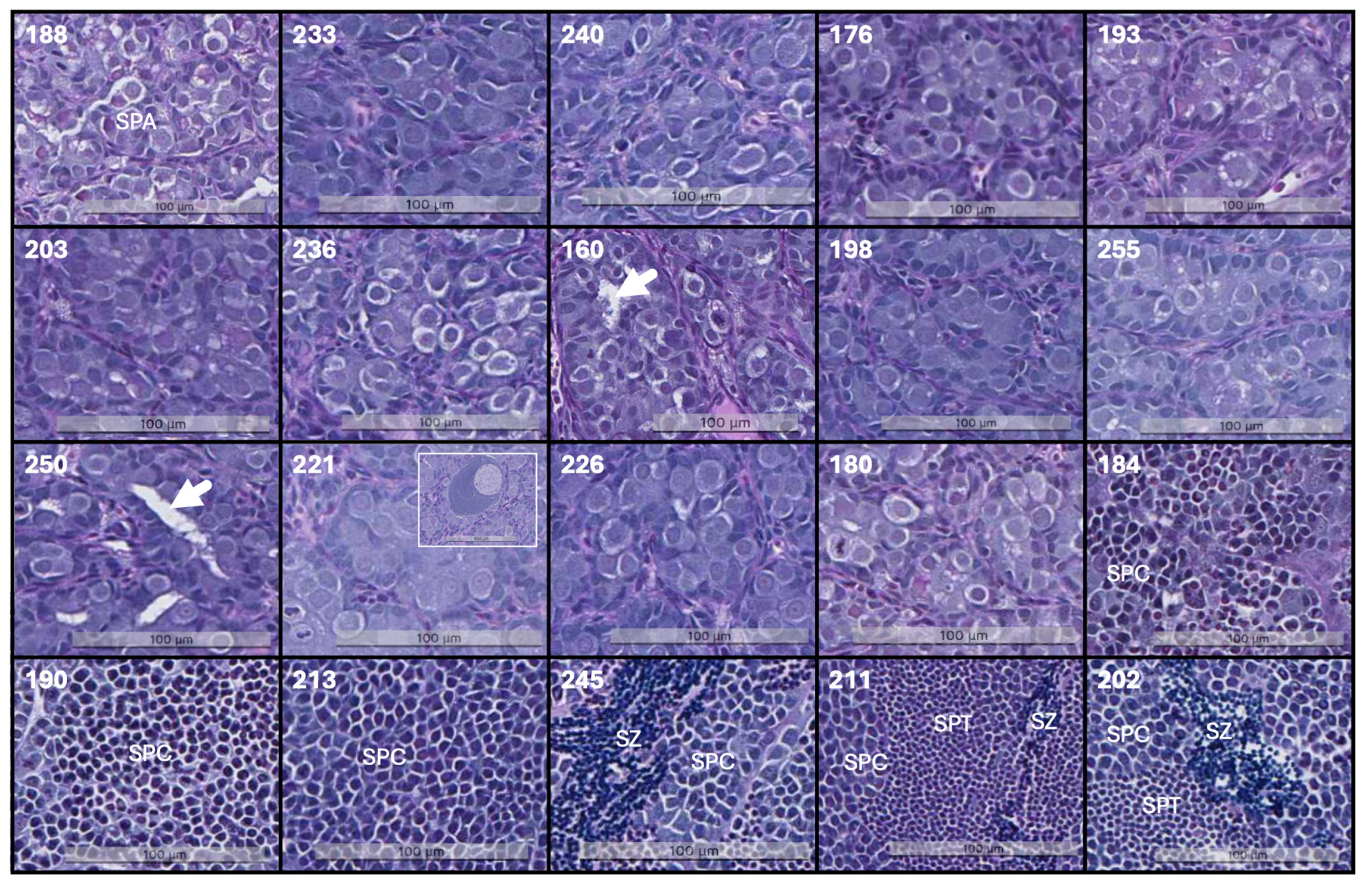

| FISH ID | Stage (I–V)/Most Advanced Cell Type | Stage (I–V)/Dominating Germ Cell Type | Size of Germinative Compartments | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 188 | I/SPA | I/SPA | Small (<80 μm) | |
| 233 | I/SPA | I/SPA | Small (<80 μm) | |
| 240 | I/SPA | I/SPA | Small (<80 μm) | |
| 176 | I/SPA | I/SPA | Small (<80 μm) | |
| 193 | I/SPA | I/SPA | Small (<80 μm) | |
| 203 | I/SPA | I/SPA | Medium (80–140 μm) | tubules, high cell division |
| 236 | I/SPA | I/SPA | Small (<80 μm) | |
| 160 | I/SPA | I/SPA | Medium (80–140 μm) | tubules, high cell division |
| 198 | I/SPA | I/SPA | Small (<80 μm) | oocytes |
| 255 | I/SPA | I/SPA | Small (<80 μm) | oocytes |
| 250 | I/SPA | I/SPA | Small (<80 μm) | |
| 221 | I/SPA | I/SPA | Small (<80 μm) | oocytes |
| 226 | I/SPA | I/SPA | Small (<80 μm) | |
| 180 | I/SPA | I/SPA | Small (<80 μm) | |
| 184 | IV/SPT | II/SPB | Medium (80–140 μm) | |
| 190 | IV/SPT | III/SPC | Large (43–500 μm) | |
| 213 | III/SC | III/SPC | Large (43–500 μm) | |
| 245 | V/SZ | III/SPC | Large (43–500 μm) | |
| 211 | V/SZ | III/SPC | Large (43–500 μm) | |
| 202 | V/SZ | III/SPC | Large (43–500 μm) |
| Genes | All | Gonad-Specific | % Gonad-Specific |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSA | 3524 | 584 | 16.6 |
| LSA | 4268 | 214 | 5.0 |
| Total | 7792 | 798 | 10.2 |
| Functional Group | Genes Number | Gonad-Specific LSA/HSA | Mean Fold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell cycle | 239 | 5/70 | 1.8 |
| Chromosome | 212 | 1/58 | 2.1 |
| DNA repair | 38 | 0/16 | 2.7 |
| Cilia | 83 | 1/59 | 3.8 |
| Antigen presentation | 84 | 0/0 | −4.3 |
| Chemokine | 20 | 0/1 | −4.1 |
| Antiviral | 211 | 0/0 | −3.8 |
| Complement | 40 | 2/1 | −4.0 |
| Immunglobulins | 40 | 0/0 | −8.2 |
| Lymphocyte | 111 | 0/0 | −3.4 |
| Secreted proteins | 25 | 7/1 | −3.1 |
| Endocrine | 70 | 11/4 | −2.2 |
| Growth factors | 84 | 4/3 | −2.6 |
| Differentiation | 255 | 9/8 | −2.2 |
| Differetiation-hox | 59 | 9/2 | −2.5 |
| Angiogenesis | 34 | 0/1 | −3.1 |
| Bone, cartilage | 28 | 3/2 | −2.8 |
| Neural | 200 | 10/3 | −2.2 |
| Epithelium | 26 | 0/3 | −2.5 |
| Extracellular matrix | 101 | 2/7 | −2.6 |
| Collagens | 66 | 3/1 | −2.5 |
| Gene | Fold |
|---|---|
| Apopolysialoglycoprotein | −5.5 |
| Barrier-to-autointegration factor (banf) | −4.4 |
| Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B-like (p27kip1) | −7.8 |
| Cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-binding 1 (cpebp1) | −3.6 |
| Fetuin-B-like | −4.5 |
| Glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase | −3.3 |
| Late histone H2A.2.2-like | −2.1 |
| LIM homeobox 8a | −3.4 |
| Oocyte-specific histone RNA stem-loop-binding 2 | −2.1 |
| Ovostatin-like (8 genes) | −4.7 |
| P43 5S RNA-binding protein-like (2 genes) | −4.2 |
| LSM14 homolog B-like (lsm14b) | −2.0 |
| Zona pellucida sperm-binding 3-like (zp3, 5 genes) | −13.5 |
| Zona pellucida sperm-binding 4-like (zp4, 4 genes) | −6.8 |
| Gene | Fold |
|---|---|
| Dead end protein 1 (dnd) | −2.5 |
| Nanos homolog 2-like | −6.8 |
| GATA-type zinc finger protein 1 (zglp1) | −3.5 |
| Nodal homolog (2 genes) | −13.2 |
| Anti-mullerian hormone (amh) | −25.3 |
| Gonadal somatic cell-derived factor (gsdf) | −5.7 |
| Interferon regulatory factor 9 (irf9) | −73.2 |
| Forkhead box protein L2-like (foxl2) | −5.4 |
| LIM homeobox 2b | −2.0 |
| LIM homeobox 8a | −3.4 |
| Inhibin beta A chain (2 genes) | −6.5 |
| Inhibin, alpha | −4.1 |
| Androgen receptor | −4.4 |
| Progesterone receptor | −4.9 |
| Follicle stimulating hormone receptor | −7.0 |
| GABA receptor subunit alpha-2 | −20.9 |
| Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2C | −8.6 |
| Metabotropic glutamate receptor 8-like | −3.3 |
| Glycoprotein hormone alpha-2 | 4.6 |
| E2F transcription factor 4 | 2.9 |
| Furin-like | 3.2 |
| Progonadoliberin-1 isoform 2 | 6.0 |
| Protein boule-like | 3.7 |
| Scm-like with four MBT protein 1 (sfmbt1) | 2.2 |
| Transcription factor SOX-30 | 6.8 |
| Tudor domain containing 12 (tdrd12) | 3.1 |
| Gene | Fold |
|---|---|
| 25-hydroxycholesterol 7-alpha-hydroxylase | −2.4 |
| 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase | −4.2 |
| 3-oxo-5-beta-steroid 4-dehydrogenase | −4.0 |
| Corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase isozyme 2 | −5.0 |
| Cytochrome P450 1B1-like | −2.3 |
| Cytochrome P450, family 17A1 | −5.4 |
| Dehydrogenase/reductase SDR family 11 | −2.8 |
| Hydroxysteroid 11-beta dehydrogenase 2 | −6.0 |
| Hydroxysteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase 1-like | 4.2 |
| Gene | Fold |
|---|---|
| Flagella, motility | |
| Cilia and flagella associated protein 61 | 7.9 |
| Dynein heavy chain 10, axonemal | 8.6 |
| Dynein light chain 4, axonemal | 9.4 |
| Male germ cell-associated kinase | 7.0 |
| Primary cilia formation | 8.3 |
| Radial spoke head protein 6 homolog A | 7.9 |
| Ropporin-1-like | 8.2 |
| Sperm associated antigen 16 | 10.1 |
| Sperm flagellar protein 2-like | 9.1 |
| Sperm-associated antigen 6 | 8.3 |
| WD repeat-containing protein 96 | 7.4 |
| Meiosis | |
| HORMA domain-containing protein 1 | 17.0 |
| Meiotic recombination protein DMC1/LIM15 | 12.0 |
| Meiotic recombination protein REC114-like | 13.3 |
| Meiotic recombination protein SPO11 | 7.1 |
| Minichromosome maintenance domain 2 | 7.1 |
| SHC SH2-domain binding protein 1-like | 15.3 |
| Spermatogenesis-associated protein 22-like | 7.7 |
| Synaptonemal complex central element 1 | 11.1 |
| Synaptonemal complex protein 3 like | 8.3 |
| Zebrafish testis-expressed 38 | 7.0 |
| Zinc finger protein 541-like | 7.4 |
| Various roles | |
| MORN repeat-containing protein (morn) | 7.5 |
| Sodium/hydrogen exchanger 10-like (slc9a10) | 7.6 |
| Testis-specific gene 10 protein | 6.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skjold, V.; Afanasyev, S.; Burgerhout, E.; Sveen, L.; Rørvik, K.-A.; Mota, V.F.C.N.; Dessen, J.-E.; Krasnov, A. Endocrine and Transcriptome Changes Associated with Testicular Growth and Differentiation in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 5337-5351. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060319
Skjold V, Afanasyev S, Burgerhout E, Sveen L, Rørvik K-A, Mota VFCN, Dessen J-E, Krasnov A. Endocrine and Transcriptome Changes Associated with Testicular Growth and Differentiation in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(6):5337-5351. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060319
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkjold, Vetle, Sergey Afanasyev, Erik Burgerhout, Lene Sveen, Kjell-Arne Rørvik, Vasco Felipe Cardoso Neves Mota, Jens-Erik Dessen, and Aleksei Krasnov. 2024. "Endocrine and Transcriptome Changes Associated with Testicular Growth and Differentiation in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.)" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 6: 5337-5351. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060319
APA StyleSkjold, V., Afanasyev, S., Burgerhout, E., Sveen, L., Rørvik, K.-A., Mota, V. F. C. N., Dessen, J.-E., & Krasnov, A. (2024). Endocrine and Transcriptome Changes Associated with Testicular Growth and Differentiation in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(6), 5337-5351. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46060319





