Could Gas6/TAM Axis Provide Valuable Insights into the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Clinical Manifestation of SSc
1.2. Complications of SSc
1.3. Pathogenesis of SSc
1.3.1. Vascular Injury
1.3.2. Inflammation
1.3.3. Activation of Fibroblasts
1.3.4. Autoantibodies in SSc
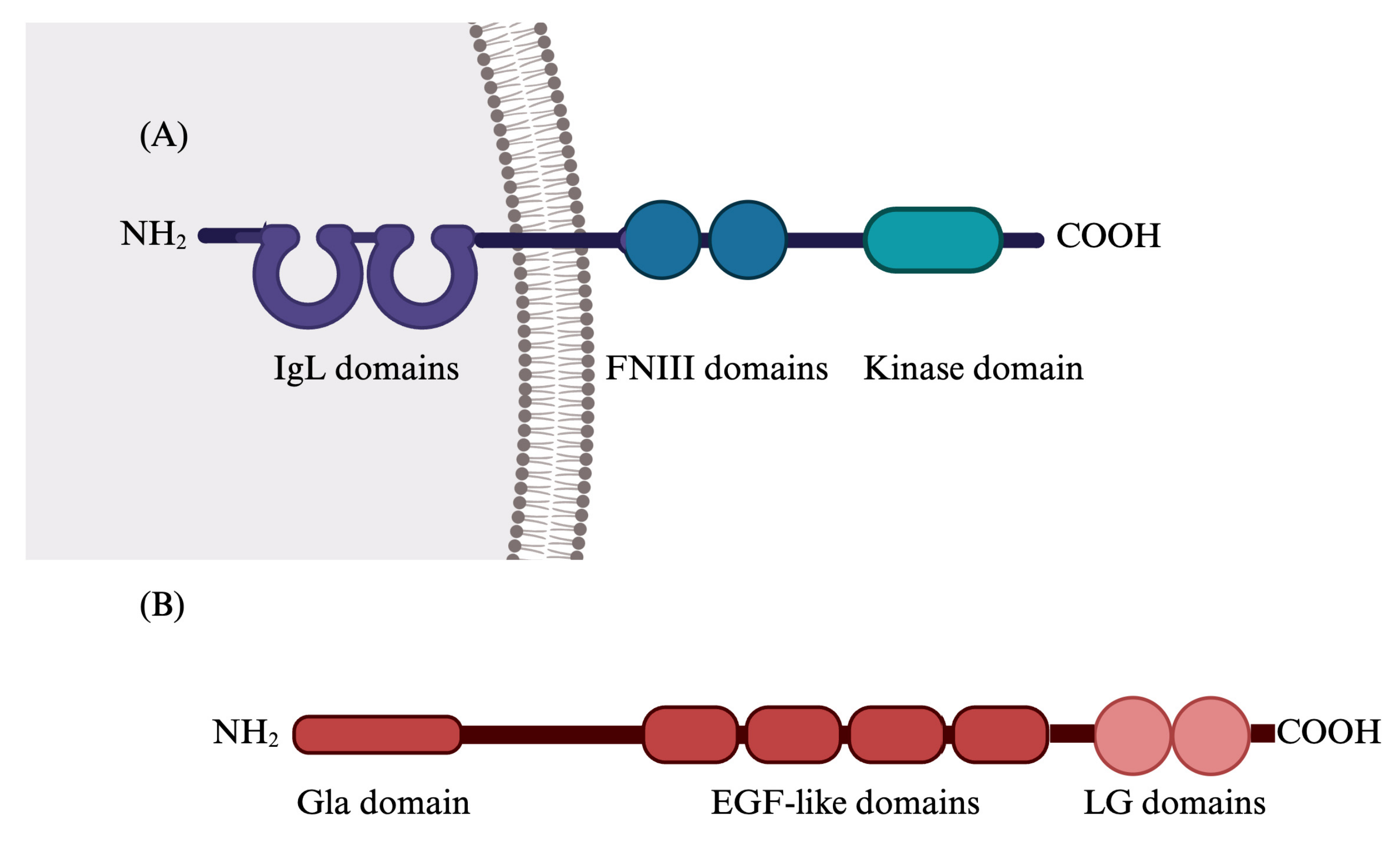
2. Gas6/TAM System
2.1. Gas6/TAM System’s Functions
2.2. Gas6/TAM System in Human Diseases
2.2.1. Gas6/TAM in Cancer
2.2.2. Gas6/TAM System in Liver Diseases
2.2.3. Gas6/TAM System in Lung Diseases
2.2.4. Gas6/TAM System in Infectious Diseases
2.2.5. Gas6/TAM System in Cardiovascular Diseases
2.2.6. Gas6/TAM System in Rheumatic Diseases
2.3. Gas6/TAM System in Systemic Sclerosis
3. Treatment of SSc
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbot, S.; Bossingham, D.; Proudman, S.; de Costa, C.; Ho-Huynh, A. Risk Factors for the Development of Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2018, 2, rky041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamasco, A.; Hartmann, N.; Wallace, L.; Verpillat, P. Epidemiology of Systemic Sclerosis and Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhai, M.; Meune, C.; Boubaya, M.; Avouac, J.; Hachulla, E.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; Riemekasten, G.; Airò, P.; Joven, B.; Vettori, S.; et al. Mapping and Predicting Mortality from Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.; Scirè, C.A.; Talarico, R.; Airo, P.; Alexander, T.; Allanore, Y.; Bruni, C.; Codullo, V.; Dalm, V.; De Vries-Bouwstra, J.; et al. Systemic Sclerosis: State of the Art on Clinical Practice Guidelines. RMD Open 2018, 4, e000782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra-Sepúlveda, A.; Esquinca-González, A.; Benavides-Suárez, S.A.; Sordo-Lima, D.E.; Caballero-Islas, A.E.; Cabral-Castañeda, A.R.; Rodríguez-Reyna, T.S. Systemic Sclerosis Pathogenesis and Emerging Therapies, beyond the Fibroblast. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 4569826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemke, G. Biology of the TAM Receptors. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a009076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothlin, C.V.; Ghosh, S.; Zuniga, E.I.; Oldstone, M.B.A.; Lemke, G. TAM Receptors Are Pleiotropic Inhibitors of the Innate Immune Response. Cell 2007, 131, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Lemke, G. Homeostatic Regulation of the Immune System by Receptor Tyrosine Kinases of the Tyro 3 Family. Science 2001, 293, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ma, Z.; Hu, W.; Wang, D.; Gong, B.; Fan, C.; Jiang, S.; Li, T.; Gao, J.; Yang, Y. Molecular Insights of Gas6/TAM in Cancer Development and Therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaradat, S.K.; Ayoub, N.M.; Al Sharie, A.H.; Aldaod, J.M. Targeting Receptor Tyrosine Kinases as a Novel Strategy for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 23, 15330338241234780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, A.L.; Assassi, S.; Denton, C.P. Skin Involvement in Early Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis: An Unmet Clinical Need. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2022, 18, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderkötter, C.; Riemekasten, G. Pathophysiology and Clinical Consequences of Raynaud’s Phenomenon Related to Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, A.L. The Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment of Raynaud Phenomenon. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Yafawi, R.; Knauft, M.E.; Stokem, K.; Palminteri, J.M.; Wirth, J.A. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Encycl. Cardiovasc. Res. Med. 2018, 1–4, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherbeck, N.; Tamby, M.C.; Bussone, G.; Dib, H.; Perros, F.; Humbert, M.; Mouthon, L. The Role of Inflammation and Autoimmunity in the Pathophysiology of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 44, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussone, G.; Mouthon, L. Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolewski, P.; Maślińska, M.; Wieczorek, M.; Łagun, Z.; Malewska, A.; Roszkiewicz, M.; Nitskovich, R.; Szymańska, E.; Walecka, I. Systemic Sclerosis—Multidisciplinary Disease: Clinical Features and Treatment. Reumatologia 2019, 57, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, A.U.; Steen, V.; Valentini, G. Pulmonary Complications: One of the Most Challenging Complications of Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2009, 48 (Suppl. S3), 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, J.E.; Denton, C.P.; Johnson, S.R.; Fernandez-Codina, A.; Hudson, M.; Nevskaya, T. State-of-the-Art Evidence in the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.; O’reilly, S. The Immunopathogenesis of Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 195, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doridot, L.; Jeljeli, M.; Chêne, C.; Batteux, F. Implication of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis via Inflammation, Autoimmunity and Fibrosis. Redox Biol. 2019, 25, 101122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraemer, R.; Birrer, P.; Schöni, M.H. Dose-Response Relationships and Time Course of the Response to Systemic Beta Adrenoreceptor Agonists in Infants with Bronchopulmonary Disease. Thorax 1988, 43, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randone, S.B.; Guiducci, S.; Cerinic, M.M. Systemic Sclerosis and Infections. Autoimmun. Rev. 2008, 8, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablo-Moreno, J.A.D.; Serrano, L.J.; Revuelta, L.; Sánchez, M.J.; Liras, A. The Vascular Endothelium and Coagulation: Homeostasis, Disease, and Treatment, with a Focus on the Von Willebrand Factor and Factors VIII and V. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Ladner, U.; Distler, O.; Ibba-Manneschi, L.; Neumann, E.; Gay, S. Mechanisms of Vascular Damage in Systemic Sclerosis. Autoimmunity 2009, 42, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Liu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zou, P.; Xiao, R. Further Insight into Systemic Sclerosis from the Vasculopathy Perspective. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 166, 115282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Noviani, M.; Chellamuthu, V.R.; Albani, S.; Low, A.H.L. The Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis: The Origin of Fibrosis and Interlink with Vasculopathy and Autoimmunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabquer, B.J.; Hou, Y.; Del Galdo, F.; Kenneth, H.G.; Gerber, M.L.; Jimenez, S.A.; Seibold, J.R.; Koch, A.E. The Proadhesive Phenotype of Systemic Sclerosis Skin Promotes Myeloid Cell Adhesion via ICAM-1 and VCAM-1. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glauzy, S.; Olson, B.; May, C.K.; Parisi, D.; Massad, C.; Hansen, J.E.; Ryu, C.; Herzog, E.L.; Meffre, E. Defective Early B Cell Tolerance Checkpoints in Patients With Systemic Sclerosis Allow the Production of Self Antigen–Specific Clones. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worrell, J.C.; O’Reilly, S. Bi-Directional Communication: Conversations between Fibroblasts and Immune Cells in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 113, 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bon, L.; Popa, C.; Huijbens, R.; Vonk, M.; York, M.; Simms, R.; Hesselstrand, R.; Wuttge, D.M.; Lafyatis, R.; Radstake, T.R.D.J. Distinct Evolution of TLR-Mediated Dendritic Cell Cytokine Secretion in Patients with Limited and Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, Y. Cytokines Involved in the Pathogenesis of SSc and Problems in the Development of Anti-Cytokine Therapy. Cells 2021, 10, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, B.; Brembilla, N.C.; Chizzolini, C. Interplay between Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts: A Systematic Review Providing a New Angle for Understanding Skin Fibrotic Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truchetet, M.E.; Brembilla, N.C.; Chizzolini, C. Current Concepts on the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 64, 262–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihn, H. Scleroderma, Fibroblasts, Signaling, and Excessive Extracellular Matrix. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2005, 7, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbane, A.J.; Denton, C.P.; Holme, A.M. Scleroderma Pathogenesis: A Pivotal Role for Fibroblasts as Effector. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, J.; Abraham, D. Systemic Sclerosis: A Prototypic Multisystem Fibrotic Disorder. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, S.; Jones, R.E.; Huang, G.-Q.; Gay, R.E. Immunohistologic Demonstration of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor (PDGF) and Sis-Oncogene Expression in Scleroderma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1989, 92, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynn, T.A.; Ramalingam, T.R. Mechanisms of Fibrosis: Therapeutic Translation for Fibrotic Disease. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, D. New Insights into Fibrosis from the ECM Degradation Perspective: The Macrophage-MMP-ECM Interaction. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi, Y.; Takehara, K. Anti-Nuclear Autoantibodies in Systemic Sclerosis: News and Perspectives. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2018, 3, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, M.; Hudson, M.; Bentow, C.; Roup, F.; Beretta, L.; Pilar Simeón, C.; Guillén-Del-Castillo, A.; Casas, S.; Fritzler, M.J. Autoantibodies to Stratify Systemic Sclerosis Patients into Clinically Actionable Subsets. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruganandam, M.; Ariza-hutchinson, A.; Patel, R.A.; Sibbitt, W.L., Jr. Biomarkers in the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 4633–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavazzana, I.; Vojinovic, T.; Airo, P.; Fredi, M.; Ceribelli, A.; Pedretti, E. Systemic Sclerosis—Specific Antibodies: Novel and Classical Biomarkers. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 64, 412–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Maggio, G.; Confalonieri, P.; Salton, F.; Trotta, L.; Ruggero, L.; Kodric, M.; Geri, P.; Hughes, M.; Bellan, M.; Gilio, M.; et al. Biomarkers in Systemic Sclerosis: An Overview. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 7775–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsunomiya, A.; Oyama, N.; Hasegawa, M. Potential Biomarkers in Systemic Sclerosis: A Literature Review and Update. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wermuth, P.J.; Piera-velazquez, S.; Jimenez, S.A. Identification of Novel Systemic Sclerosis Biomarkers Employing Aptamer Proteomic Analysis. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehra, S.; Walker, J.; Patterson, K.; Fritzler, M.J. Autoimmunity Reviews Autoantibodies in Systemic Sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 12, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jury, E.C.; Morrow, W.J.W. Leaders Autoantibodies and Overlap Syndromes in Autoimmune Rheumatic Disease. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 54, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, R.J.; Antonicelli, F. Autoantibodies Associated with Connective Tissue Diseases: What Meaning for Clinicians? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linger, R.M.A.; Keating, A.K.; Earp, H.S.; Graham, D.K. TAM Receptor Tyrosine Kinases: Biologic Functions, Signaling, and Potential Therapeutic Targeting in Human Cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2008, 100, 35–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfioletti, G.; Brancolini, C.; Avanzi, G.; Schneider, C. The Protein Encoded by a Growth Arrest-Specific Gene (Gas6) Is a New Member of the Vitamin K-Dependent Proteins Related to Protein S, a Negative Coregulator in the Blood Coagulation Cascade. Mol. Cell Biol. 1993, 13, 4976–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biology, R.T.; Davra, V.; Kimani, S.G.; Calianese, D.; Birge, R.B. Ligand Activation of TAM Family and Therapeutic Response. Cancers 2016, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, M.R.; Chen, J.; Hammonds, R.G.; Sadick, M.; Godowsk, P.J. Characterization of Gas6, a Member of the Superfamily of G Domain-Containing Proteins, as a Ligand for Rse and Axl. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 9785–9790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, K.; Ohashi, K.; Arita, H.; Zong, C.; Hanafusa, H.; Mizuno, K.; Hanafusa, H.; Mizuno, K. Cell Biology and Metabolism: Identification of the Product of Growth Arrest-specific Gene 6 as a Common Ligand for Axl, Sky, and Mer Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 30022–30027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, T.; Knyazev, P.G.; Clout, N.J.; Cheburkin, Y.; Ullrich, A.; Timpl, R.; Hohenester, E. Structural Basis for Gas6—Axl Signalling. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, I.N. Mechanisms of Activation of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases: Monomers or Dimers. Cells 2014, 3, 304–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J. Review Cell Signaling by Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Cell 2010, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorp, E.; Vaisar, T.; Subramanian, M.; Mautner, L.; Blobel, C.; Tabas, I. Shedding of the Mer Tyrosine Kinase Receptor Is Mediated by ADAM17 Protein through a Pathway Involving Reactive Oxygen Species, Protein Kinase Cδ, and P38 Mitogen- Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK). J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 33335–33344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orme, J.J.; Du, Y.; Vanarsa, K.; Mayeux, J.; Li, L.; Arriens, C.; Min, S.; Hutcheson, J.; Davis, L.S.; Chong, B.F.; et al. Heightened Cleavage of Axl Receptor Tyrosine Kinase by ADAM Metalloproteases May Contribute to Disease Pathogenesis in SLE. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 169, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurance, S.; Lemarié, C.A.; Blostein, M.D. Growth Arrest-Specific Gene6 (Gas6) and Vascular Hemostasis. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2012, 3, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutusaus, A.; Marí, M.; Ortiz-Pérez, J.T.; Nicolaes, G.A.F.; Morales, A.; García de Frutos, P. Role of Vitamin K-Dependent Factors Protein S and GAS6 and TAM Receptors in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19-Associated Immunothrombosis. Cells 2020, 9, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Fernández, L.; Bellido-Martín, L.; De Frutos, P.G. Growth Arrest-Specific Gene 6 (GAS6): An Outline of Its Role in Haemostasis and Inflammation. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 100, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, L.A.; Graham, D.K.; Di Paola, J.; Branchford, B.R. GAS6/TAM Pathway Signaling in Hemostasis and Thrombosis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelillo-scherrer, A.; Burnier, L.; Flores, N.; Savi, P.; Demol, M.; Schaeffer, P.; Herbert, J.; Lemke, G.; Goff, S.P.; Matsushima, G.K.; et al. Role of Gas6 Receptors in Platelet Signaling during Thrombus Stabilization and Implications for Antithrombotic Therapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaragno, M.G.; Cavet, M.E.; Yan, C.; Tai, L.; Jin, Z.; Haendeler, J.; Berk, B.C. Gas6 Inhibits Apoptosis in Vascular Smooth Muscle: Role of Axl Kinase and Akt. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2004, 37, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolo, D.; Ferreira, L.L.; Di Tizio, A.; Ruaro, B.; Patrucco, F.; Bellan, M. A Review: The Potential Involvement of Growth Arrest-Specific 6 and Its Receptors in the Pathogenesis of Lung Damage and in Coronavirus Disease 2019. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothlin, C.V.; Carrera-silva, E.A.; Bosurgi, L.; Ghosh, S. TAM Receptor Signaling in Immune Homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 355–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alciato, F.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Sola, D.; Castello, L.; Avanzi, G.C. TNF-Alpha, IL-6, and IL-1 Expression Is Inhibited by GAS6 in Monocytes/Macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolino, M.; Penninger, J.M. The Role of TAM Family Receptors in Immune Cell Function: Implications for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2016, 8, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, T.; Zhang, Y. Toll-like Receptor-Mediated Inhibition of Gas 6 and ProS Expression Facilitates Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Mouse Macrophages. Immunology 2011, 135, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstyn-, T.; Fresia, C.R. TAM Receptors in Phagocytosis: Beyond the Mere Internalization of Particles. Immunol. Rev. 2023, 319, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, H.A.; Maylock, C.A.; Williams, J.A.; Paweletz, C.P.; Shu, H.; Shacter, E. Serum-Derived Protein S Binds to Phosphatidylserine and Stimulates the Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Cells. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrotra, P.; Ravichandran, K.S. Drugging the Efferocytosis Process: Concepts and Opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 601–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, C.; Ding, A. Review Nonresolving Inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahebkar, A. The Role of Efferocytosis in Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.R. The Clearance of Dead Cells by Efferocytosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avanzi, G.C.; Gallicchio, M.; Bottarel, F.; Gammaitoni, L.; Cavalloni, G.; Buonfiglio, D.; Bragardo, M.; Bellomo, G.; Albano, E.; Fantozzi, R.; et al. GAS6 Inhibits Granulocyte Adhesion to Endothelial Cells. Blood 1998, 91, 2334–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collett, G.; Wood, A.; Alexander, M.Y.; Varnum, B.C.; Boot-handford, R.P.; Ohanian, V.; Ohanian, J.; Fridell, Y.; Canfield, A.E. Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Axl Modulates the Osteogenic Differentiation of Pericytes. Circ. Res. 2003, 92, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaragno, M.G.; Wuthrich, D.A.; Poppa, V.; Gill, D.; Lindner, V.; Berk, B.C.; Corson, M.A. Increased Expression of Axl Tyrosine Kinase after Vascular Injury and Regulation by G Protein-Coupled Receptor Agonists in Rats. Circ. Res. 1998, 83, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Xuan, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, R.; Jin, H.; Dong, H. How Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotype Switching Contributes to Vascular Disease. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 2, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanbasic, I.; Cuerquis, J.; Varnum, B.; Blostein, M.D. Intracellular Signaling Pathways Involved in Gas6-Axl-Mediated Survival of Endothelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2004, 4, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjwa, M.; Bellido-martin, L.; Lin, Y.; Lutgens, E.; Delesque-touchard, N.; Herve, C.; Moura, R.; Billiau, A.D.; Aparicio, C.; Levi, M.; et al. Gas6 Promotes Inflammation by Enhancing Interactions between Endothelial Cells, Platelets, and Leukocytes. Blood 2016, 111, 4096–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Park, H.; Woo, S.; Park, E.; Kang, J.L. RhoA/Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B/Mitogen- Activated Protein Kinase Signaling after Growth Arrest—Specific Protein 6/Mer Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Engagement Promotes Epithelial Cell Growth and Wound Repair via Upregulation of Hepatocyte Growth Factor in Macrophages. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 350, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.L. Gas6 Prevents Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Alveolar Epithelial Cells via Production of PGE2, PGD2 and Their Receptors. Cells 2019, 6, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellan, M.; Cittone, M.G.; Tonello, S.; Rigamonti, C.; Castello, L.M.; Gavelli, F.; Pirisi, M.; Sainaghi, P.P. Gas6/TAM System: A Key Modulator of the Interplay between Inflammation and Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Chun, T. Anti-Inflammatory Role of Tam Family of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases via Modulating Macrophage Function. Mol. Cells 2019, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárcena, C.; Stefanovic, M.; Tutusaus, A.; Joannas, L.; Menéndez, A.; García-ruiz, C.; Sancho-bru, P.; Caballeria, J.; Rothlin, C.V.; Fernández-checa, J.C.; et al. Gas6/Axl Pathway Is Activated in Chronic Liver Disease and Its Targeting Reduces Fibrosis via Hepatic Stellate Cell Inactivation. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirne, C.; Rigamonti, C.; De Benedittis, C.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Bellan, M.; Burlone, M.E.; Castello, L.M.; Avanzi, G.C. Review Article Gas6/TAM Signaling Components as Novel Biomarkers of Liver Fibrosis. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 2304931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.; Dongiovanni, P.; Corey, K.E.; Birge, R.B.; Valenti, L.; Cai, B.; Dongiovanni, P.; Corey, K.E.; Wang, X.; Shmarakov, I.O.; et al. Macrophage MerTK Promotes Liver Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Article Macrophage MerTK Promotes Liver Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2019, 31, 406–421.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.; Xu, X.; Yu, Q.; Yang, X.; He, J.; Tang, X.X. Elevated Expression of Macrophage MERTK Exhibits Profibrotic Effects and Results in Defective Regulation of Efferocytosis Function in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; He, J.; Li, Y. Novel Therapeutic Targets in Liver Fibrosis. Front. Mol. B 2021, 8, 766855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellan, M.; Pogliani, G.; Marconi, C.; Minisini, R.; Franzosi, L.; Alciato, F.; Magri, A.; Avanzi, G.C.; Pirisi, M.; Sainaghi, P.P. Gas6 as a Putative Noninvasive Biomarker of Hepatic Fibrosis. Biomarks Med. 2016, 6, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, S.; Gilchrist, S.E.; Hafizi, S. Gas6 Induces Myelination through Anti-Inflammatory IL-10 and TGF-β Upregulation in White Matter and Glia. Cells 2020, 9, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Nikolic-paterson, D.J.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-β: The Master Regulator of Fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankin, E.B.; Fuh, K.C.; Taylor, T.E.; Krieg, A.J.; Musser, M.; Yuan, J.; Wei, K.; Kuo, C.J.; Longacre, T.A.; Giaccia, A.J. AXL Is an Essential Factor and Therapeutic Target for Metastatic Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 6, 7570–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linger, R.M.A.; Cohen, R.A.; Cummings, C.T.; Sather, S.; Middleton, D.H.G.; Lu, X.; Baro, A.E. Mer or Axl Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition Promotes Apoptosis, Blocks Growth and Enhances Chemosensitivity of Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncogene 2012, 32, 3420–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Png, K.J.; Halberg, N.; Yoshida, M.; Tavazoie, S.F. A MicroRNA Regulon That Mediates Endothelial Recruitment and Metastasis by Cancer Cells. Nature 2012, 481, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosurgi, L.; Bernink, J.H.; Delgado, V.; Gagliani, N.; Joannas, L.; Schmid, E.T. Paradoxical Role of the Proto-Oncogene Axl and Mer Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Colon Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13091–13096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, J.; Couderc, G.; Tarte, K.; Jourdan, M.; Requirand, G.; Delteil, M. Identifying Intercellular Signaling Genes Expressed in Malignant Plasma Cells by Using Complementary DNA Arrays. Blood 2016, 98, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.K.; Salzberg, D.B.; Kurtzberg, J.; Sather, S.; Matsushima, G.K.; Keating, A.K.; Lovell, M.A.; Williams, S.A.; Dawson, T.L.; Schell, M.J.; et al. Human Cancer Biology Ectopic Expression of the Proto-Oncogene Mer in Pediatric T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 2662–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.M.; Greenwade, M.M.; Palisoul, M.L.; Opara, G.; Massad, K.; Guo, L.; Zhao, P.; Beck-noia, H.; Hagemann, I.S.; Hagemann, R.; et al. Therapeutic Inhibition of the Receptor Tyrosine Kinase AXL Improves Sensitivity to Platinum and Taxane in Ovarian Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 18, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straten, P. TAM Receptor Inhibition-Implications for Cancer and the Immune System. Cancers 2021, 13, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstyn-Cohen, T.; Maimon, A. TAM Receptors, Phosphatidylserine, Inflammation, and Cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.K.; Deryckere, D.; Davies, K.D.; Earp, H.S. The TAM Family: Phosphatidylserine Sensing Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Gone Awry in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 769–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Tian, R.; Yong, B.; Luo, C.; Tan, P.; Shen, J.; Peng, T. Gas6/Axl Mediates Tumor Cell Apoptosis, Migration and Invasion and Predicts the Clinical Outcome of Osteosarcoma Patients. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 435, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ma, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, W.; Deng, C.; Jiang, S.; Li, T.; Chen, F. Targeting Gas6/TAM in Cancer Cells and Tumor Microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, A.E.J.; Le, J.P.; Sather, S.; Pernu, B.M.; Graham, D.K.; Pierce, A.M.; Keating, A.K. Mer Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition Impedes Glioblastoma Multiforme Migration and Alters Cellular Morphology. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4171–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, K.; Shieh, Y.; Lee, C.; Shiah, S.; Wu, C. Axl Promotes Cell Invasion by Inducing MMP-9 Activity through Activation of NF- j B and Brg-1. Oncogene 2008, 27, 4044–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wang, H.; Logsdon, C.D.; Rashid, A.; Fleming, J.B. Overexpression of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Axl Promotes Tumor Cell Invasion and Survival in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2011, 117, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z.; Ding, S. The Crosstalk Between Tumor- Associated Macrophages (TAMs) and Tumor Cells and the Corresponding Targeted Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 590941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, R.; Valls, A.F.; Yerbes, R.; Von Richter, S.; Almodovar, D.; Ulrich, A.; Schmidt, T. TAM Receptors Tyro3 and Mer as Novel Targets in Colorectal Cancer. Oncotarget 1991, 7, 56355–56370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimani, S.G.; Kumar, S.; Bansal, N.; Singh, K.; Kholodovych, V.; Comollo, T.; Peng, Y.; Kotenko, S.V.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Bertino, J.R.; et al. Small Molecule Inhibitors Block Gas6-Inducible TAM Activation and Tumorigenicity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep43908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, K.V.; Amend, S.R.; Pienta, K.J. Targeting Tyro3, Axl and MerTK (TAM Receptors): Implications for Macrophages in the Tumor Microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.J.W.; Rahbech, A. FOCUSSED RESEARCH REVIEW TAM—Ing T Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment: Implications for TAM Receptor Targeting. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Zhang, W.; Menachof, K.K.; Hill, A.A.; Rinella, S.; Kirkpatrick, G.; Page, L.S.; Stashko, M.A.; Jordan, C.T.; Wei, Q.; et al. Efficacy of a Mer and Flt3 Tyrosine Kinase Small Molecule Inhibitor, UNC1666, in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6722–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minson, K.A.; Smith, C.C.; DeRyckere, D.; Libbrecht, C.; Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Huey, M.G.; Lasater, E.A.; Kirkpatrick, G.D.; Stashko, M.A.; Zhang, W.; et al. The MERTK/FLT3 Inhibitor MRX-2843 Overcomes Resistance-Conferring FLT3 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e85630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, Y.B.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, C.G.; Hong, M.H.; Kim, H.R.; Cho, B.C.; Lim, S.M. The Development of AXL Inhibitors in Lung Cancer: Recent Progress and Challenges. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 811247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Siemann, D.W. Therapeutic Targeting of the Gas6/Axl Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zang, H.; Wen, Q.; Fan, S. AXL in Cancer: A Modulator of Drug Resistance and Therapeutic Target. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, O.; Geng, A.; Flint, E.; Singanayagam, A.; Ercan, C.; Possamai, L.; Patel, V.C.; Kuenzler, P.; Meier, M.; Soysal, S.; et al. AXL Expression on Homeostatic Resident Liver Macrophages Is Reduced in Cirrhosis Following GAS6 Production by Hepatic Stellate Cells. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 16, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrich, V.; Breitenecker, K.; Djerlek, L.; Ortmayr, G.; Mikulits, W. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Control of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by TAM Receptors. Cancers 2021, 13, 5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metastasis, L.; Cedex, V.; Siba, S. Association of SIBA Treatment and a Met—Depleted Diet Inhibits in Vltro Growth and in Vivo Metastatic Spread of Experimenta l Tumor Cell Lines. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 1988, 6, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutusaus, A.; De Frutos, P.G.; Morales, A. Genetic and Clinical Data Reinforce the Role of GAS6 and TAM Receptors in Liver Fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 983–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolo, D.; Ferreira, L.L.; Vincenzi, F.; Vercellino, N.; Minisini, R.; Latini, F.; Ferrari, B.; Burlone, M.E.; Pirisi, M.; Bellan, M. From MASH to HCC: The Role of Gas6/TAM Receptors. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1332818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llacuna, L.; Bárcena, C.; Bellido-Martín, L.; Fernández, L.; Stefanovic, M.; Marí, M.; García-Ruiz, C.; Fernández-Checa, J.C.; García de Frutos, P.M.A. Growth Arrest-Specific Protein 6 Is Hepatoprotective against Murine Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Hepatology 2011, 52, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafdil, F.; Deveaux, V.; Zafrani, E.; Mavier, P.; Nakano, T.; Laperche, Y.; Brouillet, A. Growth Arrest-Specific Protein 6 Deficiency Impairs Liver Tissue Repair after Acute Toxic Hepatitis in Mice. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallat, A.; Lotersztajn, S. Cellular Mechanisms of Tissue Fibrosis. 5. Novel Insights into Liver Fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2013, 305, C789–C799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastore, M.; Caligiuri, A.; Raggi, C.; Navari, N.; Piombanti, B.; Di Maira, G.; Rovida, E.; Piccinni, M.P.; Lombardelli, L.; Logiodice, F.; et al. Macrophage MerTK Promotes Profibrogenic Cross-Talk with Hepatic Stellate Cells via Soluble Mediators. JHEP Rep. 2022, 4, 100444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, K.; Yan, Z.; Xia, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, L.; Zou, Q. Axl Expression Stratifies Patients with Poor Prognosis after Hepatectomy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espindola, M.S.; Habiel, D.M.; Narayanan, R.; Jones, I.; Coelho, A.L.; Murray, L.A.; Jiang, D.; Noble, P.W.; Hogaboam, C.M. Targeting of TAM Receptors Ameliorates Fibrotic Mechanisms in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujino, N.; Kubo, H.; Maciewicz, R.A. Phenotypic Screening Identifies Axl Kinase as a Negative Regulator of an Alveolar Epithelial Cell Phenotype. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 97, 1047–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Wu, C.; Lin, J.; Peng, S.; Lee, C. Gas6/Axl Signaling Attenuates Alveolar Inflammation in Ischemia-Reperfusion- Induced Acute Lung Injury by up-Regulating SOCS3-Mediated Pathway. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, A.; Rello, S.R.; Cristóbal, H.; Fiz-López, A.; Arribas, E.; Marí, M.; Tutusaus, A.; de la Cal-Sabater, P.; Nicolaes, G.A.F.; Ortiz-Pérez, J.T.; et al. Growth Arrest-Specific Factor 6 (Gas6) Is Increased in Covid-19 Patients and Predicts Clinical Outcome. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonello, S.; Rizzi, M.; Matino, E.; Costanzo, M.; Casciaro, G.F.; Croce, A.; Rizzi, E.; Zecca, E.; Pedrinelli, A.; Vassia, V.; et al. Baseline Plasma Gas6 Protein Elevation Predicts Adverse Outcomes in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 1568352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolo, D.; Onghia, D.D.; Tonello, S.; Minisini, R.; Baricich, A.; Gramaglia, C.; Patrucco, F.; Zeppegno, P.; Acquaviva, A.; Balbo, P.E.; et al. Decreased Gas6 and SAxl Plasma Levels Are Associated with Hair Loss in COVID-19 Survivors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 2019, 6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Qiu, Z.; Hou, Y.; Deng, X.; Xu, W.; Zheng, T.; Wu, P.; Xie, S. AXL Is a Candidate Receptor for SARS-CoV-2 That Promotes Infection of Pulmonary and Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vago, J.P.; Amaral, F.A.; van de Loo, F.A.J. Resolving Inflammation by TAM Receptor Activation. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 227, 107893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhaddou, M.; Memon, D.; Meyer, B.; White, K.M.; Rezelj, V.V.; Correa Marrero, M.; Polacco, B.J.; Melnyk, J.E.; Ulferts, S.; Kaake, R.M.; et al. The Global Phosphorylation Landscape of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cell 2020, 182, 685–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagórska, A.; Través, P.G.; Lew, E.D.; Dransfield, I.; Lemke, G. Diversification of TAM Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Function. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meertens, L.; Carnec, X.; Lecoin, M.P.; Ramdasi, R.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Lew, E.; Lemke, G.; Schwartz, O.; Amara, A. The TIM and TAM Families of Phosphatidylserine Receptors Mediate Dengue Virus Entry. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morizono, K.; Chen, I.S.Y. Role of Phosphatidylserine Receptors in Enveloped Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 4275–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meertens, L.; Labeau, A.; Dejarnac, O.; Cipriani, S.; Sinigaglia, L.; Bonnet-Madin, L.; Le Charpentier, T.; Hafirassou, M.L.; Zamborlini, A.; Cao-Lormeau, V.M.; et al. Axl Mediates ZIKA Virus Entry in Human Glial Cells and Modulates Innate Immune Responses. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batlle, M.; Recarte-Pelz, P.; Roig, E.; Castel, M.A.; Cardona, M.; Farrero, M.; Ortiz, J.T.; Campos, B.; Pulgarín, M.J.; Ramírez, J.; et al. AXL Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Is Increased in Patients with Heart Failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 173, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Huang, R.; Xu, Y.; Lv, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pan, X.; Dong, J.; Gao, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; et al. Plasma GAS6 Predicts Mortality Risk in Acute Heart Failure Patients: Insights from the DRAGON-HF Trial. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Fu, Y. Downregulated Circulating Long Non-Coding RNA GAS6-AS1 Screens and Predicts Acute Myocardial Infarction. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2023, 27, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.; Thorp, E.B.; Doran, A.C.; Sansbury, B.E.; Daemen, M.J.A.P.; Dorweiler, B.; Spite, M.; Fredman, G.; Tabas, I. MerTK Receptor Cleavage Promotes Plaque Necrosis and Defective Resolution in Atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McShane, L.; Tabas, I.; Lemke, G.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Maffia, P. TAM Receptors in Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Hu, F.; Zhu, H. Soluble TAM Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Correlation with Disease Activity and Bone Destruction. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 192, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassyouni, I.H.; El-Wakd, M.M.; Azab, N.A.; Bassyouni, R.H. Diminished Soluble Levels of Growth Arrest Specific Protein 6 and Tyrosine Kinase Receptor Axl in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humby, F.; Durez, P.; Buch, M.H.; Lewis, M.J.; Rizvi, H.; Rivellese, F.; Nerviani, A.; Giorli, G.; Mahto, A.; Montecucco, C.; et al. Rituximab versus Tocilizumab in Anti-TNF Inadequate Responder Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (R4RA): 16-Week Outcomes of a Stratified, Biopsy-Driven, Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 4 Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerviani, A.; Boutet, M.A.; Ghirardi, G.M.; Goldmann, K.; Sciacca, E.; Rivellese, F.; Pontarini, E.; Prediletto, E.; Abatecola, F.; Caliste, M.; et al. Axl and MerTK Regulate Synovial Inflammation and Are Modulated by IL-6 Inhibition in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vago, J.P.; Valdrighi, N.; Blaney-Davidson, E.N.; Hornikx, D.L.A.H.; Neefjes, M.; Barba-Sarasua, M.E.; Thielen, N.G.M.; van den Bosch, M.H.J.; van der Kraan, P.M.; Koenders, M.I.; et al. Gas6/Axl Axis Activation Dampens the Inflammatory Response in Osteoarthritic Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes and Synovial Explants. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Brand, B.T.; Abdollahi-Roodsaz, S.; Vermeij, E.A.; Bennink, M.B.; Arntz, O.J.; Rothlin, C.V.; Van Den Berg, W.B.; Van De Loo, F.A.J. Therapeutic Efficacy of Tyro3, Axl, and Mer Tyrosine Kinase Agonists in Collagen-Induced Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Wang, J.; Ma, N.; Yang, M.; Fu, H.; Liang, Y.; Huang, F.; Yang, Z.; Zhong, R. The Association of Tyro3/Axl/Mer Signaling with Inflammatory Response, Disease Activity in Patients with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome. Jt. Bone Spine 2015, 82, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturfelt, G.; Bengtsson, A.A.; Ekman, C.; Jo, A. Plasma Concentrations of Gas6 and SAxl Correlate with Disease Activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xing, L.; Ma, J.; Yu, C. Plasma SMer, SAxl and GAS6 Levels Correlate with Disease Activity and Severity in Lupus Nephritis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 49, e13064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellan, M.; Quaglia, M.; Nerviani, A.; Mauro, D.; Lewis, M.; Goegan, F.; Gibbin, A.; Pagani, S.; Salmi, L.; Molinari, L.; et al. Increased Plasma Levels of Gas6 and Its Soluble Tyrosine Kinase Receptors Mer and Axl Are Associated with Immunological Activity and Severity of Lupus Nephritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellan, M.; Dimagli, A.; Piccinino, C.; Giubertoni, A.; Ianniello, A.; Grimoldi, F.; Sguazzotti, M.; Nerviani, A.; Barini, M.; Carriero, A.; et al. Role of Gas6 and TAM Receptors in the Identification of Cardiopulmonary Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis and Scleroderma Spectrum Disorders. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 2696173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothlin, C.V.; Lemke, G. TAM Receptor Signaling and Autoimmune Disease. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, A.; Bournazos, S.; Franz, S.; Perretti, M.; Morgan, B.P.; Haslett, C.; Dransfield, I. Glucocorticoids Induce Protein S-Dependent Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Neutrophils by Human Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2167–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Kuwana, M. Nintedanib for the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Autoantibodies | Phenotypes | Target | Clinical Associations |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACA | lcSSc | ACA are mainly directed towards three centromere proteins, namely CENP-A, B, and C. | Cutaneous calcinosis, dermal thickness of hands and/or feet distally from elbow and knee, respectively, and PAH. |
| Anti-topo I | dcSSc | Anti-topo I are directed towards a nuclear protein of 70–100 kD, clustered with DNA molecules and involved in altering DNA chain conformation during cellular replication. | Ischemic digital ulcers, flexion contractures in metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints, hand disability, and progressive pulmonary fibrosis. |
| Anti-RNA pol III | dcSSc | Anti-RNA pol III antibodies are reactive with RNA polymerase III. | Joint contractures, scleroderma renal crisis |
| Anti-Th/To | lcSSc | Anti-Th/To are directed towards protein components of the RNase MRP complex. | ILD and pericarditis. |
| Treatments | Effects | Involvement in Other Conditions | Possible Involvement of Gas6/TAM Axis | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOC and RTX, bDMARDs | TOC: Inhibition of the IL-6-mediated signaling pathways, leading to a reduction in inflammation and immune response modulation.RTX: Depletion of B cells. | Proven. | Increased expression of Axl and MerTK in the RA synovial tissue, suggesting that IL-6 inhibition may exert part of its anti-inflammatory effects through upregulation of TAM receptors. | [152] |
| Prednisolone, glucocorticoids | Anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. | Proven. | Glucocorticoids can upregulate the expression of MerTK enhancing the clearance of apoptotic cells and promoting anti-inflammatory pathway. | [160,161] |
| Nintedanib, tyrosine kinase inhibitor | It targets multiple tyrosine kinases involved in the processes of fibrosis, inflammation, and vascular remodeling. | Proven. | Gas6/TAM receptor activity contributes to the activation of pulmonary fibroblasts in IPF and targeting of TAM receptors alleviates fibrotic mechanisms. | [131] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apostolo, D.; D’Onghia, D.; Nerviani, A.; Ghirardi, G.M.; Sola, D.; Perazzi, M.; Tonello, S.; Colangelo, D.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Bellan, M. Could Gas6/TAM Axis Provide Valuable Insights into the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis? Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 7486-7504. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46070444
Apostolo D, D’Onghia D, Nerviani A, Ghirardi GM, Sola D, Perazzi M, Tonello S, Colangelo D, Sainaghi PP, Bellan M. Could Gas6/TAM Axis Provide Valuable Insights into the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis? Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(7):7486-7504. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46070444
Chicago/Turabian StyleApostolo, Daria, Davide D’Onghia, Alessandra Nerviani, Giulia Maria Ghirardi, Daniele Sola, Mattia Perazzi, Stelvio Tonello, Donato Colangelo, Pier Paolo Sainaghi, and Mattia Bellan. 2024. "Could Gas6/TAM Axis Provide Valuable Insights into the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis?" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 7: 7486-7504. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46070444
APA StyleApostolo, D., D’Onghia, D., Nerviani, A., Ghirardi, G. M., Sola, D., Perazzi, M., Tonello, S., Colangelo, D., Sainaghi, P. P., & Bellan, M. (2024). Could Gas6/TAM Axis Provide Valuable Insights into the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis? Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(7), 7486-7504. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46070444









