Drug Pipeline for MASLD: What Can Be Learned from the Successful Story of Resmetirom
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Resmetirom: A Breakthrough in MASLD/MASH Management
2.1. Mechanism of Action
2.2. Early Clinical Trials
2.3. Phase 2 Trial Results
2.4. Comprehensive Phase 3 Trials
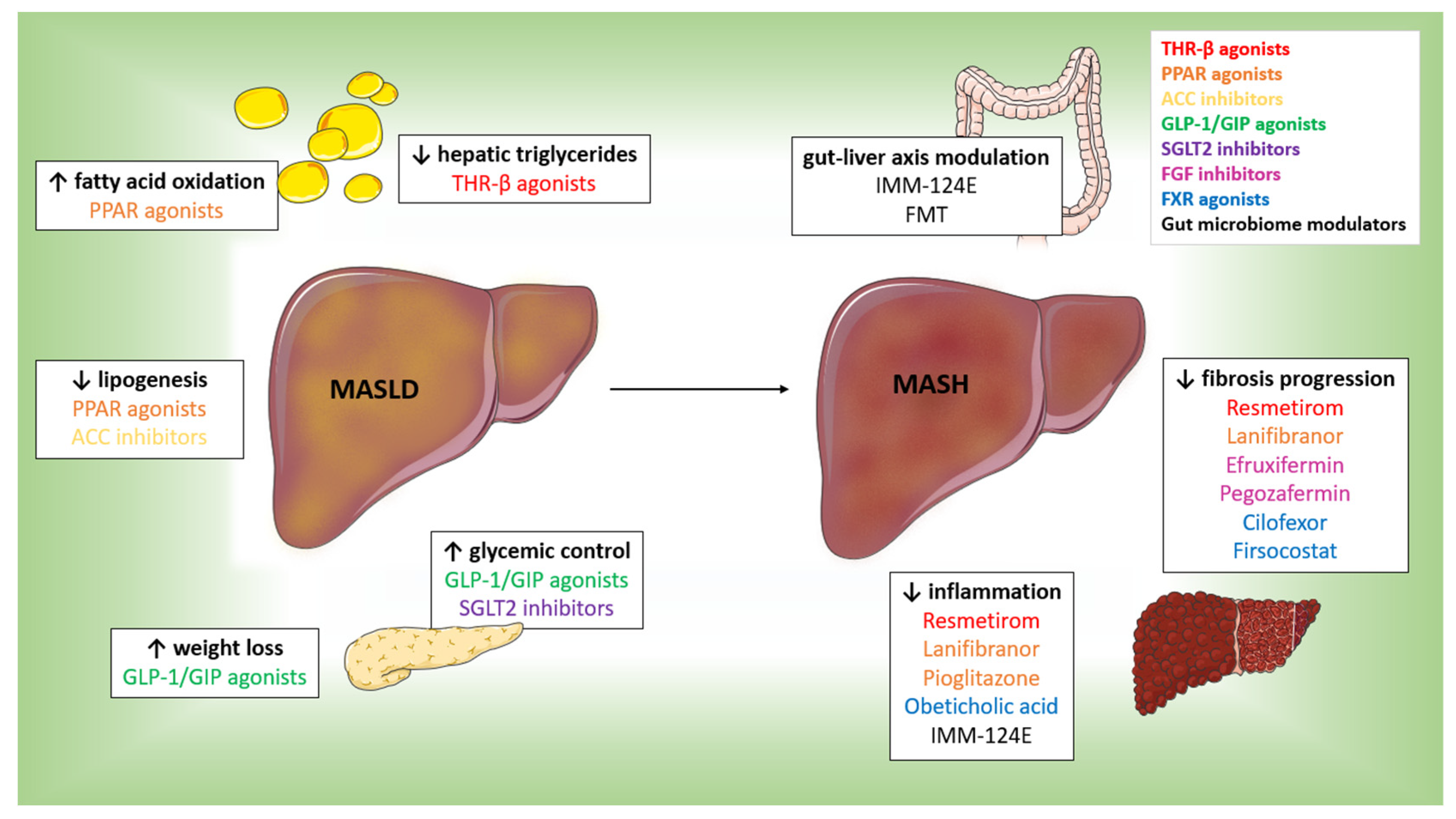
3. Comparison with Other Therapeutic Approaches
3.1. THR-β Agonists
3.2. GLP-1 and GIP Receptor Agonists
3.3. SGLT2 Inhibitors
3.4. PPAR Agonists
3.5. FGF and ACC Inhibitors
3.6. FXR Agonists
3.7. Gut Microbiome Modulators
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miao, L.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Cao, Y.Y.; Zheng, M.H. Current status and future trends of the global burden of MASLD. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 35, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Kang, D.; Choi, S.C.; Sinn, D.H.; Gwak, G.Y. Cardiometabolic risk factors and coronary atherosclerosis progression in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: The influential role of quantity over type. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 40, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yki-Järvinen, H. Diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ristic-Medic, D.; Bajerska, J.; Vucic, V. Crosstalk between dietary patterns, obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 3314–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Montoro, J.I.; Martínez-Sánchez, M.A.; Balaguer-Román, A.; Fernández-Ruiz, V.E.; Hernández-Barceló, J.E.; Ferrer-Gómez, M.; Frutos, M.D.; Núñez-Sánchez, M.; Fernández-García, J.C.; Ramos-Molina, B. Triglyceride to HDL Cholesterol Ratio for the Identification of MASLD in Obesity: A Liver Biopsy-Based Case-Control Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, J.; Galli, L.; Speidl, W.S.; Krychtiuk, K.A. Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2025, 27, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, K.L.; Smith, C.I.; Schwarzenberg, S.J.; Jessurun, J.; Boldt, M.D.; Parks, E.J. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandireddy, R.; Sakthivel, S.; Gupta, P.; Behari, J.; Tripathi, M.; Singh, B.K. Systemic impacts of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) on heart, muscle, and kidney related diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1433857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrini, E.; Sullivan, S.; Klein, S. Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Biochemical, metabolic, and clinical implications. Hepatology 2010, 51, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L. Energy metabolism in the liver. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaenisch, R.; Bird, A. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: How the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33 (Suppl. S3), 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, G.N. Epidemiology and risk-stratification of NAFLD-associated HCC. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpino, G.; Del Ben, M.; Pastori, D.; Carnevale, R.; Baratta, F.; Overi, D.; Francis, H.; Cardinale, V.; Onori, P.; Safarikia, S.; et al. Increased Liver Localization of Lipopolysaccharides in Human and Experimental NAFLD. Hepatology 2020, 72, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bedossa, P.; Guy, C.D.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Loomba, R.; Taub, R.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Neff, G.W.; Rinella, M.E.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Resmetirom in NASH with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisnovali, N.F.; Haney, C.; Goedeke, L. Rezdiffra™ (resmetirom): A THR-β agonist for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 45, 1081–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezhilarasan, D. Thyromimetics and MASLD: Unveiling the Novel Molecules Beyond Resmetirom. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 40, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omaña-Guzmán, I.; Rosas-Diaz, M.; Martínez-López, Y.E.; Perez-Navarro, L.M.; Diaz-Badillo, A.; Alanis, A.; Bustamante, A.; Castillo-Ruiz, O.; Del Toro-Cisneros, N.; Esquivel-Hernandez, D.A.; et al. Strategic interventions in clinical randomized trials for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and obesity in the pediatric population: A systematic review with meta-analysis and bibliometric analysis. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akcam, M.; Boyaci, A.; Pirgon, O.; Kaya, S.; Uysal, S.; Dundar, B.N. Therapeutic effect of metformin and vitamin E versus prescriptive diet in obese adolescents with fatty liver. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2011, 81, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavine, J.E.; Schwimmer, J.B.; Van Natta, M.L.; Molleston, J.P.; Murray, K.F.; Rosenthal, P.; Abrams, S.H.; Scheimann, A.O.; Sanyal, A.J.; Chalasani, N.; et al. Effect of vitamin E or metformin for treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: The TONIC randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2011, 305, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheen, A.J. Beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on fatty liver in type 2 diabetes: A common comorbidity associated with severe complications. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 45, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J. Vitamin E in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 40, 551–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefer, M.; Petrovic, A.; Roguljic, L.K.; Kolaric, T.O.; Kizivat, T.; Wu, C.H.; Tabll, A.A.; Smolic, R.; Vcev, A.; Smolic, M. Green Tea Polyphenol (-)-Epicatechin Pretreatment Mitigates Hepatic Steatosis in an In Vitro MASLD Model. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 8981–8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravina, A.G.; Pellegrino, R.; Romeo, M.; Ventriglia, L.; Scognamiglio, F.; Tuccillo, C.; Loguercio, C.; Federico, A. The use of bicarbonate-sulphate-calcium-magnesium and sodium-low drinkable water improves functional gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 57, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G.; Tilg, H. Thyroid hormone receptor-beta agonists: New MASLD therapies on the horizon. Gut 2024, 73, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, T.; Liu, K.; Chilambe, L.O.; Khare, S. NAFLD and NAFLD Related HCC: Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares De Oliveira, L.; Ritter, M.J. Thyroid hormone and the Liver. Hepatol. Commun. 2025, 9, e0596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalik, M.A.; Columbano, A.; Perra, A. Thyroid Hormones, Thyromimetics and Their Metabolites in the Treatment of Liver Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cable, E.E.; Finn, P.D.; Stebbins, J.W.; Hou, J.; Ito, B.R.; van Poelje, P.D.; Linemeyer, D.L.; Erion, M.D. Reduction of hepatic steatosis in rats and mice after treatment with a liver-targeted thyroid hormone receptor agonist. Hepatology 2009, 49, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taub, R.; Chiang, E.; Chabot-Blanchet, M.; Kelly, M.J.; Reeves, R.A.; Guertin, M.C.; Tardif, J.C. Lipid lowering in healthy volunteers treated with multiple doses of MGL-3196, a liver-targeted thyroid hormone receptor-β agonist. Atherosclerosis 2013, 230, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.W. Selective Agonists of Thyroid Hormone Receptor Beta: Promising Tools for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 39, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, L.; Kim, A.; Ni, B.; Celi, F.S. Thyroid hormone action and liver disease, a complex interplay. Hepatology 2025, 81, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Targher, G. Hepatic thyroid hormone receptor-β signalling: Mechanisms and recent advancements in the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Ratziu, V.; Anstee, Q.M.; Noureddin, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Bedossa, P.; Bashir, M.R.; Schneider, D.; Taub, R.; et al. Design of the phase 3 MAESTRO clinical program to evaluate resmetirom for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 59, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratziu, V.; Scanlan, T.S.; Bruinstroop, E. Thyroid hormone receptor-β analogues for the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Yang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, N.; Yuan, P.; Yang, T.; Xing, J.; Li, J. Increased mitochondrial fission drives the reprogramming of fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma cells through suppression of Sirtuin 1. Cancer Commun. 2022, 42, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanthier, L.; Grbic, D.; Plourde, M.; Cauchon, M. Among patients with metabolic dysfunction associated steatohepatitis (MASH), is resmetirom 80 or 100mg superior to placebo in reversing MASH and/or fibrosis on liver biopsy, and is it safe? Rev. Med. Interne 2024, 45, 395–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarna, R.; Shetty, S.; Pappachan, J.M. Efficacy and safety of Resmetirom, a selective thyroid hormone receptor-β agonist, in the treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, H.T.; Alhatemi, A.Q.M.; Riaz, S.; Al-Ghuraibawi, M.A.; Alabide, A.S.; Saeed, H.; Sulaiman, F.A.; Alhussain, M.A.A.; Shallan, M.A.; Al-Obaidi, A.D.; et al. Unveiling Resmetirom: A systematic review and meta-analysis on its impact on liver function and safety in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis treatment. JGH Open 2024, 8, e70025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petta, S.; Targher, G.; Romeo, S.; Pajvani, U.B.; Zheng, M.H.; Aghemo, A.; Valenti, L.V.C. The first MASH drug therapy on the horizon: Current perspectives of resmetirom. Liver Int. 2024, 44, 1526–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levien, T.L.; Baker, D.E. Resmetirom. Hosp. Pharm. 2024, 60, 00185787241278571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.-D.; Liu, W.-Y.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Zheng, M.-H. Letter: Drug interaction in resmetirom times. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 60, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejitual, E.; Awais, M.F.; Modi, D.; Gul, U.; Obeidat, K.; Ahmed, N.; Waheed, M.D.; Hirani, S. Effectiveness of Resmetirom in Reducing Cholesterol Levels in Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2024, 16, e70859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittla, P.; Paidimarri, S.P.; Ayuthu, S.; Chauhan, Y.D.; Saad, M.Z.; Mirza, A.A.; Khan, S. Resmetirom: A Systematic Review of the Revolutionizing Approach to Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis Treatment Focusing on Efficacy, Safety, Cost-Effectiveness, and Impact on Quality of Life. Cureus 2024, 16, e69919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchi, R. Thyroid Hormone Analogues: An Update. Thyroid 2020, 30, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bashir, M.R.; Guy, C.D.; Zhou, R.; Moylan, C.A.; Frias, J.P.; Alkhouri, N.; Bansal, M.B.; Baum, S.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; et al. Resmetirom (MGL-3196) for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 2012–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bashir, M.; Moussa, S.E.; McCarty, K.; Pablo Frias, J.; Taub, R.; Alkhouri, N. Effects of Resmetirom on Noninvasive Endpoints in a 36-Week Phase 2 Active Treatment Extension Study in Patients with NASH. Hepatol. Commun. 2021, 5, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.A.; Taub, R.; Neff, G.W.; Lucas, K.J.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Alkhouri, N.; Bashir, M.R. Resmetirom for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2919–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroes, A.R.; Vos, M.; Benninga, M.A.; Koot, B.G.P. Pediatric MASLD: Current understanding and practical approach. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2024, 184, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrigal Pharmaceuticals Completes Enrollment of Clinical Outcomes Study of Resmetirom in Patients with Compensated NASH/MASH Cirrhosis. Available online: https://ir.madrigalpharma.com/news-releases/news-release-details/madrigal-pharmaceuticals-completes-enrollment-clinical-outcomes (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Leith, D.; Lin, Y.Y.; Brennan, P. Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: A Deadly Synergy. Touchrev. Endocrinol. 2024, 20, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gancheva, S.; Roden, M.; Castera, L. Diabetes as a risk factor for MASH progression. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2024, 217, 111846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martagón, A.J.; Lin, J.Z.; Cimini, S.L.; Webb, P.; Phillips, K.J. The amelioration of hepatic steatosis by thyroid hormone receptor agonists is insufficient to restore insulin sensitivity in ob/ob mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatner, D.F.; Weismann, D.; Beddow, S.A.; Kumashiro, N.; Erion, D.M.; Liao, X.H.; Grover, G.J.; Webb, P.; Phillips, K.J.; Weiss, R.E.; et al. Thyroid hormone receptor-β agonists prevent hepatic steatosis in fat-fed rats but impair insulin sensitivity via discrete pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 305, E89–E100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Sun, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.D.; Fan, J.G. Pipeline of New Drug Treatment for Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2024, 12, 802–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Waskowicz, L.R.; Lim, A.; Liao, X.H.; Lian, B.; Masamune, H.; Refetoff, S.; Tran, B.; Koeberl, D.D.; Yen, P.M. A Liver-Specific Thyromimetic, VK2809, Decreases Hepatosteatosis in Glycogen Storage Disease Type Ia. Thyroid 2019, 29, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safety and Tolerability of VK2809 in Patients with Primary Hypercholesterolemia and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02927184 (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- VK2809 A Phase 2B, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter Study to Assess the Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of VK2809 Administered for 52 Weeks Followed by a 4-Week Off-Drug Phase in Subjects With Biopsy Proven Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis with Fibrosis. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04173065 (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- A Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of VK2809 for 52 Weeks in Subjects with Biopsy Proven NASH (VOYAGE). Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04173065 (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Raja, A.; Subhash Sagar, R.; Saeed, S.; Zia Ul Haq, A.; Khan, O.; Dileep Bhimani, P.; Raja, S.; Deepak, F.; Ahmed, M.; Ashir Shafique, M.; et al. Safety and efficacy of resmetirom in the treatment of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Med. Surg. 2024, 86, 4130–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, P.N.; Ambery, P. Incretins (GLP-1 receptor agonists and dual/triple agonists) and the liver. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prato, S.; Gallwitz, B.; Holst, J.J.; Meier, J.J. The incretin/glucagon system as a target for pharmacotherapy of obesity. Obes. Rev. 2022, 23, e13372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovic, A.; Igrec, D.; Rozac, K.; Bojanic, K.; Kuna, L.; Kolaric, T.O.; Mihaljevic, V.; Sikora, R.; Smolic, R.; Glasnovic, M.; et al. The Role of GLP1-RAs in Direct Modulation of Lipid Metabolism in Hepatic Tissue as Determined Using In Vitro Models of NAFLD. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 4544–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardullo, S.; Morieri, M.L.; Daniele, G.; Fiorentino, T.V.; Mezza, T.; Tricò, D.; Consoli, A.; Del Prato, S.; Giorgino, F.; Piro, S.; et al. GLP1-GIP receptor co-agonists: A promising evolution in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2024, 61, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, P.R.C.; Filho, V.O.C.; Noronha, M.M.; Hyppolito, E.B.; Saldanha, E.F.; Motta, R.V. Influence of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on hepatic events in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 40, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheen, A.J. Semaglutide, once weekly GLP-1 receptor agonist (Ozempic®). Rev. Med. Liege 2019, 74, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Newsome, P.N.; Buchholtz, K.; Cusi, K.; Linder, M.; Okanoue, T.; Ratziu, V.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sejling, A.S.; Harrison, S.A.; Investigators, N.-A. Placebo-Controlled Trial of Subcutaneous Semaglutide in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Armstrong, M.J.; Jara, M.; Kjær, M.S.; Krarup, N.; Lawitz, E.; Ratziu, V.; Sanyal, A.J.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. Semaglutide 2·4 mg once weekly in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-related cirrhosis: A randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, J.; Hsiang, J.C.; Taneja, R.; Koo, S.H.; Soon, G.H.; Kam, C.J.; Law, N.M.; Ang, T.L. Randomized trial comparing effects of weight loss by liraglutide with lifestyle modification in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldelli, A.; Cusi, K.; Fernández Landó, L.; Bray, R.; Brouwers, B.; Rodríguez, Á. Effect of tirzepatide versus insulin degludec on liver fat content and abdominal adipose tissue in people with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-3 MRI): A substudy of the randomised, open-label, parallel-group, phase 3 SURPASS-3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Kaplan, L.M.; Frías, J.P.; Wu, Q.; Du, Y.; Gurbuz, S.; Coskun, T.; Haupt, A.; Milicevic, Z.; Hartman, M.L.; et al. Triple-Hormone-Receptor Agonist Retatrutide for Obesity—A Phase 2 Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nespoux, J.; Vallon, V. Renal effects of SGLT2 inhibitors: An update. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2020, 29, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchay, M.S.; Krishan, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Farooqui, K.J.; Singh, M.K.; Wasir, J.S.; Bansal, B.; Kaur, P.; Jevalikar, G.; Gill, H.K.; et al. Effect of Empagliflozin on Liver Fat in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial (E-LIFT Trial). Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Suzuki, K.; Kato, K.; Jojima, T.; Iijima, T.; Murohisa, T.; Iijima, M.; Takekawa, H.; Usui, I.; Hiraishi, H.; et al. Evaluation of the effects of dapagliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, on hepatic steatosis and fibrosis using transient elastography in patients with type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Manghi, F.P.; Smith, W.B.; Alpenidze, D.; Aizenberg, D.; Klarenbeek, N.; Chen, C.Y.; Zuckerman, E.; Ravussin, E.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; et al. Licogliflozin for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2a study. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phrueksotsai, S.; Pinyopornpanish, K.; Euathrongchit, J.; Leerapun, A.; Phrommintikul, A.; Buranapin, S.; Chattipakorn, N.; Thongsawat, S. The effects of dapagliflozin on hepatic and visceral fat in type 2 diabetes patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 2952–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachou, M.; Flevari, P.; Nasiri-Ansari, N.; Varytimiadis, C.; Kalaitzakis, E.; Kassi, E.; Androutsakos, T. The role of anti-diabetic drugs in NAFLD. Have we found the Holy Grail? A narrative review. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 80, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadkarni, G.N.; Ferrandino, R.; Chang, A.; Surapaneni, A.; Chauhan, K.; Poojary, P.; Saha, A.; Ferket, B.; Grams, M.E.; Coca, S.G. Acute Kidney Injury in Patients on SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Propensity-Matched Analysis. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1479–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubia, B.; Poupardin, O.; Barth, M.; Binet, J.; Peralba, P.; Mounier, L.; Jacquier, E.; Gauthier, E.; Lepais, V.; Chatar, M.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of a Novel Series of Indole Sulfonamide Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor (PPAR) α/γ/δ Triple Activators: Discovery of Lanifibranor, a New Antifibrotic Clinical Candidate. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2246–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawrieh, S.; Noureddin, M.; Loo, N.; Mohseni, R.; Awasty, V.; Cusi, K.; Kowdley, K.V.; Lai, M.; Schiff, E.; Parmar, D.; et al. Saroglitazar, a PPAR-α/γ Agonist, for Treatment of NAFLD: A Randomized Controlled Double-Blind Phase 2 Trial. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1809–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusi, K.; Orsak, B.; Bril, F.; Lomonaco, R.; Hecht, J.; Ortiz-Lopez, C.; Tio, F.; Hardies, J.; Darland, C.; Musi, N.; et al. Long-Term Pioglitazone Treatment for Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 165, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, B.; Pawlak, M.; Lefebvre, P.; Staels, B. PPARs in obesity-induced T2DM, dyslipidaemia and NAFLD. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratziu, V.; Giral, P.; Jacqueminet, S.; Charlotte, F.; Hartemann–Heurtier, A.; Serfaty, L.; Podevin, P.; Lacorte, J.M.; Bernhardt, C.; Bruckert, E.; et al. Rosiglitazone for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: One-Year Results of the Randomized Placebo-Controlled Fatty Liver Improvement With Rosiglitazone Therapy (FLIRT) Trial. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barb, D.; Kalavalapalli, S.; Leiva, E.G.; Bril, F.; Huot-Marchand, P.; Dzen, L.; Rosenberg, J.T.; Junien, J.L.; Broqua, P.; Rocha, A.O.; et al. Pan-PPAR agonist lanifibranor improves insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in patients with T2D and MASLD. J. Hepatol. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Frias, J.P.; Neff, G.; Abrams, G.A.; Lucas, K.J.; Sanchez, W.; Gogia, S.; Sheikh, M.Y.; Behling, C.; Bedossa, P.; et al. Safety and efficacy of once-weekly efruxifermin versus placebo in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (HARMONY): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Lawitz, E.J.; Frias, J.P.; Ortiz-Lasanta, G.; Johansson, L.; Franey, B.B.; Morrow, L.; Rosenstock, M.; Hartsfield, C.L.; Chen, C.-Y.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of pegozafermin in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1b/2a multiple-ascending-dose study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.A.; Neff, G.; Guy, C.D.; Bashir, M.R.; Paredes, A.H.; Frias, J.P.; Younes, Z.; Trotter, J.F.; Gunn, N.T.; Moussa, S.E.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Aldafermin, an Engineered FGF19 Analog, in a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Patients With Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 219–231.e211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Rinella, M.E.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Trotter, J.F.; Paredes, A.H.; Arnold, H.L.; Kugelmas, M.; Bashir, M.R.; Jaros, M.J.; Ling, L.; et al. NGM282 for treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calle, R.A.; Amin, N.B.; Carvajal-Gonzalez, S.; Ross, T.T.; Bergman, A.; Aggarwal, S.; Crowley, C.; Rinaldi, A.; Mancuso, J.; Aggarwal, N.; et al. ACC inhibitor alone or co-administered with a DGAT2 inhibitor in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Two parallel, placebo-controlled, randomized phase 2a trials. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1836–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, A.; Carvajal-Gonzalez, S.; Tarabar, S.; Saxena, A.R.; Esler, W.P.; Amin, N.B. Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of a Liver-Targeting Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase Inhibitor (PF-05221304): A Three-Part Randomized Phase 1 Study. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2020, 9, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudaliar, S.; Henry, R.R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Morrow, L.; Marschall, H.U.; Kipnes, M.; Adorini, L.; Sciacca, C.I.; Clopton, P.; Castelloe, E.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the Farnesoid X Receptor Agonist Obeticholic Acid in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 574–582.e571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Dufour, J.-F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Goodman, Z.; Younossi, Z.; Harrison, S.A.; Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Bonacci, M.; Trylesinski, A.; et al. Non-invasive evaluation of response to obeticholic acid in patients with NASH: Results from the REGENERATE study. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bashir, M.R.; Lee, K.-J.; Shim-Lopez, J.; Lee, J.; Wagner, B.; Smith, N.D.; Chen, H.C.; Lawitz, E.J. A structurally optimized FXR agonist, MET409, reduced liver fat content over 12 weeks in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratziu, V.; Rinella, M.E.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Lawitz, E.; Denham, D.; Kayali, Z.; Sheikh, A.; Kowdley, K.V.; Desta, T.; Elkhashab, M.; et al. EDP-305 in patients with NASH: A phase II double-blind placebo-controlled dose-ranging study. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.; Lopez, P.; Lawitz, E.; Lucas, K.; Loeffler, J.; Kim, W.; Goh, G.b.-b.; Huang, J.-F.; Serra, C.; Andreone, P.; et al. Tropifexor for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: An adaptive, randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2a/b trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianelli, D.; Rucker, P.V.; Roland, J.; Tully, D.C.; Nelson, J.; Liu, X.; Bursulaya, B.; Hernandez, E.D.; Wu, J.; Prashad, M.; et al. Nidufexor (LMB763), a Novel FXR Modulator for the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 3868–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Noureddin, M.; Kowdley, K.V.; Kohli, A.; Sheikh, A.; Neff, G.; Bhandari, B.R.; Gunn, N.; Caldwell, S.H.; Goodman, Z.; et al. Combination Therapies Including Cilofexor and Firsocostat for Bridging Fibrosis and Cirrhosis Attributable to NASH. Hepatology 2021, 73, 625–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Phase ll, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of IMM-124E for Patients with Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02316717?term=imm-124e&rank=1 (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Saha, S.; Schnabl, B. Modulating the microbiome in chronic liver diseases—Current evidence on the role of fecal microbiota transplantation. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 19, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishay, Y.; Potruch, A.; Weksler-Zangen, S.; Shabat, Y.; Ilan, Y. Augmented antiviral T cell immunity by oral administration of IMM-124E in preclinical models and a phase I/IIa clinical trial: A method for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. Drug Dev. Res. 2022, 83, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.; Raj, R.; Elshimy, G.; Zapata, I.; Kannan, L.; Majety, P.; Edem, D.; Correa, R. Adverse Events Related to Tirzepatide. J. Endocr. Soc. 2023, 7, bvad016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francque, S.M.; Bedossa, P.; Ratziu, V.; Anstee, Q.M.; Bugianesi, E.; Sanyal, A.J.; Loomba, R.; Harrison, S.A.; Balabanska, R.; Mateva, L.; et al. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of the Pan-PPAR Agonist Lanifibranor in NASH. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhabra, M.; Vidyasagar, K.; Gudi, S.K.; Sharma, J.; Sharma, R.; Rashid, M. Efficacy and safety of saroglitazar for the management of dyslipidemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of interventional studies. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Mudaliar, S. Pioglitazone: Side effect and safety profile. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2010, 9, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintanilla Rodriguez BS, C.R. Rosiglitazone; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, S.A.; Frias, J.P.; Lucas, K.J.; Reiss, G.; Neff, G.; Bollepalli, S.; Su, Y.; Chan, D.; Tillman, E.J.; Moulton, A.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Efruxifermin in Combination with a GLP-1 Receptor Agonist in Patients with NASH/MASH and Type 2 Diabetes in a Randomized Phase 2 Study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 23, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhouri, N.; Lazas, D.; Loomba, R.; Frias, J.P.; Feng, S.; Tseng, L.; Balic, K.; Agollah, G.D.; Kwan, T.; Iyer, J.S.; et al. Clinical trial: Effects of pegozafermin on the liver and on metabolic comorbidities in subjects with biopsy-confirmed nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 58, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lieu, H.D.; Kowdley, K.V.; Goodman, Z.D.; Alkhouri, N.; Lawitz, E.; Ratziu, V.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Wong, V.W.; Younes, Z.H.; et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of aldafermin in patients with NASH and compensated cirrhosis. Hepatology 2024, 79, 674–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, L.; Wu, J.; Pan, X.; Yin, W.; Wu, Z. A Real-World Pharmacovigilance Study of FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Events for Obeticholic Acid. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2025, 34, e70084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, I.R.; Kirby, B.J.; Billin, A.N.; Xiao, D.; Song, Q.; Watkins, T.R.; Othman, A.A. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety and tolerability of cilofexor, a novel nonsteroidal Farnesoid X receptor agonist, in healthy volunteers. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2023, 16, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mechanism of Action | Agent | Advantages | Disadvantages | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| THR-β agonists | Resmetirom | Reduces hepatic fat, improves lipid profile, and lowers inflammation and fibrosis markers | Mild gastrointestinal symptoms (diarrhea, nausea), mild free T4 reduction at high doses | [30,32,36,38,45] |
| Sobetirome | Reduces hepatic triglycerides, high doses improve hyperglycemia | Lower doses impair glycemia, causing fasting hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and reduced hepatic insulin sensitivity | [53,54] | |
| Eprotirome | Reduces hepatic triglycerides | Impairs peripheral glucose disposal by lowering skeletal muscle GLUT4 levels | [53,54] | |
| VK2809 | Reduces hepatic lipogenesis, lowers lipid levels with minimal systemic impact | Mild or moderate gastrointestinal-related events | [55,56,57,58] | |
| GLP-1 and GIP Receptor Agonists | Liraglutide | Reduces weight, hepatic steatosis, and hepatocyte apoptosis | Benefits not sustained after discontinuation | [69] |
| Semaglutide | Enhances glycemic control, weight reduction, and reduces hepatic steatosis | Limited fibrosis improvement, nausea, vomiting | [61,63,64,67,68] | |
| Tirzepatide | Improves weight loss, insulin resistance, reduces liver fat | A dose-dependent increase in gastrointestinal-related events | [70,71,102] | |
| Retatrutide | Enhances weight loss and improves metabolic parameters | Higher-dose-related gastrointestinal events and dose-dependent increase in heart rate | [72] | |
| SGLT2 Inhibitors | Empagliflozin | Improves ALT levels and glycemic control | N/A | [74] |
| Dapagliflozin | Improves glycemic control, reduces liver fat, and serum alanine aminotransferase and γ-glutamyltranspeptidase levels | Acute kidney injury | [74,75,76,77,78,79] | |
| PPAR Agonists | Lanifibranor | Significant histological improvement, fibrosis reduction and anti-inflammatory effects | Gastrointestinal-related events, peripheral edema, anemia, and weight gain | [80,81,82,83,85,103] |
| Saroglitazar | Improves histological and metabolic markers in MASH | Gastritis, asthenia, and pyrexia | [81,104] | |
| Pioglitazone | Improves insulin sensitivity, reduces liver inflammation, 51% MASH resolution | Weight gain, fluid retention | [82,83,105] | |
| Rosiglitazone | Normalizes transaminase levels in MASH patients and reduces liver fat percentage | Increases LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and total cholesterol | [84,106] | |
| FGF Inhibitors | Efruxifermin | Reduces fibrosis, improves metabolic parameters | Mild to moderate gastrointestinal events | [86,107] |
| Pegozafermin | Reduces fibrosis, improves metabolic outcomes | Mild/moderate nausea and diarrhea | [87,108] | |
| Aldafermin | Reduces liver fat | Diarrhea | [88,109] | |
| NGM282 | Significant reduction in hepatic steatosis | Injection site reactions, diarrhea, and nausea | [89] | |
| ACC Inhibitors | PF-05221304 | Significant reduction in liver fat | N/A | [90,91] |
| FXR Agonists | Obeticholic acid | Improves insulin sensitivity, reduces inflammatory markers | Pruritus, fatigue, constipation, abdominal distention | [92,93,110] |
| EDP-305 | Improves ALT and lipid profiles | High incidence of pruritus, dizziness, nausea, diarrhea | [95] | |
| MET409 | Improves ALT and lipid profiles | N/A | [94] | |
| Tropifexor | Significantly reduces ALT, liver fat, and NAS | Pruritus | [96] | |
| Cilofexor | Improvements in liver parameters in patients with advanced fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis | Headache | [98,111] | |
| Firsocostat | Improvements in liver parameters in patients with advanced fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis | Nausea, diarrhea, and headache | [98] | |
| Gut Microbiome Modulators | IMM-124E | Reduces inflammation, improves liver enzymes (AST and ALT), no reported adverse effects | No impact on liver fat noted in a single 24-week trial | [99,101] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knezović, E.; Hefer, M.; Blažanović, S.; Petrović, A.; Tomičić, V.; Srb, N.; Kirner, D.; Smolić, R.; Smolić, M. Drug Pipeline for MASLD: What Can Be Learned from the Successful Story of Resmetirom. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030154
Knezović E, Hefer M, Blažanović S, Petrović A, Tomičić V, Srb N, Kirner D, Smolić R, Smolić M. Drug Pipeline for MASLD: What Can Be Learned from the Successful Story of Resmetirom. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(3):154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030154
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnezović, Elizabeta, Marija Hefer, Suzana Blažanović, Ana Petrović, Vice Tomičić, Nika Srb, Damir Kirner, Robert Smolić, and Martina Smolić. 2025. "Drug Pipeline for MASLD: What Can Be Learned from the Successful Story of Resmetirom" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 3: 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030154
APA StyleKnezović, E., Hefer, M., Blažanović, S., Petrović, A., Tomičić, V., Srb, N., Kirner, D., Smolić, R., & Smolić, M. (2025). Drug Pipeline for MASLD: What Can Be Learned from the Successful Story of Resmetirom. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(3), 154. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030154







