Evaluation of the Antiaging Potential of the Dendropanax morbiferus-Derived Compound Dendropanoxide in TNF-α-Stimulated Human Dermal Fibroblasts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatment Preparation
2.3. Cell Viability
2.4. Intercellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Generation Assay
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Total RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
| Gene | Primer Sequences | |
|---|---|---|
| Human SPINK5 | Sense Anti-Sense | 5′-GCCTGACTCTTGGAAAGAAA-3′ 3′-CAGTTGTCACTGGTTCTACA-5’ |
| Human LOR | Sense Anti-Sense | 5′-GTGGGAGCGTCAAGTACTCC-3′ 3′-AGAGTAGCCGCAGACAGAGC-5’ |
| Human IVL | Sense Anti-Sense | 5′-CAACTGGAGCTCCCAGAGCAGC-3′ 3′-AACACAGGCTGCTCCAGCTGC-5’ |
| Human AQP3 | Sense Anti-Sense | 5′-TCTTTGACCAGTTCATAGGCAC-3′ 3′-GGCAGGGTTGACGGCATAG-5’ |
| Human FLG | Sense Anti-Sense | 5′-GGACTCTGAGAGGCGATCTG-3′ 3′-TGCTCCCGAGAAGATCCAT-5’ |
| Human KRT1 | Sense Anti-Sense | 5′-CTGGCAGACATGGGGATAGTGTG-3′ 3′-CTGATGGTGGTGTGGCTTGTGCT-5’ |
| Human β-actin | Sense Anti-Sense | 5′-AGAGATGGCCACGGCTGCTT-3′ 5′-ATTTGCGGTGGACGATGGAG-3′ |
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Structure of DP

3.2. Survival of NHDFs and NHEKs Treated with DP

3.3. Effects of DP on Intracellular ROS Accumulation in TNF-α-Stimulated NHDFs
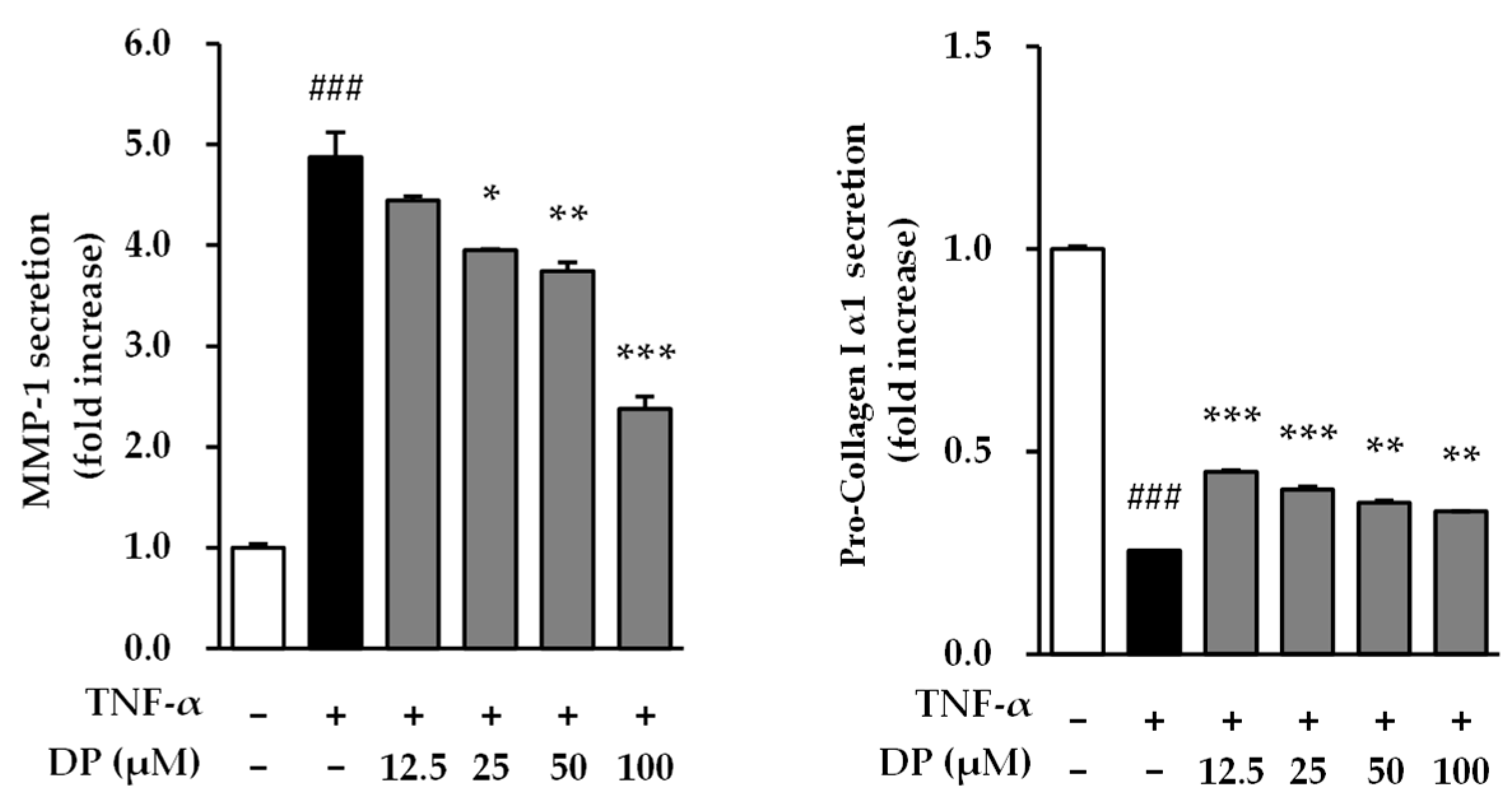
3.4. Effects of DP on Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 and Type 1 Pro-Collagen Secretion in TNF-α-Stimulated NHDFs
3.5. Effects of DP on Inflammatory Response in TNF-α-/IFN-γ-Stimulated NHEKs
3.6. Effects of DP on the Skin Barrier in TNF-α-/IFN-γ-Stimulated NHEKs
3.7. Phosphorylation of JNK, ERK, and p38 by DP on TNF-α-Induced NHDFs

4. Discussion
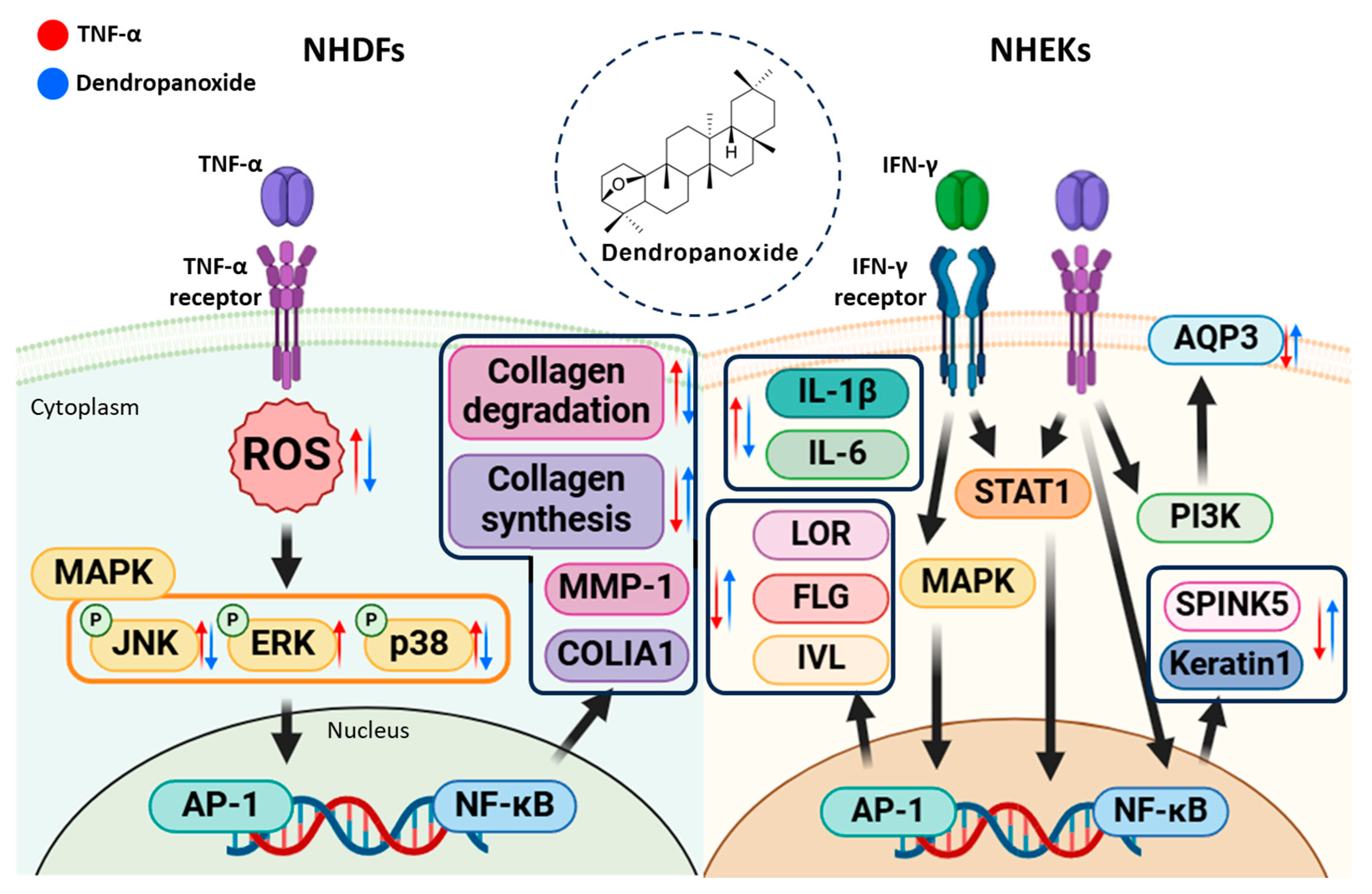
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP-1 | Activator Protein 1 |
| AQP3 | Aquaporin 3 |
| D. morbiferus | Dendropanax morbiferus |
| DP | Dendropanoxide |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| FLG | Filaggrin |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-Gamma |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| IVL | Involucrin |
| JNK | c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase |
| LOR | Loricrin |
| MAPKs | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases |
| MMP-1 | Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa-Light-Chain-Enhancer of Activated B Cells |
| NHDFs | Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SPINK5 | Serine Peptidase Inhibitor, Kazal-Type 5 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| UVA | Ultraviolet A |
| UVB | Ultraviolet B |
References
- Yousef, H.; Alhajj, M.; Sharma, S. Anatomy, skin (integument), epidermis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Baroni, A.; Buommino, E.; De Gregorio, V.; Ruocco, E.; Ruocco, V.; Wolf, R. Structure and function of the epidermis related to barrier properties. Clin. Dermatol. 2012, 30, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, K.A.; Roberts, M.S. The structure and function of skin. In Dermatological and Transdermal Formulations; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 19–58. [Google Scholar]
- Wickett, R.R.; Visscher, M.O. Structure and function of the epidermal barrier. Am. J. Infect. Control 2006, 34, S98–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolarsick, P.A.; Kolarsick, M.A.; Goodwin, C. Anatomy and physiology of the skin. J. Dermatol. Nurses Assoc. 2011, 3, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potekaev, N.N.; Borzykh, O.B.; Medvedev, G.V.; Pushkin, D.V.; Petrova, M.M.; Petrov, A.V.; Dmitrenko, D.V.; Karpova, E.I.; Demina, O.M.; Shnayder, N.A. The role of extracellular matrix in skin wound healing. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, F.H.; Kelkar, N.; Deshmukh, T. Molecular basis for mechanical properties of ECMs: Proposed role of fibrillar collagen and proteoglycans in tissue biomechanics. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonté, F.; Girard, D.; Archambault, J.-C.; Desmoulière, A. Skin changes during ageing. Biochem. Cell Biol. Ageing Part II Clin. Sci. 2019, 91, 249–280. [Google Scholar]
- Raskin, R.E. Skin and subcutaneous tissue. In Canine and Feline Cytology: A Color Atlas and Interpretation Guide; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 34–90. [Google Scholar]
- Zwick, R.K.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Horsley, V.; Plikus, M.V. Anatomical, physiological, and functional diversity of adipose tissue. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 68–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ressler, S.; Bartkova, J.; Niederegger, H.; Bartek, J.; Scharffetter-Kochanek, K.; Jansen-Dürr, P.; Wlaschek, M. p16INK4A is a robust in vivo biomarker of cellular aging in human skin. Aging Cell 2006, 5, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaar, M. Clinical and histological features of intrinsic versus extrinsic skin aging. In Skin Aging; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Tobin, D.J. Introduction to skin aging. J. Tissue Viability 2017, 26, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krutmann, J.; Schikowski, T.; Morita, A.; Berneburg, M. Environmentally-induced (extrinsic) skin aging: Exposomal factors and underlying mechanisms. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, M. Exogenous factors in skin aging. Environ. Factors Ski. Dis. 2007, 35, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Benedetto, A.V. The environment and skin aging. Clin. Dermatol. 1998, 16, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, R.E.; Gibbs, N.K.; Griffiths, C.E.; Sherratt, M.J. Damage to skin extracellular matrix induced by UV exposure. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wlaschek, M.; Tantcheva-Poór, I.; Naderi, L.; Ma, W.; Schneider, L.A.; Razi-Wolf, Z.; Schüller, J.; Scharffetter-Kochanek, K. Solar UV irradiation and dermal photoaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2001, 63, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jager, T.; Cockrell, A.; Du Plessis, S. Ultraviolet light induced generation of reactive oxygen species. Ultrav. Light Hum. Health Dis. Environ. 2017, 996, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Zorov, D.B.; Juhaszova, M.; Sollott, S.J. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 909–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranneh, Y.; Ali, F.; Akim, A.M.; Hamid, H.A.; Khazaai, H.; Fadel, A. Crosstalk between reactive oxygen species and pro-inflammatory markers in developing various chronic diseases: A review. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2017, 60, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusamy, V.; Piva, T.J. The UV response of the skin: A review of the MAPK, NFκB and TNFα signal transduction pathways. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2010, 302, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarosh, D.; Both, D.; Kibitel, J.; Anderson, C.; Elmets, C.; Brash, D.; Brown, D. Regulation of TNFα production and release in human and mouse keratinocytes and mouse skin after UV-B irradiation. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2000, 16, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisby, S.; Hauser, C. Transcriptional regulation of tumor necrosis factor-α in keratinocytes mediated by interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α. Exp. Dermatol. 2002, 11, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segre, J.A. Epidermal barrier formation and recovery in skin disorders. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Koning, H.; Van Den Bogaard, E.; Bergboer, J.; Kamsteeg, M.; van Vlijmen-Willems, I.; Hitomi, K.; Henry, J.; Simon, M.; Takashita, N.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A. Expression profile of cornified envelope structural proteins and keratinocyte differentiation-regulating proteins during skin barrier repair. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 166, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boury-Jamot, M.; Daraspe, J.; Bonté, F.; Perrier, E.; Schnebert, S.; Dumas, M.; Verbavatz, J.-M. Skin aquaporins: Function in hydration, wound healing, and skin epidermis homeostasis. In Aquaporins; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 205–217. [Google Scholar]
- Tricarico, P.M.; Mentino, D.; De Marco, A.; Del Vecchio, C.; Garra, S.; Cazzato, G.; Foti, C.; Crovella, S.; Calamita, G. Aquaporins are one of the critical factors in the disruption of the skin barrier in inflammatory skin diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandilands, A.; Sutherland, C.; Irvine, A.D.; McLean, W.I. Filaggrin in the frontline: Role in skin barrier function and disease. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, W.; Kumar, V.; Beer, H.-D.; Richter, M.; Wohlenberg, C.; Reuter, U.; Thiering, S.; Staratschek-Jox, A.; Hofmann, A.; Kreusch, F. Keratin 1 maintains skin integrity and participates in an inflammatory network in skin through interleukin-18. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 5269–5279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ågren, M.S.; Schnabel, R.; Christensen, L.H.; Mirastschijski, U. Tumor necrosis factor-α-accelerated degradation of type I collagen in human skin is associated with elevated matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1 and MMP-3 ex vivo. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 94, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimni, M.E.; Harkness, R.D. Molecular structure and functions of collagen. In Collagen; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 1–78. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, H.; Shimbo, K.; Inoue, Y.; Takino, Y.; Kobayashi, H. Importance of amino acid composition to improve skin collagen protein synthesis rates in UV-irradiated mice. Amino Acids 2012, 42, 2481–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, G.J.; Kang, S.; Varani, J.; Bata-Csorgo, Z.; Wan, Y.; Datta, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Mechanisms of photoaging and chronological skin aging. Arch. Dermatol. 2002, 138, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwar, H.S.; Griffiths, C.E.; Fisher, G.J.; Hamilton, T.A.; Voorhees, J.J. Reduced type I and type III procollagens in photodamaged adult human skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1995, 105, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reunanen, N.; Li, S.-P.; Ahonen, M.; Foschi, M.; Han, J.; Kähäri, V.-M. Activation of p38α MAPK enhances collagenase-1 (matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-1) and stromelysin-1 (MMP-3) expression by mRNA stabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 32360–32368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuben, P.M.; Cheung, H.S. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) gene expression by protein kinases. Front Biosci 2006, 11, 1199–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.; Cheong, Y.-K.; Kim, N.-H.; Chung, H.-T.; Kang, D.G.; Pae, H.-O. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive oxygen species: How can ROS activate MAPK pathways? J. Signal Transduct. 2011, 2011, 792639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCubrey, J.A.; LaHair, M.M.; Franklin, R.A. Reactive oxygen species-induced activation of the MAP kinase signaling pathways. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liacini, A.; Sylvester, J.; Li, W.Q.; Huang, W.; Dehnade, F.; Ahmad, M.; Zafarullah, M. Induction of matrix metalloproteinase-13 gene expression by TNF-α is mediated by MAP kinases, AP-1, and NF-κB transcription factors in articular chondrocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 288, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchowsky, A.; Frleta, D.; Vincenti, M.P. Integration of the NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase/AP-1 pathways at the collagenase-1 promoter: Divergence of IL-1 and TNF-dependent signal transduction in rabbit primary synovial fibroblasts. Cytokine 2000, 12, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, R.; Cho, D.-Y.; Su-Kim, I.; Choi, D.-K. Dendropanax morbiferus and other species from the genus Dendropanax: Therapeutic potential of its traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Kim, K.S.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, H.B.; Cao, S.; Kumar, V.; Kwak, J.H. Protective effects of dendropanoxide isolated from Dendropanax morbifera against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-J.; Kim, D.-M.; Choi, H.-B.; Jeong, M.-H.; Kwon, S.-H.; Kim, H.-R.; Kwak, J.-H.; Chung, K.-H. Dendropanoxide, a triterpenoid from dendropanax morbifera, ameliorates hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting activation of hepatic stellate cells through autophagy inhibition. Nutrients 2021, 14, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, A.; Gali, S.; Sharma, S.; Kacew, S.; Yoon, S.; Jeong, H.G.; Kwak, J.H.; Kim, H.S. Dendropanoxide alleviates Thioacetamide-induced hepatic fibrosis via inhibition of ROS production and inflammation in BALB/C mice. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.-I. Antidiabetic effects of dendropanoxide from leaves of Dendropanax morbifera Leveille in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2011, 30, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.-M.; Kim, S.-H.; Kwon, C.; Kim, S.-Y.; Yang, Y.-J.; Kim, J.-S.; Ali, M.; Ahmad, A. New chemical constituents from the bark of Dendropanax morbifera leveille and their evaluation of antioxidant activities. Molecules 2019, 24, 3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjithkumar, R.; Alhadidi, Q.; Shah, Z.A.; Ramanathan, M. Tribulusterine containing tribulus terrestris extract exhibited neuroprotection through attenuating stress kinases mediated inflammatory mechanism: In vitro and in vivo studies. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 1228–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gali, S.; Sharma, S.; Kundu, A.; Lee, E.; Han, J.H.; Shin, J.K.; Choi, J.S.; Kyung, S.Y.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, H.S. Protective effect of dendropanoxide against cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity via anti-inflammatory activities in Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2023, 33, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, H.-J.; Park, S.; Lee, J.-W.; Park, H.-J.; Baek, S.-H.; Kim, E.-K.; Yu, S.-W. Extracts from Dendropanax morbifera leaves have modulatory effects on neuroinflammation in microglia. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2016, 44, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-J.; Kwak, M.; Baek, S.-H. Neuroprotective effects of Dendropanax morbifera leaves on glutamate-induced oxidative cell death in HT22 mouse hippocampal neuronal cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 251, 112518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Kim, S.-B.; Lee, S.B.; Son, S.-R.; Choi, E.J.; Park, B.C.; Hong, E.; Kim, Y.A.; Moon, B.S.; Lee, S. Investigating the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of Nypa fruticans: A multifaceted approach to skin protection and aging. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2025, 68, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Peng, L.; Jegal, H.; Park, N.-J.; Bong, S.-K.; Lee, J.W.; Pyo, J.J.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S.-N. The soybean cultivar SCEL-1 shows potent anti-photoaging effects in a UV-induced three-dimensional human skin and hairless mouse model. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2022, 65, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Im, A.-R.; Shim, K.-S.; Seo, C.-S.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Yoo, J.S.; Choi, S.; Chae, S. Chikusetsusaponin IVa from Dolichos lablab Linne attenuates UVB-induced skin photoaging in mice by suppressing MAPK/AP-1 signaling. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2024, 67, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.-Y.; Lee, C.-D.; Ku, J.J.; Lee, S.; Lee, S. Anti-aging potential of Cephalotaxus harringtonia extracts: The role of harringtonine and homoharringtonine in skin protection. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2024, 67, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechner, N.; Schroeder, P.; Jakob, S.; Kunze, K.; Maresch, T.; Calles, C.; Krutmann, J.; Haendeler, J. Changes of MMP-1 and collagen type Iα1 by UVA, UVB and IRA are differentially regulated by Trx-1. Exp. Gerontol. 2008, 43, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wen, X.; Hao, D.; Zhang, N.; He, G.; Jiang, X. NF-κB signaling in skin aging. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2019, 184, 111160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, J.H.; Mamelak, A.J.; McElgunn, P.J.; Morison, W.L.; Sauder, D.N. Photoaging: Mechanisms and repair. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 55, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehan, S.; Meena, H.; Sharma, D.; Sankhla, R. JNK: A stress-activated protein kinase therapeutic strategies and involvement in Alzheimer’s and various neurodegenerative abnormalities. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 43, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminska, B. MAPK signalling pathways as molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy—From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Proteins Proteom. 2005, 1754, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenda, A.; Rousseau, S. p38 MAP-kinases pathway regulation, function and role in human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Cell Res. 2007, 1773, 1358–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Shi, L.Z.; Chi, H. Regulation of JNK and p38 MAPK in the immune system: Signal integration, propagation and termination. Cytokine 2009, 48, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, S.-Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.; Lee, S. Evaluation of the Antiaging Potential of the Dendropanax morbiferus-Derived Compound Dendropanoxide in TNF-α-Stimulated Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030188
Ahn S-Y, Lee S, Kim D, Lee S. Evaluation of the Antiaging Potential of the Dendropanax morbiferus-Derived Compound Dendropanoxide in TNF-α-Stimulated Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(3):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030188
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Si-Young, Sanghyun Lee, Daeyoung Kim, and Sullim Lee. 2025. "Evaluation of the Antiaging Potential of the Dendropanax morbiferus-Derived Compound Dendropanoxide in TNF-α-Stimulated Human Dermal Fibroblasts" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 3: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030188
APA StyleAhn, S.-Y., Lee, S., Kim, D., & Lee, S. (2025). Evaluation of the Antiaging Potential of the Dendropanax morbiferus-Derived Compound Dendropanoxide in TNF-α-Stimulated Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(3), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030188









