Hepatic Growth Factor as a Potential Biomarker for Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Multimodal Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Two-Sample Bidirectional MR Analysis
2.2. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing (scRNA-Seq) Analysis
2.3. RNA-Seq Analysis
3. Results
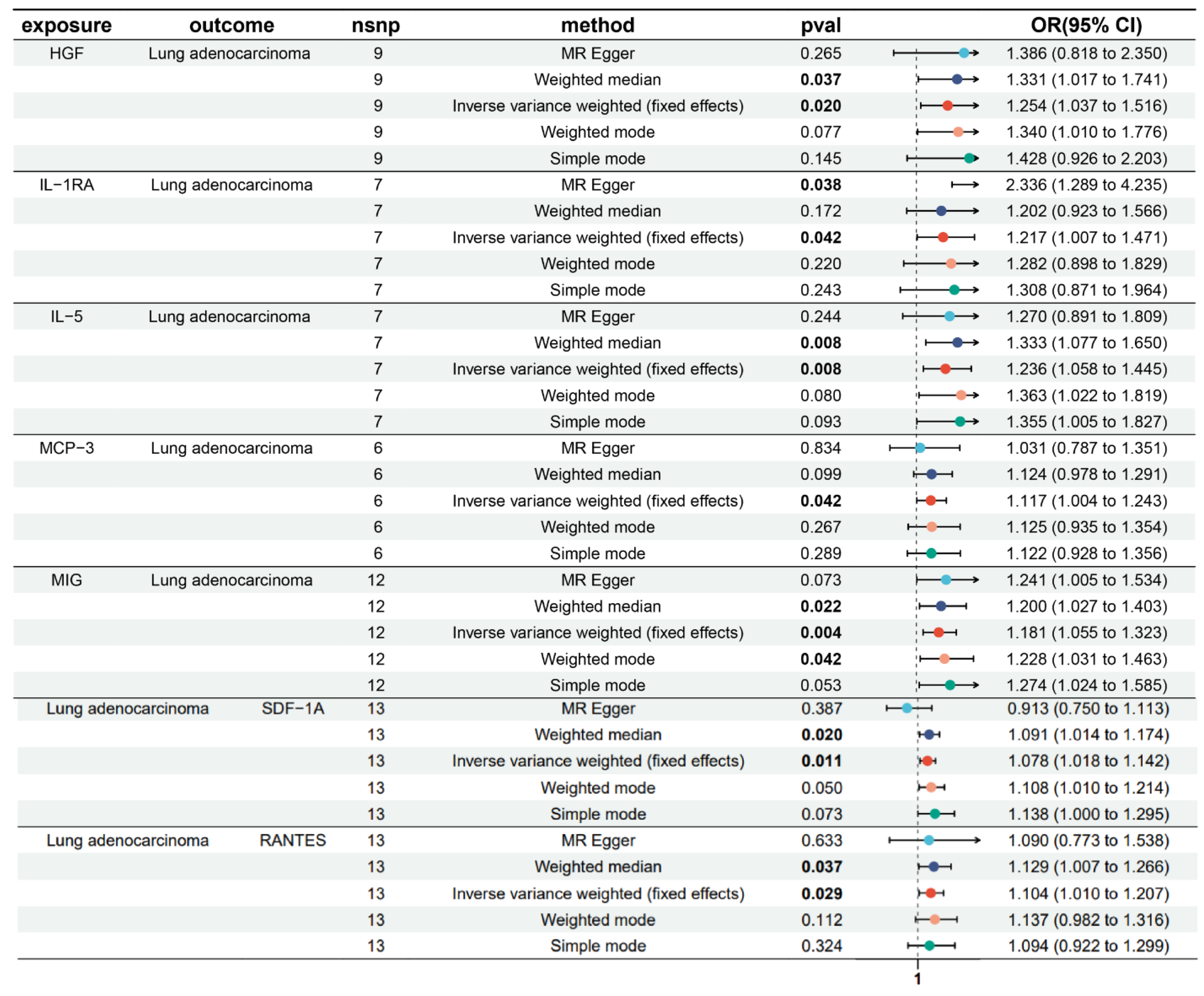
3.1. Bidirectional Causal Effects of Inflammatory Cytokines on LUAD
3.2. MR Sensitivity Analysis
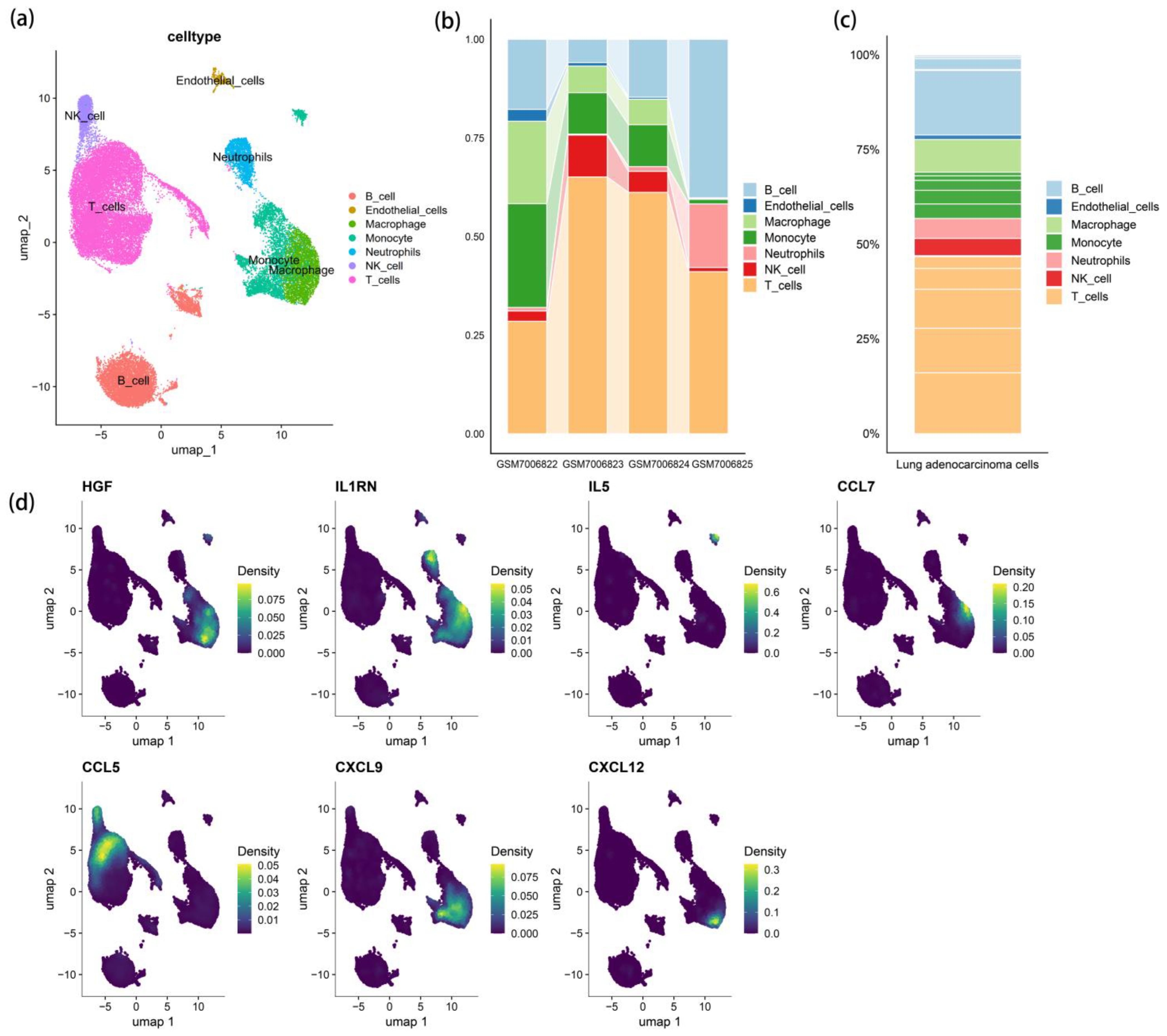
3.3. scRNA-Seq Cell Clustering and Gene Expression Profiles
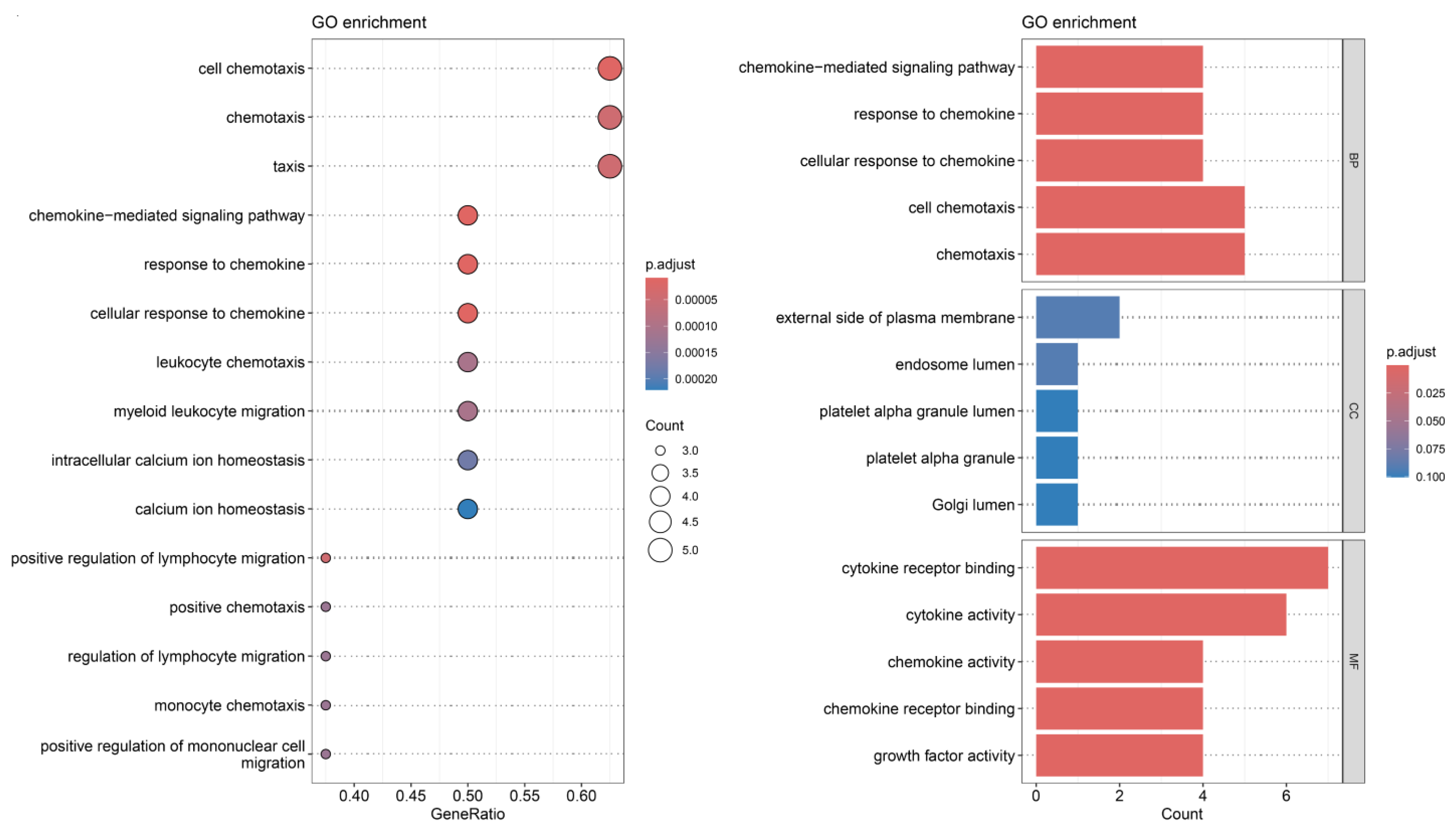
3.4. Receptor–Ligand Mediated Cell Communication
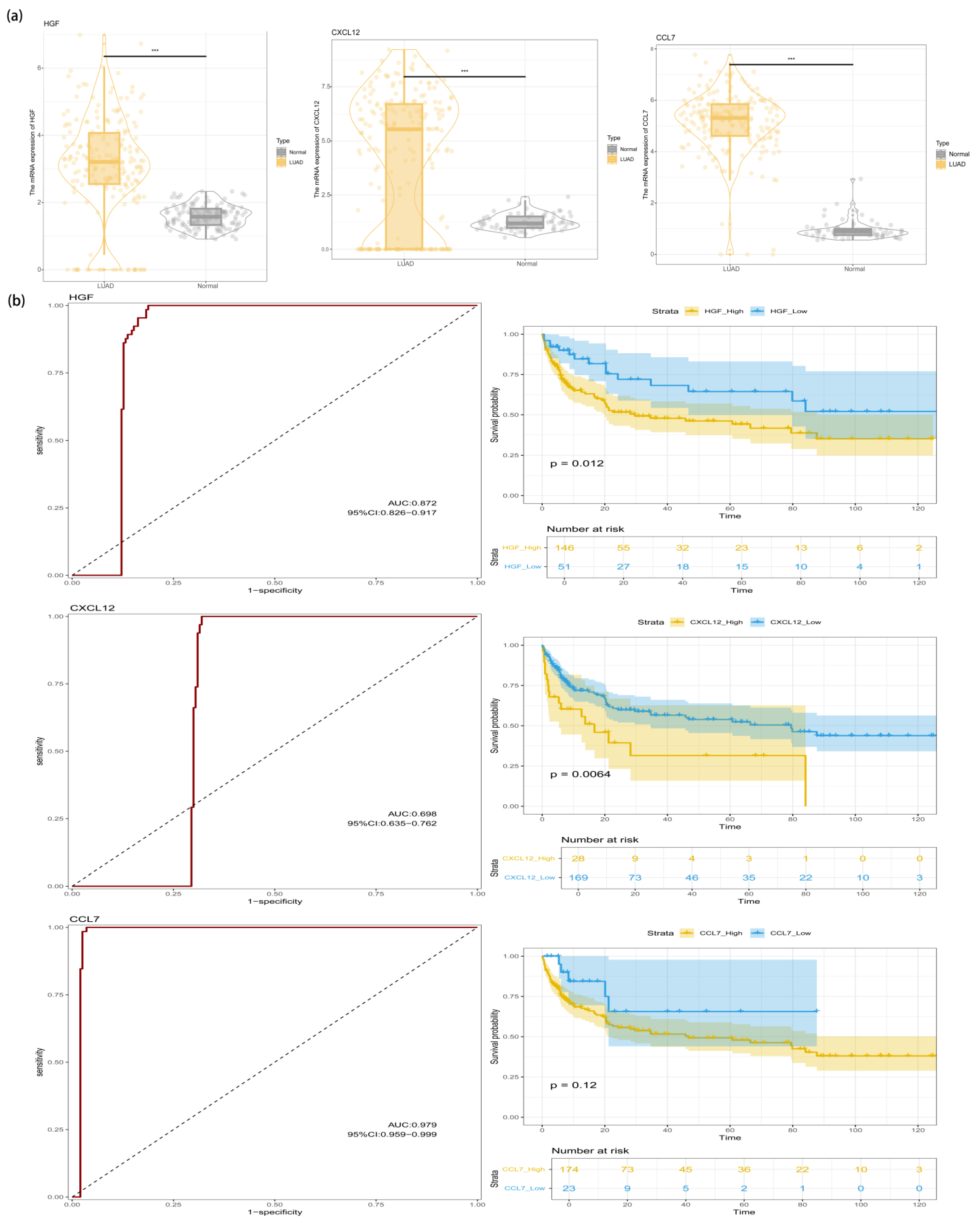
3.5. Identification of HGF in the LUAD Transcriptome
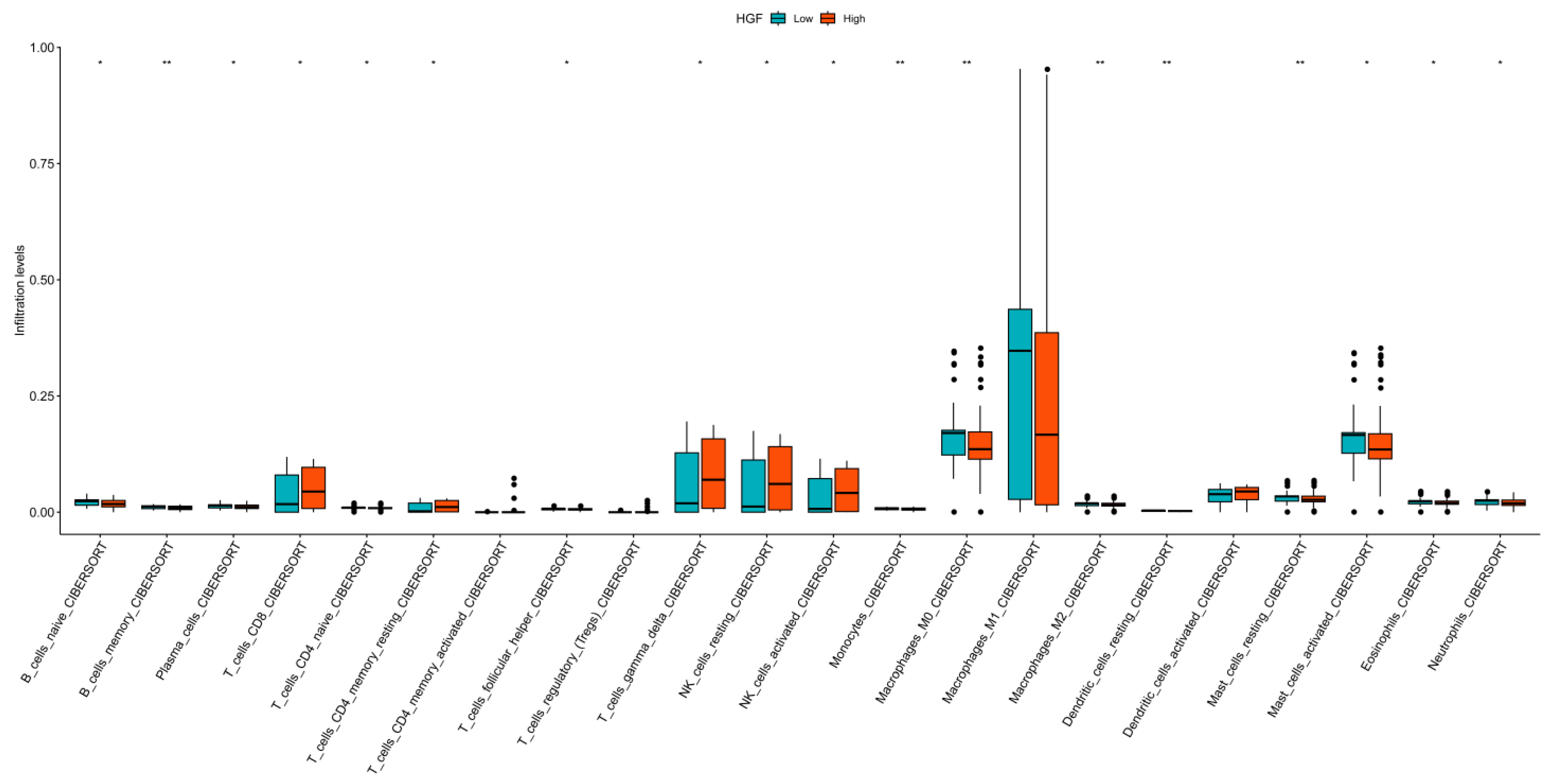
3.6. Immune Landscape Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LUAD | lung adenocarcinoma |
| MR | Mendelian randomization |
| HGF | hepatocyte growth factor |
| MCP-3 | monocyte chemoattractant protein-3 |
| MIG | monokine induced by interferon-γ |
| RANTES | regulated upon activation normal T-cell expressed and secreted |
| SDF-1A | stromal cell-derived factor-1α |
| OS | overall survival |
| IL-2 | interleukin-2 |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| GWAS | genome-wide association study |
| SNPs | single nucleotide polymorphisms |
| IVs | instrumental variables |
| scRNA-seq | Single-Cell RNA Sequencing |
| umap | uniform manifold approximation and projection |
| GO | gene ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| RF | random forest |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| K-M | Kaplan-Meier |
| IL-1RA | interleukin-1 receptor antagonist |
| IVW | Inverse variance-weighted |
| NK | natural killer |
| CCL7 | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 7 |
| CXCL9 | chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 9 |
| BP | biological process |
| MF | molecular function |
| CC | cellular component |
| PFS | progression-free survival |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung cancer |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| TKIs | tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| PD-L1 | programmed cell death ligand 1 |
References
- Denisenko, T.V.; Budkevich, I.N.; Zhivotovsky, B. Cell Death-Based Treatment of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Succony, L.; Rassl, D.M.; Barker, A.P.; McCaughan, F.M.; Rintoul, R.C. Adenocarcinoma Spectrum Lesions of the Lung: Detection, Pathology and Treatment Strategies. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 99, 102237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Wang, L.; Hou, J.; Zhu, B.; Min, Z.; Zhang, M.; Song, D.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, X. Targeting Roles of Inflammatory Microenvironment in Lung Cancer and Metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.-Y.; Chuah, K.L.; Eng, P.; Leong, S.S.; Lim, E.; Lim, T.K.; Ng, A.; Poh, W.T.; Tee, A.; Teh, M.; et al. Aspirin and Non-Aspirin Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug Use and Risk of Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberg, A.J.; Samet, J.M. Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Chest 2003, 123, 21S–49S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafri, S.H.; Shi, R.; Mills, G. Advance Lung Cancer Inflammation Index (ALI) at Diagnosis Is a Prognostic Marker in Patients with Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): A Retrospective Review. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkwill, F.; Mantovani, A. Inflammation and Cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet 2001, 357, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Visser, K.E.; Joyce, J.A. The Evolving Tumor Microenvironment: From Cancer Initiation to Metastatic Outgrowth. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 374–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlon, K.C.; Miljkovic, M.D.; Waldmann, T.A. Cytokines in the Treatment of Cancer. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019, 39, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.R.; Charles, K.A.; Hoare, S.A.; Rye, R.L.; Jodrell, D.I.; Aird, R.E.; Vora, R.; Prabhakar, U.; Nakada, M.; Corringham, R.E.; et al. A Clinical Study Assessing the Tolerability and Biological Effects of Infliximab, a TNF-Alpha Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, M.L.; Obermueller, E.; Maisey, N.R.; Hoare, S.; Edmonds, K.; Li, N.F.; Chao, D.; Hall, K.; Lee, C.; Timotheadou, E.; et al. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha as a New Target for Renal Cell Carcinoma: Two Sequential Phase II Trials of Infliximab at Standard and High Dose. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4542–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sollis, E.; Mosaku, A.; Abid, A.; Buniello, A.; Cerezo, M.; Gil, L.; Groza, T.; Güne¸s, O.; Hall, P.; Hayhurst, J. The NHGRI-EBI GWASCatalog: Knowledgebase and Deposition Resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D977–D985. Available online: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/ (accessed on 25 June 2024). [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base Platform Supports Systematic Causal Inference across the Human Phenome. eLife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuhashi, A.; Koyama, K.; Ogino, H.; Afroj, T.; Nguyen, N.T.; Yoneda, H.; Otsuka, K.; Sugimoto, M.; Kondoh, O.; Nokihara, H.; et al. Identification of Fibrocyte Cluster in Tumors Reveals the Role in Antitumor Immunity by PD-L1 Blockade. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aran, D.; Looney, A.P.; Liu, L.; Wu, E.; Fong, V.; Hsu, A.; Chak, S.; Naikawadi, R.P.; Wolters, P.J.; Abate, A.R.; et al. Reference-Based Analysis of Lung Single-Cell Sequencing Reveals a Transitional Profibrotic Macrophage. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.-Q.; Ding, K.; Strumpf, D.; Weir, B.A.; Meyerson, M.; Pennell, N.; Thomas, R.K.; Naoki, K.; Ladd-Acosta, C.; Liu, N.; et al. Prognostic and Predictive Gene Signature for Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Resected Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4417–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Aerts, J.; den Hamer, B.; van Ijcken, W.; den Bakker, M.; Riegman, P.; van der Leest, C.; van der Spek, P.; Foekens, J.A.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; et al. Gene Expression-Based Classification of Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinomas and Survival Prediction. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, D.G.; Kardia, S.L.; Huang, C.C.; Giordano, T.J.; Levin, A.M.; Misek, D.E.; Lin, L.; Chen, G.; Gharib, T.G.; Thomas, D.G.; et al. Gene-Expression Profiles Predict Survival of Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okayama, H.; Kohno, T.; Ishii, Y.; Shimada, Y.; Shiraishi, K.; Iwakawa, R.; Furuta, K.; Tsuta, K.; Shibata, T.; Yamamoto, S.; et al. Identification of Genes Upregulated in ALK-Positive and EGFR/KRAS/ALK-Negative Lung Adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and Tumor Progression: Signaling Pathways and Targeted Intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Xue, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Song, Y.; Qi, Y. The Role of Tumor Inflammatory Microenvironment in Lung Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 688625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, S.; Luciano, M.; Horejs-Hoeck, J. The Cytokine Network in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): A Focus on pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Mediators. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2018, 43, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. IL-6 and Related Cytokines as the Critical Lynchpins between Inflammation and Cancer. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Lenz, H.-J. Targeting IL-8 in Colorectal Cancer. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Shi, M.; Peng, L.-X.; Wei, W.; Li, X.-J.; Guo, Z.-X.; Li, S.-H.; Zhong, C.; Qian, C.-N.; Guo, R.-P. Dovitinib Preferentially Targets Endothelial Cells Rather than Cancer Cells for the Inhibition of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth and Metastasis. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hendricks, D.T.; Wamunyokoli, F.; Parker, M.I. A Growth-Related Oncogene/CXC Chemokine Receptor 2 Autocrine Loop Contributes to Cellular Proliferation in Esophageal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3071–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Wen, Y.; Wang, C.; Kang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Soulika, A.M.; Liu, B.; Zhao, M.; Han, X.; et al. Lung Adenocarcinoma-related TNF-α-dependent Inflammation Upregulates MHC-II on Alveolar Type II Cells through CXCR-2 to Contribute to Treg Expansion. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 12197–12213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Sui, Q.; Jin, X.; Shan, G.; Huang, Y.; Yi, Y.; Zeng, D.; Zhao, M.; Zhan, C.; Wang, Q.; et al. IL6-STAT3-C/EBPβ-IL6 Positive Feedback Loop in Tumor-Associated Macrophages Promotes the EMT and Metastasis of Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2024, 43, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, B.; Hu, M.; Lou, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Qian, J.; Chu, T.; Han, B. CXCL9 as a Prognostic Inflammatory Marker in Early-Stage Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, K.; Hu, S.; Lou, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Han, B. MDC and BLC Are Independently Associated with the Significant Risk of Early Stage Lung Adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-L.; Lai, T.-C.; Lee, W.-J.; Chen, Y.-C.; Ho, K.-H.; Hung, W.-Y.; Yang, Y.-C.; Chan, M.-H.; Hsieh, F.-K.; Chung, C.-L.; et al. Sustaining the Activation of EGFR Signal by Inflammatory Cytokine IL17A Prompts Cell Proliferation and EGFR-TKI Resistance in Lung Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ou, W.; Cai, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, W.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q. Interleukin-32 Contributes to Invasion and Metastasis of Primary Lung Adenocarcinoma via NF-kappaB Induced Matrix Metalloproteinases 2 and 9 Expression. Cytokine 2014, 65, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Fragala, M.S.; McElhaney, J.E.; Kuchel, G.A. Conceptual and Methodological Issues Relevant to Cytokine and Inflammatory Marker Measurements in Clinical Research. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.R.; Fanidi, A.; Grankvist, K.; Muller, D.C.; Brennan, P.; Manjer, J.; Byrnes, G.; Hodge, A.; Severi, G.; Giles, G.G.; et al. Inflammatory Cytokines and Lung Cancer Risk in 3 Prospective Studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 185, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, A.M.; Varghese, S.; Xu, H.; Alexander, H.R. Interleukin-1 and Cancer Progression: The Emerging Role of Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist as a Novel Therapeutic Agent in Cancer Treatment. J. Transl. Med. 2006, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R.; Kunkel, S.L.; Standiford, T.J.; Chensue, S.W.; Rolfe, M.W.; Orringer, M.B.; Whyte, R.I.; Burdick, M.D.; Danforth, J.M.; Gilbert, A.R. The Production of Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist by Human Bronchogenic Carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 143, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yigit, M.; Değirmencioğlu, S.; Ugurlu, E.; Yaren, A. Effect of Serum Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Level on Survival of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 6, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Song, R.; Wakeland, E.K.; Pasare, C. T Cell-Intrinsic IL-1R Signaling Licenses Effector Cytokine Production by Memory CD4 T Cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.M.; Davila, D.G.; Peters, S.G. Paraneoplastic Syndromes Associated with Lung Cancer. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1993, 68, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayama, N.; Hattori, S.; Takahashi, G.; Takahashi, F.; Takeuchi, T.; Tanaka, J.; Horio, Y.; Takiguchi, H.; Tomomatsu, K.; Kitahara, A.; et al. Cytokine/Chemokine/Growth Factor Levels in Malignant Pleural Effusion of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Tokai J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2020, 45, 224–229. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S.; Su, X.-M.; Ke, L.-N.; Huang, Y.-G. CXCL9 Correlates with Antitumor Immunity and Is Predictive of a Favorable Prognosis in Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1077780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Y.; Lin, A.; Zhu, W.; Wei, T.; Luo, P.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J. Catenin Alpha-2 Mutation Changes the Immune Microenvironment in Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients Receiving Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 645862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Tan, Q.; Tao, D.; Song, Y.; Song, W.; Wang, J.; Ma, L.; Wu, D.; Feng, Y.; Yao, J.; et al. Cytokines Screening Identifies MIG (CXCL9) for Postoperative Recurrence Prediction in Operated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Cytokine 2022, 149, 155759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Bai, X.; Lu, Z.; Liu, S.; Jiang, H. LINC01094/SPI1/CCL7 Axis Promotes Macrophage Accumulation in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Tumor Cell Dissemination. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 6450721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melese, E.S.; Franks, E.; Cederberg, R.A.; Harbourne, B.T.; Shi, R.; Wadsworth, B.J.; Collier, J.L.; Halvorsen, E.C.; Johnson, F.; Luu, J.; et al. CCL5 Production in Lung Cancer Cells Leads to an Altered Immune Microenvironment and Promotes Tumor Development. Oncoimmunology 2022, 11, 2010905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, L.; Cheng, S.; Fan, Z.; Shen, Z.; Xue, W.; Zheng, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, D.; Zhang, K.; et al. Lung Adenocarcinoma-Intrinsic GBE1 Signaling Inhibits Anti-Tumor Immunity. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, C.J.; Arenberg, D.A.; Huang, C.-C.; Giordano, T.J.; Thomas, D.G.; Misek, D.E.; Chen, G.; Iannettoni, M.D.; Orringer, M.B.; Hanash, S.; et al. RANTES Expression Is a Predictor of Survival in Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 3803–3812. [Google Scholar]
- Sadri, F.; Rezaei, Z.; Fereidouni, M. The Significance of the SDF-1/CXCR4 Signaling Pathway in the Normal Development. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 3307–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Lei, W.; Wang, H.; Ni, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; et al. CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 Axis in Cancer: From Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 3341–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lan, W.; Xu, M.; Song, J.; Mao, J.; Li, C.; Du, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, E.; Zhang, R.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblast-Derived SDF-1 Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Lung Adenocarcinoma via CXCR4/β-Catenin/PPARδ Signalling. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.H.; Gao, Y.; Soucheray, M.; Pulido, I.; Kikuchi, E.; Rodríguez, M.L.; Gandhi, R.; Lafuente-Sanchis, A.; Aupí, M.; Alcácer Fernández-Coronado, J.; et al. CXCR7 Reactivates ERK Signaling to Promote Resistance to EGFR Kinase Inhibitors in NSCLC. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4439–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, M.S.; Liu, N.; Chen, J.R.; Pappas, J.; Ho, J.; To, C.; Viallet, J.; Park, M.; Zhu, H. Differential Expression of Met/Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor in Subtypes of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers. Lung Cancer 1998, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherardi, E.; Birchmeier, W.; Birchmeier, C.; Vande Woude, G. Targeting MET in Cancer: Rationale and Progress. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosavi, F.; Giovannetti, E.; Peters, G.J.; Firuzi, O. Combination of HGF/MET-Targeting Agents and Other Therapeutic Strategies in Cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 160, 103234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, S.; Wang, W.; Li, Q.; Yamada, T.; Kita, K.; Donev, I.S.; Nakamura, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Shimizu, E.; Nishioka, Y.; et al. Dual Inhibition of Met Kinase and Angiogenesis to Overcome HGF-Induced EGFR-TKI Resistance in EGFR Mutant Lung Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padda, S.; Neal, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A. MET Inhibitors in Combination with Other Therapies in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2012, 1, 238–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakade, J.; Takeuchi, S.; Nakagawa, T.; Ishikawa, D.; Sano, T.; Nanjo, S.; Yamada, T.; Ebi, H.; Zhao, L.; Yasumoto, K.; et al. Triple Inhibition of EGFR, Met, and VEGF Suppresses Regrowth of HGF-Triggered, Erlotinib-Resistant Lung Cancer Harboring an EGFR Mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhong, L.; Li, K.; Nishiyama, A.; Arai, S.; Yano, S.; Wang, W. EGFR-TKI Resistance Promotes Immune Escape in Lung Cancer via Increased PD-L1 Expression. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowicz, S.; Principe, D.R.; Dorman, M.J.; McHenry, A.J.; Sondarva, G.; Kumar, S.; Ananthanarayanan, V.; Simms, P.E.; Hess, A.; Rana, A. HAI-1 Is an Independent Predictor of Lung Cancer Mortality and Is Required for M1 Macrophage Polarization. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Regulates Macrophage Transition to the M2 Phenotype and Promotes Murine Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Wu, W. Influencing Factors and Significance of Tumor-associated Macrophage Polarization in Tumor Microenvironment. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi 2023, 26, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demuth, C.; Andersen, M.N.; Jakobsen, K.R.; Madsen, A.T.; Sørensen, B.S. Increased PD-L1 Expression in Erlotinib-Resistant NSCLC Cells with MET Gene Amplification Is Reversed upon MET-TKI Treatment. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68221–68229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balan, M.; Mier y Teran, E.; Waaga-Gasser, A.M.; Gasser, M.; Choueiri, T.K.; Freeman, G.; Pal, S. Novel Roles of C-Met in the Survival of Renal Cancer Cells through the Regulation of HO-1 and PD-L1 Expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 8110–8120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Tang, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Chen, Q. Targeting MET Endocytosis or Degradation to Overcome HGF-Induced Gefitinib Resistance in EGFR-Sensitive Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 682, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoker, M.; Gherardi, E.; Perryman, M.; Gray, J. Scatter Factor Is a Fibroblast-Derived Modulator of Epithelial Cell Mobility. Nature 1987, 327, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagita, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Sekiguchi, K.; Ishibashi, H.; Niho, Y.; Nakamura, T. Hepatocyte Growth Factor May Act as a Pulmotrophic Factor on Lung Regeneration after Acute Lung Injury. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 21212–21217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh-Kaw, P.R.A.V.E.E.N.A.; Zarnegar, R.E.Z.A.; Siegfried, J.M. Stimulatory Effects of Hepatocyte Growth Factor on Normal and Neoplastic Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 268, L1012–L1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmichi, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Nakamura, T. In Vivo Mitogenic Action of HGF on Lung Epithelial Cells: Pulmotrophic Role in Lung Regeneration. Am. J. Physiol. 1996, 270, L1031–L1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, S.; Yamada, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Tachibana, K.; Minami, Y.; Yatabe, Y.; Mitsudomi, T.; Tanaka, H.; Kimura, T.; Kudoh, S.; et al. Hepatocyte Growth Factor Expression in EGFR Mutant Lung Cancer with Intrinsic and Acquired Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in a Japanese Cohort. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, Y.; Hashimoto, E.; Nakatani, N.; Abe, M.; Satoh, Y.; Sakata, K.; Fujii, T.; Fujimoto-Ouchi, K.; Sugimoto, M.; Nagahashi, S.; et al. Combining Onartuzumab with Erlotinib Inhibits Growth of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Activating EGFR Mutations and HGF Overexpression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Tong, L.; Liu, B.; Qi, F.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lu, B.; et al. Plasma Hepatocyte Growth Factor as a Noninvasive Biomarker in Small Cell Lung Cancer. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heist, R.S.; Shim, H.S.; Gingipally, S.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Le, L.; Gainor, J.F.; Zheng, Z.; Aryee, M.; Xia, J.; Jia, P.; et al. MET Exon 14 Skipping in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncologist 2016, 21, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.M.; Oxnard, G.R.; Jackman, D.M.; Savukoski, D.O.; Hall, D.; Shivdasani, P.; Heng, J.C.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Jänne, P.A.; Verma, S.; et al. MET Exon 14 Mutations in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Are Associated with Advanced Age and Stage-Dependent MET Genomic Amplification and c-Met Overexpression. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhuang, J.; Sun, C. Hepatic Growth Factor as a Potential Biomarker for Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Multimodal Study. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030208
Sun M, Yu Y, Zhu H, Yao Y, Zhou X, Wang X, Zhang Y, Xu X, Zhuang J, Sun C. Hepatic Growth Factor as a Potential Biomarker for Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Multimodal Study. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(3):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030208
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Mengxuan, Yang Yu, Hanci Zhu, Yan Yao, Xintong Zhou, Xue Wang, Yubao Zhang, Xiaowei Xu, Jing Zhuang, and Changgang Sun. 2025. "Hepatic Growth Factor as a Potential Biomarker for Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Multimodal Study" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 3: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030208
APA StyleSun, M., Yu, Y., Zhu, H., Yao, Y., Zhou, X., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Xu, X., Zhuang, J., & Sun, C. (2025). Hepatic Growth Factor as a Potential Biomarker for Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Multimodal Study. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(3), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47030208







