FGFRL1: Structure, Molecular Function, and Involvement in Human Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
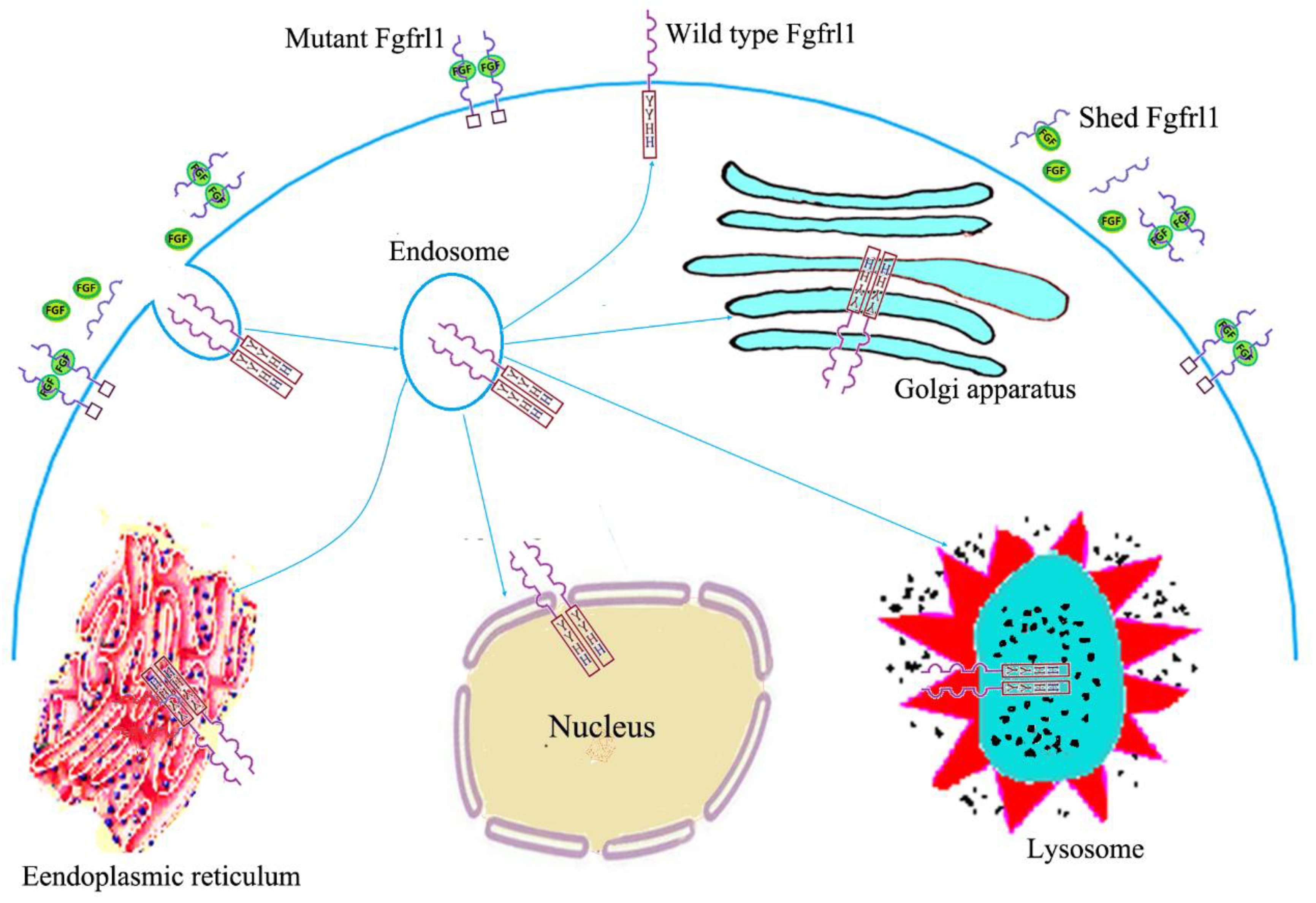
2. Structural Features, Expression Patterns, and Subcellular Location
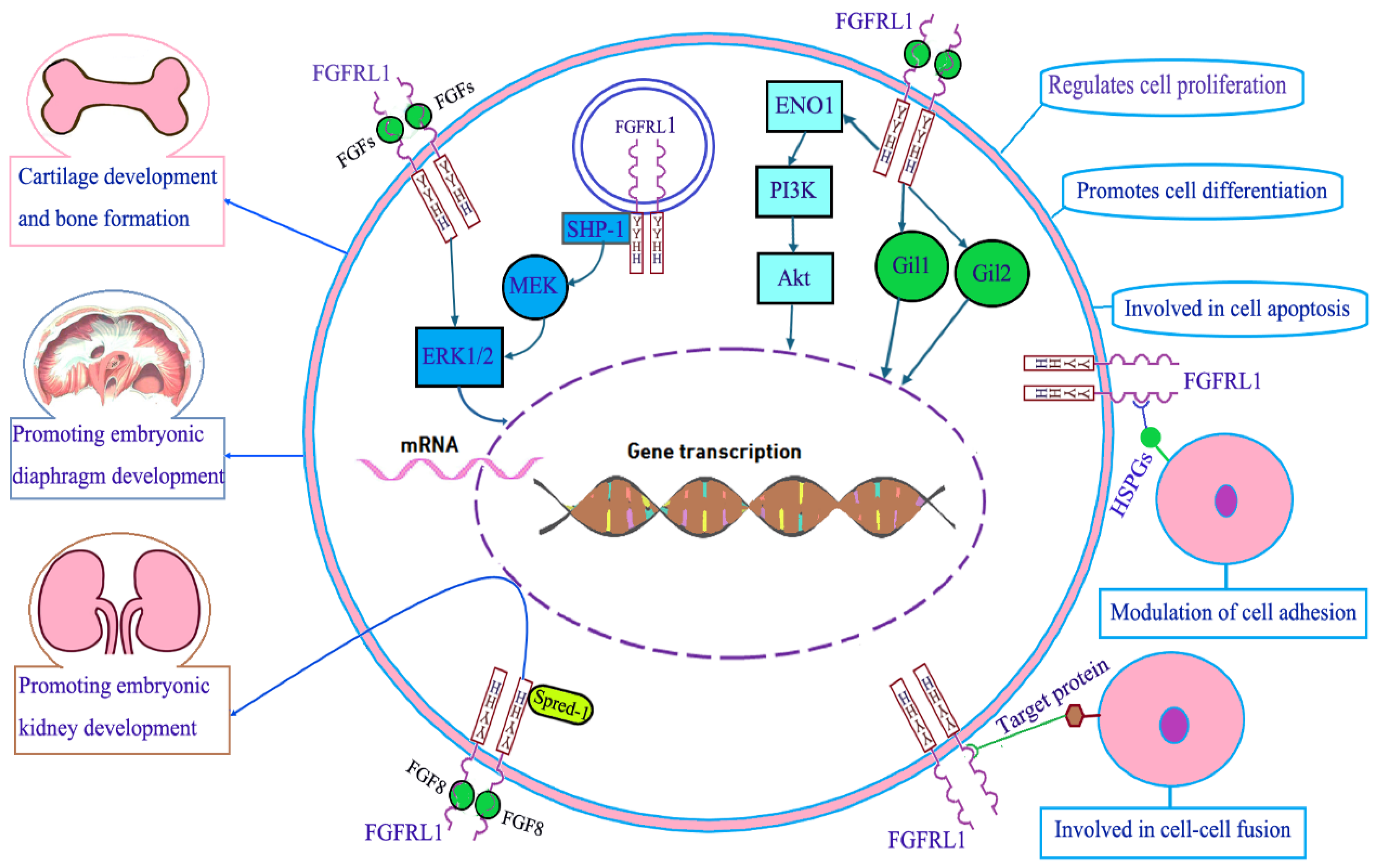
3. Molecular Function of FGFRL1
3.1. FGFRL1 in Cartilage Development and Bone Formation
3.2. FGFRL1 in Diaphragm Development
3.3. FGFRL1 in Kidney Development
3.4. FGFRL1 in Cell Proliferation, Cell Differentiation, and Cell Apoptosis
3.5. FGFRL1 in Cell Adhesion and Cell Fusion
3.6. FGFRL1 in Cell Signal Transduction
4. FGFRL1 and Human Disease
4.1. Congenital Disease
4.2. Hypertension and Osteoporosis
4.3. Degenerative Diseases of the Central Nervous System
4.4. FGFRL1 and Cancer
4.4.1. Bladder Cancer
4.4.2. Esophageal Cancer
4.4.3. Larynx Carcinoma
4.4.4. Lung Cancer
4.4.5. Osteosarcoma
4.4.6. Ovarian Cancer
4.4.7. Pancreatic Cancer
4.4.8. Prostate Cancer
| Cancers | Expression Level | Influence on Cancer Cell’s Biological Behaviors | Roles in Cancer Progression, Chemoresistance, Metastasis, and Prognosis | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bladder cancer | Upregulated in bladder cancer cell lines and tissue samples | FGFRL1 downregulation inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of bladder cancer cells | Promotes bladder cancer growth and metastasis | [85,86] |
| Esophageal cancer | Either positive or negative expression can be detected in esophageal cancer tissue | FGFRL1 accelerates cancer cell proliferation and invasion | FGFRL1 promotes the progression and metastasis of esophageal cancer. FGFRL1-positive is correlated with poor prognosis in esophageal cancer patients | [87,88] |
| Larynx carcinoma | None | Overexpression of FGFRL1 promotes the proliferation of larynx carcinoma SCC10A cells | Promotes the progression of larynx carcinoma | [50] |
| Lung cancer | Upregulated in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) tissues and multidrug-resistant SCLC cells | FGFRL1 accelerates cancer cell proliferation. Knockdown of FGFRL1 increases the chemosensitivity of chemo-resistant SCLC cells | Promotes the progression and chemoresistance of lung cancer | [64,94] |
| Osteosarcoma | Downregulated in osteosarcoma tissues compared with matched normal tissues | Overexpression of FGFRL1 inhibits osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion | Inhibits the progression of osteosarcoma | [14,96] |
| Ovarian cancer (OC) | Upregulated in both OC cells and tissues compared to the normal controls | Downregulation of FGFRL1 inhibits the proliferation and migration of OC cells | Promotes the development and progression of OC. FGFRL1 upregulation is correlated with poor prognosis | [51,97] |
| Pancreatic cancer (PC) | None | Inhibits the migration and chemoresistance of PC cells through inhibiting M2 polarization of macrophages | Inhibits the progression and chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer | [99] |
| Prostate cancer (PCa) | Upregulated in PCa tissues and PCa cells compared to the corresponding normal controls | Upregulation of FGFRL1 accelerates the malignant behaviors of PCa cells | Promotes the development and progression of PCa | [100,101] |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABS | Antley–Bixler syndrome |
| ALS | amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| Akt | protein kinase B |
| CDH | congenital diaphragmatic hernia |
| ENO1 | enolase 1 |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| ESCC | esophageal squamous cell carcinoma |
| FGF | fibroblast growth factor |
| FGFRL1 | fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 |
| FGFRs | fibroblast growth factor receptors |
| 5′UTR | 5′-non-coding sequence |
| HIF-1 | hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) |
| HSPGs | heparan sulfate proteoglycans |
| IHC | immunohistochemical |
| LOH | loss of heterozygosity |
| MEK | mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| MSCs | mesenchymal stromal cells |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung cancer |
| 3′UTR | 3′-non-coding sequence |
| OC | ovarian cancer |
| PC | pancreatic cancer |
| PCa | prostate cancer |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| SCLC | small-cell lung cancer |
| SHP-1 | Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase 1 |
| SNP | single-nucleotide polymorphism |
| 3′UTR | 3′-non-coding sequence |
| WHS | Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome |
References
- Bale, T.A. FGFR-gene family alterations in low-grade neuroepithelial tumors. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2020, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Su, N.; Yang, J.; Tan, Q.; Huang, S.; Jin, M.; Ni, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, D.; Luo, F.; et al. FGF/FGFR signaling in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poźniak, M.; Zarzycka, W.; Porębska, N.; Knapik, A.; Marczakiewicz-Perera, P.; Zakrzewska, M.; Opaliński, Ł. FGF1 fusions with the Fc fragment of IgG1 for the assembly of GFP polygons-mediated multivalent complexes recognizing FGFRs. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piasecka, D.; Braun, M.; Kitowska, K.; Mieczkowski, K.; Kordek, R.; Sadej, R.; Romanska, H. FGFs/FGFRs-dependent signaling in regulation of steroid hormone receptors-implications for therapy of luminal breast cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmer, N.J. Insights into the role of heparan sulphate in fibroblast growth factor signalling: Figure 1. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrou, I.; Weickert, M.O.; Gharanei, S.; Randeva, H.S.; Tan, B.K. Fibroblast growth factors: New insights, new targets in the management of diabetes. Minerva Endocrinol. 2017, 42, 248–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.H.; Schlessinger, J. Asymmetric tyrosine kinase arrangements in activation or autophosphorylation of receptor tyrosine kinases. Mol. Cells 2010, 29, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opaliński, Ł.; Sokołowska-Wędzina, A.; Szczepara, M.; Zakrzewska, M.; Otlewski, J. Antibody-induced dimerization of FGFR1 promotes receptor endocytosis independently of its kinase activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswarakumar, V.P.; Lax, I.; Schlessinger, J. Cellular signaling by fibroblast growth factor receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005, 16, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhou, F.; Zheng, D.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Huang, X. FGF/FGFR signaling: From lung development to respiratory diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 62, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, M.; Wirz, W.; Tag, C.G.; Mavituna, M.; Emans, N.; Korff, T.; Stoldt, V.; Gressner, A.M.; Kiefer, P. Expression pattern of fibroblast growth factors (FGFs), their receptors and antagonists in primary endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells. Growth Factors 2005, 23, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleeman, M.; Fraser, J.; McDonald, M.; Yuan, S.; White, D.; Grandison, P.; Kumble, K.; Watson, J.D.; Murison, J.G. Identification of a new fibroblast growth factor receptor, FGFR5. Gene 2001, 271, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Moon, S.; Yu, K.; Kim, U.; Koh, G.Y. A novel fibroblast growth factor receptor-5 preferentially expressed in the pancreas. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1518, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trueb, B.; Zhuang, L.; Taeschler, S.; Wiedemann, M. Characterization of FGFRL1, a novel fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor preferentially expressed in skeletal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 33857–33865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprajita Sharma, R. Comprehending fibroblast growth factor receptor like 1: Oncogene or tumor suppressor? Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2021, 29, 100472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, S.D.; Amann, R.; Wyder, S.; Trueb, B. Comparison of the gene expression profiles from normal and Fgfrl1 deficient mouse kidneys reveals downstream targets of Fgfrl1 signaling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrams, J.M.; Jiao, Y. Keeping it simple: What mouse models of Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome can tell us about large chromosomal deletions. Dis. Model. Mech. 2009, 2, 315–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, P.; Hannes, F.; Suttie, M.; Devriendt, K.; Vermeesch, J.R.; Faravelli, F.; Forzano, F.; Parekh, S.; Williams, S.; McMullan, D.; et al. Fine-grained facial phenotype-genotype analysis in Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 20, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. The role of fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of cancers including those of the urinary bladder. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 151, 104567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, J.; Yan, W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Fang, W. FGFR families: Biological functions and therapeutic interventions in tumors. Med. Comm. 2023, 4, e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemann, M.; Trueb, B. Characterization of a novel protein (FGFRL1) from human cartilage related to FGF receptors. Genomics 2000, 69, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Falquet, L.; Trueb, B. Genome-wide comparison of FGFRL1 with structurally related surface receptors. Exp. Ther. Med. 2010, 1, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, L.; Bluteau, G.; Trueb, B. Phylogenetic analysis of receptor FgfrL1 shows divergence of the C-terminal end in rodents. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 186, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trueb, B. Biology of FGFRL1, the fifth fibroblast growth factor receptor. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.W.; Jin, H.S.; Eom, Y.B. FGFRL1 and FGF genes are associated with height, hypertension, and osteoporosis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0273237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, S.; Somorjai, I.; Garcia-Fernandez, J.; Lamonerie, T.; Escriva, H. FGFRL1 is a neglected putative actor of the FGF signalling pathway present in all major metazoan phyla. BMC. Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyeler, M.; Trueb, B. Fgfrl1, a fibroblast growth factor receptor-like gene, is found in the cephalochordate Branchiostoma floridae but not in the urochordate Ciona intestinalis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 145, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueb, B.; Neuhauss, S.C.; Baertschi, S.; Rieckmann, T.; Schild, C.; Taeschler, S. Fish possess multiple copies of fgfrl1, the gene for a novel FGF receptor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1727, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueb, B.; Taeschler, S. Expression of FGFRL1, a novel fibroblast growth factor receptor, during embryonic development. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 17, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluteau, G.; Zhuang, L.; Amann, R.; Trueb, B. Targeted disruption of the intracellular domain of receptor FgfrL1 in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porębska, N.; Latko, M.; Kucińska, M.; Zakrzewska, M.; Otlewski, J.; Opaliński, Ł. Targeting cellular trafficking of fibroblast growth factor receptors as a strategy for selective cancer treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francavilla, C.; Cattaneo, P.; Berezin, V.; Bock, E.; Ami, D.; de Marco, A.; Christofori, G.; Cavallaro, U. The binding of NCAM to FGFR1 induces a specific cellular response mediated by receptor trafficking. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 187, 1101–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieckmann, T.; Zhuang, L.; Flück, C.E.; Trueb, B. Characterization of the first FGFRL1 mutation identified in a craniosynostosis patient. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1792, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Steinberg, F.; Zhuang, L.; Beyeler, M.; Kälin, R.E.; Mullis, P.E.; Brändli, A.W.; Trueb, B. The FGFRL1 receptor is shed from cell membranes, binds fibroblast growth factors (FGFs), and antagonizes FGF signaling in Xenopus embryos. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 2193–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.T.; Zheng, G.D.; Sun, Y.W.; Chen, J.; Jiang, X.Y.; Zou, S.M. Divergent functions of fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 genes in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 187, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.; Flores, M.V.; Murison, G.; Crosier, K.; Crosier, P. An essential role for zebrafish Fgfrl1 during gill cartilage development. Mech. Dev. 2006, 123, 925–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, J.E.; Hegde, A.; Andrade, A.C.; Nilsson, O.; Baron, J. Fibroblast growth factor expression in the postnatal growth plate. Bone 2007, 40, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mienaltowski, M.J.; Huang, L.; Stromberg, A.J.; MacLeod, J.N. Differential gene expression associated with postnatal equine articular cartilage maturation. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2008, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.A.; Kemp, J.P.; Youlten, S.E.; Laurent, L.; Logan, J.G.; Chai, R.C.; Vulpescu, N.A.; Forgetta, V.; Kleinman, A.; Mohanty, S.T.; et al. An atlas of genetic influences on osteoporosis in humans and mice. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baertschi, S.; Zhuang, L.; Trueb, B. Mice with a targeted disruption of the Fgfrl1 gene die at birth due to alterations in the diaphragm. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 6241–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingemann, J.; Doi, T.; Ruttenstock, E.M.; Puri, P. Downregulation of FGFRL1 contributes to the development of the diaphragmatic defect in the nitrofen model of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 21, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gofin, Y.; Mackay, L.P.; Machol, K.; Keswani, S.; Potocki, L.; Di Gregorio, E.; Naretto, V.G.; Brusco, A.; Hernandez-Garcia, A.; Scott, D.A. Evidence that FGFRL1 contributes to congenital diaphragmatic hernia development in humans. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2021, 185, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, R.; Wyder, S.; Slavotinek, A.M.; Trueb, B. The FgfrL1 receptor is required for development of slow muscle fibers. Dev. Biol. 2014, 394, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, S.D.; Steinberg, F.; Beyeler, M.; Villiger, P.M.; Trueb, B. The murine Fgfrl1 receptor is essential for the development of the metanephric kidney. Dev. Biol. 2009, 335, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, S.D.; Beauchamp, P.; Zhuang, L.; Villiger, P.M.; Trueb, B. Functional domains of the FgfrL1 receptor. Dev. Biol. 2020, 461, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perantoni, A.Q.; Timofeeva, O.; Naillat, F.; Richman, C.; Pajni-Underwood, S.; Wilson, C.; Vainio, S.; Dove, L.F.; Lewandoski, M. Inactivation of FGF8 in early mesoderm reveals an essential role in kidney development. Development 2005, 132, 3859–3871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieshammer, U.; Cebrián, C.; Ilagan, R.; Meyers, E.; Herzlinger, D.; Martin, G.R. FGF8 is required for cell survival at distinct stages of nephrogenesis and for regulation of gene expression in nascent nephrons. Development 2005, 132, 3847–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, L.; Dong, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, C.; Feng, L.; Xie, Y.; Tang, X. Overexpression of fibroblast growth factor receptor like 1 (FGFRL1) inhibits proliferation and migration of HCT116 human colon cancer cells, and promotes their apoptosis. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2022, 38, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Sato, F.; Shimada, Y.; Tanaka, E.; Sakai, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Tsujimoto, G. MicroRNA-210 regulates cancer cell proliferation through targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 (FGFRL1). J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Wen, M.; Lei, M.; Peng, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, Z. MiR-210 links hypoxia with cell proliferation regulation in human laryngocarcinoma cancer. J. Cell Biochem. 2015, 116, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, H.; Wu, Z.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C. FGFRL1 promotes ovarian cancer Pprogression by crosstalk with Hedgehog signaling. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 7438608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kähkönen, T.E.; Ivaska, K.K.; Jiang, M.; Büki, K.G.; Väänänen, H.K.; Härkönen, P.L. Role of fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFR) and FGFR like-1 (FGFRL1) in mesenchymal stromal cell differentiation to osteoblasts and adipocytes. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2018, 461, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, M.; Nakagama, H. FGF receptors: Cancer biology and therapeutics. Med. Res. Rev. 2014, 34, 280–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dianat-Moghadam, H.; Teimoori-Toolabi, L. Implications of fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) in cancer: From prognostic to therapeutic applications. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 852–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.H.; Chen, R.; Li, D.S.; Luo, A.H.; Guo, L.L. HuR affects chemoresistance of small cell lung cancer by regulating FGFRL1 expression. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 24, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieckmann, T.; Kotevic, I.; Trueb, B. The cell surface receptor FGFRL1 forms constitutive dimers that promote cell adhesion. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Steinberg, F.; Trueb, B. Receptor FGFRL1 acts as a tumor suppressor in nude mice when overexpressed in HEK 293 Tet-On cells. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 4524–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, F.; Gerber, S.D.; Rieckmann, T.; Trueb, B. Rapid fusion and syncytium formation of heterologous cells upon expression of the FGFRL1 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 37704–37715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueb, B.; Steinberg, F. A net-like structure with pores is observed during cell fusion induced by the receptor FGFRL1. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2011, 4, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Trueb, B. Evolution of the fusogenic activity of the receptor FGFRL1. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 625–626, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trueb, B.; Amann, R.; Gerber, S.D. Role of FGFRL1 and other FGF signaling proteins in early kidney development. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 2505–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, L.; Vogel, M.; Villiger, P.M.; Trueb, B. Dissecting the interaction of FGF8 with receptor FGFRL1. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Li, D.; Zheng, M.; Chen, B.; Wei, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Huang, W.; Tong, Q.; Wang, Q.; et al. FGFRL1 affects chemoresistance of small-cell lung cancer by modulating the PI3K/Akt pathway via ENO1. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Seubert, B.; Stahl, E.; Dietz, H.; Reuning, U.; Moreno-Leon, L.; Ilie, M.; Hofman, P.; Nagase, H.; Mari, B.; et al. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 induces a pro-tumourigenic increase of miR-210 in lung adenocarcinoma cells and their exosomes. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3640–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Brink, G.R. Hedgehog signaling in development and homeostasis of the gastrointestinal tract. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 1343–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.N.; Altamentova, S.M.; Kilkenny, D.M.; Rocheleau, J.V. Fibroblast growth factor receptor like-1 (FGFRL1) interacts with SHP-1 phosphatase at insulin secretory granules and induces beta-cell ERK1/2 protein activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 17859–17870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szybowska, P.; Kostas, M.; Wesche, J.; Haugsten, E.M.; Wiedlocha, A. Negative regulation of FGFR (fibroblast growth factor receptor) signaling. Cells 2021, 10, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Villiger, P.; Trueb, B. Interaction of the receptor FGFRL1 with the negative regulator Spred1. Cell Signal. 2011, 23, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, A.; Carey, J.C.; South, S.T. Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome: A review and update. Am. J. Med. Genet. C Semin. Med. Genet. 2015, 169, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, J.C.; Lortz, A.; Mendel, A.; Battaglia, A. Natural history study of adults with Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome 2: Patient-reported outcomes study. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2021, 185, 2065–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catela, C.; Bilbao-Cortes, D.; Slonimsky, E.; Kratsios, P.; Rosenthal, N.; Te Welscher, P. Multiple congenital malformations of Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome are recapitulated in Fgfrl1 null mice. Dis. Model Mech. 2009, 2, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engbers, H.; van der Smagt, J.J.; van ‘t Slot, R.; Vermeesch, J.R.; Hochstenbach, R.; Poot, M. Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome facial dysmorphic features in a patient with a terminal 4p16.3 deletion telomeric to the WHSCR and WHSCR 2 regions. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 17, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.P.; Wang, L.K.; Chern, S.R.; Wu, P.S.; Chen, S.W.; Wu, F.T.; Chen, L.F.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wang, W. Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome: Prenatal diagnosis and molecular cytogenetic char77acterization of a de novo distal deletion of 4p (4p16.1 → pter) in a fetus with facial cleft and preaxial polydactyly. Taiwan J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 59, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cheng, L.; Chen, K.; Wu, J.; Peng, R.; Tang, Y.L.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, P.; Huang, Z.P. Identification of novel single-nucleotide variants with potential of mediating malfunction of microRNA in congenital heart disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 739598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas-Torres, V.M.; Gallardo-Blanco, H.L.; Salinas-Torres, R.A.; Cerda-Flores, R.M.; Lugo-Trampe, J.J.; Villarreal-Martínez, D.Z.; Ibarra-Ramírez, M.; Martínez de Villarreal, L.E. Whole exome sequencing identifies multiple novel candidate genes in familial gastroschisis. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LopezJimenez, N.; Gerber, S.; Popovici, V.; Mirza, S.; Copren, K.; Ta, L.; Shaw, G.M.; Trueb, B.; Slavotinek, A.M. Examination of FGFRL1 as a candidate gene for diaphragmatic defects at chromosome 4p16.3 shows that Fgfrl1 null mice have reduced expression of Tpm3, sarcomere genes and Lrtm1 in the diaphragm. Hum. Genet. 2010, 127, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Gao, J.; Cui, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Mei, L.; Zhao, L.; Cai, D.; et al. A towering genome: Experimentally validated adaptations to high blood pressure and extreme stature in the giraffe. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe9459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton-Cheh, C.; Johnson, T.; Gateva, V.; Tobin, M.D.; Bochud, M.; Coin, L.; Najjar, S.S.; Zhao, J.H.; Heath, S.C.; Eyheramendy, S.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies eight loci associated with blood pressure. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Y.Q.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, H.; Hou, D.; Mi, J. Gene-gene interactions and associations of six hypertension related single nucleotide polymorphisms with obesity risk in a Chinese children population. Gene 2018, 679, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Choi, H.J.; Estrada, K.; Leo, P.J.; Li, J.; Pei, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Shen, H.; Liu, Y.Z.; et al. Multistage genome-wide association meta-analyses identified two new loci for bone mineral density. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 1923–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Hu, B.; Cai, F.; Xu, Q.; Pan, S.; Wu, Y.; Song, W. Distinct effects of SDC3 and FGFRL1 on selective neurodegeneration in AD and PD. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e22773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helferich, A.M.; Ruf, W.P.; Grozdanov, V.; Freischmidt, A.; Feiler, M.S.; Zondler, L.; Ludolph, A.C.; McLean, P.J.; Weishaupt, J.H.; Danzer, K.M. α-synuclein interacts with SOD1 and promotes its oligomerization. Mol. Neurodegener. 2015, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Ma, G.; Li, H.; Zeng, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wang, X.; Shan, S.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, J.; Cheng, G. Shared genetics and comorbid genes of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2023, 38, 1813–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Tillaart, S.A.; Corver, W.E.; Ruano Neto, D.; ter Haar, N.T.; Goeman, J.J.; Trimbos, J.B.; Fleuren, G.J.; Oosting, J. Loss of heterozygosity and copy number alterations in flow-sorted bulky cervical cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- di Martino, E.; Taylor, C.F.; Roulson, J.A.; Knowles, M.A. An integrated genomic, transcriptional and protein investigation of FGFRL1 as a putative 4p16.3 deletion target in bladder cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013, 52, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shi, L.; Yi, C.; Yang, Y.; Chang, L.; Song, D. MiR-210-3p inhibits the tumor growth and metastasis of bladder cancer via targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 1738–1753. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimada, Y.; Okumura, T.; Nagata, T.; Hashimoto, I.; Sawada, S.; Yoshida, T.; Fukuoka, J.; Shimizu, K.; Tsukada, K. Expression analysis of fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 (FGFRL1) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Esophagus 2014, 11, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, Y.; Okumura, T.; Takei, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Nagata, T.; Hori, T.; Tsuchiya, S.; Tsukada, K.; Shimizu, K. Role of fibroblast growth factor receptors in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Esophagus 2016, 13, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kaushik, V.; Saraya, A.; Sharma, R. Aberrant expression of FGFRL1 in esophageal cancer and its regulation by miR-107. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2023, 24, 1331–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, Y.; Matsumura, T.; Watanabe, K.; Nakamine, H.; Sudo, T.; Shimizu, K.; Shimada, Y. FGFRL1 deficiency reduces motility and tumorigenic potential of cells derived from oesophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.F. Hypoxia and the tumor microenvironment. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211036304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afsar, S.; Syed, R.U.; Bin Break, M.K.; Alsukaybi, R.H.; Alanzi, R.A.; Alshobrmi, A.M.; Alshagdali, N.M.; Alshammari, A.D.; Alharbi, F.M.; Alshammari, A.M.; et al. The dual role of MiR-210 in the aetiology of cancer: A focus on hypoxia-inducible factor signalling. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2024, 253, 155018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Fan, P.; Ma, R.; Wang, Q.; He, L.; Niu, H.; Luo, Q. MiR-210 regulates lung adenocarcinoma by targeting HIF-1α. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Yu, Z.; Dong, W.; Cui, X.; Ma, J.; Li, S. Long non-coding RNA FGD5-AS1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation through sponging hsa-miR-107 to up-regulate FGFRL1. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20193309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, J.; Hu, H.; Tu, L.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, F. Lung CSC-derived exosomal miR-210-3p contributes to a pro-metastatic phenotype in lung cancer by targeting FGFRL1. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 6324–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X. miR-210 promotes human osteosarcoma cell migration and invasion by targeting FGFRL1. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 2229–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schild, C.; Trueb, B. Aberrant expression of FGFRL1, a novel FGF receptor, in ovarian tumors. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 16, 1169–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, C.L.; DeBoever, C.; Jepsen, K.; Saenz, C.C.; Carson, D.A.; Frazer, K.A. Systematic transcriptome analysis reveals tumor-specific isoforms for ovarian cancer diagnosis and therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3050–E3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Cui, J.; Liang, X.; Chen, T.; Lu, C.; Peng, T. Pancreatic cancer stem cell-derived exosomal miR-210 mediates macrophage M2 polarization and promotes gemcitabine resistance by targeting FGFRL1. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 127, 111407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Toriseva, M.; Afshan, S.; Cangiano, M.; Fey, V.; Erickson, A.; Seikkula, H.; Alanen, K.; Taimen, P.; Ettala, O.; et al. Increased expression and altered cellular localization of fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 (FGFRL1) are associated with prostate cancer progression. Cancers 2022, 14, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, J.; Wang, D. LncRNA VPS9D1-AS1 regulates miR-187-3p/fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 axis to promote proliferation, migration, and invasion of prostate cancer cells. Chin. J. Physiol. 2023, 66, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xia, T.; Li, G.; Tian, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, R.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Y.; Lan, K.; et al. MicroRNA-210 promotes cancer angiogenesis by targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor-like 1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2553–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Shi, C.J.; Du, L.J.; Jiang, Y.H.; Su, J.M. Expression of fibroblast growth factor receptor like 1 protein in oral squamous cell carcinoma and its influence on tumor cell proliferation and migration. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2020, 38, 558–565. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, R.Z.; Zhang, J.Z.; Jing, C.Q.; Li, C.S.; Zhuo, H.Q. Fibroblast growth factor receptor-like-1: A new therapeutic target and unfavorable prognostic indicator for rectal adenocarcinoma. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2020, 40, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, L.; Feng, L.; Wang, C.; Xie, Y. FGFRL1: Structure, Molecular Function, and Involvement in Human Disease. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040286
Guan L, Feng L, Wang C, Xie Y. FGFRL1: Structure, Molecular Function, and Involvement in Human Disease. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2025; 47(4):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040286
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Lina, Li Feng, Chaoli Wang, and Yongen Xie. 2025. "FGFRL1: Structure, Molecular Function, and Involvement in Human Disease" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47, no. 4: 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040286
APA StyleGuan, L., Feng, L., Wang, C., & Xie, Y. (2025). FGFRL1: Structure, Molecular Function, and Involvement in Human Disease. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 47(4), 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47040286





