The Exon Junction Complex Controls the Efficient and Faithful Splicing of a Subset of Transcripts Involved in Mitotic Cell-Cycle Progression
Abstract
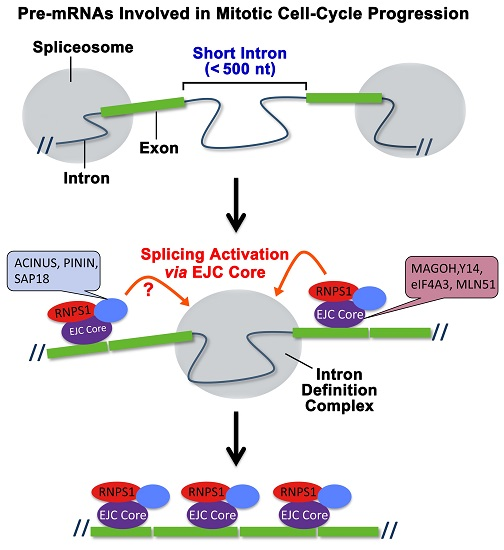
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The EJC Core Component Y14 Is Required for Efficient and Faithful Splicing of a Subset of Transcripts
2.2. The Targets of Y14-Mediated Splicing Activation Are Short Introns in Genes Involved in Cell Cycle Progression
2.3. The Binding of the EJC Core Is Required for Splicing Activation of a Model Pre-mRNA
2.4. RNPS1 Is a Key Factor in EJC Core-Mediated Splicing Activation
3. Discussion
3.1. The EJC as a Master Splicing Controller of Genes Involved in Cell Cycle Progression
3.2. Molecular Mechanisms of EJC-Mediated Splicing Regulation
4. Experimental Procedures
4.1. Plasmid Constructions and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Culture and siRNA Knockdown
4.3. RNA-Seq Analysis
4.4. Tethering Experiments
4.5. Immunoprecipitation Experiments
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Le Hir, H.; Sauliere, J.; Wang, Z. The exon junction complex as a node of post-transcriptional networks. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayeda, A.; Badolato, J.; Kobayashi, R.; Zhang, M.Q.; Gardiner, E.M.; Krainer, A.R. Purification and characterization of human RNPS1: A general activator of pre-mRNA splicing. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 4560–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakashita, E.; Tatsumi, S.; Werner, D.; Endo, H.; Mayeda, A. Human RNPS1 and its associated factors: A versatile alternative pre-mRNA splicing regulator in vivo. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 1174–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trembley, J.H.; Tatsumi, S.; Sakashita, E.; Loyer, P.; Slaughter, C.A.; Suzuki, H.; Endo, H.; Kidd, V.J.; Mayeda, A. Activation of pre-mRNA splicing by human RNPS1 is regulated by CK2 phosphorylation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 1446–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lykke-Andersen, J.; Shu, M.D.; Steitz, J.A. Communication of the position of exon–exon junctions to the mRNA surveillance machinery by the protein RNPS1. Science 2001, 293, 1836–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viegas, M.H.; Gehring, N.H.; Breit, S.; Hentze, M.W.; Kulozik, A.E. The abundance of RNPS1, a protein component of the exon junction complex, can determine the variability in efficiency of the Nonsense Mediated Decay pathway. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 4542–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCracken, S.; Longman, D.; Johnstone, I.L.; Caceres, J.F.; Blencowe, B.J. An evolutionarily conserved role for SRm160 in 3’-end processing that functions independently of exon junction complex formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 44153–44160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwerk, C.; Prasad, J.; Degenhardt, K.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; White, E.; Tempst, P.; Kidd, V.J.; Manley, J.L.; Lahti, J.M.; Reinberg, D. ASAP, a novel protein complex involved in RNA processing and apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 2981–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joselin, A.P.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Schwerk, C. Loss of Acinus inhibits oligonucleosomal DNA fragmentation but not chromatin condensation during apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 12475–12484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Iratni, R.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Reinberg, D. Histone deacetylases and SAP18, a novel polypeptide, are components of a human Sin3 complex. Cell 1997, 89, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Erkelenz, S.; Rattay, S.; Dehof, A.K.; Hildebrandt, A.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Schaal, H.; Schwerk, C. Human SAP18 mediates assembly of a splicing regulatory multiprotein complex via its ubiquitin-like fold. RNA 2010, 16, 2442–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, P.; Sugrue, S.P. Characterization of pinin, a novel protein associated with the desmosome-intermediate filament complex. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 135, 1027–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Lou, P.J.; Leu, S.; Ouyang, P. Modulation of alternative pre-mRNA splicing in vivo by pinin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 294, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murachelli, A.G.; Ebert, J.; Basquin, C.; Le Hir, H.; Conti, E. The structure of the ASAP core complex reveals the existence of a Pinin-containing PSAP complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelle, L.; Cloutier, A.; Toutant, J.; Shkreta, L.; Thibault, P.; Durand, M.; Garneau, D.; Gendron, D.; Lapointe, E.; Couture, S.; et al. Proteins associated with the exon junction complex also control the alternative splicing of apoptotic regulators. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 954–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauliere, J.; Haque, N.; Harms, S.; Barbosa, I.; Blanchette, M.; Le Hir, H. The exon junction complex differentially marks spliced junctions. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 1269–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roignant, J.Y.; Treisman, J.E. Exon junction complex subunits are required to splice Drosophila MAP kinase, a large heterochromatic gene. Cell 2010, 143, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, D.L.; Watkins-Chow, D.E.; Schreck, K.C.; Pierfelice, T.J.; Larson, D.M.; Burnetti, A.J.; Liaw, H.J.; Myung, K.; Walsh, C.A.; Gaiano, N.; et al. The exon junction complex component Magoh controls brain size by regulating neural stem cell division. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nothwang, H.G.; Tamura, T.; Tanaka, K.; Ichihara, A. Sequence analyses and inter-species comparisons of three novel human proteasomal subunits, HsN3, HsC7-I and HsC10-II, confine potential proteolytic active-site residues. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1219, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, N.H.; Kunz, J.B.; Neu-Yilik, G.; Breit, S.; Viegas, M.H.; Hentze, M.W.; Kulozik, A.E. Exon-junction complex components specify distinct routes of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay with differential cofactor requirements. Mol. Cell 2005, 20, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Murigneux, V.; Le Hir, H. Transcriptome-wide modulation of splicing by the exon junction complex. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishigaki, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Tatsuno, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Shimasaki, T.; Iwabuchi, K.; Tomosugi, N. Depletion of RNA-binding protein RBM8A (Y14) causes cell cycle deficiency and apoptosis in human cells. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2013, 238, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, J.S.; Ho, A.L.; Tse, A.N.; Coward, J.; Cheema, H.; Ambrosini, G.; Keen, N.; Schwartz, G.K. Aurora B kinase regulates the postmitotic endoreduplication checkpoint via phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein at serine 780. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 2218–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigg, E.A. Mitotic kinases as regulators of cell division and its checkpoints. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredi, J.J. The Mdm2-p53 relationship evolves: Mdm2 swings both ways as an oncogene and a tumor suppressor. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.N.; Roe, A.E.; Donehower, L.A.; Bradley, A. Rescue of embryonic lethality in Mdm2-deficient mice by absence of p53. Nature 1995, 378, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes de Oca Luna, R.; Wagner, D.S.; Lozano, G. Rescue of early embryonic lethality in mdm2-deficient mice by deletion of p53. Nature 1995, 378, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, R.; Handler, D.; Ish-Horowicz, D.; Brennecke, J. The exon junction complex is required for definition and excision of neighboring introns in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 1772–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malone, C.D.; Mestdagh, C.; Akhtar, J.; Kreim, N.; Deinhard, P.; Sachidanandam, R.; Treisman, J.; Roignant, J.Y. The exon junction complex controls transposable element activity by ensuring faithful splicing of the piwi transcript. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 1786–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berget, S.M. Exon recognition in vertebrate splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 2411–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, M.C.; Will, C.L.; Luhrmann, R. The spliceosome: Design principles of a dynamic RNP machine. Cell 2009, 136, 701–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishima, Y.; Fukao, A.; Kishimoto, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Fujiwara, T.; Inoue, K. Translational inhibition by deadenylation-independent mechanisms is central to microRNA-mediated silencing in zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumura, K.; Taniguchi, I.; Sakamoto, H.; Ohno, M.; Inoue, K. U1-independent pre-mRNA splicing contributes to the regulation of alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumura, K.; Kato, A.; Jin, Y.; Ideue, T.; Hirose, T.; Kataoka, N.; Fujiwara, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Inoue, K. Tissue-specific splicing regulator Fox-1 induces exon skipping by interfering E complex formation on the downstream intron of human F1γ gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 5303–5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ideue, T.; Sasaki, Y.T.; Hagiwara, M.; Hirose, T. Introns play an essential role in splicing-dependent formation of the exon junction complex. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1993–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuya, T.; Tange, T.O.; Sonenberg, N.; Moore, M.J. eIF4AIII binds spliced mRNA in the exon junction complex and is essential for nonsense—Mediated decay. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.; Trapnell, C.; Donaghey, J.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Improving RNA-Seq expression estimates by correcting for fragment bias. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.; Pimentel, H.; Trapnell, C.; Pachter, L. Identification of novel transcripts in annotated genomes using RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2325–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fukumura, K.; Wakabayashi, S.; Kataoka, N.; Sakamoto, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Nakai, K.; Mayeda, A.; Inoue, K. The Exon Junction Complex Controls the Efficient and Faithful Splicing of a Subset of Transcripts Involved in Mitotic Cell-Cycle Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081153
Fukumura K, Wakabayashi S, Kataoka N, Sakamoto H, Suzuki Y, Nakai K, Mayeda A, Inoue K. The Exon Junction Complex Controls the Efficient and Faithful Splicing of a Subset of Transcripts Involved in Mitotic Cell-Cycle Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(8):1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081153
Chicago/Turabian StyleFukumura, Kazuhiro, Shunichi Wakabayashi, Naoyuki Kataoka, Hiroshi Sakamoto, Yutaka Suzuki, Kenta Nakai, Akila Mayeda, and Kunio Inoue. 2016. "The Exon Junction Complex Controls the Efficient and Faithful Splicing of a Subset of Transcripts Involved in Mitotic Cell-Cycle Progression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 8: 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081153
APA StyleFukumura, K., Wakabayashi, S., Kataoka, N., Sakamoto, H., Suzuki, Y., Nakai, K., Mayeda, A., & Inoue, K. (2016). The Exon Junction Complex Controls the Efficient and Faithful Splicing of a Subset of Transcripts Involved in Mitotic Cell-Cycle Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(8), 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081153