Mineralization of High-Concentration Aqueous Aniline by Hybrid Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Ozonation Device
2.3. Electrochemical Oxidation Device
2.4. The Hybrid Process
2.5. Modification of Activated Carbon (AC)
- The material was washed with deionized water until the washing effluent was nearly colorless and then dried in a hot air oven at 105 °C for 2 h;
- A 40 mL volume of 30% (wt%) NaOH aqueous was added to 20 g of dried AC, oscillated for 2 h at 30 °C, allowed to sediment for 24 h, and then filtered to remove retrieve the solid;
- The modified AC was dried in an oven at 100 °C for 2 h, rinsed with ionized water to neutrality, dried for 24 h at 105 °C, and then dried.
2.6. Analytical Methods and Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparation of Three Oxidation Process
3.1.1. Aniline Concentration and COD Removal
3.1.2. Variation of pH
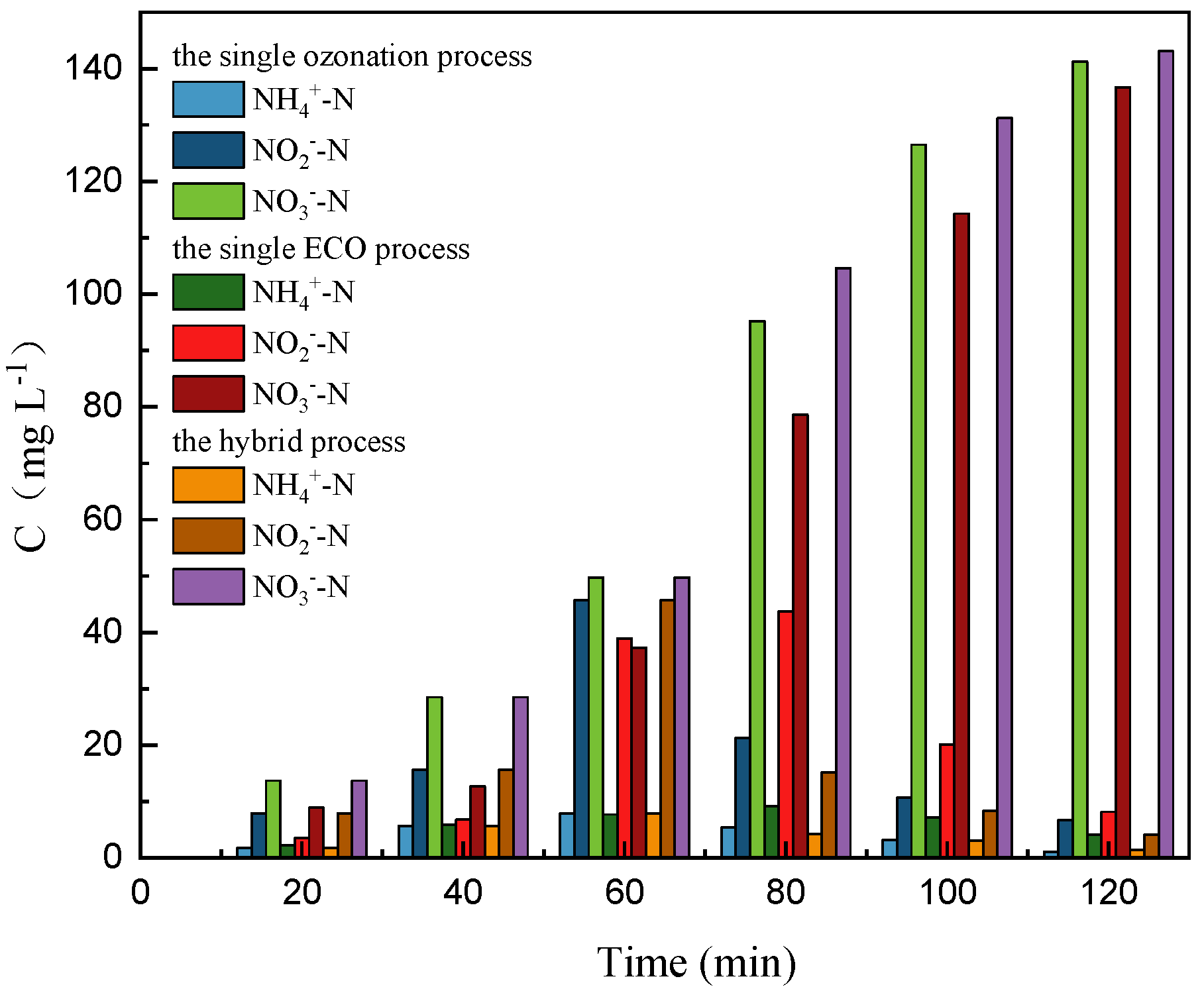
3.1.3. Variation of Nitrogen and Conductivity
3.2. Optimized Influencing Factors of the Hybrid Process
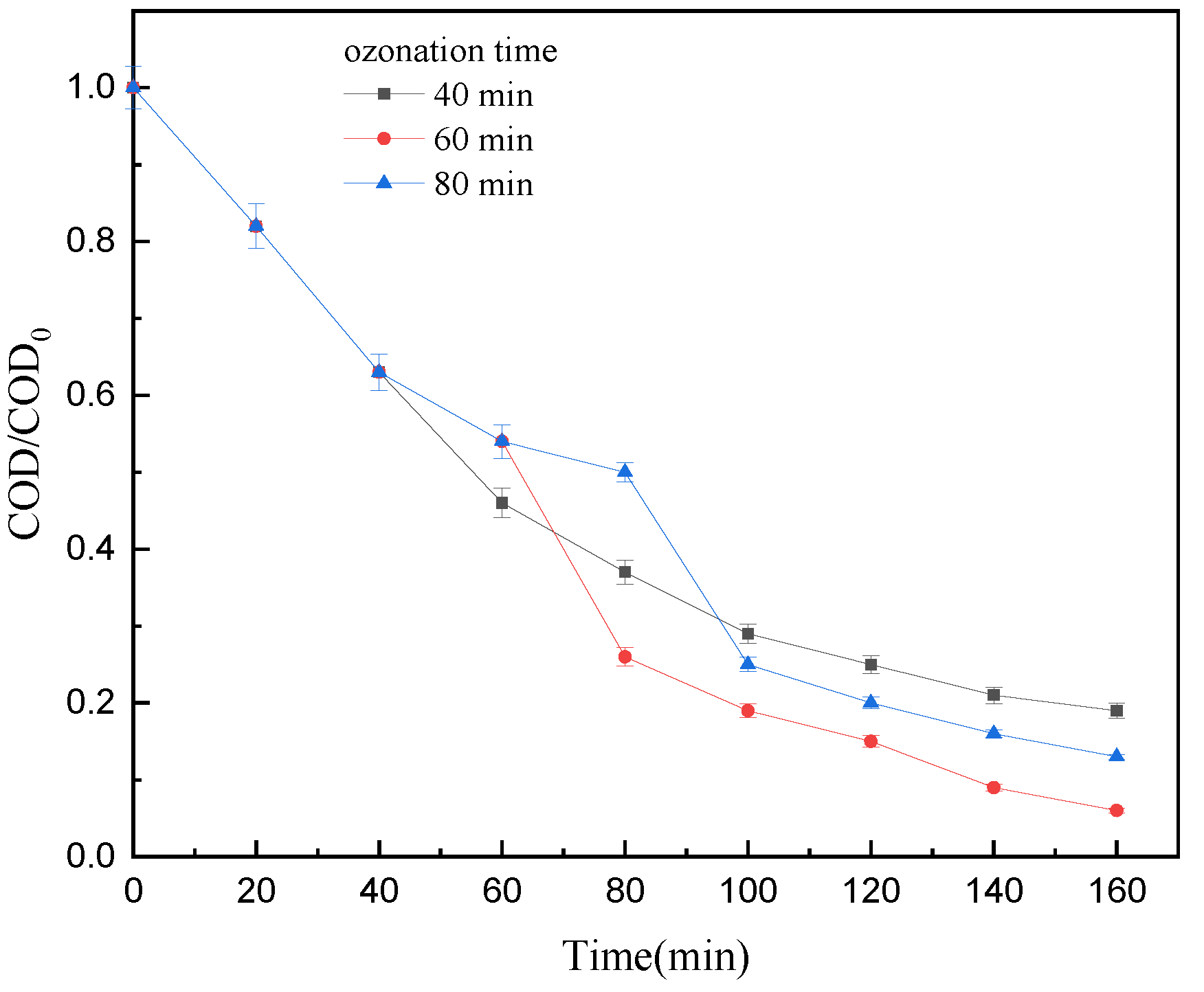
3.2.1. Ozonation Time
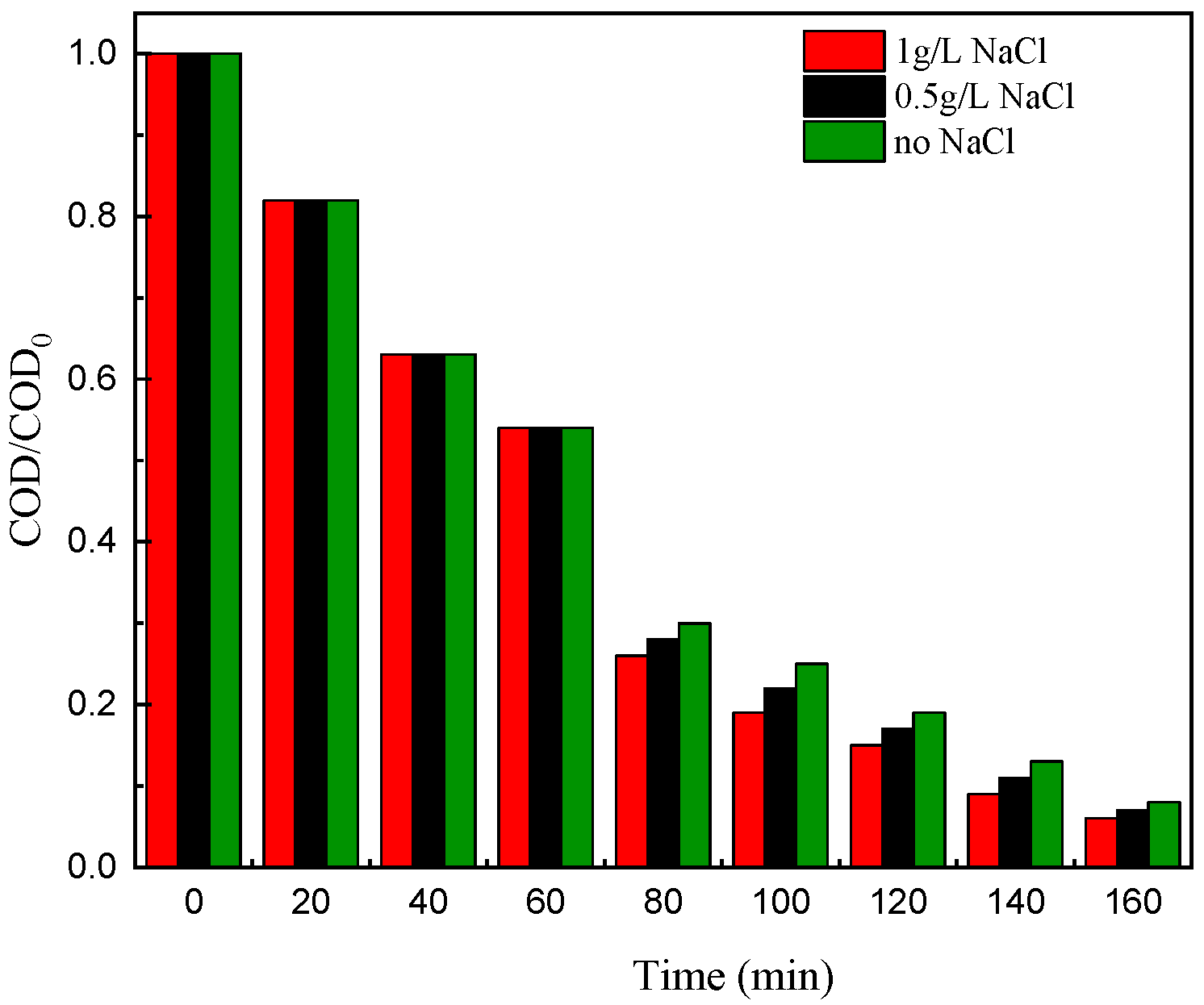
3.2.2. Nitrite and Nitrate as Electrolyte
3.2.3. Assessment on the Hybrid Process
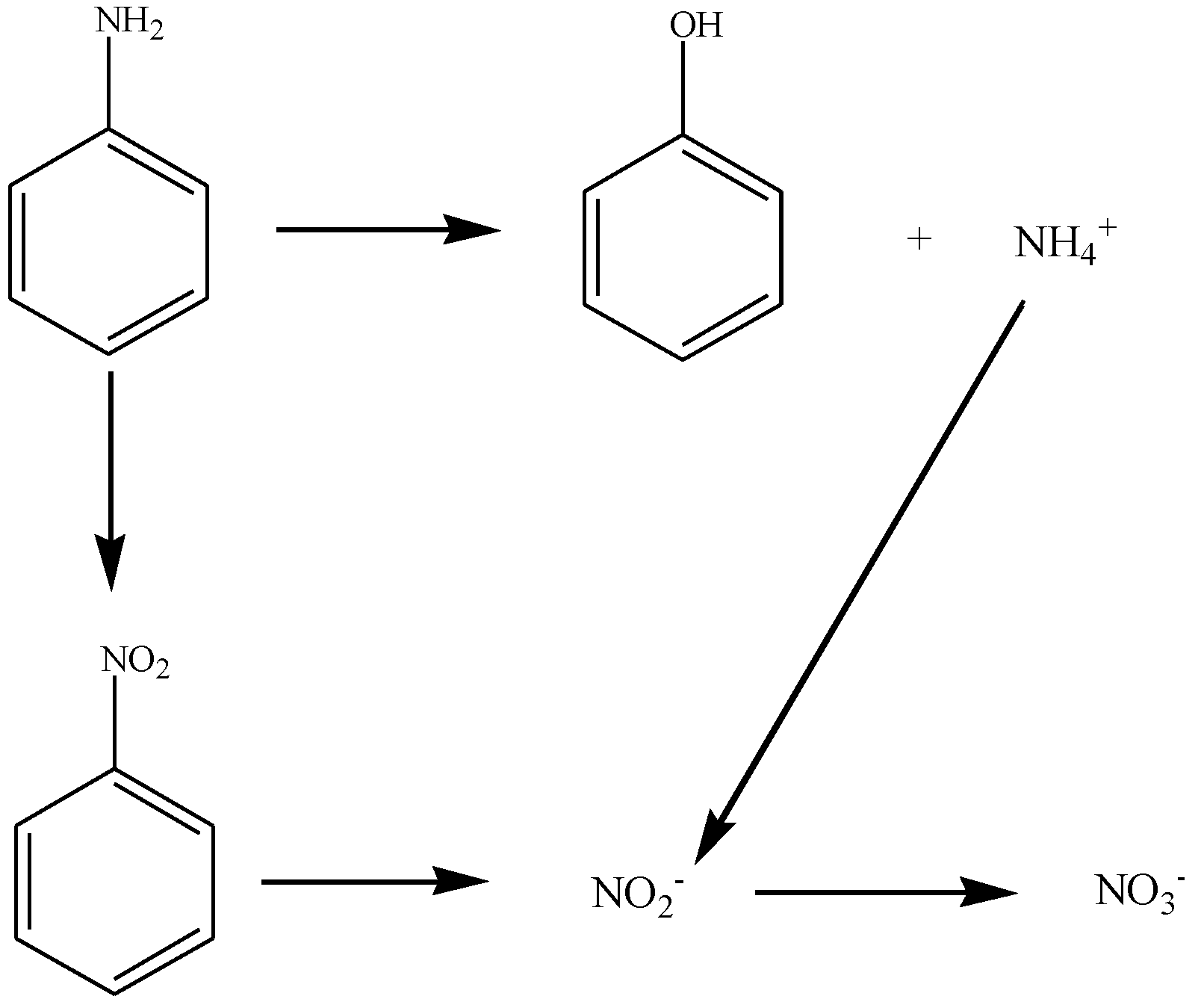
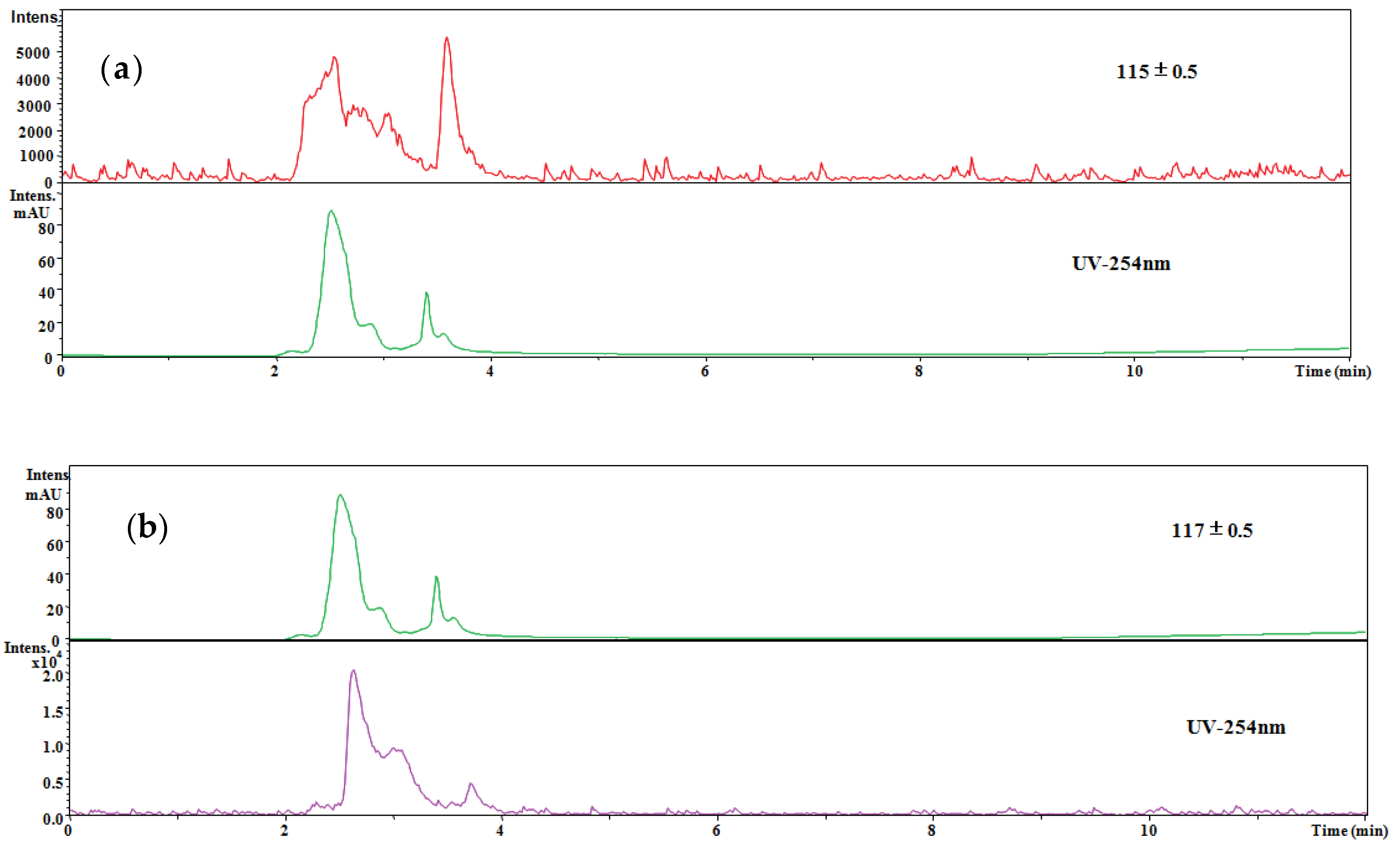
3.3. The Merits and Mechanism of Hybrid Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, A.H.; Aziz, H.A.; Khan, N.A.; Dhingra, A.; Ahmed, S.; Naushad, M. Effect of seasonal variation on the occurrences of high-risk pharmaceutical in drain-laden surface water: A risk analysis of Yamuna River. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.A.; Ahmed, S.; Farooqi, I.H.; Ali, I.; Vambol, V.; Changani, F.; Yousefi, M.; Vambol, S.; Khan, S.U.; Khan, A.H. Occurrence, sources and conventional treatment techniques for various antibiotics present in hospital wastewaters: A critical review. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 129, 115921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, N.C.; Bassin, J.P.; Sant’Anna, G.L.; Dezotti, M. Ozonation of the dye reactive red 239 and biodegradation of ozonation products in amoving-bed biofilm reactor: Revealing reaction products and degradation pathways. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 144, 104742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.; Shen, D.; Wu, C. Biodegradation of aniline by a novel bacterial mixed culture AC. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 125, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fana, Y.; Chen, X.; Yao, Z. A novel inhibition mechanism of aniline on nitrification: Aniline degradation competes dissolved oxygen with nitrification. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 145205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sun, C.; Liu, R. Enrichment and domestication of a microbial consortium for degrading aniline. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreiro, C.; Villota, N.; Lombraña, J.I.; Rivero, M.J. An efficient catalytic process for the treatment of genotoxic aniline wastewater using a new granular activated carbon-supported titanium dioxide composite. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Chen, G.; Sang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Man, R.; Huang, J. Oxygen-rich hyper-cross-linked polymers with hierarchical porosity for aniline adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 368, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Wang, Q.; Qian, Y. Simultaneous removal of aniline, antimony and chromium by ZVI coupled with H2O2: Implication for textile wastewater treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 368, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyuncu, H.; Kul, A.R. Removal of aniline from aqueous solution by activated kaolinite: Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 569, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M. Microbial community and function evaluation in the start-up period of bioaugmented SBR fed with aniline wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 319, 124148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, M.; Li, Y.; Meng, L. Simultaneous removal of antimony, chromium and aniline by forward osmosis membrane: Preparation, performance and mechanism. Desalination 2021, 520, 115363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Qiu, Z.; Cheng, W. Photocatalytic degradation of aniline by magnetic nanomaterials Fe3O4@SiO2@BiO1.8·0.04H2O/Ag3PO4. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 755, 137747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chena, J.; Shena, C.; Guoa, B. Photocatalytic oxidation of aniline over MO/TiO2 (M = Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba) under visible light irradiation. Catal. Today 2019, 335, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Malloum, A.; Bornman, C. Novel green adsorbents for removal of aniline from industrial effluents: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 345, 118167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, C.; Xu, Q. Mass transport and pervaporation recovery of aniline with high-purity from dilute aqueous solution by PEBA/PVDF composite membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 268, 118708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, A.; Monteagudo, J.M.; Martín, I.S. Solar photo-degradation of aniline with rGO/TiO2 composites and persulfate. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhaya, V.; Rekhate, J.K. Srivastava. Recent advances in ozone-based advanced oxidation processes for treatment of wastewater—A review. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2020, 3, 100031. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Influencing factors for the Fenton-like of biological sponge iron system and its degradation mechanism of aniline. Process Biochem. 2021, 101, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y. A highly efficient cathode based on modified graphite felt for aniline degradation by electro-Fenton. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.F.; da Silva, Á.R.L.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A. Understanding the electro-catalytic effect of benzene ring substitution on the electrochemical oxidation of aniline and its derivatives using BDD anode: Cyclic voltammetry, bulk electrolysis and theoretical calculations. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 369, 137688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Guo, C.; Xu, X. Co/Fe and Co/Al layered double oxides ozone catalyst for the deep degradation of aniline: Preparation, characterization and kinetic model. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Hu, J. Catalytic ozonation for effective degradation of aniline by sulfur-doped copper–nickel bimetallic oxide in aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jia, N.; Song, K. Sulfur-doped copper-yttrium bimetallic oxides: A novel and efficient ozonation catalyst for the degradation of aniline. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 236, 116248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yi, G.; Li, P. Electrochemical oxidation of hydroquinone using Eu-doped PbO2 electrodes: Electrode characterization, influencing factors and degradation pathways. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 895, 115493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Meng, L. Importance of Combined Electrochemical Process Sequence and Electrode Arrangements: A Lab-scale Trial of Real Reverse Osmosis Landfill Leachate Concentrate. Water Res. 2021, 192, 116849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Cho, W.-C.; Poo, K.-M.; Choi, S.; Kim, T.-N.; Son, E.-B.; Choi, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.M.; Chae, K.-J. Refractory oil wastewater treatment by dissolved air flotation, electrochemical advanced oxidation process, and magnetic biochar integrated system. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 36, 101358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Chen, N.; Feng, C. Degradation of nitrogen-containing refractory organic wastewater using a novel alternating-anode electrochemical system. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Viswanathan, K.; Boopathy, R. Three dimensional electro catalytic oxidation of aniline by boron doped mesoporous activated carbon. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.; Ao, Z.; Duan, X. Degradation of aniline by electrochemical activation of peroxydisulfate at MWCNT cathode: The proofed concept of nonradical oxidation process. Chemosphere 2019, 206, 4324–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; Pinto, M.F.; Neves, I.C. Electrochemical oxidation of aniline at mono and bimetallic electrocatalysts supported on carbon nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, P.C.C.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Pereira, M.F.R. Ozonation of aniline promoted by activated carbon. Chemosphere 2002, 67, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese, N. Water and Wastewater Monitoring Methods; Chinese Environmental Science Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tekle-R€ottering, A.; von Sonntag, C.; Reisz, E. Ozonation of anilines: Kinetics, stoichiometry, product identification and elucidation of pathways. Water Res. 2019, 98, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyama, S.T. Chemical and catalytic properties of ozone. Catal. Rev. 2000, 42, 279–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shao, D.; Xu, H. Fabrication of a stable Ti/TiOxHy/Sb-SnO2 anode for aniline degradation in different electrolytes. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, C.Z.; Lu, J. Electro–catalytic degradation of bisphenol A with modified Co3O4/β–PbO2/Ti electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 118, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arts, A.; de Groot, M.T.; van der Schaaf, J. Current efficiency and mass transfer effects in electrochemical oxidation of C1 and C2 carboxylic acids on boron doped diamond electrodes. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2021, 6, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Gunten, U. Ozonation of drinking water: Part I. Oxidation kinetics and product formation. Water Res. 2000, 37, 1443–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesavan, L.; Kalekar, A.M.; Damlin, P. Reduced graphene oxide supported palladium nano-shapes for electrooxidation of oxalic acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 847, 113167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Queiroz, J.L.A.; da Silva, A.R.L.; de Moura, D.C. Electrochemical study of carboxylic acids with Nb-supported boron doped diamond anode. Part 1: Potentiodynamic measurements and bulk oxidations. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 794, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.J.; Huang, C.P.; Chan, Y.H. Electrochemical degradation of oxalic acid over highly reactive nanotextured γ– and α–MnO2/carbon electrode fabricated by KMnO4 reduction on loofah sponge–derived active carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 379, 120759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

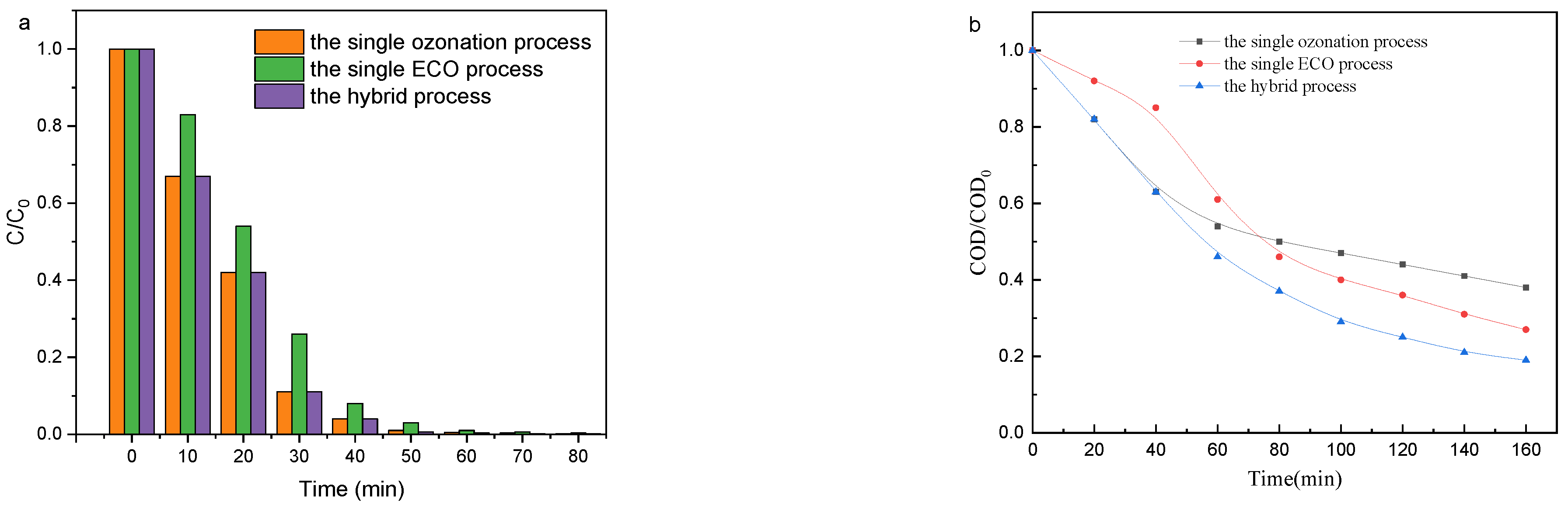



| Industries | Role of Aniline | Wastewater Kinds |
|---|---|---|
| synthetic paints | raw material | paint |
| dyestuffs | raw material of dyes and auxiliaries | dye |
| rubbers | vulcafor, ingredients raw material | rubber |
| pesticides | raw material | pesticide |
| plastics | intermediate | plastic |
| pharmaceuticals | raw material and intermediate | pharmaceutical |
| Index | Indirect Discharge Limited Value |
|---|---|
| pH | 6–9 |
| COD (mg·L−1) | 200 |
| BOD5 (mg·L−1) | 50 |
| Chroma | 80 |
| Ammonia-nitrogen (mg·L−1) | 30 |
| Total nitrogen (mg·L−1) | 50 |
| Total phosphorus (mg·L−1) | 1.5 |
| Aniline (mg·L−1) | 1.0 |
| Item | Hybrid Process |
|---|---|
| pH | 7.5 |
| COD (mg·L−1) | 189 |
| BOD5 (mg·L−1) | 46 |
| Chroma | 23 |
| Ammonia–nitrogen (mg·L−1) | 3.3 |
| Total nitrogen (mg·L−1) | 115.8 |
| Anilines (mg·L−1) | 0.8 |
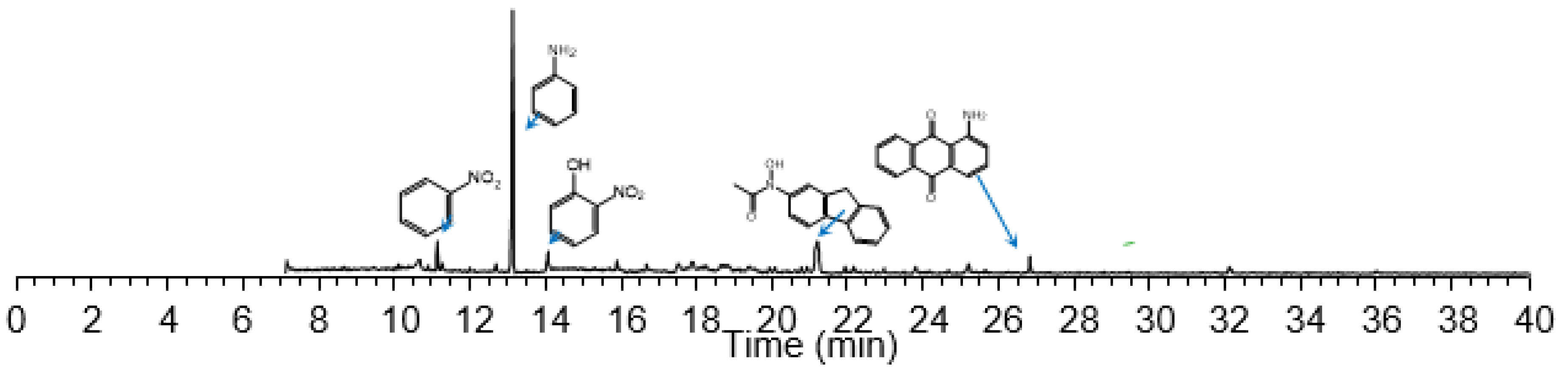
| Intermediate Products | Ozonation Time, min | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 120 | |
| maleic acid | 9,191,232 | 10,263,980 | 6,847,330 | 2,749,407 | 793,610 |
| p-aminophenol | 1,306,363 | ||||
| succinic acid | 585,062 | 3,029,264 | 361,816 | ||
| p-nitrophenol | 14,714,904 | 314,472 | |||
| benzoquinone | 4,896,324 | ||||
| Intermediate Products | ECO Time, min | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 200 | |
| maleic acid | 3,732,405 | 4,341,021 | 6,001,241 | 11,612,253 | 2,994,023 |
| p-aminophenol | 4,041,304 | ||||
| quinoline | 1,633,427 | ||||
| dimethylbenzidine | 1,134,261 | ||||
| diphenylamine ethylene diketone | 1,214,627 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q. Mineralization of High-Concentration Aqueous Aniline by Hybrid Process. Water 2022, 14, 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040630
Zhang H, Zhou Y, Guo S, Wang Z, Wang Q. Mineralization of High-Concentration Aqueous Aniline by Hybrid Process. Water. 2022; 14(4):630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040630
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haibing, Yasong Zhou, Shaohui Guo, Zhipu Wang, and Qing Wang. 2022. "Mineralization of High-Concentration Aqueous Aniline by Hybrid Process" Water 14, no. 4: 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040630
APA StyleZhang, H., Zhou, Y., Guo, S., Wang, Z., & Wang, Q. (2022). Mineralization of High-Concentration Aqueous Aniline by Hybrid Process. Water, 14(4), 630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14040630




