Microneedles in Action: Microneedling and Microneedles-Assisted Transdermal Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Microneedle Technologies
2.1. Fabrication Materials in Microneedles
2.1.1. Silicone and Metals
2.1.2. Sugars
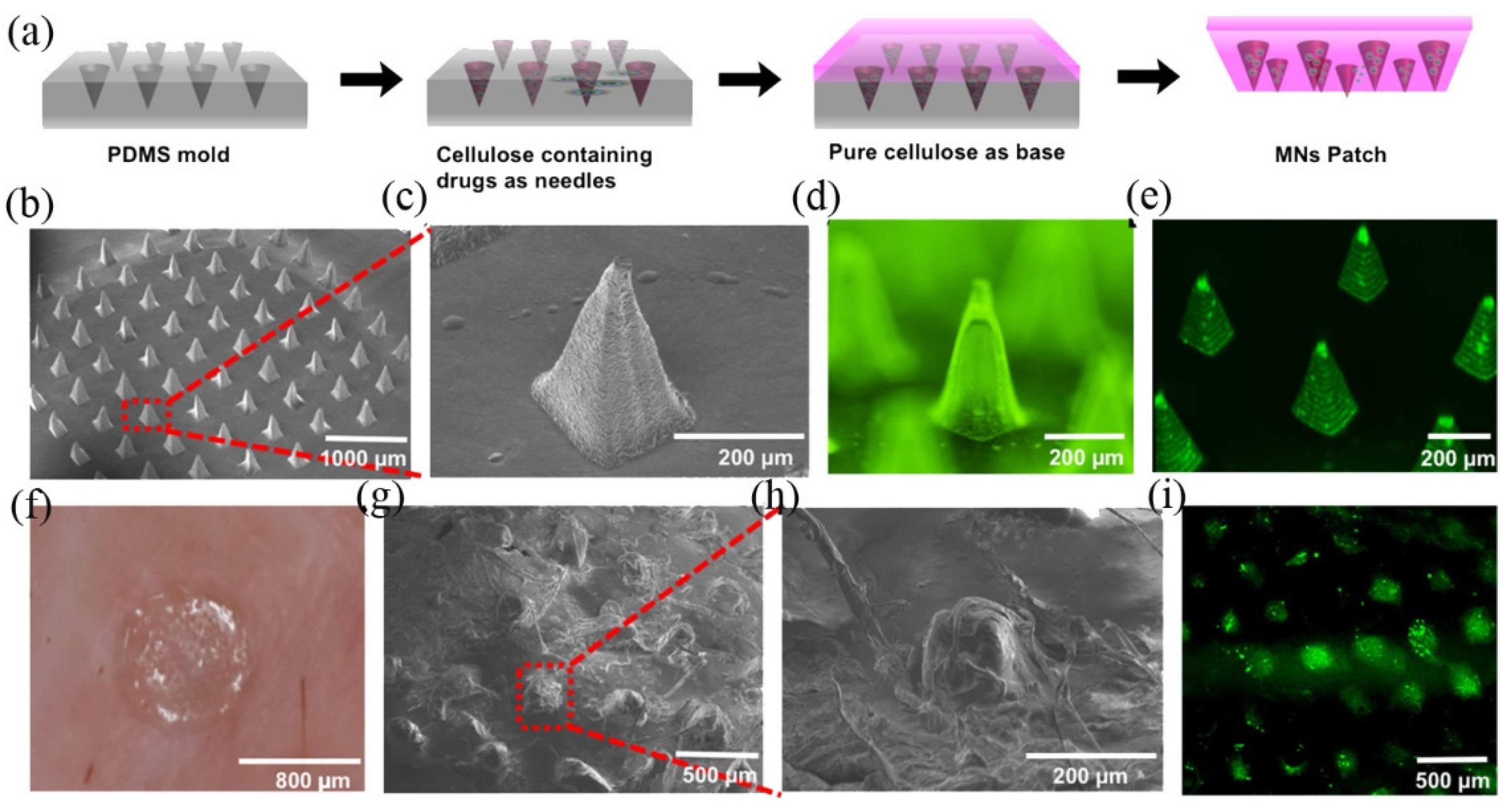
2.1.3. Natural Biomacromolecules
2.1.4. Synthetic Macromolecules
2.2. Structural Types in Microneedles
2.2.1. Hollow Microneedles
2.2.2. Solid Microneedles
2.3. Functional Types in Microneedles
2.3.1. Dissolving Microneedles
2.3.2. Coated Microneedles
3. Microneedles in Action
3.1. Microneedling for Non-Lesion and Non-Cancerous Skins
3.2. Microneedle-Assisted Transdermal Delivery for Cancerous Skin Diseases
4. Future Perspective on Microneedling and Microneedles
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boer, M.; Duchnik, E.; Maleszka, R.; Marchlewicz, M. Structural and biophysical characteristics of human skin in maintaining proper epidermal barrier function. Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2016, 33, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, K.A.; Odland, G.F. Regional differences in the thickness (cell layers) of the human stratum corneum: An ultrastructural analysis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1974, 62, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouwstra, J.A.; Dubbelaar, F.E.; Gooris, G.S.; Ponec, M. The lipid organisation in the skin barrier. Acta Derm.-Venereol. Suppl. 2000, 208, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bos, J.D.; Meinardi, M.M. The 500 Dalton rule for the skin penetration of chemical compounds and drugs. Exp. Dermatol. 2000, 9, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, R.H.; Hadgraft, J.; Bucks, D.A. Transdermal drug delivery and cutaneous metabolism. Xenobiotica Fate Foreign Compd. Biol. Syst. 1987, 17, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merisko-Liversidge, E.; Liversidge, G.G. Nanosizing for oral and parenteral drug delivery: A perspective on formulating poorly-water soluble compounds using wet media milling technology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, P.; Subramony, J.A. Nanotherapeutics in oral and parenteral drug delivery: Key learnings and future outlooks as we think small. J. Control. Release 2018, 272, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitragotri, S.; Blankschtein, D.; Langer, R. Ultrasound-mediated transdermal protein delivery. Science 1995, 269, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Park, J.H.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for drug and vaccine delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1547–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalia, Y.N.; Naik, A.; Garrison, J.; Guy, R.H. Iontophoretic drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 619–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, B.E.; Blankschtein, D.; Langer, R. Low-frequency sonophoresis: Application to the transdermal delivery of macromolecules and hydrophilic drugs. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 1415–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Charoo, N.A.; Rahman, Z.; Repka, M.A.; Murthy, S.N. Electroporation: An avenue for transdermal drug delivery. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Langer, R. Transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushik, S.; Hord, A.H.; Denson, D.D.; McAllister, D.V.; Smitra, S.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Lack of Pain Associated with Microfabricated Microneedles. Anesth. Analg. 2001, 92, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gill, H.S.; Denson, D.D.; Burris, B.A.; Prausnitz, M.R. Effect of microneedle design on pain in human volunteers. Clin. J. Pain 2008, 24, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Singh, T.R.R.; Tunney, M.M.; Morrow, D.I.J.; McCarron, P.A.; O’Mahony, C.; Woolfson, A.D. Microneedle arrays allow lower microbial penetration than hypodermic needles in vitro. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2513–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, S.; Foulad, D.P.; Atanaskova Mesinkovska, N. Safety Profile for Microneedling: A Systematic Review. Dermatol. Surg. 2021, 47, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, J.; Gupta, S.; Kumari, R.; Gupta, G.D.; Rai, V.K. Microneedle Array: Applications, Recent Advances, and Clinical Pertinence in Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Innov. 2021, 16, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Biodegradable polymer microneedles: Fabrication, mechanics and transdermal drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 104, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Raj Singh, T.R.; Woolfson, A.D. Microneedle-based drug delivery systems: Microfabrication, drug delivery, and safety. Drug Deliv. 2010, 17, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheung, K.; Das, D.B. Microneedles for drug delivery: Trends and progress. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2338–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waghule, T.; Singhvi, G.; Dubey, S.K.; Pandey, M.M.; Gupta, G.; Singh, M.; Dua, K. Microneedles: A smart approach and increasing potential for transdermal drug delivery system. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badran, M.M.; Kuntsche, J.; Fahr, A. Skin penetration enhancement by a microneedle device (Dermaroller) in vitro: Dependency on needle size and applied formulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 36, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, Y.; Kochba, E.; Hung, I.; Kenney, R. Intradermal vaccination using the novel microneedle device MicronJet600: Past, present, and future. Hum. Vaccin Immunother. 2015, 11, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matriano, J.A.; Cormier, M.; Johnson, J.; Young, W.A.; Buttery, M.; Nyam, K.; Daddona, P.E. Macroflux microprojection array patch technology: A new and efficient approach for intracutaneous immunization. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, S.; McAllister, D.V.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microfabricated Microneedles: A Novel Approach to Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Sci. 1998, 87, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, N.; Mulcahy, A.; Ye, S.R.; Morrissey, A. Process optimization and characterization of silicon microneedles fabricated by wet etch technology. Microelectron. J. 2005, 36, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, L.; Yuan, W.; Liang, L. Fabrication of a Ti porous microneedle array by metal injection molding for transdermal drug delivery. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cormier, M.; Johnson, B.; Ameri, M.; Nyam, K.; Libiran, L.; Zhang, D.D.; Daddona, P. Transdermal delivery of desmopressin using a coated microneedle array patch system. J. Control. Release 2004, 97, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyano, T.; Tobinaga, Y.; Kanno, T.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Takeda, H.; Wakui, M.; Hanada, K. Sugar micro needles as transdermic drug delivery system. Biomed. Microdevices 2005, 7, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnelly, R.F.; Morrow, D.I.; Singh, T.R.; Migalska, K.; McCarron, P.A.; O’Mahony, C.; Woolfson, A.D. Processing difficulties and instability of carbohydrate microneedle arrays. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2009, 35, 1242–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Hagiwara, E.; Saeki, A.; Sugioka, N.; Takada, K. Feasibility of microneedles for percutaneous absorption of insulin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 29, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, X.; Chang, J.-h.; Ju, B.-K.; Pak, J.J. Rapidly dissolving fibroin microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 1632–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwood, D.N.; Preda, R.C.; Yücel, T.; Wang, X.; Lovett, M.L.; Kaplan, D.L. Materials fabrication from Bombyx mori silk fibroin. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1612–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.B.; Kluge, J.A.; Guziewicz, N.A.; Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk-based stabilization of biomacromolecules. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stinson, J.A.; Raja, W.K.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.B.; Diwan, I.; Tutunjian, S.; Panilaitis, B.; Omenetto, F.G.; Tzipori, S.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk Fibroin Microneedles for Transdermal Vaccine Delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, K.; Hirobe, S.; Yokota, Y.; Ayabe, Y.; Seto, M.; Quan, Y.-S.; Kamiyama, F.; Tougan, T.; Horii, T.; Mukai, Y.; et al. Transcutaneous immunization using a dissolving microneedle array protects against tetanus, diphtheria, malaria, and influenza. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jin, M.-N.; Quan, Y.-S.; Kamiyama, F.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. The development and characteristics of novel microneedle arrays fabricated from hyaluronic acid, and their application in the transdermal delivery of insulin. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Ise, A.; Morita, H.; Hasegawa, R.; Ito, Y.; Sugioka, N.; Takada, K. Two-Layered Dissolving Microneedles for Percutaneous Delivery of Peptide/Protein Drugs in Rats. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Luo, H.; Lu, W.; Luan, H.; Wu, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Pi, J.; Lim, C.Y.; Wang, H. Rapidly Dissolvable Microneedle Patches for Transdermal Delivery of Exenatide. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 3348–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mönkäre, J.; Reza Nejadnik, M.; Baccouche, K.; Romeijn, S.; Jiskoot, W.; Bouwstra, J.A. IgG-loaded hyaluronan-based dissolving microneedles for intradermal protein delivery. J. Control. Release 2015, 218, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Yoshimitsu, J.; Shiroyama, K.; Sugioka, N.; Takada, K. Self-dissolving microneedles for the percutaneous absorption of EPO in mice. J. Drug Target. 2006, 14, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.Y.; Han, M.H.; Lee, S.S.; Choi, Y.H. Mass producible and biocompatible microneedle patch and functional verification of its usefulness for transdermal drug delivery. Biomed. Microdevices 2009, 11, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Araci, Z.; Inayathullah, M.; Manickam, S.; Zhang, X.; Bruce, M.A.; Marinkovich, M.P.; Lane, A.T.; Milla, C.; Rajadas, J.; et al. Polyvinylpyrrolidone microneedles enable delivery of intact proteins for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7767–7774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Perez, E.M.; Larrañeta, E.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Kissenpfennig, A.; Hegarty, S.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. Repeat application of microneedles does not alter skin appearance or barrier function and causes no measurable disturbance of serum biomarkers of infection, inflammation or immunity in mice in vivo. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takano, N.; Tachikawa, H.; Miyano, T.; Nishiyabu, K. Insertion Testing of Polyethylene Glycol Microneedle Array into Cultured Human Skin with Biaxial Tension. J. Solid Mech. Mater. Eng. 2009, 3, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buddhadev Paul, C.; Frederik, C.; Piet De, M.; Chris Van, H.; Robert, P. A high aspect ratio SU-8 fabrication technique for hollow microneedles for transdermal drug delivery and blood extraction. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 064006. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, S.J.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, H.S.; Kwon, T.H. Fabrication of microneedle array using LIGA and hot embossing process. Microsyst. Technol. 2005, 11, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, D.V.; Wang, P.M.; Davis, S.P.; Park, J.H.; Canatella, P.J.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microfabricated needles for transdermal delivery of macromolecules and nanoparticles: Fabrication methods and transport studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13755–13760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, S.P.; Martanto, W.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Hollow metal microneedles for insulin delivery to diabetic rats. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 52, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardeniers, H.J.G.E.; Luttge, R.; Berenschot, E.J.W.; Boer, M.J.D.; Yeshurun, S.Y.; Hefetz, M.; Oever, R.V.T.; Berg, A.V.D. Silicon micromachined hollow microneedles for transdermal liquid transport. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2003, 12, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoeber, B.; Liepmann, D. Arrays of hollow out-of-plane microneedles for drug delivery. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2005, 14, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayakumar, K.B.; Hegde, G.M.; Nayak, M.M.; Dinesh, N.S.; Rajanna, K. Fabrication and characterization of gold coated hollow silicon microneedle array for drug delivery. Microelectron. Eng. 2014, 128, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Das, D.B. A new paradigm for numerical simulation of microneedle-based drug delivery aided by histology of microneedle-pierced skin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 1993–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burton, S.A.; Ng, C.Y.; Simmers, R.; Moeckly, C.; Brandwein, D.; Gilbert, T.; Johnson, N.; Brown, K.; Alston, T.; Prochnow, G.; et al. Rapid intradermal delivery of liquid formulations using a hollow microstructured array. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, J.; Gill, H.S.; Andrews, S.N.; Prausnitz, M.R. Kinetics of skin resealing after insertion of microneedles in human subjects. J. Control. Release 2011, 154, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martanto, W.; Davis, S.P.; Holiday, N.R.; Wang, J.; Gill, H.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Transdermal delivery of insulin using microneedles in vivo. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wermeling, D.P.; Banks, S.L.; Hudson, D.A.; Gill, H.S.; Gupta, J.; Prausnitz, M.R.; Stinchcomb, A.L. Microneedles permit transdermal delivery of a skin-impermeant medication to humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2058–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ita, K. Transdermal Delivery of Drugs with Microneedles-Potential and Challenges. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ita, K. Dissolving microneedles for transdermal drug delivery: Advances and challenges. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, H.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Coated microneedles for transdermal delivery. J. Control. Release 2007, 117, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haj-Ahmad, R.; Khan, H.; Arshad, M.S.; Rasekh, M.; Hussain, A.; Walsh, S.; Li, X.; Chang, M.W.; Ahmad, Z. Microneedle Coating Techniques for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 486–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gill, H.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Coating formulations for microneedles. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Prow, T.W.; Crichton, M.L.; Jenkins, D.W.; Roberts, M.S.; Frazer, I.H.; Fernando, G.J.; Kendall, M.A. Dry-coated microprojection array patches for targeted delivery of immunotherapeutics to the skin. J. Control. Release 2009, 139, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, M.G.; Vrdoljak, A.; O’Mahony, C.; Oliveira, J.C.; Moore, A.C.; Crean, A.M. Determination of parameters for successful spray coating of silicon microneedle arrays. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 415, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunn, P.F.; Grace, J.M.; Snarski, S.R. The mixing of electrically-charged droplets between and within electrohydrodynamic fine sprays. J. Aerosol Sci. 1994, 25, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahony, C.; Hilliard, L.; Kosch, T.; Bocchino, A.; Sulas, E.; Kenthao, A.; O’Callaghan, S.; Clover, A.J.P.; Demarchi, D.; Bared, G. Accuracy and feasibility of piezoelectric inkjet coating technology for applications in microneedle-based transdermal delivery. Microelectron. Eng. 2017, 172, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, E.A.; O’Mahony, C.; Cronin, M.; O’Mahony, T.; Moore, A.C.; Crean, A.M. Dissolvable microneedle fabrication using piezoelectric dispensing technology. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 500, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, D. Percutaneous Collagen Induction: An Alternative to Laser Resurfacing. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2002, 22, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litchman, G.; Nair, P.A.; Badri, T.; Kelly, S.E. Microneedling. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing Copyright© 2022; StatPearls Publishing LLC: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, Y.Z.; Al-Niaimi, F.; Madan, V. Comparative Efficacy and Patient Preference of Topical Anaesthetics in Dermatological Laser Treatments and Skin Microneedling. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2015, 8, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, L.; Marquardt, Y.; Amann, P.; Heise, R.; Huth, L.; Wagner-Schiffler, S.; Huth, S.; Baron, J.-M. Comprehensive molecular characterization of microneedling therapy in a human three-dimensional skin model. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camirand, A.; Doucet, J. Needle Dermabrasion. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 1997, 21, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.; Han, S.; Pongprutthipan, M.; Disphanurat, W.; Kakar, R.; Nodzenski, M.; Pace, N.; Kim, N.; Yoo, S.; Veledar, E.; et al. Efficacy of a Needling Device for the Treatment of Acne Scars: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2014, 150, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, Y.S.; Horowitz, R.; Hashim, P.W.; Nia, J.K.; Farberg, A.S.; Goldenberg, G. Update on acne scar treatment. Cutis 2018, 102, 21–25, 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.R.; Lee, E.G.; Lee, H.J.; Yoon, M.S. Assessment of treatment efficacy and sebosuppressive effect of fractional radiofrequency microneedle on acne vulgaris. Lasers Surg. Med. 2013, 45, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Goo, J.W.; Shin, J.; Chung, W.S.; Kang, J.M.; Kim, Y.K.; Cho, S.B. Use of fractionated microneedle radiofrequency for the treatment of inflammatory acne vulgaris in 18 Korean patients. Dermatol. Surg. 2012, 38, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijaya Lakshmi, Y.; Swetha Reddy, L.; Naga Neelima Devi, K.; Phani Kumar, K.; Guru Karthik, G.; Srinivas Chakravarthy, P.; Nageswar Rao, K. Evaluation of Microneedling Therapy in Management of Facial Scars. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2020, 31, e214–e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, I.M.C.; Costa, M.C. Microneedling for Varicella Scars in a Dark-Skinned Teenager. Dermatol. Surg. 2014, 40, 333–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Jang, Y.H.; Son, Y.H.; Lee, C.S.; Bae, J.Y.; Park, J.M. Management of Hypertrophic Scar after Burn Wound Using Microneedling Procedure (Dermastamp®). J. Korean Burn Soc. 2009, 12, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, S.E.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, M.N. Treatment of Striae Distensae Using Needling Therapy: A Pilot Study. Dermatol. Surg. 2012, 38, 1823–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.; She, J.; Lin, D.-A.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, W.-F.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Jin, L.; Xie, X.; Su, Y.-X. Microneedle-Mediated Delivery of Lipid-Coated Cisplatin Nanoparticles for Efficient and Safe Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33060–33069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Dong, L.; Du, H.; Mao, J.; Xie, Y.; Wang, H.; Lan, J.; Lou, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wen, J.; et al. 5-Aminolevulinic Acid-Loaded Hyaluronic Acid Dissolving Microneedles for Effective Photodynamic Therapy of Superficial Tumors with Enhanced Long-Term Stability. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.-C.; Lin, Z.-W.; Ling, M.-H. Near-Infrared Light-Activatable Microneedle System for Treating Superficial Tumors by Combination of Chemotherapy and Photothermal Therapy. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, A.D.; Fritz, J.M.; Lenardo, M.J. A guide to cancer immunotherapy: From T cell basic science to clinical practice. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, P.M. The skin barrier as an innate immune element. Semin. Immunopathol. 2007, 29, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaric, M.; Lyubomska, O.; Touzelet, O.; Poux, C.; Al-Zahrani, S.; Fay, F.; Wallace, L.; Terhorst, D.; Malissen, B.; Henri, S.; et al. Skin Dendritic Cell Targeting via Microneedle Arrays Laden with Antigen-Encapsulated Poly-d,l-lactide-co-Glycolide Nanoparticles Induces Efficient Antitumor and Antiviral Immune Responses. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2042–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.T.T.; Yin, Y.; Thambi, T.; Kim, B.S.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, D.S. Highly potent intradermal vaccination by an array of dissolving microneedle polypeptide cocktails for cancer immunotherapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmamed, M.F.; Chen, L. A Paradigm Shift in Cancer Immunotherapy: From Enhancement to Normalization. Cell 2018, 175, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Intlekofer, A.M.; Thompson, C.B. At the bench: Preclinical rationale for CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockade as cancer immunotherapy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 94, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Ye, Y.; Hochu, G.M.; Sadeghifar, H.; Gu, Z. Enhanced Cancer Immunotherapy by Microneedle Patch-Assisted Delivery of Anti-PD1 Antibody. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 2334–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, Q.; Hochu, G.M.; Xin, H.; Wang, C.; Gu, Z. Synergistic Transcutaneous Immunotherapy Enhances Antitumor Immune Responses through Delivery of Checkpoint Inhibitors. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8956–8963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellor, A.L.; Lemos, H.; Huang, L. Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase and Tolerance: Where Are We Now? Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.C.; Ling, M.H.; Wang, K.W.; Lin, Z.W.; Lai, B.H.; Chen, D.H. Near-infrared light-responsive composite microneedles for on-demand transdermal drug delivery. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petukhova, T.A.; Hassoun, L.A.; Foolad, N.; Barath, M.; Sivamani, R.K. Effect of Expedited Microneedle-Assisted Photodynamic Therapy for Field Treatment of Actinic Keratoses: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2017, 153, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogunjimi, A.T.; Lawson, C.; Carr, J.; Patel, K.K.; Ferguson, N.; Brogden, N.K. Micropore Closure Rates following Microneedle Application at Various Anatomical Sites in Healthy Human Subjects. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2021, 34, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Brand Name | Manufacturer | Type | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dermaroller® | Derma Spark Product Inc., Vancouver, BC, Canada | Metallic MN Array | Used to treat acne, stretch marks, hair loss. Able to enhance drug absorption (minoxidil, hyaluronic acid, etc.). | [24] |
| MicroHyala® | CosMED Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Kyoto, Japan | Dissolvable MN Patch | It contains hyaluronic acid that is released into the skin to treat wrinkles. | |
| VaxMat® | TheraJect Inc., Fremont, CA, USA | Dissolvable MN Patch | It is used to deliver macromolecules, like proteins, peptides, and vaccines. | |
| Micro-Trans® | Valeritas Inc., Bridgewater, NJ, USA | Microneedle Patch | It delivers the drug into the dermis without limitations of drug size, structure, charge, or the patient’s skin characteristics. | |
| Drugmat® | TheraJect Inc., Fremont, CA, USA | Dissolvable MN Patch | It delivers hundreds of micrograms of drug rapidly through the stratum corneum into the epidermal tissue. | |
| Nanoject® | Debiotech S.A., Lausanne, Switzerland | Microneedle Array | Useful for intradermal and hypodermic drug delivery and interstitial fluid diagnostics | |
| Soluvia® | Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA | Hollow MN Array | It is a prefillable microinjection system for accurate intradermal delivery of drugs and vaccines. | [25] |
| IDflu®/Intanza® | Sanofi Pasteur, Lyon, France | Intradermal MN Injection | Prefilled with influenza vaccine for intradermal influenza vaccination. | [25] |
| MicronJet 600TM | NanoPass Technologies Ltd., Nes Ziona, Israel | Intradermal MN Injection | It has been used for intradermal immunization | [25] |
| Micronjet® | NanoPass Technologies Ltd., Nes Ziona, Israel | Intradermal MN Injection | It is used with any standard syringe for painless delivery of drugs, protein, and vaccines. | |
| Macroflux® | Zosano Pharma Corp., Fremont, CA, USA | Metallic MN Array | Delivery of peptides and vaccines | [26] |
| Microcor® | Corium Inc., Boston, MA, USA | Dissolvable MN Patch | Deliver small and large molecules, like proteins, peptides, and vaccines. | |
| Dermapan® | DermapenWorld, Belrose Sydney, NSW, Australia | Microneedle Array | Used for treating various skin conditions, ranging from acne, stretch mark, and hair loss, and can enhance drug absorption. | |
| Microstructured Transdermal Patch | 3M Company, Maplewood, MN, USA | Hollow MN Array | It delivers liquid formulations over a range of viscosities. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, D.-J.; Kim, H.-J. Microneedles in Action: Microneedling and Microneedles-Assisted Transdermal Delivery. Polymers 2022, 14, 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081608
Lim D-J, Kim H-J. Microneedles in Action: Microneedling and Microneedles-Assisted Transdermal Delivery. Polymers. 2022; 14(8):1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081608
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Dong-Jin, and Hong-Jun Kim. 2022. "Microneedles in Action: Microneedling and Microneedles-Assisted Transdermal Delivery" Polymers 14, no. 8: 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081608
APA StyleLim, D.-J., & Kim, H.-J. (2022). Microneedles in Action: Microneedling and Microneedles-Assisted Transdermal Delivery. Polymers, 14(8), 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081608






