Marine Alkylpurines: A Promising Group of Bioactive Marine Natural Products †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Purines Alkylated Only with Methyl Groups
2.1. Adenine and Guanine Derivatives
2.2. Isoguanine Derivatives
2.3. Xanthine Derivatives
2.4. 8-Oxopurine Derivatives
3. N-Alkylpurines with Substituents Other Than Methyl
3.1. Terpenylpurines
3.1.1. Terpenylpurines with an Acyclic Diterpenoid
3.1.2. Terpenylpurines with a Monocyclic Diterpenoid
3.1.3. Terpenylpurines with a Bicyclic Diterpenoid
Agelasines with a Clerodane Type Diterpenoid
Agelasines with an Halimane Type Diterpenoid
Agelasines with a Labdane Type Diterpenoid
Diterpenylpurines Other Than Agelasines
3.1.4. Terpenylpurines with a Diazepinopurine Heterocyclic System
3.2. Other Alkylpurines
4. Nucleoside Derivatives
5. Synthetic Approaches towards the Natural Alkylpurines and/or Bioactive Analogues
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 235–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skropeta, D.; Wei, L. Recent advances in deep-sea natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 999–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosemeyer, H. The chemodiversity of purine as a constituent of natural products. Chem. Biodivers. 2004, 1, 361–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, D.; List, P.H. Zur konstitution des zooanemonins und des herbipolins. Hoppe-Seyler’s Z. Physiol. Chem. 1960, 318, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, D.; List, P.H. Konstitution des spongopurins, einer in der natur neuen purinbase. Hoppe-Seyler’s Z. Physiol. Chem. 1961, 323, 192–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, H.; Matsunaga, S.; Fusetani, N. Isolation of 1-methylherbipoline, a purine base, from a marine sponge, Jaspis sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 837–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, J.; Ishizuka, E.; Nakao, Y.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Isolation of 1-methylherbipoline salts of halisulfate-1 and of suvanine as serine protease inhibitors from a marine sponge, Coscinoderma mathewsi. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 248–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.A.; Christensen, L.V.; Richardson, A.D.; da Rocha, R.M.; Ireland, C.M. Rigidin E, a new pyrrolopyrimidine alkaloid from a Papua New Guinea tunicate Eudistoma species. Mar. Drugs 2003, 1, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, B.S.; Battershill, C.N.; Copp, B.R. 1,3-Dimethylguanine, a new purine from the New Zealand ascidian Botrylloides leachi. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 638–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasdemir, D.; Mangalindan, G.C.; Concepcion, G.P.; Harper, M.K.; Ireland, C.M. 3,7-Dimethylguanine, a new purine from a Philippine sponge Zyzzya fuliginosa. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 49, 1628–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Lateff, A.; Alarif, W.M.; Asfour, H.Z.; Ayyad, S.E.N.; Khedr, A.; Badria, F.A.; Al-lihaibi, S.S. Cytotoxic effects of three new metabolites from Red Sea marine sponge, Petrosia sp. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 37, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, B.; Baker, B.J.; McClintock, J.B. Purine and nucleoside metabolites from the Antarctic sponge Isodictya erinacea. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, A.N.; Babcock, R.C.; Lambert, G.; Copp, B.R. N2,N2,7-Trimethylguanine, a new trimethylated guanine natural product from the New Zealand ascidian, Lissoclinum notti. Nat. Prod. Lett. 2001, 15, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G. 1,3,7-Trimethylguanine from the sponge Latrunculia brevis. J. Nat. Prod. 1987, 50, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wagoner, R.M.; Jompa, J.; Tahir, A.; Ireland, C.M. Trypargine alkaloids from a previously undescribed Eudistoma sp. ascidian. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, Y.; Bremner, J.B.; Davis, A.; Samosorn, S. Isolation and NMR spectroscopic clarification of the alkaloid 1,3,7-trimethylguanine from the ascidian Eudistoma maculosum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 20, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, S.S.; Whitehill, A.B.; Trapido-Rosenthal, H.G.; Ireland, C.M. Isolation and characterization of 1,3-dimethylisoguanine from the Bermudian sponge Amphimedon viridis. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 727–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chehade, C.C.; Dias, R.L.A.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; Ferreira, A.G.; Costa, L.V.; Rangel, M.; Malpezzi, E.L.A.; de Freitas, J.C.; Hajdu, E. 1,3-Dimethylisoguanine, a new purine from the marine sponge Amphimedon viridis. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.J.; Inagaki, M.; Higuchi, R.; Miyamoto, T.; Ono, M.; Kuwano, M.; Van Soest, R.W.M. 1,3-Dimethylisoguaninium, an antiangiogenic purine analog from the sponge Amphimedon paraviridis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 731–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, B.S.; Battershill, C.N.; Copp, B.R. Isolation of 2-(3′-bromo-4′-hydroxyphenol)ethanamine from the New Zealand ascidian Cnemidocarpa bicornuta. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 857–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copp, B.R.; Wassvik, C.M.; Lambert, G.; Page, M.J. Isolation and characterization of the new purine 1,3,7-trimethylisoguanine from the New Zealand ascidian Pseudodistoma cereum. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1168–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cafieri, F.; Fattorusso, E.; Mangoni, A.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Longamide and 3,7-dimethylisoguanine, two novel alkaloids from the marine sponge Agelas longissima. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 7893–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Ng, P.-L.; Schmitz, F.J.; Hossain, M.B.; van der Helm, D.; Kelly-Borges, M. Makaluvic acids A and B: Novel alkaloids from the marine sponge Zyzzya fuliginosus. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1104–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penez, N.; Culioli, G.; Perez, T.; Briand, J.F.; Thomas, O.P.; Blache, Y. Antifouling properties of simple indole and purine alkaloids from the Mediterranean gorgonian Paramuricea clavata. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2304–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L.; Martin, M.T.; Vacelet, J.; Guyot, M. Mucronatine, a new N-methyl purine from the French Mediterranean marine sponge Stryphnus mucronatus. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 7257–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suciati; Garson, M.J.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Pierens, G.K. A new N,N-dimethyl purine from an Australian dictyoceratid sponge. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2011, 41, 1669–1672. [Google Scholar]
- Ashour, M.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Ebel, R.; Wray, V.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Proksch, P. New purine derivatives from the marine sponge Petrosia nigricans. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay, B.S.; Almeida, A.M.P.; Smith, C.J.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; da Rocha, R.M.; Ireland, C.M. 6-Methoxy-7-methyl-8-oxoguanine, an unusual purine from the ascidian Symplegma rubra. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1573–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capon, R.J.; Rooney, F.; Murray, L.M. 1,9-Dimethylhypoxanthine from a Southern Australian marine sponge Spongosorites species. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 261–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Fu, M.; Tian, S.; Liu, Y. A new pyrimidinedione derivative from the gorgonian coral Verrucella umbraculum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimino, G.; de Giulio, A.; de Rosa, S.; de Stefano, S.; Puliti, R.; Mattia, C.A.; Mazzarella, L. Isolation and X-ray crystal structure of a novel 8-oxopurine compound from a marine sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 1985, 48, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelnik, R.; Haraguchi, M.; Matida, A.K.; Lavie, D.; Frolow, F.; Weis, A.L. X-ray molecular structure of caissarone, a novel purine derivative from the sea-anemone Bunodosoma caissarum Correa 1964. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1986, 2051–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Saito, T.; Mori, S.; Chikazawa, J. Synthesis of the sea anemone purine caissarone. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, J.C.; Sawaya, M.I. Anomalies in sea-urchin egg development induced by a novel purine isolated from the sea-anemone Bunodosoma caissarum. Toxicon 1986, 24, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.A.; de Freitas, J.C.; Porreca, F.; Eisenhour, C.M.; Lukas, R.; Huxtable, R.J. The sea anemone purine, caissarone: Adenosine receptor antagonism. Toxicon 1995, 33, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleton, D.R.; Page, M.J.; Lambert, G.; Copp, B.R. 1,3-Dimethyl-8-oxoisoguanine, a new purine from the New Zealand ascidian Pseudodistoma cereum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2004, 18, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurada, T.; Gill, M.B.; Frausto, S.; Copits, B.; Noguchi, K.; Shimamoto, K.; Swanson, G.T.; Sakai, R. Novel N-methylated 8-oxoisoguanines from Pacific sponges with diverse neuroactivities. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 6089–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Mohamed, G.A.; Shaala, L.A.; Badr, J.M.; Bamanie, F.H.; Ibrahim, S.R.M. New purine alkaloids from the Red Sea marine tunicate Symplegma rubra. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 13, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundersen, L.L. Synthesis and biological activities of marine terpene-adenine hybrids and synthetic analogs. Phytochem. Rev. 2013, 12, 467–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordaliza, M. Terpenyl-purines from the sea. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 833–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, E.; Devlin, J.P. Agelasine: Novel quaternary 9-methyladenine from sponge Agelas dispar. Can. J. Chem. 1975, 53, 1690–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyzers, R.A.; Gray, C.A.; Schleyer, M.H.; Whibley, C.E.; Hendricks, D.T.; Davies-Coleman, M.T. Malonganenones A–C, novel tetraprenylated alkaloids from the Mozambique gorgonian Leptogorgia gilchristi. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 2200–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorek, H.; Rudi, A.; Benayahu, Y.; Ben-Califa, N.; Neumann, D.; Kashman, Y. Nuttingins A–F and malonganenones D–H, tetraprenylated alkaloids from the Tanzanian gorgonian Euplexaura nuttingi. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.R.; Li, P.L.; Tang, X.L.; Qi, X.; Li, G.Q. Cytotoxic tetraprenylated alkaloids from the South China Sea gorgonian Euplexaura robusta. Chem. Biodivers. 2012, 9, 2218–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.H.; Cai, Y.H.; Fan, C.Q.; Tang, G.H.; Luo, H.B.; Yin, S. Six new tetraprenylated alkaloids from the South China Sea gorgonian Echinogorgia pseudossapo. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capon, R.J.; Faulkner, D.J. Antimicrobial metabolites from a Pacific sponge, Agelas sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 1819–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Nakamura, H.; Kobayashi, J.; Ohizumi, Y.; Hirata, Y. Agelasine-E and agelasine-F, novel monocyclic diterpenoids with a 9-methyladeninium unit possessing inhibitory effects on Na,K-ATPase isolated from the Okinawan Sea sponge Agelas nakamurai Hoshino. Tetrahedron Lett. 1984, 25, 3719–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalindan, G.C.; Talaue, M.T.; Cruz, L.J.; Franzblau, S.G.; Adams, L.B.; Richardson, A.D.; Ireland, C.M.; Concepcion, G.P. Agelasine F from a Philippine Agelas sp. sponge exhibits in vitro antituberculosis activity. Planta Med. 2000, 66, 364–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, G.R.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Bourne, G.T.; Arm, C.A.; Leet, J.E.; Knight, J.C.; Pettit, R.K.; Chapuis, J.C.; Doubek, D.L.; et al. Isolation and structures of axistatins 1–3 from the Republic of Palau marine sponge Agelas axifera Hentschel. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakkestuen, A.K.; Gundersen, L.L.; Petersen, D.; Utenova, B.T.; Vik, A. Synthesis and antimycobacterial activity of agelasine E and analogs. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdjul, D.B.; Yamazaki, H.; Kanno, S.I.; Takahashi, O.; Kirikoshi, R.; Ukai, K.; Namikoshi, M. Structures and biological evaluations of agelasines isolated from the Okinawan marine sponge Agelas nakamurai. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, L.L.; Sun, J.B.; Yang, F.; Liu, M.; Tang, J.; Sun, F.; Jiao, W.H.; Wang, S.P.; Zhang, W.; Lin, H.W. New diterpene alkaloids from the marine sponge Agelas mauritiana. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 23970–23976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Wu, H.M.; Ohizumi, Y.; Hirata, Y. Agelasine-A, -B, -C and -D, novel bicyclic diterpenoids with a 9-methyladeninium unit possessing inhibitory effects on Na,K-ATPase from the Okinawan Sea sponge Agelas sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1984, 25, 2989–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.M.; Nakamura, H.; Kobayashi, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Ohizumi, Y.; Hirata, Y. Structures of agelasines, diterpenes having a 9-methyladeninium chromophore isolated from the Okinawan marine sponge Agelas nakamurai Hoshino. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1986, 59, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcul, L.; Tenney, K.; Ratnam, J.; McKerrow, J.H.; Crews, P. Structural variations to the 9-N-methyladeninium diterpenoid hybrid commonly isolated from Agelas sponges. Aust. J. Chem. 2010, 63, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Schmitz, F.J.; Tanner, R.S.; Kelly-Borges, M. Agelasines H and H, 9-methyladenine-containing diterpenoids from an Agelas sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appenzeller, J.; Mihci, G.; Martin, M.T.; Gallard, J.F.; Menou, J.L.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Hooper, J.; Petek, S.; Chevalley, S.; Valentin, A.; et al. Agelasines J, K, and L from the Solomon Islands marine sponge Agelas cf. mauritiana. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1451–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stout, E.P.; Yu, L.C.; Molinski, T.F. Antifungal diterpene alkaloids from the Caribbean sponge Agelas citrina: Unified configurational assignments of agelasidines and agelasines. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 5131–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, T.; Iwai, T.; Takahashi-Nakaguchi, A.; Fromont, J.; Gonoi, T.; Kobayashi, J.I. Agelasines O–U, new diterpene alkaloids with a 9-N-methyladenine unit from a marine sponge Agelas sp. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 9738–9744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Hamann, M.T.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, M.Y.; Gong, X.B.; Xiao, J.R.; Chen, W.S.; Lin, H.W. Antimicrobial metabolites from the Paracel Islands sponge Agelas mauritiana. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, L.; Song, W.; Tang, X.; de Voogd, N.J.; Wang, Q.; Chu, M.; Li, P.; Li, G. Alkaloids and polyketides from the South China Sea sponge Agelas aff. nemoechinata. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14323–14329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K.; Ishibashi, M.; Shigemori, H.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, J. Agelasine G, a new antileukemic alkaloid from the Okinawan marine sponge Agelas sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1992, 40, 766–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, H.; Kanno, S.I.; Abdjul, D.B.; Namikoshi, M. A bromopyrrole-containing diterpene alkaloid from the Okinawan marine sponge Agelas nakamurai activates the insulin pathway in Huh-7 human hepatoma cells by inhibiting protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2207–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, T.; Adachi, K.; Shizuri, Y. New agelasine compound from the marine sponge Agelas mauritiana as an antifouling substance against macroalgae. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, I.S.; García, N.; Sexmero, A.J.; Basabe, P.; Díez, D.; Urones, J.G. Synthesis of (+)-agelasine C. A structural revision. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 11672–11678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.J.; Tang, X.L.; Qin, G.F.; Sun, Y.T.; Li, L.; de Voogd, N.J.; Li, P.L.; Li, G.Q. Pyrrole derivatives and diterpene alkaloids from the South China Sea sponge Agelas nakamurai. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1600446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathiafshar, R.; Allen, T.M. Biologically active metabolites from Agelas mauritiana. Can. J. Chem. 1988, 66, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathiafshar, R.; Allen, T.M.; Krueger, C.A.; Cook, D.A.; Clanachan, A.S.; Vriend, R.; Baer, H.P.; Cass, C.E. Some pharmacological activities of novel adenine-related compounds isolated from a marine sponge Agelas mauritiana. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1989, 67, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertiani, T.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Ortlepp, S.; van Soest, R.W.M.; de Voogd, N.J.; Wray, V.; Hentschel, U.; Kozytska, S.; Mueller, W.E.G.; Proksch, P. From anti-fouling to biofilm inhibition: New cytotoxic secondary metabolites from two Indonesian Agelas sponges. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 1297–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwagawa, T.; Kaneko, M.; Okamura, H.; Nakatani, M.; van Soest, R.W.M. New alkaloids from the Papua New Guinean sponge Agelas nakamurai. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1310–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wang, B.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tang, X.L.; Wang, Q.; Chu, M.J.; Li, P.L.; Li, G.Q. Two new diterpene alkaloids from the South China Sea sponge Agelas aff. nemoechinata. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 1048–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosief, T.; Rudi, A.; Stein, Z.; Goldberg, I.; Gravalos, G.M.D.; Schleyer, M.; Kashman, Y. Asmarines A–C; three novel cytotoxic metabolites from the marine sponge Raspailia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 3323–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosief, T.; Rudi, A.; Kashman, Y. Asmarines A–F, novel cytotoxic compounds from the marine sponge Raspailia species. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudi, A.; Shalom, H.; Schleyer, M.; Benayahu, Y.; Kashman, Y. Asmarines G and H and barekol, three new compounds from the marine sponge Raspailia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudi, A.; Aknin, M.; Gaydou, E.; Kashman, Y. Asmarines I, J, and K and nosyberkol: Four new compounds from the marine sponge Raspailia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1932–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, K.K.; Shenvi, R.A. Conjuring a supernatural product—DelMarine. Synlett 2016, 27, 1145–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, A.R.; Duffy, S.; Avery, V.M. Aplidiopsamine A, an antiplasmodial alkaloid from the temperate Australian ascidian, Aplidiopsis confluata. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 8291–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.E.; Roth, G.P.; Hoffman, J.K.; Divlianska, D.B.; Pechter, D.; Sennett, S.H.; Guzman, E.A.; Linley, P.; McCarthy, P.J.; Pitts, T.P.; et al. Isolation, synthesis, and biological activity of aphrocallistin, an adenine-substituted bromotyramine metabolite from the hexactinellida sponge Aphrocallistes beatrix. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1178–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, M.; Trotter, N.; Vijayasarathy, S.; Salim, A.A.; Khalil, Z.G.; Lacey, E.; Capon, R.J. Isolation and synthesis of N-acyladenine and adenosine alkaloids from a Southern Australian marine sponge, Phoriospongia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 5902–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killday, K.B.; Yarwood, D.; Sills, M.A.; Murphy, P.T.; Hooper, J.N.; Wright, A.E. Microxine, a new cdc2 kinase inhibitor from the Australian marine sponge Microxina species. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 525–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.J.; Fenical, W. Aplidiamine, a unique zwitterionic benzyl hydroxyadenine from the Western Australian marine ascidian Aplidiopsis sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itaya, T.; Hozumi, Y.; Kanai, T.; Ohta, T. Syntheses of the marine ascidian purine aplidiamine and its 9-β-d-ribofuranoside. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 4695–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, J.L.B.; Lin, Z.; Imperial, J.S.; Antunes, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Olivera, B.M.; Schmidt, E.W. Small molecules in the cone snail arsenal. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 4933–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayer, S.W.; Andersen, R.J.; He, C.H.; Clardy, J. Phidolopin, a new purine derivative from the bryozoan Phidolopora pacifica. J. Org. Chem. 1984, 49, 3869–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.H.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Li, Q.X. A cytotoxic sesquiterpene alkaloid from the South China Sea gorgonian Subergorgia suberosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1288–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, H. Purine alkaloids from the South China Sea gorgonian Subergorgia suberosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 716–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.H.; Zhang, S.; Gao, C.H.; Li, Q.X. Purine and pyrimidine derivatives from the South China Sea gorgonian Subergorgia suberosa. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 56, 993–994, retracted in Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
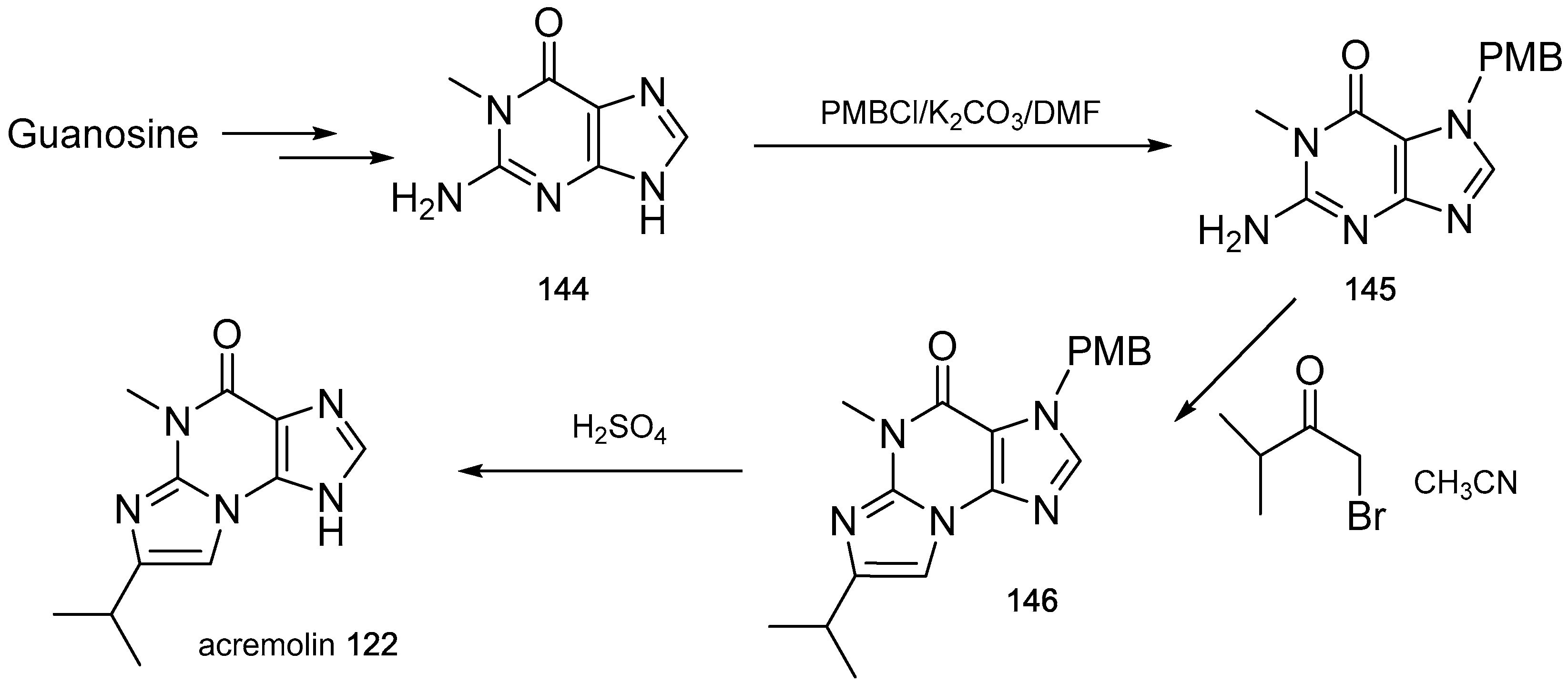
- Julianti, E.; Oh, H.; Lee, H.S.; Oh, D.C.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Acremolin, a new 1H-azirine metabolite from the marine-derived fungus Acremonium strictum. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 2885–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banert, K. Acremolin, a stable natural product with an antiaromatic 1H-azirine moiety? A structural reorientation. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 6443–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januar, L.A.; Molinski, T.F. Acremolin from acremonium strictum is N-2,3-etheno-2′-isopropyl-1-methylguanine, not a 1H-azirine. Synthesis and structural revision. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 2370–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Qin, X.; Lin, X.; Kaliyaperumal, K.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Ju, Z.; Tu, Z.; Liu, Y. Sydoxanthone C and acremolin B produced by deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO Ind09F01. J. Antibiot. 2015, 68, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namikoshi, M.; Rinehart, K.L. Bioactive compounds produced by cyanobacteria. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1996, 17, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiese, M.; D’Agostino, P.M.; Mihali, T.K.; Moffitt, M.C.; Neilan, B.A. Neurotoxic alkaloids: Saxitoxin and its analogs. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2185–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.Z.; Zhang, S.F.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L. Paralytic shellfish toxin biosynthesis in cyanobacteria and dinoflagellates: A molecular overview. J. Proteom. 2016, 135, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wu, X.; Shen, N.; Wang, C. Four new 6-oxy purine alkaloids from the South China Sea sponge, Haliclona cymaeformis. J. Ocean Univ. China 2017, 16, 1183–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, J.; Koeck, M. Hybrid pyrrole-imidazole alkaloids from the sponge Agelas sceptrum. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, W.; Burke, D.C. Contributions to the study of marine products. XXXIX. The nucleosides of sponges. III. Spongothymidine and spongouridine. J. Org. Chem. 1955, 20, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, R.M.; Bandarian, V. Biosynthesis of pyrrolopyrimidines. Bioorg. Chem. 2012, 43, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.M.; Chen, Y.N.; Zeng, Z.; Gao, C.H.; Su, X.; Peng, Y. Marine nucleosides: Structure, bioactivity, synthesis and biosynthesis. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5817–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird-Lambert, J.; Marwood, J.F.; Davies, L.P.; Taylor, K.M. 1-Methylisoguanosine: An orally active marine natural product with skeletal-muscle and cardiovascular effects. Life Sci. 1980, 26, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, F.A.; Fuhrman, G.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Pavelka, L.A.; Mosher, H.S. Doridosine: A new hypotensive N-methylpurine riboside from the nudibranch Anisodoris nobilis. Science 1980, 207, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Nachman, R.J.; Pavelka, L.; Mosher, H.S.; Fuhrman, F.A.; Fuhrman, G.J. Doridosine, 1-methylisoguanosine, from Anisodoris nobilis; structure, pharmacological properties and synthesis. J. Nat. Prod. 1981, 44, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, P.L.; Yen, M.H.; Shyu, W.S.; Chern, J.W. Doridosine derivatives: Binding at adenosine receptors and in vivo effects. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 243, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Trotter, N.S. N-3,5′-Cycloxanthosine, the first natural occurrence of a cyclonucleoside. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1689–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menna, M.; Aiello, A.; D’Aniello, F.; Fattorusso, E.; Imperatore, C.; Luciano, P.; Vitalone, R. Further investigation of the Mediterranean sponge Axinella polypoides: Isolation of a new cyclonucleoside and a new betaine. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2509–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.S.; Chen, C.S.; Chien, T.C.; Yeh, J.Y.; Kuo, C.C.; Talekar, R.S.; Chern, J.W. Nucleosides. IX. Synthesis of purine N-3,5′-cyclonucleosides and N-3,5′-cyclo-2′,3′-seconucleosides via Mitsunobu reaction as TIBO-like derivatives. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2004, 23, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.L.; La Kim, E.; Wang, H.; Hong, J.; Shin, S.; Lee, C.K.; Jung, J.H. Epimeric methylsulfinyladenosine derivatives from the marine ascidian Herdmania momus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4701–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, W.; Edrada, R.; Ebel, R.; Wray, V.; Proksch, P. New alkaloids from the Mediterranean sponge Hamigera hamigera. Mar. Drugs 2004, 2, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamison, M.T.; Boddy, C.N.; Molinski, T.F. Salvadenosine, a 5′-deoxy-5′-(methylthio) nucleoside from the Bahamian tunicate Didemnum sp. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 9992–9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Searle, P.A.; Molinski, T.F. Trachycladine A and trachycladine B: 2′-C-methyl-5′-deoxyribofuranosyl nucleosides from the marine sponge Trachycladus laevispirulifer. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 4296–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiba, T.; Nakao, Y.; Scheuer, P.J.; Sata, N.U.; Kellyborges, M. Kumusine, a chloroadenine riboside from a sponge, Theonella sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 3977–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, I.; Higa, T. A chloroadenine riboside-type nucleoside from the marine sponge Theonella cupola. J. Fac. Pharm. Ankara 2000, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Abou-Hussein, D.R.; Badr, J.M.; Youssef, D.T.A. Dragmacidoside: A new nucleoside from the Red Sea sponge Dragmacidon coccinea. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
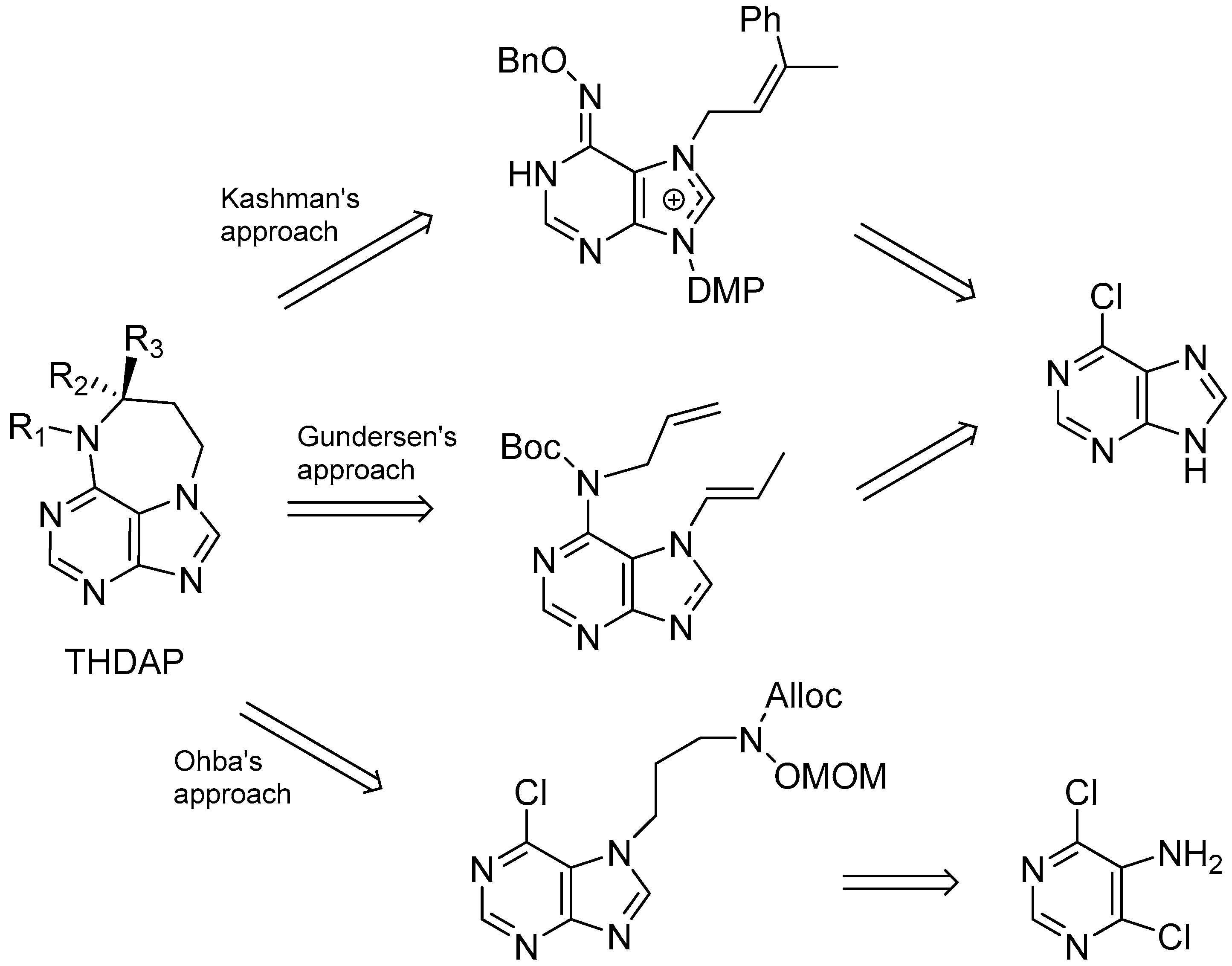
- Gordaliza, M.; Baraldi, P.G. Synthetic approaches towards the marine alkyl purines. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 2798–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotek, V.; Tobrman, T.; Dvorak, D. Highly efficient and broad-scope protocol for the preparation of 7-substituted 6-halopurines via N-9-Boc-protected 7,8-dihydropurines. Synthesis 2012, 44, 610–618. [Google Scholar]
- Legraverend, M. Recent advances in the synthesis of purine derivatives and their precursors. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 8585–8603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Graceffa, R.F.; Boezio, A.A. Direct, regioselective N-alkylation of 1,3-azoles. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itaya, T.; Takada, Y.; Kanai, T.; Kaneko, M.; Fujii, T. Purines. LXXVI. Alkylation of 8-oxoadenine derivatives: Syntheses of 3,7-dialkyl-, 3,9-dialkyl-, and 3,7,9-trialkyl-8-oxoadenines. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 45, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itaya, T.; Takada, Y.; Kanai, T.; Fujii, T. Purines. LXXVIII. An alternative synthesis of the sea anemone purine alkaloid caissarone. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 45, 1867–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Saito, T.; Mori, S. Purines. XLIII. A total synthesis of the marine sponge base 6-imino-1,9-dimethyl-8-oxopurine. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 2146–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Saito, T.; Mori, S. Purines. XLIV.: A kinetic-study of the Dimroth rearrangement of the marine sponge purine 1,9-dimethyl-8-oxoadenine and related compounds. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 2591–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Mori, S.; Chikazawa, J.; Kanai, T.; Fujii, T. Purines. LVII. Regioselective alkylation of N6,9-disubstituted 8-oxoadenines: Syntheses of the sea anemone purine caissarone and some positional isomers and analogs. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 41, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Chang, S.J.; Gibala, K.S.; Resendiz, M.J.E. 8-Oxo-7,8-dihydroadenine and 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroadenosine—Chemistry, structure, and function in RNA and their presence in natural products and potential drug derivatives. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 6706–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vik, A.; Hedner, E.; Charnock, C.; Tangen, L.W.; Samuelsen, O.; Larsson, R.; Bohlin, L.; Gundersen, L.L. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic activity of agelasine and agelasimine analogs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 4016–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proszenyak, A.; Charnock, C.; Hedner, E.; Larsson, R.; Bohlin, L.; Gundersen, L.L. Synthesis, antimicrobial and antineoplastic activities for agelasine and agelasimine analogs with a β-cyclocitral derived substituent. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2007, 340, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proszenyak, A.; Braendvang, M.; Charnock, C.; Gundersen, L.-L. The first synthesis of ent-agelasine F. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggen, H.; Gundersen, L.-L. Synthetic studies directed towards agelasine analogs—Synthesis, tautomerism, and alkylation of 2-substituted N-methoxy-9-methyl-9H-purin-6-amines. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 2008, 5099–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggen, H.; Bohlin, L.; Burman, R.; Charnock, C.; Felth, J.; Gorbitz, C.H.; Larsson, R.; Tamm, T.; Gundersen, L.-L. 2-Substituted agelasine analogs: Synthesis and biological activity, and structure and reactivity of synthetic intermediates. Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roggen, H.; Charnock, C.; Burman, R.; Felth, J.; Larsson, R.; Bohlin, L.; Gundersen, L.-L. Antimicrobial and antineoplastic activities of agelasine analogs modified in the purine 2-position. Arch. Pharm. Chem. Life Sci. 2011, 344, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamgordani, E.J.; Paulsen, J.; Gundersen, L.L. Selective N-7 alkylation of 3-methylhypoxanthine; the first synthesis of malonganenone J. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 4926–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, M.; Kawase, N.; Fujii, T.; Aoe, K.; Okamura, K.; Fathiafshar, R.; Allen, T.M. Racemic syntheses of agelasimine-A and agelasimine-B, bicyclic diterpenoids from the marine sponge Agelas mauritiana. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 6101–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, M.; Kawase, N.; Fujii, T. Total syntheses of (+/−)-agelasimine-a, (+/−)-agelasimine-B, and (+/−)-purino-diterpene and the structure of diacetylagelasimine-A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 8250–8257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piers, E.; Breau, M.L.; Han, Y.X.; Plourde, G.L.; Yeh, W.L. Total synthesis of cis-clerodane diterpenoids: (−)-agelasine-A and (+)-(3R,4S,5R,8S,9R,10S)-3,4-epoxyclerod-13-en-15,16-olide. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1995, 26, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, M.; Iizuka, K.; Ishibashi, H.; Fujii, T. Syntheses and absolute configurations of the marine sponge purines (+)-agelasimine-A and (+)-agelasimine-B. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 16977–16986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iio, H.; Asao, K.; Tokoroyama, T. Syntheses of agelasin B and its analogues. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1985, 12, 774–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, F.J.; Villamizar, J.E. Use of (+)-manool in the synthesis of natural products. Part II. Diterpenes and relatives. J. Chem. Res. 2013, 37, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valles, E.; García, P.A.; Miguel del Corral, J.M.; Perez, M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Calhelha, R.C.; San Feliciano, A.; Castro, M.A. Synthesis and cytotoxic evaluation of new terpenylpurines. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 105412–105420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappo, D.; Shimony, S.; Kashman, Y. Synthesis of 9-substituted tetrahydrodiazepinopurines: Studies toward the total synthesis of asmarines. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vik, A.; Gundersen, L.-L. Synthetic studies directed towards asmarines; construction of the tetrahydrodiazepinopurine moiety by ring closing metathesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 1931–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, M.; Tashiro, T. Preparatory study for the synthesis of the marine sponge alkaloids asmarines A–F: Synthesis of their heterocyclic portions. Heterocycles 2002, 57, 1235–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.K.; Iwasaki, K.; Umotoy, J.C.; Wolan, D.W.; Shenvi, R.A. Nitrosopurines en route to potently cytotoxic asmarines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2410–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Li, W.; Ruan, Z.; Yang, R.; Mao, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Wu, J. Concise total synthesis of two marine natural nucleosides: Trachycladines A and B. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 1681–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peitsinis, Z.V.; Melidou, D.A.; Stefanakis, J.G.; Evgenidou, H.; Koumbis, A.E. A versatile total synthesis of trachycladines A and B and their analogues. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 2014, 8160–8166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peitsinis, Z.V.; Mitrakas, A.G.; Nakiou, E.A.; Melidou, D.A.; Kalamida, D.; Kakouratos, C.; Koukourakis, M.I.; Koumbis, A.E. Trachycladines and analogues: Synthesis and evaluation of anticancer activity. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









































| Diterpenoid Skeleton | Agelasines |
|---|---|
| Clerodane type | agelasines A, B, G, H, I, K, L, M, N, P, Q, R, U, V |
| ageloxime B | |
| Halimane type | agelasines C, J, O, S |
| agelasimines A, B | |
| gelasines A, B | |
| Labdane type | agelasines D, T |
| ageloxime D | |
| Monocyclic diterpenoid | agelasines E, F |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García, P.A.; Valles, E.; Díez, D.; Castro, M.-Á. Marine Alkylpurines: A Promising Group of Bioactive Marine Natural Products. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010006
García PA, Valles E, Díez D, Castro M-Á. Marine Alkylpurines: A Promising Group of Bioactive Marine Natural Products. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía, Pablo A., Elena Valles, David Díez, and María-Ángeles Castro. 2018. "Marine Alkylpurines: A Promising Group of Bioactive Marine Natural Products" Marine Drugs 16, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010006
APA StyleGarcía, P. A., Valles, E., Díez, D., & Castro, M.-Á. (2018). Marine Alkylpurines: A Promising Group of Bioactive Marine Natural Products. Marine Drugs, 16(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010006








