Algal Oxylipins Mediate the Resistance of Diatoms against Algicidal Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
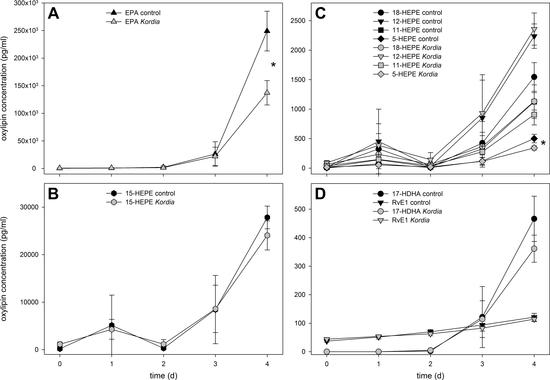
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Algal Cultivation and Quantification
3.2. Bacterial Cultivation and Quantification
3.3. Co-Cultivation Experiment
3.4. Wound Activation and Oxylipin Profiling
3.5. Extracellular Oxylipin Profiling
3.6. Determination of Concentration-Dependent 15-HEPE Activity Against K. algicida
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hutchinson, G.E. The paradox of the plankton. Am. Nat. 1961, 95, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianora, A.; Bentley, M.G.; Caldwell, G.S.; Casotti, R.; Cembella, A.D.; Engström-Öst, J.; Halsband, C.; Sonnenschein, E.; Legrand, C.; Llewellyn, C.A.; et al. The relevance of marine chemical ecology to plankton and ecosystem function: An emerging field. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1625–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohnert, G.; Steinke, M.; Tollrian, R. Chemical cues, defence metabolites and the shaping of pelagic interspecific interactions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selander, E.; Kubanek, J.; Hamberg, M.; Andersson, M.X.; Cervin, G.; Pavia, H. Predator lipids induce paralytic shellfish toxins in bloom-forming algae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 6395–6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenwasser, S.; Mausz, M.A.; Schatz, D.; Sheyn, U.; Malitsky, S.; Aharoni, A.; Weinstock, E.; Tzfadia, O.; Ben-Dor, S.; Feldmesser, E.; et al. Rewiring host lipid metabolism by large viruses determines the fate of Emiliania huxleyi, a bloom-forming alga in the ocean. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 2689–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohnert, G.; Boland, W. The oxylipin chemistry of attraction and defense in brown algae and diatoms. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2002, 19, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Donk, E.; Ianora, A.; Vos, M. Induced defences in marine and freshwater phytoplankton: A review. Hydrobiologia 2011, 668, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohnert, G. Phospholipase A(2) activity triggers the wound-activated chemical defense in the diatom Thalassiosira rotula. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippolito, G.; Tucci, S.; Cutignano, A.; Romano, G.; Cimino, G.; Miralto, A.; Fontana, A. The role of complex lipids in the synthesis of bioactive aldehydes of the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1686, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rettner, J.; Werner, M.; Meyer, N.; Werz, O.; Pohnert, G. Survey of the C20 and C22 oxylipin family in marine diatoms. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 828–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippolito, G.; Lamari, N.; Montresor, M.; Romano, G.; Cutignano, A.; Gerecht, A.; Cimino, G.; Fontana, A. 15S-lipoxygenase metabolism in the marine diatom Pseudo-nitzschia delicatissima. New Phytol. 2009, 183, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanjappa, D.; d’Ippolito, G.; Gallo, C.; Zingone, A.; Fontana, A. Oxylipin diversity in the diatom family Leptocylindraceae reveals DHA derivatives in marine diatoms. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 368–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tammilehto, A.; Nielsen, T.G.; Krock, B.; Moller, E.F.; Lundholm, N. Induction of domoic acid production in the toxic diatom Pseudo-nitzschia seriata by Calanoid copepods. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 159, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidle, K.D.; Vardi, A. A chemical arms race at sea mediates algal host-virus interactions. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, N.; Bigalke, A.; Kaulfuss, A.; Pohnert, G. Strategies and ecological roles of algicidal bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 880–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, S.A.; Parker, M.S.; Armbrust, E.V. Interactions between diatoms and bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Yi, H.; Chun, J.; Bae, K.S.; Ahn, T.Y.; Kim, S.J. Kordia algicida gen. Nov., sp nov., an algicidal bacterium isolated from red tide. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, C.; Pohnert, G.; Uversky, V.N. Induction of protease release of the resistant diatom Chaetoceros didymus in response to lytic enzymes from an algicidal bacterium. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, C.; Pohnert, G. Interactions of the algicidal bacterium Kordia algicida with diatoms: Regulated protease excretion for specific algal lysis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.R.; Amin, S.A.; Raina, J.B.; Stocker, R. Zooming in on the phycosphere: The ecological interface for phytoplankton-bacteria relationships. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeggstrom, J.Z.; Funk, C.D. Lipoxygenase and leukotriene pathways: Biochemistry, biology, and roles in disease. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5866–5898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, H. Biosynthesis, metabolization and biological importance of the primary 15-lipoxygenase metabolites 15-hydro(pero)xy-5Z,8Z,11Z,13E-eicosatetraenoic acid and 13-hydro(pero)xy-9Z,11E-octadecadienoic acid. Prog. Lipid Res. 1996, 35, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidoudez, C.; Pohnert, G. Growth phase specific release of polyunsaturated aldehydes by the diatom Skeletonema marinoi. J. Plankton Res. 2008, 30, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ippolito, G.; Romano, G.; Caruso, T.; Spinella, A.; Cimino, G.; Fontana, A. Production of octadienal in the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 885–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ippolito, G.; Romano, G.; Iadicicco, O.; Miralto, A.; Ianora, A.; Cimino, G.; Fontana, A. New birth-control aldehydes from the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum: Characterization and biogenesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 6133–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Zaman, S.; Raha, A.K. Phytoplankton cell volume and diversity in Indian sundarbans. Indian J. Geo-Mar. Sci. 2014, 43, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Olenina, I.; Hajdu, S.; Edler, L.; Andersson, A.; Wasmund, N.; Busch, S.; Göbel, J.; Gromisz, S.; Huseby, S.; Huttunen, M.; et al. Biovolumes and Size-Classes of Phytoplankton in the Baltic Sea; Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2006; p. 106. [Google Scholar]
- Vidoudez, C.; Casotti, R.; Bastianini, M.; Pohnert, G. Quantification of dissolved and particulate polyunsaturated aldehydes in the adriatic sea. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reymond, P.; Weber, H.; Damond, M.; Farmer, E.E. Differential gene expression in response to mechanical wounding and insect feeding in arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidoudez, C.; Pohnert, G. Comparative metabolomics of the diatom Skeletonema marinoi in different growth phases. Metabolomics 2012, 8, 654–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meyer, N.; Rettner, J.; Werner, M.; Werz, O.; Pohnert, G. Algal Oxylipins Mediate the Resistance of Diatoms against Algicidal Bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16120486
Meyer N, Rettner J, Werner M, Werz O, Pohnert G. Algal Oxylipins Mediate the Resistance of Diatoms against Algicidal Bacteria. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(12):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16120486
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeyer, Nils, Johanna Rettner, Markus Werner, Oliver Werz, and Georg Pohnert. 2018. "Algal Oxylipins Mediate the Resistance of Diatoms against Algicidal Bacteria" Marine Drugs 16, no. 12: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16120486
APA StyleMeyer, N., Rettner, J., Werner, M., Werz, O., & Pohnert, G. (2018). Algal Oxylipins Mediate the Resistance of Diatoms against Algicidal Bacteria. Marine Drugs, 16(12), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16120486