Abstract
Extremophilic fungi have been found to develop unique defences to survive extremes of pressure, temperature, salinity, desiccation, and pH, leading to the biosynthesis of novel natural products with diverse biological activities. The present review focuses on new extremophilic fungal natural products published from 2005 to 2017, highlighting the chemical structures and their biological potential.
1. Introduction
The term “extremophile” was first proposed by MacElroy in 1974 to describe a broad group of organisms which lived optimally under extreme conditions [1], and the taxonomic range of them has been expanded from prokaryotes to all three domains—Eucarya, Bacteria, and Archaea [2]. Extremophiles are classified into seven categories according to different extreme habitats. Piezophiles reside under high hydrostatic pressure, which have been isolated from the deep-sea sediments (>3000 m depth) and the guts of bottom-dwelling animals [3,4,5]. Organisms whose optimal growth temperature ranges from 50 to 80 °C or exceeds 80 °C are called thermophiles or hyperthermophiles respectively, which have been mainly isolated from hot springs, deep-sea hydrothermal vents, and decaying plant matter [6]. Psychrophiles living in the other extreme thermal habitat have been obtained from the Antarctic, the Arctic, and glacial regions [7]. Halophiles are defined as organisms requiring >3% NaCl for growth [6]. Xerophiles thrive under the desiccated and have been discovered in ashes and deserts [8]. Acidophiles or alkaliphiles show optimal growth at pH values <4 and >9 respectively [6]. Organisms from these extreme habitats require special survival strategies for growing and reproducing, and the adaptation to such conditions requires the modification of gene regulation and metabolic pathways [9,10,11,12,13], thus extremophiles seem to be good potential candidates for novel natural products.
Several reviews discussing natural products from special environments have been published over the last decade, and the topics include natural products from cold water [14,15], polar regions [16,17], and deep sea [18,19]. In 2009 Wilson and Brimble reviewed the studies on the structure of molecules isolated from the extremes of life [6], while those compounds were mainly isolated from bacteria and actinomycetes. Few reviews focused on the secondary metabolites from extremophilic fungi.
This review focuses on the source, chemistry, and biology of novel natural products which were derived from extremophilic fungi. These fungal products are classified according to extremophile classifications, and when a fungal strain falls under multiple classifications, it is grouped under the dominant environmental factor. In addition, the table (Table 1) including the chemical structure types, biological activities and references of all novel natural products will help readers to better understand their underlying potential as drug candidates. It is worth noting that in compiling this review all isolated strains were selected strictly according to the above categories and that strains which do not meet the standards were not cited. For example, one strain was isolated from the deep sea but its underwater depth was less than 3000 m, which did not meet the criteria of piezophiles. Therefore, we did not include it in this review.

Table 1.
Novel natural products isolated from extremophilic fungi.
2. Piezophilic Fungi
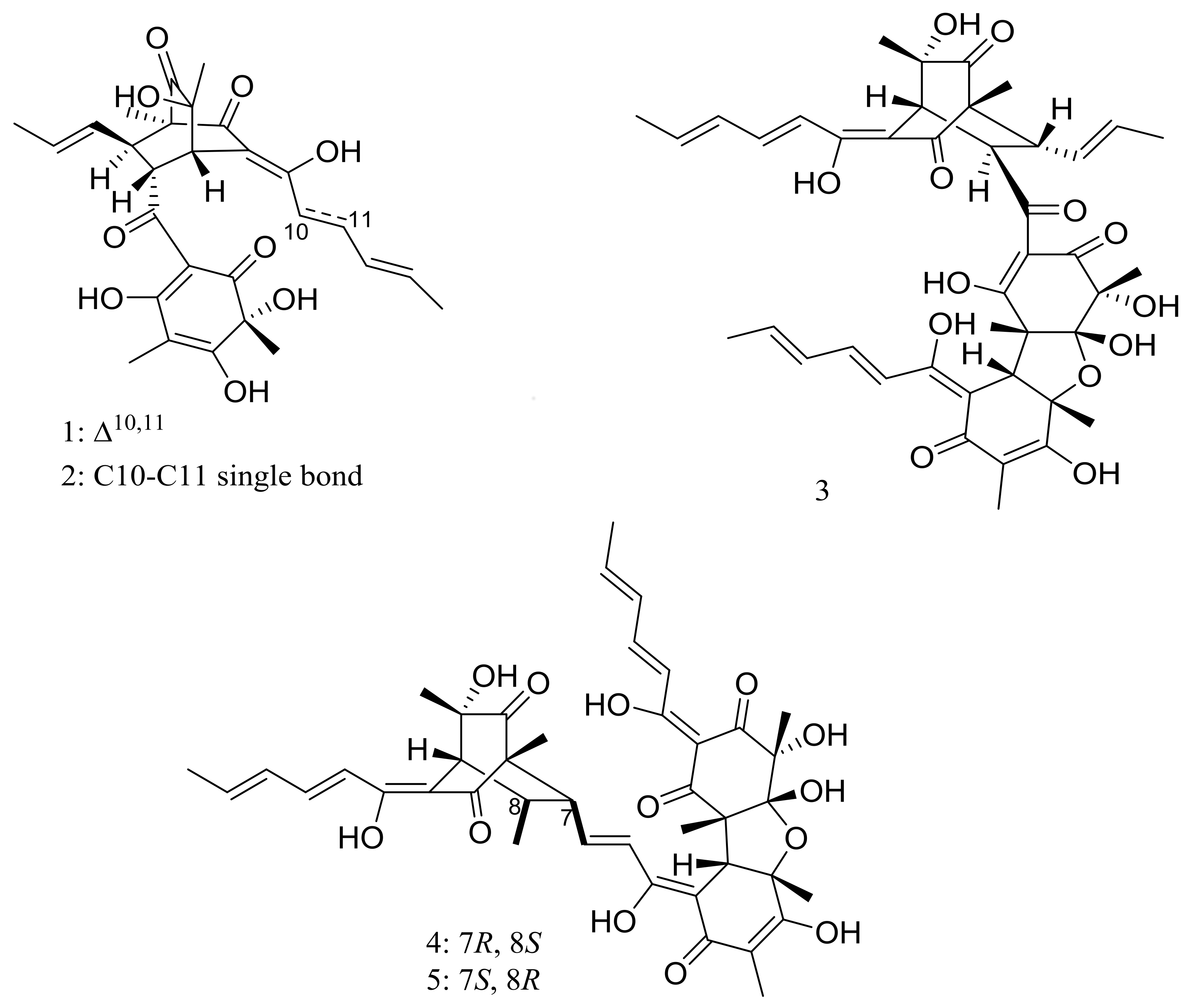
Phialocephala sp. FL30r obtained from an underwater sample (depth 5059 m, the east Pacific) was a powerful producer of diverse sorbicillin-type compounds. Two new bisorbicillinoids, oxosorbiquinol (1) and dihydrooxosorbiquinol (2) (Figure 1) [20], four new sorbicillin trimers, trisorbicillinones A–D (3–6) (Figure 1) [21,22], one new sorbicillin dimer, dihydrotrichodermolide (7) (Figure 1), one new sorbicillin monomer, dihydrodemethylsorbicillin (8) (Figure 1), and one novel benzofuran derivative, phialofurone (9) (Figure 1) [23] have been described from this fungal strain since 2007. The cytotoxic activity (IC50) of compounds 1 and 2 against several cancer cell lines (P388, HL60, BEL7402, and K562) ranged from 8.9 to 68.2 μM. Compound 3 showed cytotoxic activity against P388 and HL60 cells with IC50 values of 9.10 and 3.14 μM respectively, while compounds 4–7 exhibited weaker activities against P388 and K562 cells. Compounds 8 and 9 exhibited potent activities against P388 cells with IC50 values of 0.1 and 0.2 μM respectively.
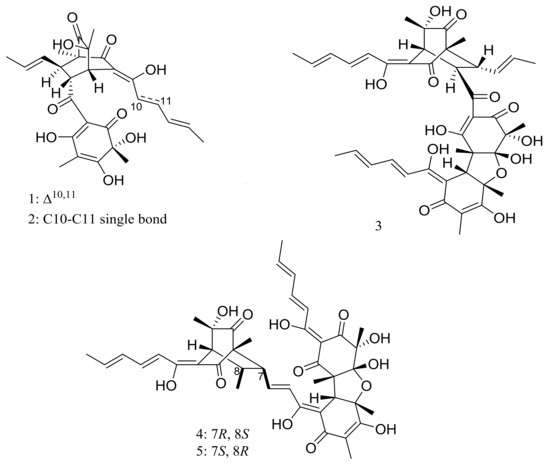
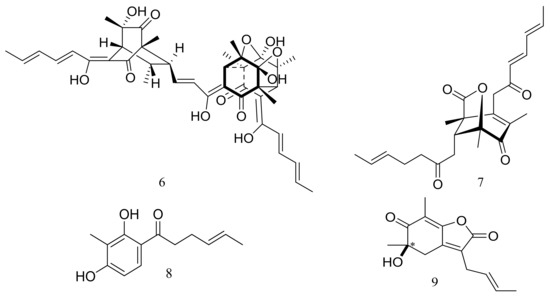
Figure 1.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 1–9). * Absolute configuration is not determined.
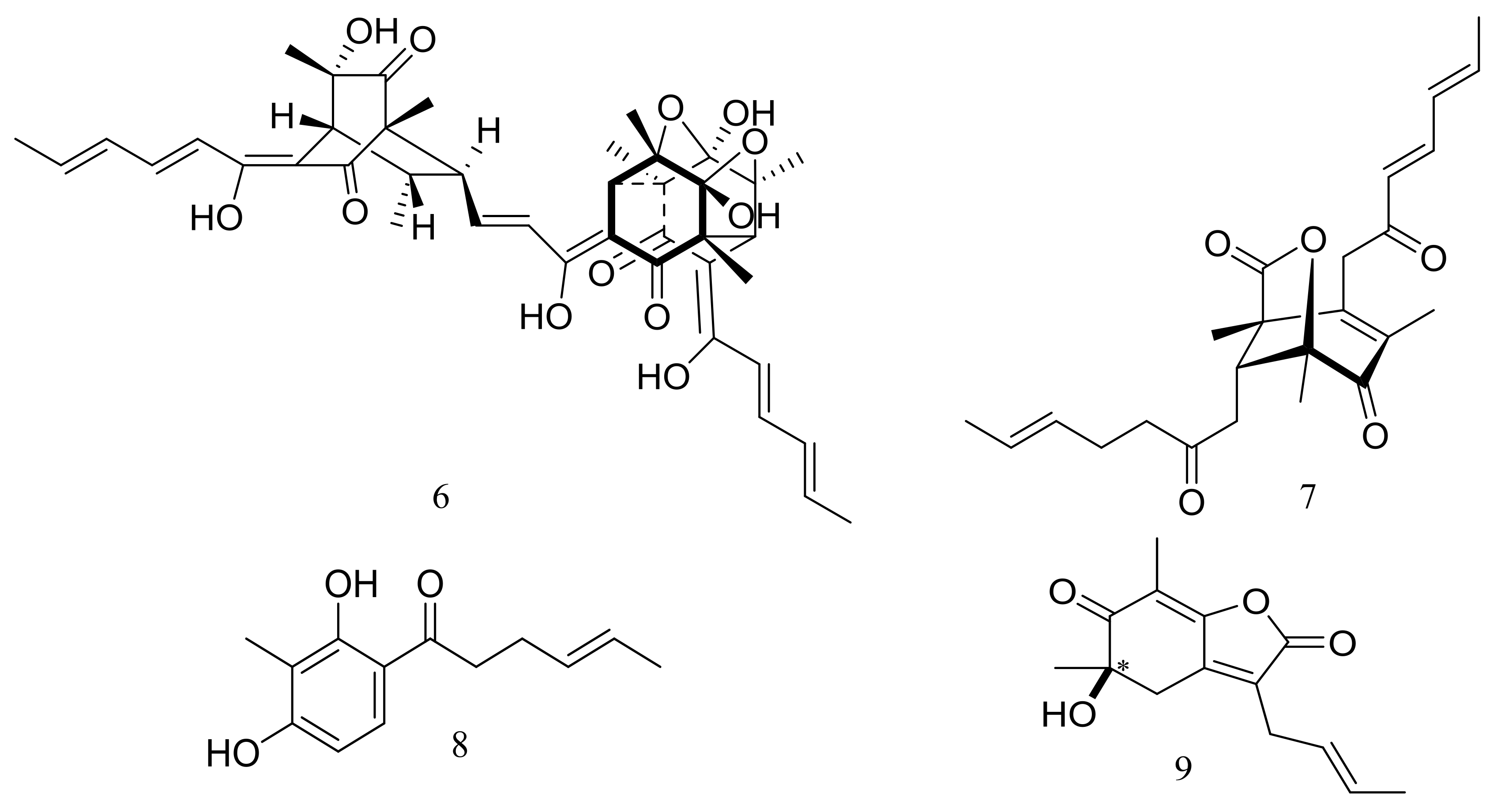
Brevicompanines D–H (10–14) (Figure 2) are five new diketopiperazine alkaloids produced by the deep-sea sediment-derived fungus Penicillium sp. F1 (depth 5080 m). Compounds were assessed for their anti-inflammatory activities on LPS-challenged BV2 cells, 11 and 14 displaying IC50 values of 27 and 45 μg/mL respectively, other compounds being found inactive. According to the structure-bioactivity relationship, authors supposed that substitutions at the N-6 position may contribute to the anti-inflammatory activity [24].
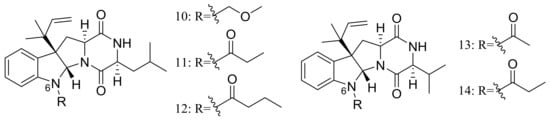
Figure 2.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 10–14).
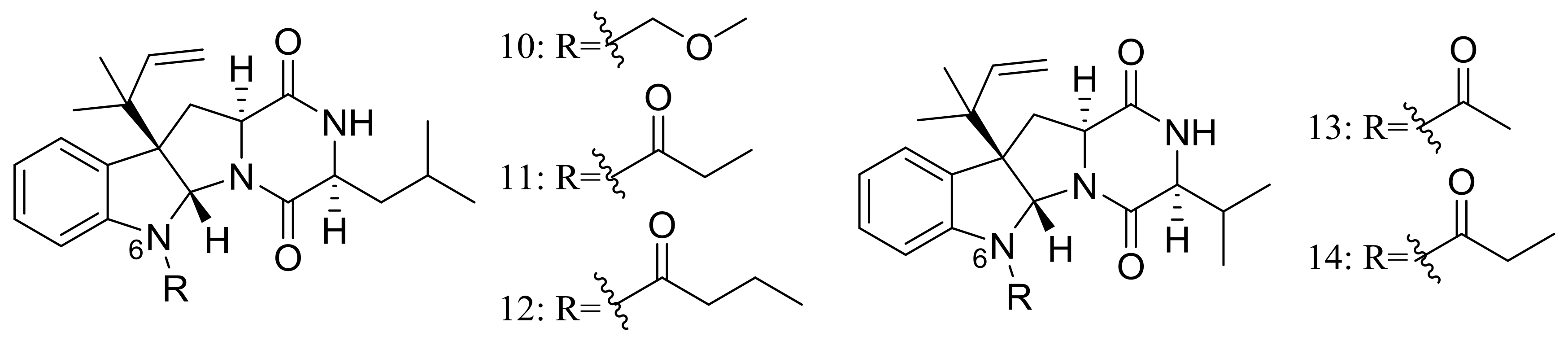
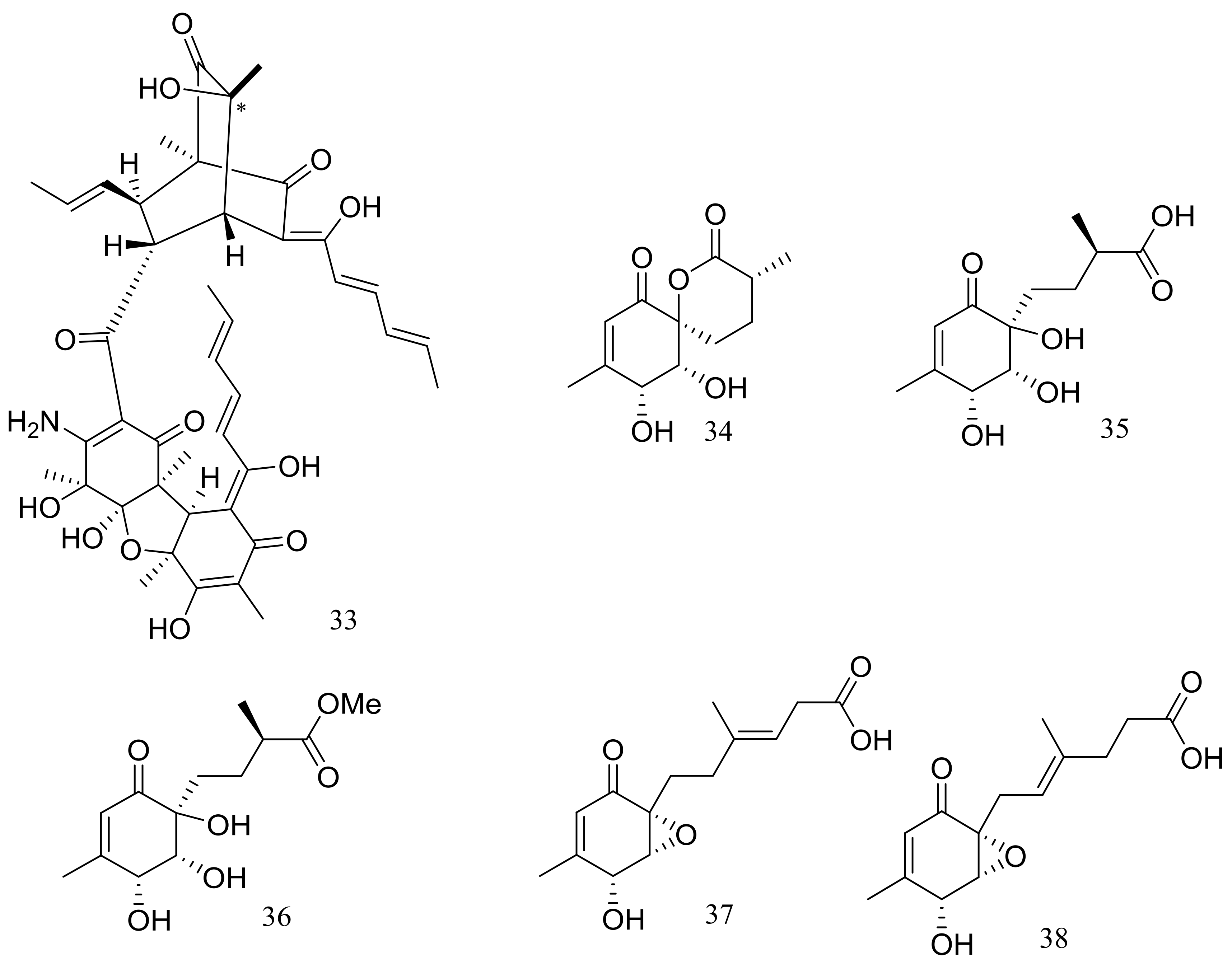
In 2009 and 2010 several new alkaloids named meleagrins B–E (15–18) and roquefortines F–I (19–22) (Figure 3) , along with six new diterpenes named conidiogenones B–G (23–28) (Figure 3) were described from the deep-sea sediment-derived Penicillium sp. F23-2 (depth 5080 m) [25,26]. Compound 15 showed moderate cytotoxic activity against HL60, MOLT4, A549, and BEL7402 cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 1.8 to 6.7 μM, while compounds 17 and 18 showed weaker activities against A549 cell line with IC50 values of 32.2 and 55.9 μM respectively. Further elucidation of the potential cytotoxic mechanism by flow cytometric analysis indicated that 15 could induce HL60 cells apoptosis at 5 and 10 μM. In addition, compound 24 showed potent selective cytotoxic activity against HL60 and BEL7420 cells with IC50 values of 0.038 and 0.97 μM respectively. This study represented the first report on the antitumor activity of the conidiogenone diterpenes. In 2013 five new nitrogen-containing sorbicillinoids, sorbicillamines A–E (29–33) (Figure 3) were obtained from the PYG liquid culture of this fungal strain. Despite of their interesting structures no cytotoxic activity (HeLa, BEL7402, HEK-293, and HCT116 cell lines) was detected for these metabolites [27]. Guided by the OSMAC approach, in 2015 the same Penicillium species afforded another five new ambuic acid analogues named penicyclones A–E (34–38) (Figure 3) , which exhibited antibacterial activities against Staphylococcus aureus with MIC values ranging from 0.3 to 1.0 μg/mL [28].
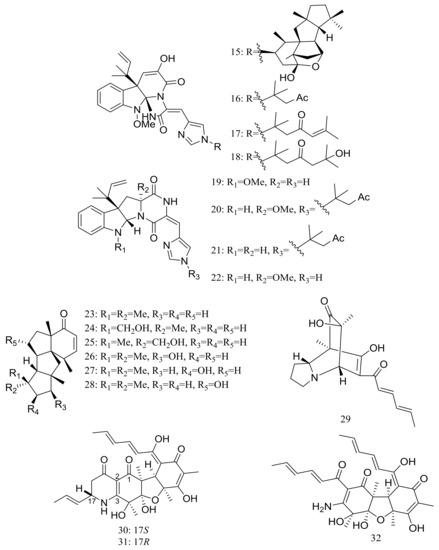

Figure 3.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 15–38). * Absolute configuration is not determined.
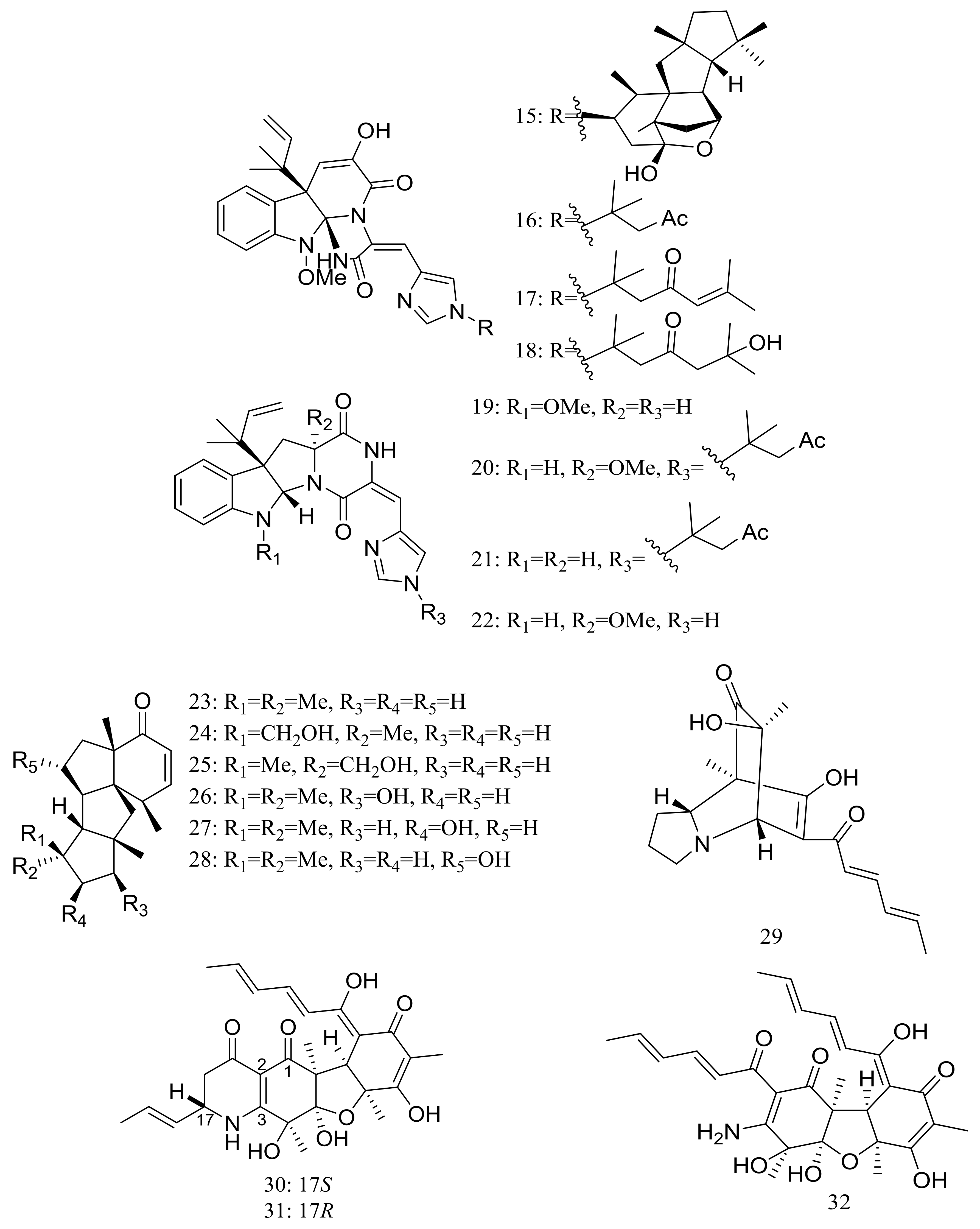
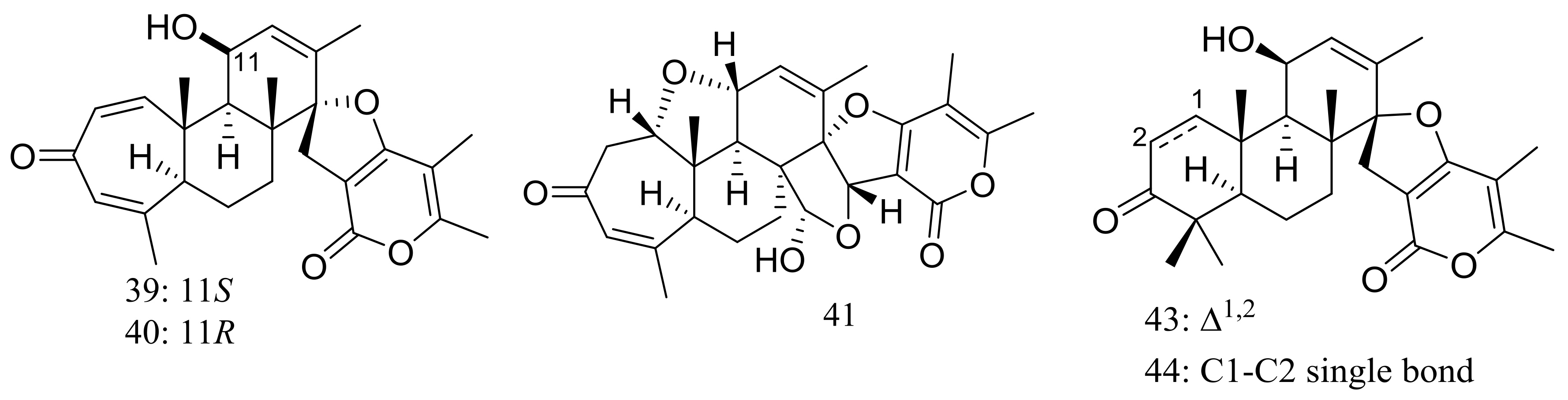
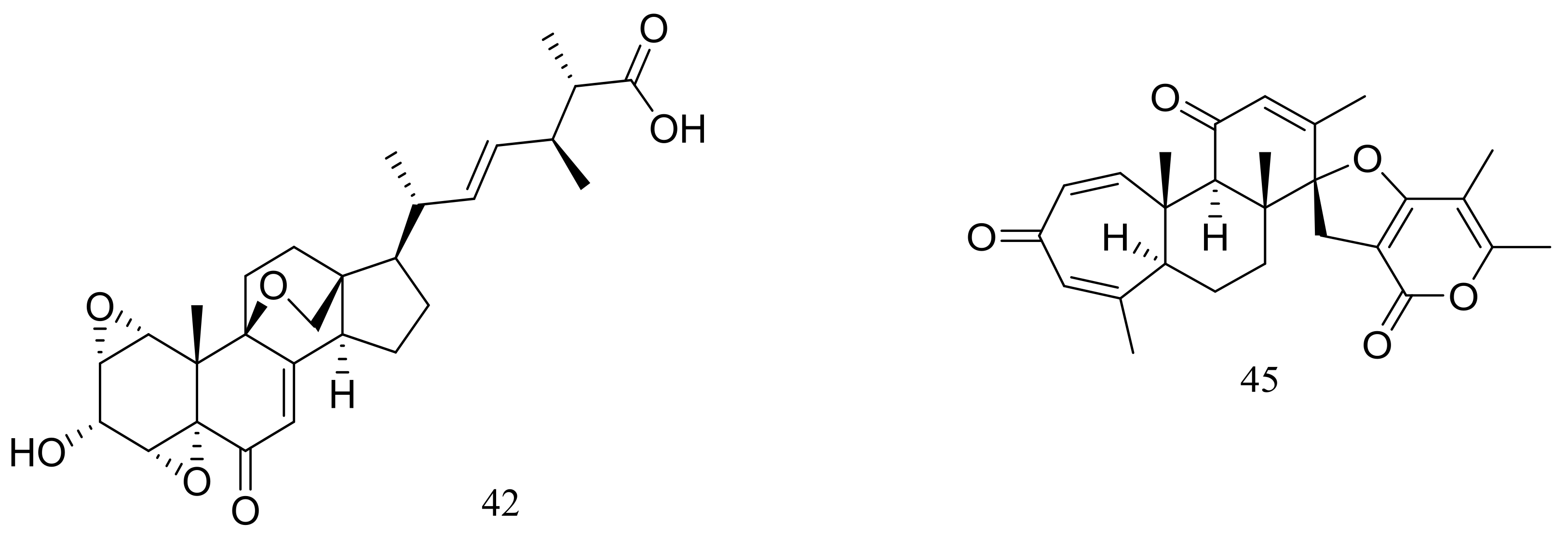
Breviones F–H (39–41) (Figure 4) were produced by the deep-sea sediment-derived Penicillium sp. (MCCC 3A00005) (depth 5115 m, the east Pacific). These three new breviane spiroditerpenoids exhibited cytotoxic activity against HeLa cells with inhibitory rates of 25.2%, 44.9%, and 25.3% at 10 μg/mL, respectively. Effects on HIV-1 inhibition in C8166 cells were tested and an EC50 value for compound 39 was 14.7 μM [29]. From the same Penicillium strain one new polyoxygenated sterol named sterolic acid (42) and three new breviane spiroditerpenoids namend breviones I–K (43–45) (Figure 4) were published later. Compound 43 exhibited cytotoxic activity against MCF7 and A549 cells with IC50 values of 7.44 and 32.5 μM respectively [30].
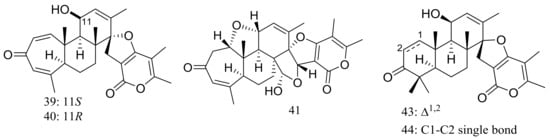

Figure 4.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 39–45).
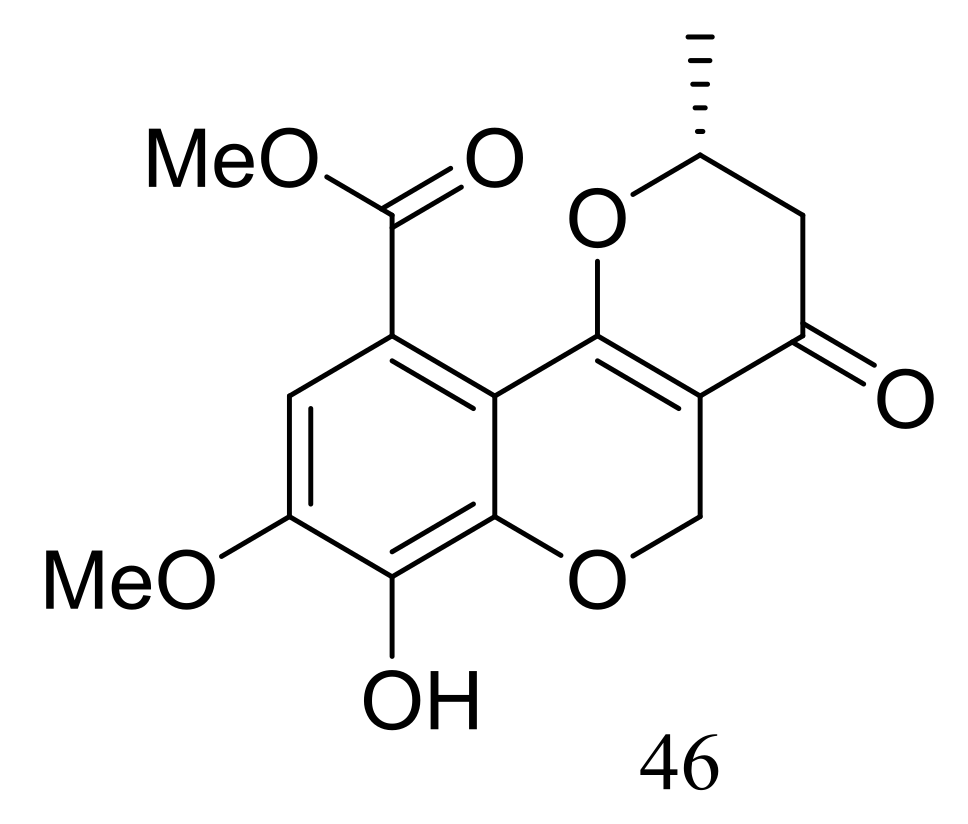
Ascomycotin A (46) (Figure 5) was isolated from the deep-sea sediment-derived Ascomycota sp. Ind19F07 (depth 3614 m, the Indian Ocean) grown on the rice solid media. No antimicrobial activity (Acinetobacter baumannii (ATCC 19606), Klebsiella pneumoniae (ATCC 13883), Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922), Staphyloccocus aureus (ATCC 29213) and Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC 29212)) was detected [31].
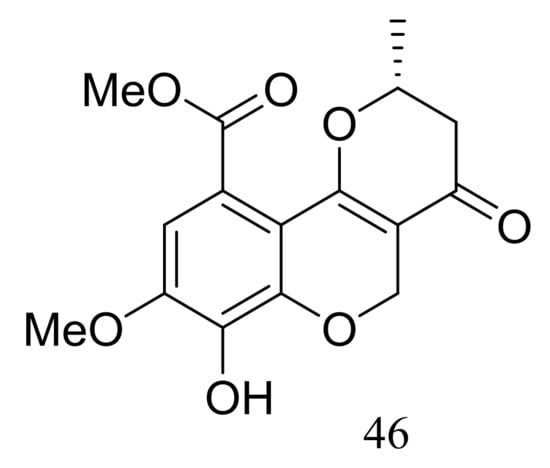
Figure 5.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compound 46).
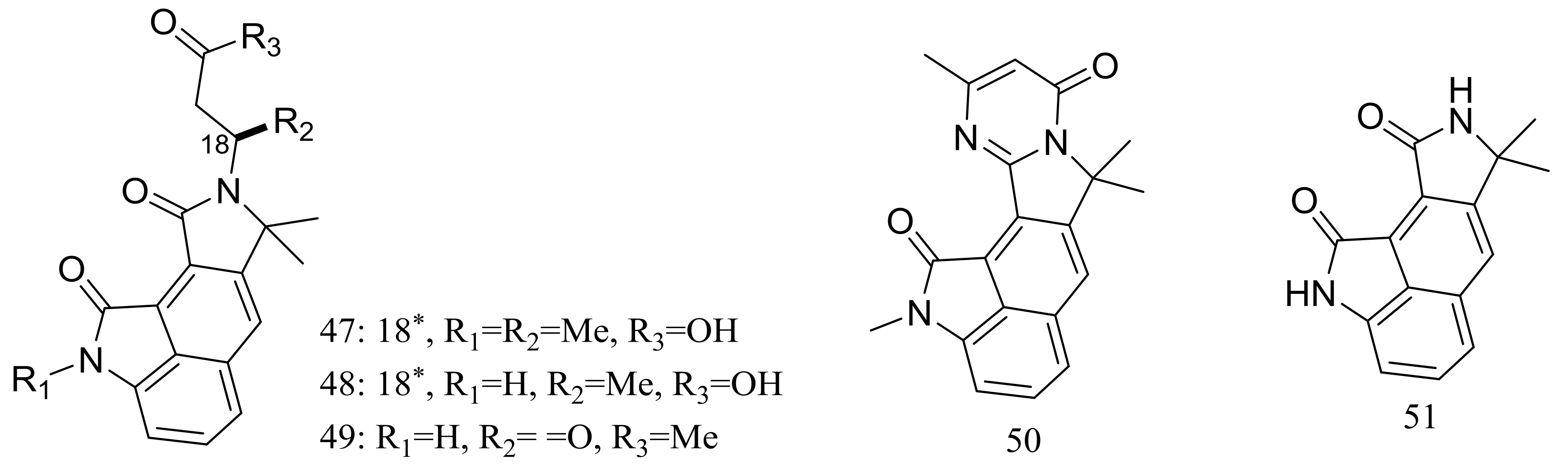
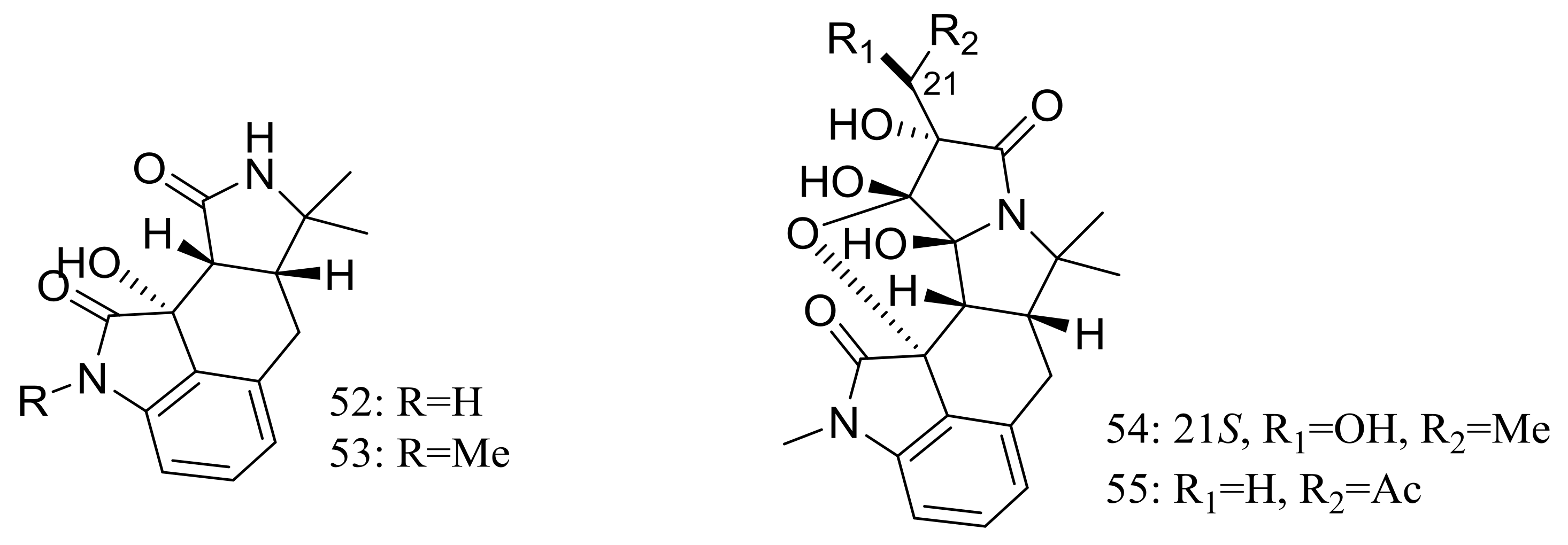
Cyclopiamides B–J (47–55) (Figure 6), nine new cyclopiamide analogues belonging to oxindole alkaloids were produced by the deep-sea-derived fungal strain Penicillium commune DFFSCS026 (depth 3563 m, the South China Sea). Toxic activities against brine shrimp of all nine compounds were almost the same with IC50 values ranging from 14.1 to 38.5 μg/mL, which suggested that structural modifications at the indole system might not significantly affect their toxic activities. No cytotoxic (HepG-2 and HeLa cell lines) or antiviral (N1H1) activities were detected [32].
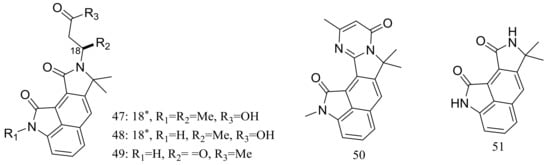
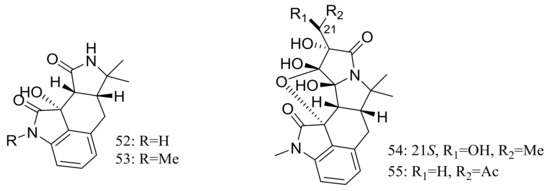
Figure 6.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 47–55). * Absolute configuration is not determined.
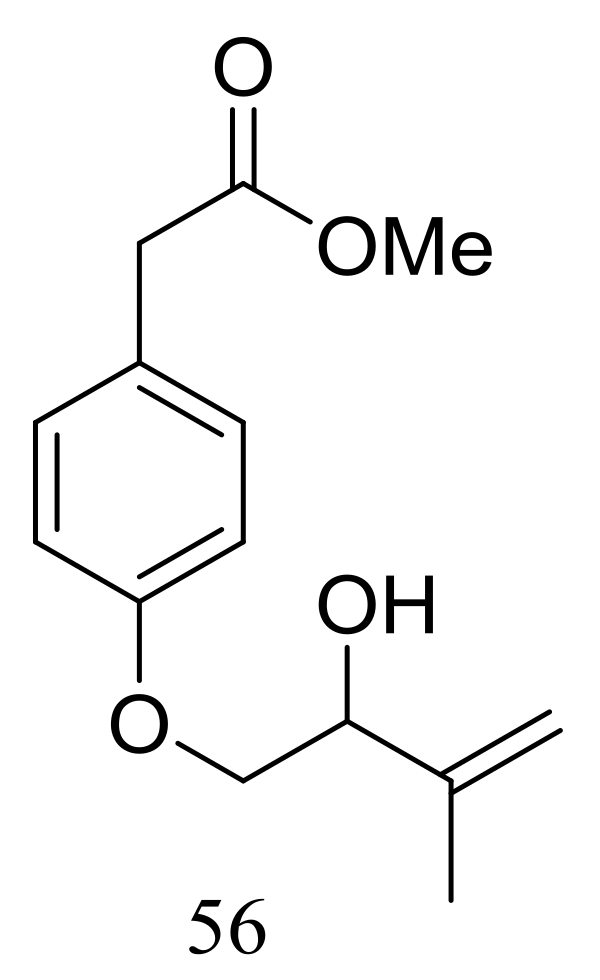
A new hydroxyphenylacetic acid named westerdijkin A (56) (Figure 7) was isolated from a deep-sea sediment-derived fungal strain Aspergillus westerdijkiae SCSIO 05233 (depth 4593 m, the South China Sea). Neither antimicrobial (Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus pumilus, Staphylococcus aureus, and Candida albicans), anticancer (K562 and HL-60 cell lines), nor antifouling (Balanus amphitrite) activities were detected [33].
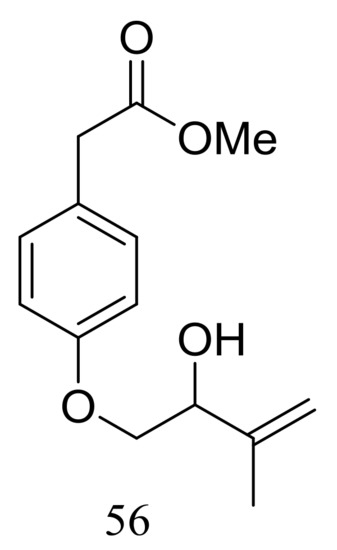
Figure 7.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compound 56).
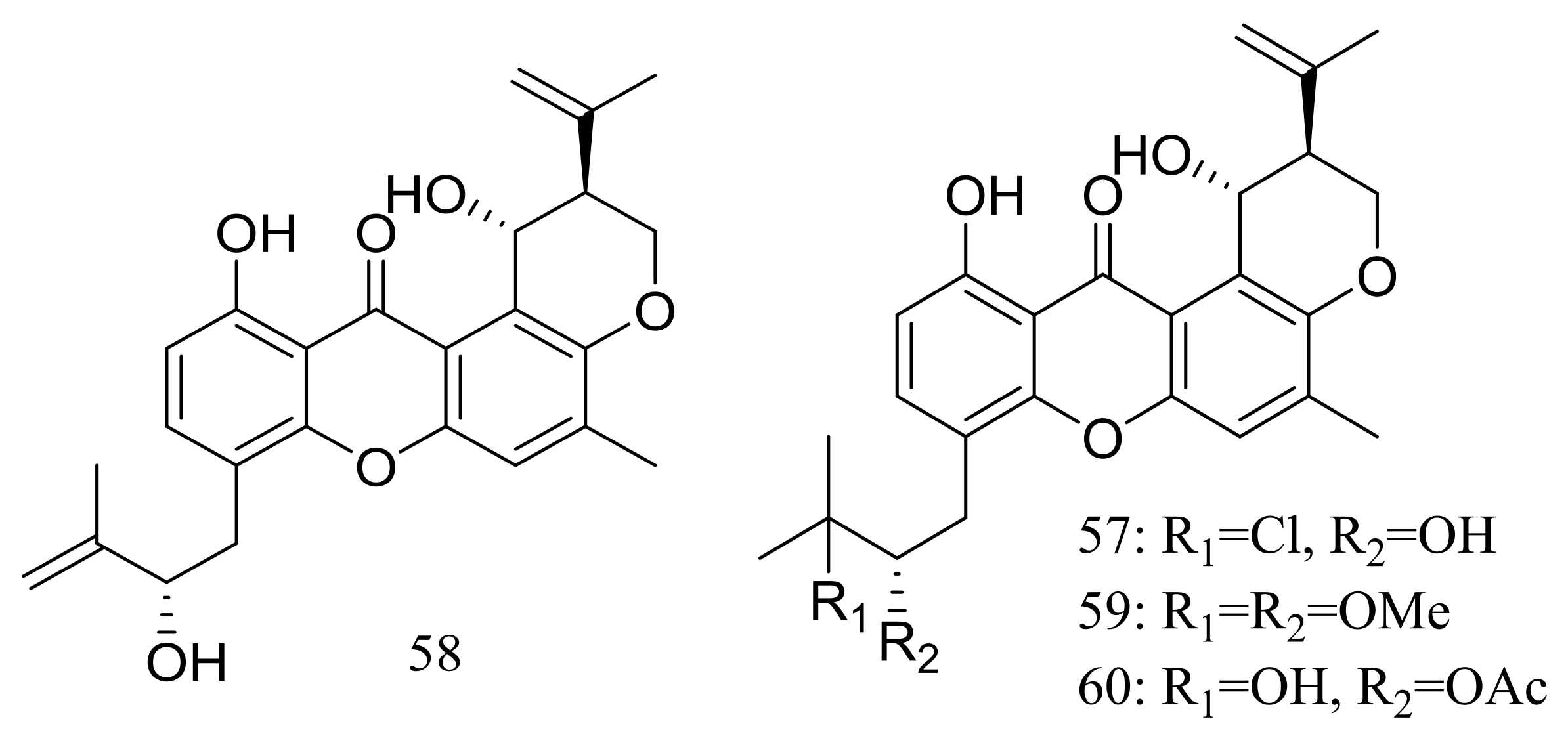
Four new prenylxanthones, emerixanthones A–D (57–60) (Figure 8) were isolated from Emericella sp. SCSIO 05240 (depth 3258 m, the South China Sea). Compounds 57 and 59 exhibited weak antibacterial activities against six pathogens (Escherichia coli (ATCC 29922), Klebsiella pneumoniae (ATCC 13883), Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 29213), Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC 29212), Acinetobacter baumannii (ATCC 19606), and Aeromonas hydrophila (ATCC 7966), while 60 displayed mild antifungal activity against six agricultural pathogens (Fusarium sp., Penicillium sp., Aspergillus niger, Rhizoctonia solani, Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. niveum, and Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cucumeris). The biosynthetic pathway of these metabolites was proposed [34].

Figure 8.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 57–60).
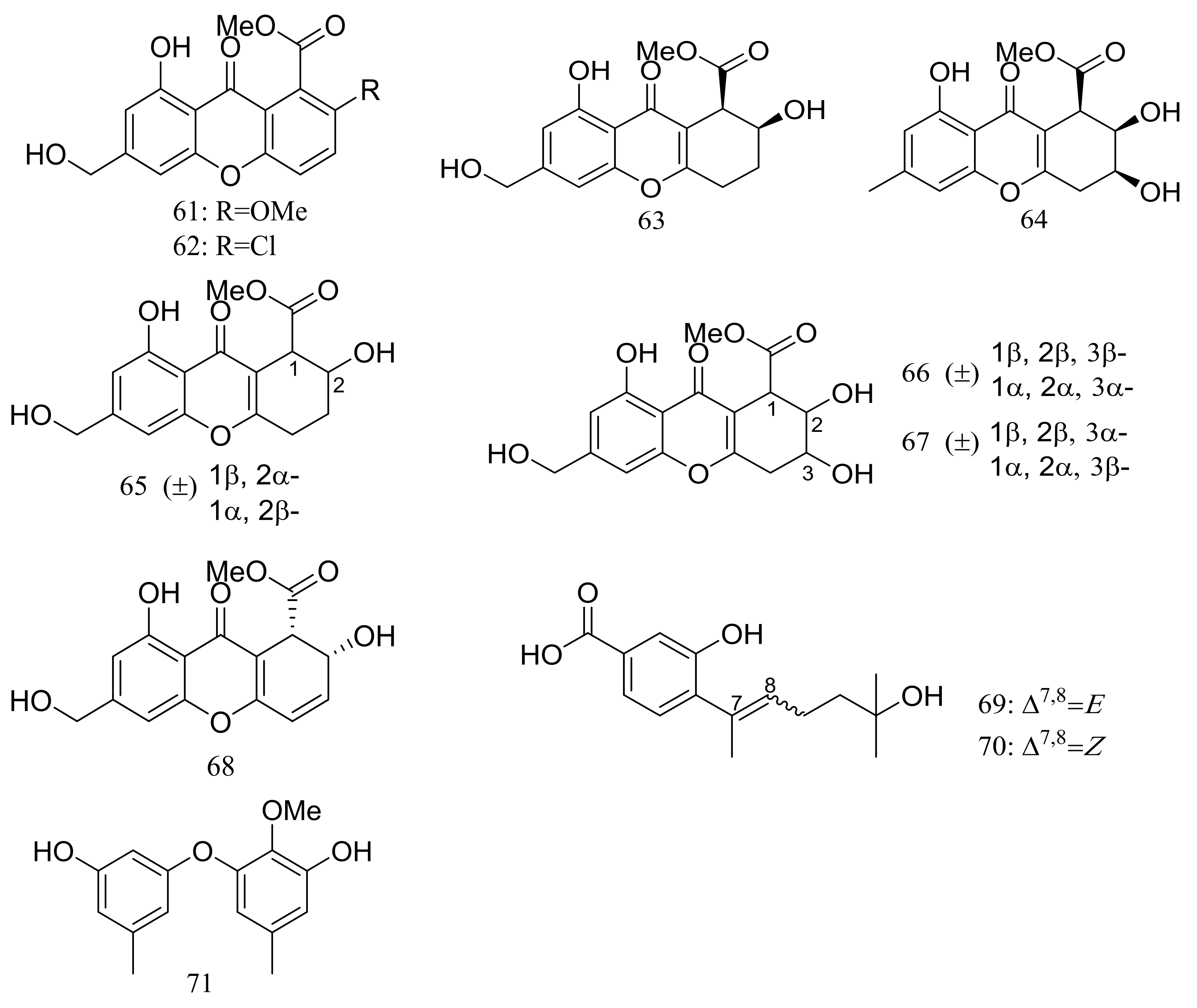
Engyodontiumones A–J (61–70) and 2-methoxyl cordyol C (71) (Figure 9) have been described as metabolites of Engyodontium album DFFSCS021 taken from a 3739 m deep-sea sediment sample in the South China Sea. Compound 68 exhibited cytotoxic activity against U937 cells (IC50 4.9 μM) and antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis at a concentration of 25 μg/disc [35].
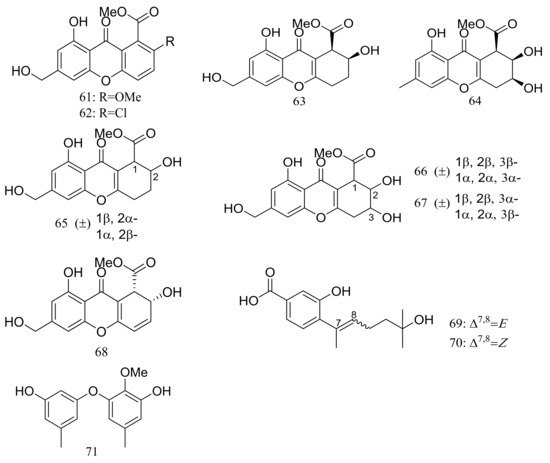
Figure 9.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 61–71).
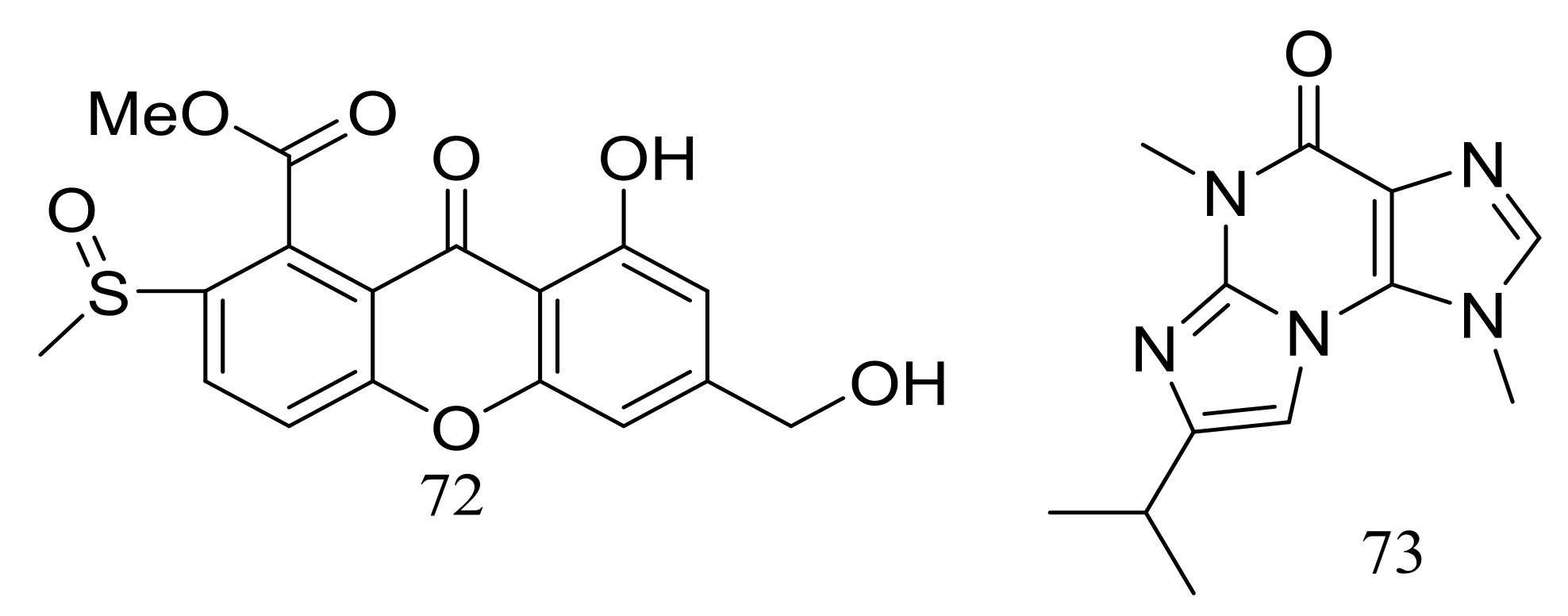
The solid fermentation of the deep-sea fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO Ind09F01 (depth 4530 m, the Indian Ocean) yielded a new xanthone named sydoxanthone C (72) and a new alkaloid named acremolin B (73) (Figure 10). Two compounds exhibited no cytotoxic (Hela, DU145, and U937 cell lines) or COX-2 inhibitory activities [36].
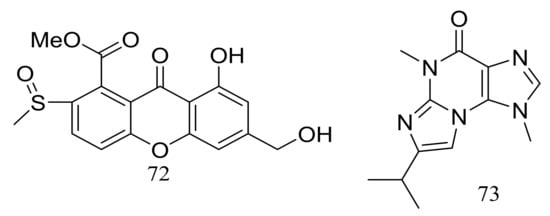
Figure 10.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 72–73).
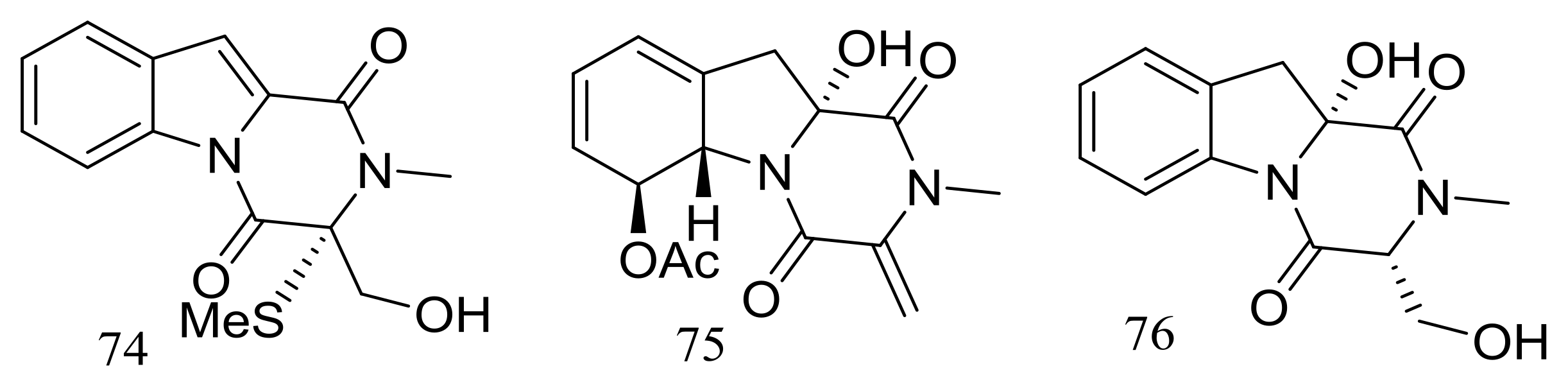
Dichotocejpins A–C (74–76) (Figure 11) are three new diketopiperazines produced by Dichotomomyces cejpii FS110 (depth 3941 m). The inhibitory activity of compound 74 (IC50 138 μM) against α-glucosidase was much stronger than that of the positive control acarbose (IC50 463 μM) [37].
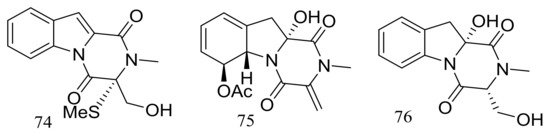
Figure 11.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 74–76).
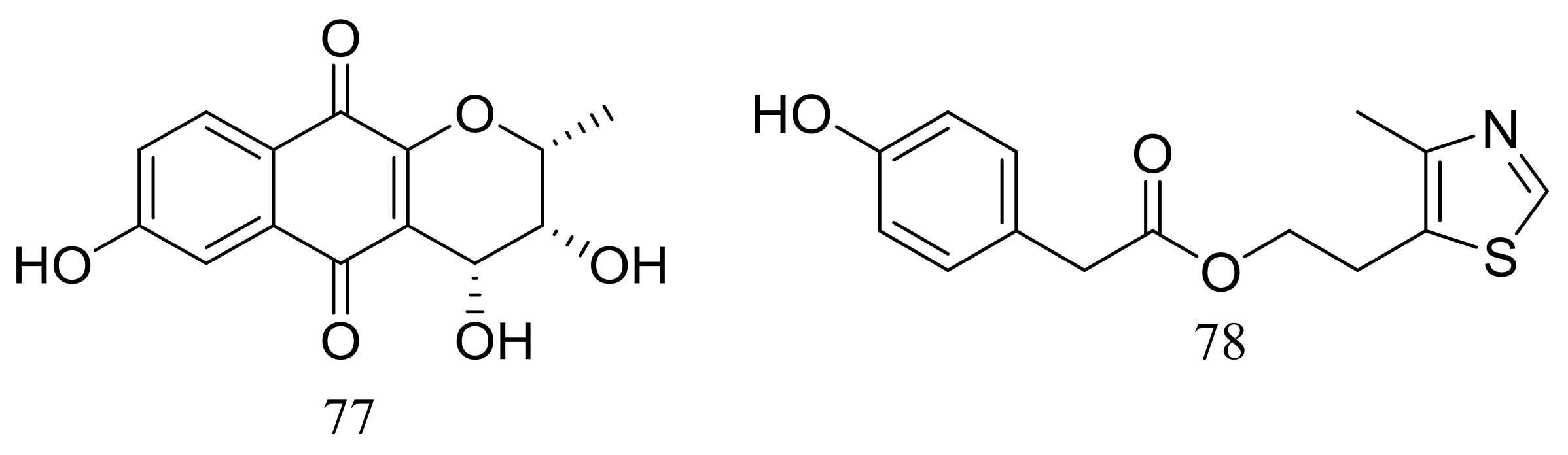
Acaromycin A (77) (Figure 12), a new naphtha-[2,3-b] pyrandione analogue and acaromyester A (78) (Figure 12), a new thiazole analogue were isolated from Acaromyces ingoldii FS121 (depth 3415 m, the South China Sea). Pronounced cytotoxic activities against four cancer cell lines (MCF-7, NCI-H460, SF-268, and HepG-2) were described for compound 77 with IC50 values less than 10 μM [38].
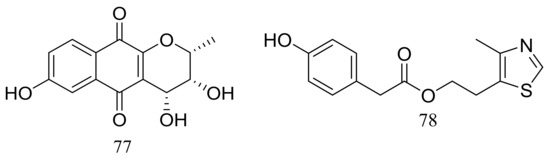
Figure 12.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 77–78).
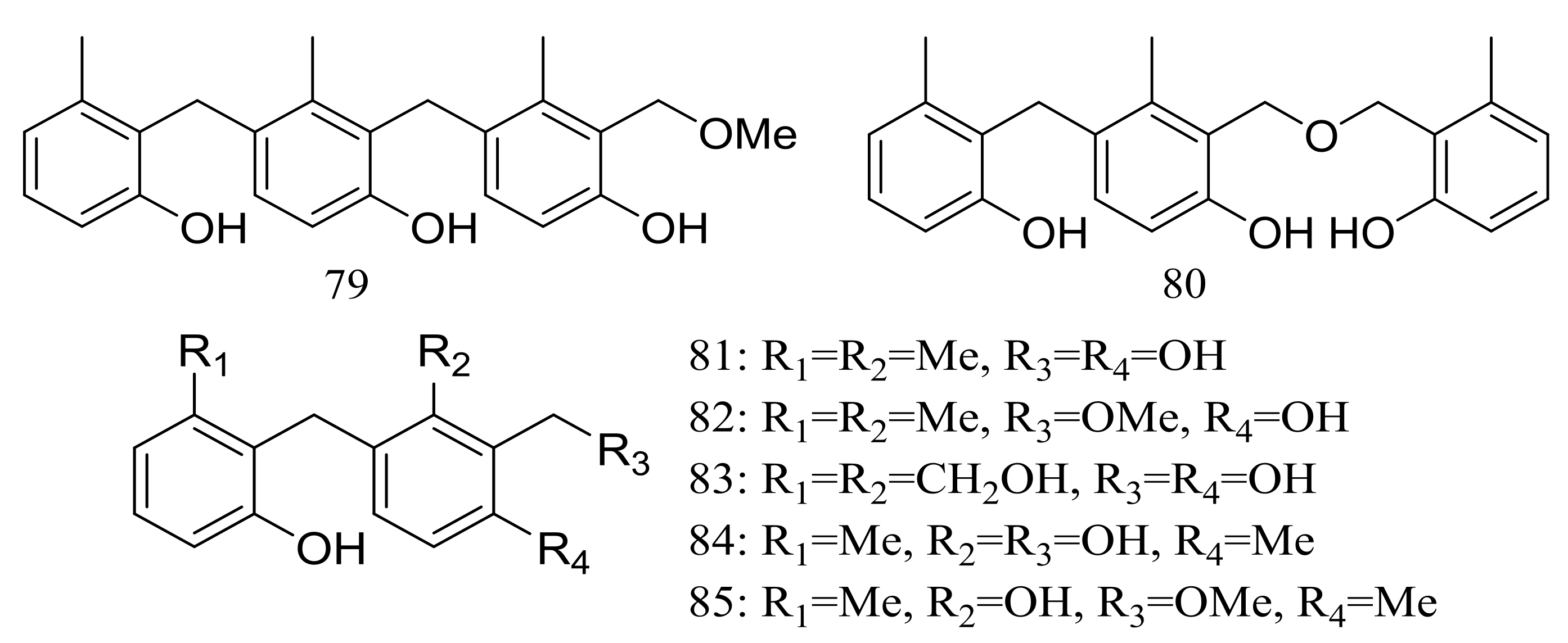
The trimeric peniphenylanes A–B (79–80) and dimeric peniphenylanes C–G (81–85) (Figure 13) are seven new 6-methylsaligenin derivatives obtained from Penicillium fellutanum HDN14-323 (depth 5752 m, the Indian Ocean). When tested for cytotoxic activity compound 82 proved to be the best active to HeLa cells (IC50 9.3 μM) [39].
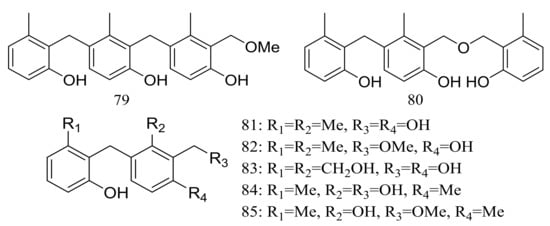
Figure 13.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 79–85).
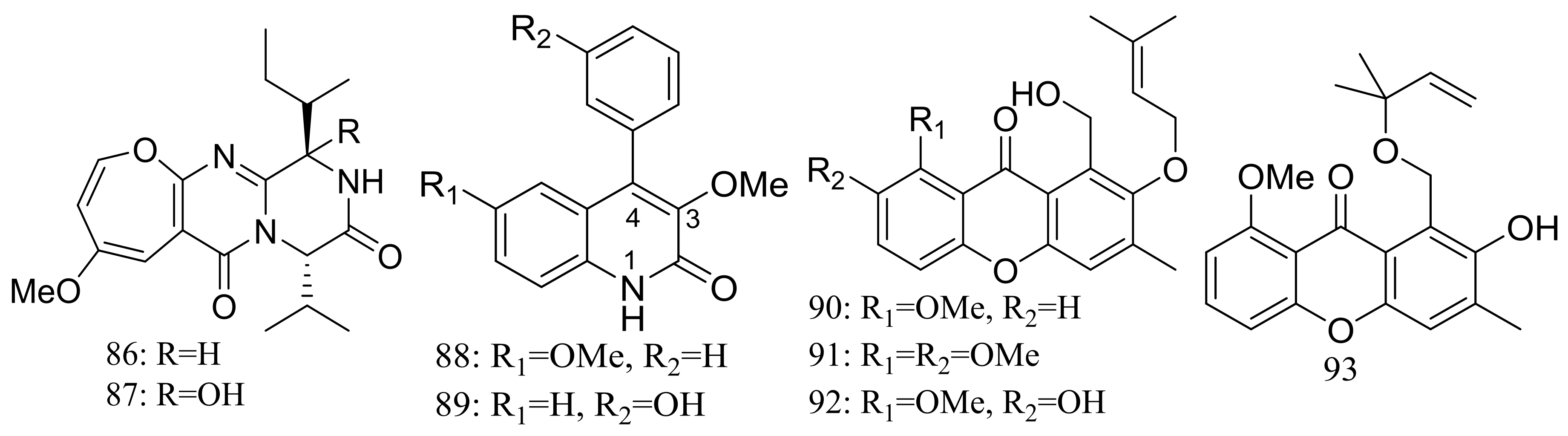
The deep-sea sediment-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor SCSIO 05879 (depth 3972 m, the Indian Ocean) was found to produce two new oxepine-containing diketopiperazine-type alkaloids named versicoloids A–B (86–87) (Figure 14), two new 4-aryl-quinolin-2-one alkaloids (88–89) (Figure 14), and four new prenylated xanthones named versicones A–D (90–93) (Figure 14). Compounds 86 and 87 displayed the same MIC valued of 1.6 μg/mL against Colletotrichum acutatum [40].
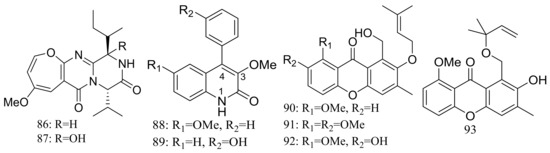
Figure 14.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 86–93).
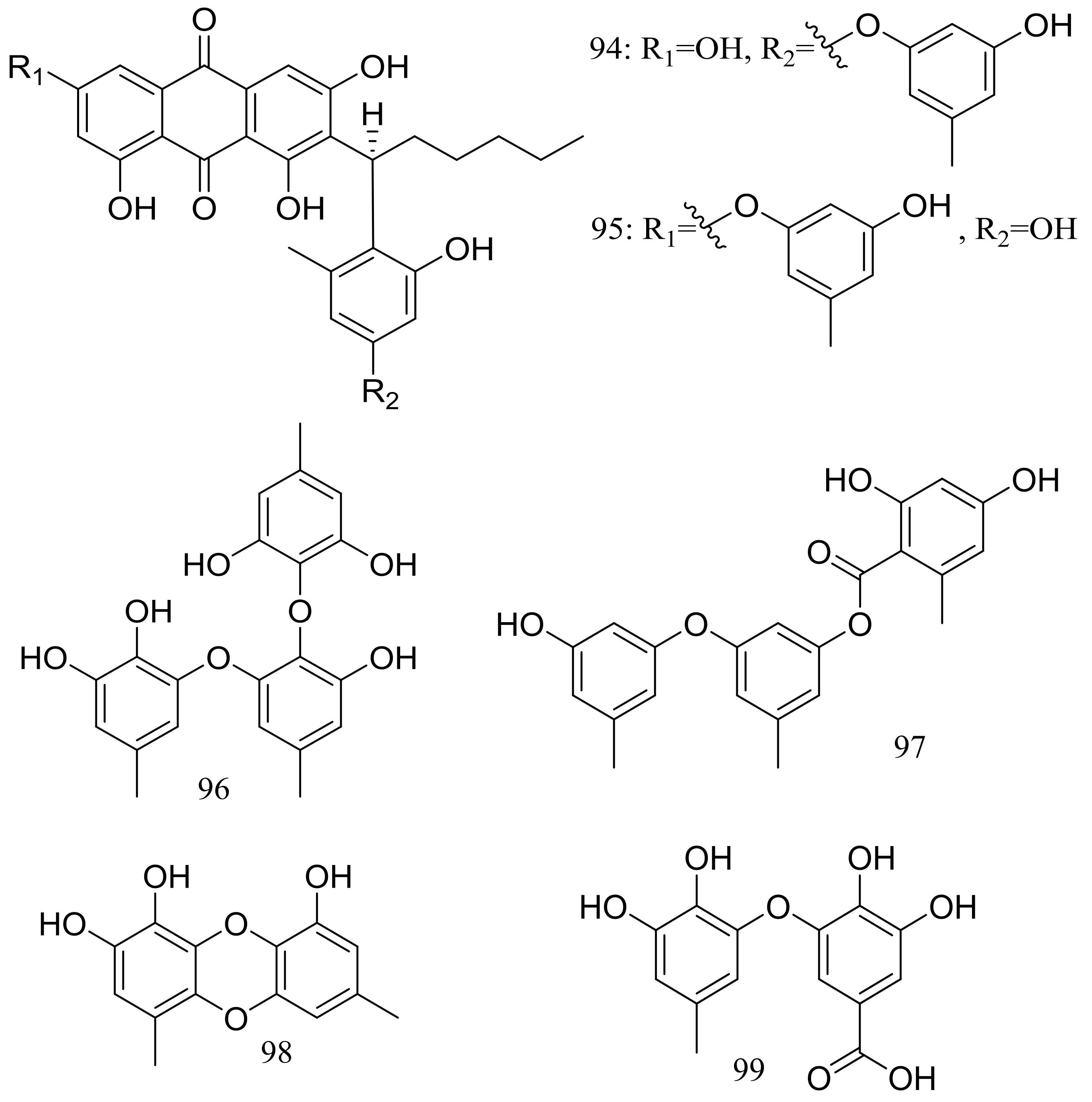
Aspergilols A–F (94–99) (Figure 15) were isolated from fermentations of the deep-sea fungus Aspergillus versicolor (A-21-2-7) (depth 3002 m, the South China Sea). Compound 98 significantly activated the Nrf2, which regulated the expression of antioxidant proteins that protect against oxidant damage [41].
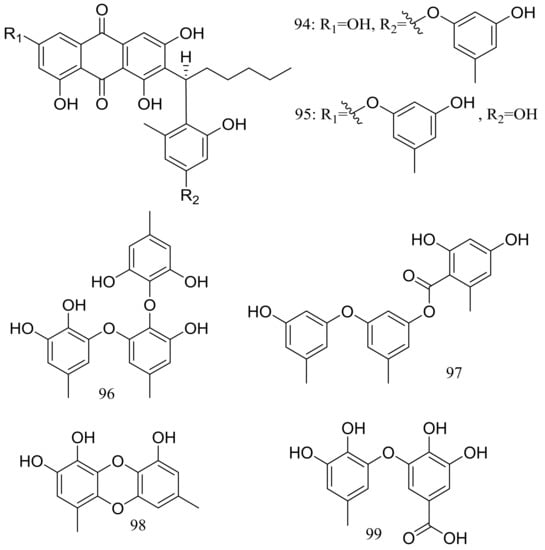
Figure 15.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 94–99).
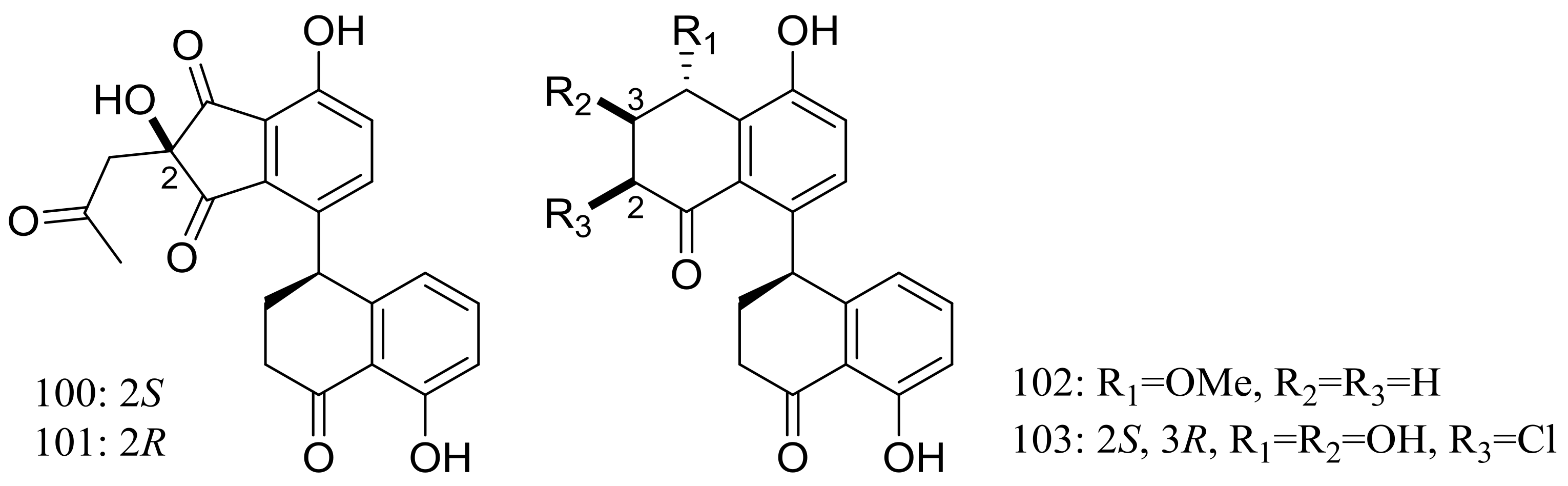
The clindanones A–B (100–101) and cladosporols F–G (102–103) (Figure 16) are four new polyketides isolated from the deep-sea fungus Cladosporium cladosporioides HDN14-342 (depth 3471 m, the Indian Ocean). Compounds 102–103 showed moderate cytotoxic activity against HeLa, K562, and HCT-116 cell lines with IC50 values of 3.9 to 23.0 μM [42].
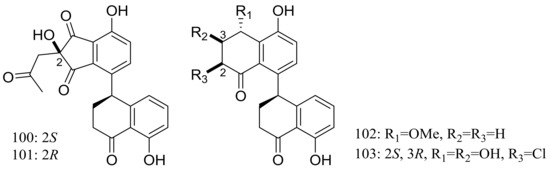
Figure 16.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 100–103).
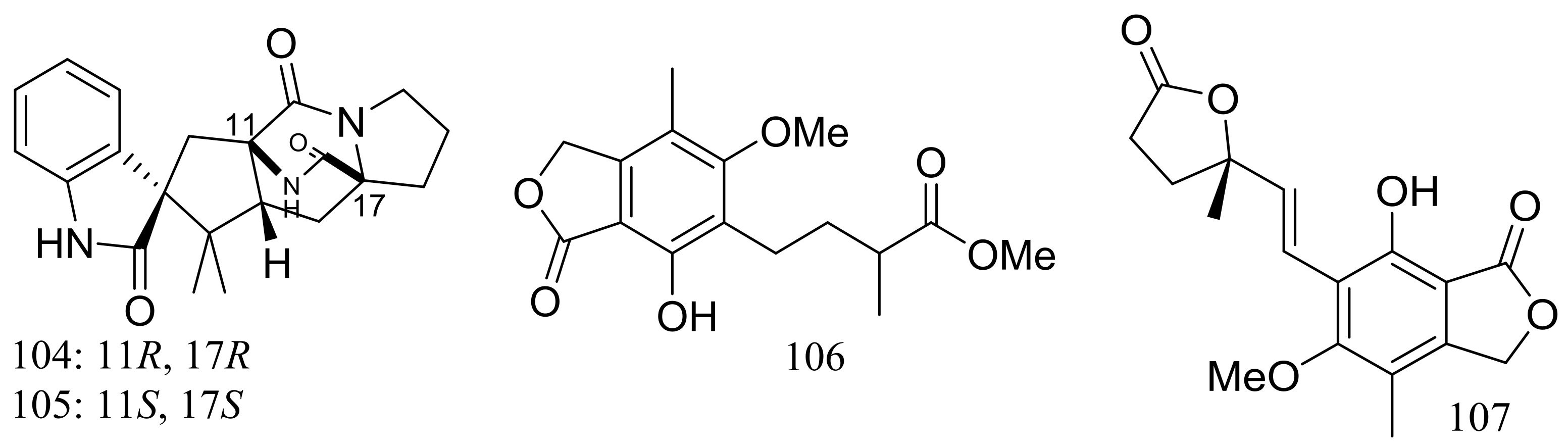
The fungal strain Penicillium brevicompactum DFFSCS025 (depth 3928 m, the South China Sea) produced two new brevianamides, brevianamids X–Y (104–105) and two new mycochromenic acid derivatives (106–107) (Figure 17). Compound 106 showed strong antilarval activity against Bugula neritina with an EC50 value of 13.7 μM [43].
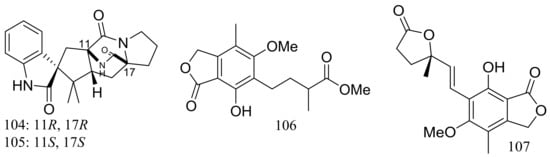
Figure 17.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 104–107).
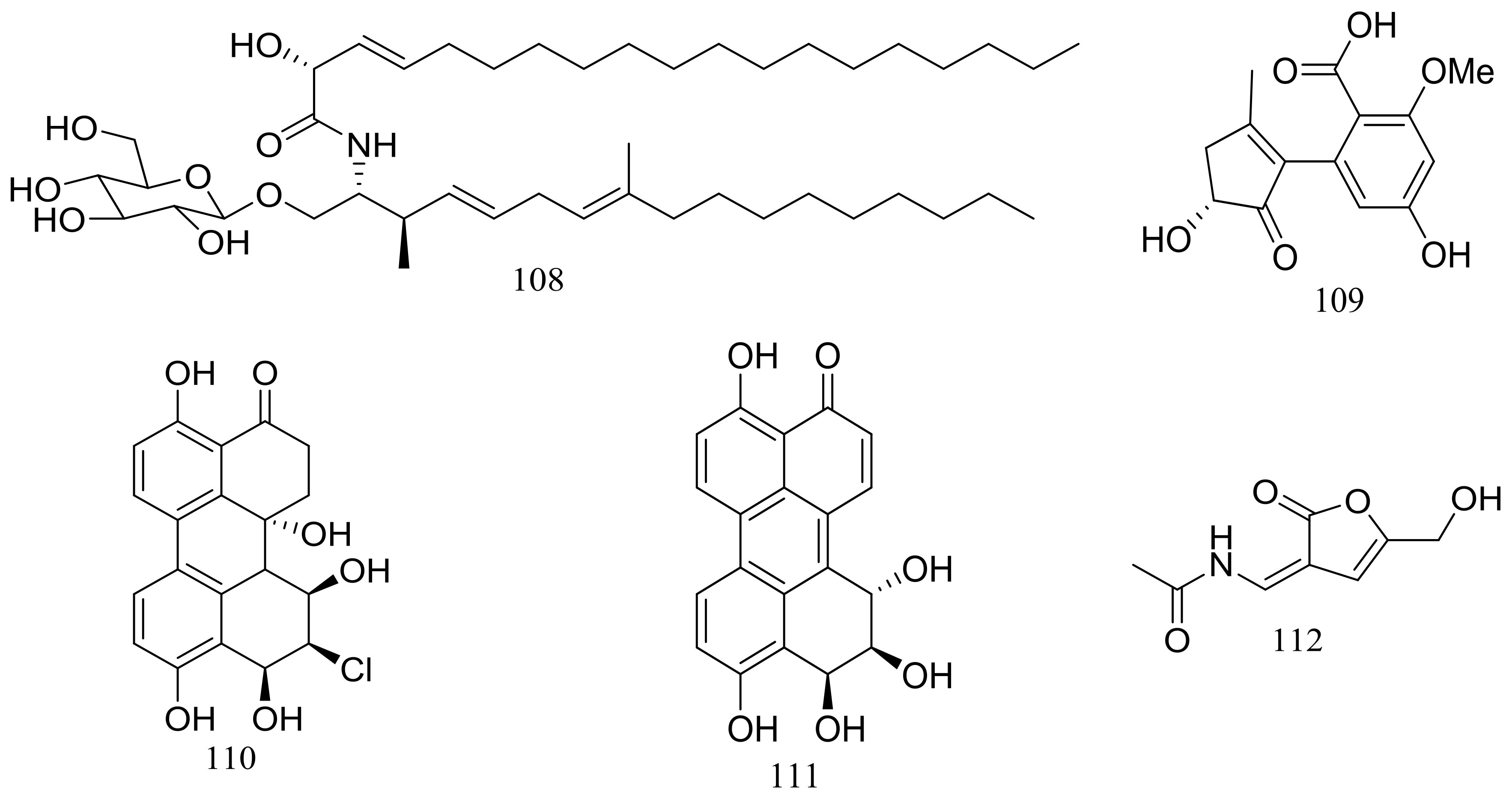
In exploring for new BRD4 inhibitors, five new compounds including one new cerebroside (108) (Figure 18), one new alternaric acid (109) (Figure 18), two new perylenequinones (110–111) (Figure 18), and 2-(N-vinylacetamide)-4-hydroxymethyl-3-ene-butyrolactone (112) (Figure 18) were isolated from fermentations of Alternaria sp. NH-F6 (depth 3927 m, the South China Sea). Compound 111 was a potent inhibitor with an inhibition rate of 88.1% at 10 μM, while 110 had a moderate inhibition at rate of 57.7% at the same concentration [44].
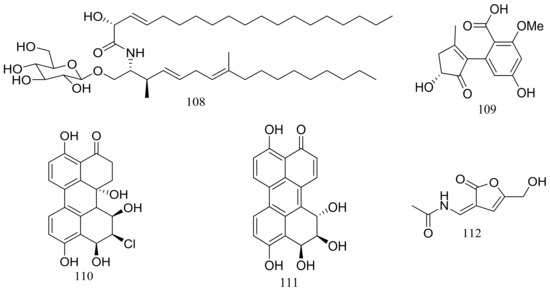
Figure 18.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 108–112).
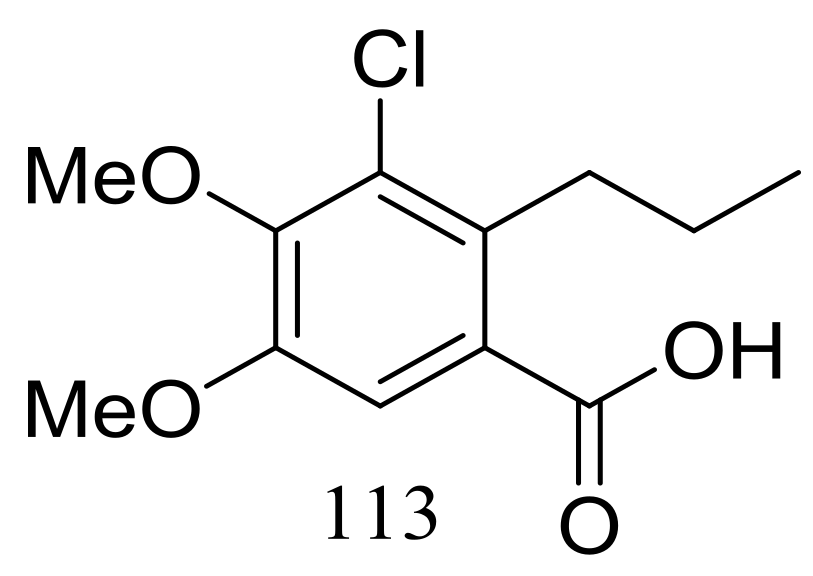
Engyodontiumin A (113) (Figure 19) was produced by the deep-sea-derived fungus Engyodontium album (depth 3542 m, the Atlantic Ocean). This novel benzoic acid derivative displayed moderate antibacterial activity against Aspergillus niger, MRSA, Vibrio vulnificus, Vibrio rotiferianus, and Vibrio campbellii. The experimental data on the antimicrobial activity were not provided in the original article [45].
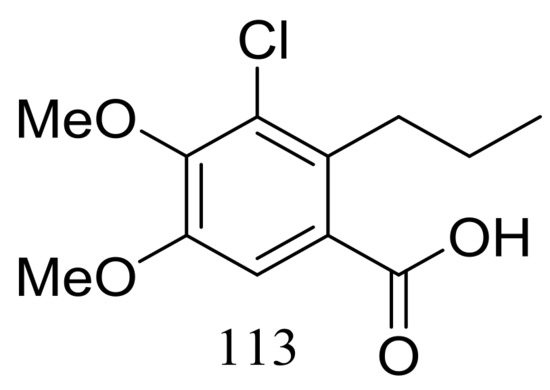
Figure 19.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compound 113).
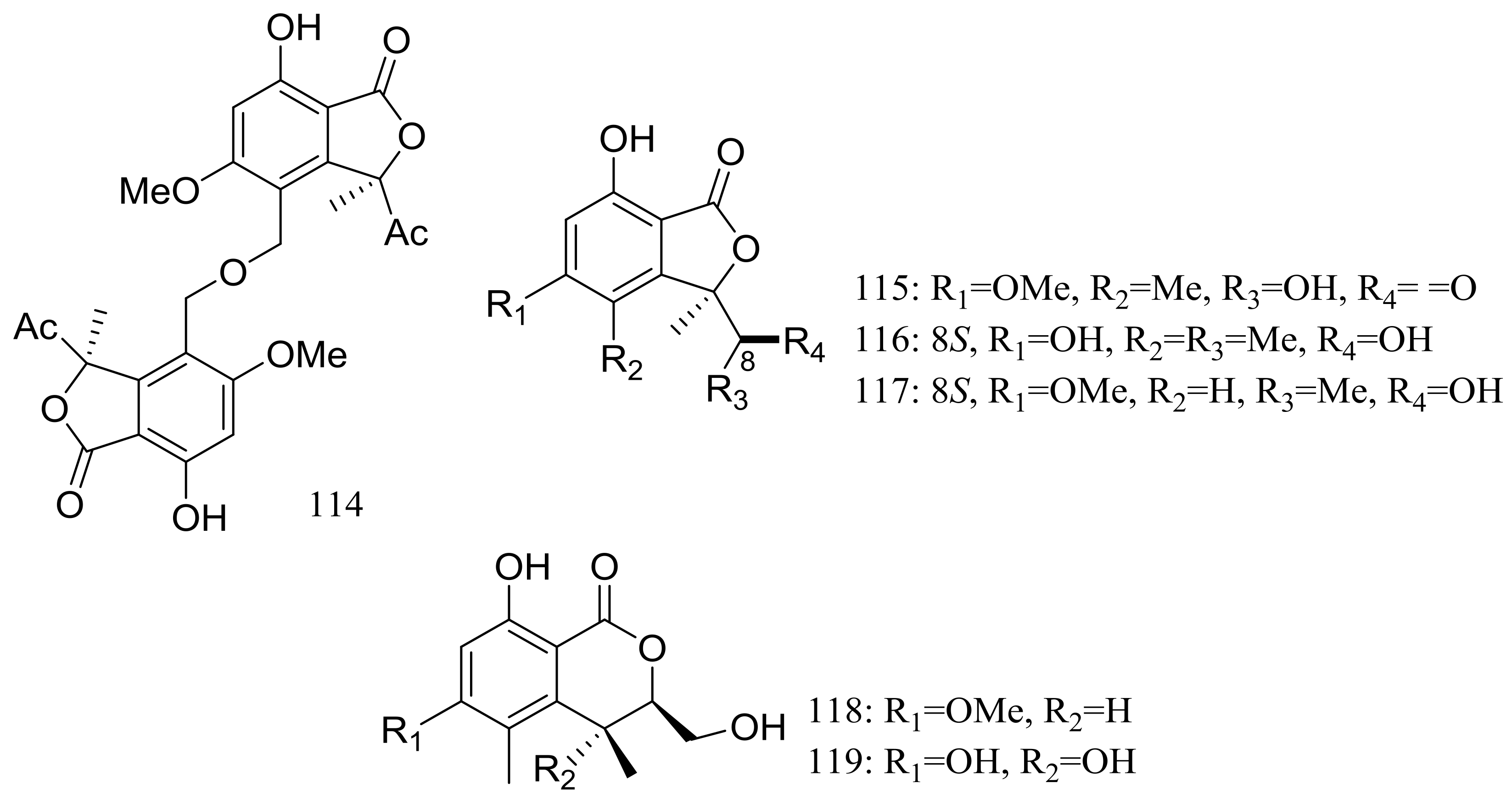
In exploration for novel bioactive marine natural products, four new isobenzofuanones named leptosphaerins JM (114–117) and two new isochromenones named clearanols I–J (118–119) (Figure 20) were isolated from Leptosphaeria sp. SCSIO 41005 (depth 3614 m, the Indian Ocean). When evaluated for biological activity, no cytotoxicity (K562, MCF-7, and SGC7901 cell lines) or antiviral activity (H3N2, EV71, and HIV viruses) was detected [46].
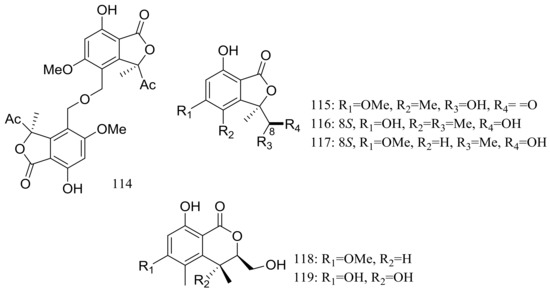
Figure 20.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 114–119).
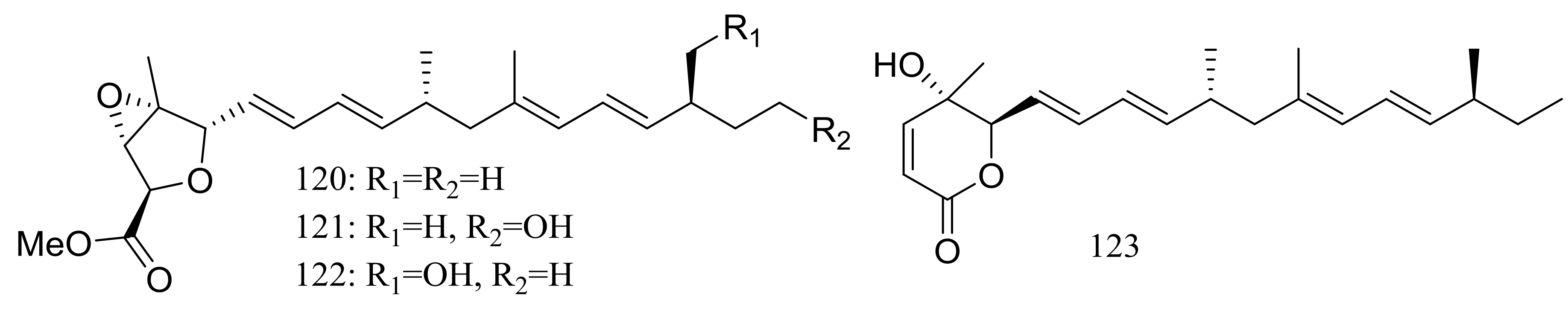
A mixed culture of the deep-sea-derived fungus Talaromyces aculeatus (depth 3386 m, the Indian Ocean) and the mangrove-derived fungus Penicillium variabile (Fujian Province of China) afforded four new polyketides, penitalarins A–C (120–122) and nafuredin B (123) (Figure 21). None of these compounds was produced by either of the two fungi when cultured alone under the same conditions. Compound 123 inhibited a panel of cancer cell lines (HeLa, K562, HCT-116, HL-60, A549, and MCF-7) with IC50 values ranging from 1.2 to 9.8 μM (doxorubicin as positive control IC50 0.2 to 0.8 μM) [47].
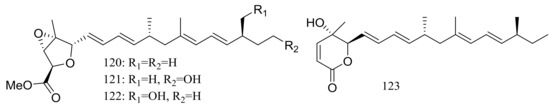
Figure 21.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 120–123).
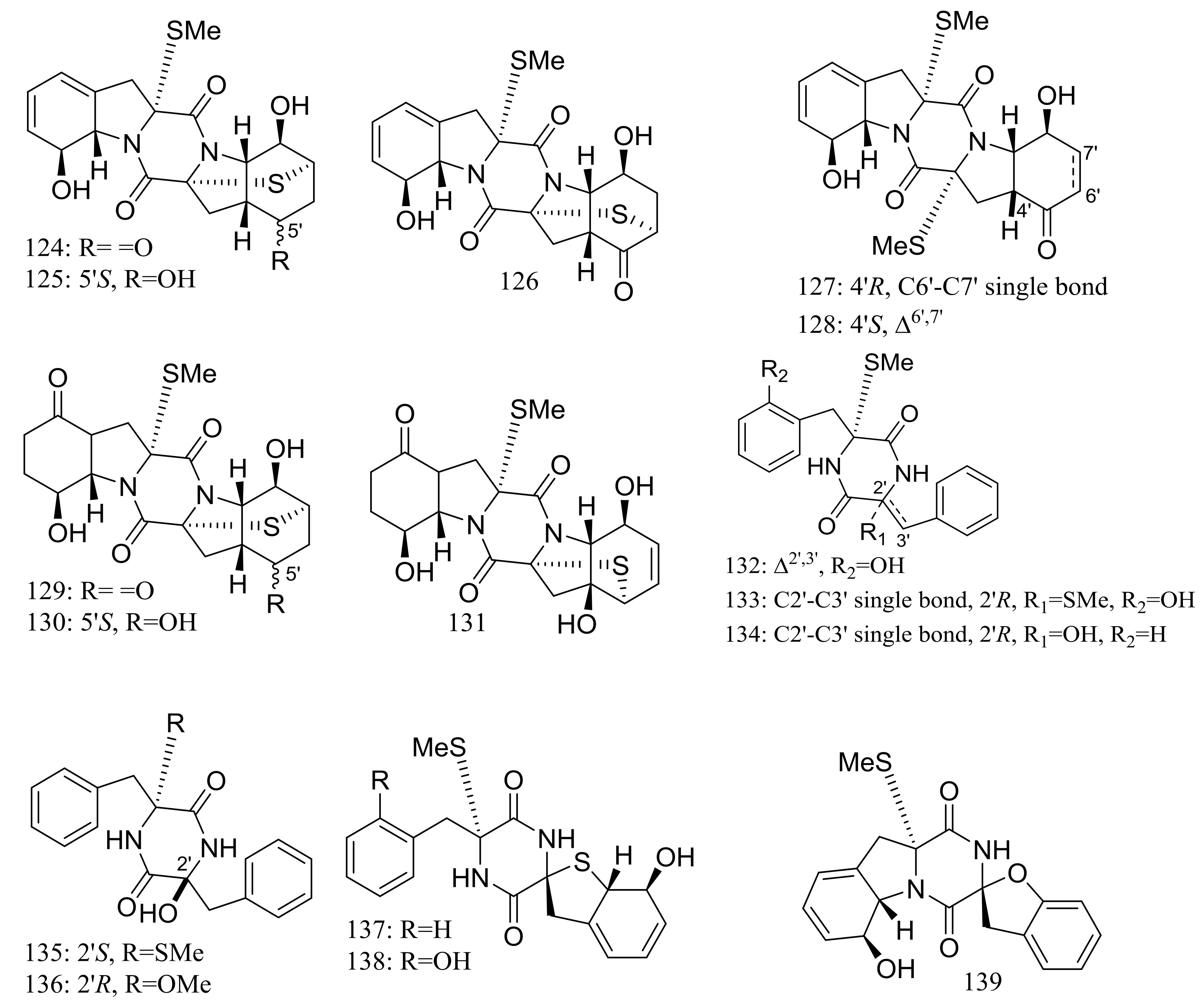
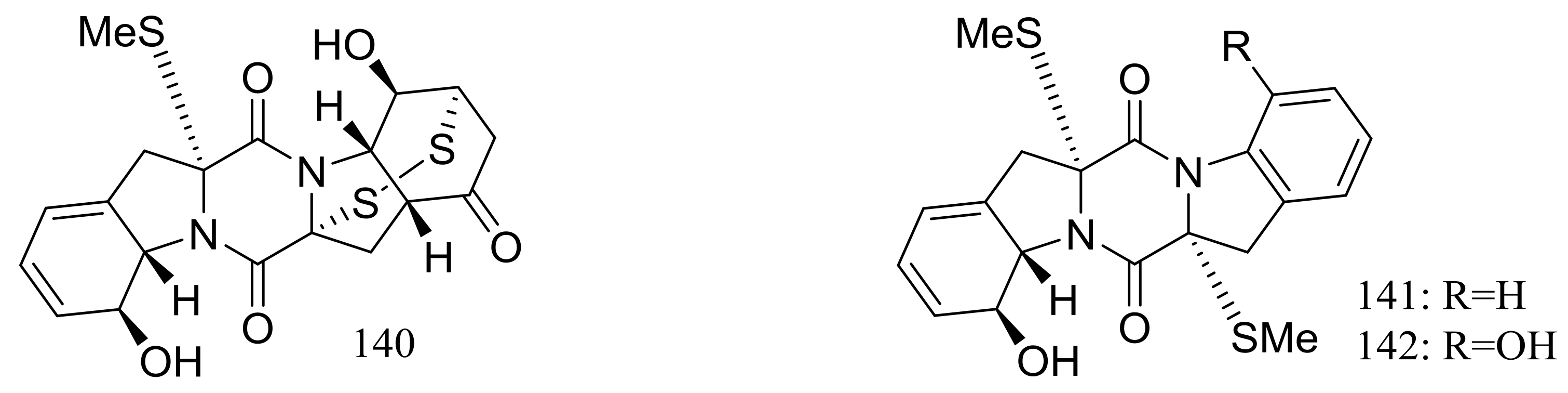
Nineteen new thiodiketopiperazine-type alkaloids named eutypellazines A–S (124–142) (Figure 22) [48,49] were produced by the marine-derived fungus Eutypella sp. MCCC 3A00281 (depth 5610 m, the South Atlantic Ocean). Inhibitory effects on HIV-1 replication in pNL4.3Env-.Luc co-transfected 293T cells were tested and IC50 values for compounds 124–135 ranged from 3.2 to 18.2 μM (EFV as the positive control IC50 0.1 μM). In addition, compound 133 could reactivate latent HIV-1 in J-Lat A2 cells in a dose-dependent manner. When tested for antimicrobial activity compounds 139–142 were active to Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 and vancomycin-resistant enterococci with MIC values of 32/32, 16/16, 32/32, and 16/32 μM respectively.

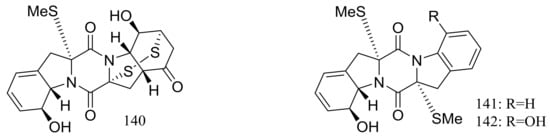
Figure 22.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compounds 124–142).
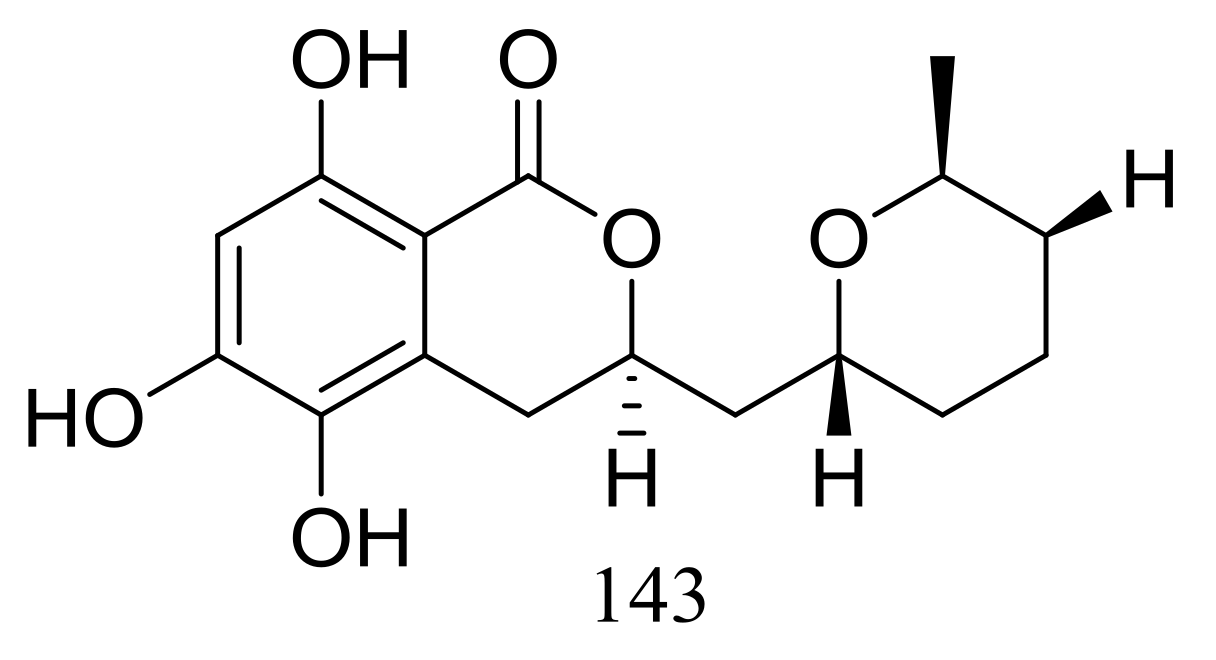
The cultured broth of the sea cucumber-derived fungus Penicillium coralligerum YK-247 (depth 3064 m, São Paulo Plateau, off Brazil) potently inhibited the growth of Saprolegnia parasitica. Further chromatographic fractionation of the cultured broth led to the isolation of cladomarine (143) (Figure 23) which showed selective antimicrobial activity against Saprolegnia parasitica and Pythium sp. sakari1 at a concentration of 10 μg/disc [50].
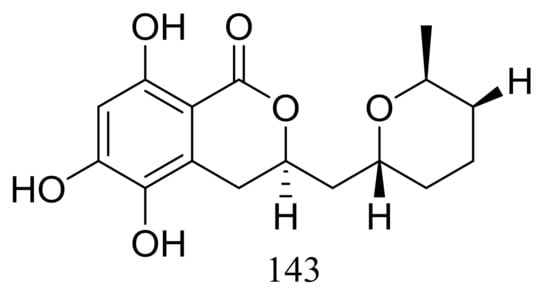
Figure 23.
Novel natural products derived from piezophilic fungi (compound 143).
3. Psychrophilic Fungi
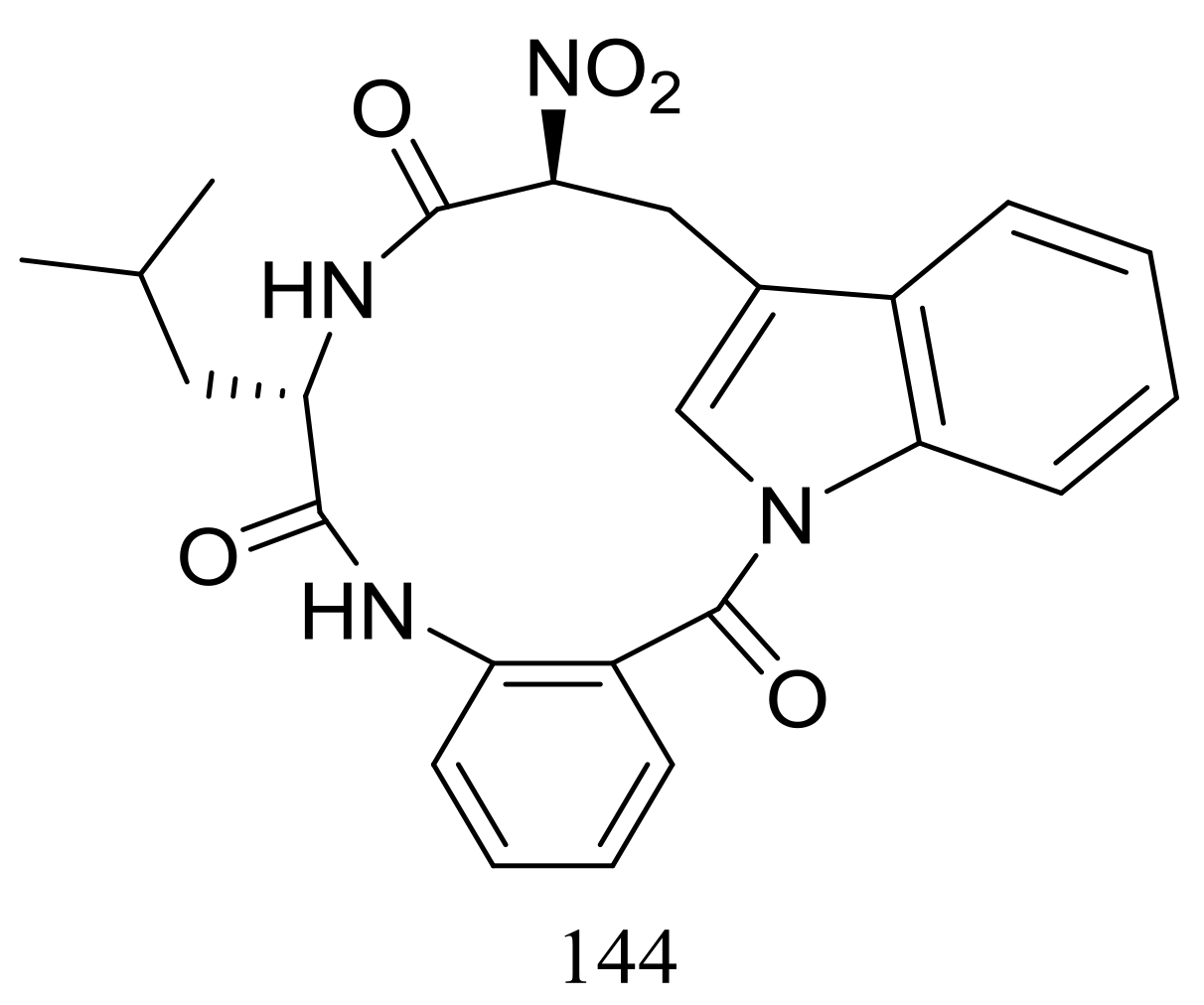
Psychrophilin D (144) (Figure 24), a new cyclic nitropeptide was isolated from Penicillium algidum derived from a soil sample in Greenland. This compound exhibited moderate cytotoxic activity against P388 murine leukaemia cells with an ID50 value of 10.1 μg/mL. When evaluated for antimicrobial, antiviral, anticancer and antiplasmodial activities compound 144 proved to be inactive [51].
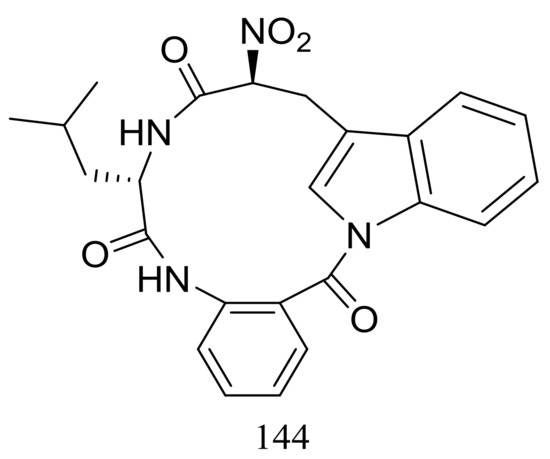
Figure 24.
Novel natural products derived from psychrophilic fungi (compound 144).
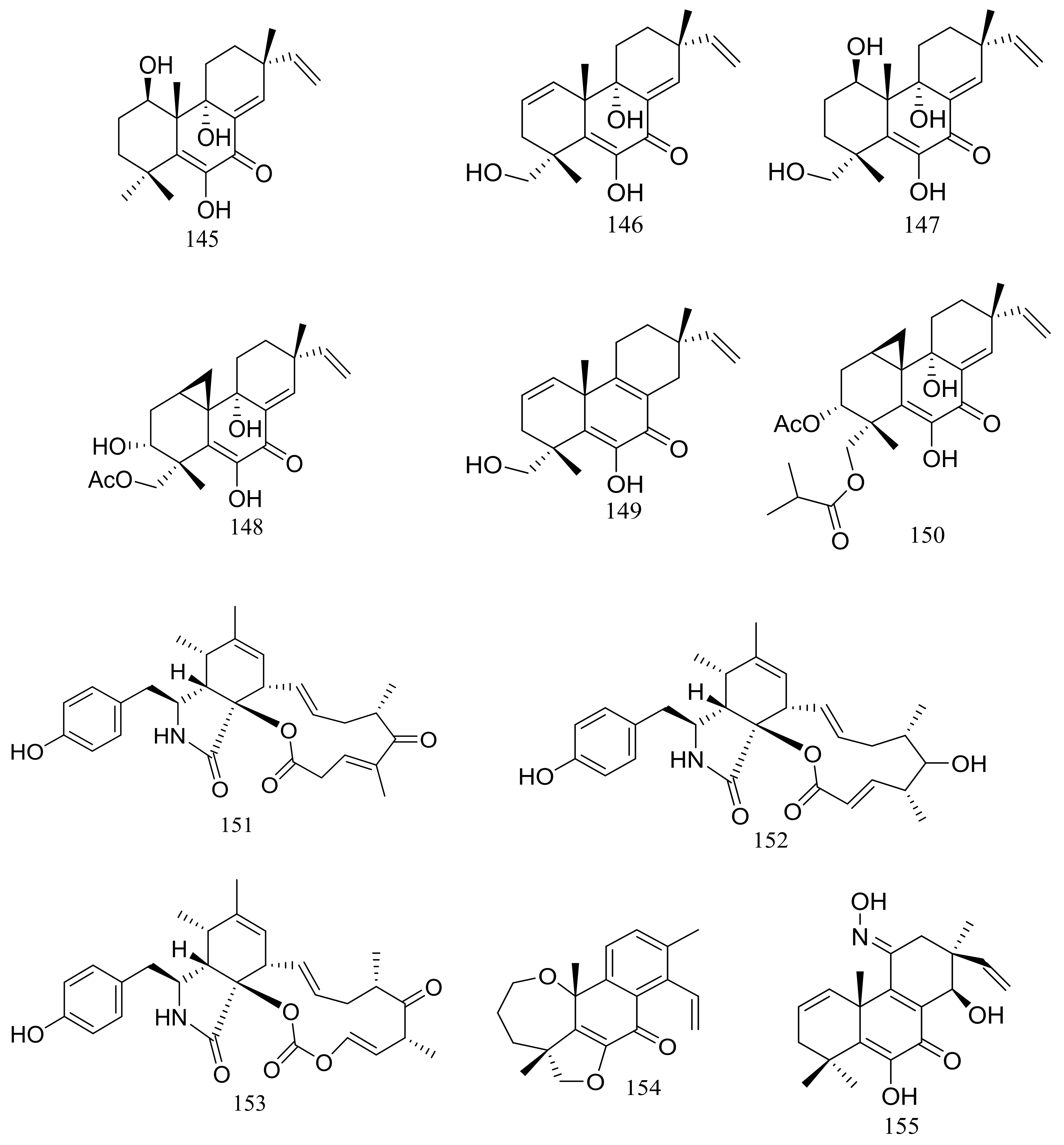
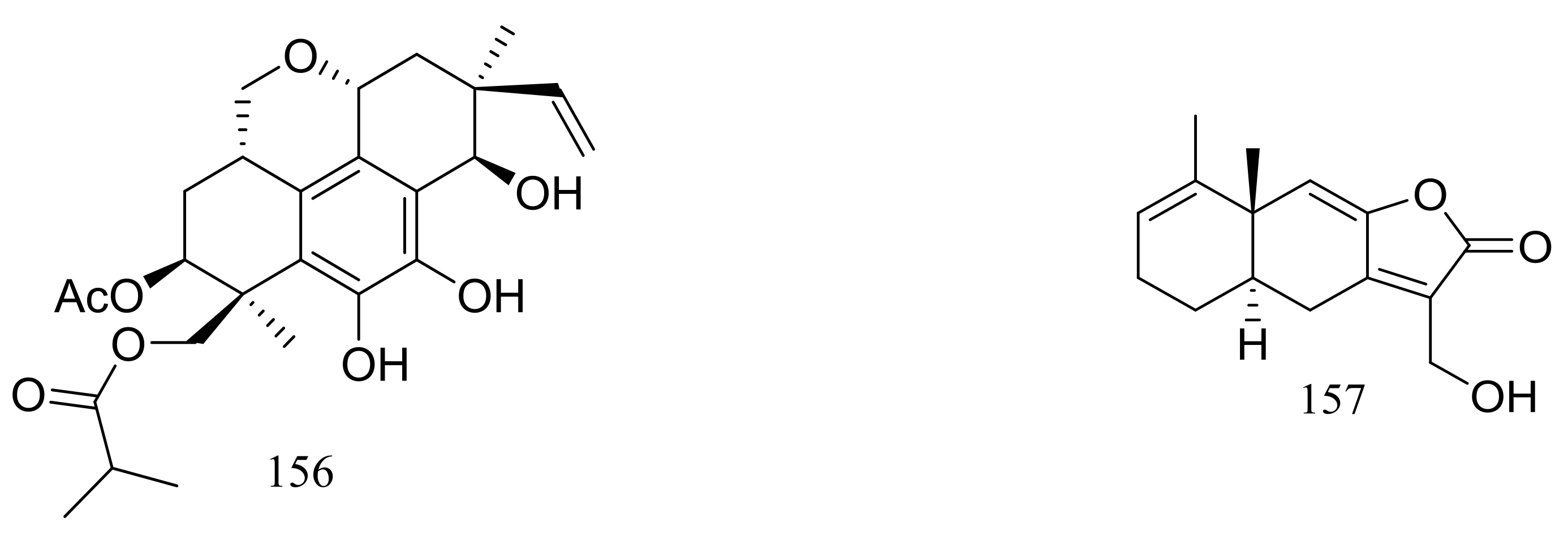
In 2005 Oh et al. discovered libertellenones A–D (145–148) (Figure 25) when co-cultured a marine-derived fungus with a unicellular marine bacterium. Libertellenone D (148) demonstrated potent cytotoxicity (IC50 0.76 μM) against HCT-116 cell line, whereas the other libertellenones exhibited weaker activities (IC50 15, 15 and 53 μM respectively) [52]. In 2014 libertellenones G (149) and H (150) (Figure 25) together with 145 and 147 were isolated from Eutypella sp. D-1, which was derived from a soil sample collected on London Island of Kongsfjorden of Ny-Ålesund District (altitude of 100 m), Arctic. Compound 149 showed moderate antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Staphylococcus aureus. Compound 150 showed slight cytotoxicity against several cancer cell lines (MCF-7, H460, U251, SW-1990, Hela, Huh-7, and SG7901) with IC50 values between 3.31 and 44.1 μM. According to the structure-bioactivity relations, the cyclopropane ring in 148 and 150 appears to be an important structural feature associated with their biological activity [53]. Later Chu’s group found that 150 biosynthesis was significantly elevated (16.4 folds) with ethanol treatment, and further study showed that the gene transcription levels of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaric acyl coenzyme A reductase and geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase were up-regulated by ethanol stimulation [54]. Several new compounds including cytochalasins Z24, Z25, Z26 (151–153) (Figure 25) [55], eutypenoids A–C (154–156) (Figure 25) [56], and eut-Guaiane sesquiterpene (157) (Figure 25) [57] have been described from the same fungal strain since 2014. Compound 151 exhibited a moderate cytotoxicity against MCF-7 cells with an IC50 value of 9.33 μM. Compound 155 was able to suppress the proliferation of BALB/c mice splenocytes under ConA induction. Antibacterial activity (Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Staphylococcus aureus) of compound 157 was comparable to that of ampicillin but cytotoxic activity against SGC7901 cells was very weak (IC50 39.8 μM).

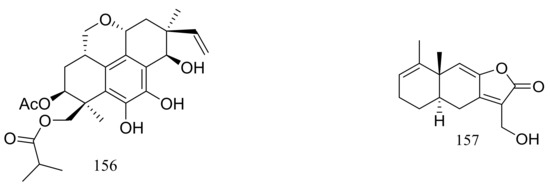
Figure 25.
Novel natural products derived from psychrophilic fungi (compounds 145–157).
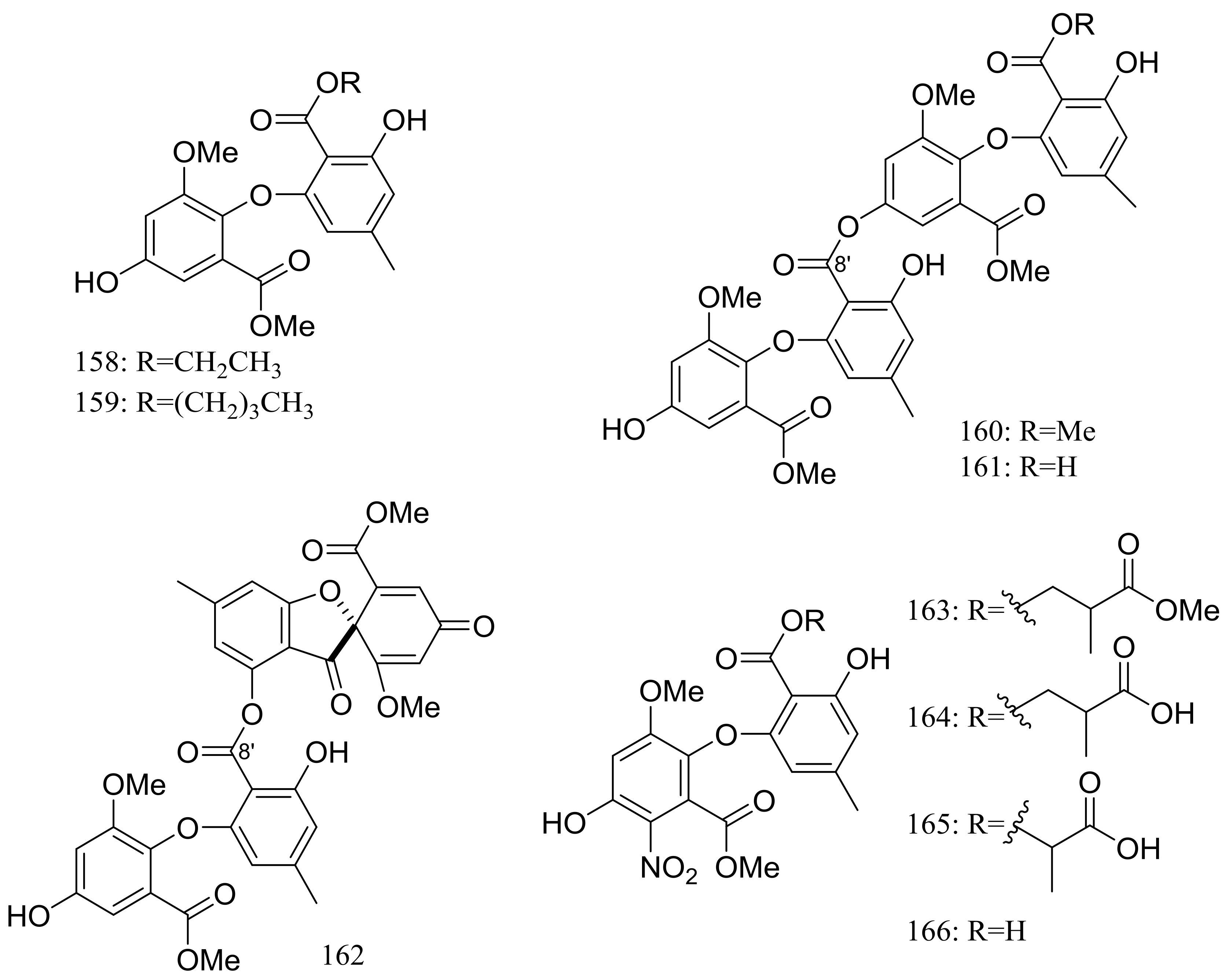
In search for new antifungal and antibacterial natural products, five asterric acid derivatives named ethyl asterrate (158), n-butyl asterrate (159) and geomycins A–C (160–162) (Figure 26) were isolated from an Antarctic Geomyces species. Compound 161 showed significant antifungal activity against A. fumigatus (ATCC 10894) with IC50/MIC values of 0.86/29.5 µM (the positive control fluconazole IC50/MIC 7.35/163.4 µM). Compound 162 exhibited moderate antimicrobial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria with IC50 values ranging from 12.9 to 36.2 µM [58]. In 2015 four nitroasterric acid derivatives named pseudogymnoascins A–C (163–165) and 3-nitroasterric acid (166) (Figure 26) were described as metabolites of a sponge-associated fungus Pseudogymnoascus sp. F09-T18-1, which was collected from the King George Island of Antarctic. No antimicrobial activity was observed at MIC > 64 μg/mL. Compared with compounds 161 and 162, the lack of antimicrobial activities of compounds 163–166 suggested the activity lied in the size of substituent at C-8′ and/or the presence of the nitro group in the molecule [59].
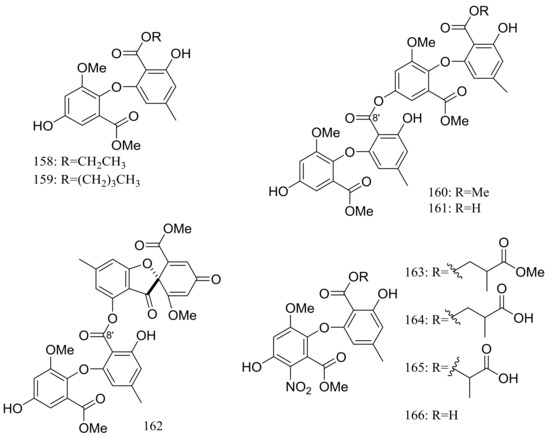
Figure 26.
Novel natural products derived from psychrophilic fungi (compounds 158–166).
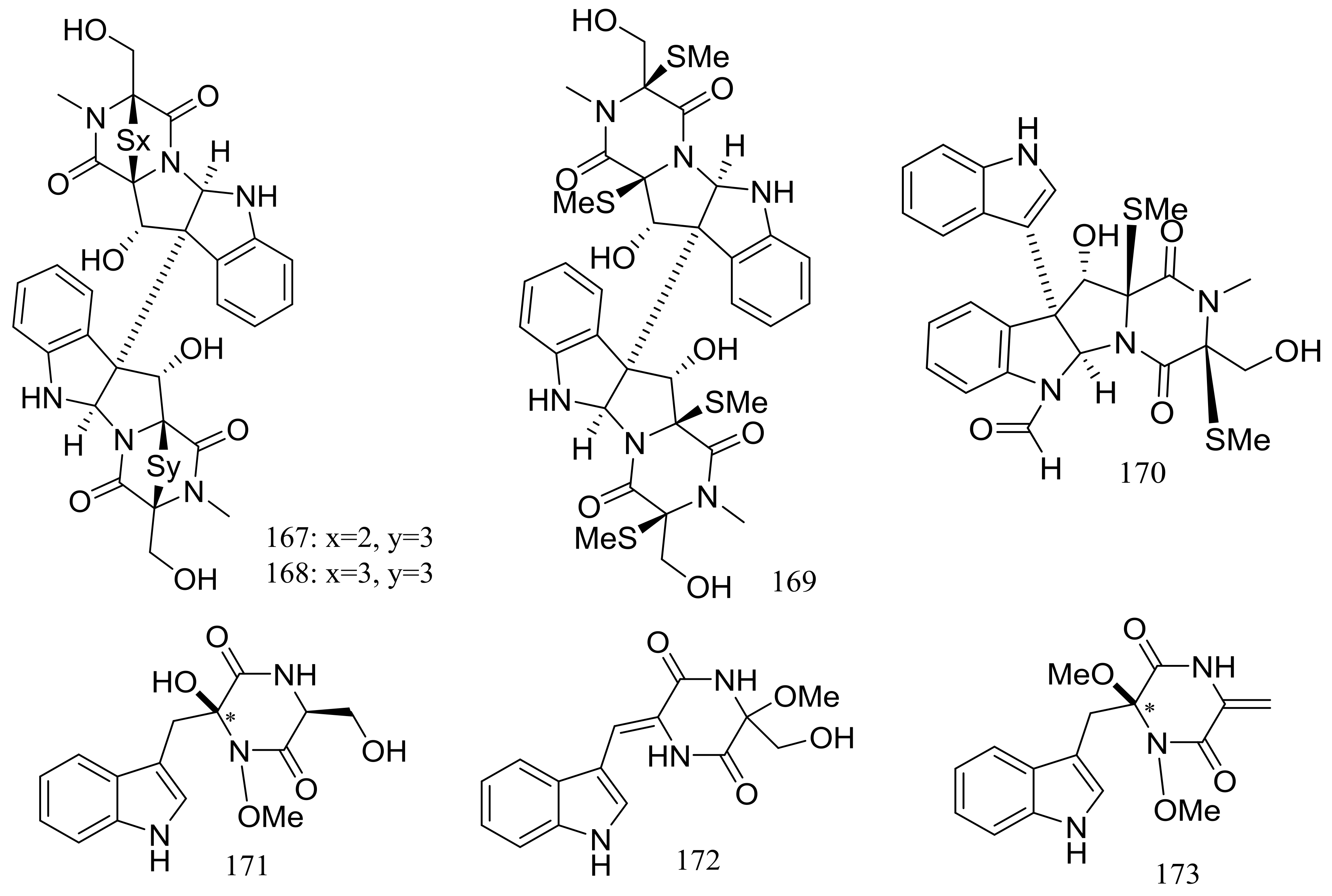
Several piperazine-type compounds, chetracins B–D (167–169) and oidioperazines A–D (170–173) (Figure 27) were produced by the soil-derived Antarctic fungus Oidiodendron truncatum GW3-13 which was obtained near the Great Wall station (Chinese Antarctic station). When tested for cytotoxic activities against a panel of cancer cell lines (HCT-8, Bel-7402, BGC-823, A549, and A2780) compound 167 proved to be the most active (IC50 0.003 to 0.028 μM), whereas 168 and 169 were less active (IC50 0.14 to 1.83 μM) [60].

Figure 27.
Novel natural products derived from psychrophilic fungi (compounds 167–173). * Absolute configuration is not determined.
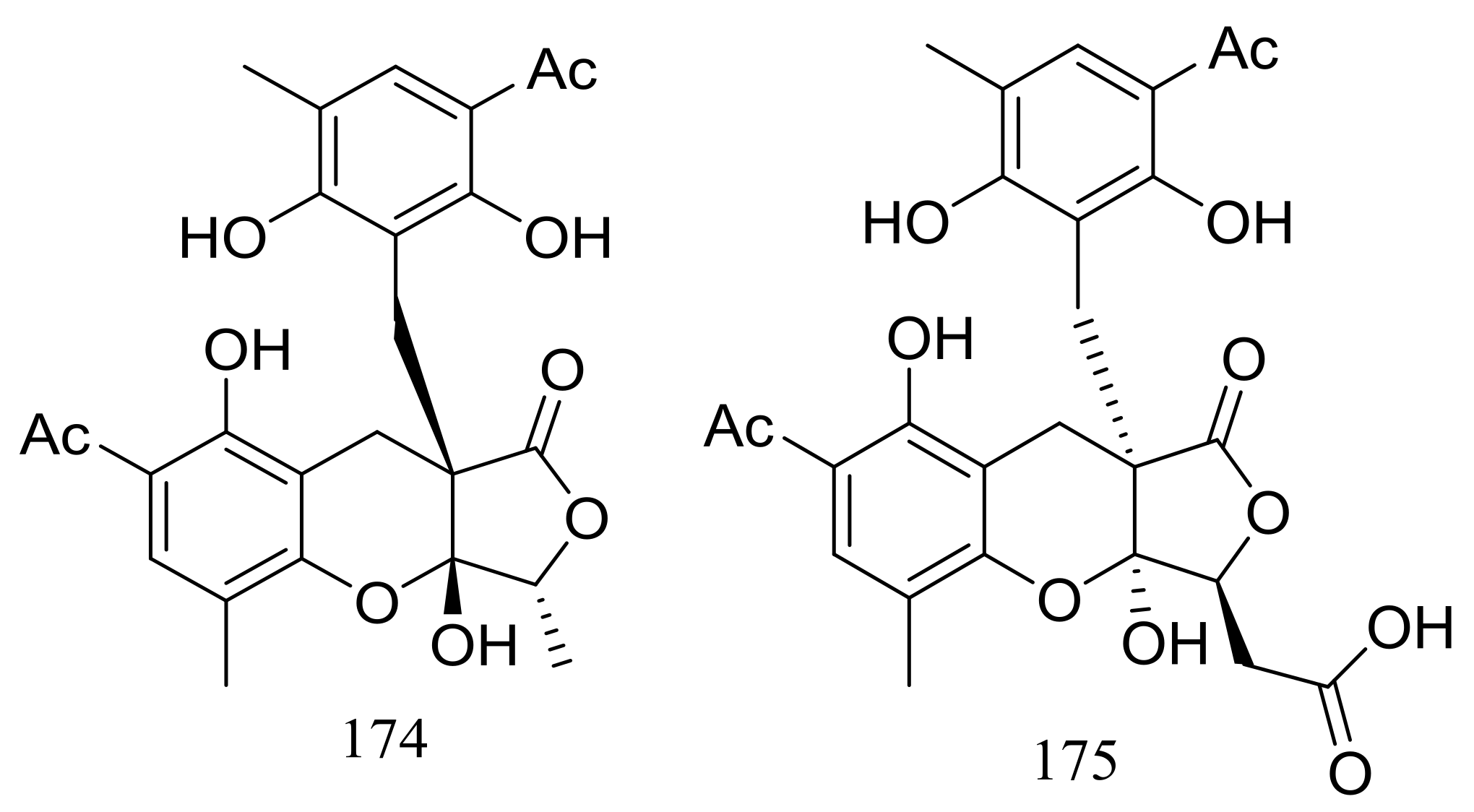
Two highly oxygenated polyketides, penilactones A and B (174 and 175) (Figure 28) featuring a new carbon skeleton formed from two 3,5-dimethyl-2,4-diol-acetophenone units and a γ-butyrolactone moiety were produced by the Antarctic marine-derived fungus Penicillium crustosum PRB-2. A plausible biogenetic pathway was proposed in the original article. Effects on NF-κB inhibition (in transient transfection and reporter gene expression assay) in RAW264.7 cells were tested and compound 174 showed very weak activity with a rate of 40% at 10 mM (the positive control PDTC inhibitory rate 85% at 0.1 mM) [61].
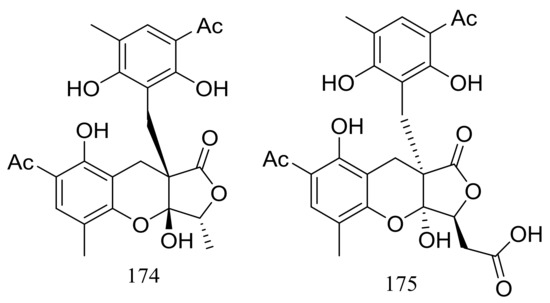
Figure 28.
Novel natural products derived from psychrophilic fungi (compounds 174–175).
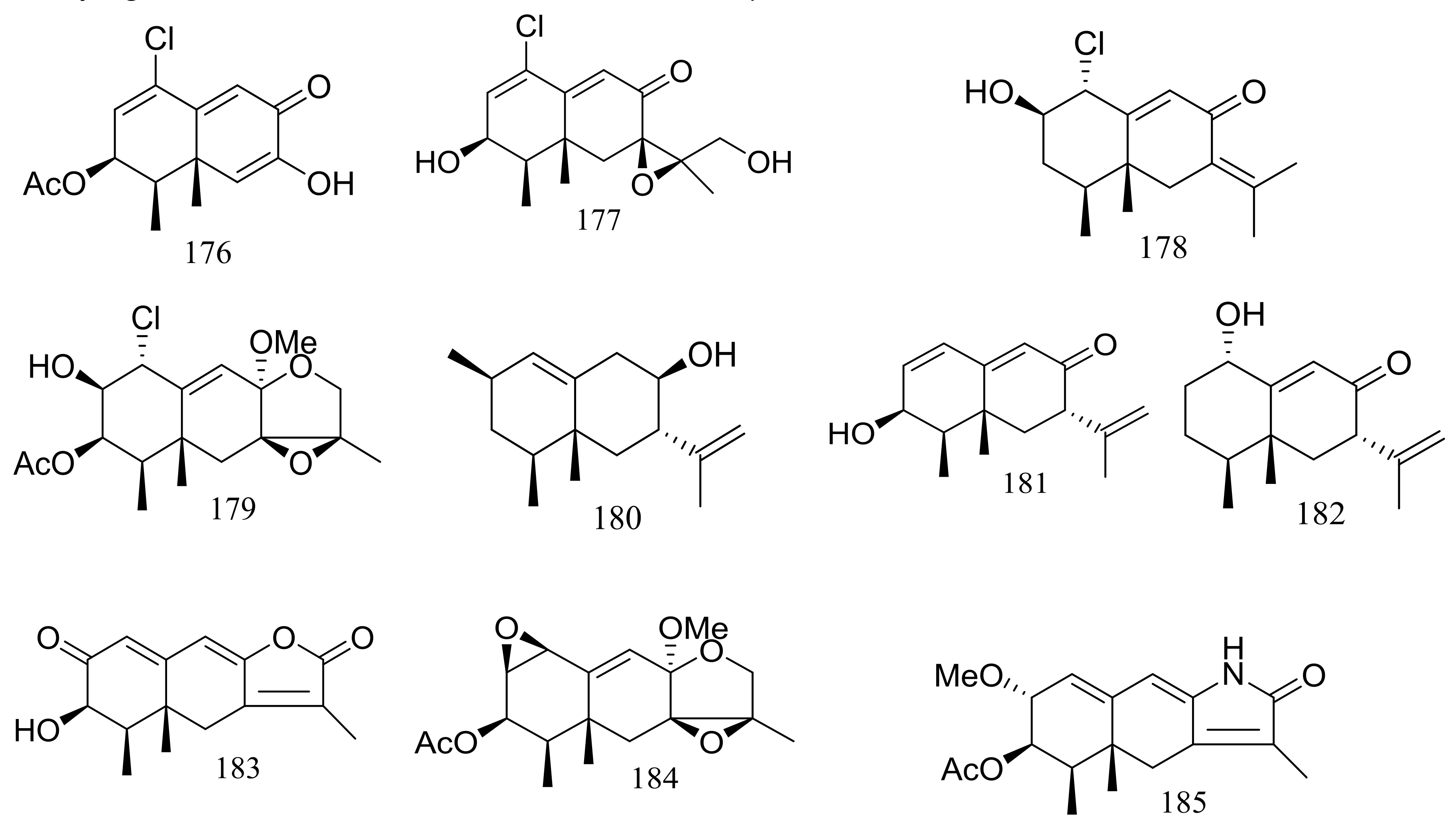
Several interesting eremophilane-type sesquiterpenes with high structural diversity have been described for Penicillium sp. PR19N-1 derived from a sludge sample in Prydz Bay (−1000 m), Antarctica. In 2013 four new chloro-eremophilane sesquiterpenes (176–179) (Figure 29) were isolated from this fungal strain and the plausible metabolic network was proposed. Compound 176 displayed modest cytotoxic activity against HL-60 and A549 cell lines with IC50 values of 11.8 and 12.2 μM respectively, whereas the other compounds exhibited no activities. [62]. Soon later another five new eremophilane-type sesquiterpenes (180–184) and a rare lactam-type eremophilane (185) (Figure 29) were isolated from the same Penicillium strain. When tested for cytotoxic activities against HL-60 and A-549 cells only 180 and 184 proved to be active and compound 184 displayed strong cytotoxic activity against A-549 cells with an IC50 value of 5.2 μM [63].
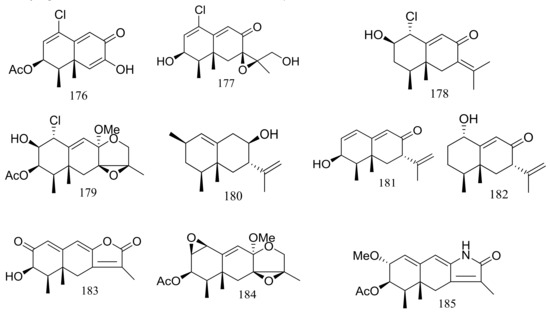
Figure 29.
Novel natural products derived from psychrophilic fungi (compounds 176–185).
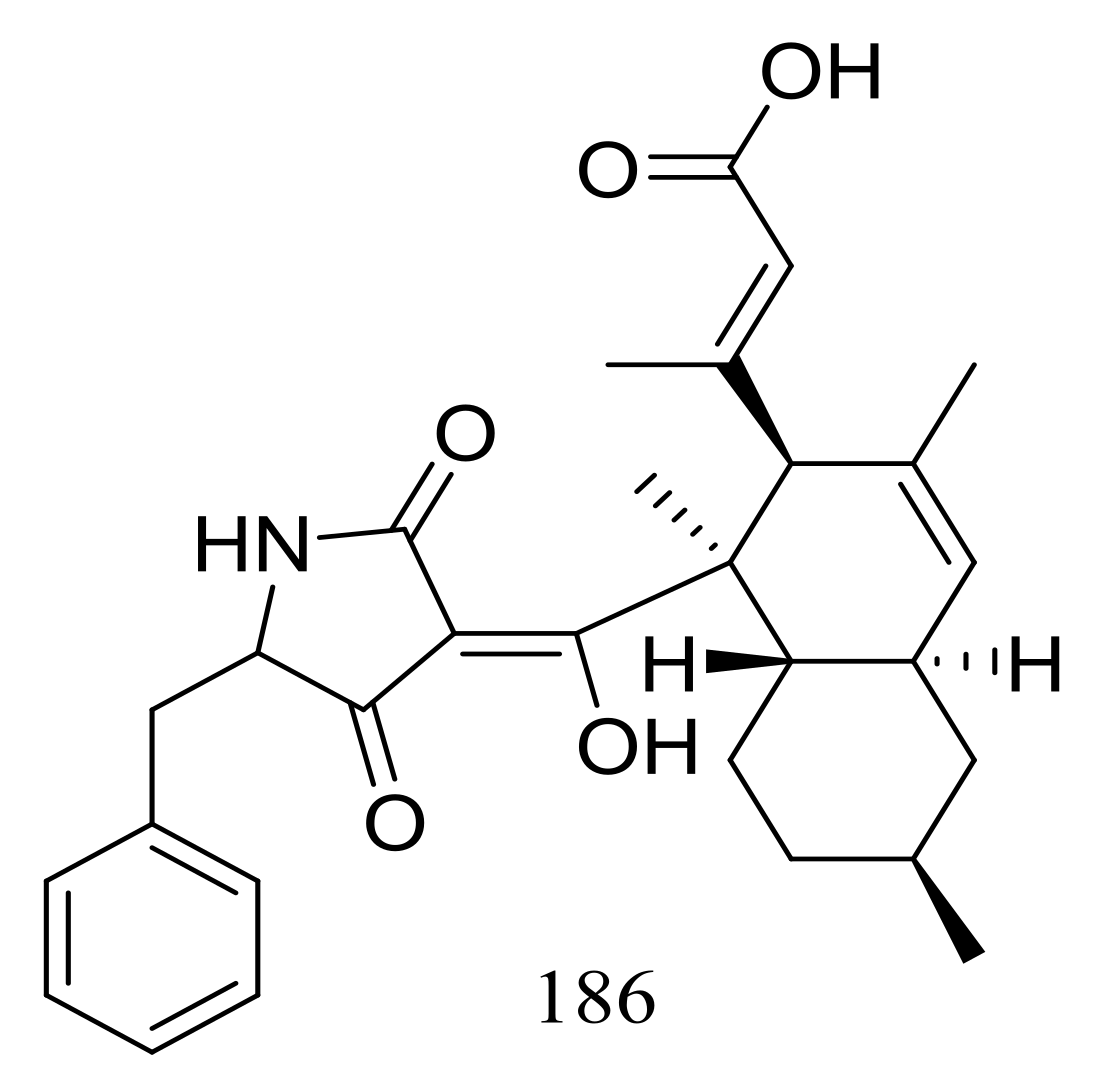
Two different Lindgomycetaceae strains KF970 and LF327 obtained from different marine habitats (Antarctic and the Kiel Fjord, Baltic Sea) both produced lindgomycin (186) (Figure 30), an unusual polyketide with a unique 5-benzylpyrrolidine-2,4-dione unit at the tetramic acid substructure. Antibiotic activity (Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) of compound 186 were two times less than that of chloramphenicol (the positive control) [64].
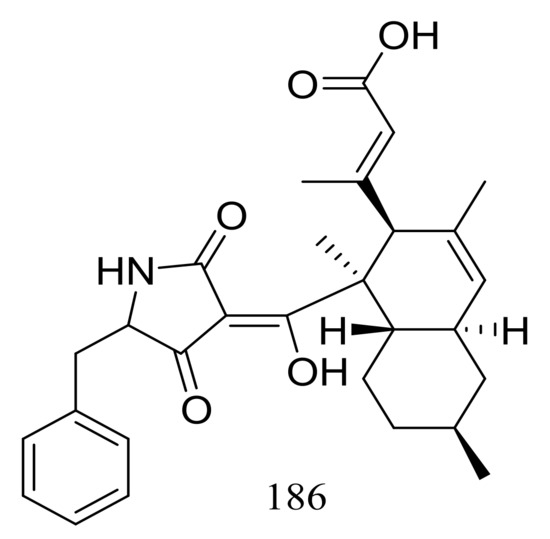
Figure 30.
Novel natural products derived from psychrophilic fungi (compound 186).
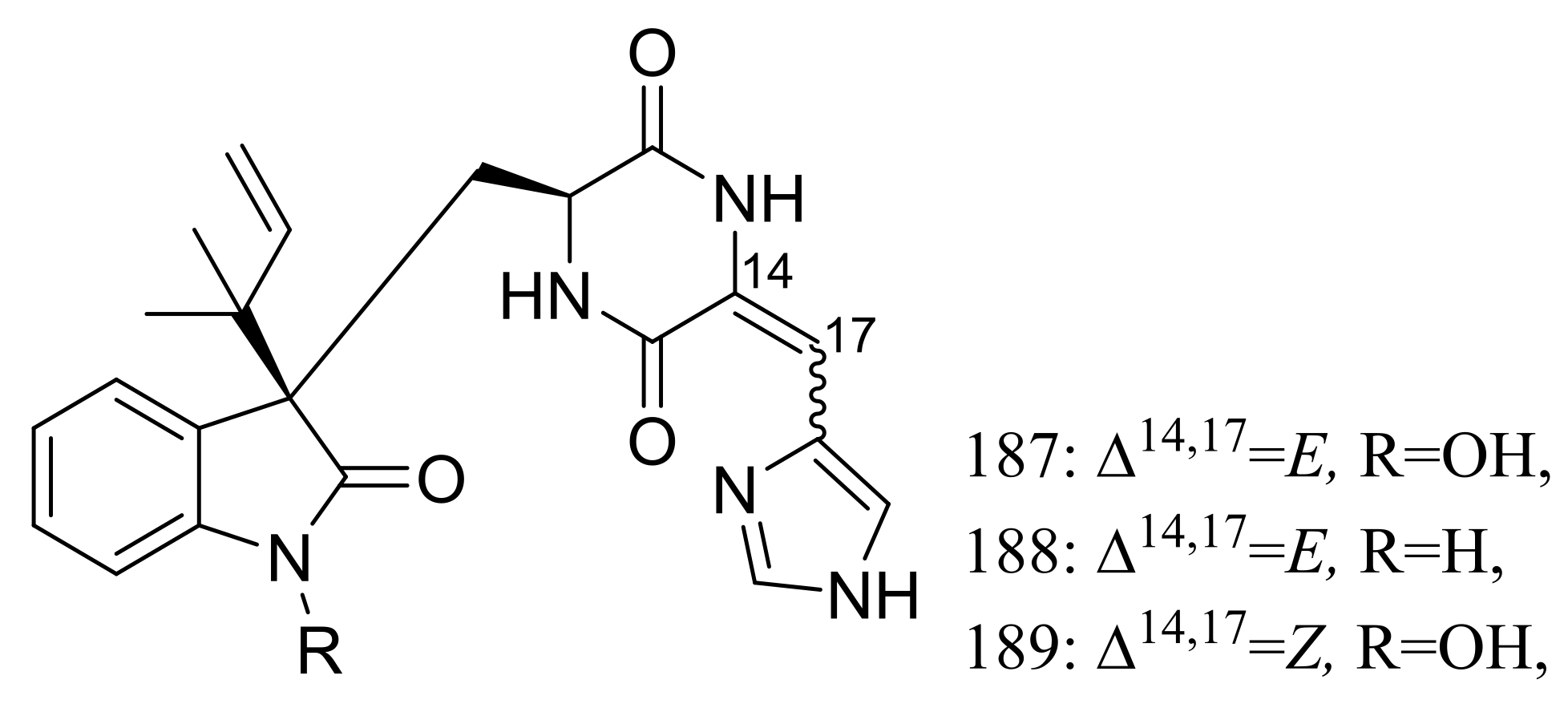
The psychrotolerant fungus Penicillium sp. SCSIO 05705 collected nearby the Great Wall station (Chinese Antarctic station) afforded three new indolyl diketopiperazine derivatives, penillines A–B (187–188) and isopenilline A (189) (Figure 31). In the general bioactivity profiling programs including antiviral, cytotoxic, antibacterial and antituberculosis evaluation, all compounds were found inactive [65].
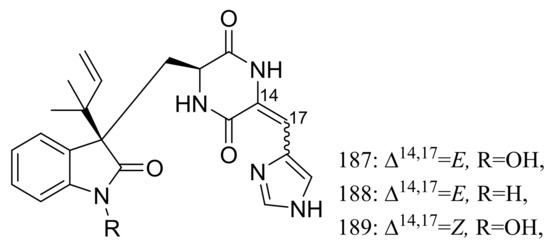
Figure 31.
Novel natural products derived from psychrophilic fungi (compounds 187–189).
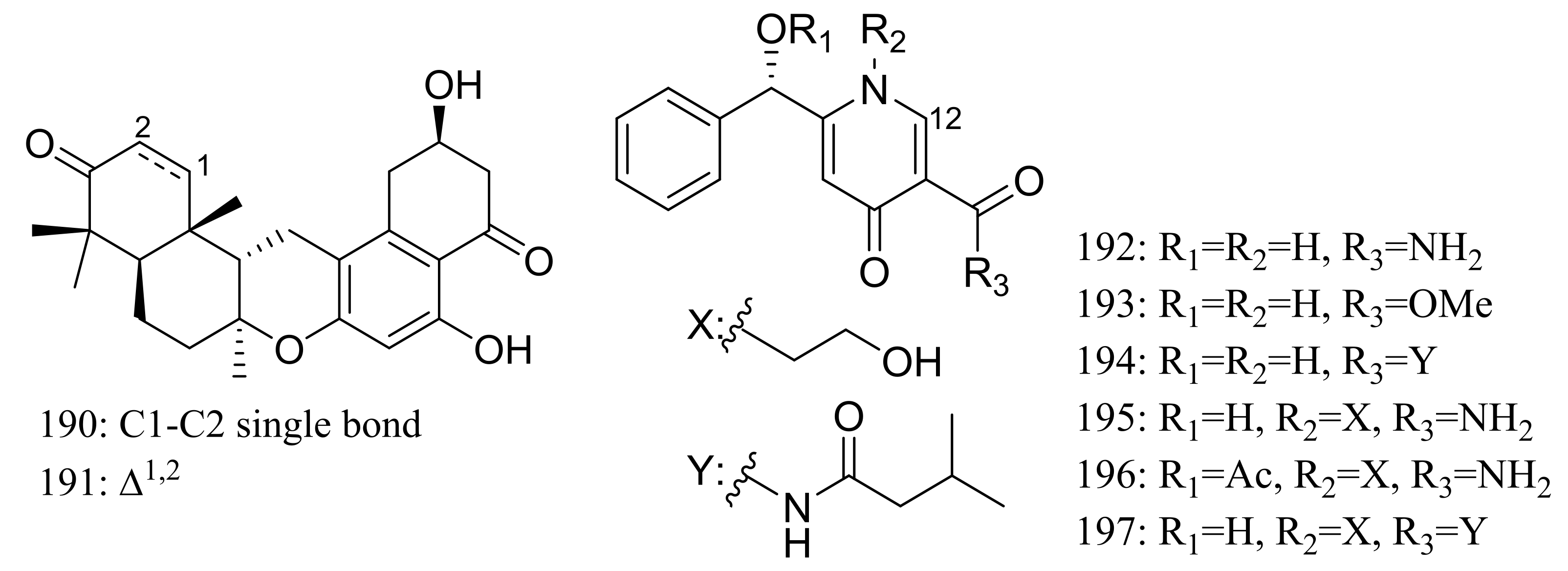
Chrodrimanins I (190) and J (191) (Figure 32), two new meroterpenoids were isolated from the moss-derived Penicillium funiculosum GWT2-24, collected at the China Great Wall Station in Antarctica. Distinguished from the reported chrodrimanins, compounds 190 and 191 possessed a unique cyclohexanone instead of a δ-lactone ring. Neither antiviral activity (H1N1) nor cytotoxic activity (K562, HL60, HeLa, and A549 cell lines) was detected [66]. From the same fungal strain, six new pyridine alkaloids named penipyridones A–F (192–197) (Figure 32) were published later. When screened for lowering of oleic acid elicited lipid accumulation in HepG2 hepatocytes, compounds 192, 193 and 196 remarkably reduced intracellular lipid accumulation as well as the total cholesterol and triglyceride quantification at 10 μM [67].
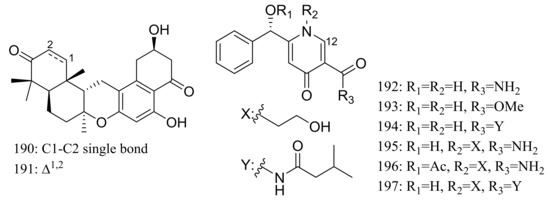
Figure 32.
Novel natural products derived from psychrophilic fungi (compounds 190–197).
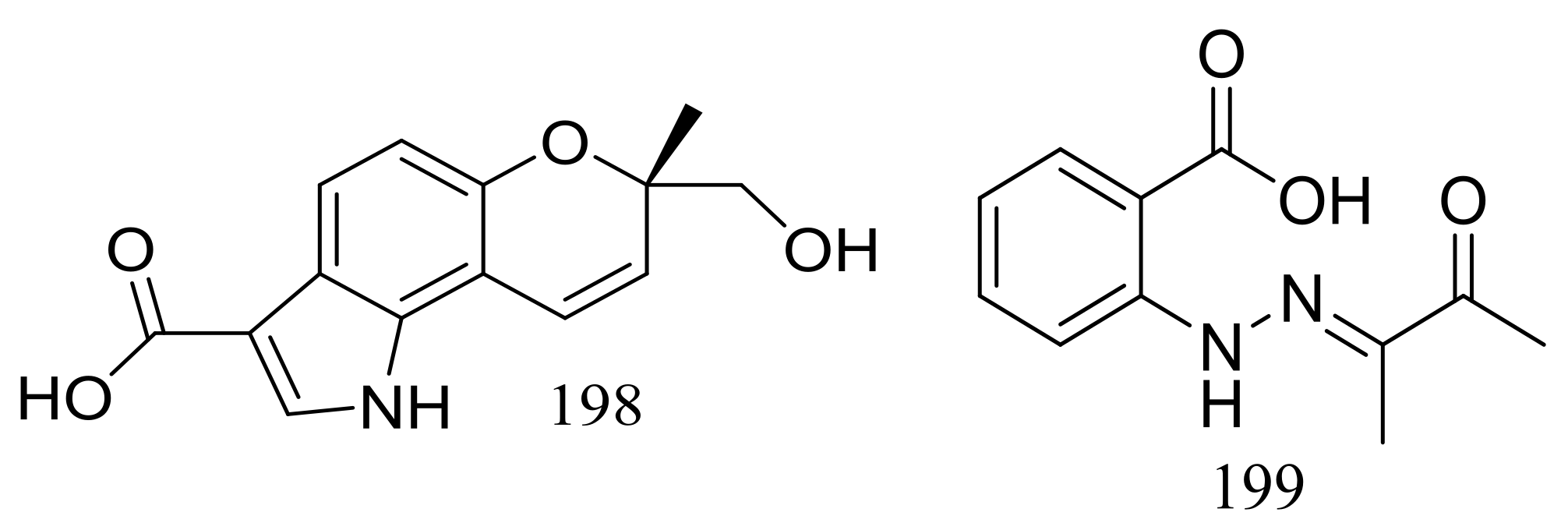
Exopisiod B (198) and farylhydrazone C (199) (Figure 33) were produced by a soil-derived fungus Penicillium sp. HDN14-431 collected from mesolittoral zone in Antarctic. Both compounds exhibited no cytotoxicity (K562, A549, HCT116, and HeLa cell lines) at IC50 > 10 μM, but compound 199 was slightly against Proteusbacillus vulgaris with an MIC value of 22.5 μM [68].
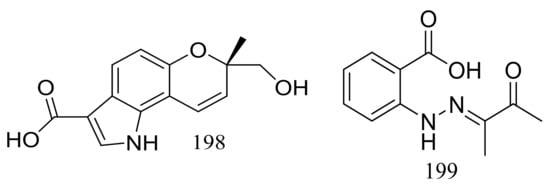
Figure 33.
Novel natural products derived from psychrophilic fungi (compounds 198–199).
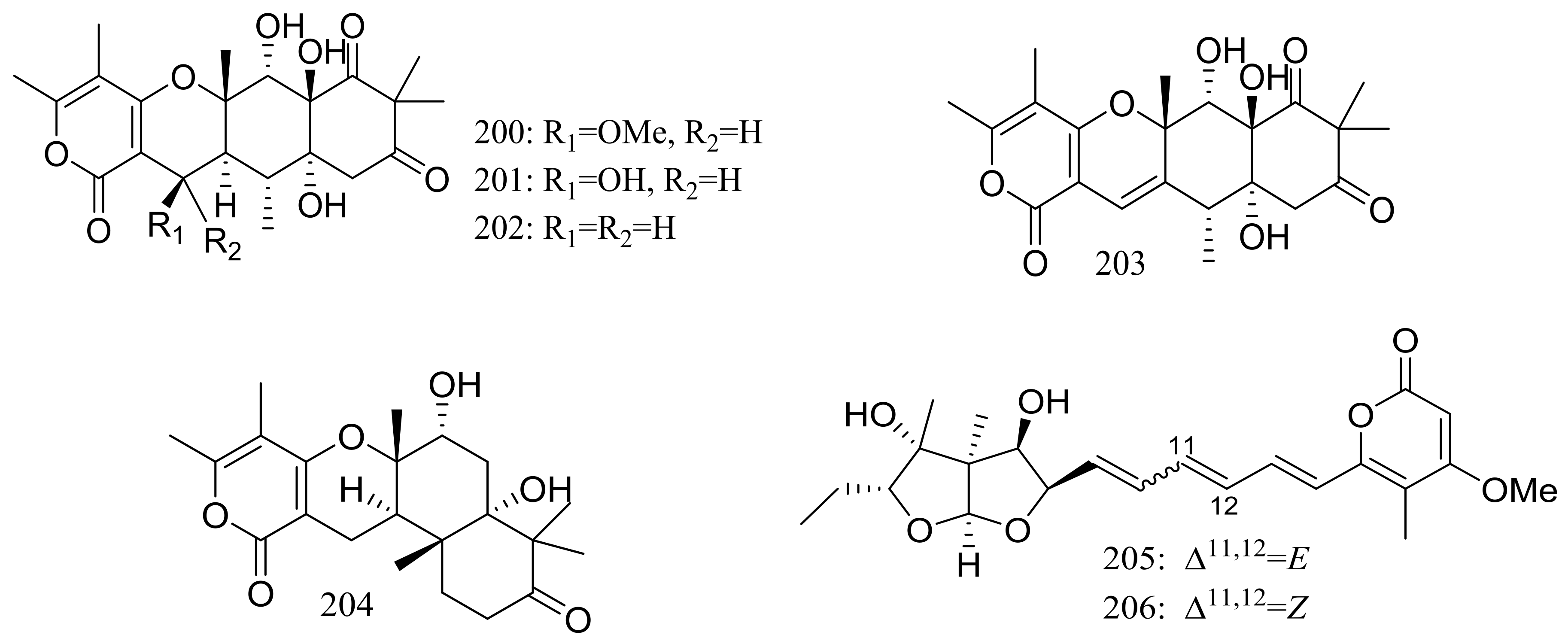
The soil-derived fungus Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis SCSIO 05702 collected near the Great Wall station (Chinese Antarctic station) yielded five new highly oxygenated α-pyrone merosesquiterpenoids named ochraceopones A–E (200–204), the known asteltoxin (205), and a new double bond isomer of asteltoxin named isoasteltoxin (206) (Figure 34). Compounds 200–203 possessed a linear tetracyclic carbon skeleton, which was distinguished from the reported angular tetracycle structure. Compounds 200, 205, and 206 displayed antiviral activity against the H1N1 and H3N2 influenza viruses with IC50 values of >20.0/12.2, 0.54/0.84, and 0.23/0.66 μM, respectively (the positive control tamiflu IC50 16.9/18.5 nM). In addition, the selectivity indexes (SI = CC50/IC50) of anti-H1N1 activity of 205 (SI = 0.44) and 206 (SI = 2.35) suggested that the geometry of the ∆11 double bond in the polyene chain might accelerate the anti-H1N1 activity and selectivity index [69].
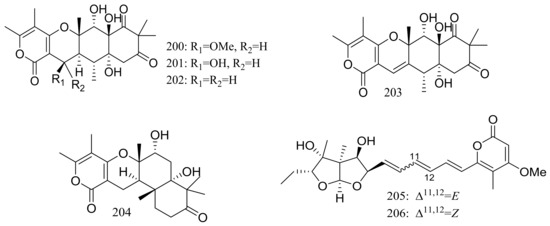
Figure 34.
Novel natural products derived from psychrophilic fungi (compounds 200–206).
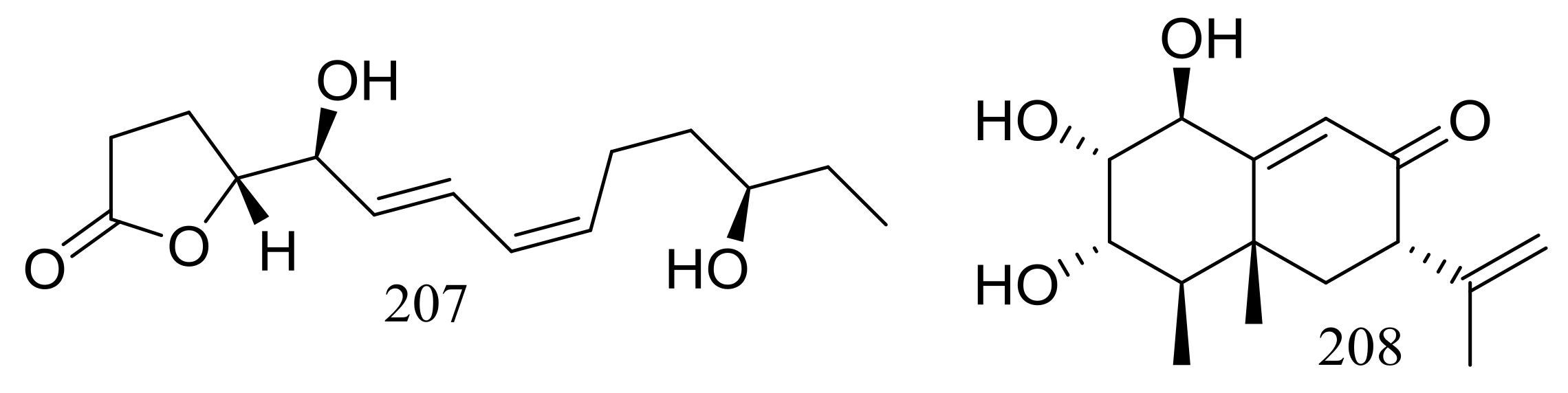
A furanone derivative, butanolide A (207) and a sesquiterpene, guignarderemophilane F (208) (Figure 35) were produced by the Antarctic seabed sediment-derived fungus Penicillium sp. S-1-18 via the bioassay guidance. Compound 207 could moderately inhibited protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) with an IC50 value of 27.4 μM [70].
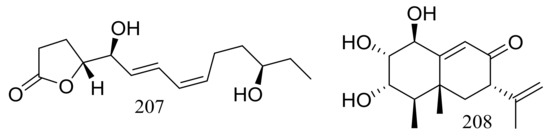
Figure 35.
Novel natural products derived from psychrophilic fungi (compounds 207–208).
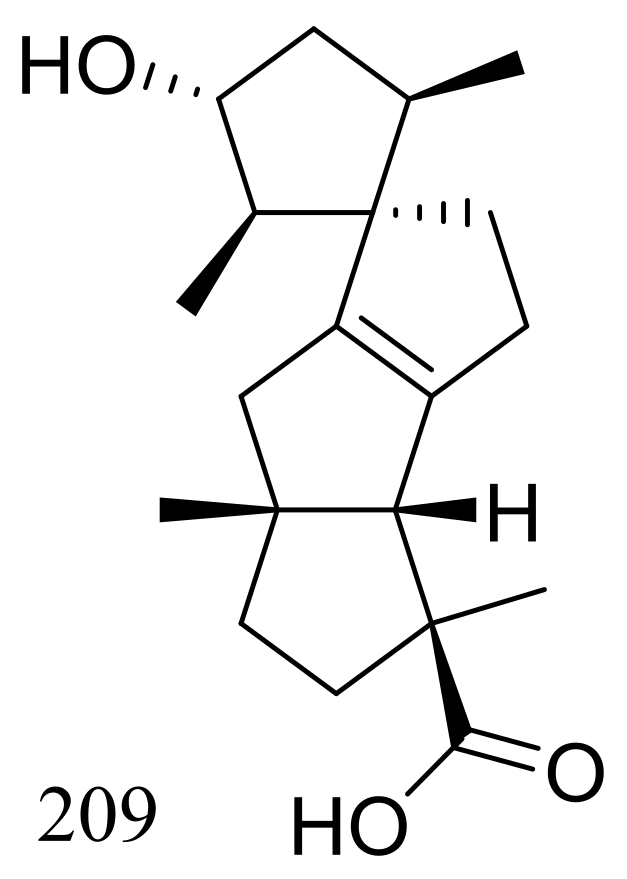
Penicillium granulatum MCCC 3A00475 obtained from the Prydz Bay of Antarctica yielded an unusual spirocyclic diterpene named spirograterpene A (209) (Figure 36). Antiallergic effect was tested in immunoglobulin E-mediated rat mast RBL-2H3 cells and compound 209 was just little weaker active than loratadine at 20 μg/mL [71].
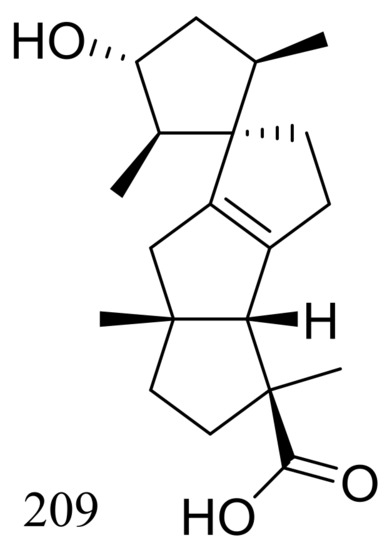
Figure 36.
Novel natural products derived from psychrophilic fungi (compound 209).
4. Thermophilic Fungi
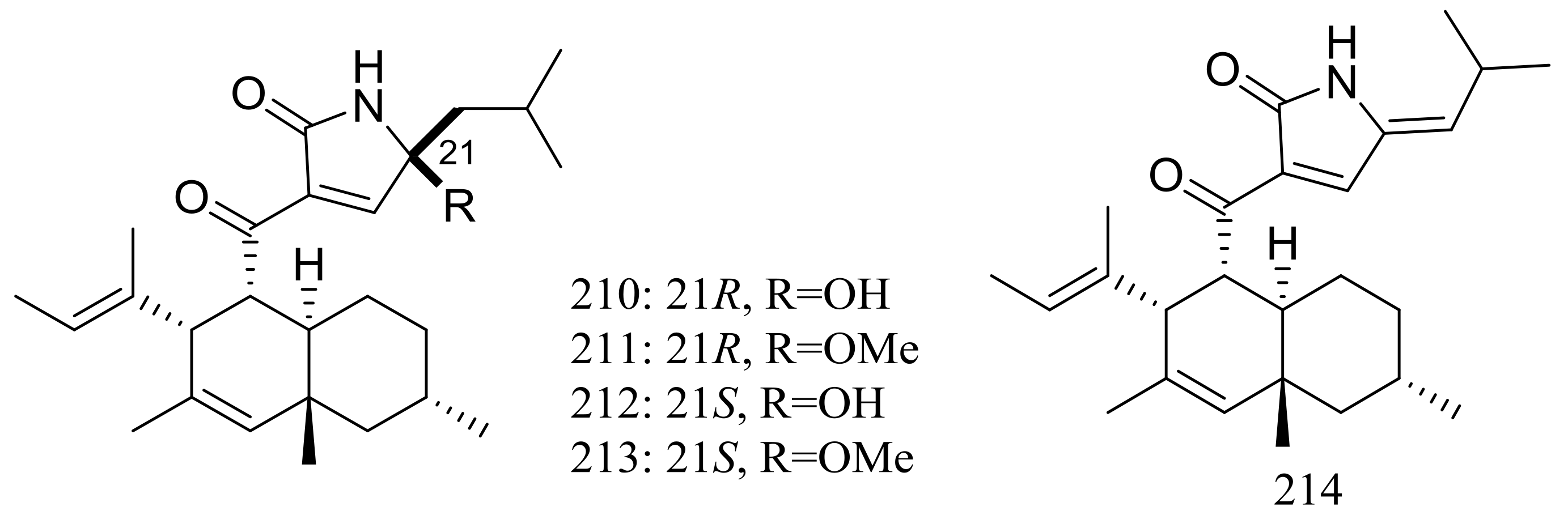
Five new polyketides (210–214) (Figure 37) were produced by Myceliophthora thermophila obtained from the soil of fumaroles in Taiwan. Compounds 210–212 showed cytotoxic activity against A549, Hep3B, MCF-7 and HepG2 cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 0.25 to 1.30 μg/mL [72].

Figure 37.
Novel natural products derived from thermophilic fungi (compounds 210–214).
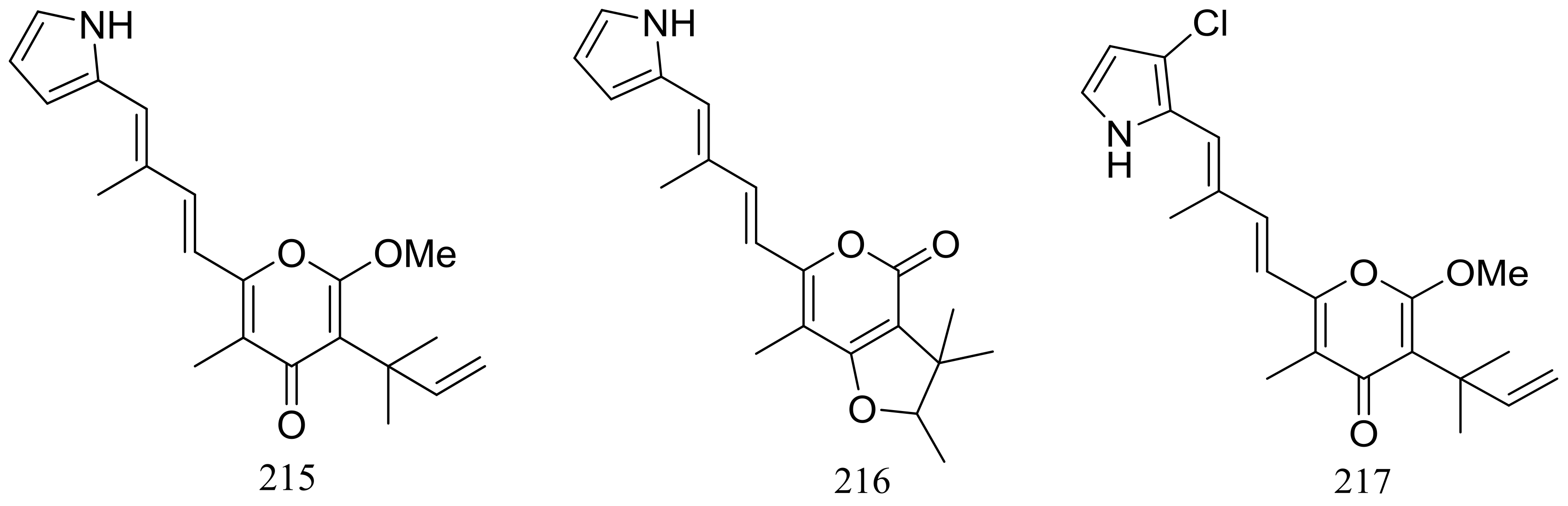
The EtOAc extract of the mass mycelium and PDA media of Malbranchea sulfurea which was obtained from the soil of fumaroles in Sihchong River Hot Spring Zone, displayed strong cytotoxicity against several cancer cell lines. Further bioassay-guided fractionation and chromatographic separation of the extract led to the isolation of six photosensitive polyketides named malbranpyrroles A–F (215–220) (Figure 38). Cytotoxic activities against PANC-1, HepG2 and MCF-7 cancer cell lines were tested and IC50 values for compounds 217–220 ranged from 3 to 11 μM. Flow cytometric measurement for cell cycle analysis showed that when treated by the malbranpyrroles the percentage of MCF-7 and HepG2 cells in G0/G1 phase was slightly increased, and the results suggested that these cytotoxic compounds could arrest the two cancer cell lines at G0 phase via inhibiting some cellular signaling pathways. According to the structure-bioactivity relations, the chlorine atom might be the pharmacophore for cytotoxicity [73].
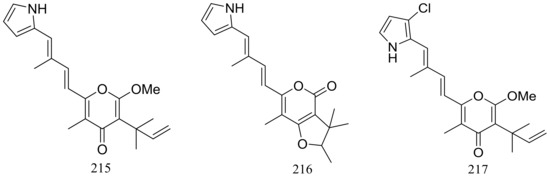

Figure 38.
Novel natural products derived from thermophilic fungi (compounds 215–220).
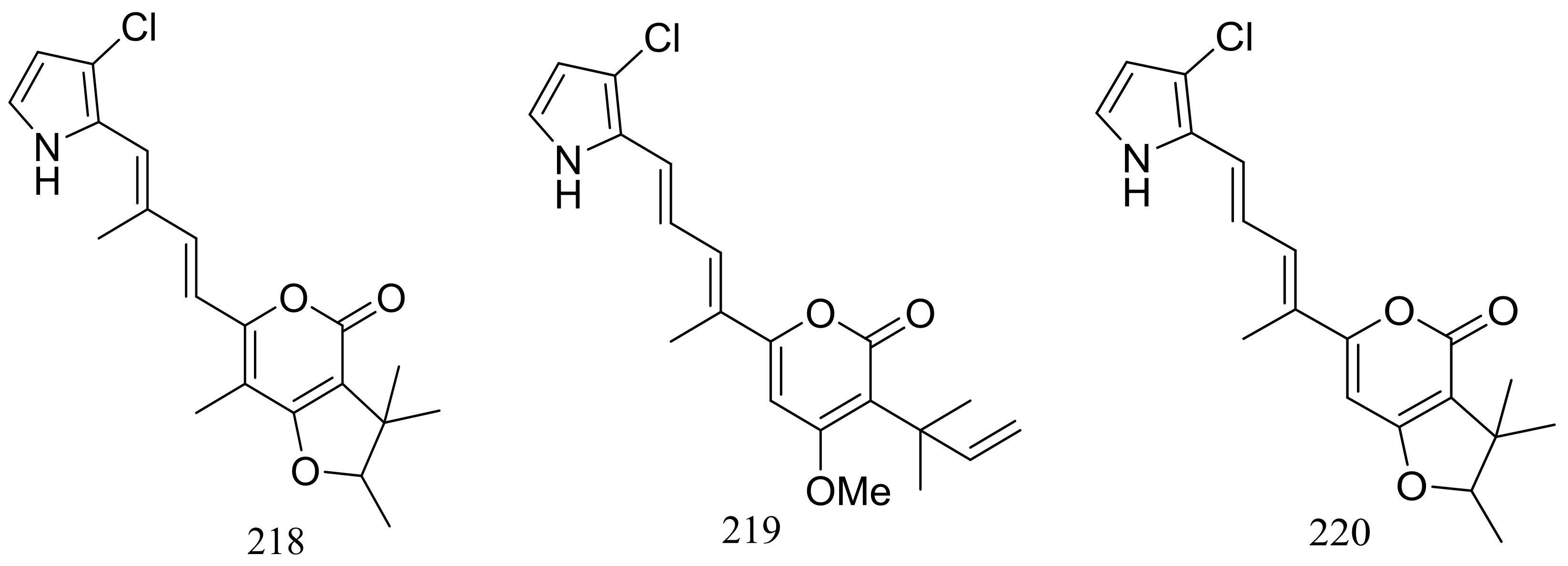
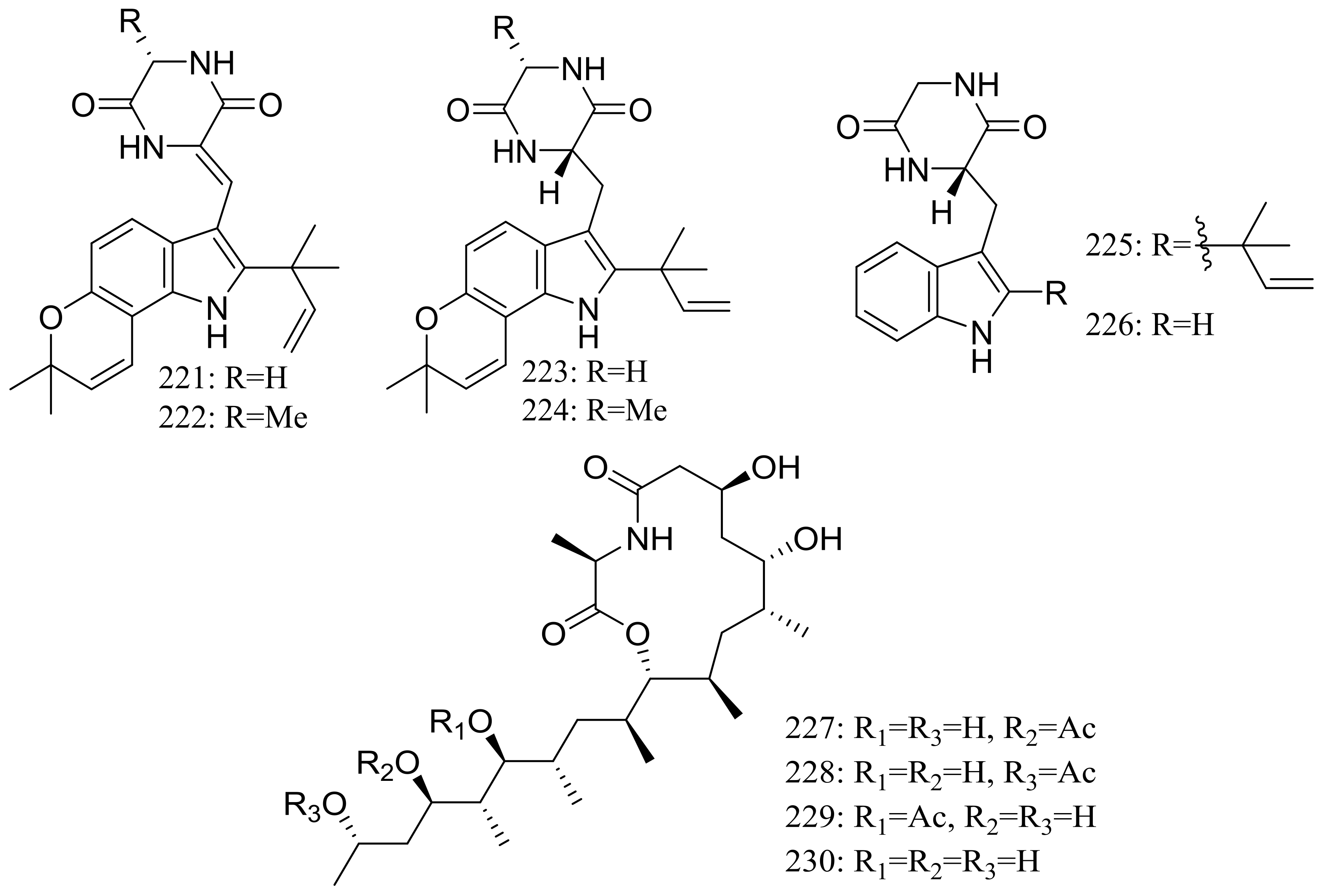
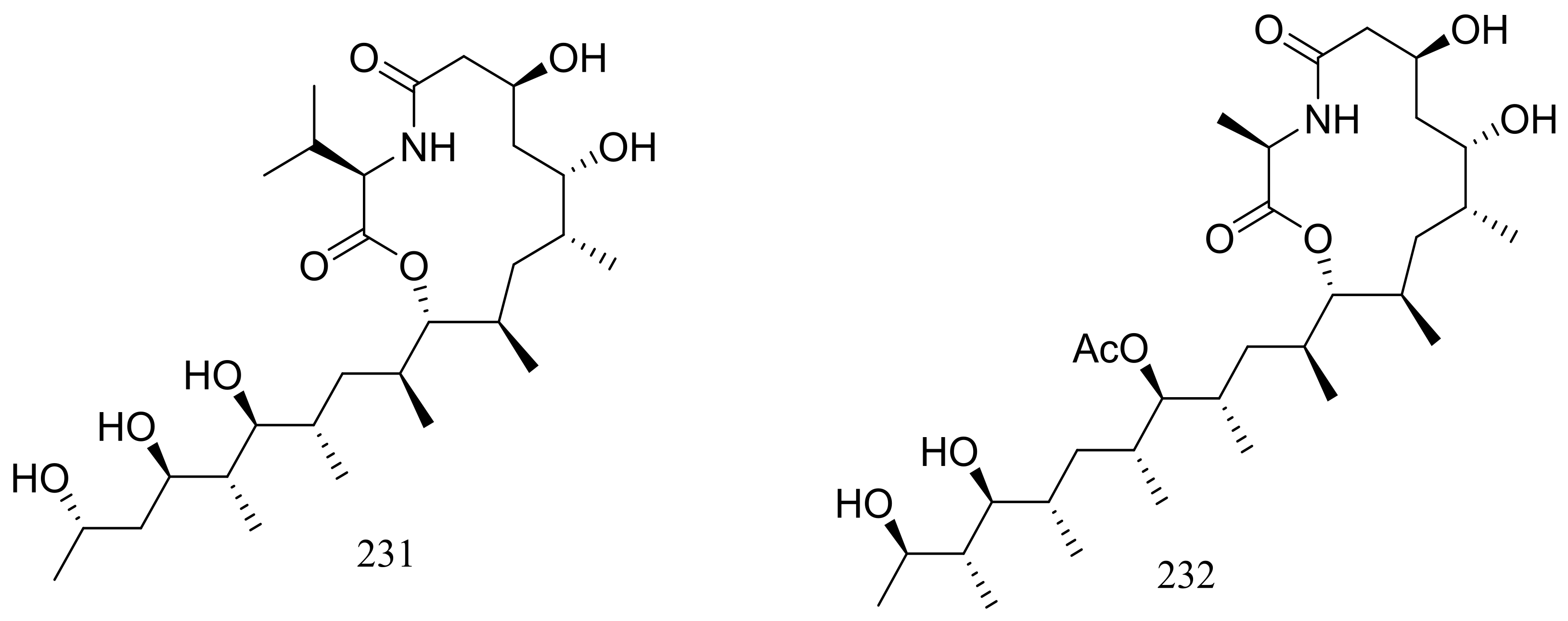
From two fungal strains Talaromyces thermophilus YM1-3 and YM3-4, both collected from Tengchong hot springs, six new indole alkaloids including talathermophilins A–B (221–222) (Figure 39) [74], two analogues of notoamide E (223 and 224), one analogue of preechinulin (225), and a natural occurring cyclo (glycyltryptophyl) (226) (Figure 39) [75], as well as a novel class of PKS-NRPS hybrid molecules named thermolides A–F (226–232) (Figure 39) [76] have been described. Compounds 221 and 222 exhibited moderate nematicidal activities against the worms of the free-living nematode Panagrellus redivivus with rates of 38% and 44% at 400 μg/mL for 72 h respectively. Compounds 227–232 possessed a 13-membered lactam-bearing macrolactone but only 227 and 228 displayed potent nematicidal activities against three notorious nematodes (Meloidogyne incognita, Bursaphelenches siylopilus, and Panagrellus redivivus) with LC50 values between 0.5 and 1 μg/mL. No information on the biological activities of compounds 223–226 was given.
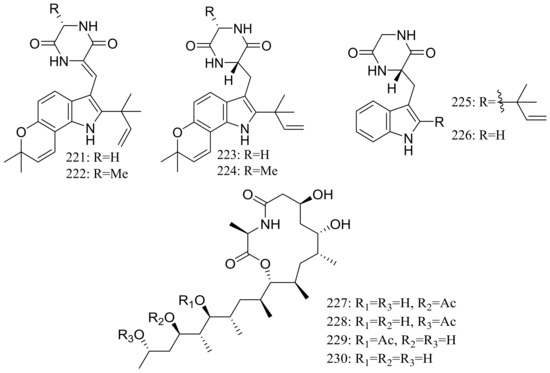
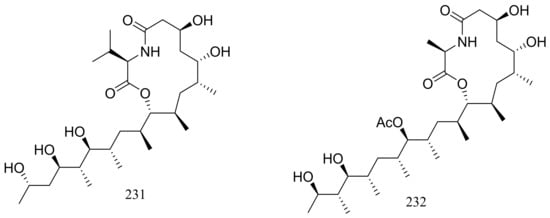
Figure 39.
Novel natural products derived from thermophilic fungi (compounds 221–232).
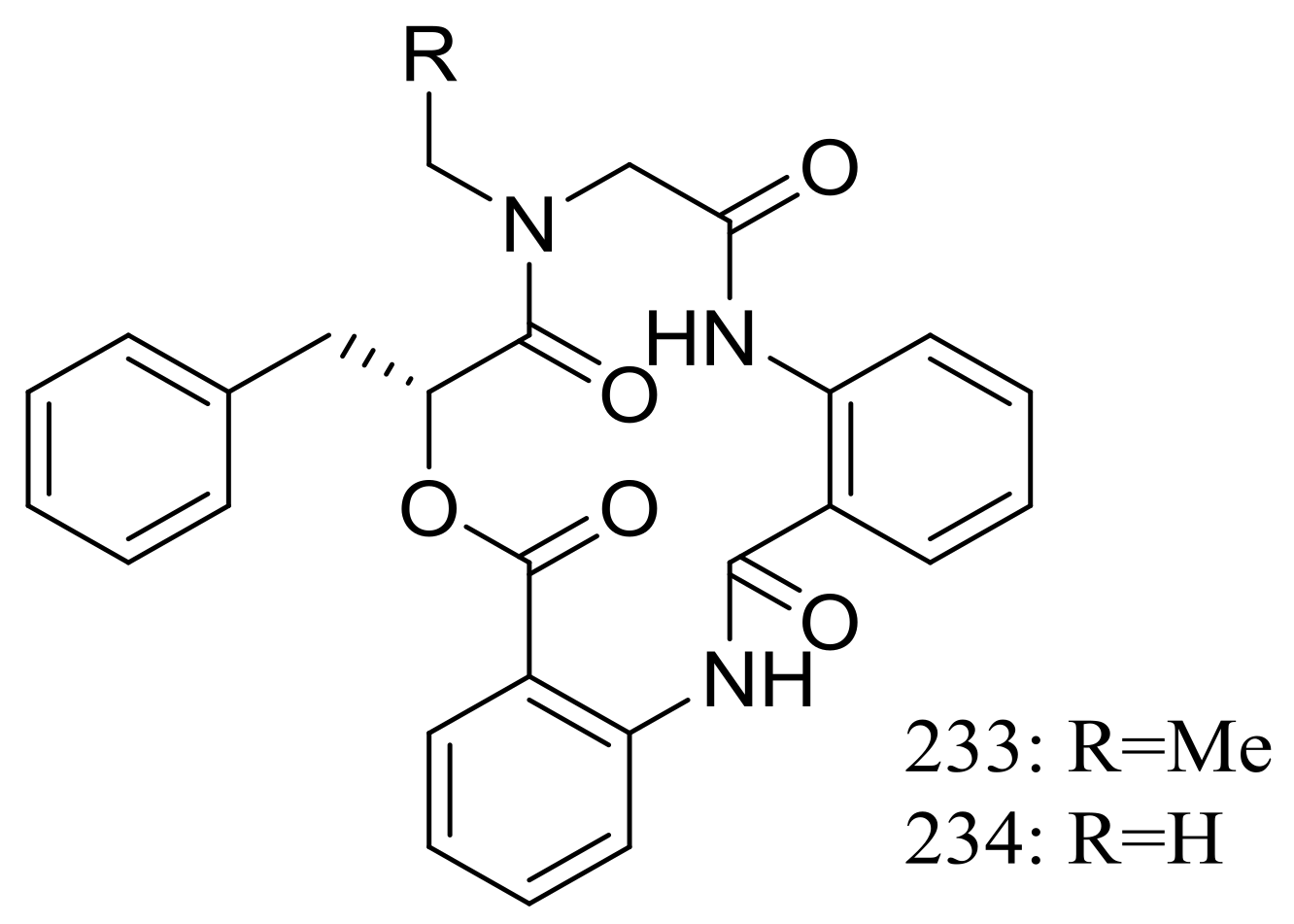
Clavatustides A–B (233–234) (Figure 40) containing an unusual anthranilic acid dimer and a D-phenyllactic acid residues were produced by Aspergillus clavatus C2WU isolated from the crab Xenograpsus testudinatus, which lived at extreme, toxic habitat around the sulphur-rich hydrothermal vents in Taiwan Kueishantao. The two novel cyclodepsipeptides significantly suppressed the proliferation of HepG2 cells in a dose-dependent manner, and cell cycle analysis suggested that 233 and 234 could induce G1 arrest and inhibit G1/S phase transition [77].
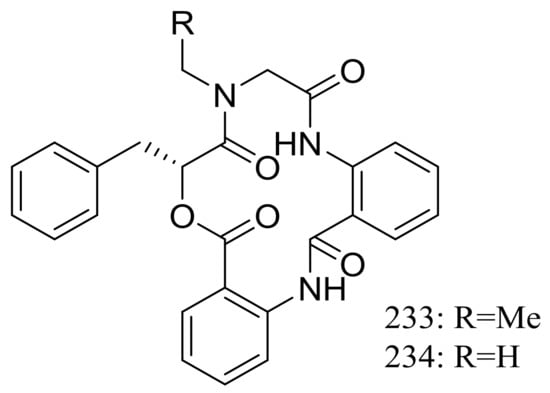
Figure 40.
Novel natural products derived from thermophilic fungi (compounds 233–234).
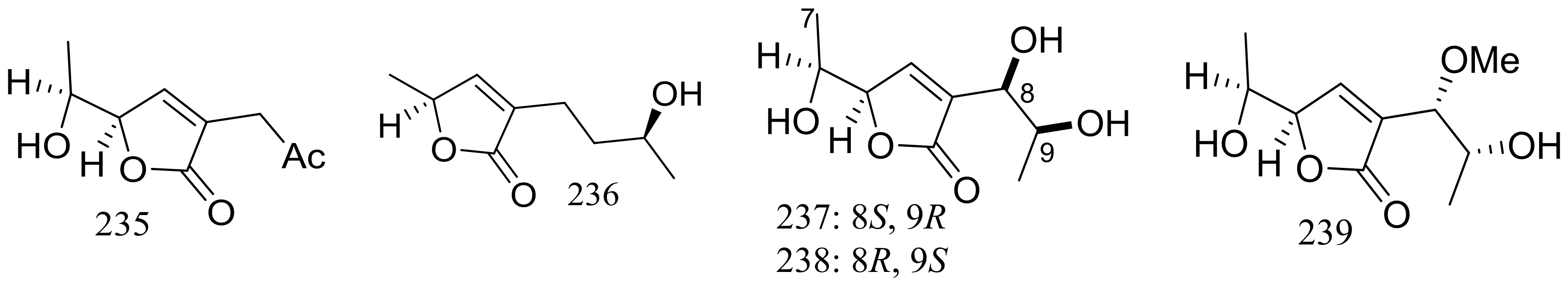
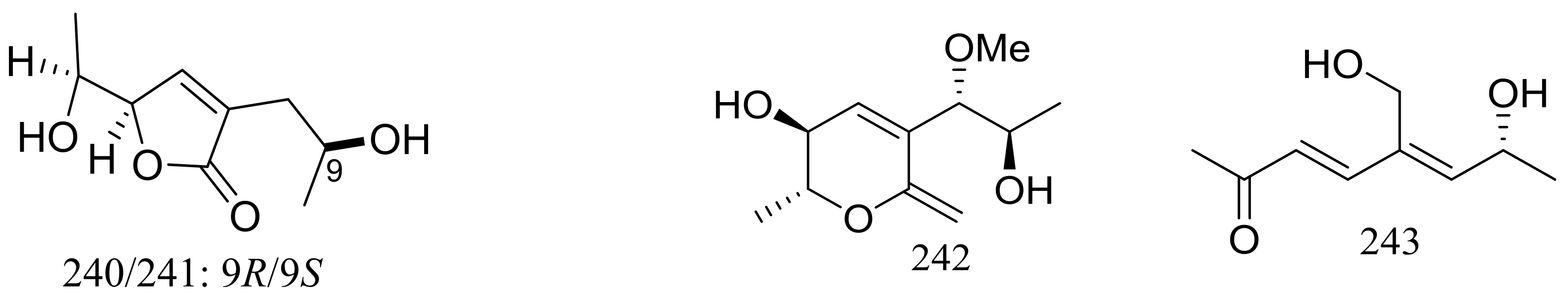
Nine new C9 polyketides named aspiketolactonol (235), aspilactonols A–F (236–241), aspyronol (242) and epiaspinonediol (243) (Figure 41) have been described as metabolites of Aspergillus sp. 16-02-1, which was collected at a Lau Basin hydrothermal vent (depth 2255 m, 114 °C) in the Southwest Pacific. Compounds 240 and 241 were obtained as a mixture in a diastereomeric ratio of 1:1. The possible biosynthetic pathways for all compounds were proposed and discussed. The cytotoxic activities (IC50 value) against HL-60 cells of compounds 242 and 243 were 241.2 and 192.9 μM respectively. For compounds 235–241 very weak cytotoxic activities (K562, HL-60, HeLa, or BGC-823) were observed with inhibitory rates less than 20% at 100 μg/mL [78].


Figure 41.
Novel natural products derived from thermophilic fungi (compounds 235–243).
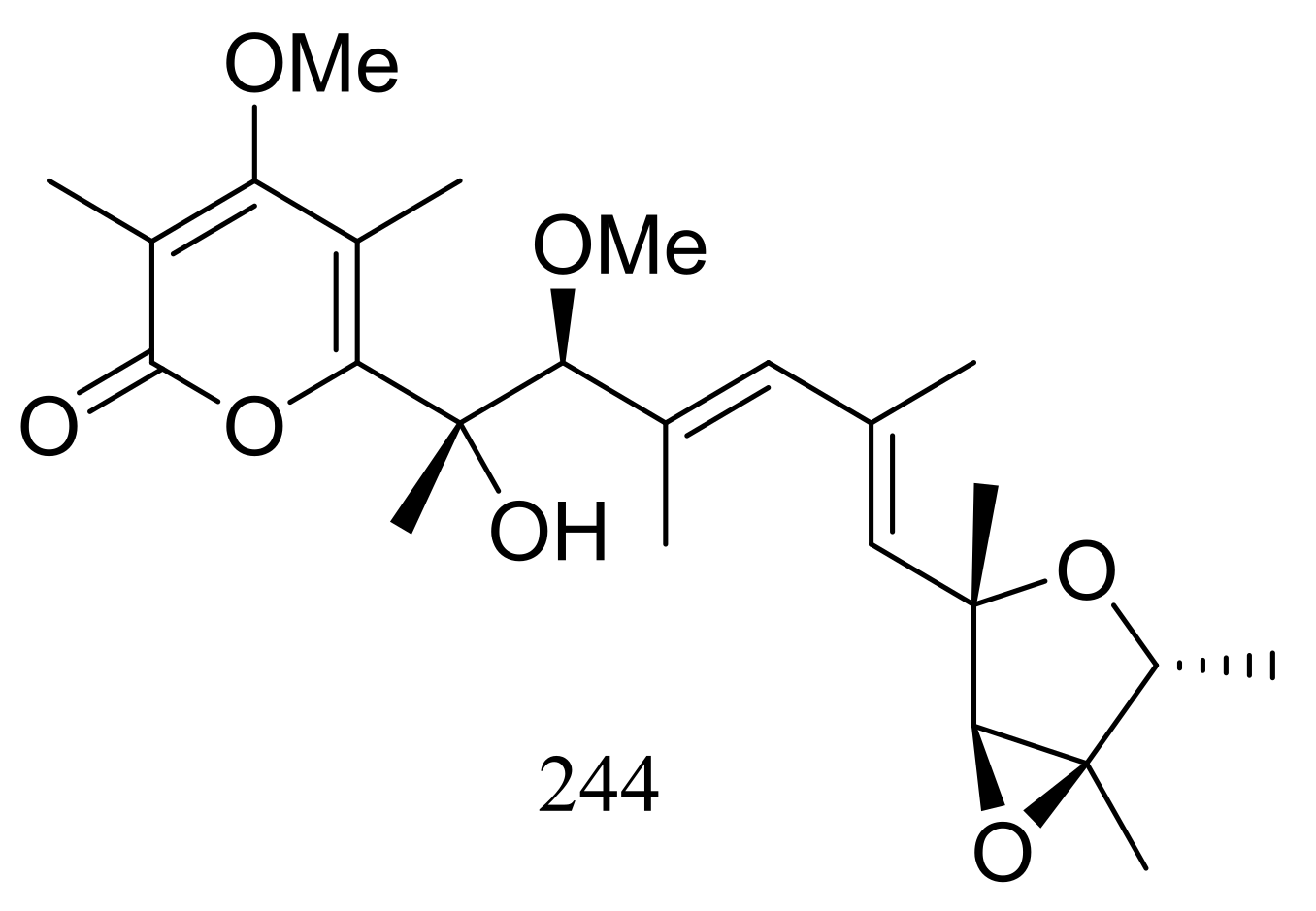
A hydrothermal vent fungus Penicillium sp. Y-50-10 collected from the sulfur rich sediment (Kueishantao, Taiwan) yielded methyl isoverrucosidinol (244) (Figure 42). This new verrucosidin derivative displayed weak antibiotic activity against Bacillus subtilis with an MIC value of 32 μg/mL [79].
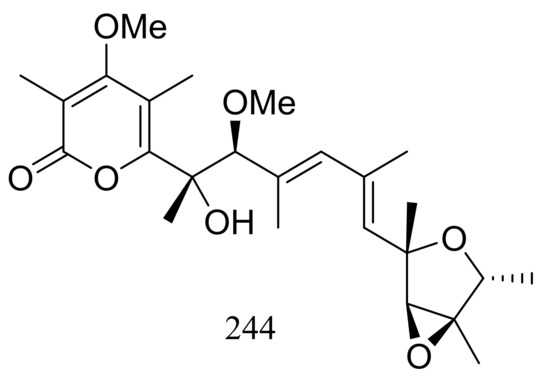
Figure 42.
Novel natural products derived from thermophilic fungi (compound 244).
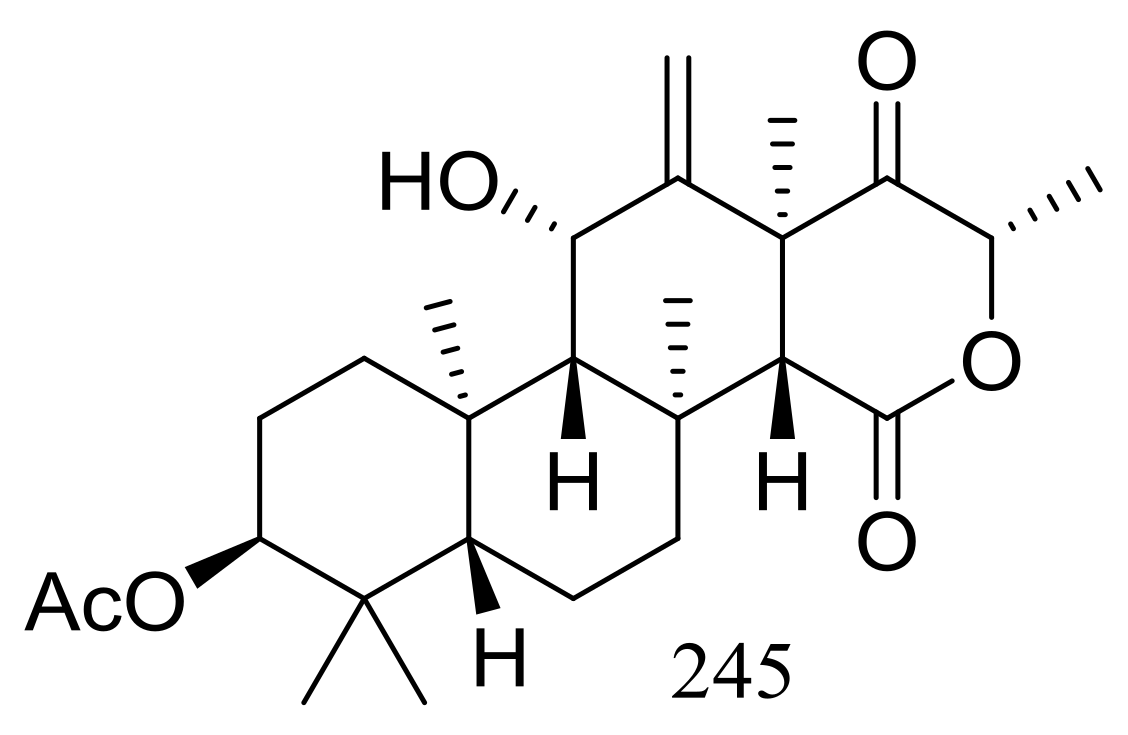
The soil-derived thermophilic fungal strain Aspergillus terreus TM8 collected from a hot desert place (~50 °C) in South Egypt produced a new highly oxygenated tetracyclic meroterpenoid, terretonin M (245) (Figure 43). The crude extract of the mass mycelium and solid rice meida could slightly inhibit the growth of Proteus sp., Candida albicans, and Streptococcus pyogenes, while authors failed to isolate the active ingredient [80].
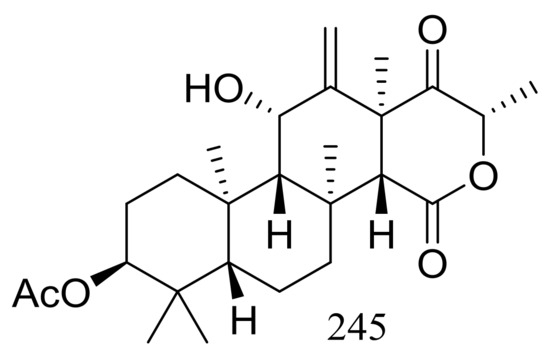
Figure 43.
Novel natural products derived from thermophilic fungi (compound 245).
5. Halophilic Fungi
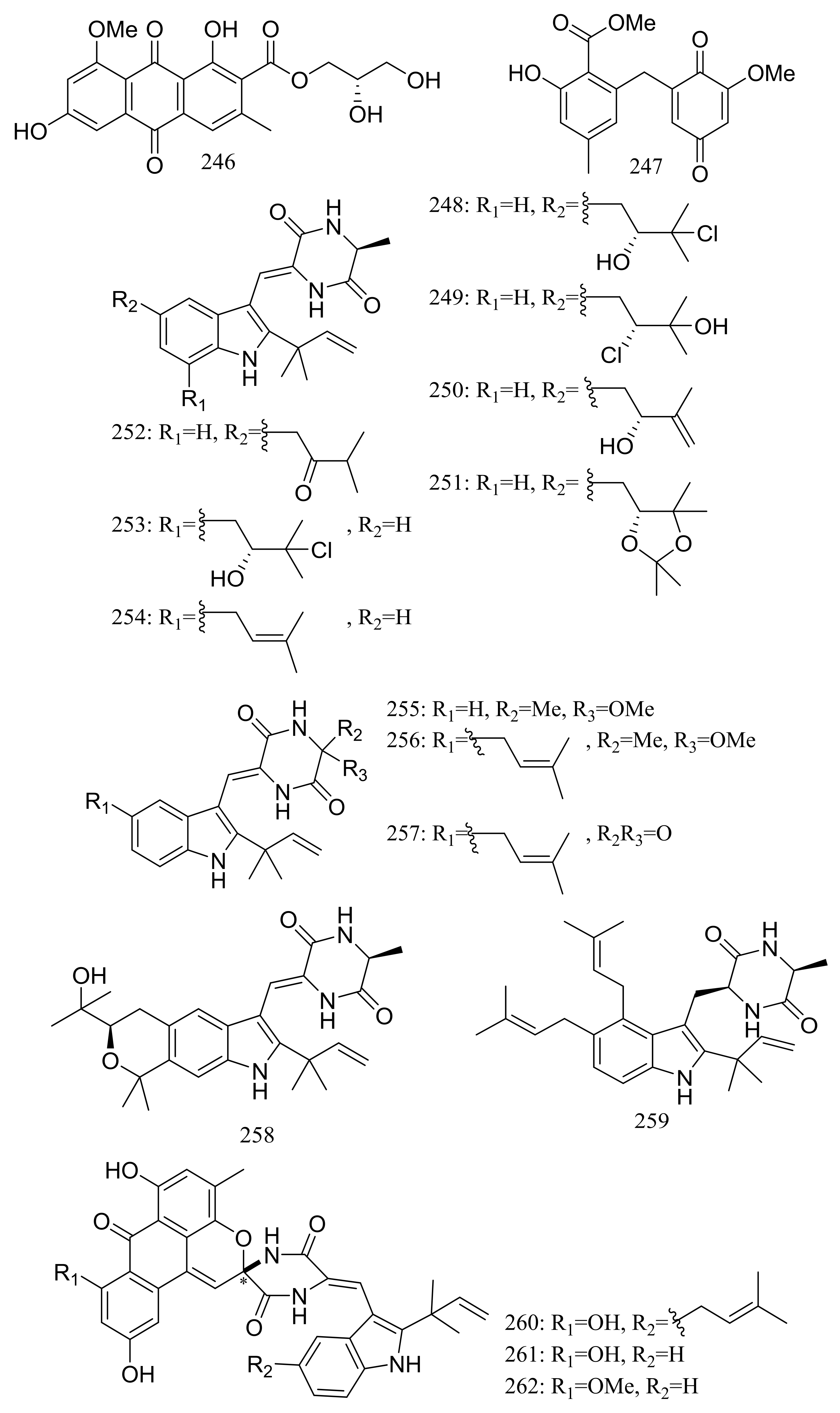
Diverse novel compounds have been described from the halotolerant fungal strain Aspergillus variecolor B-17, which was isolated from the sediments collected in Jilantai salt field, Alashan, Inner Mongolia, China. Variecolorquinones A–B (246–247) (Figure 44) are two new quinone type compounds with cytotoxic activities against A549 cells (compound 246, IC50 3.0 μM), HL60 cells (compound 247, IC50 1.3 μM) and P388 cells (compound 247, IC50 3.7 μM) [81]. Variecolorins A–L (248–259) (Figure 44) exhibited no cytotoxicity (P388, HL-60, BEL-7402, and A-549 cell lines) but A–K (248–258) showed weak radical-scavenging activity against DPPH with IC50 values ranging from 75 to 102 μM [82]. Variecolortides A–C (260–262) (Figure 44) shared an unprecedented ‘spiro-anthronopyranoid diketopiperazine’ structure with a stable hemiaminal function. All three compounds showed weak cytotoxic activity against K-562 cell line with IC50 values of 61, 69 and 71 μM respectively (the positive control paclitaxel IC50 0.93 μM) and showed very slight radical-scavenging activity against DPPH radical with IC50 values of 63, 84 and 91 μM, respectively (the positive control vitamin C IC50 22 μM) [83].
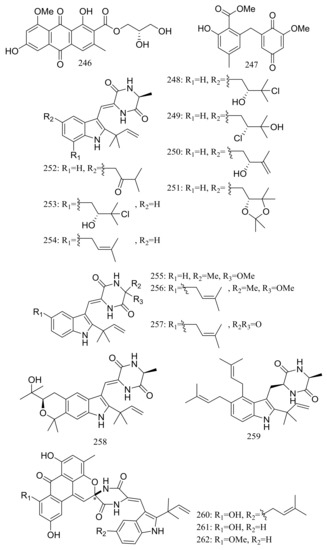
Figure 44.
Novel natural products derived from halophilic fungi (compounds 246–262). * Absolute configuration is not determined.
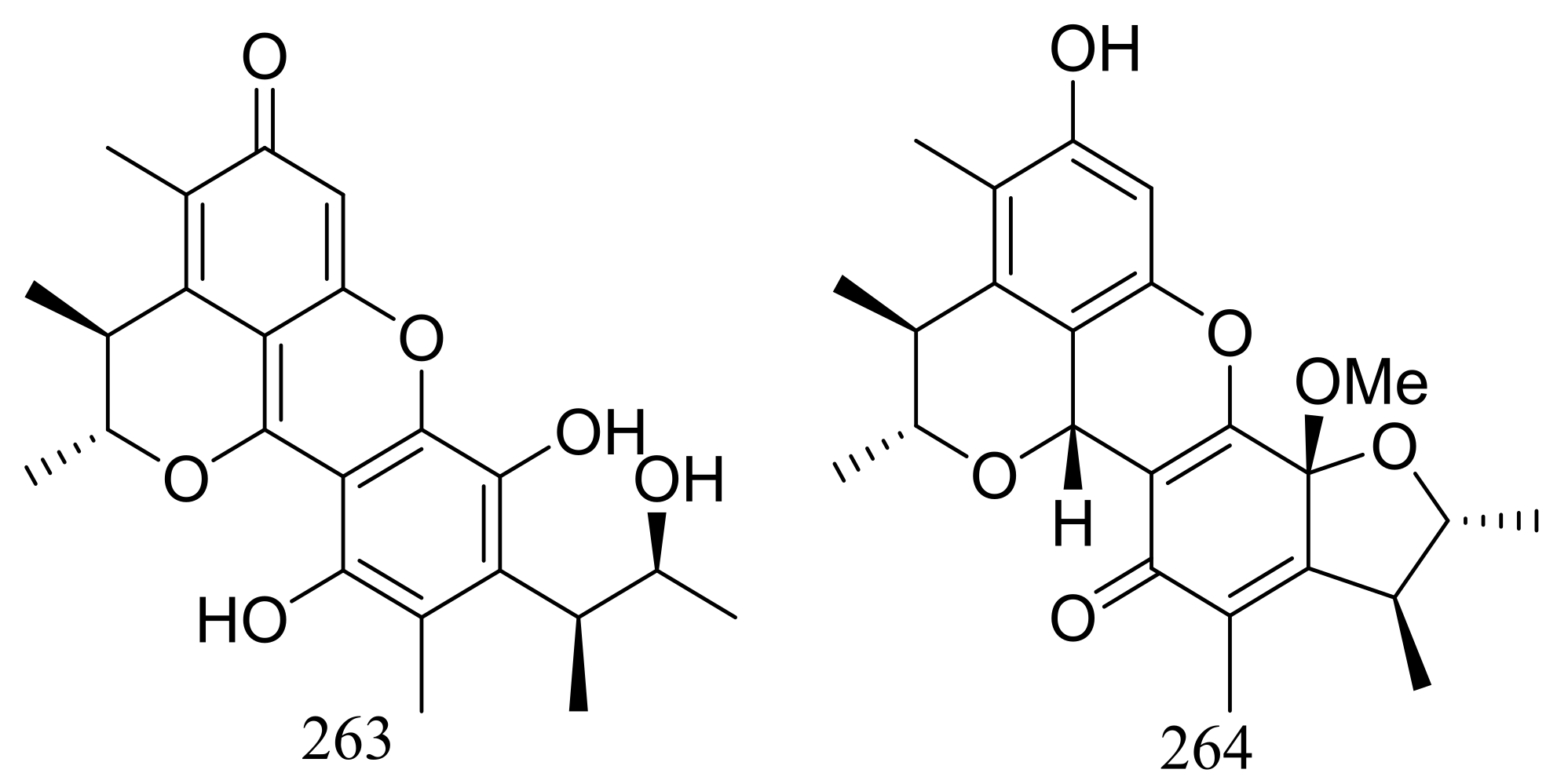
Pennicitrinone C (263) and penicitrinol B (264) (Figure 45), two new citrinin dimers were produced by the halotolerant fungal strain Penicillium citrinum B-57 obtained from the sediments in Jilantai salt field, Alashan, Inner Mongolia, China. Compound 263 scavenged DPPH radicals with IC50 value of 55.3 μM (the positive control L-ascorbic acid IC50 22.7 μM) but exhibited no cytotoxic activity against P388, A549, BEL7402 or HL60 cell lines (IC50 > 50 μM) [84].
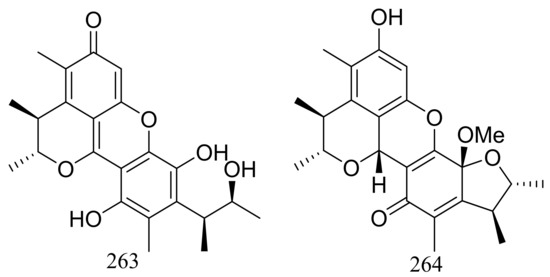
Figure 45.
Novel natural products derived from halophilic fungi (compounds 263–264).
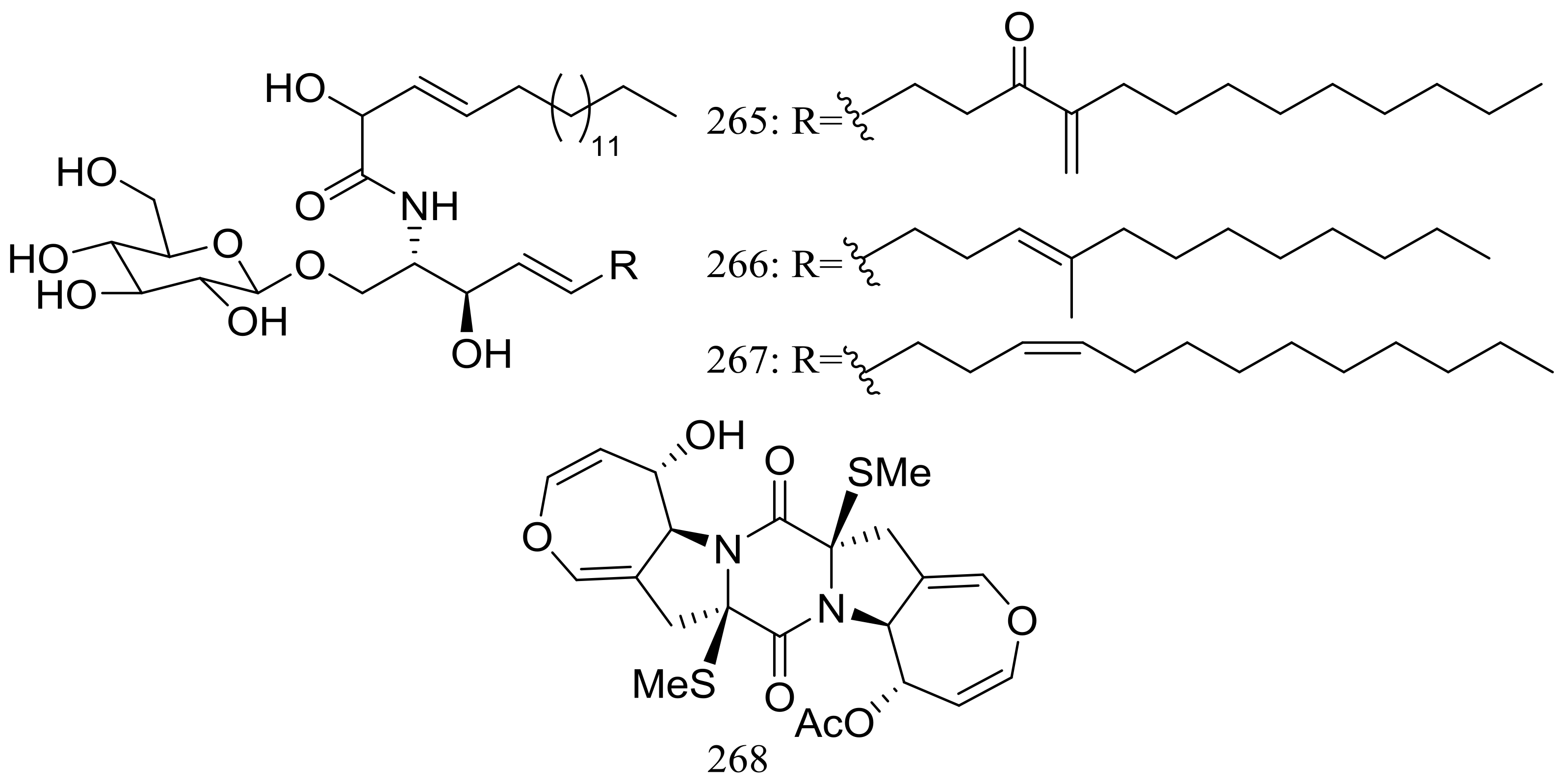
Three new cerebrosides, alternarosides A–C (265–267) and one new diketopiperazine alkaloid, alternarosin A (268) (Figure 46) were produced by the halotolerant fungus Alternaria raphani THW-18, which was obtained from a sediment sample in the Hongdao sea salt field, China. Antimicrobial activities against Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Candida albicans were evaluated and MIC values for four compounds ranged from 70 to 400 μM. Neither cytotoxicity (P388, HL-60, A549, and BEL-7402 cell lines) nor DPPH radical-scavenging activity was detected [85].
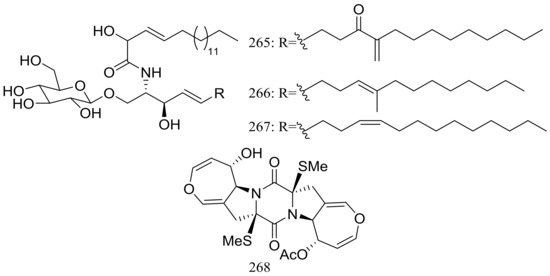
Figure 46.
Novel natural products derived from halophilic fungi (compounds 265–268).
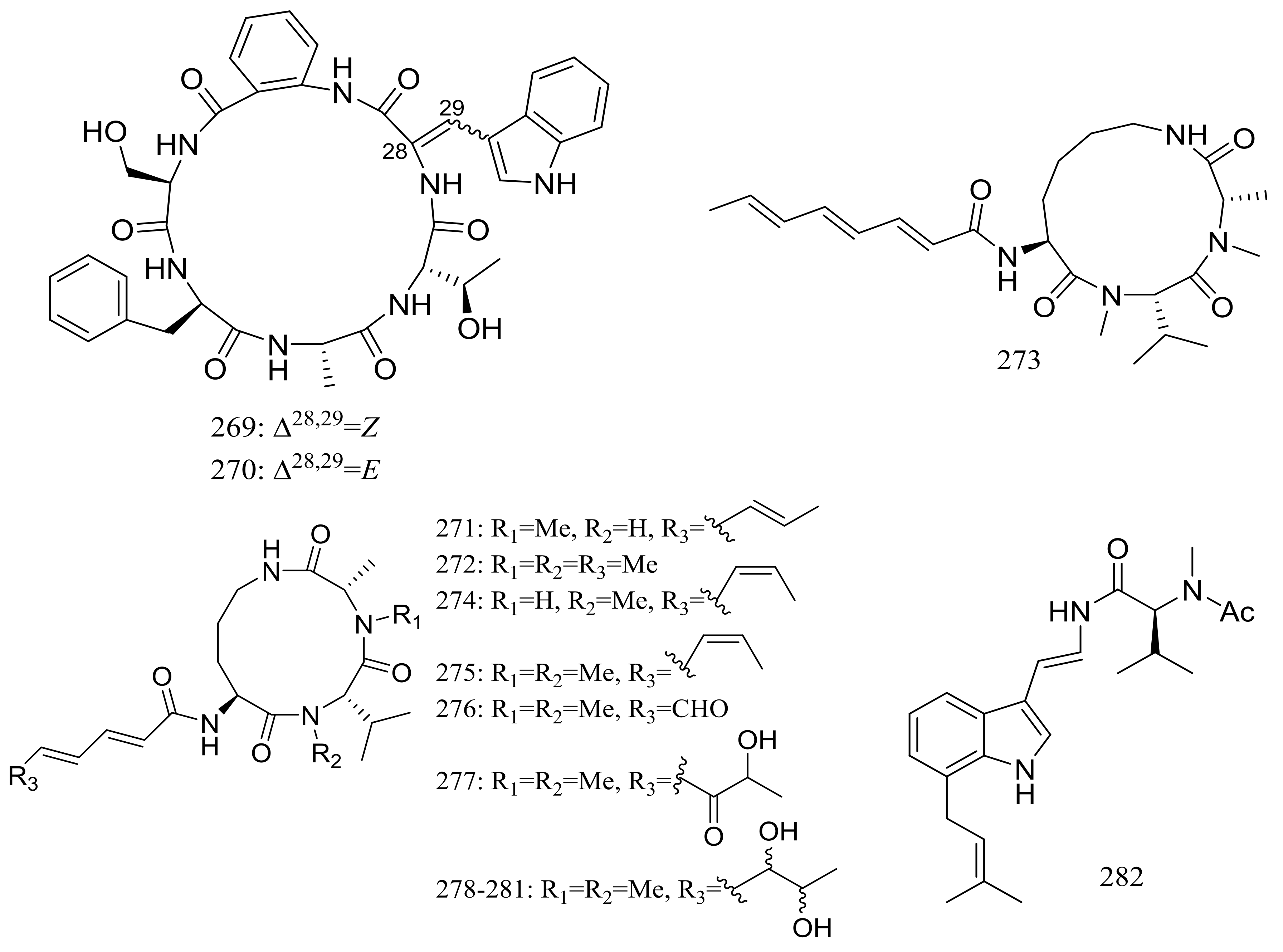
Sclerotides A–B (269–270) (Figure 47) were novel cyclic hexapeptides produced by the halotolerant Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 (the Putian Sea Salt Field, China) in a nutrient-limited hypersaline medium. In the general bioactivity profiling programs including cytotoxic and antimicrobial testing, both compounds inhibited Candida albicans with MIC values of 7.0 and 3.5 μM respectively. Besides, compound 270 displayed weak cytotoxic activity against HL-60 cells (IC50 56.1 μM) and antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa (MIC 35.3 μM) [86]. The same research group subsequently obtained eleven new aspochracin-type cyclic tripeptides named sclerotiotides A–K (271–281) (Figure 47) [87] and one new cytotoxic indole-3-ethenamide (282) (Figure 47) [88] from the same halotolerant fungal strain in a nutrient-rich hypersaline medium. Compounds 278–281 were four isomers with the same molecular formula, and the NMR data suggested that 278/280 and 279/281 were enantiotopic in the fatty acid moiety respectively. When evaluated for antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities compounds 271, 272, 276, and 279 exhibited antifungal activities against Candida albicans with MIC values of 7.5, 3.8, 30, and 6.7 μM respectively, while compound 282 showed cytotoxic activity against A-549 and HL-60 cells with IC50 values of 3.0 and 27 μM respectively.

Figure 47.
Novel natural products derived from halophilic fungi (compounds 269–282).
6. Xerophilic Fungi
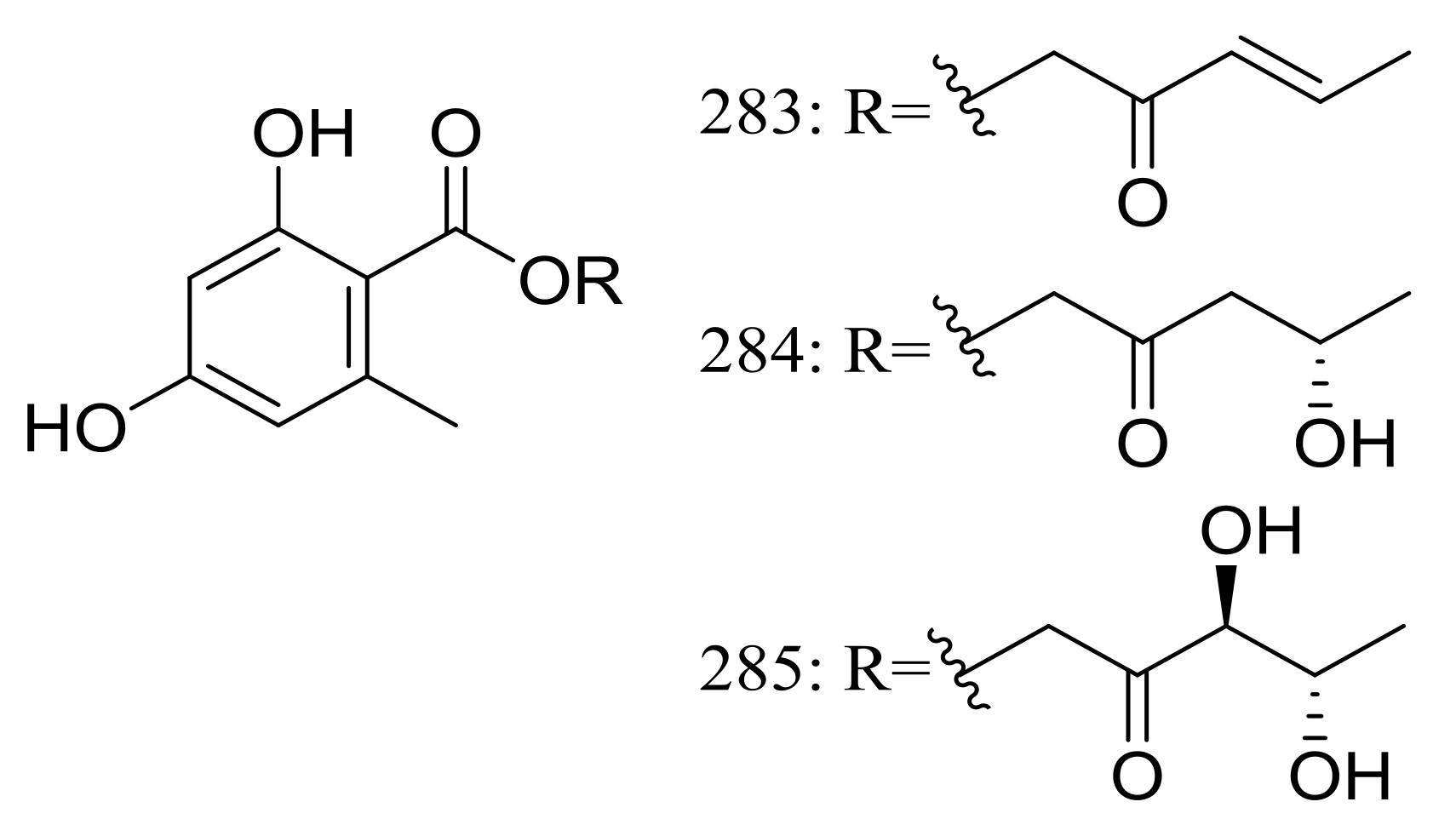
Globosumones A–C (283–285) (Figure 48) are three new esters of orsellinic acid isolated from Chaetomium globosum endophytic on Ephedra fasciculata (Mormon tea), which was collected from the Sonoran Desert. Cytotoxic activities against four cancer cell lines (NCI-H460, MCF-7, SF-268, and MIA Pa Ca-2) were tested and only compounds 283 and 284 were moderately active with IC50 values of 6.5 to 30.2 μM (the positive control doxorubicin IC50 0.01 to 0.07 μM) [89].
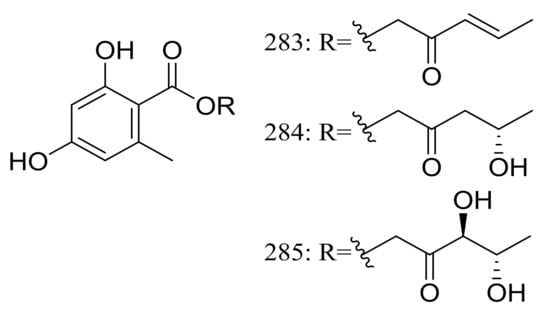
Figure 48.
Novel natural products derived from xerophilic fungi (compounds 283–285).
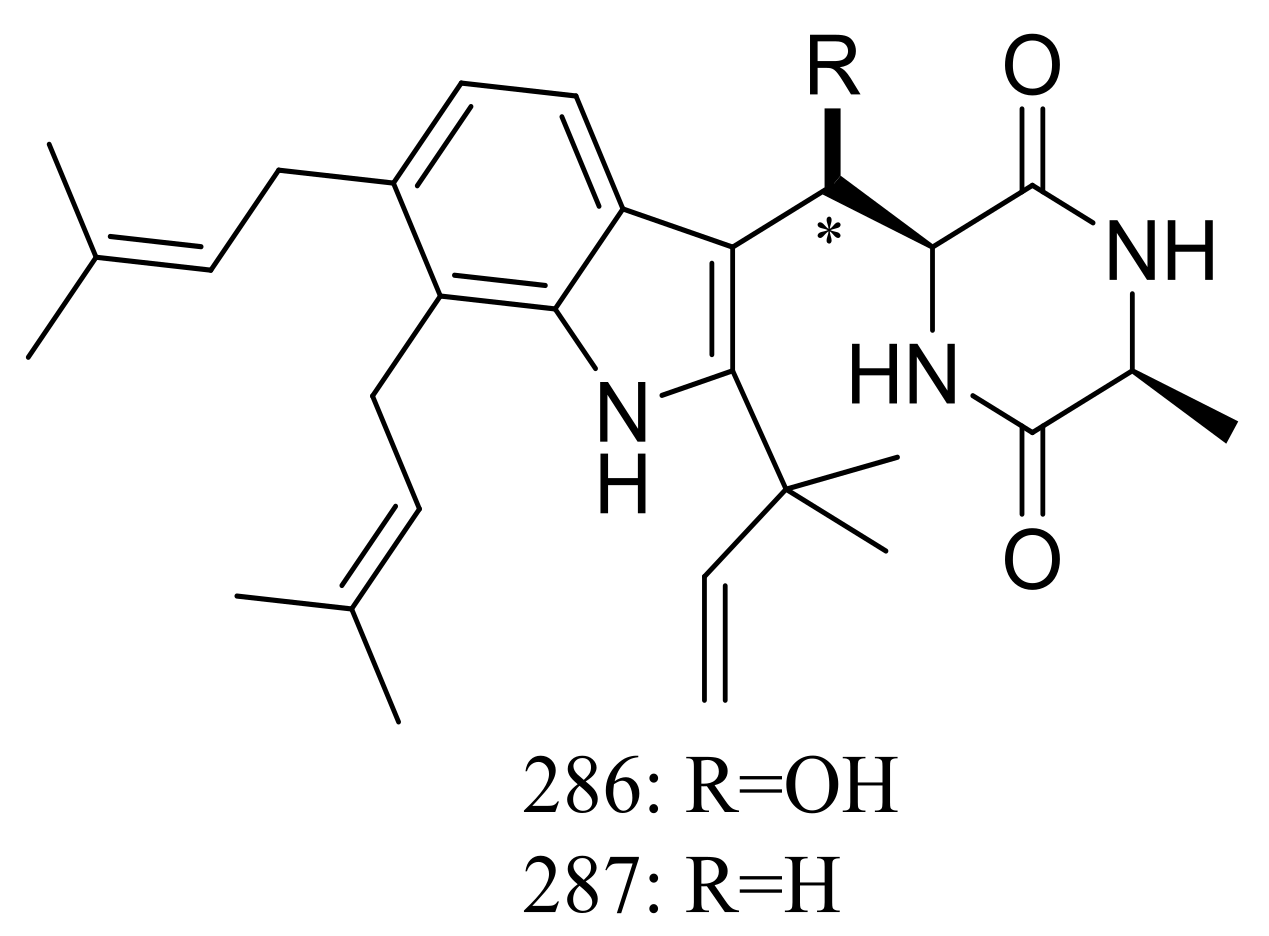
The xerophilic fungus Aspergillus restrictus A-17 obtained from house dust yielded two new dioxopiperazine derivatives, arestrictins A–B (286–287) (Figure 49). The biological activity of them was not tested [90].
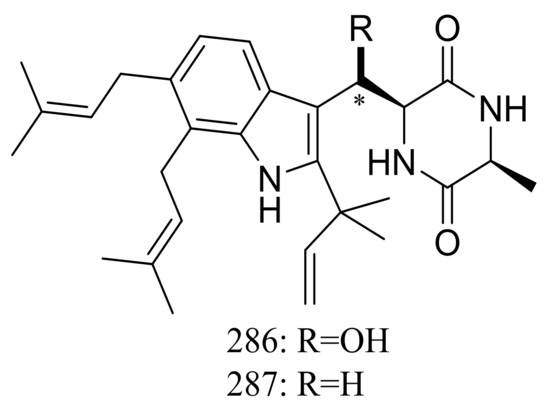
Figure 49.
Novel natural products derived from xerophilic fungi (compounds 286–287). * Absolute configuration is not determined.
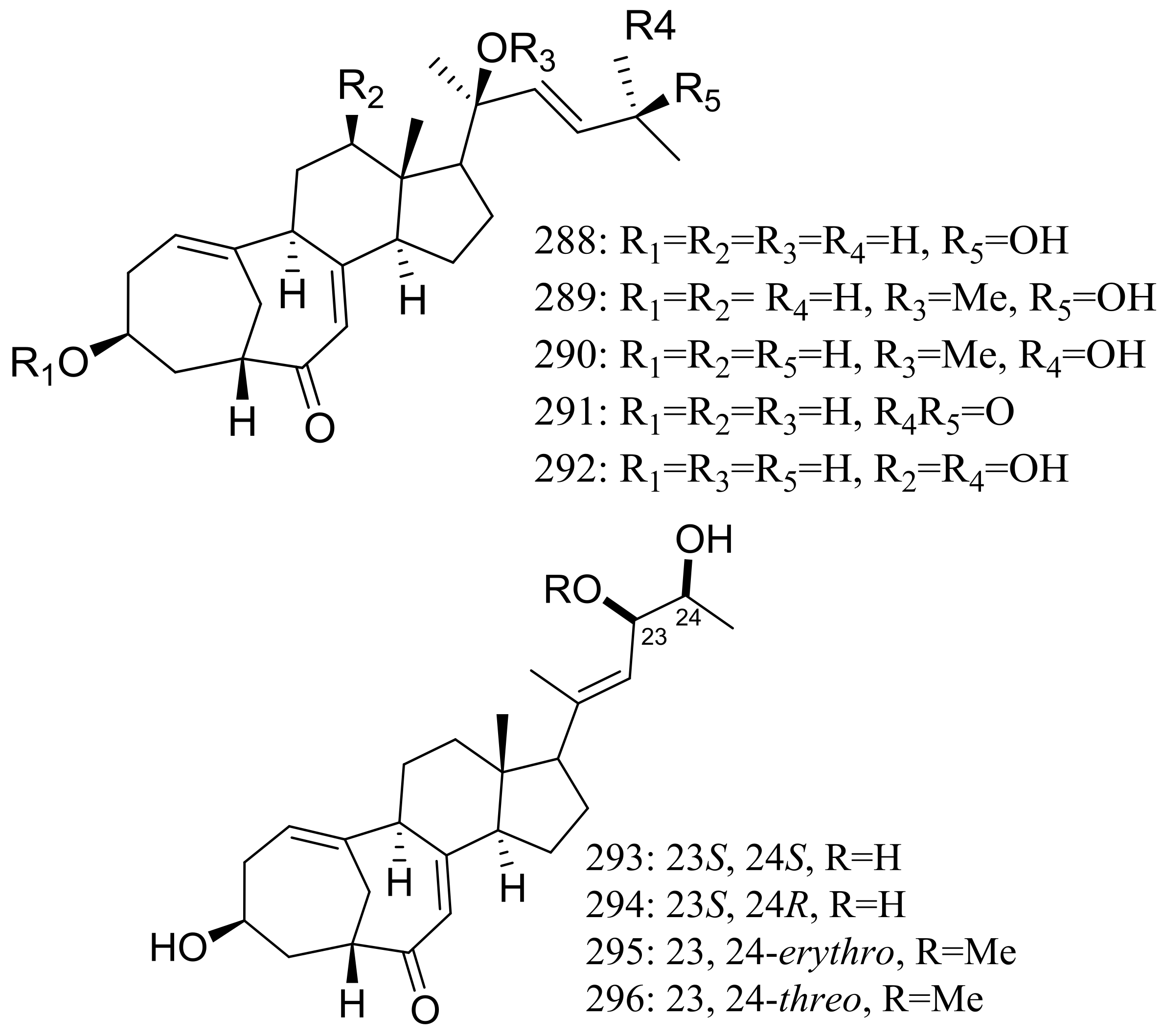
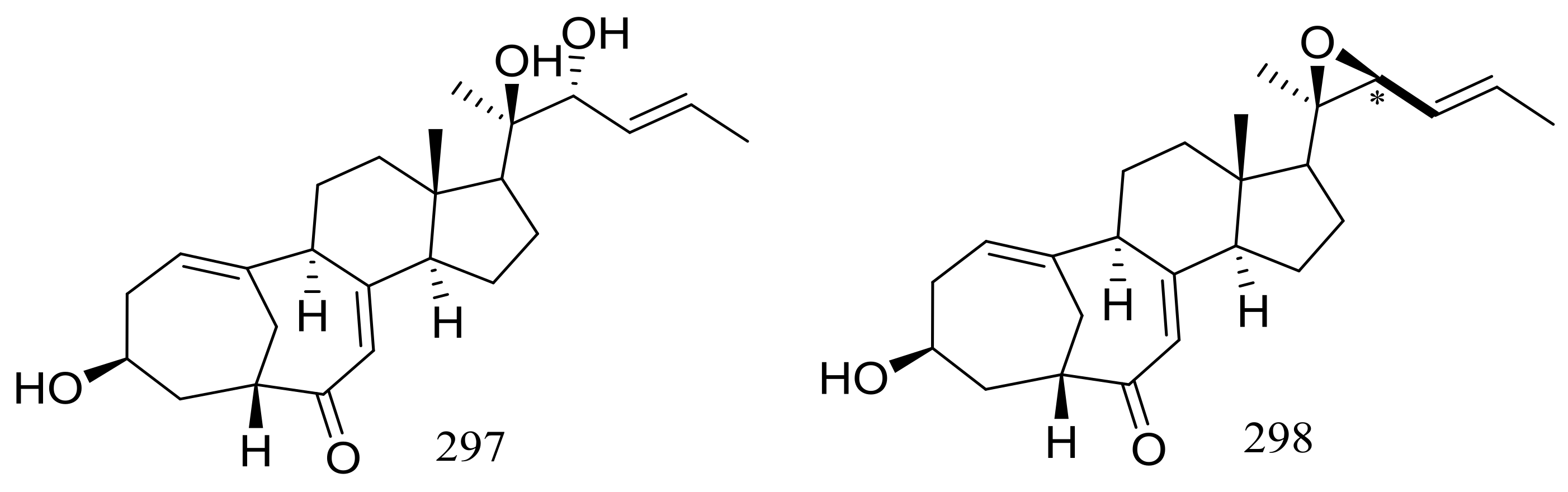
The culture broth of the volcanic ash-derived fungus Penicillium citrinum HGY1-5 collected from the extinct volcano Huguangyan in Guangdong, China, afforded eleven new unusual C25 steroid isomers with bicyclo[4.4.1]A/B rings named 24-epi-cyclocitrinol (288), 20-O-methyl-24-epicyclocitrinol (289), 20-O-methylcyclocitrinol (290), 24-oxocyclocitrinol (291), 12R-hydroxycyclocitrinol (292), neocyclocitrinols B and D (293 and 294), erythro-23-O-methylneocyclocitrinol (295), threo-23-O-methylneocyclocitrinol (296), isocyclocitrinol B (297), and precyclocitrinol B (298) (Figure 50). The evaluation for biological activity of all steroids with the cAMP assay in GPR12-CHO and WT-CHO cells indicated that compounds 288, 293 and 296 could induce the production of cAMP in GPR12-transfected CHO cells at 10 μM [91].
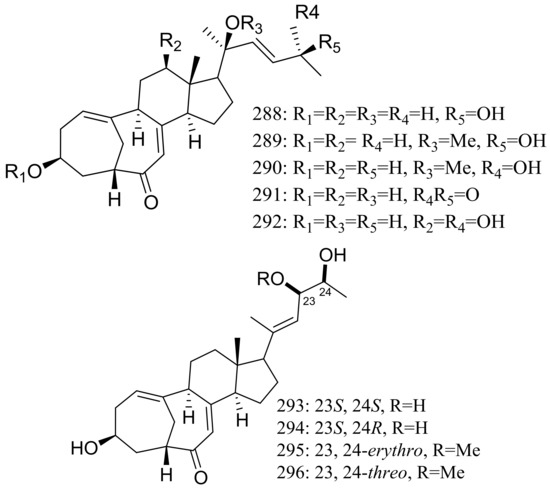
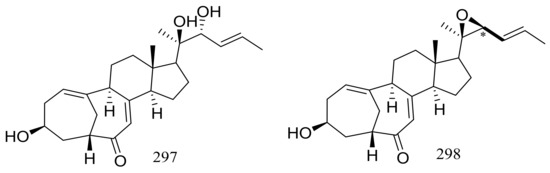
Figure 50.
Novel natural products derived from xerophilic fungi (compounds 288–298). * Absolute configuration is not determined.
7. Acidophilic or Alkaliphilic Fungi
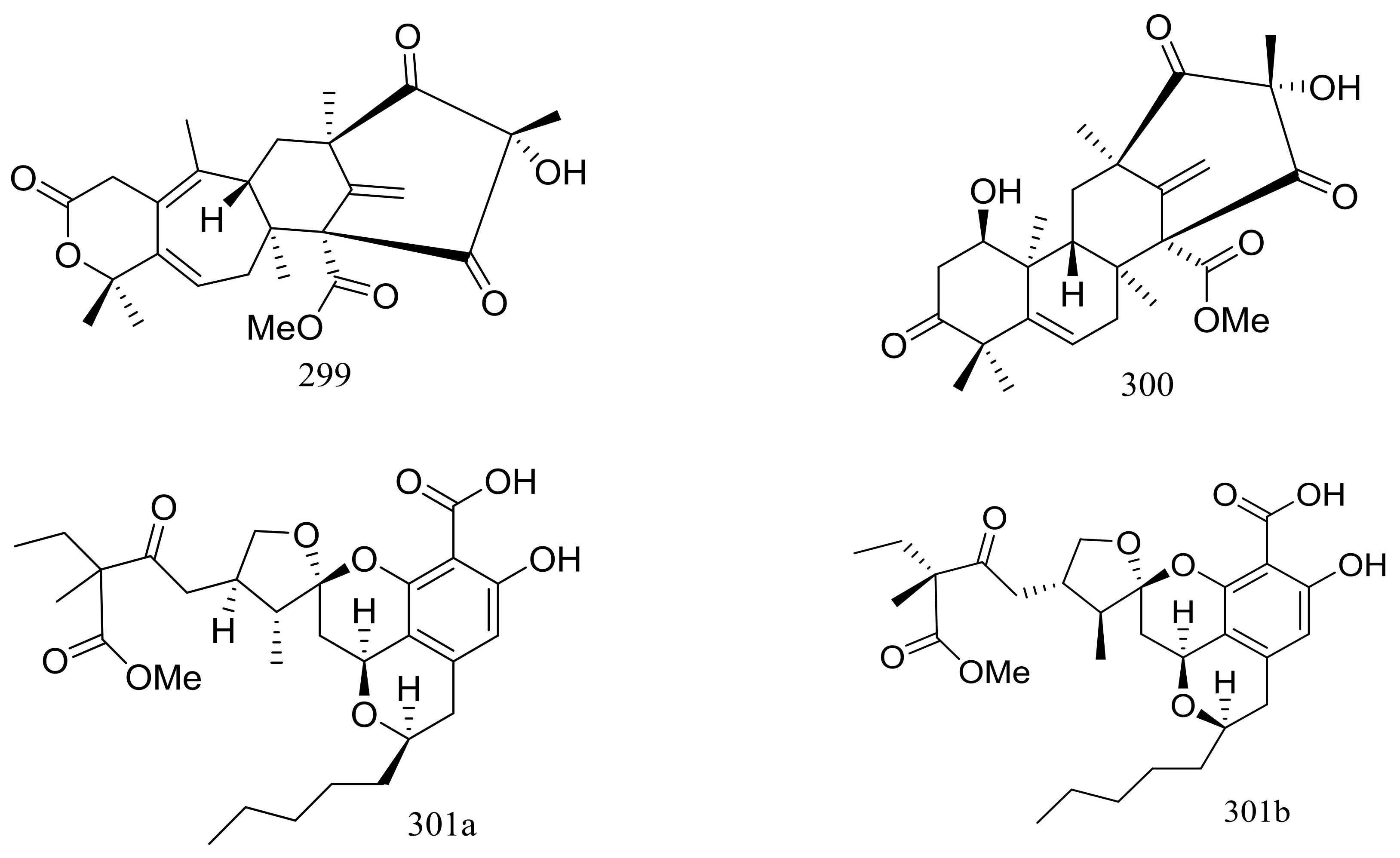
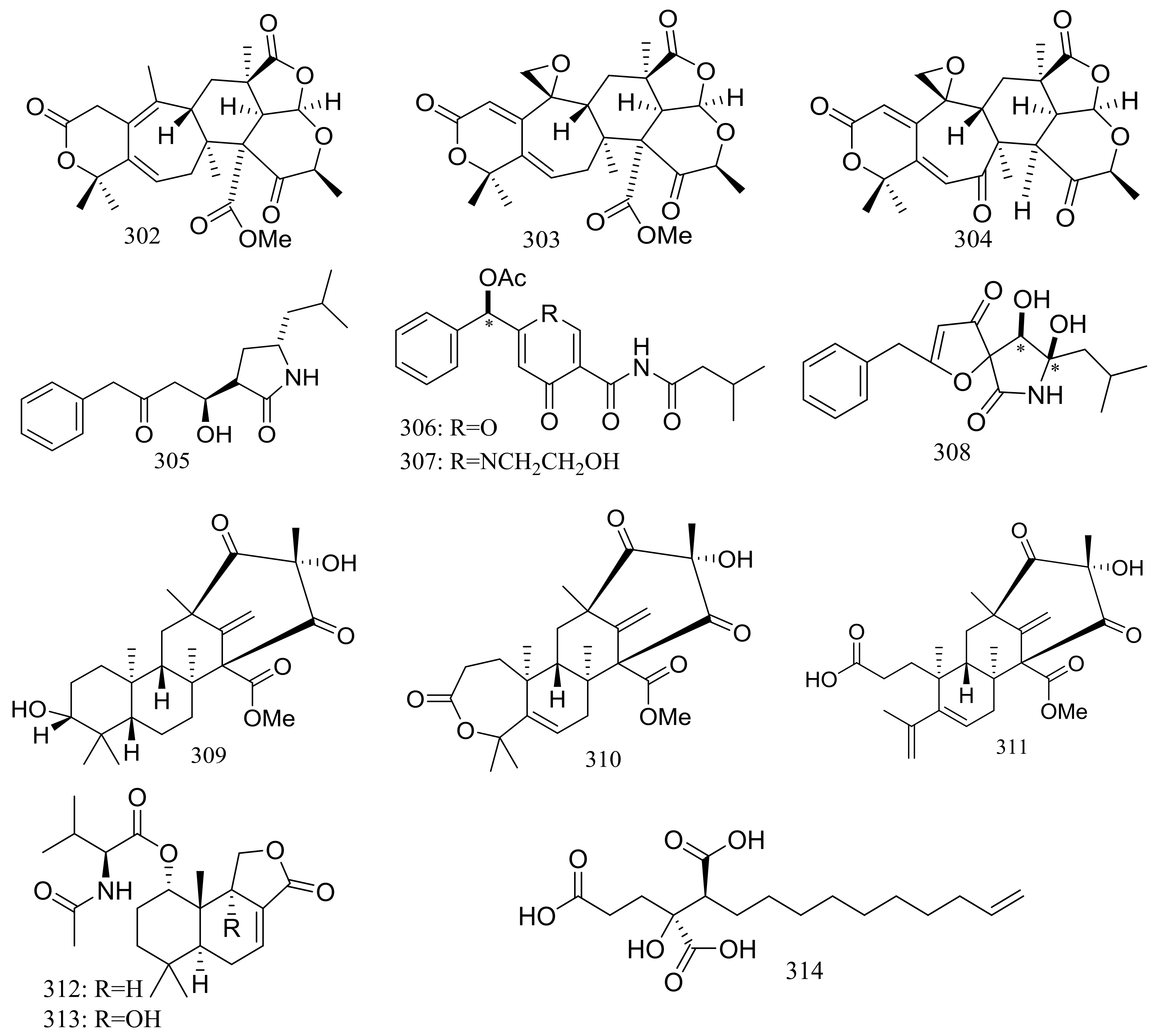
Since 2004, several new compounds have been obtained from Penicillium species growing in the Berkeley Pit Lake (Butte, Montana), which is an abandoned open-pit copper mine filled with 30 billion gallons of acidic, metal-contaminated water. Two novel hybrid polyketide-terpenoids named berkeleydione (299) and berkeleytrione (300) (Figure 51) [92], one novel spiroketal named berkelic acid (301a) (Figure 51) [93], as well as berkeleyacetals A–C (302–304) (Figure 51) [94] were isolated from an unidentified Penicillium species. In 2018 Fürstner group revised the absolute configuration of berkelic acid (301b) through an elegant synthetic, NMR, and crystallographic study [95]. Compounds 299–304 were found to be inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) and the cysteine protease caspase-1 (Casp-1) in the micromolar or millimolar range. In addition, compounds 299 and 304 displayed cytotoxic activity against NCI-H460 cells (GI50 0.398 μM), while 301 against OVCAR-3 cells (GI50 0.091 μM). Berkeleyamides A–D (305–308) (Figure 51) [96] and berkeleyones A–C (309–311) (Figure 51) [97] were isolated from Penicillium rubrum. Compounds 305–308 were able to suppress caspase-1 and MMP-3 in the low micromolar range. Effects on inhibiting the production of interleukin 1-β in THP-1 cells was tested and IC50 values for compounds 309 and 310 were 2.7 and 3.7 μM respectively (the positive control Ac-YVAD-CHO IC50 2.0 μM). Two new drimane sesquiterpene lactones named berkedrimanes A–B (312–313) and one new tricarboxylic acid derivative (314) (Figure 51) were produced by Penicillium solitum. Compounds 312 and 313 inhibited caspase-1 and caspase-3 in the micromolar range and mitigated the production of IL-1β by intact inflammasomes at low micromolar concentrations [98].
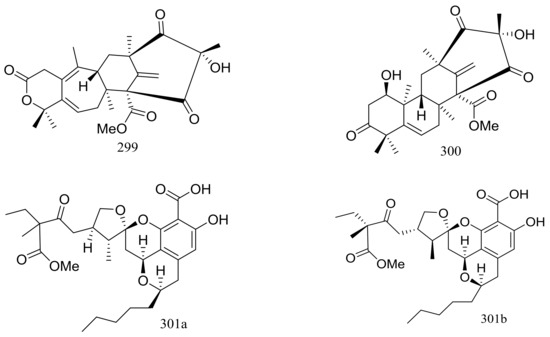

Figure 51.
Novel natural products derived from acidophilic or alkaliphilic fungi (compounds 299–314). * Absolute configuration is not determined.
8. Conclusions
In this review, a total of 314 novel compounds (161 bioactive ones) from extremophilic fungi have been compiled, including 58 terpenoids/steroids, 130 alkaloids/peptides/amides, 50 quinones/phenols, 14 esters/lactones, 11 xanthones, 31 polyketides, and 20 other structure compounds. All compounds were obtained from 56 fungal strains, most of which were asexual stages of ascomycetes e.g., Penicillium sp. (21 strains), Aspergillus sp. (11 strains), and other species (22 strains). Only one basidiomycete (Acaromyces sp.) and one zygomycete (Malbranchea sp.) appeared in the present review.
As demonstrated by this review, fungi from extreme environments are a rich source for novel natural products, even though the research on them is not as up-to-date as the research on fungi in other mesophilic environments due to the difficulties in both sample collection and cultivation. However, with the fast development of modern instruments and techniques in the post-genomic era, some groups have obtained many new compounds from one strain by changing its cultivation conditions or creating a mutant, which significantly contributes to make full use of these precious biological resources.
Author Contributions
X.Z. wrote the manuscript; S.-J.L., J.-J.L., Z.-Z.L., and C.-Q.Z. provided critical reviews and revisions of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (NSFC) grant number [81173505].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
References
- Macelroy, R.D. Some comments on the evolution of extremophiles. BioSystem 1974, 6, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woese, C.R.; Kandler, O.; Wheelis, M.L. Towards a natural system of organisms: Proposal for the domains archaea, bacteria, and eucarya. PNAS 1990, 87, 4576–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skropeta, D. Deep-sea natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 1131–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yayanos, A.A. Microbiology to 10,500 meters in the deep sea. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 49, 777–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horikoshi, K. Barophiles: Deep-sea microorganisms adapted to an extreme environment. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1998, 1, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, Z.E.; Brimble, M.A. Molecules derived from the extremes of life. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 44–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deming, J.W. Psychrophiles and polar regions. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.D.; Johansen, J.R. Microbiotic crusts and ecosystem processes. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1999, 18, 183–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetter, K.O. Extremophiles and their adaptation to hot environments. FEBS Lett. 1999, 452, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchioli, R.; Thomas, T.; Curmi, P.M.G. Cold stress response in archaea. Extremophiles 2000, 4, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madern, D.; Ebel, C.; Zaccai, G. Halophilic adaptation of enzymes. Extremophiles 2000, 4, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothschild, L.J.; Mancinelli, R.L. Life in extreme environments. Nature 2001, 409, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakchung, A.A.H.; Simpson, P.J.L.; Codd, R. Life on earth. Extremophiles continue to move the goal posts. Environ. Chem. 2006, 3, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebar, M.D.; Heimbegner, J.L.; Baker, B.J. Cold-water marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 774–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldatou, S.; Baker, B.J. Cold-water marine natural products, 2006 to 2016. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 585–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing-Tang, L.; Xiao-Ling, L.; Xiao-Yu, L.; Yun, G.; Bo, H.; Bing-Hua, J.; Heng, Z. Bioactive natural products from the antarctic and arctic organisms. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, Y.-L.; Zhao, F.-C. Secondary metabolites from polar organisms. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skropeta, D.; Wei, L. Recent advances in deep-sea natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 999–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-T.; Xue, Y.-R.; Liu, C.-H. A brief review of bioactive metabolites derived from deep-sea fungi. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, F.; Cai, S.; Zeng, X.; Xiao, X.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W. Two new bisorbicillinoids isolated from a deep-sea fungus, Phialocephala sp. FL30r. J. Antibiot. 2007, 60, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, F.; Xiao, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W. Trisorbicillinone a, a novel sorbicillin trimer, from a deep sea fungus, Phialocephala sp. FL30r. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 5235–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Cai, S.; Zhu, T.; Wang, F.; Xiao, X.; Gu, Q. Three new sorbicillin trimers, trisorbicillinones b, c, and d, from a deep ocean sediment derived fungus, Phialocephala sp. FL30r. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 5101–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-H.; Cai, S.-X.; Zhu, T.-J.; Wang, F.-P.; Xiao, X.; Gu, Q.-Q. New cytotoxic metabolites from a deep-sea-derived fungus, Phialocephala sp., strain FL30r. Chem. Biodivers. 2011, 8, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Yang, X.; Zhu, T.; Wang, F.; Xiao, X.; Park, H.; Gu, Q. Diketopiperazine alkaloids from a deep ocean sediment derived fungus Penicillium sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Li, D.; Zhu, T.; Cai, S.; Wang, F.; Xiao, X.; Gu, Q. New alkaloids and diterpenes from a deep ocean sediment derived fungus Penicillium sp. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Feng, T.; Zhao, B.; Li, D.; Cai, S.; Zhu, T.; Wang, F.; Xiao, X.; Gu, Q. Alkaloids from a deep ocean sediment-derived fungus Penicillium sp. and their antitumor activities. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Peng, J.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Keyzers, R.A.; Li, D. Sorbicillamines a–e, nitrogen-containing sorbicillinoids from the deep-sea-derived fungus Penicillium sp. F23-2. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 2106–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Penicyclones a–e, antibacterial polyketides from the deep-sea-derived fungus Penicillium sp. F23-2. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2699–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ye, D.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Che, Y. Breviane spiroditerpenoids from an extreme-tolerant Penicillium sp. isolated from a deep sea sediment sample. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ye, D.; Shao, Z.; Cui, C.; Che, Y. A sterol and spiroditerpenoids from a Penicillium sp. isolated from a deep sea sediment sample. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.-Q.; Lin, X.-P.; Liu, J.; Kaliyaperumal, K.; Ai, W.; Ju, Z.-R.; Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.-W.; Liu, Y. Ascomycotin a, a new citromycetin analogue produced by Ascomycota sp. Ind19F07 isolated from deep sea sediment. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Nong, X.; Wei, X.; Qi, S. Oxindole alkaloids from the fungus Penicillium commune DFFSCS026 isolated from deep-sea-derived sediments. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredimoses, M.; Zhou, X.; Ai, W.; Tian, X.; Yang, B.; Lin, X.; Xian, J.-Y.; Liu, Y. Westerdijkin a, a new hydroxyphenylacetic acid derivative from deep sea fungus Aspergillus westerdijkiae SCSIO 05233. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredimoses, M.; Zhou, X.; Lin, X.; Tian, X.; Ai, W.; Wang, J.; Liao, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, B.; Yang, X.; et al. New prenylxanthones from the deep-sea derived fungus Emericella sp. SCSIO 05240. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Nong, X.; Xu, X.; Qi, S. Cytotoxic polyketides from the deep-sea-derived fungus Engyodontium album DFFSCS021. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Qin, X.; Lin, X.; Kaliyaperumal, K.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Ju, Z.; Tu, Z.; Liu, Y. Sydoxanthone c and acremolin b produced by deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO Ind09F01. J. Antibiot. 2015, 68, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Sun, Z.-H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.-C.; Liu, H.-X.; Li, H.-H.; Zhang, W.-M. Dichotocejpins a–c: New diketopiperazines from a deep-sea-derived fungus Dichotomomyces cejpii FS110. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.-W.; Liu, H.-X.; Sun, Z.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Tan, Y.-Z.; Zhang, W.-M. Secondary metabolites from the deep-sea derived fungus Acaromyces ingoldii FS121. Molecules 2016, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, W.; He, X.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Peniphenylanes a–g from the deep-sea-derived fungus Penicillium fellutanum HDN14-323. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; He, W.; Huang, X.; Tian, X.; Liao, S.; Yang, B.; Wang, F.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y. Antifungal new oxepine-containing alkaloids and xanthones from the deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor SCSIO 05879. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2910–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Yu, S.; Lin, W. Antioxidative phenolic compounds from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, X.; Liu, C.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Clindanones a and b and cladosporols f and g, polyketides from the deep-sea derived fungus Cladosporium cladosporioides HDN14-342. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 76498–76504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Nong, X.; Wang, J.; Qi, S. Brevianamides and mycophenolic acid derivatives from the deep-sea-derived fungus Penicillium brevicompactum DFFSCS025. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, B.; Ma, Z. Inhibitors of BRD4 protein from a marine-derived fungus Alternaria sp. NH-F6. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Liao, Y.; Chen, J. Secondary metabolites produced by the deep-sea-derived fungus Engyodontium album. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2017, 53, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Lin, X.; Salendra, L.; Pang, X.; Dai, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y. Isobenzofuranones and isochromenones from the deep-sea derived fungus Leptosphaeria sp. SCSIO 41005. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; He, X.; Zhang, G.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Inducing secondary metabolite production by combined culture of Talaromyces aculeatus and Penicillium variabile. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 3167–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Liu, D.; Shao, Z.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Eutypellazines a-m, thiodiketopiperazine-type alkaloids from deep sea derived fungus Eutypella sp. MCCC 3A00281. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 33580–33590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Liu, D.; Shao, Z.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Eutypellazines n−s, new thiodiketopiperazines from a deep sea sediment derived fungus Eutypella sp. with anti-VRE activities. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 3695–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Sakai, K.; Nagano, Y.; Orui Sakaguchi, S.; Lima, A.O.; Pellizari, V.H.; Iwatsuki, M.; Takishita, K.; Nonaka, K.; Fujikura, K.; et al. Cladomarine, a new anti-saprolegniasis compound isolated from the deep-sea fungus, Penicillium coralligerum YK-247. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 911–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalsgaard, P.W.; Larsen, T.O.; Christophersen, C. Bioactive cyclic peptides from the psychrotolerant fungus Penicillium algidum. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.-C.; Jensen, P.R.; Kauffman, C.A.; Fenical, W. Libertellenones a–d: Induction of cytotoxic diterpenoid biosynthesis by marine microbial competition. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 5267–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.-L.; Liu, J.-T.; Liu, X.-Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, B.-H.; Zheng, H. Pimarane diterpenes from the arctic fungus Eutypella sp. D-1. J. Antibiot. 2014, 67, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Xu, N.; Gao, Y.; Sun, X.; Yin, Y.; Cai, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Stimulatory effect of ethanol on libertellenone h biosynthesis by arctic fungus Eutypella sp. D-1. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 39, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-T.; Hu, B.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.-P.; Jiao, B.-H.; Lu, X.-L.; Liu, X.-Y. Bioactive tyrosine-derived cytochalasins from fungus Eutypella sp. D-1. Chem. Biodivers. 2014, 11, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-Q.; Chen, X.-C.; Chen, Z.-Q.; Wang, G.-M.; Zhu, S.-G.; Yang, Y.-F.; Chen, K.-X.; Liu, X.-Y.; Li, Y.-M. Eutypenoids a–c: Novel pimarane diterpenoids from the arctic fungus Eutypella sp. D-1. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Zhang, J.-P.; Yu, H.-B.; Liu, X.-Y.; Lu, X.-L.; Jiao, B.-H. A new sesquiterpene lactone from fungus Eutypella sp. D-1. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 1676–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, B.; Liu, S.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Che, Y. Bioactive asterric acid derivatives from the antarctic ascomycete fungus Geomyces sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1643–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, L.; Jiménez, C.; Rodríguez, J.; Areche, C.; Chávez, R.; Henríquez, M.; de la Cruz, M.; Díaz, C.; Segade, Y.; Vaca, I. 3-nitroasterric acid derivatives from an antarctic sponge-derived Pseudogymnoascus sp. Fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, D.; Luan, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T. Cytotoxic metabolites from the antarctic psychrophilic fungus Oidiodendron truncatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Ma, H.; Zhu, T.; Li, J.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Penilactones a and b, two novel polyketides from antarctic deep-sea derived fungus Penicillium crustosum PRB-2. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 9745–9749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Lin, A.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, D. Four new chloro-eremophilane sesquiterpenes from an antarctic deep-sea derived fungus, Penicillium sp. PR19N-1. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.; Wu, G.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, D. New eremophilane-type sesquiterpenes from an antarctic deep-sea derived fungus, Penicillium sp. PR19N-1. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Wiese, J.; Labes, A.; Kramer, A.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Lindgomycin, an unusual antibiotic polyketide from a marine fungus of the Lindgomycetaceae. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4617–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; He, W.; Qin, X.; Wei, X.; Tian, X.; Liao, L.; Liao, S.; Yang, B.; Tu, Z.; Chen, B.; et al. Three new indolyl diketopiperazine metabolites from the antarctic soil-derived fungus Penicillium sp. SCSIO 05705. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 68736–68742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Che, Q.; Li, D.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T. Chrodrimanins i and j from the antarctic moss-derived fungus Penicillium funiculosum GWT2-24. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Wu, C.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Guo, P.; Li, D. Penipyridones a–f, pyridone alkaloids from Penicillium funiculosum. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, M.-L.; Sun, G.-Y.; Li, N.; Gu, Q.-Q.; Li, D.-H.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.-J. Exopisiod b and farylhydrazone c, two new alkaloids from the antarctic-derived fungus Penicillium sp. HDN14-431. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 18, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wei, X.; Qin, X.; Tian, X.; Liao, L.; Li, K.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, T.; et al. Antiviral merosesquiterpenoids produced by the antarctic fungus Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis SCSIO 05702. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.-H.; Yu, H.-B.; Liu, X.-Y.; Lu, X.-L.; Jiao, B.-H. Furanone derivative and sesquiterpene from antarctic marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp. S-1-18. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Fan, Z.-W.; Xie, C.-L.; Liu, Q.; Luo, Z.-H.; Liu, G.; Yang, X.-W. Spirograterpene a, a tetracyclic spiro-diterpene with a fused 5/5/5/5 ring system from the deep-sea-derived fungus Penicillium granulatum MCCC 3A00475. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2174–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.L.; Lu, C.P.; Chen, M.Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Wu, S.H. Cytotoxic polyketides containing tetramic acid moieties isolated from the fungus Myceliophthora Thermophila: Elucidation of the relationship between cytotoxicity and stereoconfiguration. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 6985–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Liao, W.-Y.; Liu, W.-Y.; Liaw, C.-C.; Shen, C.-N.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Wu, S.-H. Discovery of new natural products by intact-cell mass spectrometry and LC-SPE-NMR: Malbranpyrroles, novel polyketides from thermophilic fungus Malbranchea sulfurea. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 11573–11580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.-S.; Niu, X.-M.; Wang, Y.-L.; Guo, J.-P.; Pan, W.-Z.; Huang, X.-W.; Zhang, K.-Q. Isolation of putative biosynthetic intermediates of prenylated indole alkaloids from a thermophilic fungus Talaromyces thermophilus. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4356–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.-P.; Tan, J.-L.; Wang, Y.-L.; Wu, H.-Y.; Zhang, C.-P.; Niu, X.-M.; Pan, W.-Z.; Huang, X.-W.; Zhang, K.-Q. Isolation of talathermophilins from the thermophilic fungus Talaromyces thermophilus YM3-4. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2278–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.-P.; Zhu, C.-Y.; Zhang, C.-P.; Chu, Y.-S.; Wang, Y.-L.; Zhang, J.-X.; Wu, D.-K.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Niu, X.-M. Thermolides, potent nematocidal pks-nrps hybrid metabolites from thermophilic fungus Talaromyces thermophilus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 20306–20309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Ye, P.; Chen, A.C.-T.; Wang, K.; Liu, P.; He, S.; Wu, X.; Gan, L.; Ye, Y.; Wu, B. Two novel hepatocellular carcinoma cycle inhibitory cyclodepsipeptides from a hydrothermal vent crab-associated fungus Aspergillus clavatus C2WU. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-W.; Li, C.-W.; Cui, C.-B.; Hua, W.; Zhu, T.-J.; Gu, Q.-Q. Nine new and five known polyketides derived from a deep sea-sourced Aspergillus sp. 16-02-1. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Shi, Y.; Auckloo, N.B.; Chen, X.; Chen, A.C.-T.; Tao, X.; Wu, B. An unusual conformational isomer of verrucosidin backbone from a hydrothermal vent fungus, Penicillium sp. Y-50-10. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaaban, M.; El-Metwally, M.M.; Abdel-Razek, A.A.; Laatsch, H. Terretonin m: A new meroterpenoid from the thermophilic Aspergillus terreus TM8 and revision of the absolute configuration of penisimplicins. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, T.; Tao, H.; Lu, Z.; Fang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W. Two new cytotoxic quinone type compounds from the halotolerant fungus Aspergillus variecolor. J. Antibiot. 2007, 60, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-L.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Tao, H.-W.; Zhu, T.-J.; Fang, Y.-C.; Gu, Q.-Q.; Zhu, W.-M. Isoechinulin-type alkaloids, variecolorins a–l, from halotolerant Aspergillus variecolor. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-L.; Zhu, T.-J.; Tao, H.-W.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Fang, Y.-C.; Gu, Q.-Q.; Zhu, W.-M. Three novel, structurally unique spirocyclic alkaloids from the halotolerant B-17 fungal strain of Aspergillus variecolor. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 2913–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.-Y.; Lin, Z.-J.; Wang, W.-L.; Du, L.; Zhu, T.-J.; Fang, Y.-C.; Gu, Q.-Q.; Zhu, W.-M. Citrinin dimers from the halotolerant fungus Penicillium citrinum B-57. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Tao, H.; Peng, X.; Liu, P.; Zhu, W. Cerebrosides of the halotolerant fungus Alternaria raphani isolated from a sea salt field. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1695–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Zhu, H.; Hong, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Zhu, W. Novel cyclic hexapeptides from marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5262–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hong, K.; Liu, P.; Zhu, W. Cyclic tripeptides from the halotolerant fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, J.-K.; Qu, H.-J.; Liu, P.-P.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W.-M. A new cytotoxic indole-3-ethenamide from the halotolerant fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashyal, B.P.; Wijeratne, E.M.K.; Faeth, S.H.; Gunatilaka, A.A.L. Globosumones a−c, cytotoxic orsellinic acid esters from the sonoran desert endophytic fungus Chaetomium globosum. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itabashi, T.; Matsuishi, N.; Hosoe, T.; Toyazaki, N.; Udagawa, S.; Imai, T.; Adachi, M.; Kawai, K. Two new dioxopiperazine derivatives, arestrictins a and b, isolated from Aspergillus restrictus and Aspergillus penicilloides. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Zhu, T.; Fang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W. Unusual C25 steroid isomers with bicyclo[4.4.1]a/b rings from a volcano ash-derived fungus Penicillium citrinum. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierle, D.B.; Stierle, A.A.; Hobbs, J.D.; Stokken, J.; Clardy, J. Berkeleydione and berkeleytrione, new bioactive metabolites from an acid mine organism. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierle, A.A.; Stierle, D.B.; Kelly, K. Berkelic acid, a novel spiroketal with selective anticancer activity from an acid mine waste fungal extremophile. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 5357–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierle, D.B.; Stierle, A.A.; Patacini, B. The berkeleyacetals, three meroterpenes from a deep water acid mine waste Penicillium. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1820–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, C.F.; Paradise, C.L.; Lynch, V.M.; Yoshimoto, F.K.; De Brabander, J.K. A biosynthetically inspired synthesis of (−)-berkelic acid and analogs. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stierle, A.A.; Stierle, D.B.; Patacini, B. The berkeleyamides, amides from the acid lake fungus Penicillum rubrum. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierle, D.B.; Stierle, A.A.; Patacini, B.; McIntyre, K.; Girtsman, T.; Bolstad, E. Berkeleyones and related meroterpenes from a deep water acid mine waste fungus that inhibit the production of interleukin 1-β from induced inflammasomes. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2273–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierle, D.B.; Stierle, A.A.; Girtsman, T.; McIntyre, K.; Nichols, J. Caspase-1 and -3 inhibiting drimane sesquiterpenoids from the extremophilic fungus Penicillium solitum. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).