Effect of Tetrodotoxin Pellets in a Rat Model of Postherpetic Neuralgia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Uniformity of TTX Pellets Content
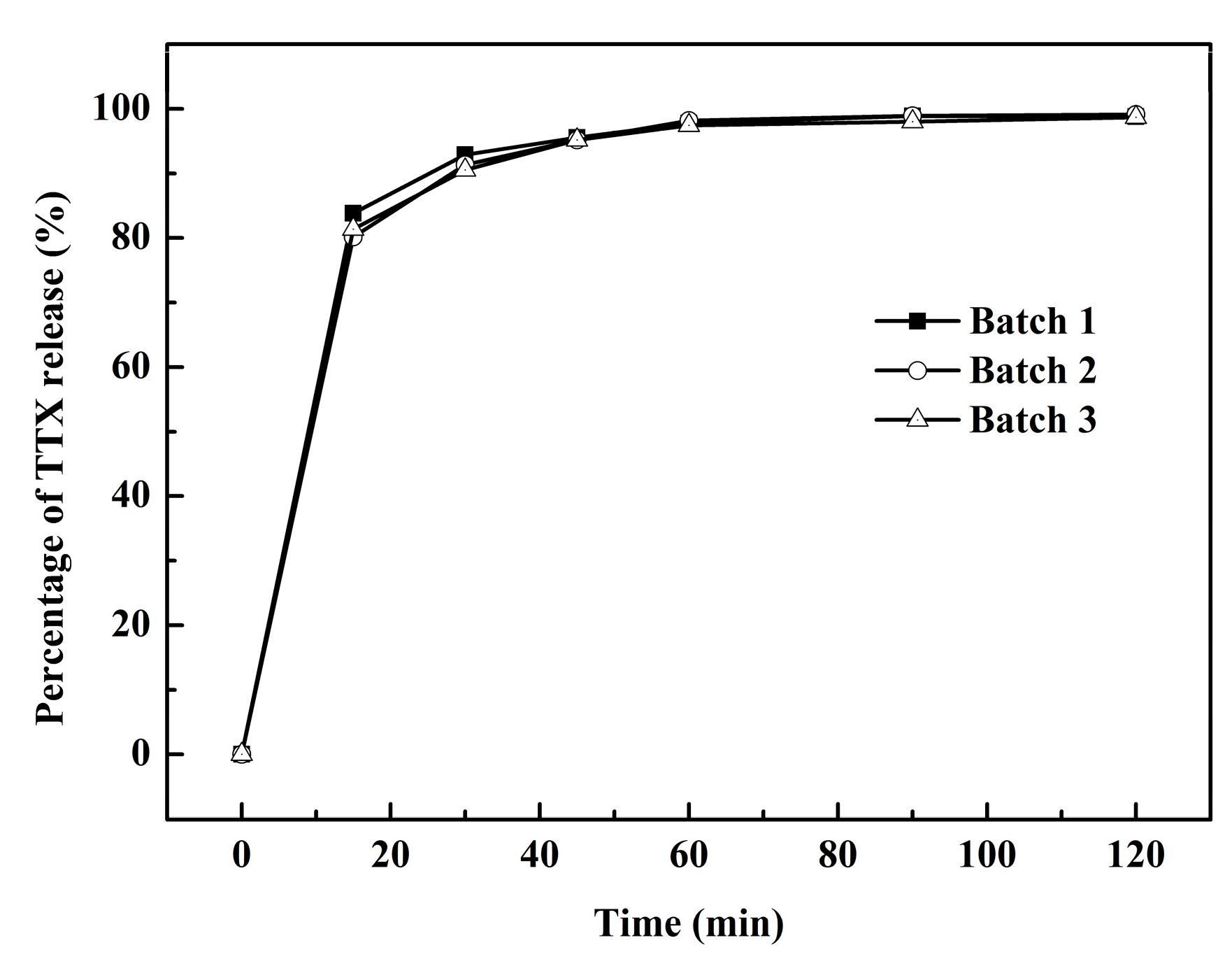
2.2. Percentage of TTX Pellets Released In Vitro
2.3. Effect of TTX Pellets in a RTX-Induced Rat Model
2.3.1. Effect of RTX on Mechanical and Thermal Allodynia
2.3.2. Effect of TTX Pellets on Mechanical and Thermal Allodynia Induced by RTX
2.3.3. Effect of TTX Pellets at Different Doses on Mechanical Allodynia
2.3.4. Effect of TTX Pellets and TTX Injection on Mechanical Allodynia
2.4. Acute Toxicity of TTX Pellets
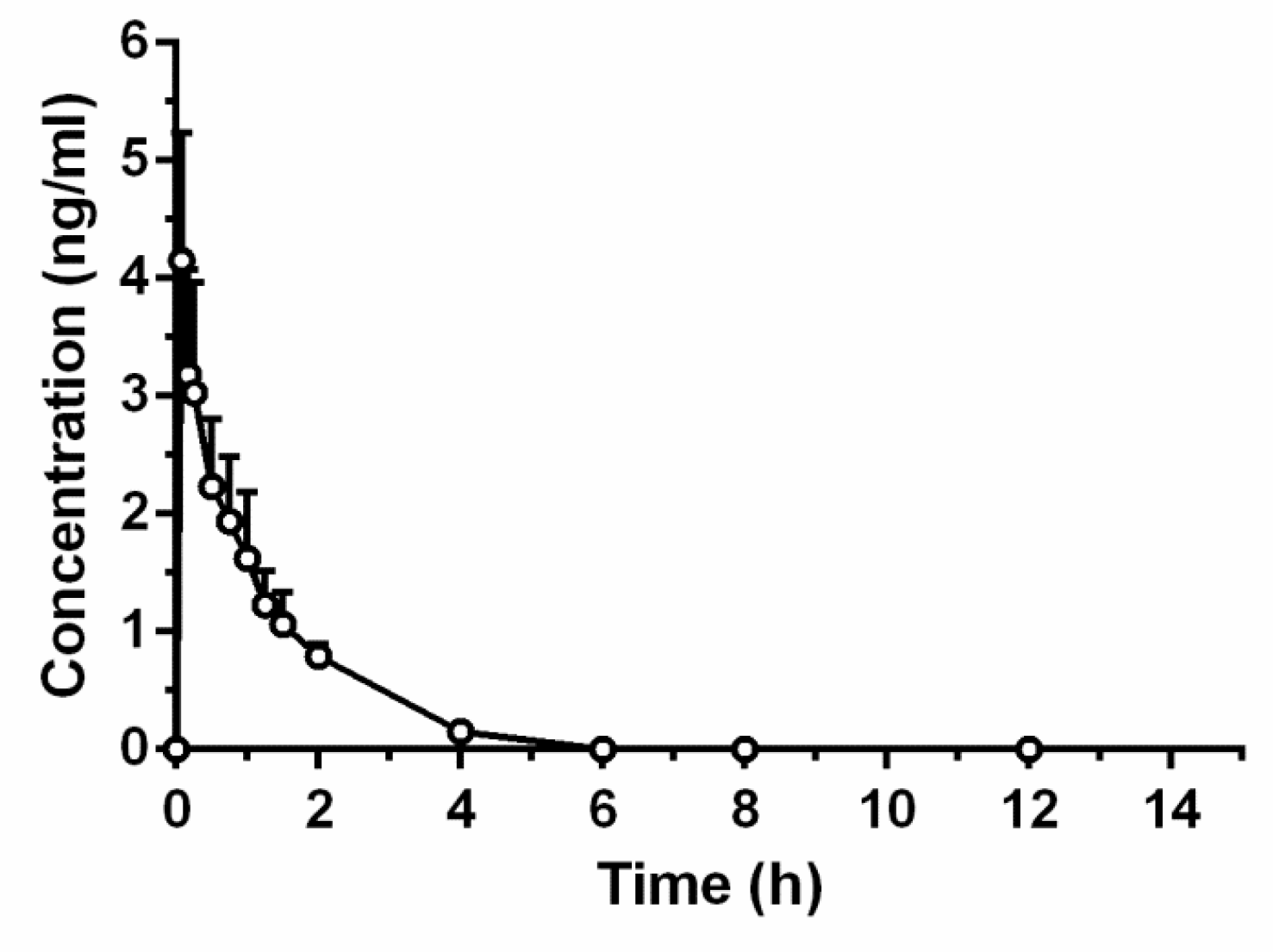
2.5. Pharmacokinetics Following Intragastric TTX Pellets Administration
2.5.1. TTX Injection
2.5.2. Intragastric TTX Pellets
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Animals and Experimental Design
4.2.1. Animals
4.2.2. Experimental Design for RTX-Induced PHN
4.2.3. Nociceptive Behavioral Tests
4.2.4. Statistical Analysis
4.3. TTX Pellets Content
4.4. Release of TTX Pellets
4.5. Preparation of TTX Pellets
4.5.1. Preparation of Drug-Loaded Pellets
4.5.2. Preparation of TTX Pellets by Coating
4.6. Pharmacokinetic Studies
4.6.1. TTX Administration and Plasma Sample Collection
4.6.2. Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometric Conditions (UPLC/MS/MS)
Liquid Chromatography Conditions
Mass Spectrometry Conditions
4.6.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sadosky, A.; Scd, M.D.; Brandenburg, N.A.; Strauss, M. A review of the epidemiology of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and less commonly studied neuropathic pain conditions. Pain Pract. 2008, 8, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilden, D.H.; Cohrs, R.J.; Mahalingam, R. VZV vasculopathy and postherpetic neuralgia: Progress and perspective on antiviral therapy. Neurology 2005, 64, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmader, K.E. Epidemiology and impact on quality of life of postherpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy. Clin. J. Pain 2002, 18, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavin, P.D.; Tremper, L.; Smith, A.; Williams, G.; Brooker, C. Transdermal oxycodone patch for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Pain Manag. 2017, 7, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworkin, R.H.; Portenoy, R.K. Pain and its persistence in herpes zoster. Pain 1996, 67, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworkin, R.H.; Corbin, A.E.; Young, J.P.; Sharma, U.; Lamoreaux, L.; Bockbrader, H.; Garofalo, E.A.; Poole, R.M. Pregabalin for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Neurology 2003, 60, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, W. Prescription opioid addiction and chronic pain: More than a feeling. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017, 173, S73–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.Y.; Hsieh, C.H.; Hwang, D.F. Development of standardized methodology for identifying toxins in clinical samples and fish species associated with tetrodotoxin-borne poisoning incidents. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 24, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayser, V.; Viguier, F.; Ioannidi, M.; Bernard, J.F.; Latrémolière, A.; Michot, B.; Vela, J.M.; Buschmann, H.; Hamon, M.; Bourgoin, S. Differential anti-neuropathic pain effects of tetrodotoxin in sciatic nerve-versus infraorbital nerve-ligated rats—Behavioral, pharmacological and immunohistochemical investigations. Neuropharmacology 2010, 58, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, P.; Levine, J.D. Antihyperalgesic effect of tetrodotoxin in rat models of persistent muscle pain. Neuroscience 2015, 311, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, P.G.; Alvarez, P.; Levine, J.D. Topical tetrodotoxin attenuates photophobia induced by corneal injury in the rat. J. Pain 2015, 16, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beloeil, H.; Ababneh, Z.; Chung, R.; Zurakowski, D.; Mulkern, R.V.; Berde, C.B. Effects of bupivacaine and tetrodotoxin on carrageenan-induced hind paw inflammation in rats (Part 1): Hyperalgesia, edema, and systemic cytokines. Anesthesiology 2006, 105, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalziel, R.G.; Bingham, S.; Sutton, D.; Grant, D.; Champion, J.M.; Dennis, S.A.; Quinn, J.P.; Bountra, C.; Mark, M.A. Allodynia in rats infected with varicella zoster virus—A small animal model for post-herpetic neuralgia. Brain Res. Rev. 2004, 46, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasaki, I.; Andoh, T.; Shiraki, K.; Kuraishi, Y. Allodynia and hyperalgesia induced by herpes simplex virus type-1 infection in mice. Pain 2000, 86, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.R.; Pan, H.L. Effect of systemic and intrathecal gabapentin on allodynia in a new rat model of postherpetic neuralgia. Brain Res. 2005, 1042, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Y.; Song, Y.H.; Higuera, E.S.; Luo, Z.D. Spinal dorsal horn calcium channel α2δ-1 subunit upregulation contributes to peripheral nerve injury-induced tactile allodynia. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 8494–8499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Shum, F.H.K. Composition of Sodium Channel Blocking Compound. U.S. Patent 6,559,154, 6 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hagen, N.A.; Cantin, L.; Constant, J.; Haller, T.; Blaise, G.; Ong-Lam, M.; Souich, P.D.; Korz, W.; Lapointe, B. Tetrodotoxin for moderate to severe cancer-related pain: A multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-design trial. Pain Res. Manag. 2017, 2017, 7212713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, F.R.; Entrena, J.M.; Cendán, C.M.; Pozo, E.D.; Vela, J.M.; Baeyens, J.M. Tetrodotoxin inhibits the development and expression of neuropathic pain induced by paclitaxel in mice. Pain 2008, 137, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, B.; Chen, H.; Han, J.; Xie, Q.; He, J.; Bai, K.; Dong, Y.; Yi, R. A study of 11-[3H]-tetrodotoxin absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) in adult sprague-dawley rats. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.A.; Straube, S.; Wiffen, P.J.; Derry, S.; Mcquay, H.J. Pregabalin for acute and chronic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009, 39, CD007076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.A.; Wiffen, P.J.; Derry, S.; Mcquay, H.J. Gabapentin for Chronic Neuropathic Pain and Fibromyalgia in Adults; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; p. CD007938. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto, F.R.; Cobos, E.J.; Tejada, M.Á.; Sánchez-Fernández, C.; González-Cano, R.; Cendán, C.M. Tetrodotoxin (TTX) as a therapeutic agent for pain. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 281–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Marine-sourced anti-cancer and cancer pain control agents in clinical and late preclinical development†. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagen, N.A.; Du, S.P.; Lapointe, B.; Onglam, M.; Dubuc, B.; Walde, D.; Love, R.; Ngoc, A.H. Tetrodotoxin for moderate to severe cancer pain: A randomized, double blind, parallel design multicenter study. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2008, 35, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.R.; Pan, H.L. Hypersensitivity of spinothalamic tract neurons associated with diabetic neuropathic pain in rats. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 87, 2726–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etman, M.; Nada, H.; Nada, A.; Ismail, F.; Moustafa, M.; Khalil, S. In vivo evaluation of ketorolac sustained release pellets using a new HPLC method. Eur. J. Parenter. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 15, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, S.; Pandey, P.; Mishra, D.; Singh, U.K. A validated stability indicating HPLC method for the determination of process-related impurities in pantoprazole bulk drug and formulations. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, C.; Ferreira, P.D. Assessment of the in-vivo drug release from pellets film-coated with a dispersion of high amylose starch and ethylcellulose for potential colon delivery. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanakis, M.; Niopas, I. Determination of atenolol in human plasma by HPLC with fluorescence detection: Validation and application in a pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2013, 51, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasmoto, T.; Michishita, T. Fluorometric determination of tetrodotoxin by high performance liquid chromatography. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1985, 49, 3077–3080. [Google Scholar]
- Yotsu, M.; Endo, A.; Yasumoto, T. An improved tetrodotoxin analyzer. J. Agric. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1989, 53, 893–895. [Google Scholar]
- Walash, M.I.; Belal, F.; El-Enany, N.; Eid, M.; El-Shaheny, R.N. Stability-indicating HPLC method with fluorescence detection for determination of methocarbamol in tablets. Application to therapeutic drug monitoring. J. Liquid Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2012, 35, 2021–2041. [Google Scholar]
- Dukić-Ott, A.; Remon, J.P.; Foreman, P.; Vervaet, C. Immediate release of poorly soluble drugs from starch-based pellets prepared via extrusion/spheronisation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 67, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caccavo, D.; Lamberti, G.; Cafaro, M.M.; Barba, A.A.; Kazlauske, J.; Larsson, A. Mathematical modeling of the drug release from an ensemble of coated pellets. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1797–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Seo, D.Y.; Lee, H.E.; Wang, I.C.; Kim, W.S.; Jeong, M.Y.; Choi, G.J. In line NIR quantification of film thickness on pharmaceutical pellets during a fluid bed coating process. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 403, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraete, G.; De Jaeghere, W.; Vercruysse, J.; Grymonpré, W.; Vanhoorne, V.; Stauffer, F.; De Beer, T.; Bezuijen, A.; Remon, J.P.; Vervaet, C. The use of partially hydrolysed polyvinyl alcohol for the production of high drug-loaded sustained release pellets via extrusion-spheronisation and coating: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 517, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Sample | Content (%) | Average Content (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 97.02 | 99.21 | 1.83 |
| 2 | 97.97 | ||
| 3 | 99.42 | ||
| 4 | 100.02 | ||
| 5 | 97.11 | ||
| 6 | 99.78 | ||
| 7 | 102.20 | ||
| 8 | 97.16 | ||
| 9 | 101.06 | ||
| 10 | 100.33 |
| Dose (μg/kg) | ♀ | ♂ | Death |
|---|---|---|---|
| 814 | 4/5 | 4/5 | 8/10 |
| 692 | 3/5 | 3/5 | 6/10 |
| 588 | 4/5 | 2/5 | 6/10 |
| 500 | 3/5 | 3/5 | 6/10 |
| 425 | 2/5 | 1/5 | 3/10 |
| Total | 16/25 | 13/25 | 29/50 |
| LD50 | 441.2 | 573.95 | 517.43 |
| Dose (μg/kg) | Gender | Body Weight | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Day | 7 Day | ||
| 814 | ♂ | 197.6 ± 5.03 | 247 (n = 1) |
| ♀ | 188.4 ± 7.47 | 196 (n = 1) | |
| 692 | ♂ | 189.2 ± 10.62 | 230 ± 16.97 (n = 2) |
| ♀ | 189.8 ± 6.30 | 202 ± 5.66 (n = 2) | |
| 588 | ♂ | 184.8 ± 4.60 | 237 ± 10.82 (n = 3) |
| ♀ | 193.0 ± 9.17 | 215 (n = 1) | |
| 500 | ♂ | 188.8 ± 8.56 | 226.5 ± 7.78 (n = 2) |
| ♀ | 190.8 ± 9.58 | 199 ± 6.74 (n = 2) | |
| 425 | ♂ | 193.6 ± 6.54 | 250 ± 7.21 (n = 4) |
| ♀ | 187.2 ± 4.60 | 201.5 ± 13.44 (n = 3) | |
| Parameters | Unit | Intravenous Tetrodotoxin of 6 μg/kg |
|---|---|---|
| AUC0–t | ng·h/mL | 4.42 ± 0.90 |
| AUC0–∞ | ng·h/mL | 4.63 ± 0.90 |
| t1/2 | h | 0.92 ± 0.17 |
| CL | mL/h/kg | 1349.40 ± 326.75 |
| Vd | mL/kg | 1824.68 ± 709.84 |
| Parameters | Unit | Intragastric Tetrodotoxin of 100 μg/kg |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax | ng/mL | 0.93 ± 0.23 |
| Tmax | h | 2.08 ± 0.49 |
| AUC0–t | ng·h/mL | 4.91 ± 0.99 |
| AUC0–∞ | ng·h/mL | 5.82 ± 1.65 |
| t1/2 | h | 3.23 ± 1.74 |
| CL | mL/h/kg | 18,188.62 ± 4234.34 |
| Vd | mL/kg | 76,276.28 ± 22,601.44 |
| F | 6.7% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, B.; Sun, J.; Zheng, H.; Le, Q.; Wang, C.; Bai, K.; He, J.; He, H.; Dong, Y. Effect of Tetrodotoxin Pellets in a Rat Model of Postherpetic Neuralgia. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060195
Hong B, Sun J, Zheng H, Le Q, Wang C, Bai K, He J, He H, Dong Y. Effect of Tetrodotoxin Pellets in a Rat Model of Postherpetic Neuralgia. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(6):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060195
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Bihong, Jipeng Sun, Hongzhi Zheng, Qingqing Le, Changsen Wang, Kaikai Bai, Jianlin He, Huanghuang He, and Yanming Dong. 2018. "Effect of Tetrodotoxin Pellets in a Rat Model of Postherpetic Neuralgia" Marine Drugs 16, no. 6: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060195
APA StyleHong, B., Sun, J., Zheng, H., Le, Q., Wang, C., Bai, K., He, J., He, H., & Dong, Y. (2018). Effect of Tetrodotoxin Pellets in a Rat Model of Postherpetic Neuralgia. Marine Drugs, 16(6), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060195






