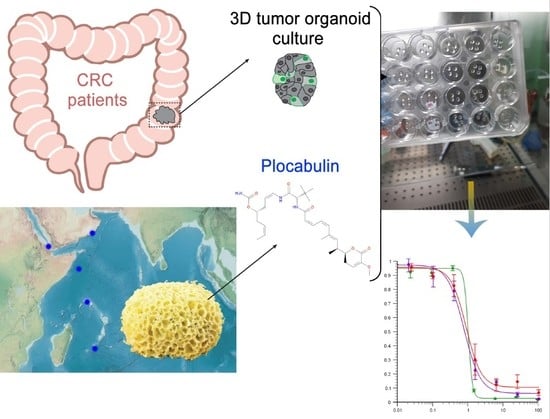
Plocabulin Displays Strong Cytotoxic Activity in a Personalized Colon Cancer Patient-Derived 3D Organoid Assay
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
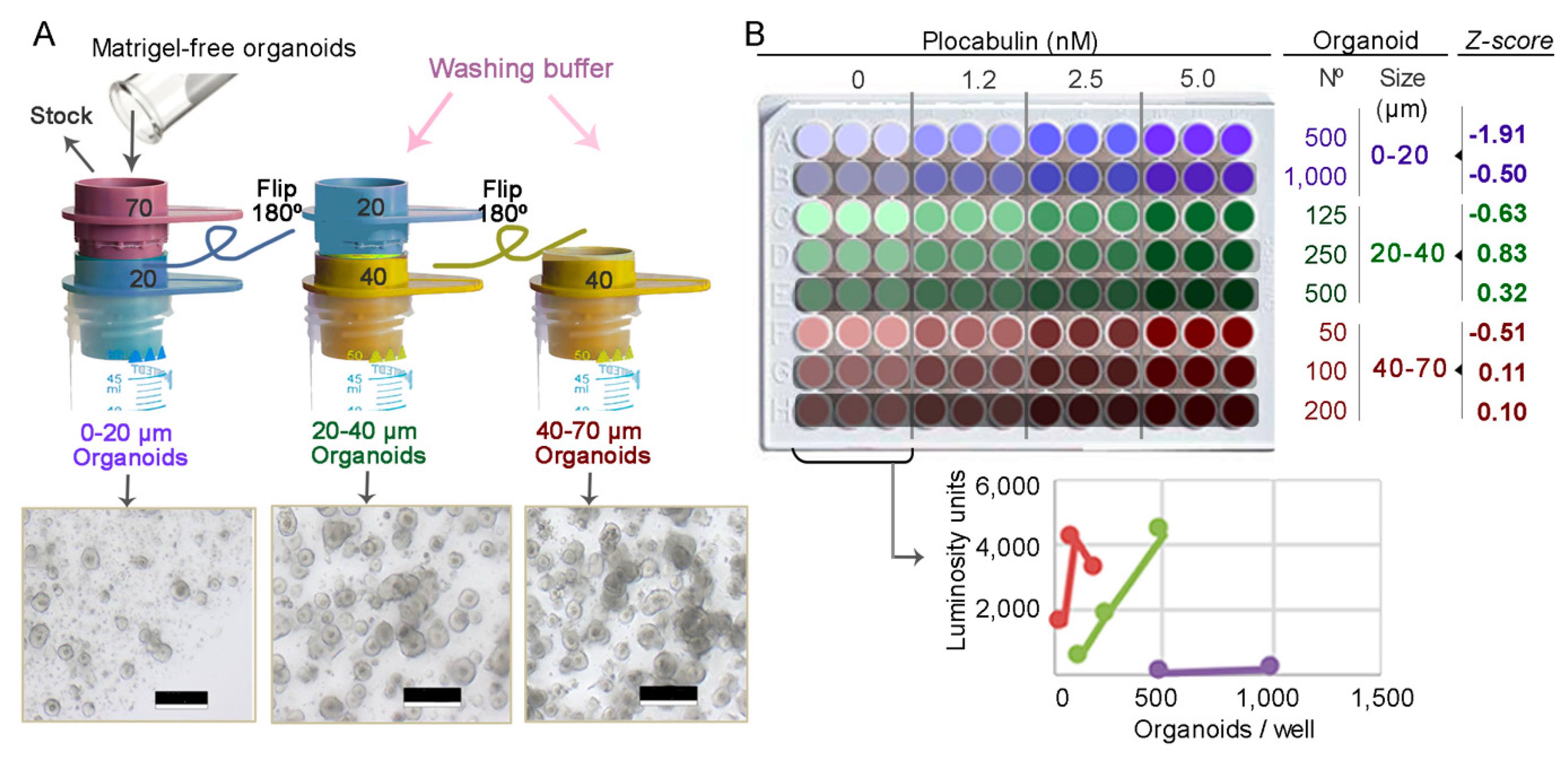
2.1. 3D Organoid Culture and Optimization of Drug-Assays
2.2. Plocabulin Cytotoxic Activity in Patient-Derived Tumor Organoids
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Samples and Ethical Guidelines
4.2. Reagents
4.3. 3D Tumor Organoid Cultures
4.4. Immunofluorescence
4.5. Growth and Expansion of Organoid Cultures
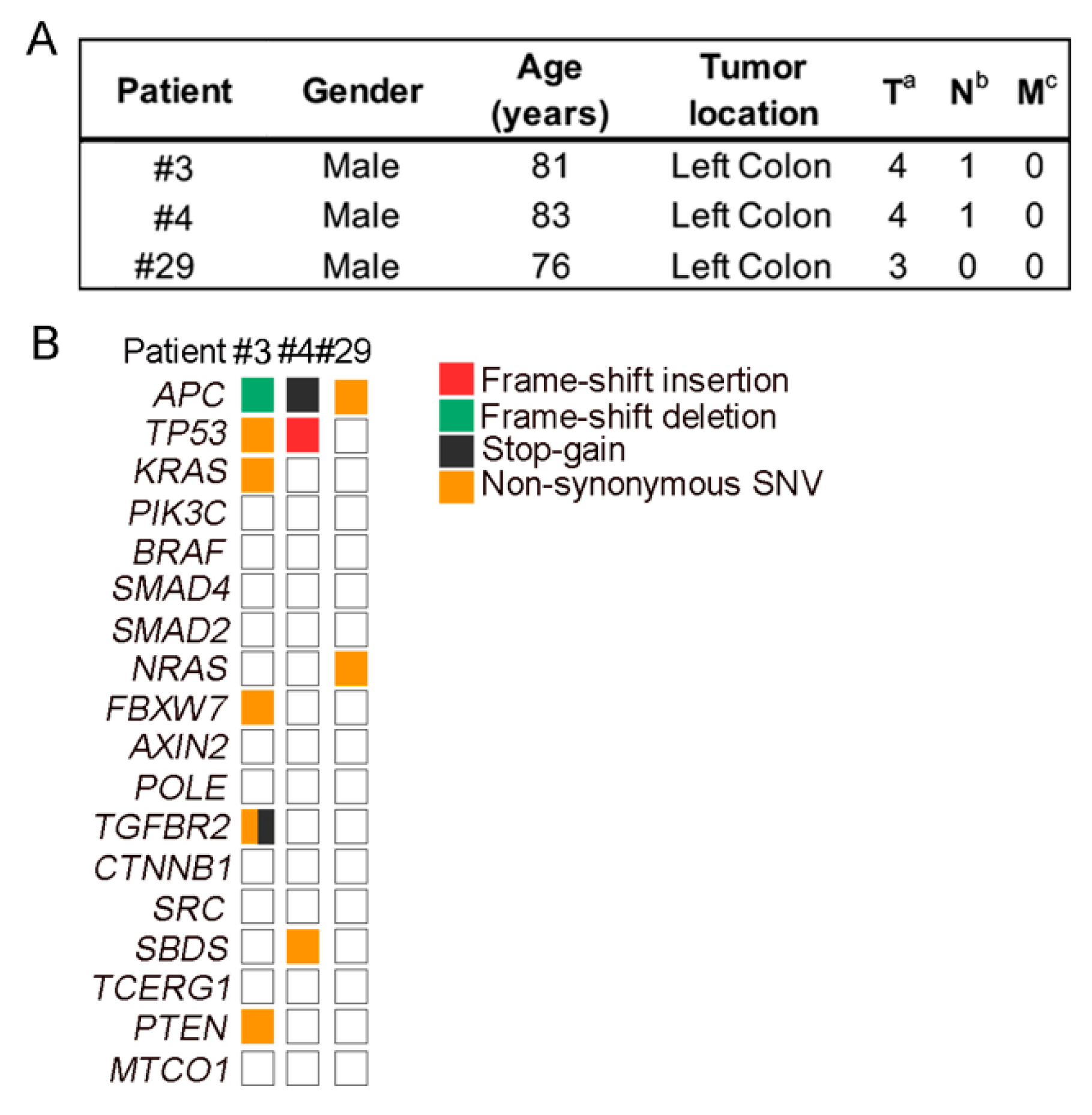
4.6. Mutational Analysis
4.7. Organoid Size Variability
4.8. Optimization of Drug Activity Assays
4.9. Z-score
4.10. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.11. Wash-Out Assays
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elez, E.; Gomez-Roca, C.; Soto Matos-Pita, A.; Argiles, G.; Valentin, T.; Coronado, C.; Iglesias, J.; Macarulla, T.; Betrian, S.; Fudio, S.; et al. First-in-human phase I study of the microtubule inhibitor plocabulin in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 37, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.B.; Evdokimov, N.M.; Lefranc, F.; Valentao, P.; Kornienko, A.; Pereira, D.M.; Andrade, P.B.; Gomes, N.G.M. Marine-Derived Anticancer Agents: Clinical Benefits, Innovative Mechanisms, and New Targets. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.J.; Coello, L.; Fernandez, R.; Reyes, F.; Rodriguez, A.; Murcia, C.; Garranzo, M.; Mateo, C.; Sanchez-Sancho, F.; Bueno, S.; et al. Isolation and first total synthesis of PM050489 and PM060184, two new marine anticancer compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10164–10171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pera, B.; Barasoain, I.; Pantazopoulou, A.; Canales, A.; Matesanz, R.; Rodriguez-Salarichs, J.; Garcia-Fernandez, L.F.; Moneo, V.; Jimenez-Barbero, J.; Galmarini, C.M.; et al. New interfacial microtubule inhibitors of marine origin, PM050489/PM060184, with potent antitumor activity and a distinct mechanism. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2084–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Diez, M.; Guillen-Navarro, M.J.; Pera, B.; Bouchet, B.P.; Martinez-Leal, J.F.; Barasoain, I.; Cuevas, C.; Andreu, J.M.; Garcia-Fernandez, L.F.; Diaz, J.F.; et al. PM060184, a new tubulin binding agent with potent antitumor activity including P-glycoprotein over-expressing tumors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 88, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prota, A.E.; Bargsten, K.; Diaz, J.F.; Marsh, M.; Cuevas, C.; Liniger, M.; Neuhaus, C.; Andreu, J.M.; Altmann, K.-H.; Steinmetz, M.O. A new tubulin-binding site and pharmacophore for microtubule-destabilizing anticancer drugs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13817–13821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galmarini, C.M.; Martin, M.; Bouchet, B.P.; Guillen-Navarro, M.J.; Martinez-Diez, M.; Martinez-Leal, J.F.; Akhmanova, A.; Aviles, P. Plocabulin, a novel tubulin-binding agent, inhibits angiogenesis by modulation of microtubule dynamics in endothelial cells. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.S.; Hildebrand, P.W. NGL Viewer: A web application for molecular visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W576–W579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jmol: an open-source Java viewer for chemical structures in 3D. Available online: http://www.jmol.org/.
- Li, M.; Izpisua Belmonte, J.C. Organoids—Preclinical Models of Human Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocana, A.; Garcia-Alonso, S.; Amir, E.; Pandiella, A. Refining Early Antitumoral Drug Development. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 922–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Shimokawa, M.; Date, S.; Takano, A.; Matano, M.; Nanki, K.; Ohta, Y.; Toshimitsu, K.; Nakazato, Y.; Kawasaki, K.; et al. A Colorectal Tumor Organoid Library Demonstrates Progressive Loss of Niche Factor Requirements during Tumorigenesis. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 18, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Huang, J.; Ning, B.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhao, W. Drug Discovery via Human-Derived Stem Cell Organoids. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weeber, F.; Ooft, S.N.; Dijkstra, K.K.; Voest, E.E. Tumor Organoids as a Pre-clinical Cancer Model for Drug Discovery. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, K.; Wu, C.; O’Rourke, K.P.; Szeglin, B.C.; Zheng, Y.; Sauve, C.-E.G.; Adileh, M.; Wasserman, I.; Marco, M.R.; Kim, A.S.; et al. A rectal cancer organoid platform to study individual responses to chemoradiation. Nat. Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooft, S.N.; Weeber, F.; Dijkstra, K.K.; McLean, C.M.; Kaing, S.; van Werkhoven, E.; Schipper, L.; Hoes, L.; Vis, D.J.; van de Haar, J.; et al. Patient-derived organoids can predict response to chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasch, C.A.; Favreau, P.F.; Yueh, A.E.; Babiarz, C.P.; Gillette, A.A.; Sharick, J.T.; Karim, M.R.; Nickel, K.P.; DeZeeuw, A.K.; Sprackling, C.M.; et al. Patient-Derived Cancer Organoid Cultures to Predict Sensitivity to Chemotherapy and Radiation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, N.; Hong, J.J.; Tofig, B.; Mapua, M.; Elashoff, D.; Moatamed, N.A.; Huang, J.; Memarzadeh, S.; Damoiseaux, R.; Soragni, A. A simple high-throughput approach identifies actionable drug sensitivities in patient-derived tumor organoids. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Wetering, M.; Francies, H.E.; Francis, J.M.; Bounova, G.; Iorio, F.; Pronk, A.; Van Houdt, W.; Van Gorp, J.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Kester, L.; et al. Prospective derivation of a living organoid biobank of colorectal cancer patients. Cell 2015, 161, 933–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachogiannis, G.; Hedayat, S.; Vatsiou, A.; Jamin, Y.; Fernandez-Mateos, J.; Khan, K.; Lampis, A.; Eason, K.; Huntingford, I.; Burke, R.; et al. Patient-derived organoids model treatment response of metastatic gastrointestinal cancers. Science 2018, 359, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Barral, A.; Costales-Carrera, A.; Buira, S.P.; Jung, P.; Ferrer-Mayorga, G.; Larriba, M.J.; Bustamante-Madrid, P.; Dominguez, O.; Real, F.X.; Guerra-Pastrian, L.; et al. Vitamin D differentially regulates colon stem cells in patient-derived normal and tumor organoids. FEBS J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Chung, T.D.; Oldenburg, K.R. A Simple Statistical Parameter for Use in Evaluation and Validation of High Throughput Screening Assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 1999, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Y.; Wu, Z. Alternative statistical parameter for high-throughput screening assay quality assessment. J. Biomol. Screen. 2007, 12, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AAT Bioquest, Inc. (2019, November 18). Quest Graph™ IC50 Calculator. Available online: https://www.aatbio.com/tools/ic50-calculator.
- Aboulkheyr Es, H.; Montazeri, L.; Aref, A.R.; Vosough, M.; Baharvand, H. Personalized Cancer Medicine: An Organoid Approach. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Sims, G.E.; Murphy, S.; Miller, J.R.; Chan, A.P. Predicting the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Robinson, J.T.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): High-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costales-Carrera, A.; Fernández-Barral, A.; Bustamante-Madrid, P.; Guerra, L.; Cantero, R.; Barbáchano, A.; Muñoz, A. Plocabulin Displays Strong Cytotoxic Activity in a Personalized Colon Cancer Patient-Derived 3D Organoid Assay. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110648
Costales-Carrera A, Fernández-Barral A, Bustamante-Madrid P, Guerra L, Cantero R, Barbáchano A, Muñoz A. Plocabulin Displays Strong Cytotoxic Activity in a Personalized Colon Cancer Patient-Derived 3D Organoid Assay. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(11):648. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110648
Chicago/Turabian StyleCostales-Carrera, Alba, Asunción Fernández-Barral, Pilar Bustamante-Madrid, Laura Guerra, Ramón Cantero, Antonio Barbáchano, and Alberto Muñoz. 2019. "Plocabulin Displays Strong Cytotoxic Activity in a Personalized Colon Cancer Patient-Derived 3D Organoid Assay" Marine Drugs 17, no. 11: 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110648
APA StyleCostales-Carrera, A., Fernández-Barral, A., Bustamante-Madrid, P., Guerra, L., Cantero, R., Barbáchano, A., & Muñoz, A. (2019). Plocabulin Displays Strong Cytotoxic Activity in a Personalized Colon Cancer Patient-Derived 3D Organoid Assay. Marine Drugs, 17(11), 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110648