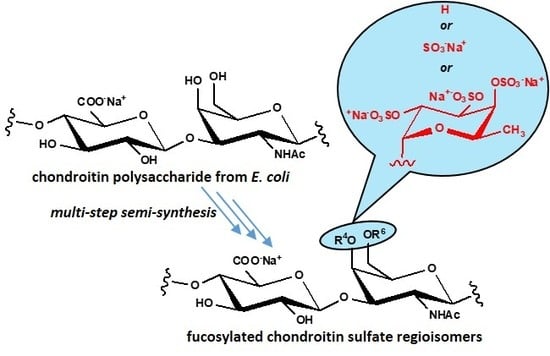
A Study for the Access to a Semi-synthetic Regioisomer of Natural Fucosylated Chondroitin Sulfate with Fucosyl Branches on N-acetyl-Galactosamine Units
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Semi-Synthesis of fCSs
2.2. Structural and Preliminary Biological Characterization of Semi-synthetic fCSs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Methods
3.2. Preparation of the Products
3.2.1. Example of Glycosylation Reaction
3.2.2. Example of Benzyl Ether Oxidative Cleavage
3.2.3. Example of Sulfation and Global Deprotection
3.2.4. Study of Chondroitin Polysaccharide Stability under Different Hydrolysis Reaction Conditions
3.2.5. Study of Benzylidene Acetal vs. Glycosidic Bond Cleavage on Chondroitin Derivative 2
3.2.6. Polysaccharide Derivative 5
3.2.7. Polysaccharide Derivative 8-i
3.2.8. Polysaccharide Derivative 8-ii
3.2.9. fCS-i–iii
3.3. Determination of Molecular Mass Data
3.4. Anti-Coagulant Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasconcelos, A.A.; Pomin, V.H. The sea as a rich source of structurally unique glycosaminoglycans and mimetics. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomin, V.H. Holothurian fucosylated chondroitin sulfate. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glauser, B.F.; Pereira, M.S.; Monteiro, R.Q.; Mourão, P.A.S. Serpin-independent anticoagulant activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 100, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyue, Y.; Sheehan, J.P. Fucosylated chondroitin sulfate inhibits plasma thrombin generation via targeting of the factor IXa heparin-binding exosite. Blood 2009, 114, 3092–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, R.J.C.; Sucupira, I.D.; Oliveira, S.-N.M.C.G.; Santos, G.R.C.; Mourão, P.A.S. Improved anticoagulant effect of fucosylated chondroitin sulfate orally administered as gastroresistant tablets. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 117, 662–670. [Google Scholar]
- Mourão, P.A.S. Perspective on the use of sulfated polysaccharides from marine organisms as a source of new antithrombotic drugs. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2770–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, P.A.G.; Ribeiro, K.A.; Valente, A.P.; Capillé, N.V.; Oliveira, S.-N.M.C.G.; Tovar, A.M.F.; Pereira, M.S.; Vilanova, E.; Mourão, P.A.S. A unique fucosylated chondroitin sulfate type II with strikingly homogeneous and neatly distributed α-fucose branches. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myron, P.; Siddiquee, S.; Al Azad, S. Fucosylated chondroitin sulfate diversity in sea cucumbers: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 112, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro-Machado, M.; Tomaz, M.A.; Fonseca, R.J.C.; Strauch, M.A.; Cons, B.L.; Borges, P.A.; Patrão-Neto, F.C.; Tavares-Henriques, M.S.; Teixeira-Cruz, J.M.; Calil-Elias, S.; et al. Occurrence of sulfated fucose branches in fucosylated chondroitin sulfate are essential for the polysaccharide effect preventing muscle damage induced by toxins and crude venom from Bothrops jararacussu snake. Toxicon 2015, 98, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourão, P.A.S.; Guimarães, M.A.M.; Mulloy, B.; Thomas, S.; Gray, E. Antithrombotic activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulphate from echinoderm: Sulphated fucose branches on the polysaccharide account for its antithrombotic action. Br. J. Haematol. 1998, 101, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourão, P.A.S.; Pereira, M.S.; Pavão, M.S.; Mulloy, B.; Tollefsen, D.M.; Mowinckel, M.C.; Abildgaard, U. Structure and anticoagulant activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from echinoderm. Sulfated fucose branches on the polysaccharide account for its high anticoagulant action. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 23973–23984. [Google Scholar]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. New insight on the structural diversity of holothurian fucosylated chondroitin sulfates. Pure Appl. Chem. 2019, 91, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, G.R.; Glauser, B.F.; Parreiras, L.A.; Vilanova, E.; Mourão, P.A.S. Distinct structures of the α-fucose branches in fucosylated chondroitin sulfates do not affect their anticoagulant activity. Glycobiology 2015, 25, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. Two fucosylated chondroitin sulfates from the sea cucumber Eupentacta fraudatrix. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Cai, C.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J.; Xue, C.; Li, G.; Yu, G. A novel structural fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from Holothuria mexicana and its effects on growth factors binding and anticoagulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. The structure of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from the sea cucumber Cucumaria frondosa. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Tsvetkova, E.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Stonik, V.A.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. Structural characterization of fucosylated chondroitin sulfates from sea cucumbers Apostichopus japonicus and Actinopyga mauritiana. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, S.; Lv, Z. Separation, purification, structures and anticoagulant activities of fucosylated chondroitin sulfates from Holothuria scabra. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.; Gao, N.; Yin, R.; Lin, L.; Xiao, C.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Purcell, S.W.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J. Precise structures of fucosylated glycosaminoglycan and its oligosaccharides as novel intrinsic factor Xase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 148, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Borodina, E.Y.; Stonik, V.A.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. A highly regular fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from the sea cucumber Massinium magnum: Structure and effects on coagulation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 167, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, R.J.C.; Oliveira, S.-N.M.C.G.; Pomin, V.H.; Mecawi, A.S.; Araujo, I.G.; Mourão, P.A.S. Effects of oversulfated and fucosylated chondroitin sulfates on coagulation. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 103, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wu, M.; Xiao, C.; Yang, L.; Zhou, L.; Gao, N.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Qin, H.; et al. Discovery of an intrinsic tenase complex inhibitor: Pure nonasaccharide from fucosylated glycosaminoglycan. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8284–8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Lin, L.; Yao, W.; Zhao, J.; Wu, M.; Li, Z. Synthesis of fucosylated chondroitin sulfate nonasaccharide as a novel anticoagulant targeting intrinsic factor Xase complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12880–12885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Chen, D.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, J.-H.; Qin, H.-B. Synthesis of trisaccharide repeating unit of fucosylated chondroitin sulfate. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 2877–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, J.; Tanaka, H.; Nakamura, A.; Takeda, N. Synthesis of β-D-GalNAc(4,6-diS)(1–4)[α-l-Fuc(2,4-diS)(1–3)]-β-D-GlcA, a novel trisaccharide unit of chondroitin sulfate with a fucose branch. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 3940–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustyuzhanina, N.E.; Bilan, M.I.; Nifantiev, N.E.; Usov, A.I. Structural analysis of holothurian fucosylated chondroitin sulfates: Degradation versus non-destructive approach. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 476, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Zhou, L.; Gao, N.; Li, Z.; Zhao, L.; Shang, F.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J. Oligosaccharides from depolymerized fucosylated glycosaminoglycan: Structures and minimum size for intrinsic factor Xase complex inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 14089–14099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimini, D.; Restaino, O.F.; Catapano, A.; De Rosa, M.; Schiraldi, C. Production of capsular polysaccharide from Escherichia coli K4 for biotechnological applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 1779–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laezza, A.; Iadonisi, A.; Pirozzi, A.V.A.; Diana, P.; De Rosa, M.; Schiraldi, C.; Parrilli, M.; Bedini, E. A modular approach to a library of semi-synthetic fucosylated chondroitin sulfate polysaccharides with different sulfation and fucosylation patterns. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 18215–18226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laezza, A.; Casillo, A.; Cosconati, S.; Biggs, C.I.; Fabozzi, A.; Paduano, L.; Iadonisi, A.; Novellino, E.; Gibson, M.I.; Randazzo, A.; et al. Decoration of chondroitin polysaccharide with threonine: Synthesis, conformational study, and ice-recrystallization inhibition activity. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2267–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedini, E.; De Castro, C.; De Rosa, M.; Di Nola, A.; Iadonisi, A.; Restaino, O.F.; Schiraldi, C.; Parrilli, M. A microbiological–chemical strategy to produce chondroitin sulfate A,C. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 6160–6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuts, P.G.M. Greene’s Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 414–428. [Google Scholar]
- Laezza, A.; Iadonisi, A.; De Castro, C.; De Rosa, M.; Schiraldi, C.; Parrilli, M.; Bedini, E. Chemical fucosylation of a polysaccharide: A semisynthetic access to fucosylated chondroitin sulfate. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2237–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daragics, K.; Fügedi, P. Regio- and chemoselective reductive cleavage of 4,6-O-benzylidene-type acetals of hexopyranosides using BH3·THF–TMSOTf. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 2914–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debenham, S.D.; Toone, E.J. Regioselective reduction of 4,6-O-benzylidenes using triethylsilane and BF3⸱Et2O. Tetrahedron Asymm. 2000, 11, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Solakyildirim, K.; Yang, B.; Beaudet, J.M.; Weyers, A.; Linhardt, R.J.; Zhang, F. Semi-synthesis of chondroitin sulfate-E from chondroitin sulfate-A. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mucci, A.; Schenetti, L.; Volpi, N. 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance identification and characterization of components of chondroitin sulfates of various origin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2000, 41, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertini, S.; Bisio, A.; Torri, G.; Benzi, D.; Terbojevich, M. Molecular weight determination of heparin and dermatan sulfate by size exclusion chromatography with a triple detector array. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Gatta, A.; De Rosa, M.; Marzaioli, I.; Busico, T.; Schiraldi, C. A complete hyaluronan hydrodynamic characterization using a size exclusion chromatography–triple detector array system during in vitro enzymatic degradation. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 404, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restaino, O.F.; Finamore, R.; Diana, P.; Marseglia, M.; Vitiello, M.; Casillo, A.; Bedini, E.; Parrilli, M.; Corsaro, M.M.; Trifuoggi, M.; et al. A multi-analytical approach to better assess the keratan sulfate contamination in animal origin chondroitin sulfate. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 958, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, Y.; Okamoto, R.; Izumi, M.; Murase, T.; Kajihara, Y. Semisynthesis of intact complex-type triantennary oligosaccharides from a biantennary oligosaccharide isolated from a natural source by selective chemical and enzymatic glycosylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3461–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Yao, W.; Meng, X.; Li, Z. Semisynthesis of chondroitin sulfate oligosaccharides based on the enzymatic degradation of chondroitin. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 7418–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Sun, J.; Cai, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, J.; Hu, B.; Shu, P.; Meng, L.; Wan, Q. 1,4-Dithiothreitol mediated cleavage of the acetal and ketal type of diol protecting groups. Org. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 2427–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedini, E.; Laezza, A.; Parrilli, M.; Iadonisi, A. A review of chemical methods for the selective sulfation and desulfation of polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 1224–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho Gomez, J.A.; Erler, U.W.; Klemm, D.O. 4-Methoxy substituted trityl groups in 6-O protection of cellulose: Homogeneous synthesis, characterization, detritylation. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1996, 197, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonn, H. Synthesis of a tri- and a hepta-saccharide which contain α-L-fucopyranosyl groups and are part of the complex type of carbohydrate moiety of glycoproteins. Carbohydr. Res. 1985, 139, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.-R.; Lai, Y.-H.; Chen, J.-H.; Liu, C.-Y.; Mong, K.-K.T. Dimethylformamide: An unusual glycosylation modulator. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7315–7320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinolfi, M.; Iadonisi, A.; Ravidà, A.; Schiattarella, M. Moisture stable promoters for selective α-fucosylation reactions: Synthesis of antigen fragments. Synlett 2004, 2, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comegna, D.; Bedini, E.; Di Nola, A.; Iadonisi, A.; Parrilli, M. The behaviour of deoxyhexose trihaloacetimidates in selected glycosylations. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinolfi, M.; Barone, G.; Guariniello, L.; Iadonisi, A. Facile cleavage of carbohydrate benzyl ethers and benzylidene acetals using the reagent NaBrO3/Na2S2O4 under two-phase conditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 8439–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedini, E.; Laezza, A.; Iadonisi, A. Chemical derivatization of sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 18, 3018–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, M.; Naggi, A.; Guglieri, S.; Santarsiero, R.; Torri, G. Complex glycosaminoglycans: Profiling substitution patterns by two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 337, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargiulo, V.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; De Castro, C. Structural analysis of chondroitin sulfate from Scyliorhinus canicula: A useful source of this polysaccharide. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mulloy, B.; Mourão, P.A.S.; Gray, E. Structure/function studies of anticoagulant sulphated polysaccharides using NMR. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 77, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vessella, G.; Traboni, S.; Cimini, D.; Iadonisi, A.; Schiraldi, C.; Bedini, E. Development of semisynthetic, regioselective pathways for accessing the missing sulfation patterns of chondroitin sulfate. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 3021–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Wen, D.; Gao, N.; Xiao, C.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Lian, W.; Peng, W.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, J. Anticoagulant and antithrombotic evaluation of native fucosylated chondroitin sulfates and their derivatives as selective inhibitors of intrinsic factor Xase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 92, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Lu, F.; Xiao, C.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wen, D.; Li, Z.; Wu, M.; Jiang, J.; et al. β-Eliminative depolymerization of the fucosylated chondroitin sulfate and anticoagulant activities of resulting fragments. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 127, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Gao, N.; Xiao, C.; Lin, L.; Purcell, S.W.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J. Modulating the degree of fucosylation of fucosylated chondroitin sulfate enhances heparin cofactor-II dependent thrombin inhibition. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 154, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | Fucosyl Donor, Glycosylation Temperature | Yield 1 [%] | DF 2 | GalNAc O-6/O-4 Branching Site Ratio 3 | α/β Fuc Ratio 3 | Mw4 [kDa] | Mw4/Mn5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fCS-i | 10, −30 °C | 50 | 0.21 | only 6-O-linked | 1:3 | 9.2 | 1.31 |
| fCS-ii | 10, −10 °C | 52 | 0.20 | 9:1 | 9:1 | 9.1 | 1.31 |
| fCS-iii | 10, 25 °C | 58 | 0.29 | 4:1 | 19:1 | 7.8 | 1.19 |
| fCS-iv | 11, −10 °C | 51 | 0.04 | n.d. 6 | n.d. 6 | n.d. 6 | n.d. 6 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vessella, G.; Traboni, S.; Pirozzi, A.V.A.; Laezza, A.; Iadonisi, A.; Schiraldi, C.; Bedini, E. A Study for the Access to a Semi-synthetic Regioisomer of Natural Fucosylated Chondroitin Sulfate with Fucosyl Branches on N-acetyl-Galactosamine Units. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120655
Vessella G, Traboni S, Pirozzi AVA, Laezza A, Iadonisi A, Schiraldi C, Bedini E. A Study for the Access to a Semi-synthetic Regioisomer of Natural Fucosylated Chondroitin Sulfate with Fucosyl Branches on N-acetyl-Galactosamine Units. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(12):655. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120655
Chicago/Turabian StyleVessella, Giulia, Serena Traboni, Anna V. A. Pirozzi, Antonio Laezza, Alfonso Iadonisi, Chiara Schiraldi, and Emiliano Bedini. 2019. "A Study for the Access to a Semi-synthetic Regioisomer of Natural Fucosylated Chondroitin Sulfate with Fucosyl Branches on N-acetyl-Galactosamine Units" Marine Drugs 17, no. 12: 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120655
APA StyleVessella, G., Traboni, S., Pirozzi, A. V. A., Laezza, A., Iadonisi, A., Schiraldi, C., & Bedini, E. (2019). A Study for the Access to a Semi-synthetic Regioisomer of Natural Fucosylated Chondroitin Sulfate with Fucosyl Branches on N-acetyl-Galactosamine Units. Marine Drugs, 17(12), 655. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17120655