New Discorhabdin Alkaloids from the Antarctic Deep-Sea Sponge Latrunculia biformis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
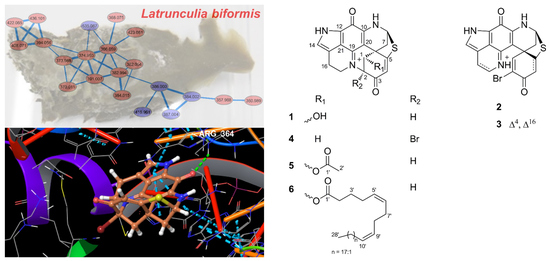
2.1. Bioactivity and Molecular Networking-guided Purification and Structural Elucidation
2.2. In Vitro Bioactivity Tests and Molecular Docking on Purified Compounds
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Procedures
4.2. Sponge Material
4.3. Extraction and Isolation
4.4. UPLC-QToF-MS/MS Analysis
4.5. Molecular Networking
4.6. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.7. Molecular Modeling and Docking
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alvarez, B.; Bergquist, P.R.; Battershill, C.N. Taxonomic revision of the genus Latrunculia du Bocage (Porifera: Demospongiae: Latrunculiidae) in New Zealand. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2002, 36, 151–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaai, T.; Gibbons, M.J.; Kelly, M.; Davies-Coleman, M. South African Latrunculiidae (Porifera: Demospongiae: Poecilosclerida): Descriptions of new species of Latrunculia du Bocage, Strongylodesma Lévi, and Tsitsikamma Samaai & Kelly. Zootaxa 2003, 371, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, M.; Sim-Smith, C.; Stone, R.; Samaai, T.; Reiswig, H.; Austin, W. New taxa and arrangements within the family Latrunculiidae (Demospongiae, Poecilosclerida). Zootaxa 2016, 4121, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capon, R.; MacLeod, J.K.; Willis, A.C. Trunculins A and B, norsesterterpene cyclic peroxides from a marine sponge, Latrunculia brevis. J. Org. Chem. 1987, 52, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.; Capon, R.; Capon, R. Trunculin-F and Contrunculin-A and -B: Novel oxygenated norterpenes From a Southern Australian marine sponge, Latrunculia conulosa. Aust. J. Chem. 1993, 46, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampella, A.; Randazzo, A.; Borbone, N.; Luciani, S.; Trevisi, L.; Debitus, C.; D’Auria, M.V. Isolation of callipeltins A–C and of two new open-chain derivatives of callipeltin A from the marine sponge Latrunculia sp. A revision of the stereostructure of callipeltins. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 6163–6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, V.; D’Orsi, R.; Borbone, N.; D’Auria, M.V.; Bifulco, G.; Monti, M.C.; Catania, A.; Zampella, A. Callipeltins F–I: New antifungal peptides from the marine sponge Latrunculia sp. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; McCombs, J.D.; Munro, M.H.G. Discorhabdin C, a highly cytotoxic pigment from a sponge of the genus Latrunculia. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 5476–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, J.; Capon, R.J. Discorhabdin R: A new antibacterial pyrroloiminoquinone from two latrunculiid marine sponges, Latrunculia sp. and Negombata sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1527–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-F.; Fan, H.; Xiong, J.; Wu, S.-B. Discorhabdins and pyrroloiminoquinone-related alkaloids. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5465–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.; Alvarez, B.; Battershill, C.; Northcote, P.; Parthasarathy, H. Genetic, morphological, and chemical divergence in the sponge genus Latrunculia (Porifera: Demospongiae) from New Zealand. Mar. Biol. 2001, 139, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furrow, F.B.; Amsler, C.D.; McClintock, J.B.; Baker, B.J. Surface sequestration of chemical feeding deterrents in the Antarctic sponge Latrunculia apicalis as an optimal defense against sea star spongivory. Mar. Boil. 2003, 143, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, F.; Martín, R.; Rueda, A.; Fernandez, R.; Montalvo, D.; Gomez, C.; Sánchez-Puelles, J.M. Discorhabdins I and L, cytotoxic alkaloids from the sponge Latrunculia brevis. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunasekera, S.P.; Zuleta, I.A.; Longley, R.E.; Wright, A.E.; Pomponi, S.A. Discorhabdins S, T, and U, new cytotoxic pyrroloiminoquinones from a deep-water Caribbean sponge of the genus Batzella. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1615–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.-E.; Na, Z.; Jung, M.; Lee, H.-S.; Sim, C.J.; Nahm, K.; Oh, K.-B.; Shin, J. Discorhabdins from the Korean Marine Sponge Sceptrella sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y.; Harayama, Y.; Kamimura, D.; Yoshida, M.; Shibata, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Morimoto, K.; Fujioka, H.; Kita, Y. The synthetic and biological studies of discorhabdins and related compounds. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 4959–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goey, A.K.L.; Chau, C.H.; Sissung, T.M.; Cook, K.M.; Venzon, D.J.; Castro, A.; Ransom, T.R.; Henrich, C.J.; McKee, T.C.; McMahon, J.B.; et al. Screening and biological effects of marine pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids: Potential inhibitors of the HIF-1α/p300 interaction. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Janussen, D.; Peifer, C.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Tasdemir, D. Targeted isolation of tsitsikammamines from the antarctic deep-sea sponge Latrunculia biformis by molecular networking and anticancer activity. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, E.M.; Beukes, D.R.; Kelly, M.; Samaai, T.; Barrows, L.R.; Marshall, K.M.; Sincich, C.; Davies-Coleman, M.T. Cytotoxic Pyrroloiminoquinones from four new species of South African Latrunculid Sponges. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfourne, E. Analogues of marine pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids: Synthesis and antitumor properties. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolušić, E.; Larrieu, P.; Meinguet, C.; Colette, D.; Rives, A.; Blanc, S.; Ferain, T.; Pilotte, L.; Stroobant, V.; Wouters, J.; et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitory activity of derivatives of marine alkaloid tsitsikammamine A. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; A Kapono, C.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G.; Higa, T.; Sakai, R. Discorhabdin D, an antitumor alkaloid from the sponges Latrunculia brevis and Prianos sp. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 4127–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G. Cytotoxic pigments from New Zealand sponges of the genus Latrunculia: Discorhabdin A, discorhabdin B and discorhabdin C. Tetrahedron 1988, 44, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Baker, B.J.; Grimwade, J.; Leonard, A.; McClintock, J.B. Discorhabdin Alkaloids from the Antarctic Sponge Latrunculia apicalis. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grkovic, T.; Pearce, A.N.; Munro, M.H.G.; Blunt, J.W.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Copp, B.R. Isolation and characterization of diastereomers of discorhabdins H and K and assignment of absolute configuration to discorhabdins D, N, Q, S, T, and U. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1686–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Cheng, J.-F.; Ishibashi, M.; Nakamura, H.; Ohizumi, Y.; Hirata, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Lu, H.; Clardy, J. Prianosin A, a novel antileukemic alkaloid from the okinawan marine sponge Prianos melanos. Tetrahedron Lett. 1987, 28, 4939–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternhell, S. Correlation of interproton spin?spin coupling constants with structure. Q. Rev. Chem. Soc. 1969, 23, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.R.; Traquair, J.A.; Jarvis, W.R. New extracellular fatty acids in culture filtrates of Sporothrix flocculosa and S. rugulosa. Can. J. Chem. 1995, 73, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Santalova, E.A.; Gorshkova, I.A.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Guzii, A.G.; Gorbach, V.I.; Svetashev, V.I.; Stonik, V.A. A new cytotoxic fatty acid (5Z,9Z)-22-methyl-5,9-tetracosadienoic acid and the sterols from the far Eastern sponge Geodinella robusta. Lipids 2002, 37, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornprobst, J.-M.; Barnathan, G. Demospongic acids revisited. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2569–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunstone, F.; Pollard, M.; Scrimgeour, C.; Vedanayagam, H. Fatty acids. Part 50. 13C nuclear magnetic resonance studies of olefinic fatty acids and esters. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1977, 18, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grkovic, T.; Ding, Y.; Li, X.-C.; Webb, V.L.; Ferreira, D.; Copp, B.R. Enantiomeric discorhabdin alkaloids and establishment of their absolute configurations using theoretical calculations of electronic circular dichroism spectra. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 9133–9136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botić, T.; Defant, A.; Zanini, P.; Žužek, M.C.; Frangež, R.; Janussen, D.; Kersken, D.; Knez, Ž.; Mancini, I.; Sepčić, K. Discorhabdin alkaloids from Antarctic Latrunculia spp. sponges as a new class of cholinesterase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 136, 294–304. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, G.J.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Kelly-Borges, M.; Coetzee, P.S. New alkaloids from a South African latrunculid sponge. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 7135–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijoux, M.-G.; Gamble, W.R.; Hallock, Y.F.; Cardellina, J.H.; Van Soest, R.; Boyd, M.R. A new discorhabdin from two sponge genera. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 636–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Hamann, M.T. Atkamine: A New Pyrroloiminoquinone scaffold from the cold water Aleutian Islands Latrunculia sponge. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 1516–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchfield, C.; Greenberg, A.J.; Noto, G.; Morales, R.W. Unusually high levels of C24–C30 fatty acids in sponges of the class demospongiae. Lipids 1976, 11, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Řezanka, T.; Sigler, K. Odd-numbered very-long-chain fatty acids from the microbial, animal and plant kingdoms. Prog. Lipid Res. 2009, 48, 206–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchfield, C.; Marcantonio, E.E. Occurrence of 5,9,19-octacosatrienoic, 5,9-hexacosadienoic and 17-hexacosenoic acids in the marine spongeXestospongia halichondroides. Lipids 1978, 13, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbs, A.B.; Demidkova, D.A.; Dautova, T.N.; Latyshev, N.A. Fatty acid biomarkers of symbionts and unusual inhibition of tetracosapolyenoic acid biosynthesis in corals (Octocorallia). Lipids 2009, 44, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, V.; Blumenberg, M.; Hefter, J.; Pape, T.; Pomponi, S.; Reed, J.; Reitner, J.; Wörheide, G.; Michaelis, W. A chemical view of the most ancient metazoa—Biomarker chemotaxonomy of hexactinellid sponges. Naturwissenschaften 2002, 89, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botic, T.; Cör, D.; Anesi, A.; Guella, G.; Sepčić, K.; Janussen, D.; Kersken, D.; Knez, Ž. Fatty acid composition and antioxidant activity of Antarctic marine sponges of the genus Latrunculia. Polar Boil. 2015, 38, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boury-Esnault, N.; Rützler, K.; Ruetzler, K. Thesaurus of sponge morphology. Smithson. Contrib. Zool. 1997, 596, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaai, T.; Gibbons, M.J.; Kelly, M. Revision of the genus Latrunculia du Bocage, 1869 (Porifera: Demospongiae: Latrunculiidae) with descriptions of new species from New Caledonia and the Northeastern Pacific. Zootaxa 2006, 1127, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | A-375 | HCT-116 | A-549 | MB-231 | Hep G2 | HT-29 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude extract | 17.4 | 4.8 | 56.2 | 46.8 | 18.2 | 4.0 |
| Positive control | 0.13 | 10.6 | 31.4 | 15.2 | 14.6 | 3.0 |
| NO. | 1 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH, Mult. (J in Hz) | δH, Mult. (J in Hz) | δH, Mult. (J in Hz) | δH, Mult. (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 4.63 d (3.6) | 3.58 d (13.3) 3.23 d (13.3) | 5.79 d (3.6) | 5.79 d (3.6) |
| 2 | 4.15 d (3.6) | - | 4.36 d (3.6) | 4.35 d (3.6) |
| 4 | 6.14 s | 6.14 s | 6.23 s | 6.23 s |
| 7α | 2.57 dd (1.3, 12.0) | 2.66 dd (1.5, 12.1) | 2.63 dd (1.4, 12.1) | 2.64 d (1.2, 12.1) |
| 7β | 2.96 dd (3.6, 12.0) | 2.84 dd (3.5, 12.1) | 2.81 dd (3.7, 12.1) | 2.76 dd (3.6, 12.1) |
| 8 | 5.59 dd (1.3, 3.6) | 5.68 dd (1.5, 3.5) | 5.61 dd (1.4, 3.7) | 5.61 dd (1.2, 3.6) |
| 14 | 7.11 s | 7.14 s | 7.13 s | 7.13 s |
| 16 | 3.19 ddd (7.5, 13.0, 16.7) 3.06 ddd (3.0, 6.9, 16.7) | 3.10 m | 3.21 ddd (6.9, 7.5, 16.6) 3.08 ddd (2.9, 6.9, 16.6) | 3.22 ddd (6.8, 7.3, 16.6) 3.08 ddd (2.7, 6.8, 16.6) |
| 17 | 4.02 ddd (3.0, 7.5, 14.2) | 4.62 ddd (2.1, 5.6, 13.8) | 4.04 ddd (2.9, 7.5, 13.8) | 4.04 ddd (2.7, 7.3, 13.7) |
| 3.91 ddd (6.9, 13.0, 14.2) | 3.66 td (6.3, 13.8) | 3.93 td (6.9, 13.8) | 3.93 td (6.8, 13.7) | |
| 2′ | - | - | 2.15 s | 2.44 td (1.5, 7.5) |
| 3′ | - | - | - | 1.69 m |
| 4′ | - | - | - | 2.10 m |
| 5′ | - | - | - | 5.34 m |
| 6′ | - | - | - | 5.44 m |
| 7′ | - | - | - | 2.08 m |
| 8′ | - | - | - | 2.08 m |
| 9′ | - | - | - | 5.37 m |
| 10′ | - | - | - | 5.34 m |
| 11′–27′ | - | - | - | 1.25–1.40 m; 2.00–2.06 m; 5.36 m |
| 28′ | - | - | - | 0.90 t (7.0) |
| Position | 1 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δCa | δC | δC | |
| 1 | 68.5 (CH) | 42.4 (CH2) | 69.6 (CH) | 69.5 (CH) |
| 2 | 67.8 (CH) | 78.1 (C) | 64.6 (CH) | 64.6 (CH) |
| 3 | 184.8 (C) | 176.4 (C) | 183.1 (C) | 183.0 (C) |
| 4 | 114.1 (CH) | 110.9 (CH) | 114.4 (CH) | 114.4 (CH) |
| 5 | 171.5 (C) | 172.8 (C) | 171.2 (C) | 171.1 (C) |
| 6 | 48.6 (C) | 44.5 (C) | 47.0 (C) | 47.1 (C) |
| 7 | 37.4 (CH2) | 38.7 (CH2) | 37.4 (CH2) | 37.5 (CH2) |
| 8 | 63.7 (CH) | 63.1 (CH) | 63.5 (CH) | 63.5 (CH) |
| 10 | 148.6 (C) | 148.2 (C) | 149.0 (C) | 149.1 (C) |
| 11 | 167.5 (C) | 165.4 (C) | 167.1 (C) | 167.1 (C) |
| 12 | 125.6 (C) | 124.0 (C) | 125.6 (C) | 125.6 (C) |
| 14 | 127.2 (CH) | 126.0 (CH) | 127.4 (CH) | 127.4 (CH) |
| 15 | 119.2 (C) | 119.3 (C) | 119.4 (C) | 119.4 (C) |
| 16 | 20.6 (CH2) | 20.0 (CH2) | 20.7 (CH2) | 20.7 (CH2) |
| 17 | 52.8 (CH2) | 50.2 (CH2) | 52.9 (CH2) | 52.9 (CH2) |
| 19 | 150.3 (C) | 150.2 (C) | 150.4 (C) | 150.4 (C) |
| 20 | 101.8 (C) | 100.4 (C) | 100.6 (C) | 100.6 (C) |
| 21 | 122.7 (C) | 122.2 (C) | 122.7 (C) | 122.7 (C) |
| 1′ | - | 171.0 (C) | 173.6 (C) | |
| 2′ | - | 20.4 (CH3) | 34.0 (CH2) | |
| 3′ | - | - | 25.8 (CH2) | |
| 4′ | - | - | 27.5 (CH2) | |
| 5′ | - | - | 129.7 (CH) | |
| 6′ | - | - | 131.7 (CH) | |
| 7′ | - | - | 28.4 (CH2) | |
| 8′ | - | - | 28.4 (CH2) | |
| 9′ | - | - | 130.1 (CH) | |
| 10′ | - | - | 130.8 (CH) | |
| 11′–25′ | - | - | 28.1–30.9 (CH2); 130.9 (CH); 131.4 (CH) | |
| 26′ | - | - | 32.9 (CH2) | |
| 27′ | - | - | 23.7 (CH2) | |
| 28′ | - | - | 14.5 (CH3) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, F.; Peifer, C.; Janussen, D.; Tasdemir, D. New Discorhabdin Alkaloids from the Antarctic Deep-Sea Sponge Latrunculia biformis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080439
Li F, Peifer C, Janussen D, Tasdemir D. New Discorhabdin Alkaloids from the Antarctic Deep-Sea Sponge Latrunculia biformis. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(8):439. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080439
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Fengjie, Christian Peifer, Dorte Janussen, and Deniz Tasdemir. 2019. "New Discorhabdin Alkaloids from the Antarctic Deep-Sea Sponge Latrunculia biformis" Marine Drugs 17, no. 8: 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080439
APA StyleLi, F., Peifer, C., Janussen, D., & Tasdemir, D. (2019). New Discorhabdin Alkaloids from the Antarctic Deep-Sea Sponge Latrunculia biformis. Marine Drugs, 17(8), 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080439