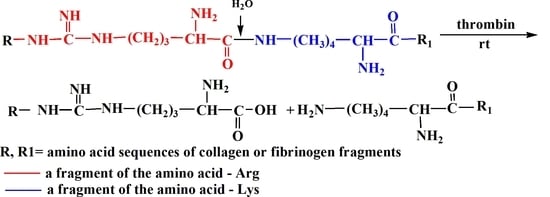
Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Marine Collagen and Fibrinogen Proteins in the Presence of Thrombin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Initial Materials for the Experiment
- distilled water;
- solutions of acetic acid with a concentration of 3% and 4%, which were prepared from glacial acetic acid by diluting with distilled water;
- acetic acid solution of cod collagen with a concentration of 3%;
- fibrinogen (Fn)—commercial product extracted from human blood plasma (Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany);
- enzyme—thrombin, proteolytic activity in 1 mL—50 IU (Research and Production Association «RENAM», Moscow, Russia);
- 1 M of sodium hydroxide solution, which was prepared from solid caustic soda by dissolving in a certain volume of distilled water;
- fibrin-collagen cell-free scaffold (provided by: Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education «Privolzhsky Research Medical University» of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation).
4.2. High Molecular Collagen Extraction Method
4.3. Methods of Protein Hydrolysis
4.4. The Method of Analysis of Molecular Weight Characteristics
4.5. Method of Analysis of Collagen, Fibrinogen, Fibrin-Collagen Scaffold Structure
5. Conclusions
- Low molecular fractions of collagen and fibrinogen hydrolysates have similar molecular weight values: Mw ~17–18 kDa and 10 kDa.
- The destruction of macromolecules of high molecular collagen to hydrolysis products takes place almost completely within the first minute mainly to the polymer fraction with Mw ~10 kDa.
- Enzymatic hydrolysis of fibrinogen goes slower than collagen, but it also occurs mainly to the polymer fraction with Mw ~10 kDa.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De la Puente, P.; Ludeña, D. Cell culture in autologous fibrin scaffolds for applications in tissue engineering. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 322, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Lv, Y. Application of collagen scaffold in tissue engineering: Recent advances and new perspectives. Polymers 2016, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pot, M.W.; Mihaila, S.M.; Te Brinke, D.; Van Der Borg, G.; Oosterwijk, E.; Daamen, W.F.; Van Kuppevelt, T.H. Introduction of specific 3D micromorphologies in collagen scaffolds using odd and even dicarboxylic acids. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 3908–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kayal, T.; Losi, P.; Pierozzi, S.; Soldani, G. A new method for fibrin-based electrospun/sprayed scaffold fabrication. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stapelfeldt, K.; Stamboroski, S.; Mednikova, P.; Brüggemann, D. Fabrication of 3D-nanofibrous fibrinogen scaffolds using salt-induced self assembly. Biofabrication 2019, 11, 025010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewle, A.; Pathak, N.; Rakshasmare, P.; Srivastava, A. Multifarious fabrication approaches of producing aligned collagen scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 779–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busra, M.F.M.; Lokanathan, Y. Recent development in the fabrication of collagen scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, A.; Ghaemi, R.V.; Webster, T.J.; Ashrafi, S.J.; Hatamian-Zaremi, A. A review of fibrin and fibrin composites for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 4937–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidenko, N.; Schuster, C.F.; Bax, D.V.; Farndale, R.W.; Hamaia, S.; Best, S.M.; Cameron, R.E. Evaluation of cell binding to collagen and gelatin: A study of the effect of 2D and 3D architecture and surface chemistry. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2016, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laurens, N.; Engelse, M.A.; Jungerius, C.; Löwik, C.W.; Van Hinsbergh, V.W.M.; Koolwijk, P. Single and combined effects of alphavbeta3- and alpha5beta1-integrins on capillary tube formation in a human fibrinous matrix. Angiogenesis 2009, 12, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.H.; Turnbull, J.; Guimond, S. Extracellular matrix and cell signalling: The dynamic cooperation of integrin, proteoglycan and growth factor receptor. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 209, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saito, M.; Takenouchi, Y.; Kunisaki, N.; Kimura, S. Complete primary structure of rainbow trout type I collagen consisting of alpha1(I)alpha2(I)alpha3(I) heterotrimers. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 2817–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralidharan, N.; Shakila, R.J.; Sukumar, D.; Jeyasekaran, G. Skin, bone and muscle collagen extraction from the trash fish, leather jacket (Odonus niger) and their characterization. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, Y.S.; Ok, Y.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kwak, J.Y.; Yoon, S. Marine collagen as a promising biomaterial for biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paradiso, F.; Fitzgerald, J.; Yao, S.; Barry, F.; Taraballi, F.; Gonzalez, D.; Conlan, R.S.; Francis, L. Marine collagen substrates for 2D and 3D ovarian cancer cell systems. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Xu, T. Biomaterials based on marine resources for 3D bioprinting applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, B.; Xu, Z.; Pinnock, C.B.; Kabbani, L.S.; Lam, M.T. Self-assembled collagen-fibrin hydrogel reinforces tissue engineered adventitia vessels seeded with human fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egorikhina, M.N.; Aleinik, D.Y.; Rubtsova, Y.P.; Levin, G.Y.; Charykova, I.N.; Semenycheva, L.L.; Bugrova, M.L.; Zakharychev, E.A. Scaffolds based on blood plasma cryoprecipitate and various types of collagen: Structural, mechanical and biological characteristics. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Meng, H.; Liu, Y.; Lee, B.P. Fibrin gel as an injectable biodegradable scaffold and cell carrier for tissue engineering. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tereshchenko, V.P.; Kirilova, I.A.; Larionov, P.M. Matrix carriers in bone tissue engineering. Successes Mod. Nat. Sci. 2015, 8, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Qin, S.; Li, B. Purification and structural aspects of type I collagen from Walleye Pollock (Theragrachalcogramma). J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2017, 26, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kezwoń, A.; Chromińska, I.; Fraczyk, T.; Wojciechowski, K. Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on surface activity and surface rheology of type I collagen. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 137, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorikhina, M.N.; Levin, G.Y.; Aleinik, D.Y.; Charykova, I.N.; Rubtsova, Y.P.; Sosnina, L.N.; Davydenko, D.V. Scaffold for substitution of skin defects based on natural biopolymers. Biol. Bull. Rev. 2018, 137, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, M.; Bergeron, R.; Komiyama, M. Bioorganic Chemistry of Enzymatic Catalysis; Mir: Moscow, Russia, 1987; p. 352. [Google Scholar]
- Semenycheva, L.L.; Valetova, N.B.; Chasova, V.O.; Podguzkova, M.V.; Zaharycheva, N.S.; Egorihina, M.N.; Astanina, M.V.; Kuznecova, Y.L. Molecular-mass parameters of collagen made from various raw materials and dynamics of parameter change in enzymic hydrolysis with pancreatine. Polym. Sci. Ser. D 2019, 4, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorikhina, M.N.; Levin, G.Y.; Charykova, I.N.; Alejnik, D.Y.; Sosnina, L.N. Method for Creating a Bioresorbable Cellular Scaffold Based on Fibrin of Blood Plasma. Patent RF No. 2,653,434, 8 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Berezov, T.T.; Korovin, B.F. Biological Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Meditsina: Moscow, Russia, 1998; p. 704. [Google Scholar]
- Vyskočilová, G.; Ebersbach, M.; Kopecká, R.; Prokeš, L.; Příhoda, J. Model study of the leather degradation by oxidation and hydrolysis. Herit. Sci. 2019, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bochkov, V.N.; Dobrovolskij, A.B.; Kushlinskij, N.E. Clinical Biochemistry, 3rd ed.; Tkachuk, V.A., Ed.; GEOTAR-Media: Moscow, Russia, 2008; p. 264. [Google Scholar]
- Momot, A.P.; Taranenko, I.A. Method for Determination of Fibrin Monomer Self-Assembly Time. Patent RF No. 2,366,955, 10 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Astanina, M.V.; Semenycheva, L.L.; Kuleshova, N.V.; Serdyuk, S.V. Method for Producing Fish Collagen Hydrolysate. Patent RF No. 2,665,589, 31 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Semenycheva, L.L.; Kuznetsova, J.L.; Valetova, N.B.; Geras’kina, E.V.; Tarankova, O.A. Method for Producing of Acetic Dispersion of High Molecular Fish Collagen. Patent RF No. 2,567,171, 10 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
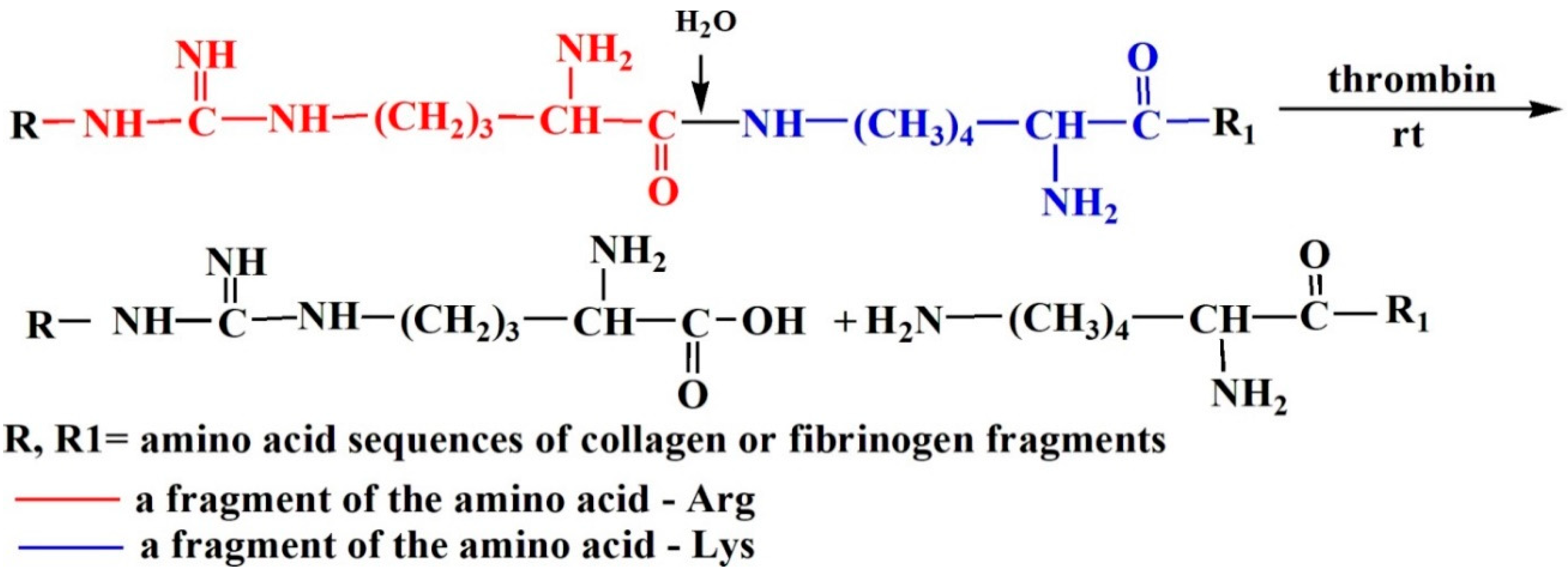



| Item No. | Sample | Parameter Values during Hydrolysis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial (Mw, kDa) | 1 min (Mw, kDa) | 60 min (Mw, kDa) | 3 days (Mw, kDa) | ||||||
| Value | Fraction, % | Value | Fraction, % | Value | Fraction, % | Value | Fraction, % | ||
| 1 | CC | 235–300 | 96 | 127 | 15 | 124 | 16 | 121 | 16 |
| 2 | 18 | 4 | 18 | 2 | 18 | 2 | 18 | 4 | |
| 3 | – | – | 10 | 83 | 10 | 82 | 10 | 80 | |
| 4 | Fn | 320–340 | 65 | 320–340 | 61 | 320–340 | 53 | 320–340 | 16 |
| 5 | 17 | 10 | 17 | 18 | 17 | 14 | 17 | 24 | |
| 6 | 10 | 25 | 10 | 21 | 10 | 33 | 10 | 60 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Semenycheva, L.L.; Egorikhina, M.N.; Chasova, V.O.; Valetova, N.B.; Kuznetsova, Y.L.; Mitin, A.V. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Marine Collagen and Fibrinogen Proteins in the Presence of Thrombin. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18040208
Semenycheva LL, Egorikhina MN, Chasova VO, Valetova NB, Kuznetsova YL, Mitin AV. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Marine Collagen and Fibrinogen Proteins in the Presence of Thrombin. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(4):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18040208
Chicago/Turabian StyleSemenycheva, Ludmila L., Marfa N. Egorikhina, Victoria O. Chasova, Natalya B. Valetova, Yulia L. Kuznetsova, and Alexander V. Mitin. 2020. "Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Marine Collagen and Fibrinogen Proteins in the Presence of Thrombin" Marine Drugs 18, no. 4: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18040208
APA StyleSemenycheva, L. L., Egorikhina, M. N., Chasova, V. O., Valetova, N. B., Kuznetsova, Y. L., & Mitin, A. V. (2020). Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Marine Collagen and Fibrinogen Proteins in the Presence of Thrombin. Marine Drugs, 18(4), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18040208