Evaluation and Transcriptome Analysis of the Novel Oleaginous Microalga Lobosphaera bisecta (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta) for Arachidonic Acid Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Evaluation of Oleaginous Microalga L. bisecta SAG2043 for Lipid and AA Production
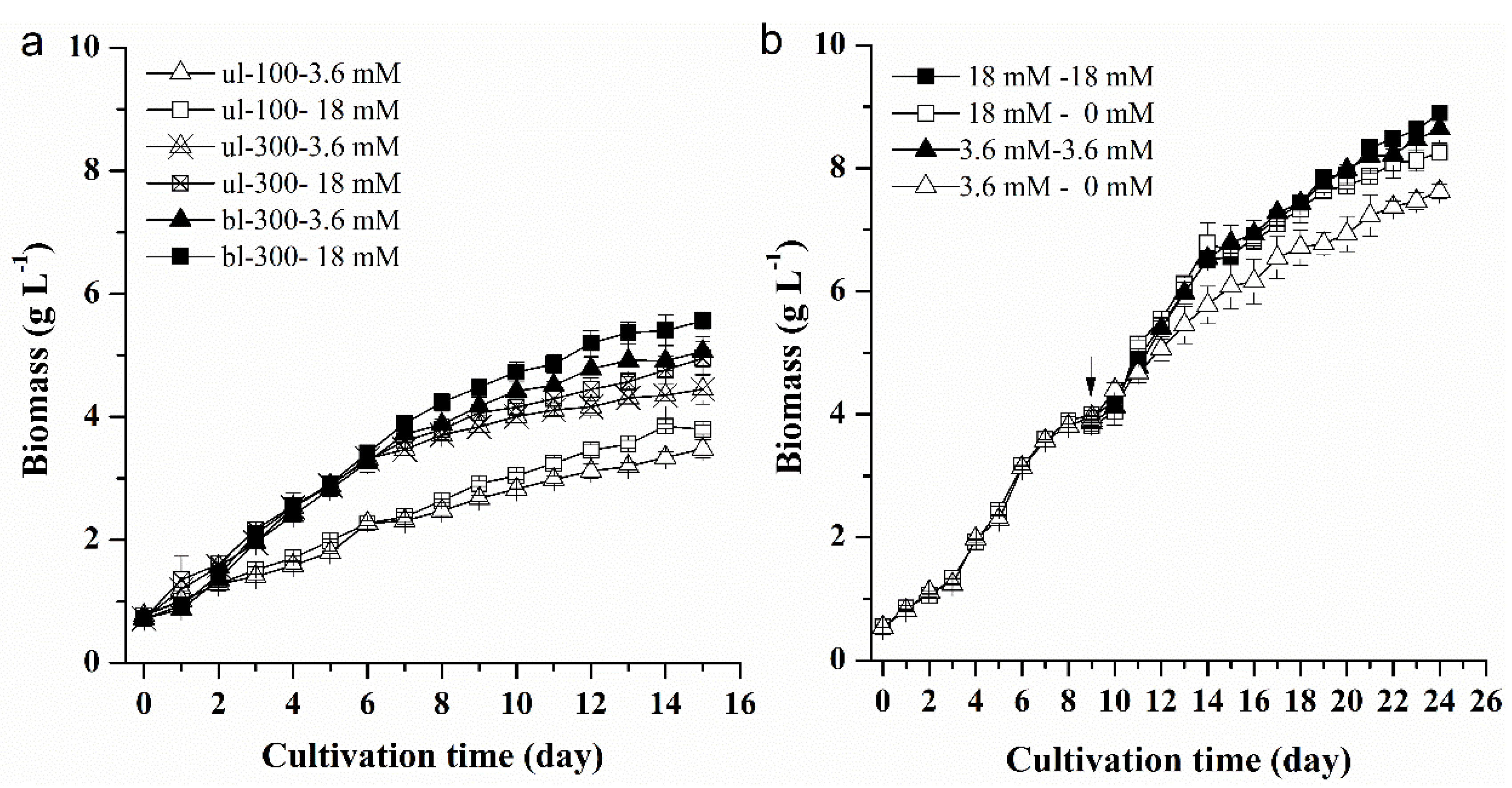
2.1.1. Effects of Different Nitrogen Concentrations, Light Intensity, and Medium Replacement on the Growth of L. bisecta SAG2043
2.1.2. Effects of Different Nitrogen Concentrations, Light Intensity and Medium Replacement on the Lipid Content of L. bisecta SAG2043
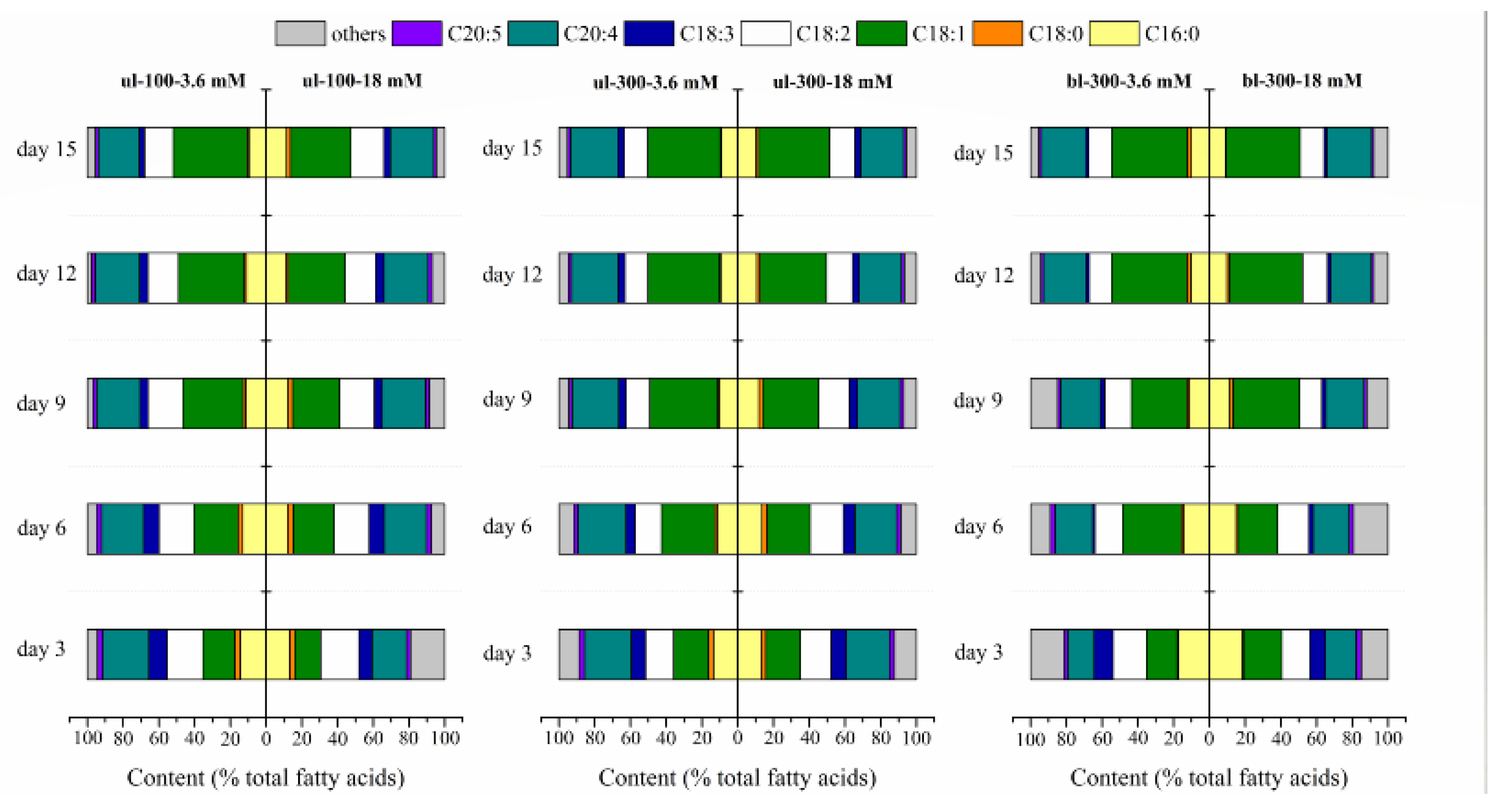
2.1.3. Effects of Different Nitrogen Concentrations, Light Intensity, and Medium Replacement on the Fatty Acids Profile of L. bisecta SAG2043
2.1.4. The Proportion of AA within the Lipid Components of L. bisecta SAG2043
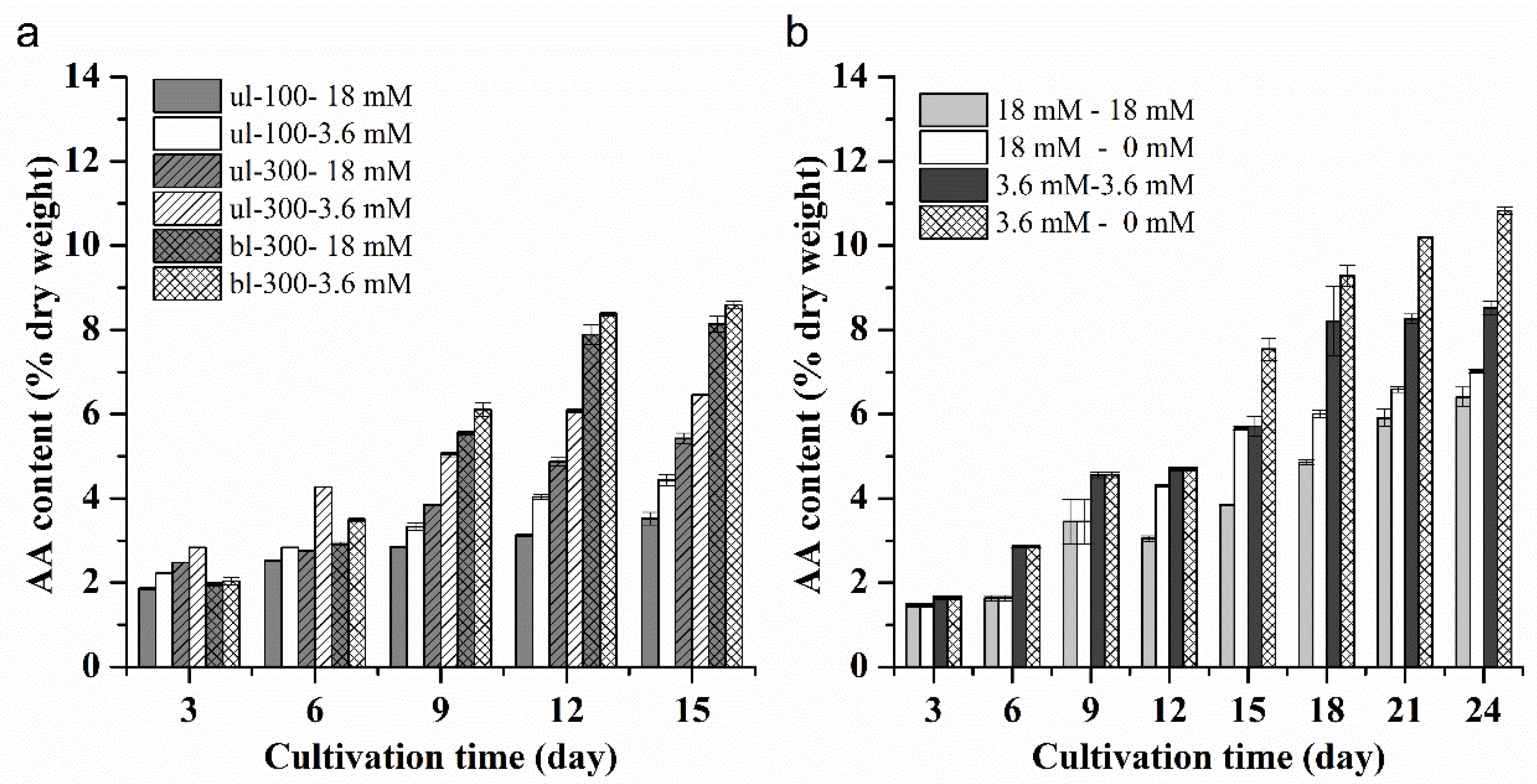
2.1.5. Effects of Different Nitrogen Concentrations, Light Intensity and Medium Replacement on the Lipid and AA Productivity of L. bisecta SAG2043
2.2. Transcriptome Analysis of the Novel Oleaginous Microalga L. bisecta SAG2043 Revealed Its Potential Mechanism for AA Synthesis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Algal Strain and Culture Conditions
3.2. Experimental Design
3.2.1. Interactive Effects of Nitrogen Concentrations and Light Intensities on the Growth of L. bisecta SAG2043
3.2.2. The Effects of Different Nitrogen Concentrations and Medium Replacement Treatments on the Growth of L. bisecta SAG2043
3.3. Analysis Methods
3.3.1. Biomass Measurement
3.3.2. Lipid Extraction and Determination
3.3.3. Fatty Acids Analysis
3.3.4. Separation of Lipid Fractions and Quantification
3.3.5. RNA Extraction, Library Construction, Sequencing, Assembly and Functional Annotation
3.3.6. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) Analysis
3.3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Shanab, S.M.; Hafez, R.M.; Fouad, A.S. A review on algae and plants as potential source of arachidonic acid. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 11, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.J.; Ren, L.J.; Nie, Z.K.; Huang, H.; Ouyang, P.K. Fungal arachidonic acid-rich oil: Research, development and industrialization. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2014, 34, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, V.S.; Hafez, E.A.A. Synopsis of arachidonic acid metabolism: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 11, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, O.P.; Singh, A. Omega-3/6 fatty acids: Alternative sources of production. Process. Biochem. 2005, 40, 3627–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.B.; Liu, F.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, Z.G. A Δ-9 fatty acid desaturase gene in the microalga Myrmecia incisa Reisigl: Cloning and functional analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, J.D. The promising future of microalgae: Current status, challenges, and optimization of a sustainable and renewable industry for biofuels, feed, and other products. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigogno, C.; Khozin-Goldberg, I.; Boussiba, S.; Vonshak, A.; Cohen, Z. Lipid and fatty acid composition of the green oleaginous alga Parietochloris incisa, the richest plant source of arachidonic acid. Phytochemistry 2002, 60, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, I.; Hodac, L.; Friedl, T.; Feussner, I. Fatty acid profiles and their distribution patterns in microalgae: A comprehensive analysis of more than 2000 strains from the SAG culture collection. BMC Plant. Biol. 2011, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Řezanka, T.; Lukavský, J.; Nedbalová, L.; Sigler, K. Production of structured triacylglycerols from microalgae. Phytochemistry 2014, 104, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, E.S.; Hwang, J.H.; El-Dalatony, M.M.; Kurade, M.B.; Kabra, A.N.; Abou-Shanab, R.A.; Kim, K.H.; Yang, I.S.; Govindwar, S.P.; Kim, S.; et al. Enhancement of microalgal growth and biocomponent-based transformations for improved biofuel recovery: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 258, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaya, Y.; Azuma, H.; Kiyota, M. Effects of temperature, CO2/O2 concentrations and light intensity on cellular multiplication of microalgae, Euglena gracilis. Adv. Space Res. 2005, 35, 1584–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Qi, M.; Xiang, Q.; Yao, C.; Yongkui, Z.; Lan, X. Storage of starch and lipids in microalgae: Biosynthesis and manipulation by nutrients. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 291, 121894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, C.; Bai, F.W.; Zhao, X.Q. Effects of nitrogen concentration and media replacement on cell growth and lipid production of oleaginous marine microalga Nannochloropsis oceanica DUT01. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 78, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, B.; Lu, X.; Cheng, K.W.; Chen, F. Staged cultivation enhances biomass accumulation in the green growth phase of Haematococcus pluvialis. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 233, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gao, B.; Wu, M.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C. A novel strategy for the hyper-production of astaxanthin from the newly isolated microalga Haematococcus pluvialis JNU35. Algal Res. 2019, 39, 101466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aratboni, H.A.; Rafiei, N.; Garcia-Granados, R.; Alemzadeh, A.; Morones-Ramírez, J.R. Biomass and lipid induction strategies in microalgae for biofuel production and other applications. Microb. Cell Fact. 2019, 18, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lari, Z.; Moradi-kheibari, N.; Ahmadzadeh, H.; Abrishamchi, P.; Moheimani, N.R.; Murry, M.A. Bioprocess engineering of microalgae to optimize lipid production through nutrient management. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 3235–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, S.; Rai, M.P.; Sharma, R. Effect of nitrogen on growth and lipid content of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 7, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.H.; Huang, S.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Hasunuma, T.; Kondo, A.; Chang, J.S. Bioethanol production using carbohydrate-rich microalgae biomass as feedstock. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 135, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fon-Sing, S.; Borowitzka, M.A. Isolation and screening of euryhaline Tetraselmis spp. suitable for large-scale outdoor culture in hyper saline media for biofuels. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, C.; Hu, G.; Li, F. Effects of light intensity on the growth and lipid accumulation of microalga Scenedesmus sp. 11-1 under nitrogen limitation. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2012, 166, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, T.; Ota, S.; Yamazaki, T.; Hirata, A.; Zachleder, V.; Kawano, S. Starch and lipid accumulation in eight strains of six Chlorella species under comparatively high light intensity and aeration culture conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 158, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Chen, Z.; Xue, S.; Zhang, W. Increased lipid production of the marine oleaginous microalgae Isochrysis zhangjiangensis (Chrysophyta) by nitrogen supplement. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6710–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knothe, G. Production and properties of biodiesel from algal oils. In Algae for Biofuels and Energy; Borowitzka, M.A., Moheimani, N.R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 207–221. [Google Scholar]
- Breuer, G.; Lamers, P.P.; Martens, D.E.; Draaisma, R.B.; Wijffels, R.H. The impact of nitrogen starvation on the dynamics of triacylglycerol accumulation in nine microalgae strains. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 124, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lim, S.R.; Jeong, D.G.; Kim, J.H. Characterization of an Oleaginous Unicellular Green Microalga, Lobosphaera incisa (Reisigl, 1964) Strain K-1, Isolated From a Tidal Flat in the Yellow Sea, Republic of Korea. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klok, A.J.; Martens, D.E.; Wijffels, R.H.; Lamers, P.P. Simultaneous growth and neutral lipid accumulation in microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 134, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar-Méndez, A.; Miernyk, J.A.; Randall, D.D. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity in plant cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenka, S.K.; Carbonaro, N.; Park, R.; Miller, S.M.; Thorpe, I.; Li, Y. Current advances in molecular, biochemical, and computational modeling analysis of microalgal triacylglycerol biosynthesis. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1046–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, D.; Yoon, K.; Zhu, S.; Sommerfeld, M.; Hu, Q. Molecular and cellular mechanisms for lipid synthesis and accumulation in microalgae: Biotechnological implications. In Handbook of Microalgal Culture: Applied Phycology and Biotechnology, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 545–565. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, K.D.; Ohlrogge, J.B. Compartmentation of triacylglycerol accumulation in plants. J. Biolog. Chem. 2012, 287, 2288–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Lopez, N.; Usher, S.; Sayanova, O.V.; Napier, J.A.; Haslam, R.P. Modifying the lipid content and composition of plant seeds: Engineering the production of LC-PUFA. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, J.G.; Browse, J. The Δ8-desaturase of Euglena gracilis: An alternate pathway for synthesis of 20-carbon polyunsaturated fatty acids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 365, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisonneuve, S.; Bessoule, J.J.; Lessire, R.; Delseny, M.; Roscoe, T.J. Expression of rapeseed microsomal lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase isozymes enhances seed oil content in Arabidopsis. Plant. Physiol. 2010, 152, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, K.; Han, D.; Li, Y.; Sommerfeld, M.; Hu, Q. Phospholipid: Diacylglycerol acyltransferase is a multifunctional enzyme involved in membrane lipid turnover and degradation while synthesizing triacylglycerol in the unicellular green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The Plant. Cell 2012, 24, 3708–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Yang, J.; Lei, X.; Xia, S.; Li, A.; Zhang, C. Characterization of cell structural change, growth, lipid accumulation, and pigment profile of a novel oleaginous microalga, Vischeria stellata (Eustigmatophyceae), cultured with different initial nitrate supplies. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khozin-Goldberg, I.; Shrestha, P.; Cohen, Z. Mobilization of arachidonyl moieties from triacylglycerols into chloroplastic lipids following recovery from nitrogen starvation of the microalga Parietochloris incisa. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2005, 1738, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Christie, W.W.; Han, X. Analysis of simple lipid classes. In Lipid Analysis, 4th ed.; Christie, W.W., Han, X., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2012; pp. 69–90. [Google Scholar]
- Yongmanitchai, W.; Ward, O.P. Separation of lipid classes from Phaeodactylum tricornutum using silica cartridges. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 3405–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Gao, B.; Wu, M.; Wang, F.; Zhang, C. Comparative transcriptome analysis of a long-time span two-step culture process reveals a potential mechanism for astaxanthin and biomass hyper-accumulation in Haematococcus pluvialis JNU35. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Chen, Z. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Assembly | Results | Annotation | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Number | 43,440 | COG | 4690 |
| Total Length (bp) | 41,805,231 | GO | 5695 |
| Mean Length (bp) | 962.37 | KEGG | 4404 |
| N50 Length (bp) | 2833 | KOG | 6267 |
| 200–300 | 17,294 (39.81%) | Pfam | 8398 |
| 300–500 | 12,004 (27.63%) | Swiss-Prot | 6080 |
| 500–1 kbp | 5146 (11.85%) | eggNOG | 9068 |
| 1 kbp–2 kbp | 2930 (6.74%) | Nr | 10,116 |
| >2 kbp | 6066 (13.96%) | All annotated | 10,655 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, B.; Huang, L.; Lei, X.; Meng, G.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C. Evaluation and Transcriptome Analysis of the Novel Oleaginous Microalga Lobosphaera bisecta (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta) for Arachidonic Acid Production. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050229
Gao B, Huang L, Lei X, Meng G, Liu J, Zhang C. Evaluation and Transcriptome Analysis of the Novel Oleaginous Microalga Lobosphaera bisecta (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta) for Arachidonic Acid Production. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(5):229. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050229
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Baoyan, Luodong Huang, Xueqing Lei, Ge Meng, Jianguo Liu, and Chengwu Zhang. 2020. "Evaluation and Transcriptome Analysis of the Novel Oleaginous Microalga Lobosphaera bisecta (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta) for Arachidonic Acid Production" Marine Drugs 18, no. 5: 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050229
APA StyleGao, B., Huang, L., Lei, X., Meng, G., Liu, J., & Zhang, C. (2020). Evaluation and Transcriptome Analysis of the Novel Oleaginous Microalga Lobosphaera bisecta (Trebouxiophyceae, Chlorophyta) for Arachidonic Acid Production. Marine Drugs, 18(5), 229. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050229




