Highly Oxygenated Constituents from a Marine Alga-Derived Fungus Aspergillus giganteus NTU967
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation and Characterization of Secondary Metabolites
2.2. Anticancer and Anti-Angiogenic Assays of Secondary Metabolites
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fungal Strain and Culture
3.3. Extraction and Isolation of Secondary Metabolites
3.4. Cell Culture
3.5. Biologic Assay for Anticancer Activity
3.6. Biologic Assay for Anti-Angiogenic Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rateb, M.E.; Ebel, R. Secondary metabolites of fungi from marine habitats. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 290–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Meng, W.; Cao, C.; Wang, J.; Shan, W.; Wang, Q. Antibacterial and antifungal compounds from marine fungi. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3479–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Ding, L.; Wang, N.; Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, B.; He, B.; Wu, B.; Jin, H. Isolation and characterization of two new metabolites from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. LS34 by OSMAC approach. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, R.; Bai, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Exploring structural diversity of microbe secondary metabolites using OSMAC strategy: A literature review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoang, T.P.T.; Roullier, C.; Boumard, M.C.; Robiou du Pont, T.; Nazih, H.; Gallard, J.F.; Pouchus, Y.F.; Beniddir, M.A.; Grovel, O. Metabolomics-driven discovery of meroterpenoids from a mussel-derived penicillium ubiquetum. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 2501–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selegato, D.M.; Freire, R.T.; Pilon, A.C.; Biasetto, C.R.; de Oliveira, H.C.; de Abreu, L.M.; Araujo, A.R.; da Silva Bolzani, V.; Castro-Gamboa, I. Improvement of bioactive metabolite production in microbial culture – A systems approach by OSMAC and deconvolution-based 1H NMR quantification. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2019, 57, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.J.; Li, D.Y.; Li, Y.C.; Hua, H.M.; Ma, E.L.; Li, Z.L. Caryophyllene sesquiterpenes from the marine-derived fungus Ascotricha sp. ZJ-M-5 by the one strain-many compounds strategy. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1367–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.F. Seaweeds of Northeastern Taiwan; National Taiwan Museum: Taipei, Taiwan, 2000; pp. 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.S.; Yang, Y.L.; Wu, C.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Lee, C.K.; Tzean, S.S.; Lee, T.H. Efficient identification of fungal antimicrobial principles by tandem MS and NMR database. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raistrick, H. Patulin in the common cold collaborative research on a derivative of Penicillin patulum Bainier. Lancet 1943, 242, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, N.; Yu, J.Q.; Beale, P.; Hug, F. Dose and sequence dependent synergism from the combination of oxaliplatin with emetine and patulin against colorectal cancer. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2019, 20, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buechi, G.; Luk, K.C.; Kobbe, B.; Townsend, J.M. Four new mycotoxins of Aspergillus clavatus related to tryptoquivaline. J. Org. Chem. 1977, 42, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, N.; Inoue, Y.; Sekine, M.; Hayakawa, Y.; Homma, H.; Omura, S.; Tomoda, H. Relative and absolute stereochemistry of quinadoline B, an inhibitor of lipid droplet synthesis in macrophages. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 5273–5276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata-Sena, M.; Ramos, A.A.; Buttachon, S.; Castro-carvalho, B.; Marques, P.; Dethoup, T.; Kijjoa, A.; Rocha, E. Cytotoxic activity of secondary metabolites from marine-derived fungus Neosartorya siamensis in human cancer cells. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 1862–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; Wang, G.J.; Pang, K.L.; Lee, C.K.; Kuo, Y.H.; Lin, R.K.; Lee, T.H. Angiogenesis inhibitors and anti-inflammatory agents from Phoma sp. NTOU4195. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2983–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, R.S.; Ahirwar, B. A steroidal derivative from Trigonella foenumgraecum L. that induces apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
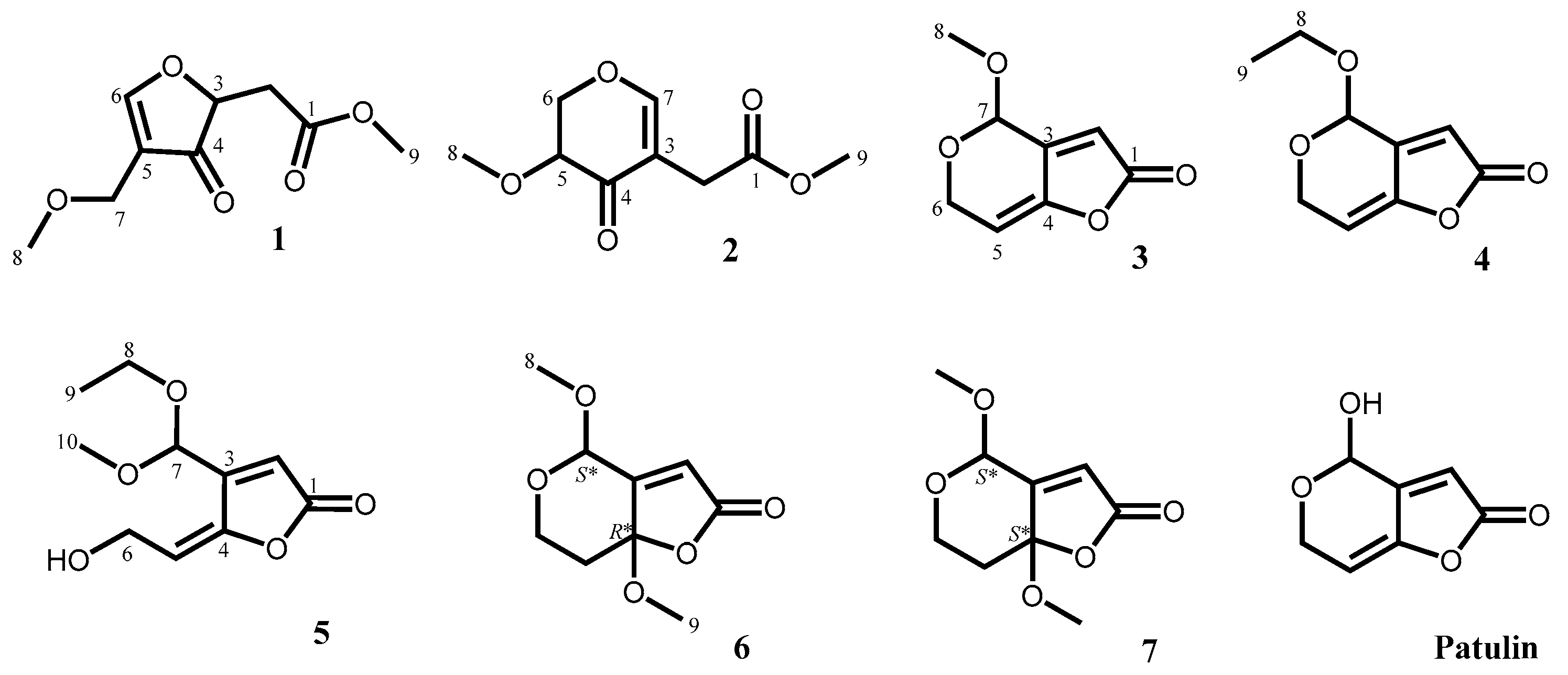


| No. | 1 a,b | 2 a,b | 3 a,b | 4 a,b | 5 a,b | 6 a,b | 7 a,b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 172.9 s | 173.6 s | 170.6 s | 170.6 s | 169.6 s | 170.6 s | 170.6 s |
| 2 | 36.7 t | 31.1 t | 111.9 d | 111.1 d | 119.7 d | 117.1 d | 119.9 d |
| 3 | 69.7 d | 111.7 s | 147.5 s | 147.6 s | 156.5 s | 163.9 s | 160.9 s |
| 4 | 191.8 s | 191.3 s | 150.9 s | 151.3 s | 148.2 s | 107.6 s | 107.2 s |
| 5 | 116.2 s | 77.3 d | 109.3 d | 109.4 d | 115.3 d | 40.3 t | 41.9 t |
| 6 | 166.1 d | 72.3 t | 60.0 t | 60.0 t | 57.3 t | 62.3 t | 58.3 t |
| 7 | 75.9 t | 164.0 d | 95.9 d | 94.8 d | 97.6 d | 98.8 d | 97.4 d |
| 8 | 57.7 q | 58.7 q | 56.5 q | 65.6 t | 62.8 t | 57.3 q | 55.5 q |
| 9 | 52.7 q | 52.5 q | 15.4 q | 15.4 q | 51.2 q | 52.2 q | |
| 10 | 53.2 q |
| No. | 1 a | 2 b | 3 b | 4 b | 5 b | 6 b | 7 b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | |||||||
| 2 | 2.61 d (6.2) | 3.14 s | 6.60 s | 6.05 s | 6.31 s | 6.12 s | 6.23 s |
| 3 | 4.55 c | ||||||
| 4 | |||||||
| 5 | 3.70 t (4.7) | 6.02 m | 6.02 m | 5.85 t (6.9) | 1.91 m | 1.99 m | |
| 2.38 dt (13.5, 2.1) | 2.34 d (13.2) | ||||||
| 6 | 7.66 s | 4.49 d (4.7) | 4.37 dd (17.5, 4.4) | 4.36 dd (17.3, 4.4) | 4.40 d (6.9) | 3.76 td (12.2, 2.1) | 3.71 m |
| 4.56 dd (17.5, 2.5) | 4.56 dd (17.3, 2.6) | 4.01 m | 4.10 td (12.0, 2.0) | ||||
| 7 | 4.55 c | 7.50 s | 5.68 s | 5.79 s | 5.52 s | 5.11 s | 5.52 s |
| 8 | 3.35 s | 3.45 s | 3.54 s | 3.71 m | 3.63 m | 3.60 s | 3.46 s |
| 3.91 m | |||||||
| 9 | 3.71 s | 3.67 s | 1.26 t (7.1) | 1.24 t (7.1) | 3.23 s | 3.19 s | |
| 10 | 3.36 s |
| Compounds | Anticancer (IC50, μM) | Anti-Angiogenesis (IC50, μM) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SK-Hep-1 a | PC-3 b | EPC c | |
| Compound 3 | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 7.3 ± 0.3 | 4.6 ± 0.3 |
| Patulin | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | 4.7 ± 0.2 |
| Paclitaxel d | 0.011 ± 0.002 | 0.013 ± 0.002 | – |
| Sorafenib d | – | – | 4.8 ± 0.3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.-J.; Wang, S.-W.; Chiang, Y.-R.; Pang, K.-L.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Shih, T.-Y.; Lee, T.-H. Highly Oxygenated Constituents from a Marine Alga-Derived Fungus Aspergillus giganteus NTU967. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060303
Chen J-J, Wang S-W, Chiang Y-R, Pang K-L, Kuo Y-H, Shih T-Y, Lee T-H. Highly Oxygenated Constituents from a Marine Alga-Derived Fungus Aspergillus giganteus NTU967. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(6):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060303
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jih-Jung, Shih-Wei Wang, Yin-Ru Chiang, Ka-Lai Pang, Yueh-Hsiung Kuo, Tsai-Yen Shih, and Tzong-Huei Lee. 2020. "Highly Oxygenated Constituents from a Marine Alga-Derived Fungus Aspergillus giganteus NTU967" Marine Drugs 18, no. 6: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060303
APA StyleChen, J.-J., Wang, S.-W., Chiang, Y.-R., Pang, K.-L., Kuo, Y.-H., Shih, T.-Y., & Lee, T.-H. (2020). Highly Oxygenated Constituents from a Marine Alga-Derived Fungus Aspergillus giganteus NTU967. Marine Drugs, 18(6), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18060303






