Exploration of the Electrophilic Reactivity of the Cytotoxic Marine Alkaloid Discorhabdin C and Subsequent Discovery of a New Dimeric C-1/N-13-Linked Discorhabdin Natural Product
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Reactivity towards Thiols
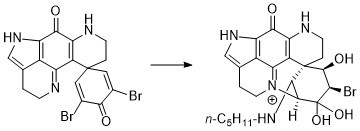
2.2. Reactivity towards Amines
2.3. Reaction with Lysozyme
2.4. A Cyclic Carbinolamine Analogue of Discorhabdin C
2.5. Isolation of a New Example of a C-N-Linked Discorhabdin Dimer
2.6. Assessing Biological Activities
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Semi-Synthesis
4.2.1. Thiopentanyl-Discorhabdin C Adduct (4)
4.2.2. N-Acetyl-l-Cysteinyl Discorhabdin C Adduct (5)
4.2.3. Aminopentane Discorhabdin C Dihydrate Adduct (6)
4.2.4. Discorhabdin C Hydrogenation Product (7)
4.3. Isolation and Purification of Discorhabdin C (2) and Dimer (8)
4.4. Biological Assays
4.4.1. Antitumour Cytotoxicity
4.4.2. Antiparasitic and L6 Cytotoxicity Assays
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antunes, E.M.; Copp, B.R.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Samaai, T. Pyrroloiminoquinone and related metabolites from marine sponges. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.-F.; Fan, H.; Xiong, J.; Wu, S.-B. Discorhabdins and Pyrroloiminoquinone-Related Alkaloids. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5465–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; McCombs, J.D.; Munro, M.H.G. Discorhabdin C, a highly cytotoxic pigment from a sponge of the genus Latrunculia. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 5476–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G. Cytotoxic pigments from New Zealand sponges of the genus Latrunculia: Discorhabdin A, discorhabdin B and discorhabdin C. Tetrahedron 1988, 44, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Janussen, D.; Tasdemir, D. New discorhabdin B dimers with anticancer activity from the Antarctic deep-sea sponge Latrunculia biformis. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Pandey, P.; Janussen, D.; Chittiboyina, A.G.; Ferreira, D.; Tasdemir, D. Tridiscorhabdin and didiscorhabdin, the first discorhabdin oligomers linked with a direct C–N bridge from the sponge Latrunculia biformis collected from the deep sea in Antarctica. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Y.; Hamann, M.T. Atkamine: A new pyrroloiminoquinone scaffold from the cold water Aleutian Islands Latrunculia sponge. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 1516–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, Y.K.; Wang, X.J.; Sims, J.; Wang, B.; Pandey, P.; Welsh, C.L.; Stone, R.P.; Avery, M.A.; Doerksen, R.J.; Ferreira, D.; et al. Computationally assisted discovery and assignment of a highly strained and PANC-1 selective alkaloid from Alaska’s deep ocean. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4338–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Peifer, C.; Janussen, D.; Tasdemir, D. New discorhabdin alkaloids from the Antarctic deep-sea sponge Latrunculia biformis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goey, A.K.L.; Chau, C.H.; Sissung, T.M.; Cook, K.M.; Venzon, D.J.; Castro, A.; Ransom, T.R.; Henrich, C.J.; McKee, T.C.; McMahon, J.B.; et al. Screening and biological effects of marine pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids: Potential inhibitors of the HIF-1α/p300 interaction. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, E.M.; Strope, J.D.; Beedie, S.; Huang, P.A.; Goey, A.K.L.; Cook, K.; Schofield, C.J.; Chau, C.H.; Cadelis, M.M.; Copp, B.R.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of discorhabdins in antiangiogenic and antitumor models. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ford, J.; Capon, R.J. Discorhabdin R: A new antibacterial pyrroloiminoquinone from two Latrunculiid marine sponges, Latrunculia sp. and Negombata sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1527–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, M.; Ding, Y.; Wang, B.; Tekwani, B.L.; Schinazi, R.F.; Franzblau, S.; Kelly, M.; Stone, R.; Li, X.-C.; Ferreira, D.; et al. Anti-infective discorhabdins from a deep-water Alaskan sponge of the genus Latrunculia. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeon, J.-E.; Na, Z.; Jung, M.; Lee, H.-S.; Sim, C.J.; Nahm, K.; Oh, K.-B.; Shin, J. Discorhabdins from the Korean marine sponge Sceptrella sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y.; Harayama, Y.; Kamimura, D.; Yoshida, M.; Shibata, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Morimoto, K.; Fujioka, H.; Kita, Y. The synthetic and biological studies of discorhabdins and related compounds. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 4959–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, C.F.C.; Grkovic, T.; Pearce, A.N.; Copp, B.R. Investigation of the electrophilic reactivity of the cytotoxic marine alkaloid discorhabdin B. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 3092–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.F.C.; Cadelis, M.M.; Copp, B.R. Exploration of the influence of spiro-dienone moiety on biological activity of the cytotoxic marine alkaloid discorhabdin P. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 4779–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G.; Higa, T.; Sakai, R. Discorhabdin D, an antitumor alkaloid from the sponges Latrunculia brevis and Prianos sp. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 4127–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grkovic, T.; Pearce, A.N.; Munro, M.H.G.; Blunt, J.W.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Copp, B.R. Isolation and characterization of diastereomers of discorhabdins H and K and assignment of absolute configuration to discorhabdins D, N, Q, S, T, and U. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1686–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, H.J.; Jautelat, M.; Messe, M.T.; Weigert, F.J.; Roberts, J.D. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. carbon-13 spectra of steroids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1969, 91, 7445–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadelis, M.M.; Copp, B.R. Investigation of the electrophilic reactivity of the biologically active marine sesquiterpenoid onchidal and model compounds. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2229–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.A.; Buchanan, M.S.; Duffy, S.; Avery, V.M.; Charman, S.A.; Charman, W.N.; White, K.L.; Shackleford, D.M.; Edstein, M.D.; Andrews, K.T.; et al. Antimalarial activity of pyrroloiminoquinones from the Australian marine sponge Zyzzya sp. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 5851–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Copp, B.R.; Fulton, K.F.; Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G. natural and synthetic derivatives of discorhabdin C, a cytotoxic pigment from the New Zealand sponge Latrunculia cf. bocagei. J. Org. Chem. 1994, 59, 8233–8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemaker, R.H. The NCI60 human tumour cell line anticancer drug screen. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.V.; Kumar, V.; Velez, C.; Zayas, B. Imidazolium-derived ionic salts induce inhibition of cancerous cell growth through apoptosis. MedChemCommun 2014, 5, 1404–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, I.; Sener, B.; Kaiser, M.; Brun, R.; Tasdemir, D. Inhibitory activity of marine sponge-derived natural products against parasitic protozoa. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| No. | 4 | No. | 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (Mult., J in Hz) a | δC b | δH (Mult., J in Hz) c | δC d | ||
| 1 | - | 169.7 | - | 167.5 | |
| 2 | 6.41 (s) | 121.7 | 6.56/6.58 (s) | 122.2/122.4 | |
| 3 | - | 176.2 | - | 176.2 | |
| 4 | - | 125.9 | - | 126.0 | |
| 5 | 7.72 (s) | 152.1 | 7.71 (s) | 152.2 | |
| 6 | 47.3 | 47.3 | |||
| 7 | 2.39–2.33 (m) | 39.2/39.4 | 2.34 (m) | 39.2/39.4 | |
| 2.16–2.12 (m) | 2.13 (m) | ||||
| 8 | 3.92–3.87 (m) | 39.2/39.4 | 3.88 (m) | 39.2/39.4 | |
| 3.73–3.67 (m) | 3.69 (m) | ||||
| 10 | - | 154.1 | - | 154.2 | |
| 11 | - | 166.4 | - | 166.4 | |
| 12 | - | 125.3 | - | 125.4 | |
| 14 | 7.21 (s) | 127.9 | 7.20 (s) | 127.9 | |
| 15 | 121.4 | - | 121.5 | ||
| 16 | 2.95–2.83 (m) | 19.6 | 2.89 (m) | 19.5 | |
| 17 | 3.79 (t, 7.4) | 45.2 | 3.84–3.76 (m) | 45.3/45.4 | |
| 19 | - | 156.2 | - | 156.1 | |
| 20 | - | 94.8 | - | 94.3 | |
| 21 | - | 124.6 | - | 124.6 | |
| S-n-C5H11 | S-NAc-cysteine | ||||
| 2’ | 3.03–2.95 (m) | 32.2/32.5 | 2′ | 3.54/3.57 (m) | 33.8/34.2 |
| 3’ | 1.75–1.69 (m) | 28.4 | 3.21/3.27 (m) | ||
| 4’ | 1.47–1.33 (m) | 32.2/32.5 | 3′ | 4.71/4.75 (m) | 51.5/52.0 |
| 5’ | 1.47–1.33 (m) | 23.2 | 5′ | - | 173.5 |
| 6’ | 0.92 (t, 7.2) | 14.2 | 6′ | 1.94/1.97 (s) | 22.4 |
| 7′ | - | 168.1 |
| No. | δH (Mult., J in Hz) | δC |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.28 (d, 2.3) | 55.3 |
| 2 | 4.38 (d, 2.3) | 66.7 |
| 3 | - | 98.0 |
| 4 | 4.42 (d, 3.4) | 57.5 |
| 5 | 4.15 (br m) | 75.8 |
| 6 | 41.7 | |
| 7 | 2.53 (d, 14.0) | 25.0 |
| 1.74 (m) | ||
| 8 | 3.90 (dd, 14.0, 4.3) | 40.5 |
| 3.62 (m) | ||
| 10 | - | 155.2 |
| 11 | - | 168.2 |
| 12 | - | 126.0 |
| 14 | 7.22 (s) | 131.0 |
| 15 | 122.1 | |
| 16 | 3.04 (m) | 22.2 |
| 17 | 4.22 (m) | 55.4 |
| 4.06 (m) | ||
| 19 | - | 154.2 |
| 20 | - | 92.0 |
| 21 | - | 125.7 |
| 2’ | 3.19 (t, 8.0) | 50.5 |
| 3’ | 1.74 (m) | 27.4 |
| 4’ | 1.34 (m) | 30.6 |
| 5’ | 1.34 (m) | 24.2 |
| 6’ | 0.88 (m) | 15.7 |
| No. | δH (Mult., J in Hz) | δC |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.85 (t, 7.2) | 33.8 |
| 2 | 2.28–2.14 (m) | 35.9 |
| 3 | - | 92.0 |
| 4 | 2.28–2.14 (m) | 35.9 |
| 5 | 1.85 (t, 7.2) | 33.8 |
| 6 | - | 35.1 |
| 7 | 1.68 (t, 5.5) | 36.2 |
| 8 | 3.46 (t, 5.5) | 39.1 |
| 10 | - | 151.4 |
| 11 | - | 167.7 |
| 12 | - | 124.8 |
| 14 | 7.10 (s) | 126.5 |
| 15 | - | 121.2 |
| 16 | 2.91 (t, 7.1) | 21.1 |
| 17 | 4.15 (t, 7.1) | 45.8 |
| 19 | - | 157.1 |
| 20 | - | 106.4 |
| 21 | - | 125.4 |
| No. | δH (Mult., J in Hz) a | δC b | No. | δH (Mult., J in Hz) a | δC b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.81 (s) | 156.0 | 1’ | 6.44 (d, 2.0) | 54.1 |
| 2 | - | 124.9 | 2’ | 4.29 (d, 2.0) | 71.2 |
| 3 | - | 177.0 | 3’ | - | 98.4 |
| 4 | - | 124.9 | 4’ | Obscured | 58.6 |
| 5 | 7.81 (s) | 156.0 | 5’ | 4.16 (br m) | 76.0 |
| 6 | - | 47.7 | 6’ | - | 42.8 |
| 7 | 2.15 (t, 5.5) | 35.3 | 7’ | 2.31 (dd, 13.5, 2.4) | 24.3 |
| 8 | 3.76 (m) | 41.1 | 1.07 (td, 13.5, 5.4) | ||
| 10 | - | 154.9 | 8’ | 3.89 (m) | 40.6 |
| 11 | - | 169.6 | 3.56 (m) | ||
| 12 | - | 126.6 | 10’ | - | 154.9 |
| 14 | 6.86 (s) | 130.1 | 11’ | - | 168.8 |
| 15 | - | 124.5 | 12’ | - | 125.5/126.2 |
| 16 | 2.72 (m) | 20.7 | 14’ | 7.24 (s) | 130.8 |
| 17 | 3.89 (m) | 46.6 | 15’ | - | 122.3 |
| 19 | - | 156.5 | 16’ | 3.06 (m) | 22.2 |
| 20 | - | 93.7/94.0 | 17’ | 4.13 (m) | 55.4 |
| 21 | - | 126.6 | 4.04 (m) | ||
| 19’ | - | 154.2 | |||
| 20’ | - | 93.7/94.0 | |||
| 21’ | - | 125.5/126.2 |
| Compound (NSC) 1 | GI50 2 | TGI 2 | LC50 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 (626162) | 0.13 | 0.36 | 2.3 |
| 4 (789237) | 1.4 | 3.9 | 10.5 |
| Compd. | T. B. Rhod.b | T. Cruzic | L. Don.d | P. Falc. K1 e | L6 f | SI Pf g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 99% (1.5) | 100% (1.5) | 57% (1.5) | 100% (1.5) | n.t. h | - |
| 2 | 99% (1.4) | 100% (1.4) | 47% (1.4) | 100% (1.4) | n.t. | - |
| 6 | n.t. | n.t. | n.t. | 0.25 | 0.81 | 3.2 |
| 7 | n.t. | n.t. | n.t. | 0.09 | 1.7 | 19 |
| 8 | 0.71 | 11.1 | 18.7 | 6.4 | 2.1 | 0.3 |
| 9 | n.t. | n.t. | n.t. | 0.40 | 0.11 | 0.3 |
| 10 | 99% (1.8) | 100% (1.8) | 75% (1.8) | 100% (1.8) | n.t. | - |
| 11 | 1.4 | 29 | 64 | 1.6 | 9.1 | 5.7 |
| 12 | 2.3 | 63 | 94 | 12 | 17 | 1.4 |
| 13 | 0.40 | 3.6 | 7.2 | 0.03 | 1.1 | 37 |
| 14 | 1.3 | 9% (12) | 20% (1.9) | 20% (1.9) | 11 | - |
| 15 | 100% (1.5) | 100% (1.5) | 97% (1.5) | 100% (1.5) | n.t. | - |
| 16 | n.t. | n.t. | n.t. | 1.7 | 6.1 | 3.6 |
| 17 | 0.33 | 0% (0.8) | 29% (0.8) | 0.08 | 41 | 510 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lam, C.F.C.; Cadelis, M.M.; Copp, B.R. Exploration of the Electrophilic Reactivity of the Cytotoxic Marine Alkaloid Discorhabdin C and Subsequent Discovery of a New Dimeric C-1/N-13-Linked Discorhabdin Natural Product. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18080404
Lam CFC, Cadelis MM, Copp BR. Exploration of the Electrophilic Reactivity of the Cytotoxic Marine Alkaloid Discorhabdin C and Subsequent Discovery of a New Dimeric C-1/N-13-Linked Discorhabdin Natural Product. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(8):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18080404
Chicago/Turabian StyleLam, Cary F. C., Melissa M. Cadelis, and Brent R. Copp. 2020. "Exploration of the Electrophilic Reactivity of the Cytotoxic Marine Alkaloid Discorhabdin C and Subsequent Discovery of a New Dimeric C-1/N-13-Linked Discorhabdin Natural Product" Marine Drugs 18, no. 8: 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18080404
APA StyleLam, C. F. C., Cadelis, M. M., & Copp, B. R. (2020). Exploration of the Electrophilic Reactivity of the Cytotoxic Marine Alkaloid Discorhabdin C and Subsequent Discovery of a New Dimeric C-1/N-13-Linked Discorhabdin Natural Product. Marine Drugs, 18(8), 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18080404