Natural Products Repertoire of the Red Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Marine Natural Products Isolated from Marine Microorganisms
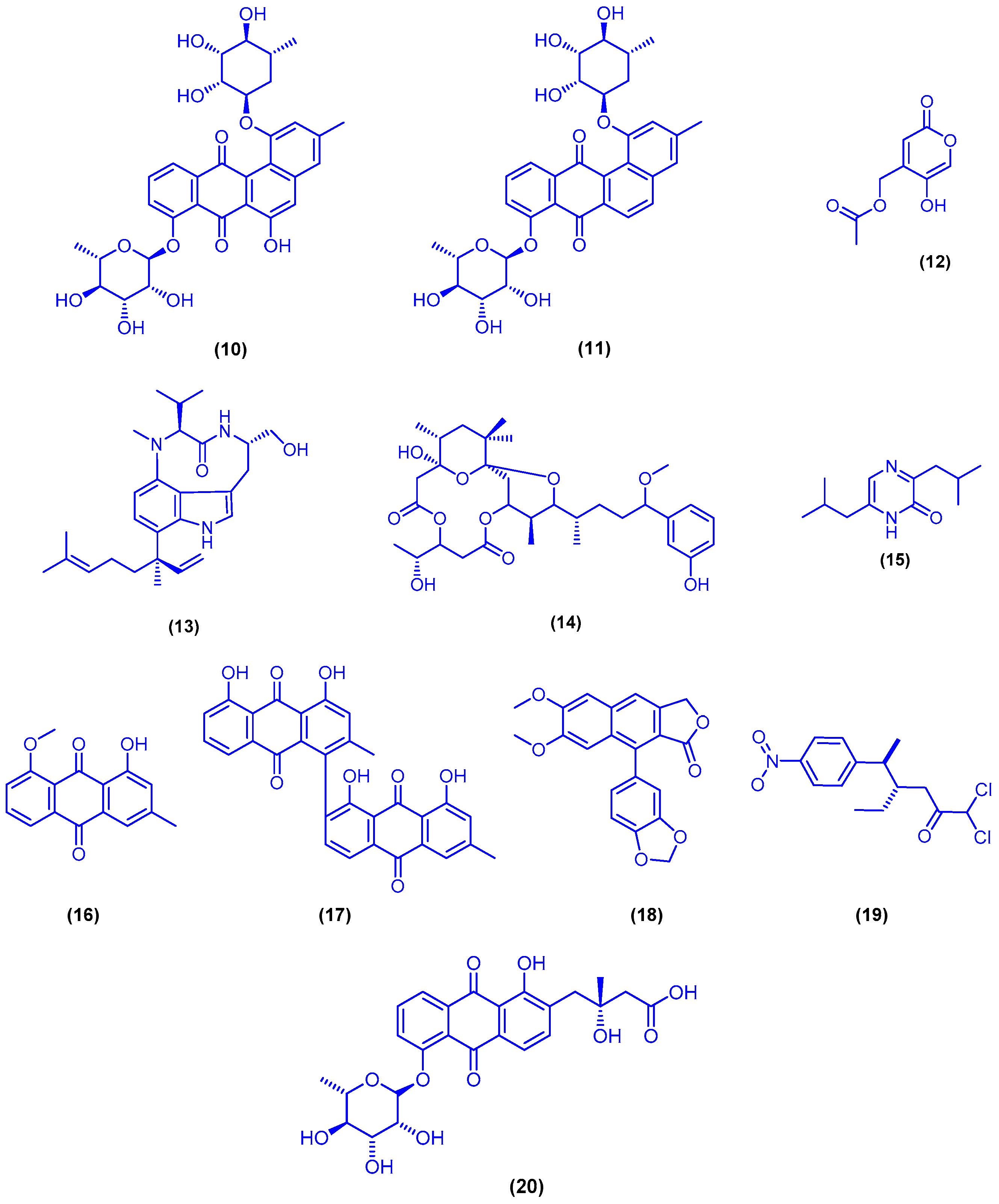
2.1. Marine Bacteria
2.2. Marine Fungi
3. Marine Natural Products Isolated from Marine Invertebrates
3.1. Sponges
3.2. Corals
3.3. Sea Hares
3.4. Tunicates
4. Marine Natural Products Isolated from Marine Algae
5. Sea Grasses
6. Genomic Potential of Red Sea Organisms
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bosworth, W.; Huchon, P.; McClay, K. The red sea and gulf of aden basins. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2005, 43, 334–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raitsos, D.E.; Pradhan, Y.; Brewin, R.J.; Stenchikov, G.; Hoteit, I. Remote sensing the phytoplankton seasonal succession of the red sea. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berumen, M.L.; Hoey, A.S.; Bass, W.H.; Bouwmeester, J.; Catania, D.; Cochran, J.E.M.; Khalil, M.T.; Miyake, S.; Mughal, M.R.; Spaet, J.L.Y.; et al. The status of coral reef ecology research in the red sea. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.Y.; Wang, Y.; Lee, O.O.; Lau, S.C.; Yang, J.; Lafi, F.F.; Al-Suwailem, A.; Wong, T.Y. Vertical stratification of microbial communities in the red sea revealed by 16s rdna pyrosequencing. ISME J. 2011, 5, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DiBattista, J.D.; Roberts, M.B.; Bouwmeester, J.; Bowen, B.W.; Coker, D.J.; Lozano-Cortés, D.F.; Howard Choat, J.; Gaither, M.R.; Hobbs, J.-P.A.; Khalil, M.T.; et al. A review of contemporary patterns of endemism for shallow water reef fauna in the red sea. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 43, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravara, A.; Carvalho, S. Nephtyidae (polychaeta, phyllodocida) from the red sea, with record of a new species. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2017, 97, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, B.W.; Rocha, L.A.; Toonen, R.J.; Karl, S.A. The origins of tropical marine biodiversity. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaither, M.R.; Bowen, B.W.; Bordenave, T.-R.; Rocha, L.A.; Newman, S.J.; Gomez, J.A.; van Herwerden, L.; Craig, M.T. Phylogeography of the reef fish cephalopholis argus(epinephelidae) indicates pleistocene isolation across the indo-pacific barrier with contemporary overlap in the coral triangle. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DiBattista, J.D.; Berumen, M.L.; Gaither, M.R.; Rocha, L.A.; Eble, J.A.; Choat, J.H.; Craig, M.T.; Skillings, D.J.; Bowen, B.W. After continents divide: Comparative phylogeography of reef fishes from the red sea and indian ocean. J. Biogeogr. 2013, 40, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.S.; Kim, S.L.; Oliver, J.S. Anthropogenic disturbance and biodiversity of marine benthic communities in antarctica: A regional comparison. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirto, S.; Gristina, M.; Sinopoli, M.; Maricchiolo, G.; Genovese, L.; Vizzini, S.; Mazzola, A. Meiofauna as an indicator for assessing the impact of fish farming at an exposed marine site. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 18, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziko, L.; Saqr, A.-H.A.; Ouf, A.; Gimpel, M.; Aziz, R.K.; Neubauer, P.; Siam, R. Antibacterial and anticancer activities of orphan biosynthetic gene clusters from atlantis ii red sea brine pool. Microb. Cell Factories 2019, 18, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eisen, J.A. Environmental shotgun sequencing: Its potential and challenges for studying the hidden world of microbes. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trommer, G.; Siccha, M.; van der Meer, M.T.; Schouten, S.; Damsté, J.S.S.; Schulz, H.; Hemleben, C.; Kucera, M. Distribution of crenarchaeota tetraether membrane lipids in surface sediments from the red sea. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.; Anlauf, H.; Kürten, S.; Lozano-Cortés, D.; Alsaffar, Z.; Cúrdia, J.; Jones, B.; Carvalho, S. Cross shelf benthic biodiversity patterns in the southern red sea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, D.J.; Lamont, P.A.; Levin, L.A.; Packer, M.; Feeley, K.; Gage, J.D. Macrofaunal communities and sediment structure across the pakistan margin oxygen minimum zone, north-east arabian sea. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2009, 56, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.B.; Moore, P.D.; Ladle, R. Biogeography: An Ecological and Evolutionary Approach; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- DeLong, E.F.; Preston, C.M.; Mincer, T.; Rich, V.; Hallam, S.J.; Frigaard, N.-U.; Martinez, A.; Sullivan, M.B.; Edwards, R.; Brito, B.R. Community genomics among stratified microbial assemblages in the ocean’s interior. Science 2006, 311, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feebarani, J.; Joydas, T.; Damodaran, R.; Borja, A. Benthic quality assessment in a naturally-and human-stressed tropical estuary. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Filho, J.R.; Souza, S.; Souza-Filho, P. Spatial and temporal changes in the structure of soft-bottom benthic communities in an amazon estuary (caeté estuary, brazil). J. Coast. Res. 2011, 440–444. [Google Scholar]
- Acker, J.; Leptoukh, G.; Shen, S.; Zhu, T.; Kempler, S. Remotely-sensed chlorophyll a observations of the northern red sea indicate seasonal variability and influence of coastal reefs. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 69, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, B.; Harrison, P.L.; Beger, M.; Pandolfi, J.M. Trait-mediated environmental filtering drives assembly at biogeographic transition zones. Ecology 2014, 95, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karakassis, I.; Eleftheriou, A. The continental shelf of crete: Structure of macrobenthic communities. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 160, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vonk, J.A.; Stapel, J. Regeneration of nitrogen (15n) from seagrass litter in tropical indo-pacific meadows. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 368, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sofianos, S.; Johns, W.E.; Murray, S. Heat and freshwater budgets in the red sea from direct observations at bab el mandeb. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2002, 49, 1323–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearman, J.K.; Irigoien, X.; Carvalho, S. Extracellular DNA amplicon sequencing reveals high levels of benthic eukaryotic diversity in the central red sea. Mar. Genom. 2016, 26, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, F.J. Climate and oceanography. Red Sea 1987, 1, 45–68. [Google Scholar]
- Hasler, H.; Ott, J.A. Diving down the reefs? Intensive diving tourism threatens the reefs of the northern red sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1788–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raitsos, D.; Hoteit, I.; Prihartato, P.; Chronis, T.; Triantafyllou, G.; Abualnaja, Y. Abrupt warming of the red sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higgins, E.; Scheibling, R.E.; Desilets, K.M.; Metaxas, A. Benthic community succession on artificial and natural coral reefs in the northern gulf of aqaba, red sea. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hossary, E.M.; Cheng, C.; Hamed, M.M.; El-Sayed Hamed, A.N.; Ohlsen, K.; Hentschel, U.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Antifungal potential of marine natural products. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 126, 631–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Balasubramanian, S.; Oelschlaeger, T.A.; Grkovic, T.; Pham, N.B.; Quinn, R.J.; Hentschel, U. Potential of marine natural products against drug-resistant fungal, viral, and parasitic infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e30–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; El-Hossary, E.M.; Oelschlaeger, T.A.; Donia, M.S.; Quinn, R.J.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Potential of marine natural products against drug-resistant bacterial infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, e237–e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shady, N.H.; El-Hossary, E.M.; Fouad, M.A.; Gulder, T.A.M.; Kamel, M.S.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Bioactive natural products of marine sponges from the genus hyrtios. Molecules 2017, 22, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F. Have marine natural product drug discovery efforts been productive and how can we improve their efficiency? Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, F.; Aires-de-Sousa, J. Computational methodologies in the exploration of marine natural product leads. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiese, J.; Imhoff, J.F. Marine bacteria and fungi as promising source for new antibiotics. Drug Dev. Res. 2019, 80, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Drugs and drug candidates from marine sources: An assessment of the current “state of play”. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerwick, W.H.; Moore, B.S. Lessons from the past and charting the future of marine natural products drug discovery and chemical biology. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Ezz, R.A.; Ibrahim, A.; Habib, E.; Wahba, A.; Kamel, H.; Afifi, M.; Hassanean, H.; Ahmed, S. Review of natural products from marine organisms in the red sea. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 8, 940–974. [Google Scholar]
- Petitbois, J.G.; Casalme, L.O.; Lopez, J.A.V.; Alarif, W.M.; Abdel-Lateff, A.; Al-Lihaibi, S.S.; Yoshimura, E.; Nogata, Y.; Umezawa, T.; Matsuda, F.; et al. Serinolamides and lyngbyabellins from an okeania sp. Cyanobacterium collected from the red sea. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2708–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; McPhail, K.L.; Gross, H.; Goeger, D.E.; Mooberry, S.L.; Gerwick, W.H. Isolation and structure of five lyngbyabellin derivatives from a papua new guinea collection of the marine cyanobacterium lyngbya majuscula. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 11723–11729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.T.; Goh, B.P.; Tripathi, A.; Lim, M.G.; Dickinson, G.H.; Lee, S.S.; Teo, S.L. Natural antifoulants from the marine cyanobacterium lyngbya majuscula. Biofouling 2010, 26, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, J.A.; Al-Lihaibi, S.S.; Alarif, W.M.; Abdel-Lateff, A.; Nogata, Y.; Washio, K.; Morikawa, M.; Okino, T. Wewakazole B, a cytotoxic cyanobactin from the cyanobacterium moorea producens collected in the red sea. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornburg, C.C.; Cowley, E.S.; Sikorska, J.; Shaala, L.A.; Ishmael, J.E.; Youssef, D.T.; McPhail, K.L. Apratoxin h and apratoxin a sulfoxide from the red sea cyanobacterium moorea producens. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thornburg, C.C.; Thimmaiah, M.; Shaala, L.A.; Hau, A.M.; Malmo, J.M.; Ishmael, J.E.; Youssef, D.T.; McPhail, K.L. Cyclic depsipeptides, grassypeptolides d and e and ibu-epidemethoxylyngbyastatin 3, from a red sea leptolyngbya cyanobacterium. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1677–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grkovic, T.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Othman, E.M.; Stopper, H.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Hentschel, U.; Quinn, R.J. Two new antioxidant actinosporin analogues from the calcium alginate beads culture of sponge-associated actinokineospora sp. Strain eg49. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 5089–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfike, A.; Attia, E.Z.; Desoukey, S.Y.; Hajjar, D.; Makki, A.A.; Schupp, P.J.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. New bioactive metabolites from the elicited marine sponge-derived bacterium actinokineospora spheciospongiae sp. Nov. AMB Express 2019, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gendy, M.M.; El-Bondkly, A.M. Production and genetic improvement of a novel antimycotic agent, saadamycin, against dermatophytes and other clinical fungi from endophytic streptomyces sp. Hedaya48. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 37, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.; Shaala, L.A.; Mohamed, G.A.; Ibrahim, S.R.; Banjar, Z.M.; Badr, J.M.; McPhail, K.L.; Risinger, A.L.; Mooberry, S.L. 2,3-seco-2,3-dioxo-lyngbyatoxin a from a red sea strain of the marine cyanobacterium moorea producens. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.; McPhail, K.L.; Elbandy, M. Malyngamide 4, a new lipopeptide from the red sea marine cyanobacterium moorea producens (formerly lyngbya majuscula). Phytochem. Lett. 2013, 6, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.; Badr, J.M.; Harakeh, S.M. Bioactive 2(1h)-pyrazinones and diketopiperazine alkaloids from a tunicate-derived actinomycete Streptomyces sp. Molecules 2016, 21, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gendy, M.M.; Hawas, U.W.; Jaspars, M. Novel bioactive metabolites from a marine derived bacterium nocardia sp. Alaa 2000. J. Antibiot. 2008, 61, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elnaggar, M.S.; Ebada, S.S.; Ashour, M.L.; Ebrahim, W.; Müller, W.E.G.; Mándi, A.; Kurtán, T.; Singab, A.; Lin, W.; Liu, Z.; et al. Xanthones and sesquiterpene derivatives from a marine-derived fungus Scopulariopsis sp. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 2411–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lefranc, F.; Nuzzo, G.; Hamdy, N.A.; Fakhr, I.; Moreno, Y.B.L.; Van Goietsenoven, G.; Villani, G.; Mathieu, V.; van Soest, R.; Kiss, R.; et al. In vitro pharmacological and toxicological effects of norterpene peroxides isolated from the red sea sponge diacarnus erythraeanus on normal and cancer cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Laphookhieo, S.; Shi, Z.; Fu, L.W.; Akiyama, S.; Chen, Z.S.; Youssef, D.T.; van Soest, R.W.; El Sayed, K.A. Reversal of p-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by sipholane triterpenoids. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 928–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angawi, R.; Saqer, E.; Abdel-Lateff, A.; Badria, F.; Ayyad, S.-E. Cytotoxic neviotane triterpene-type from the red sea sponge Siphonochalina siphonella. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2014, 10, 334–341. [Google Scholar]
- El-Beih, A.A.; El-Desoky, A.H.; Al-hammady, M.A.; Elshamy, A.I.; Hegazy, M.-E.F.; Kato, H.; Tsukamoto, S. New inhibitors of rankl-induced osteoclastogenesis from the marine sponge siphonochalina siphonella. Fitoterapia 2018, 128, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hawary, S.S.; Sayed, A.M.; Mohammed, R.; Hassan, H.M.; Rateb, M.E.; Amin, E.; Mohammed, T.A.; El-Mesery, M.; Bin Muhsinah, A.; Alsayari, A.; et al. Bioactive brominated oxindole alkaloids from the red sea sponge callyspongia siphonella. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, S.; Abraham, I.; Carvalho, P.; Kuang, Y.H.; Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.; Avery, M.A.; Chen, Z.S.; El Sayed, K.A. Sipholane triterpenoids: Chemistry, reversal of abcb1/p-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance, and pharmacophore modeling. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilozny, B.; Amagata, T.; Mooberry, S.L.; Crews, P. A new dimension to the biosynthetic products isolated from the sponge negombata magnifica. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1055–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, K.A.; Youssef, D.T.; Marchetti, D. Bioactive natural and semisynthetic latrunculins. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.A.; Khalifa, S.I.; Hamann, M.T. Antiepileptic ceramides from the red sea sponge negombata corticata. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 513–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orabi, K.Y.; El Sayed, K.A.; Hamann, M.T.; Dunbar, D.C.; Al-Said, M.S.; Higa, T.; Kelly, M. Araguspongines k and l, new bioactive bis-1-oxaquinolizidine n-oxide alkaloids from red sea specimens of xestospongia exigua. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1782–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Sayed, K.A.; Hamann, M.T.; Hashish, N.E.; Shier, W.T.; Kelly, M.; Khan, A.A. Antimalarial, antiviral, and antitoxoplasmosis norsesterterpene peroxide acids from the red sea sponge diacarnus erythraeanus. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 522–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Kelly, M.; Scheuer, P.J. Cytotoxic cyclic norterpene peroxides from a red sea sponge diacarnus e rythraenus. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1332–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.A. Tasnemoxides a−c, new cytotoxic cyclic norsesterterpene peroxides from the red sea sponge diacarnus erythraenus. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.; Mooberry, S.L. Hurghadolide a and swinholide i, potent actin-microfilament disrupters from the red sea sponge theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.; van Soest, R.W.; Fusetani, N. Callyspongenols a-c, new cytotoxic c22-polyacetylenic alcohols from a red sea sponge, callyspongia species. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 679–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.; van Soest, R.W.; Fusetani, N. Callyspongamide a, a new cytotoxic polyacetylenic amide from the red sea sponge callyspongia fistularis. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 861–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T. Hyrtioerectines a-c, cytotoxic alkaloids from the red sea sponge hyrtioserectus. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1416–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, S.; Rudi, A.; Kashman, Y.; Loya, Y. New avarone and avarol derivatives from the marine sponge dysidea cinerea. J. Nat. Prod. 1991, 54, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loya, S.; Tal, R.; Hizi, A.; Issacs, S.; Kashman, Y.; Loya, Y. Hexaprenoid hydroquinones, novel inhibitors of the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 2120–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs, S.; Hizi, A.; Kashman, Y. Toxicols ac and toxiusol-new bioactive hexaprenoid hydroquinones from toxiclona toxius. Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 4275–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs, S.; Kashman, Y. Shaagrockol B and C; two hexaprenylhydroquinone disulfates from the red sea sponge toxiclona toxius. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 2227–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Shoer, M.I.; Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.; Badr, J.M.; Habib, A.A. Bioactive brominated metabolites from the red sea sponge suberea mollis. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1464–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.; Youssef, D.; Badr, J.; Sulaiman, M.; Khedr, A. Bioactive secondary metabolites from the red sea marine verongid sponge suberea species. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badr, J.M.; Shaala, L.A.; Abou-Shoer, M.I.; Tawfik, M.K.; Habib, A.A. Bioactive brominated metabolites from the red sea sponge pseudoceratina arabica. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1472–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.; Sulaiman, M.; Behery, F.A.; Foudah, A.I.; Sayed, K.A. Subereamolline a as a potent breast cancer migration, invasion and proliferation inhibitor and bioactive dibrominated alkaloids from the red sea sponge pseudoceratina arabica. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2492–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Badr, J.M.; Sulaiman, M.; Khedr, A.; El Sayed, K.A. Bioactive alkaloids from the red sea marine verongid sponge pseudoceratina arabica. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 7837–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A. Cytotoxic psammaplysin analogues from the verongid red sea sponge aplysinella species. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, M.H.A.; Rateb, M.E.; Hetta, M.; Abdelaziz, T.A.; Sleim, M.A.; Jaspars, M.; Mohammed, R. Scalarane sesterterpenes from the egyptian red sea sponge phyllospongia lamellosa. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhady, S.S.; Al-Abd, A.M.; El-Halawany, A.M.; Alahdal, A.M.; Hassanean, H.A.; Ahmed, S.A. Antiproliferative scalarane-based metabolites from the red sea sponge hyrtios erectus. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alahdal, A.M.; Asfour, H.Z.; Ahmed, S.A.; Noor, A.O.; Al-Abd, A.M.; Elfaky, M.A.; Elhady, S.S. Anti-helicobacter, antitubercular and cytotoxic activities of scalaranes from the red sea sponge hyrtios erectus. Molecules 2018, 23, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Youssef, D.T.; Shaala, L.A.; Emara, S. Antimycobacterial scalarane-based sesterterpenes from the red sea sponge hyrtios e recta. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1782–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, D.T.; Yamaki, R.K.; Kelly, M.; Scheuer, P.J. Salmahyrtisol a, a novel cytotoxic sesterterpene from the red sea sponge hyrtios e recta. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.; Shaala, L.A.; Mohamed, G.A.; Badr, J.M.; Bamanie, F.H.; Ibrahim, S.R. Theonellamide g, a potent antifungal and cytotoxic bicyclic glycopeptide from the red sea marine sponge theonella swinhoei. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1911–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sandler, J.S.; Forsburg, S.L.; Faulkner, D.J. Bioactive steroidal glycosides from the marine sponge erylus lendenfeldi. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebreyesusa, T.; Yosief, T.; Carmely, S.; Kashmanb, Y. Dysidamide, a novel hexachloro-metabolite from a red sea sponge Dysidea sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1988, 29, 3863–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmely, S.; Gebreyesus, T.; Kashman, Y.; Skelton, B.; White, A.; Yosief, T. Dysidamide, a novel metabolite from a red sea sponge Dysidea herbacea. Aust. J. Chem. 1990, 43, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauleau, P.; Retailleau, P.; Vacelet, J.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L. New polychlorinated pyrrolidinones from the red sea marine sponge lamellodysidea herbacea. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosief, T.; Rudi, A.; Stein, Z.; Goldberg, I.; Gravalos, G.M.D.; Schleyer, M.; Kashman, Y. Asmarines A–C; three novel cytotoxic metabolites from the marine sponge Raspailia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 3323–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosief, T.; Rudi, A.; Kashman, Y. Asmarines A−F, novel cytotoxic compounds from the marine sponge raspailia species. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talpir, R.; Rudi, A.; Ilan, M.; Kashman, Y. Niphatoxin a and b; two new ichthyo- and cytotoxic tripyridine alkaloids from a marine sponge. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 3033–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L.; Martin, M.T.; Guyot, M. A new β-carboline alkaloid isolated from the marine sponge hyrtios erecta. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 3457–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacs, S.; Kashman, Y.; Loya, S.; Hizi, A.; Loya, Y. Petrosynol and petrosolic acid, two novel natural inhibitors of the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus from Petrosia sp. Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 10435–10438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawas, U.W.; El-Kassem, L.T.A.; Abdelfattah, M.S.; Elmallah, M.I.Y.; Eid, M.A.G.; Monier, M.; Marimuthu, N. Cytotoxic activity of alkyl benzoate and fatty acids from the red sea sponge hyrtios erectus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Cheng, C.; Reimer, A.; Kozjak-Pavlovic, V.; Ibrahim, A.K.; Rudel, T.; Hentschel, U.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Ahmed, S.A. Antichlamydial sterol from the red sea sponge callyspongia aff. Implexa. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Sayed, K.A.; Hamann, M.T. A new norcembranoid dimer from the red sea soft coral sinularia gardineri. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 687–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellithey, M.S.; Lall, N.; Hussein, A.A.; Meyer, D. Cytotoxic, cytostatic and hiv-1 pr inhibitory activities of the soft coral litophyton arboreum. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4917–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hegazy, M.E.; Gamal Eldeen, A.M.; Shahat, A.A.; Abdel-Latif, F.F.; Mohamed, T.A.; Whittlesey, B.R.; Pare, P.W. Bioactive hydroperoxyl cembranoids from the red sea soft coral sarcophyton glaucum. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hegazy, M.-E.F.; Mohamed, T.A.; Abdel-Latif, F.F.; Alsaid, M.S.; Shahat, A.A.; Pare, P.W. Trochelioid a and b, new cembranoid diterpenes from the red sea soft coral sarcophyton trocheliophorum. Phytochem. Lett. 2013, 6, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ibrahim, A.; Arafa, A.S. Anti-h5n1 virus metabolites from the red sea soft coral, sinularia candidula. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 2377–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Lateff, A.; Alarif, W.M.; Ayyad, S.E.; Al-Lihaibi, S.S.; Basaif, S.A. New cytotoxic isoprenoid derivatives from the red sea soft coral sarcophyton glaucum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, M.-E.F.; Moustfa, A.Y.; Mohamed, A.E.-H.H.; Alhammady, M.A.; Elbehairi, S.E.I.; Ohta, S.; Paré, P.W. New cytotoxic halogenated sesquiterpenes from the egyptian sea hare, aplysia oculifera. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 1711–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Xu, J.P.; Hogan, F.; Williams, M.D.; Doubek, D.L.; Schmidt, J.M.; Cerny, R.L.; Boyd, M.R. Isolation and structure of the human cancer cell growth inhibitory cyclodepsipeptide dolastatin 16. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, S.; Miroz, A.; McCarthy, P.; Kashman, Y. Etzionin, a new antifungal metabolite from a red sea tunicate. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 4291–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, N.E.; Selim, M.A.; Metawe, H.M.; Matloub, A.A. Cytotoxic xenicane diterpenes from the brown alga padina pavonia (l.) gaill. Phytother. Res. 2008, 22, 1610–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedara, S.R.; Abdel-Halim, O.B.; el-Sharkawy, S.H.; Salama, O.M.; Shier, T.W.; Halim, A.F. Cytotoxic hydroazulene diterpenes from the brown alga dictyota dichotoma. Z. Nat. C 2003, 58, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-El-Wafa, G.S.; Shaaban, M.; Shaaban, K.A.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Maier, A.; Fiebig, H.H.; Laatsch, H. Pachydictyols b and c: New diterpenes from dictyota dichotoma hudson. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3109–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, J.H.; Wang, G.H.; Sung, P.J.; Chiu, Y.H.; Duh, C.Y. Cytotoxic sterols from the formosan brown alga turbinaria ornata. Planta Med. 1997, 63, 571–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.K.; Youssef, A.I.; Arafa, A.S.; Foad, R.; Radwan, M.M.; Ross, S.; Hassanean, H.A.; Ahmed, S.A. Anti-h5n1 virus new diglyceride ester from the red sea grass thallasodendron ciliatum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, A.H.; Mettwally, W.S.; El Fotouh, M.A.; Rodriguez, B.; El-Dewany, A.I.; El-Toumy, S.A.; Hussein, A.A. Bioactive phenolic compounds from the egyptian red sea seagrass thalassodendron ciliatum. Z. Nat. C 2012, 67, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, M.M.; Hamdy, A.H.; El-Fiky, N.M.; Mettwally, W.S.; El-Beih, A.A.; Kobayashi, N. Anti-influenza a virus activity of a new dihydrochalcone diglycoside isolated from the egyptian seagrass thalassodendron ciliatum (forsk.) den hartog. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barone, R.; De Santi, C.; Palma Esposito, F.; Tedesco, P.; Galati, F.; Visone, M.; di Scala, A.; de Pascale, D. Marine metagenomics, a valuable tool for enzymes and bioactive compounds discovery. Front. Mar. Sci. 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurvich, E.G. Metalliferous Sediments of the World Ocean: Fundamental Theory of Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Sedimentation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Behzad, H.; Ibarra, M.A.; Mineta, K.; Gojobori, T. Metagenomic studies of the red sea. Gene 2016, 576, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eder, W.; Ludwig, W.; Huber, R. Novel 16s rrna gene sequences retrieved from highly saline brine sediments of kebrit deep, red sea. Arch. Microbiol. 1999, 172, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.R.; Field, C.; Romanuk, T.; Ngugi, D.; Siam, R.; El Dorry, H.; Stingl, U. Patterns of ecological specialization among microbial populations in the red sea and diverse oligotrophic marine environments. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 1780–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayer, T.; Neave, M.J.; Alsheikh-Hussain, A.; Aranda, M.; Yum, L.K.; Mincer, T.; Hughen, K.; Apprill, A.; Voolstra, C.R. The microbiome of the red sea coral stylophora pistillata is dominated by tissue-associated endozoicomonas bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4759–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, Z.M.; Wang, Y.; Tian, R.M.; Wong, Y.H.; Batang, Z.B.; Al-Suwailem, A.M.; Bajic, V.B.; Qian, P.Y. Symbiotic adaptation drives genome streamlining of the cyanobacterial sponge symbiont “candidatus synechococcus spongiarum”. mBio 2014, 5, e00079-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Werner, J.; Ferrer, M.; Michel, G.; Mann, A.J.; Huang, S.; Juarez, S.; Ciordia, S.; Albar, J.P.; Alcaide, M.; la Cono, V.; et al. Halorhabdus tiamatea: Proteogenomics and glycosidase activity measurements identify the first cultivated euryarchaeon from a deep-sea anoxic brine lake as potential polysaccharide degrader. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2525–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haroon, M.F.; Thompson, L.R.; Parks, D.H.; Hugenholtz, P.; Stingl, U. A catalogue of 136 microbial draft genomes from red sea metagenomes. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, T.; Seridi, L.; Moitinho-Silva, L.; Oates, M.; Liew, Y.J.; Mavromatis, C.; Wang, X.; Haywood, A.; Lafi, F.F.; Kupresanin, M.; et al. Hologenome analysis of two marine sponges with different microbiomes. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Britstein, M.; Devescovi, G.; Handley, K.M.; Malik, A.; Haber, M.; Saurav, K.; Teta, R.; Costantino, V.; Burgsdorf, I.; Gilbert, J.A.; et al. A new n-acyl homoserine lactone synthase in an uncultured symbiont of the red sea sponge theonella swinhoei. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 1274–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Moneam, N.; El-Assar, S.; Shreadah, M.; Adam, A. Isolation, identification and molecular screening of pseudomonas sp. Metabolic pathways nrps and pks associated with the red sea sponge, hyrtios aff. Erectus, egypt. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 11, 1299–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






















© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Hossary, E.M.; Abdel-Halim, M.; Ibrahim, E.S.; Pimentel-Elardo, S.M.; Nodwell, J.R.; Handoussa, H.; Abdelwahab, M.F.; Holzgrabe, U.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Natural Products Repertoire of the Red Sea. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18090457
El-Hossary EM, Abdel-Halim M, Ibrahim ES, Pimentel-Elardo SM, Nodwell JR, Handoussa H, Abdelwahab MF, Holzgrabe U, Abdelmohsen UR. Natural Products Repertoire of the Red Sea. Marine Drugs. 2020; 18(9):457. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18090457
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Hossary, Ebaa M., Mohammad Abdel-Halim, Eslam S. Ibrahim, Sheila Marie Pimentel-Elardo, Justin R. Nodwell, Heba Handoussa, Miada F. Abdelwahab, Ulrike Holzgrabe, and Usama Ramadan Abdelmohsen. 2020. "Natural Products Repertoire of the Red Sea" Marine Drugs 18, no. 9: 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18090457
APA StyleEl-Hossary, E. M., Abdel-Halim, M., Ibrahim, E. S., Pimentel-Elardo, S. M., Nodwell, J. R., Handoussa, H., Abdelwahab, M. F., Holzgrabe, U., & Abdelmohsen, U. R. (2020). Natural Products Repertoire of the Red Sea. Marine Drugs, 18(9), 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/md18090457






