Abstract
The strain Aspergillus chevalieri TM2-S6 was isolated from the sponge Axinella and identified according to internal transcribed spacer (ITS) molecular sequence homology with Aspergillus species from the section Restricti. The strain was cultivated 9 days on potato dextrose broth (PDB), and the medium evaluated as antioxidant on primary normal human dermal fibroblasts (NHDF). The cultivation broth was submitted to sterile filtration, lyophilized and used without any further processing to give the Aspergillus chevalieri TM2-S6 cultivation broth ingredient named ACBB. ACCB contains two main compounds: tetrahydroauroglaucin and flavoglaucin. Under oxidative stress, ACCB showed a significant promotion of cell viability. To elucidate the mechanism of action, the impact on a panel of hundreds of genes involved in fibroblast physiology was evaluated. Thus, ACCB stimulates cell proliferation (VEGFA, TGFB3), antioxidant response (GPX1, SOD1, NRF2), and extracellular matrix organization (COL1A1, COL3A1, CD44, MMP14). ACCD also reduced aging (SIRT1, SIRT2, FOXO3). These findings indicate that Aspergillus chevalieri TM2-S6 cultivation broth exhibits significant in vitro skin protection of human fibroblasts under oxidative stress, making it a potential cosmetic ingredient.
1. Introduction
Oxidative stress plays a major role in premature skin aging through the production of highly reactive oxygen species (ROS) [1,2,3]. ROS can damage DNA, lipids, proteins and modify transcriptional regulation of genes in skin fibroblasts [3]. Specifically, ROS-induced apoptosis of fibroblasts impacts the production of collagen, elastin and hyaluronic acid [4], resulting in wrinkle formation and skin sagging [5]. This explains the efforts of the academic and industrial sectors to discover bio-based ingredients that protect fibroblasts from ROS-induced damage.
Marine ecosystems represent an untapped reservoir of bio-resources, producing secondary bioactive metabolites and attracting growing interest within the scientific community. Besides marine invertebrates, symbiotic fungi are the main producers of bioactive compounds, some of which have been mistakenly assigned to their hosts [6,7].
Aspergillus species are widely used for the production of therapeutic agents [8]. They also produce compounds exhibiting skin related activities like whitening [9], anti-oxidant [10], anti-microbial [11] and UVA screens [12]. Moreover, our previous research indicated that another Aspergillus species, A. puulaauensis, showed significant in vitro protection of human fibroblasts injured by oxidative stress [13].
Aspergillus chevalieri was identified in 1926 and its metabolites reported for potent antioxidant activity [14]. As part of our efforts to develop cosmetics of marine origin, we report in this paper the biological activity of an ingredient issued from the marine fungi Aspergillus chevalieri TM2-S6. This strain was isolated in the frame of the EU-funded project TASCMAR, as a symbiont of a mesophotic sponge. To validate the incorporation of this ingredient in cosmetic compositions, we evaluated its protective effect on the premature aging of human fibroblasts by measuring the promotion of cell viability and the impact on genes involved in cellular protection and physiology.
2. Results
2.1. Phylogeny and Structural Investigation
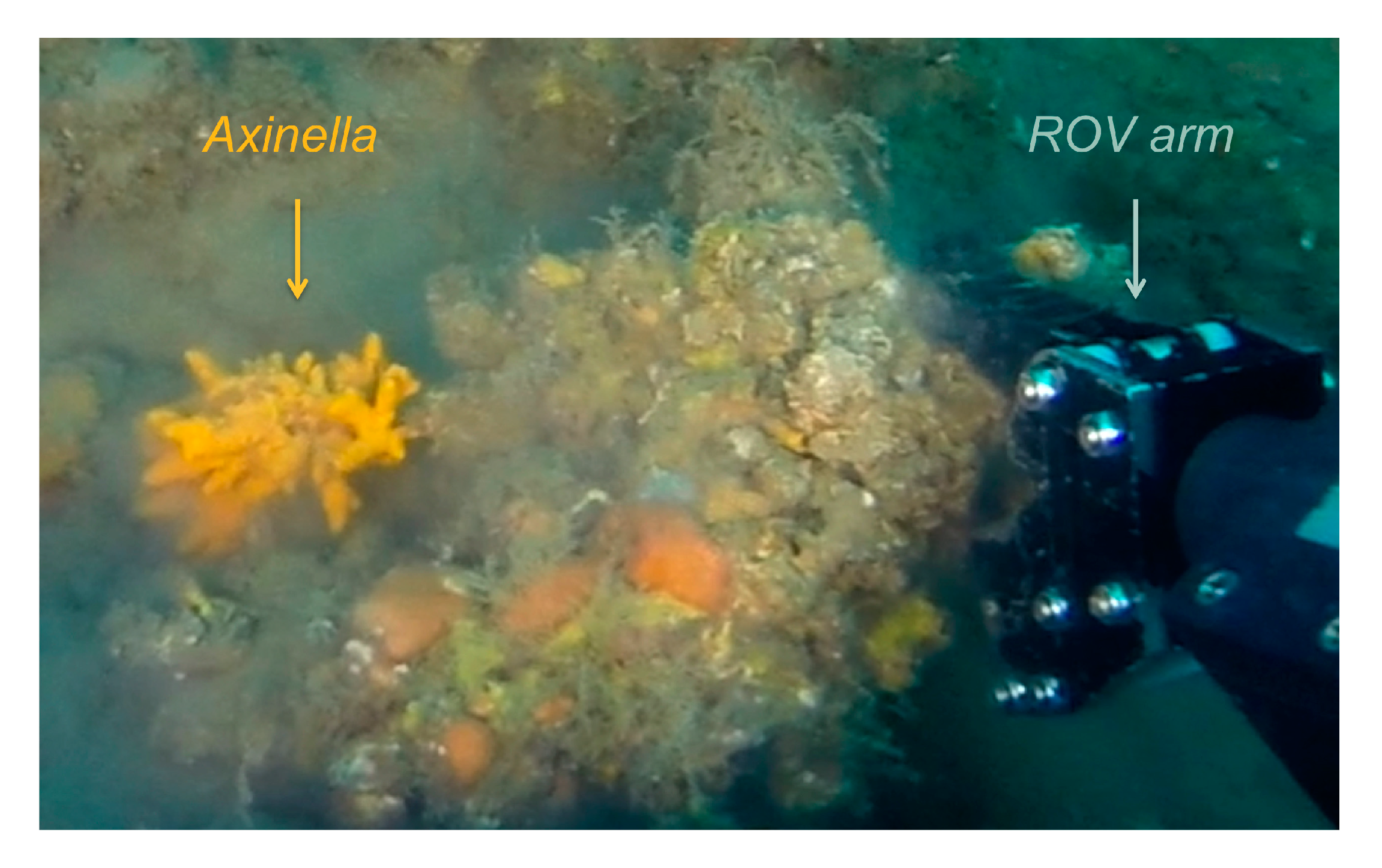
Aspergillus chevalieri TM2-S6 was isolated from the sponge Axinella collected on the upper mesophotic zone off Tel Aviv–Jaffa, Israeli Mediterranean coast (32°1′42.431″ N 34°46′42.323″ E). The sponge was collected at 38 m depth by a ROV (Remote Operating Vehicle) equipped with a collection arm (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
The sponge Axinella was collected on the upper mesophotic zone off Tel Aviv–Jaffa, Israeli Mediterranean coast by a ROV arm.
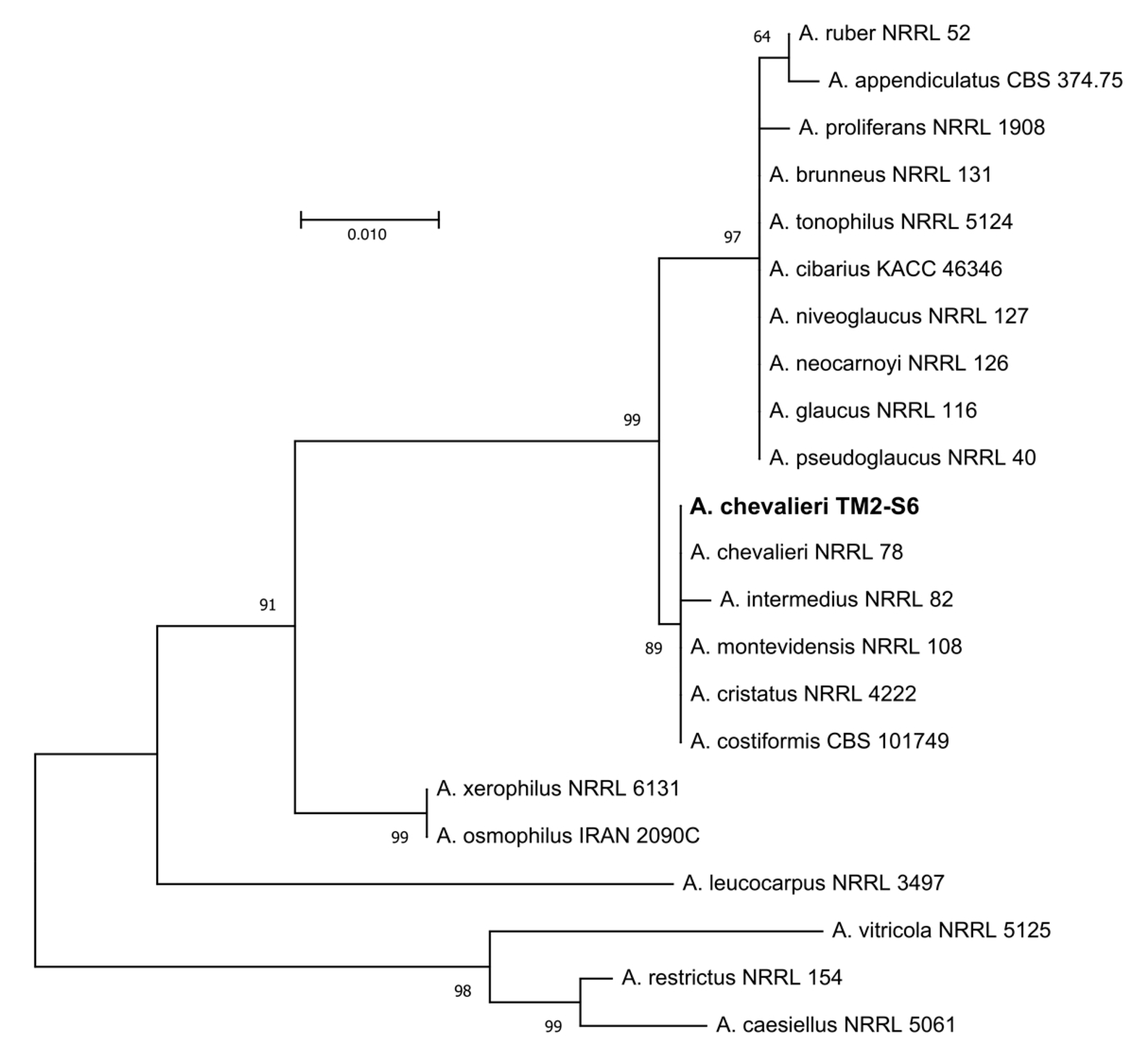
According to the phylogenetic analyses of ITS rDNA sequence, the isolate TM2-S6 described in this study belongs to the Aspergillus Restricti section of the Aspergillus genus. Based upon blast search against the “rRNA_typestrains/ITS_RefSeq_Fungi” database and subsequent phylogeny analyses, TM2-S6 isolate was assigned as Aspergillus chevalieri with the GenBank number MT256106 (Figure 2).
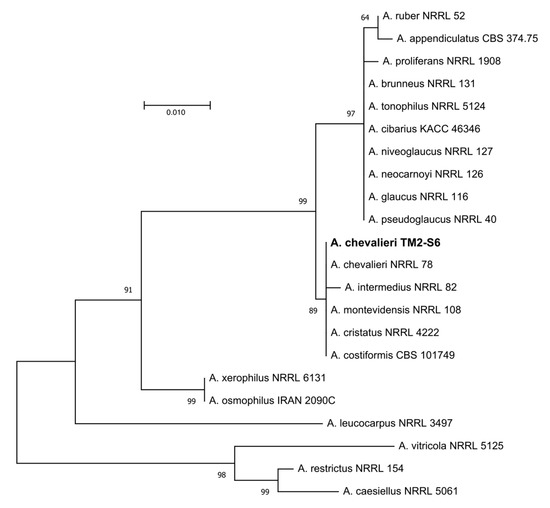
Figure 2.
Maximum likelihood tree obtained from ITS rDNA sequence alignment of the isolate TM2-S6 and Aspergillus spp. of the section Aspergillus restricti. Reliability for internal branch is indicated when geater than 60%. A. caesiellus, A. restrictus and A. crustosus from section Restricti were used as outgroup. Genbank accessions are listed in supplementary Table S1. Scale represents substitutions per site.
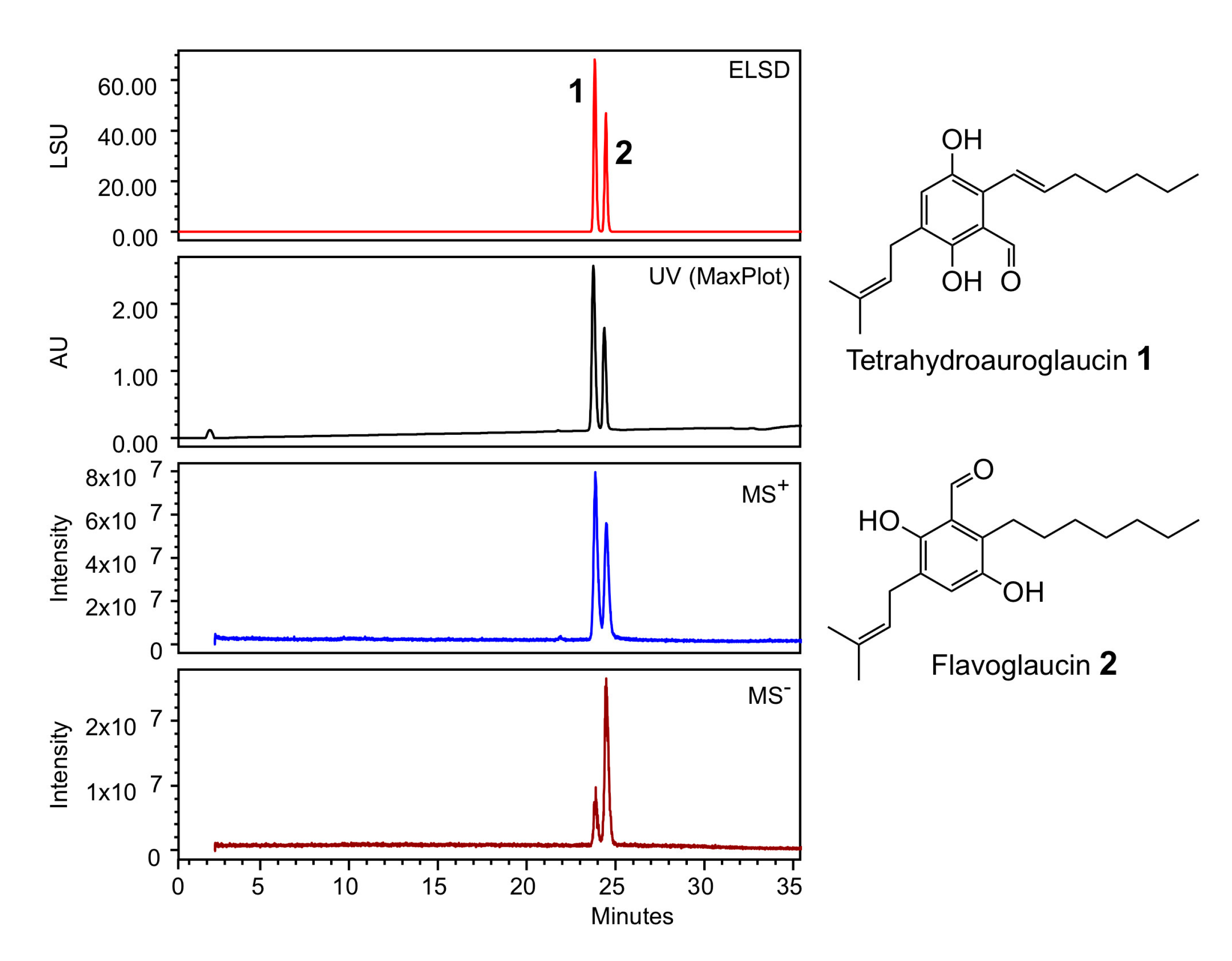
The strain was cultivated in PDB medium (Potato Dextrose Broth) composed of ingredients of plant origin. This medium is classified non-hazardous and is compatible with cosmetic formulations. After 9 days of culture, the medium was filtered, sterilized and lyophilized. The obtained powder was directly diluted to the desired concentration in the bioassay buffers, leading to the ACCB solution. Sample of ACCB solution was extracted with ethyl acetate and analyzed by HPLC coupled to a PhotoDiode Array detector (PDA), an evaporative light-scattering detector (ELSD) and a mass detector (MS). Figure 3 shows the presence of two peaks at 23,8 and 24,6 min. The peaks were dereplicated according to their 1H-NMR and HRMS spectra, and submitted to Antibase database of microbial compounds (Wiley-VCH) and natural compounds Reaxys database (Elsevier). Compound 1 was identified as tetrahydroauroglaucin and compound 2 as flavoglaucin (Supplementary Table S2, Figures S1 and S2). Both compounds have previously been isolated from Aspergillus strains; some are used in the preparation of the traditional Katsuobushi in Japanese cuisine [15,16].
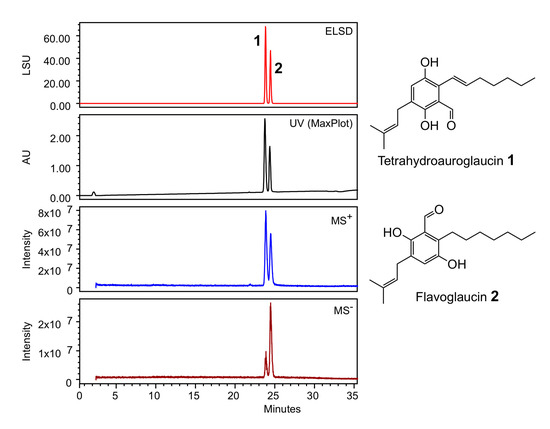
Figure 3.
HPLC analysis of the ethyl acetate extract of A. chevalieri TM2-S6 cultivation broth. ELSD: Evaporative Light-Scattering Detector; UV Max-Plot: UV absorbance using a PhotoDiode Array detector, MS+, MS−: Mass Spectrometry detection in positive and negative mode, LSU: Light-Scattering arbitrary Unit, AU: arbitrary UV unit.
2.2. Bioassays on Primary Human Fibroblasts
2.2.1. Cell Viability in Vitro
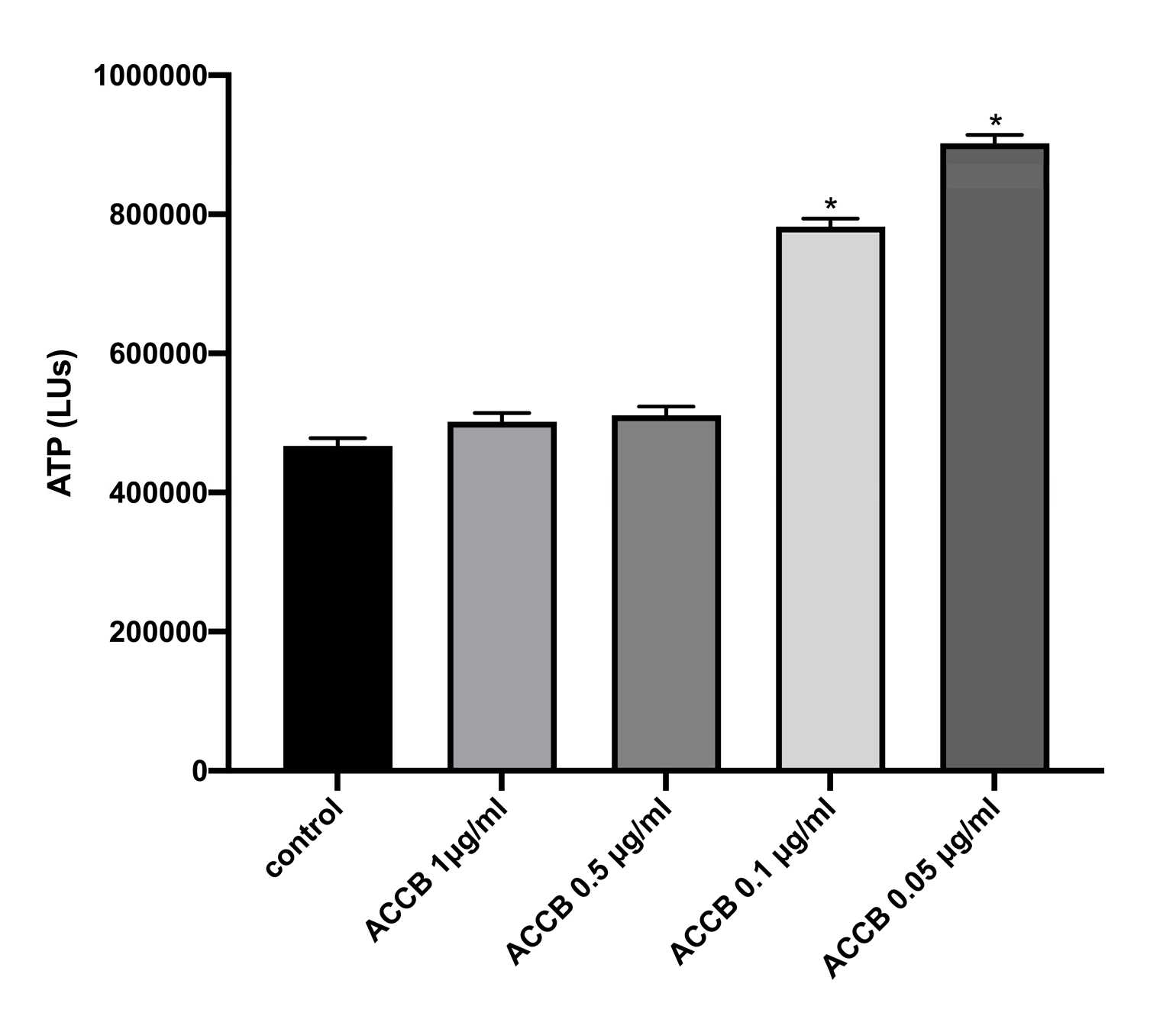
Cell viability was assessed by ATP assay. We observed that lower concentrations exhibited increased ATP levels compared to control (p < 0.05) (Figure 4), indicating that cell viability is increased in lower concentrations of ACCB.
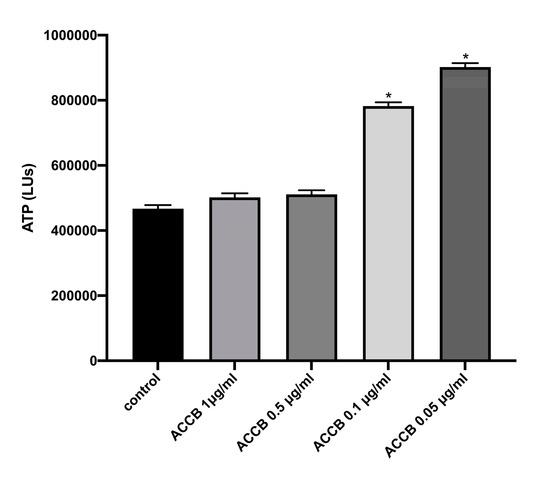
Figure 4.
ATP levels (LUs) expressed as mean ± SEM for: control (untreated NHDF cells) and NHDF cells treated with four concentrations of ACCB (1 μg/mL, 0.5 μg/mL, 0.1 μg/mL, 0.05 μg/mL) * p < 0.05 significantly different from the control (ANOVA test).
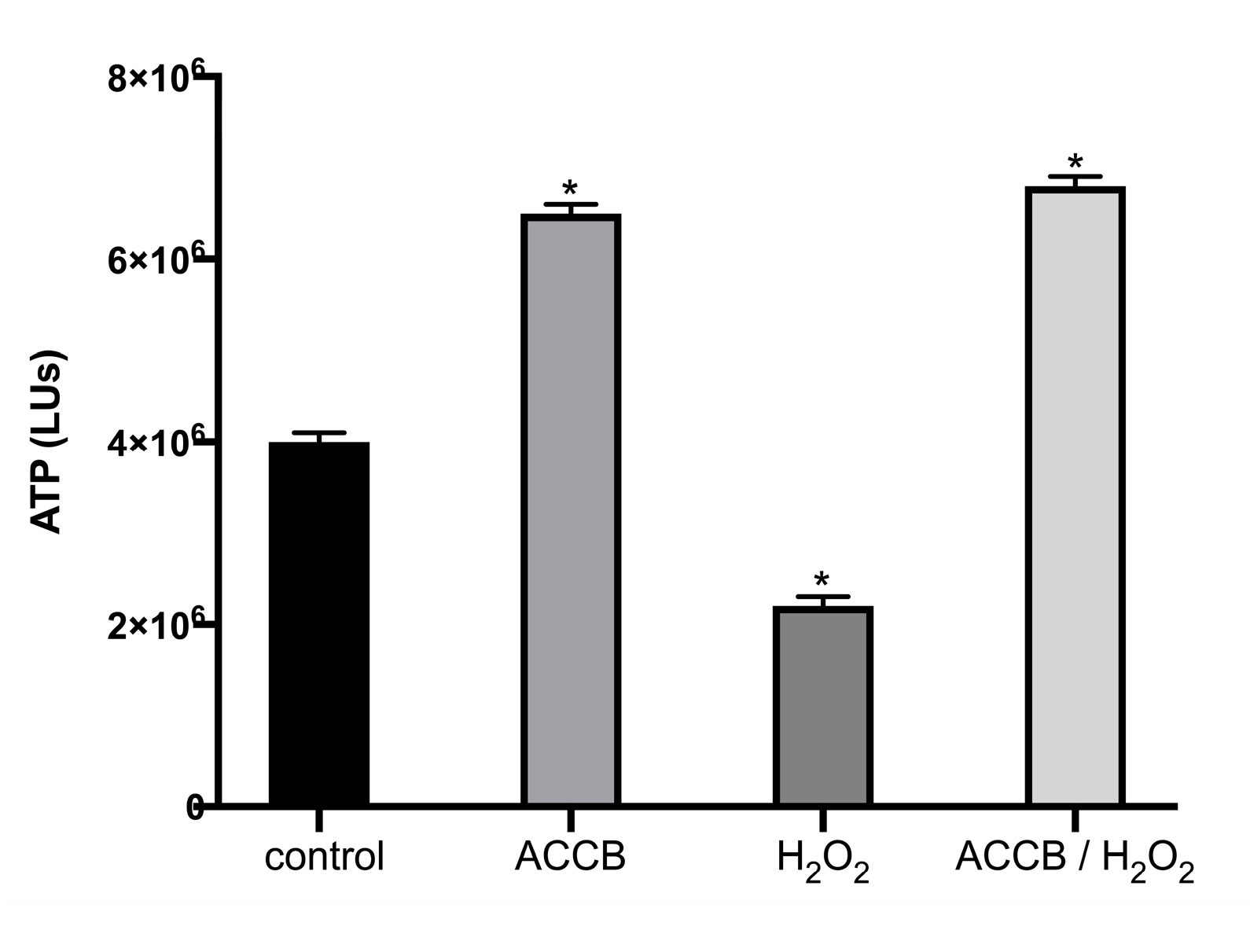
Figure 5 shows the ATP levels of NHDF cells under or without oxidative stress. We observe that, compared to untreated cells, treatment with H2O2 decreased the cell viability (ATP levels) by 30%. However, the addition of ACCB (0.05 μg/mL) not only counteracts the toxicity induced by H2O2 but maintains the high level of cell viability as for the untreated cells.
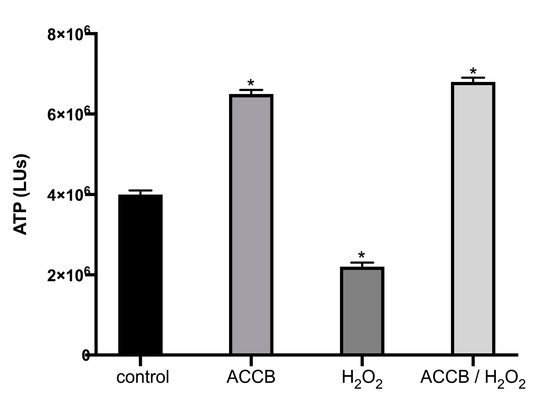
Figure 5.
ATP levels (LUs) expressed as mean ± SEM for: control (untreated NHDF cells), ACCB (NHDF cells treated with 0.05 μg/mL ACCB, H2O2 (0.5 mM) and ACCB/H2O2 (NHDF cells treated first with 0.05 μg/mL ACCB and then with H2O2). * p < 0.05 significantly different from the control (ANOVA test).
2.2.2. Genes Involved in Antioxidant Response Cell Pathway
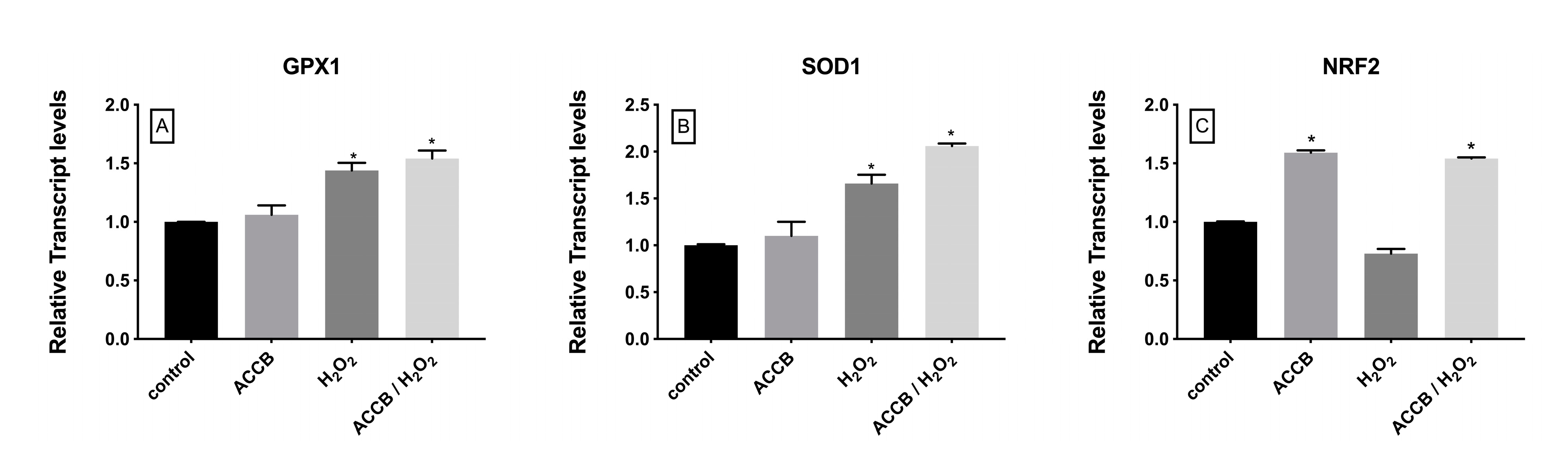
To evaluate the antioxidant activity of ACCB we measured the expression of genes involved in the cellular antioxidant response. Figure 6A–B shows that the expression of glutathione peroxidase-1 (GPX1) and superoxide dismutase-1 (SOD1) increased under oxidative stress with or without addition of ACCB; in this case the contribution of ACCB remains limited. However, compared to control (p < 0.05), the expression of the nuclear factor, erythroid 2 like 2 (NRF2) was significantly increased in cells treated with ACCB with or without H2O2-induced oxidative stress (Figure 6C).
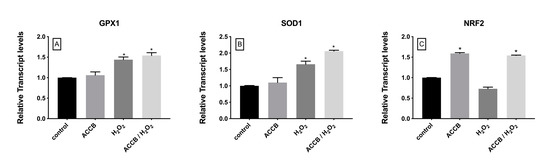
Figure 6.
Relative expression of (A) GPX1, (B) SOD1, and (C) NRF2 in control (untreated NHDF), NHDF cells treated with ACCB (0.05 μg/mL) (ACCB), NHDF cells treated with H2O2 0.5 mM (H2O2), and NHDF cells treated with ACCB and H2O2 (0.5 mM) (ACCB/ H2O2). Transcript expression levels were obtained by qPCR and the means of ACTB and GADPH were used as internal references genes. The results are presented as a fold change ± SD respect to control and represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. * p < 0.05 significantly different from control using one-way ANOVA.
2.2.3. Genes Involved in Cell Proliferation and Extracellular Matrix Organization
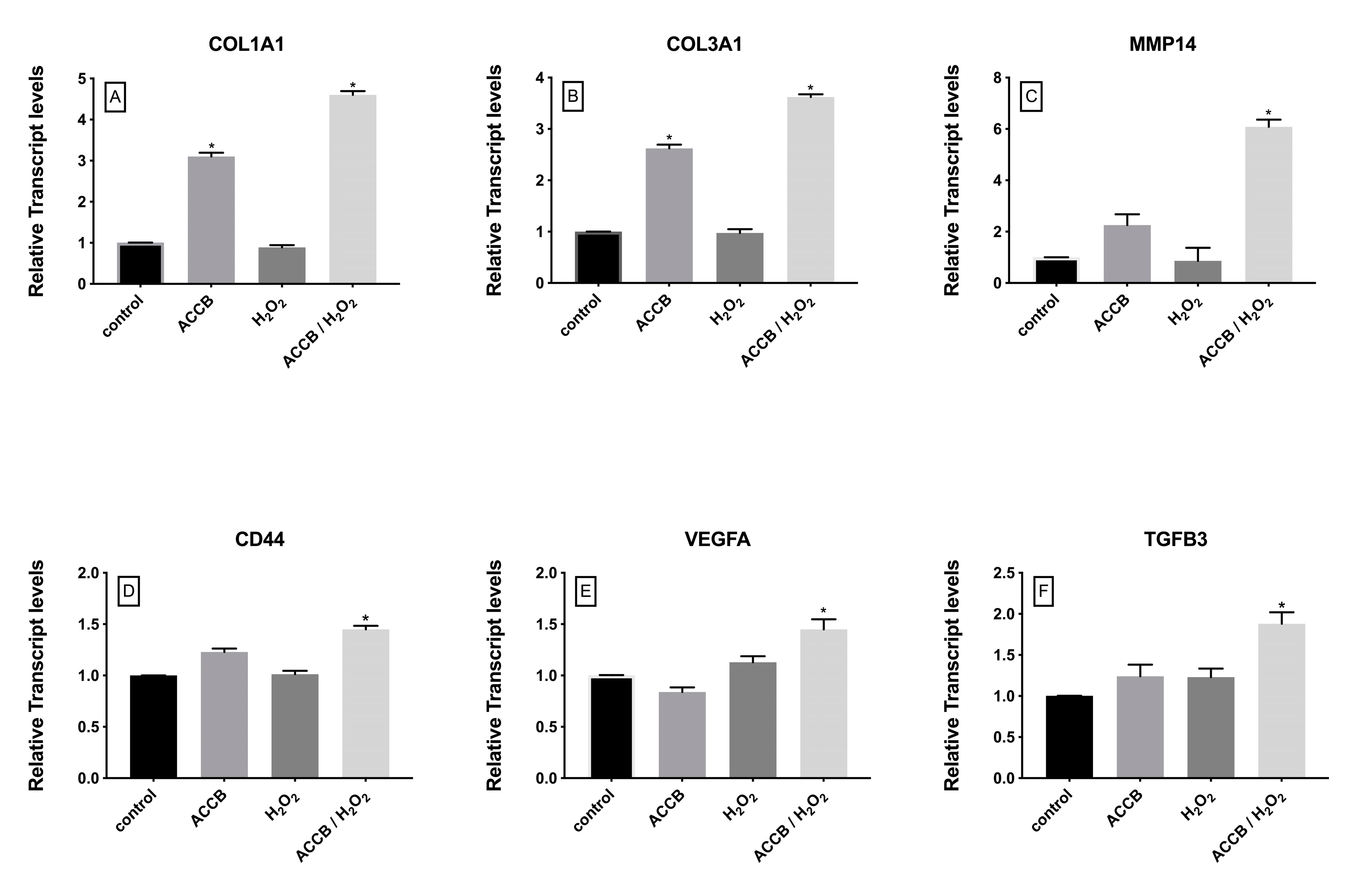
The impact of ACCB on the expression of genes involved in cell proliferation and extracellular matrix organization was also investigated. As shown in Figure 7, the expression of these genes in not impacted by the treatments of cells with H2O2, but significantly increased in ACCB treated cells, in the control and even more markedly in the H2O2 treated cells.
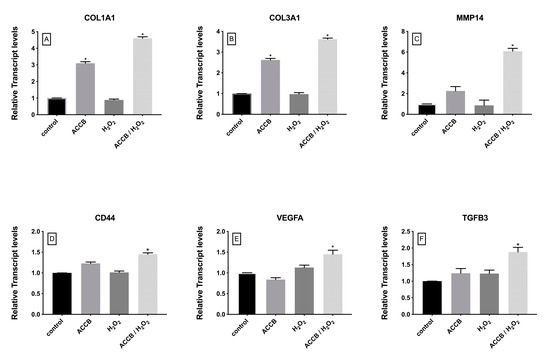
Figure 7.
Relative expression of (A) COL1A1, (B) COL3A1, (C) MMP14, (D) CD44, (E) VEGFA, and (F) TGFB3 in control (untreated NHDF), NHDF cells treated with ACCB (0.05 μg/mL) (ACCB), NHDF cells treated with H2O2 0.5 mM (H2O2), and NHDF cells treated with ACCB and H2O2 (0.5 mM) (ACCB/H2O2). Transcript expression levels were obtained by qPCR and the mean of ACTB and GADPH were used as internal references genes. The results are presented as a fold change ± SD respect to control and represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. * p < 0.05 significantly different from control using one- way ANOVA.
In detail, the expressions of collagen type I alpha 1 chain (COL1A1) and collagen type III alpha 1 chain (COL3A1) increased with the addition of ACCB under or without oxidative stress (Figure 7A,B). This significant increase is observed without oxidative stress, but is remarkably higher under H2O2 treatment. On the other hand, expressions of matrix metallopeptidase 14 (MMP14), CD44 molecule (CD44), vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFa) and transforming growth factor beta 3 (TGFB3) increased in ACCB treated NHDF cells only under oxidative stress compared to control (p < 0.05) (Figure 7C–F).
2.2.4. Genes Involved in Cell Aging Pathway
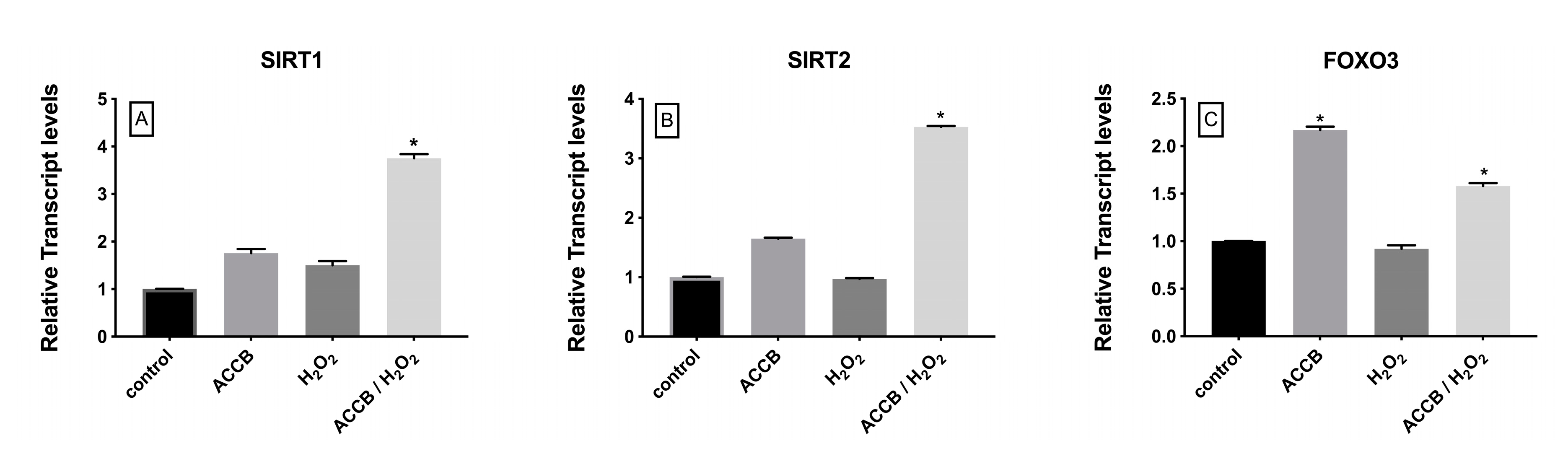
The expression of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) and sirtuin 2 (SIRT2) increased significantly in ACCB treated H2O2-induced NHDF cells compared to control (p < 0.05) (Figure 8A,B) while expression of forkhead box O3 (FOXO3) increased in ACCB treated NHDF with or without oxidative stress (p < 0.05) (Figure 8C).
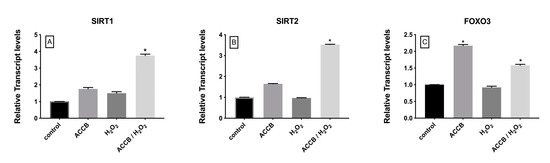
Figure 8.
Relative expression of (A) SIRT1, (B) SIRT2, and (C) FOXO3 in control (untreated NHDF), NHDF cells treated with ACCB (0.05 μg/mL) (ACCB), NHDF cells treated with H2O2 0.5 mM (H2O2), and NHDF cells treated with ACCB and H2O2 (0.5 mM) (ACCB/ H2O2). Transcripts expression levels were obtained by qPCR and the mean of ACTB and GADPH were used as internal references genes. The results are presented as a fold change ± SD respect to control and represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. * p < 0.05 significantly different from control using one-way ANOVA.
2.2.5. Genes Involved in Inflammation
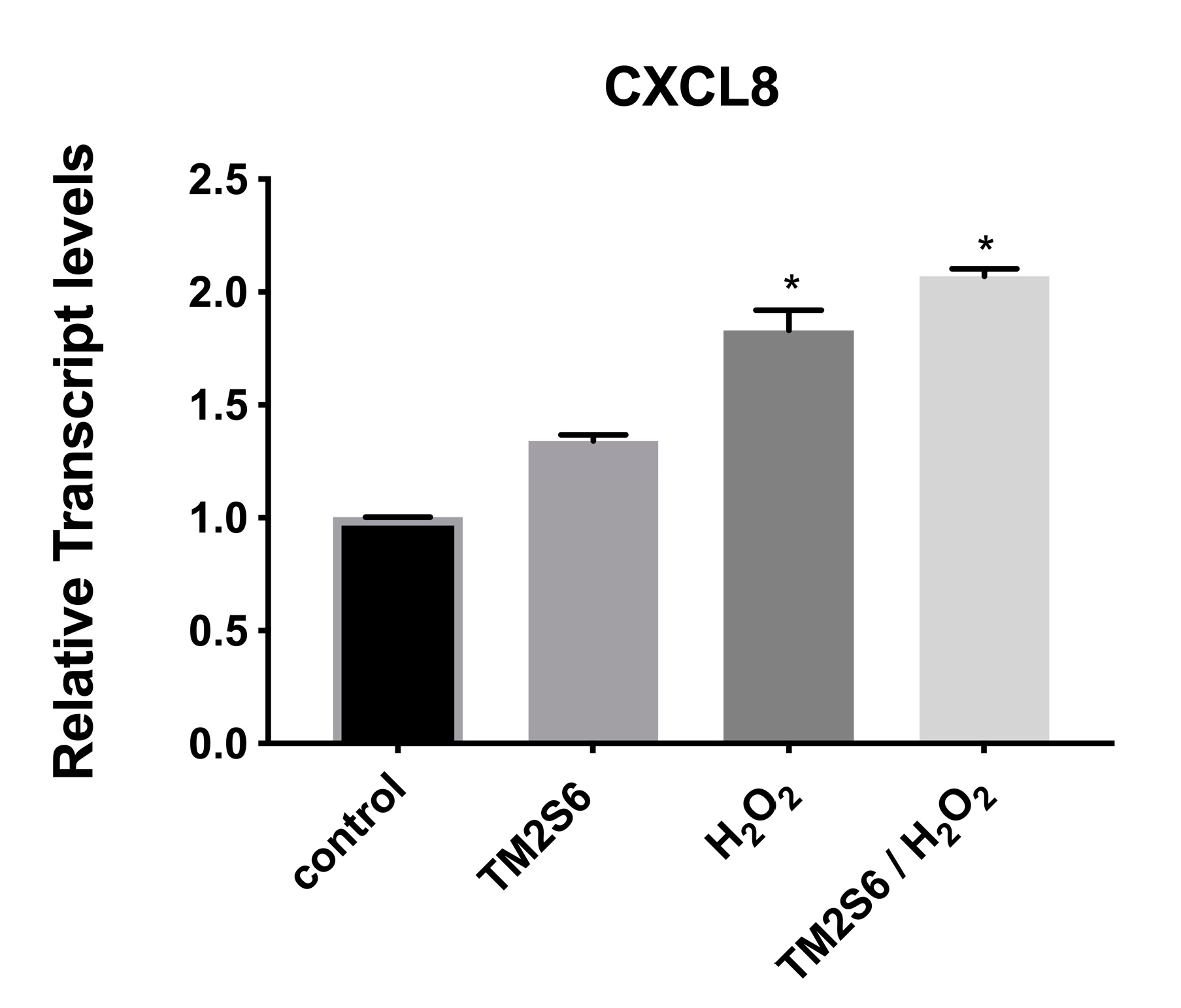
The expression of C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8 (CXCL8) was measured, showing a limited increase in NHDF cells under oxidative stress with or without addition of ACCB (p < 0.05) (Figure 9).
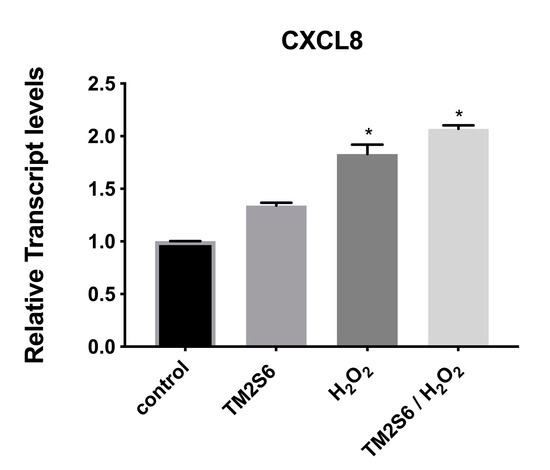
Figure 9.
Relative expression of CXCL8 in control (untreated NHDF), NHDF cells treated with ACCB (0.05 μg/mL) (ACCB), NHDF cells treated with H2O2 0.5 mM (H2O2), and NHDF cells treated with ACCB and H2O2 (0.5 mM) (ACCB/H2O2). Transcript expression levels were obtained by qPCR and the mean of ACTB and GADPH were used as internal references genes. The results are presented as a fold change ± SD respect to control and represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. * p < 0.05 significantly different from control using one-way ANOVA.
3. Discussion
This is the first report on the biological cosmetic potential of Aspergillus chevalieri TM2-S6 cultivation broth extract (ACCB). This ingredient was prepared in media and with procedures compatible with cosmetic constraints (water as solvent, medium without animal constituents, no post-cultivation processing, only sterilizing filtration). In this study, we focused on the impact of ACCB on oxidative stress, simulated by H2O2 application on human fibroblast, which plays a key role in skin health and is sensitive to the deleterious effect of oxidative stress.
Before implementing molecular bioassays, we evaluated the impact of ACCB on cell viability by measuring the intracellular levels of ATP in NHDF cells. This experiment revealed that, at low concentrations of ACCB (0.05 µg/mL), ATP level is significantly enhanced, while even at high concentrations (1 µg/mL), no toxicity is observed compared to the control. This increase is associated with the enhancement of cell proliferation and energy metabolism of NHDF cells. Previous reports supported the conclusion that increased intercellular levels of ATP could be associated with higher levels of mitochondrial activity, energy metabolism as well as cell proliferation [17,18].
To gain insight on the molecular targets of ACCB, we investigated the expression of genes involved in skin biological pathways. According to the results reported in this paper, ACCB transcriptionally modulates genes involved in antioxidant, aging, extracellular matrix organization and less on inflammation.
In terms of antioxidant response, we investigated the expression of GXP1, SOD1 and NRF2 since these genes are considered key antioxidant markers [19,20,21,22]. It has been reported that GPX1, SOD1, NRF2 are up-regulated under oxidative stress [20,23,24,25]. Similarly, our results showed a significant yet limited increase in the expression of GPX1 and SOD1 under oxidative stress. Interestingly, the expression of NRF2 was significantly increased with the addition of ACCB compared to control, regardless of the addition of H2O2. This outcome suggests a multifactorial antioxidant protective role of ACCB. The activity of ACCB on NFR2 without external oxidant damage by H2O2 could be considered as a preventive or a pro-survival action mediated by the induction of a global detoxification pathway [26].
In terms of aging pathway, we investigated the expression levels of SIRT1 and SIRT2 since sirtuins are mediators in cellular aging process either by delaying the cellular senescence or by expanding cells lifespan through the regulation of different cellular functions [27]. Our results demonstrated a significant upregulation in the expression of SIRT1 and SIRT2 in NHDF cells treated with ACCB under oxidative stress as compared with control. This upregulation is in agreement with previous reports [28,29]. In addition, we investigated the expression of FOXO3 as it has a significant regulatory role in cellular aging process as well as antioxidant response [30,31,32,33]. FOXO3 was upregulated upon treatment with ACCB with or without H2O2 treatment of NHDF cells. As for NFR2, this effect seems independent from exogenous oxidative stress with H2O2 and may be related to the preventive and protective role already reported for FOXO3 [34].
Extracellular matrix (ECM) organization has an important role in many cellular processes. In this study, we focused on the in vitro expression of COL1A1, COL3A1, MMP14 responsible for the main modulations in ECM during cellular aging process [35]. Specifically, COL1A1 and COL1A2, together, encode the type I collagen, an abundant extracellular protein in the skin [36], while COL3A1 encodes the type III collagen, an important protein for skin balance, together with collagen type I [37]. In addition, MMP14 is responsible for collagen degradation, and it has been reported that MMP14 expression is upregulated under oxidative stress [24]. Our results indicated a significant upregulation in the expression of COL1A1 and COL3A1 with the addition of ACCB with or without oxidative stress. This behavior potentially underlines that ACCB protects collagen conformation during cellular aging process. The increased expression of MMP14, in accordance with a previous report [38], corroborates the crucial role of ACCB in skin aging biological mechanism. Furthermore, we also investigated the expression of the gene CD44 as it regulates pro-proliferative as well as migratory effects of cells in high hyaluronic-abundant tissues [39]. Our results showed a significant upregulation of CD44 expression in NHDF cells treated with ACCB under oxidative stress. This potentially indicates that ACCB stimulates the production of hyaluronic acid by fibroblasts under oxidative stress.
The expression of VEGFα and TGFB3 was modulated significantly under our experimental conditions. VEGFα plays a key role in the regulation of cell proliferation during the angiogenesis process [40,41] and TGFB3 is involved in cell migration [42]. Our results showed significant increased expression of VEGFα and TGFB3 in fibroblasts treated with ACCB under oxidative stress. These results are in accordance with previous studies [43,44].
Finally, the impact of ACCB on inflammation is very limited as among other genes investigated, only the expression level of CXCL8 gene was slightly increased. CXCL8 belongs to the cytokine family with a significant role in inflammation [45].
Aspergillus chevalieri was reported in literature to produce flavoglaucin, a strong antioxidant and radical scavenger compound [15,46]. ACCB ingredient analysis by HPLC coupled to PDA, ELSD and MS detectors highlighted the presence of two main compounds, tetrahydroauroglaucin and flavoglaucin who may account for the bioactivities reported in this paper [15,16].
Future investigations are focused on the precise contribution of each of these compounds in the antioxidant role of ACCB.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strain Isolation and Identification
Aspergillus chevalieri TM2-S6 was isolated from a 1 cm3 sample of the sponge Axinella collected on the upper mesophotic zone off Tel Aviv–Jaffa, Israeli Mediterranean coast (32°1’42.431″ N 34°46’42.323″ E, 38 m depth). The sponge was collected at 38 m depth by a ROV (Remote Operating Vehicule) equipped with a collection arm (the sample is part of the TASCMAR project collection, EU H2020, grant agreement 634674). The collection permit #2016/41271 was delivered by the “Israel Nature and National Parks Protection Authority”. The sponge sample was frozen on-boat and stored until further processing. The sample was ground in sterile sea-water and heated at 50 °C for 1 h. The suspension was serially diluted, plated on selective isolation media, and incubated at 28 °C for at least 6 weeks. The strain was isolated from marine agar medium. The colony was purified on potato dextrose broth agar (PDBag, Difco, Fisher Scientific, F67403 Illkirch CEDEX, France) and marine broth agar (MBag, Difco) media and preserved in 10% glycerol solution.
4.2. Phylogeny Investigation
Genomic DNA isolation and amplification of the ITS region was performed as described previously [13]. Phylogeny inference was performed using MEGA X [47] and comprised the following steps. Sequences from TM2-S6 and Aspergillus spp. of the section Aspergillus and Restricti previously described [48] and aligned with MUSCLE [49]. After alignment, ambiguous regions were removed with Gblocks (v0.91b) [50]. The evolutionary history was inferred using the maximum likelihood method and Kimura 2-parameter model [51]. Reliability for internal branch was assessed using the bootstrap method with 1000 replicates. The tree with the highest log likelihood is shown. Accordingly, the strain was named Aspergillus chevalieri TM2-S6.
4.3. Cultivation and Extract Preparation
Aspergillus chevalieri TM2-S6 spores were conserved at −20 °C in 10% glycerol. Before cultivation, the strain was revived for 5 days on a 15 cm petri plate containing potato dextrose agar (PDBag). Sterile water (4 × 10 mL) was poured on the plate surface, and the spores were recovered from the plates by gentle scratching of the surface with a scalpel. Three plates offer 100 mL of concentrated spore suspension. This inoculum was used to cultivate the strain A. chevalieri TM2-S6 in a 20 × 2 L Erlenmeyer flask containing 1 L of potato dextrose broth medium (PDB, Difco, Fisher Scientific, F67403 Illkirch CEDEX, France over 9 days in a rotary shaker at 28 °C and 130 rpm. The culture broth was filtrated and sterilized using 0.22 µm sterile filtration units. Two liters of the filtrated culture broth were then lyophilized to give 8.25 g of crude A. chevalieri TM2-S6 cultivation broth extract (ACCB). ACCB is freely soluble in aqueous media, which is suitable for cosmetic investigations. ACCB was solubilized in NHDF cultivation media.
4.4. Human Skin Cell Culture
Primary Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts (NHDF) were purchased from Lonza Clonetics TM (Lonza, Walkersville, MD, USA) [52]. NHDF cells were cultured according to Lonza instructions in FGM™ 2 BulletKit™ mediun (Lonza, Walkersville, MD, USA) supplemented with 2% serum.
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
NHDF cells were incubated for 48 h with four concentrations of ACCB (1 μg/mL, 0.5 μg/mL, 0.1 μg/mL, 0.05 μg/mL) and then intracellular levels of ATP were measured with ViaLight HS BioAssay kit (Lonza). The same procedure was followed for the determination of ATP levels in NHDF cells treated with 0.05 μg/mL under oxidative stress. The experiments were performed in a single-tude luminator (GloMax 20/20, Promega). Three independent experiments were performed (8 technical repetitions).
4.6. H2O2 Treatment
The treatment of NHDF cells with H2O2 was performed according to a protocol described previously [13]. Moreover, the doses of H2O2 and incubation time was selected according to previously reported works [53,54].
4.7. Gene Expression Analysis by Real-Time RT-qPCR
4.7.1. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
For total RNA (tRNA) extraction, the Nucleospin RNA kit (Macherey-Nagel) was used following the manufacturer’s instructions. For the experiments, 500 ng of tRNA was used. For the synthesis of complimentary DNA (cDNA), the PrimeScript-RT reagent kit (Takara) was used.
4.7.2. RT-qPCR Analysis
qPCR was used to analyze the mRNA expression of genes modulated by ACCB under our experimental conditions as described before [13,53]. The qPCR reactions were performed in three independent biological repetitions (six technical replicates). Our results were based on the experimental conditions: untreated NHDF cells (control), NHDF cells treated with ACCB (0.05 μg/mL), NHDF cells treated with 0.5 mM H2O2 (H2O2), NHDF cells treated with ACCB (0.05 μg/mL) and 0.5 mM H2O2 (ACCB/H2O2) (Supplementary Tables S3 and S4).
4.8. Statistical Analysis
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to assess the interactions among the gene expression data on different experimental states. Multiple comparison was used for type I error likelihood. Normal distribution was confirmed for all data. All the statistical analysis was performed on SPSS 17.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) with a statistical significance level of 5%.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/18/9/460/s1, Table S1: Aspergillus species of the section Aspergillus restricti witn Genbank numbers. Table S2. Materials and methods used for analytical and structural characterization. Table S3. Relative mRNA expression ration versus control into three different treatments. Table S4. Characteristics and references of the investigated genes. Figure S1. 1H NMR and HRMS Spectra of tetrahydroauroglaucin. Figure S2. 1H NMR and HRMS Spectra of flavoglaucin.
Author Contributions
S.L. and J.O. conceived, planned and oversaw the experiments on transcriptional analysis and on ATP determination, A.B. executed the experiments on the RT-qPCR analysis and on ATP determination, G.L.G., P.L., J.O. carried out the experiments on phylogeny investigation. G.L.G., P.L., J.O. prepared the extract and achieved chemical investigations, M.W. and Y.B. collected the sponge. S.L.; G.L.G., J.O. and K.G. analyzed, integrated the datasets. S.L. and J.O. drafted the manuscript and all the other authors critically read and contributed to improving it. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by TASCMAR, a project funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under grant agreement no. 634674.
Acknowledgments
We thank EcoOcean for the use of R/V Mediterranean Explorer research vessel and of the underwater robot (ROV) as well as the professional assistance of its crew members. Collection of animals complied with a permit issued by the Israel Nature and National Parks Protection Authority.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fisher, G.J.; Kang, S.; Varani, J.; Bata-Csorgo, Z.; Wan, T.; Datta, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Mechanisms of Photoaging and Chronological Skin Aging. Arch. Dermatol. 2002, 138, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinnerthaler, M.; Bischof, J.; Streubel, M.K.; Trost, A.; Richter, K. Oxidative stress in aging human skin. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 545–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lephart, E.D. Skin aging and oxidative stress: Equol’s anti-aging effects via biochemical and molecular mechanisms. Ageing. Res. Rev. 2016, 31, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beacham, D.A.; Amatangelo, M.D.; Cukierman, E. Preparation of Extracellular Matrices Produced by Cultured and Primary Fibroblasts. Curr. Protoc. Cell. Biol. 2006, 33, 10.9.1–10.9.21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammeyer, A.; Luiten, R.M. Oxidation events and skin aging. Ageing Res Rev. 2015, 21, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, G.M.; Kehraus, S.; Seibert, S.F.; Abdel-Lateff, A.; Müller, D. Natural Products from Marine Organisms and Their Associated Microbes. Chem. Biol. Chem. 2006, 7, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.R.A.; Kavlekar, D.P.; LokaBharathi, P.A. Marine Drugs from Sponge-Microbe Association—A Review. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1417–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corinaldesi, C.; Barone, G.; Marcellini, F.; Dell’Anno, A.; Danovaro, R. Marine Microbial-Derived Molecules and Their Potential Use in Cosmeceutical and Cosmetic Products. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, M.; Eslamifar, M.; Khezri, K. Kojic acid applications in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.M.; Xu, G.M.; Li, C.S.; Wang, B.G. Antioxidant metabolites from marine alga-derived fungus Aspergillus wentii EN-48. Phytochem. Lett. 2014, 7, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Ren, B.; Chen, C.; Yu, K.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, N.; He, H.; Liu, X.; Dai, H.; et al. Three new sterigmatocystin analogues from marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor MF359. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 3753–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Kim, S.K.; Kang, J.S.; Choi, H.D.; Rho, J.R.; Son, B.W. Golmaenone, a New Diketopiperazine Alkaloid from the Marine-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2004, 52, 375–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letsiou, S.; Bakea, A.; Le Goff, G.; Lopes, P.; Gardikis, Κ.; Alonso, C.; Alvarez, P.A.; Ouazzani, J. In vitro protective effects of marine-derived Aspergillus puulaauensis TM124-S4 extract on H2O2-stressed primary human fibroblasts. Toxicol. In Vitro 2020, 66, 104869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, H.; Koc, A.; Simsek, D.; Gozcelioglu, B.; Altanlar, N.; Konuklugil, B. Isolation, identification and bioactivity screening of turkish marine-derived fungi. Farmacia 2019, 67, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Morimoto, K.; Piamasaki, T. Flavoglaucin, a Metabolite of Eurotium cheva, lieri, its Antioxidation and Synergism with Tocopherol. JAOCS 1984, 61, 1864–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, Y.; Ito, C.; Itoigawa, M.; Osawa, T. Antioxidants Produced by Eurotium herbariorum of Filamentous Fungi Used for the Manufacture of Karebushi, Dried Bonito (Katsuobushi). Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarkatti, M.; Rieder, S.A.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Evaluation of Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis in Immunotoxicity Testing. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1803, 209–230. [Google Scholar]
- Lunt, S.Y.; Vander Heiden, M.G. Aerobic glycolysis: Meeting the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2011, 27, 441–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gęgotek, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. The role of transcription factor Nrf2 in skin cells metabolism. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2015, 307, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Li, K.; Liu, Q.; Quiles, J.L.; Filosa, R.; Kamal, M.A.; Wang, F.; Kay, G.; Zou, X.; Teng, H.; et al. Protective effects of raspberry on the oxidative damage in HepG2 cells through Keap1/Nrf2-dependent signaling pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 133, 110781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurjala, A.N.; Liu, W.R.; Mogford, J.E.; Procaccini, P.S.A.; Mustoe, T.A. Age-dependent response of primary human dermal fibroblasts to oxidative stress: Cell survival, pro-survival kinases, and entrance into cellular senescence. Wound Repair Regen. 2005, 13, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, P.; Pohl, C.; Calles, C.; Marks, C.; Wild, S.; Krutmann, J. Cellular response to infrared radiation involves retrograde mitochondrial signaling. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, T.A.F.T.; Jubri, Z.; Rajab, N.; Rahim, K.A.; Yusof, Y.A.M.; Makpol, S. Gelam Honey Protects against Gamma-Irradiation Damage to Antioxidant Enzymes in Human Diploid Fibroblasts. Molecules 2013, 18, 2200–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcazar, O.; Cousins, S.W.; Marin-Castaño, M.E. MMP-14 and TIMP-2 overexpression protects against hydroquinone-induced oxidant injury in RPE: Implications for extracellular matrix turnover. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 5662–5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hseu, Y.-C.; Korivi, M.; Lin, F.-Y.; Li, M.-L.; Lin, R.-W.; Wu, J.-J.; Yang, H.-L. Trans-cinnamic acid attenuates UVA-induced photoaging through inhibition of AP-1 activation and induction of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant genes in human skin fibroblasts. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 90, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, M. Role of Nrf2 in Oxidative Stress and Toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Min, K.-J. Sirtuin signaling in cellular senescence and aging. BMB Rep. 2019, 52, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asparuhova, M.B.; Kiryak, D.; Eliezer, M.; Mihov, D.; Sculean, A. Activity of two hyaluronan preparations on primary human oral fibroblasts. J. Periodontal Res. 2019, 54, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefani, M.; Markus, M.A.; Lin, R.C.Y.; Pinese, M.; Dawes, I.W.; Morris, B.J. The Effect of Resveratrol on a Cell Model of Human Aging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2007, 1114, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyoung Kim, H.; Kyoung Kim, Y.; Song, I.-H.; Baek, S.-H.; Lee, S.-R.; Hye Kim, J.; Kim, J.-R. Down-Regulation of a Forkhead Transcription Factor, FOXO3a, Accelerates Cellular Senescence in Human Dermal Fibroblasts. J. Gerontol. Series A 2005, 60, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zhai, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, T.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yin, X. The Akt-FoxO3a-manganese superoxide dismutase pathway is involved in the regulation of oxidative stress in diabetic nephropathy. Exp. Physiol. 2013, 98, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, B.J. A forkhead in the road to longevity: The molecular basis of lifespan becomes clearer. J. Hypertens. 2005, 23, 1285–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanetti, R.J.; Voisin, S.; Russell, A.; Lamon, S. Recent advances in understanding the role of FOXO3. F1000Research. 2018, 31, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibbe, W.E.; Shi, Y. FOXO3, a Molecular Search for the Fountain of Youth. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 351–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, R.E.B.; Ogden, S.; Cotterell, L.F.; Bowden, J.J.; Bastrilles, J.Y.; Long, S.P.; Griffiths, C.E.M. A cosmetic ‘anti-ageing’ product improves photoaged skin: A double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 161, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Carrique, L.; Vadon-Le Goff, S.; Mariano, N.; Georges, R.-N.; Delolme, F.; Koivunen, P.; Myllyharju, J.; Moali, C.; Aghajari, N.; et al. Structural basis of homo- and heterotrimerization of collagen I. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remoué, N.; Molinari, J.; Andres, E.; Lago, J.C.; Barrichello, C.; Moreira, P.L. Development of an in vitro model of menopause using primary human dermal fibroblasts. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, J.C.; Puzzi, M.B. The effect of aging in primary human dermal fibroblasts. Picardo, M, editor. PLoS ONE. 2019, 14, e0219165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, A.R.; Racine, R.R.; Hennig, M.J.P.; Lokeshwar, V.B. The Role of CD44 in Disease Pathophysiology and Targeted Treatment. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, S.; Goveia, J.; Stapor, P.C.; Cantelmo, A.R.; Carmeliet, P. The multifaceted activity of VEGF in angiogenesis—Implications for therapy responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, S.; Grose, R. Regulation of Wound Healing by Growth Factors and Cytokines. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 835–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamayo, E.; Alvarez, P.; Merino, R. TGFβ Superfamily Members as Regulators of B Cell Development and Function—Implications for Autoimmunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, V.; Gopal, A.; Kumar, D.; Pathak, N.N.; Ram, M.; Jangir, B.L.; Tandan, S.K.; Kumar, D. Curcumin-induced angiogenesis hastens wound healing in diabetic rats. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 193, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.; Nigam, Y. Naturally derived factors and their role in the promotion of angiogenesis for the healing of chronic wounds. Angiogenesis 2013, 16, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, R.C.; Garcia, C.C.; Teixeira, M.M.; Amaral, F.A. The CXCL8/IL-8 chemokine family and its receptors in inflammatory diseases. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2014, 10, 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Lee, U.; Kang, J.S.; Choi, H.C.; Son, B.W. A New Radical Scavenging Anthracene Glycoside, Asperflavin Ribofuranoside, and Polyketides from a Marine Isolate of the Fungus Microsporum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, R.A.; Visagie, C.M.; Houbraken, J.; Hong, S.-B.; Hubka, V.; Klaassen, C.H.W.; Perronne, G.; Seifert, K.A.; Susca, A.; Tanney, J.B.; et al. Phylogeny, identification and nomenclature of the genus Aspergillus. Stud. Mycol. 2014, 78, 141–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castresana, J. Selection of Conserved Blocks from Multiple Alignments for Their Use in Phylogenetic Analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giampieri, F.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Mazzoni, L.; Forbes-Hernandez, T.Y.; Gasparrini, M.; Gonzàlez-Paramàs, A.M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Quiles, J.L.; Bompadre, S.; Mezzetti, B.; et al. Polyphenol-Rich Strawberry Extract Protects Human Dermal Fibroblasts against Hydrogen Peroxide Oxidative Damage and Improves Mitochondrial Functionality. Molecules 2014, 19, 7798–7816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letsiou, S.; Kalliampakou, K.; Gardikis, K.; Mantecon, L.; Infante, C.; Chatzikonstantinou, M.; Labrou, N.E.; Flemetakis, E. Skin Protective Effects of Nannochloropsis gaditana Extract on H2O2-Stressed Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaseth, T.; Kuzminov, A. Potentiation of hydrogen peroxide toxicity: From catalase inhibition to stable DNA-iron complexes. Mutat. Res. 2017, 773, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).