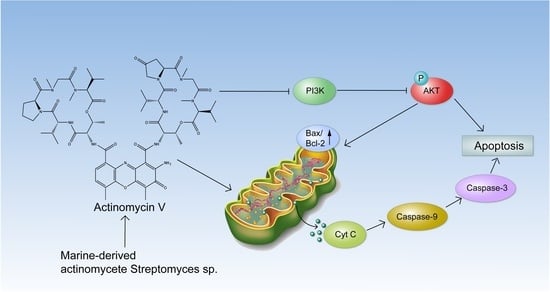
Actinomycin V Induces Apoptosis Associated with Mitochondrial and PI3K/AKT Pathways in Human CRC Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Act V Inhibited Human CRC Cell Lines
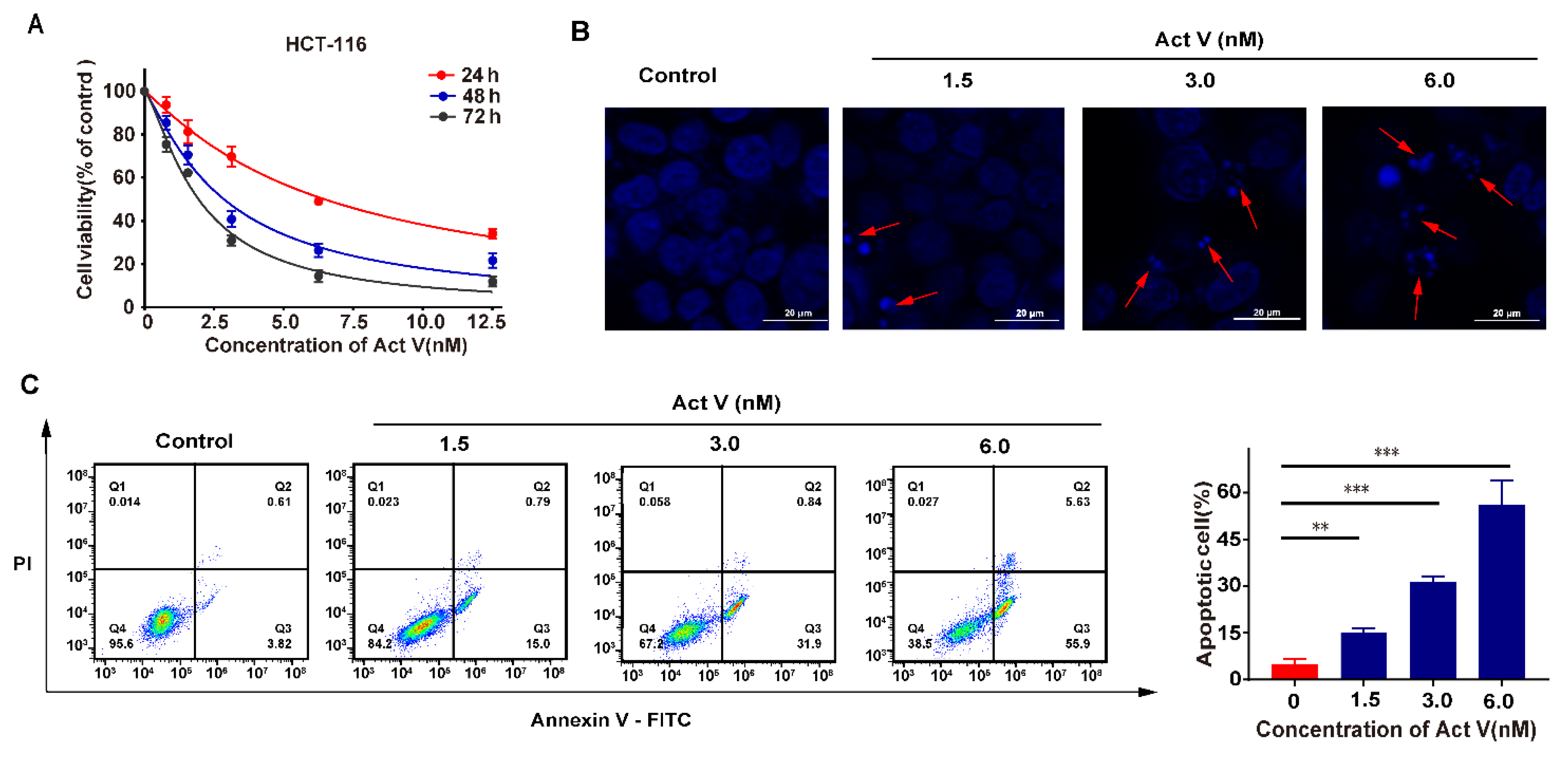
2.2. Act V Induced Apoptosis in the CRC Cell Line HCT-116
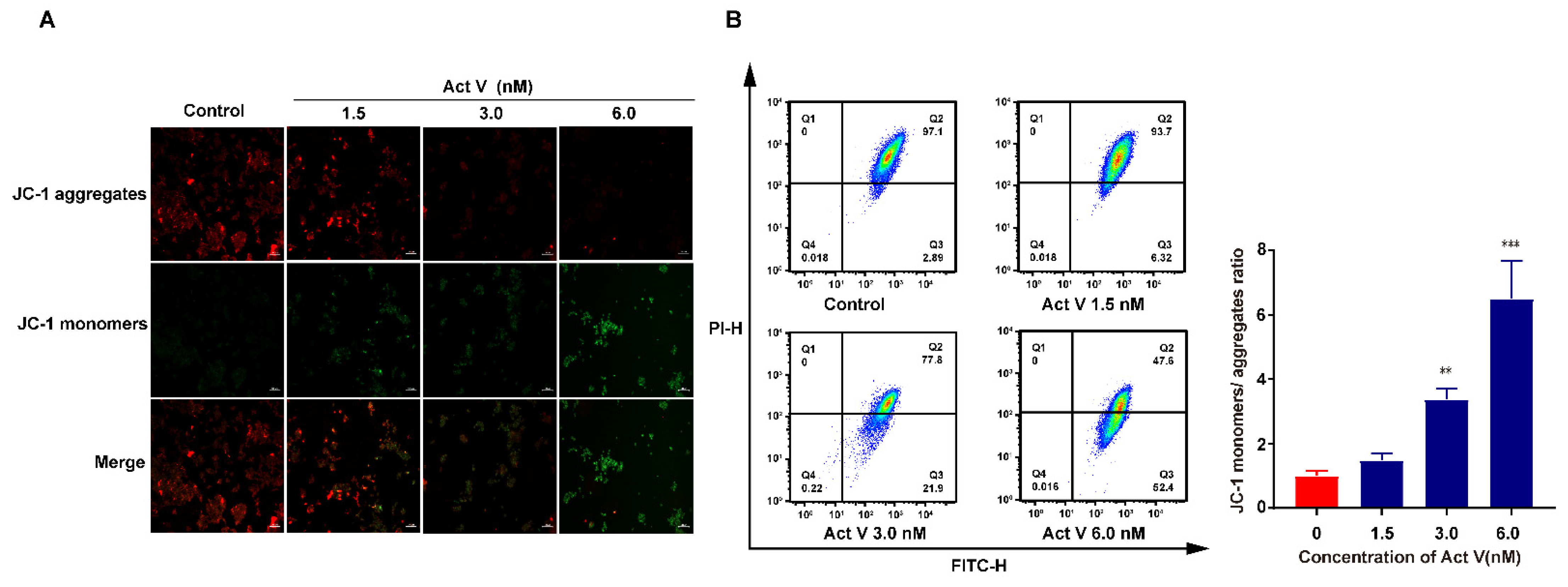
2.3. Act V Decreased Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) in the CRC Cell Line HCT-116
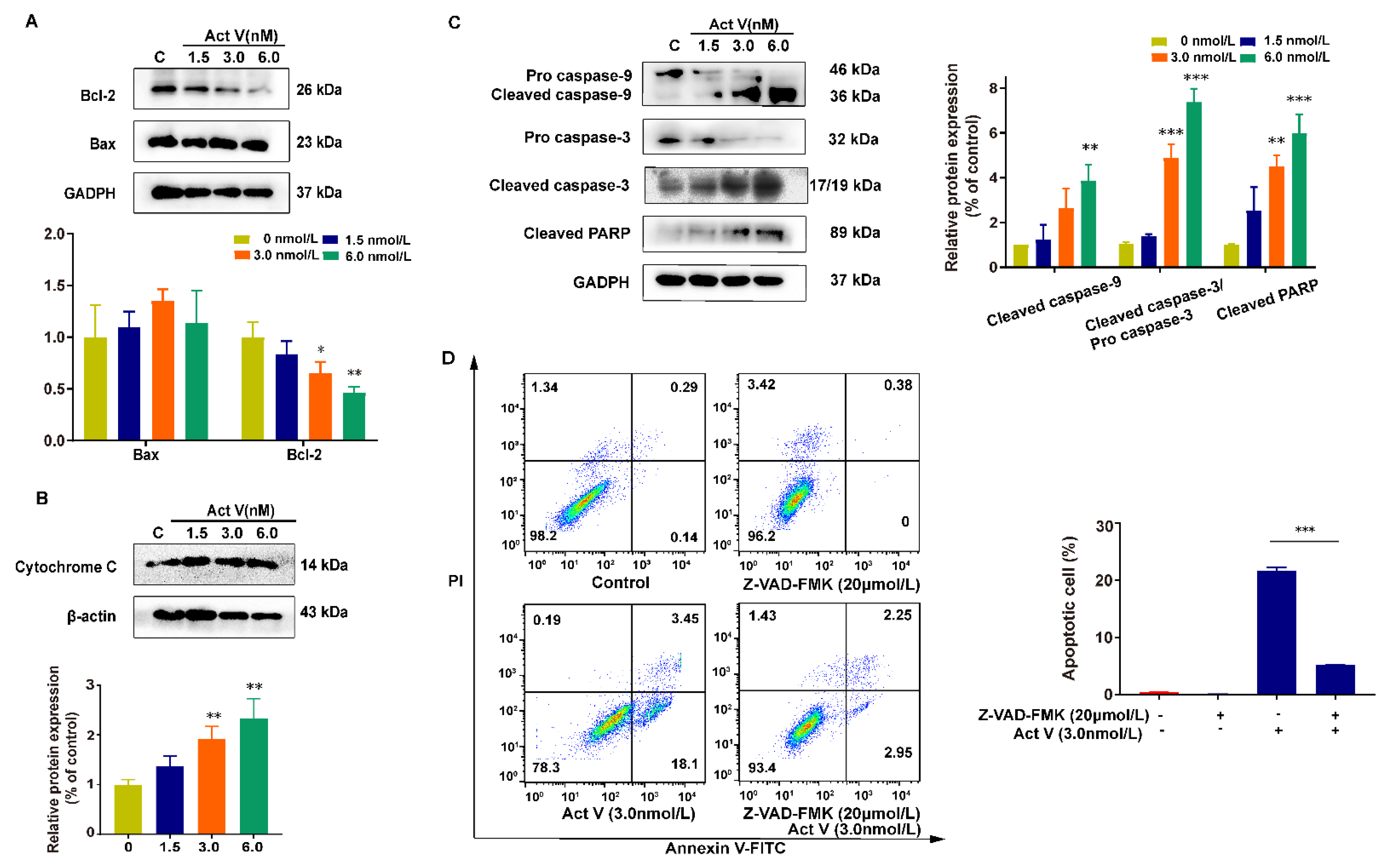
2.4. The Effect of Act V on the Expression of Proteins Related to Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathways in HCT-116 Cells
2.5. Act V Regulates the PI3K/AKT Pathway
2.6. Inhibition of PI3K Proves the Effect of Act V on the PI3K/AKT Pathway
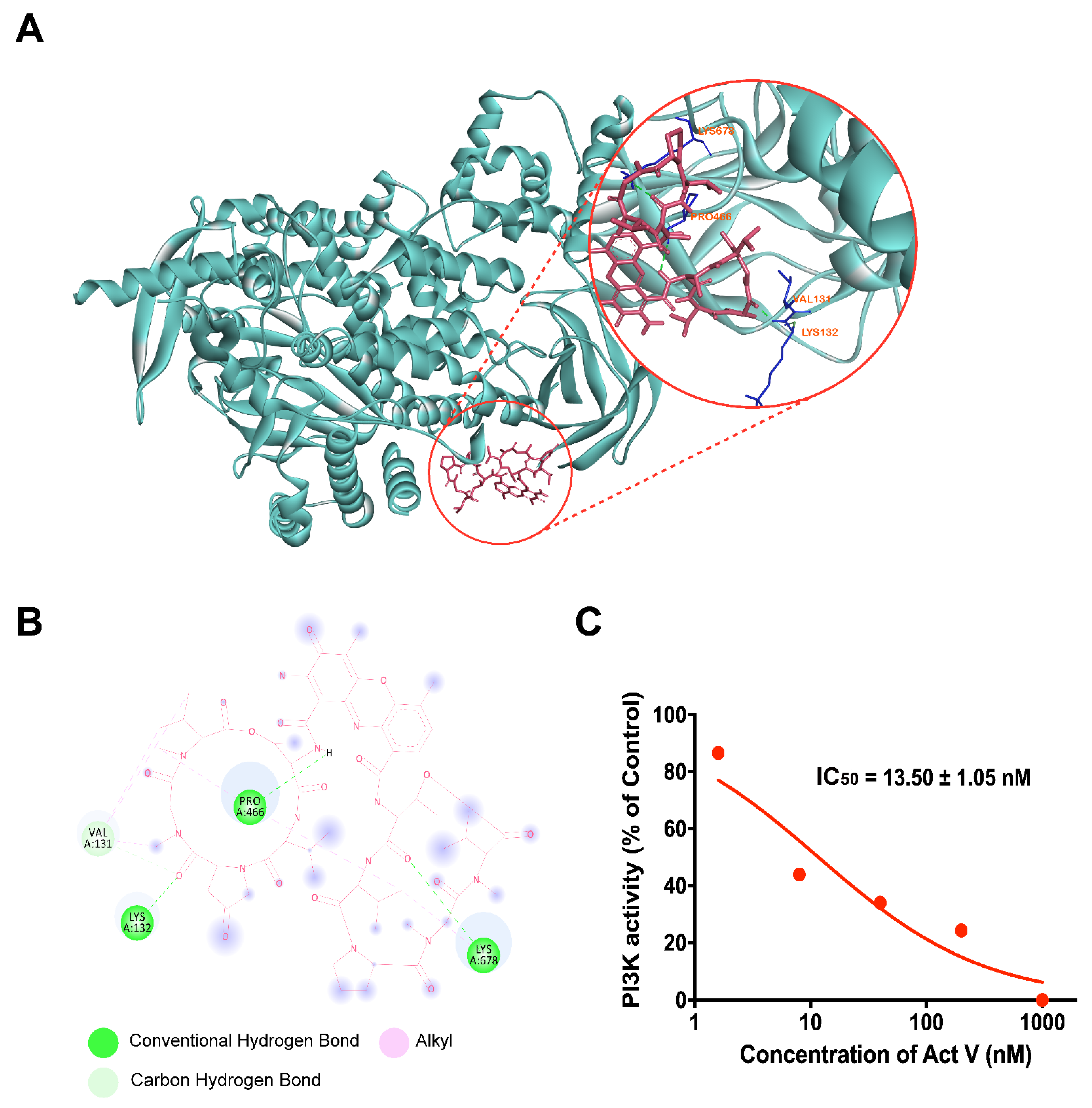
2.7. Molecular Docking Analysis of Act V against PI3K
2.8. Inhibitory Activity of Act V against PI3K Using Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence Technology (HTRF®)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical and Reagents
4.2. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.3. MTT Assay
4.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.5. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay
4.6. DAPI Staining
4.7. Preparation of Cytosolic Protein
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.10. Docking Studies
4.11. PI3K Inhibition Viability Test by Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF®) Analysis In Vitro
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farber, S. Chemotherapy in the Treatment of Leukemia and Wilms’ Tumor. JAMA 1966, 198, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.L., Jr. Chemotherapy of gestational choriocarcinoma. Cancer 1972, 30, 1517–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhang, C.; Liu, F.; Ma, J.; Jia, F.; Han, Z.; Xie, W.; Li, X. Actinomycin V Inhibits Migration and Invasion via Suppressing Snail/Slug-Mediated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Progression in Human Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells In Vitro. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.Q.; Jia, F.J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Liu, F.Y.; Ma, J.H.; Han, Z.; Xie, W.D.; Li, X. Actinomycin V Suppresses Human Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma A549 Cells by Inducing G2/M Phase Arrest and Apoptosis via the p53-Dependent Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, F.-J.; Han, Z.; Ma, J.-H.; Jiang, S.-Q.; Zhao, X.-M.; Ruan, H.; Xie, W.-D.; Li, X. Involvement of Reactive Oxygen Species in the Hepatorenal Toxicity of Actinomycin V In Vitro and In Vivo. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.J.; Du, N.; Zhang, D.B.; Zhou, X.X.; Li, X.F.; Ju, J.H.; Hu, Z.L.; Wang, L.Y. Efficient, green, and rapid strategy for separating actinomycin D and X2 using supercritical fluid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 195, 113835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertram, R.; Gram Pedersen, M.; Luciani, D.S.; Sherman, A. A simplified model for mitochondrial ATP production. J. Theor. Biol. 2006, 243, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parsons, M.J.; Green, D.R. Mitochondria in cell death. Essays Biochem. 2010, 47, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abate, M.; Festa, A.; Falco, M.; Lombardi, A.; Luce, A.; Grimaldi, A.; Zappavigna, S.; Sperlongano, P.; Irace, C.; Caraglia, M.; et al. Mitochondria as playmakers of apoptosis, autophagy and senescence. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 98, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogler, M.; Dinsdale, D.; Dyer, M.J.; Cohen, G.M. Bcl-2 inhibitors: Small molecules with a big impact on cancer therapy. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suen, D.F.; Norris, K.L.; Youle, R.J. Mitochondrial dynamics and apoptosis. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoxhaj, G.; Manning, B.D. The PI3K-AKT network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer metabolism. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janku, F.; Yap, T.A.; Meric-Bernstam, F. Targeting the PI3K pathway in cancer: Are we making headway? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 273–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, B.D.; Toker, A. AKT/PKB Signaling: Navigating the Network. Cell 2017, 169, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, M.S.; Sanches, J.M.; Seruca, R. Targeting the PI3K Signalling as a Therapeutic Strategy in Colorectal Cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1110, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoRusso, P.M. Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3803–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, A. Alpelisib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulda, S. Modulation of mitochondrial apoptosis by PI3K inhibitors. Mitochondrion 2013, 13, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.J.; Cantley, L.C. Ras, PI(3)K and mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth. Nature 2006, 441, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardai, S.J.; Hildeman, D.A.; Frankel, S.K.; Whitlock, B.B.; Frasch, S.C.; Borregaard, N.; Marrack, P.; Bratton, D.L.; Henson, P.M. Phosphorylation of Bax Ser184 by Akt regulates its activity and apoptosis in neutrophils. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 21085–21095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, X.J.; Wildey, G.M.; Howe, P.H. Evidence that Ser87 of BimEL is phosphorylated by Akt and regulates BimEL apoptotic function. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parcellier, A.; Tintignac, L.A.; Zhuravleva, E.; Hemmings, B.A. PKB and the mitochondria: AKTing on apoptosis. Cell. Signal. 2008, 20, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Tian, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, H. The effects of silencing of PI3K p85alpha on 5-FU-induced colorectal cancer cells apoptosis. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.F.; Shi, C.; Yang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Sheng, L.; Li, N. Medicinal mushroom Phellinus igniarius induced cell apoptosis in gastric cancer SGC-7901 through a mitochondria-dependent pathway. Biomed. Pharm. 2018, 102, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Nagy, L.; Fodor, T.; Liaudet, L.; Pacher, P. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases as modulators of mitochondrial activity. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fruman, D.A.; Chiu, H.; Hopkins, B.D.; Bagrodia, S.; Cantley, L.C.; Abraham, R.T. The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease. Cell 2017, 170, 605–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dayanidhi, D.L.; Thomas, B.C.; Osterberg, J.S.; Vuong, M.; Vargas, G.; Kwartler, S.K.; Schmaltz, E.; Dunphy-Daly, M.M.; Schultz, T.F.; Rittschof, D.; et al. Exploring the Diversity of the Marine Environment for New Anti-cancer Compounds. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highlights of Prescribing Information (Dactinmycin for Injection). Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/050682s033lbl.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2018).
- Bilanges, B.; Posor, Y.; Vanhaesebroeck, B. PI3K isoforms in cell signalling and vesicle trafficking. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Perry, M.W.D.; Brown, J.R.; André, F.; Okkenhaug, K. PI3K inhibitors are finally coming of age. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanker, A.B.; Kaklamani, V.; Arteaga, C.L. Challenges for the Clinical Development of PI3K Inhibitors: Strategies to Improve Their Impact in Solid Tumors. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.-D.; Ren, J.-W.; Du, Q.-Q.; Song, Y.-J.; Lin, S.-Q.; Li, X.; Li, E.-W.; Xie, W.-D. p-Terphenyls and actinomycins from a Streptomyces sp. associated with the larva of mud dauber wasp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 1869–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
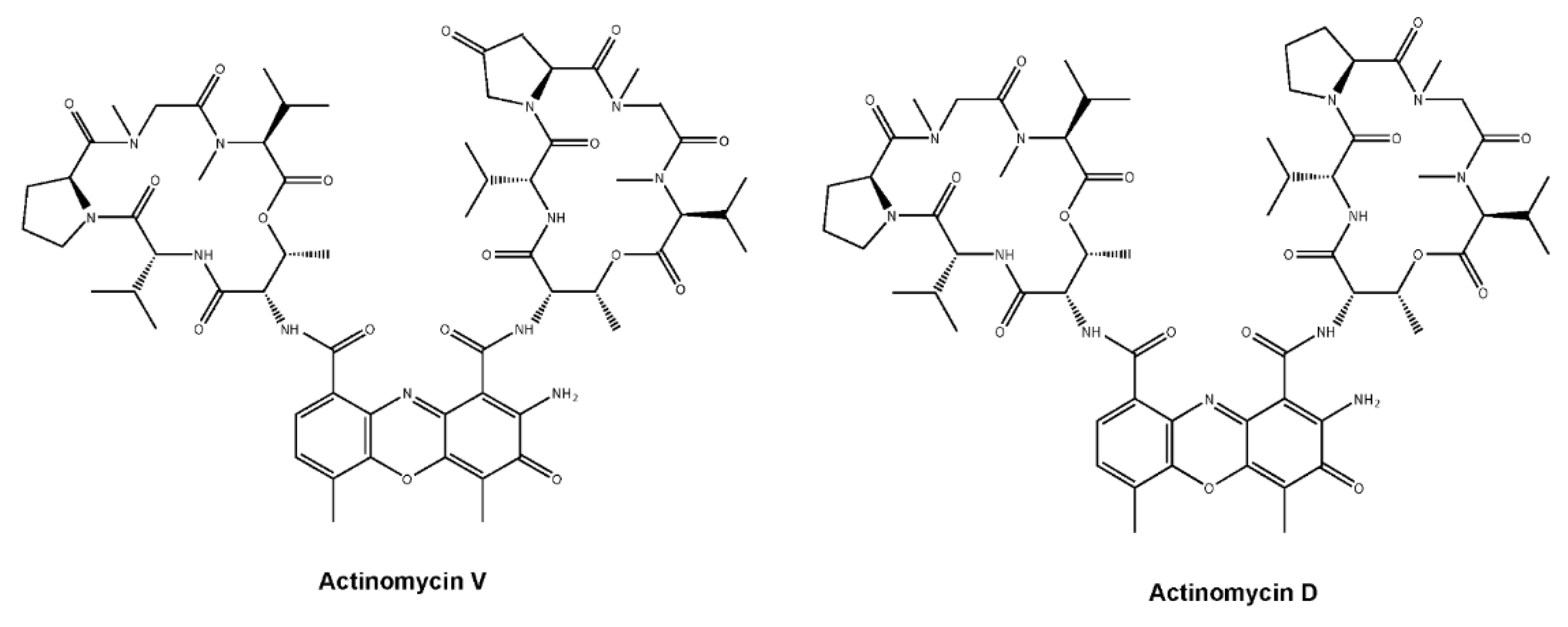


| Cell Lines | Act V | Act D |
|---|---|---|
| IC50 (nmol/L) | ||
| HCT-116 | 2.85 ± 0.10 | 10.24 ± 0.29 |
| HT-29 | 6.38 ± 0.46 | 15.27 ± 0.42 |
| SW620 | 6.43 ± 0.16 | 13.41 ± 0.23 |
| SW480 | 8.65 ± 0.31 | 11.78 ± 0.20 |
| QSG-7701 | 68.3 ± 1.2 | 66.5 ± 1.1 |
| HEK-293T | 82.6 ± 0.9 | 64.2 ± 1.6 |
| Compounds | Act V | LY294002 |
|---|---|---|
| IC50 (nmol/L) | 13.50 ± 1.05 | 390.97 ± 14.50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Zhang, E.; Ruan, H.; Ma, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, X.; Han, N.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Actinomycin V Induces Apoptosis Associated with Mitochondrial and PI3K/AKT Pathways in Human CRC Cells. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110599
Jiang S, Zhang E, Ruan H, Ma J, Zhao X, Zhu Y, Xie X, Han N, Li J, Zhang H, et al. Actinomycin V Induces Apoptosis Associated with Mitochondrial and PI3K/AKT Pathways in Human CRC Cells. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(11):599. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110599
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shiqing, E Zhang, Hang Ruan, Jiahui Ma, Xingming Zhao, Yaoyao Zhu, Xiaoyu Xie, Ningning Han, Jianjiang Li, Hao Zhang, and et al. 2021. "Actinomycin V Induces Apoptosis Associated with Mitochondrial and PI3K/AKT Pathways in Human CRC Cells" Marine Drugs 19, no. 11: 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110599
APA StyleJiang, S., Zhang, E., Ruan, H., Ma, J., Zhao, X., Zhu, Y., Xie, X., Han, N., Li, J., Zhang, H., Xie, W., & Li, X. (2021). Actinomycin V Induces Apoptosis Associated with Mitochondrial and PI3K/AKT Pathways in Human CRC Cells. Marine Drugs, 19(11), 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110599