Diversity of Conopeptides and Conoenzymes from the Venom Duct of the Marine Cone Snail Conus bayani as Determined from Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analyses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Transcriptome Sequences
2.2. Validation by Mass Spectrometry
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
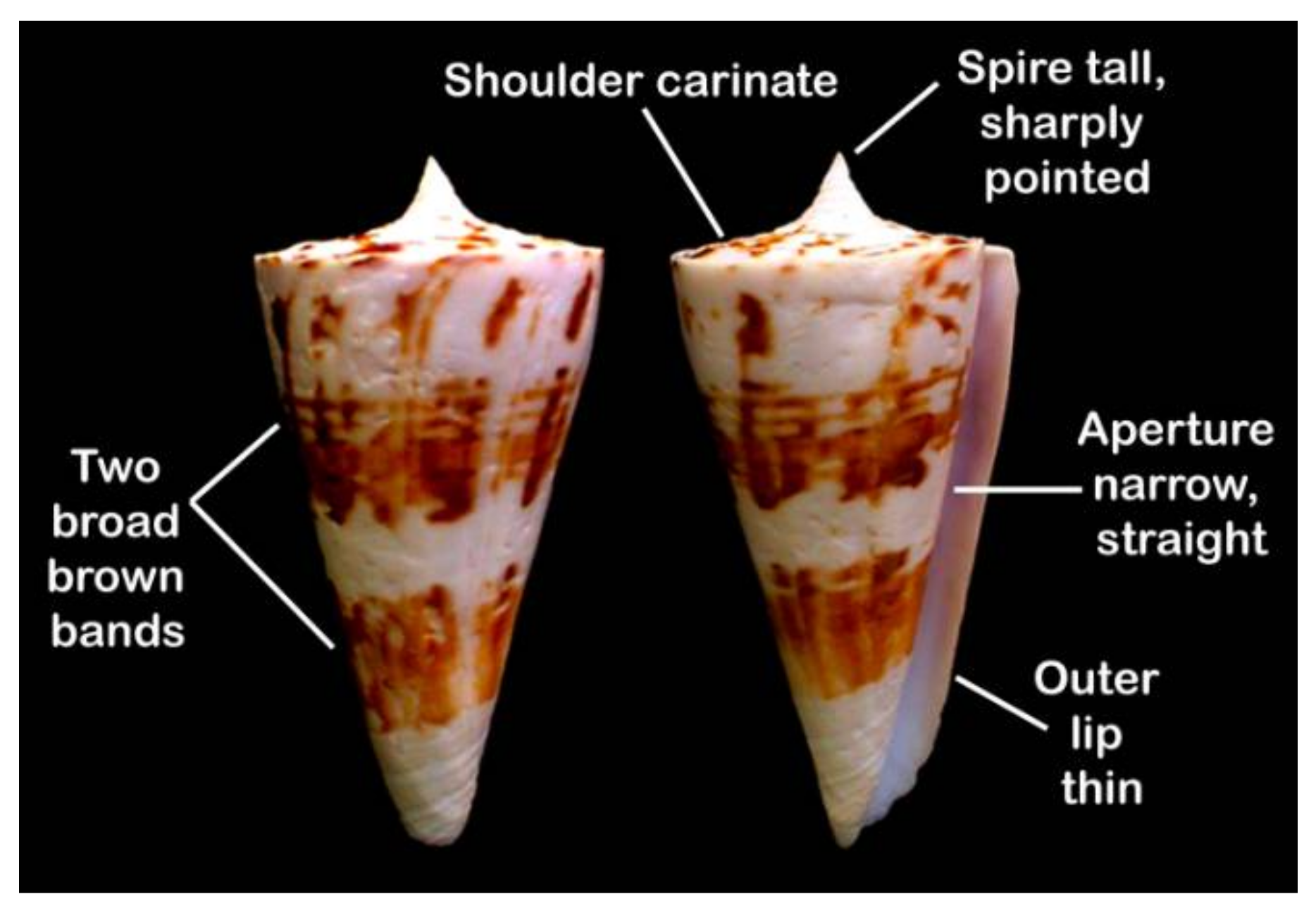
4.1. Materials
4.2. mRNA Extraction
4.3. RNA Quality Control
4.4. Transcriptome Library Preparation and Sequencing
4.5. NGS Data Analysis
4.6. Crude Venom Extraction
4.7. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
4.8. Mass Spectrometry Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arumugam, M.; Balasubramanian, T.; Kim, S.K. Marine Biomaterials. Kim, S.-K., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; ISBN 9780429086731. [Google Scholar]
- Molinski, T.F.; Dalisay, D.S.; Lievens, S.L.; Saludes, J.P. Drug development from marine natural products. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Dutertre, S.; Vetter, I.; Christie, M.J. Conus venom peptide pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 259–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himaya, S.W.A.; Lewis, R.J. Venomics-accelerated cone snail venom peptide discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Norton, R.S.; Olivera, B.M. Conotoxins down under. Toxicon 2006, 48, 780–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, A.H.; Muttenthaler, M.; Dutertre, S.; Himaya, S.W.A.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Conotoxins: Chemistry and biology. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 11510–11549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livett, B.G.; Gayler, K.R.; Khalil, Z. Drugs from the sea: Conopeptides as potential therapeutics. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akondi, K.B.; Muttenthaler, M.; Dutertre, S.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Discovery, synthesis, and structure–activity relationships of conotoxins. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5815–5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Zhangsun, D.; Luo, S. Diversity of conopeptides and their precursor genes of Conus litteratus. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, Q.; Yu, R.; Jin, A.-H.; Dutertre, S.; Craik, D.J. ConoServer: Updated content, knowledge, and discovery tools in the conopeptide database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D325–D330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, Q.; Westermann, J.-C.; Craik, D.J. Conopeptide characterization and classifications: An analysis using ConoServer. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1491–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, Q.; Westermann, J.-C.; Halai, R.; Wang, C.K.L.; Craik, D.J. ConoServer, a database for conopeptide sequences and structures. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 445–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, S.D.; Norton, R.S. Conotoxin gene superfamilies. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 6058–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giribaldi, J.; Ragnarsson, L.; Pujante, T.; Enjalbal, C.; Wilson, D.; Daly, N.L.; Lewis, R.J.; Dutertre, S. Synthesis, pharmacological and structural characterization of novel conopressins from Conus miliaris. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, C.; Huang, Y.; Bian, C.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, K.; You, X.; Lin, Z.; He, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. The first Conus genome assembly reveals a primary genetic central dogma of conopeptides in C. betulinus. Cell Discov. 2021, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grey Craig, A.; Fischer, W.H.; Rivier, J.E.; Michael McIntosh, J.; Gray, W.R. MS based scanning methodologies applied to Conus venom. In Techniques in Protein Chemistry; 1995; pp. 31–38. Tech. Protein Chem. 1995, 6, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Pardos-Blas, J.R.; Irisarri, I.; Abalde, S.; Tenorio, M.J.; Zardoya, R. Conotoxin diversity in the venom gland transcriptome of the magician’s cone, Pionoconus magus. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Fu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liang, A.; Chen, S.; Xu, A. Identifying novel conopepetides from the venom ducts of Conus litteratus through integrating transcriptomics and proteomics. J. Proteom. 2019, 192, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violette, A.; Biass, D.; Dutertre, S.; Koua, D.; Piquemal, D.; Pierrat, F.; Stöcklin, R.; Favreau, P. Large-scale discovery of conopeptides and conoproteins in the injectable venom of a fish-hunting cone snail using a combined proteomic and transcriptomic approach. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 5215–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Li, C.; Dong, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhangsun, D.; Luo, S. Discovery methodology of novel conotoxins from conus species. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutt, M.; Dutertre, S.; Jin, A.H.; Lavergne, V.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. Venomics Reveals Venom Complexity of the Piscivorous Cone Snail, Conus tulipa. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, A.; Dutertre, S.; Kaas, Q.; Lavergne, V.; Kubala, P.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Transcriptomic Messiness in the Venom Duct of Conus miles Contributes to Conotoxin Diversity. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 3824–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, C.; Gao, B.; Shi, Q. High throughput identification and validation of novel conotoxins from the chinese tubular cone snail (Conus betulinus). Toxicon 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalde, S.; Tenorio, M.J.; Afonso, C.M.L.; Zardoya, R. Comparative transcriptomics of the venoms of continental and insular radiations of West African cones. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20200794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.-H.; Dutertre, S.; Dutt, M.; Lavergne, V.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.; Alewood, P. Transcriptomic-proteomic correlation in the predation-evoked venom of the cone snail, Conus imperialis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, S.D.; Li, Q.; Lu, A.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Yandell, M.; Olivera, B.M.; Safavi-Hemami, H. The venom repertoire of Conus gloriamaris (Chemnitz, 1777), the glory of the sea. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J.B.; Subramanian, K.; Fernando, S.A.; Krishnan, K. Diversity and distribution of conidae from the TamilNadu coast of India (Mollusca: Caenogastropoda: Conidae). Zootaxa 2009, 2250, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudewi, A.A.R.; Susilawathi, N.M.; Mahardika, B.K.; Mahendra, A.N.; Pharmawati, M.; Phuong, M.A.; Mahardika, G.N. Selecting potential neuronal drug leads from conotoxins of various venomous marine cone snails in bali, Indonesia. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 19483–19490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajesh, R.P.; Franklin, J.B. Identification of conotoxins with novel odd number of cysteine residues from the venom of a marine predatory gastropod Conus leopardus found in andaman sea. Protein Pept. Lett. 2018, 25, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barghi, N.; Concepcion, G.P.; Olivera, B.M.; Lluisma, A.O. High conopeptide diversity in Conus tribblei revealed through analysis of venom duct transcriptome using two high-throughput sequencing platforms. Mar. Biotechnol. 2015, 17, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutertre, S.; Jin, A.H.; Vetter, I.; Hamilton, B.; Sunagar, K.; Lavergne, V.; Dutertre, V.; Fry, B.G.; Antunes, A.; Venter, D.J.; et al. Evolution of separate predation- and defence-evoked venoms in carnivorous cone snails. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barghi, N.; Concepcion, G.P.; Olivera, B.M.; Lluisma, A.O. Structural features of conopeptide genes inferred from partial sequences of the Conus tribblei genome. Mol. Genet. Genomics 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buczek, O.; Bulaj, G.; Olivera, B.M. Conotoxins and the posttranslational modification of secreted gene products. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 3067–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, R.B.; McDougal, O.M. The M-superfamily of conotoxins: A review. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wen, L.; Yang, S.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, P. New conotoxin SO-3 targeting N-type voltage-sensitive calcium channels. Mar. Drugs 2006, 4, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Tae, H.-S.; Xu, S.; Shao, X.; Adams, D.J.; Wang, C. Identification of a novel O-conotoxin reveals an unusual and potent inhibitor of the human α9α10 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavergne, V.; Harliwong, I.; Jones, A.; Miller, D.; Taft, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Optimized deep-targeted proteotranscriptomic profiling reveals unexplored Conus toxin diversity and novel cysteine frameworks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, R.P.; Jayaseelan, B.F.; Wilson Alphonse, C.R.; Mahmoud, A.H.; Mohammed, O.B.; Ahmed Almunqedhi, B.M.; Rajaian Pushpabai, R. Mass spectrometric identification and denovo sequencing of novel conotoxins from vermivorous cone snail (Conus inscriptus), and preliminary screening of its venom for biological activities in vitro and in vivo. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1582–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.N.; Piro, R.M.; Jäger, M. Computational Exome and Genome Analysis; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781315154770. [Google Scholar]
- Henschel, R.; Nista, P.M.; Lieber, M.; Haas, B.J.; Wu, L.-S.; LeDuc, R.D. Trinity RNA-Seq assembler performance optimization. In Proceedings of the 1st Conference of the Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment on Bridging from the Extreme to the Campus and Beyond-XSEDE ’12, Chicago, IL, USA, 16–20 July 2012; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman, A.; Martin, M.J.; O’Donovan, C.; Magrane, M.; Apweiler, R.; Alpi, E.; Antunes, R.; Arganiska, J.; Bely, B.; Bingley, M.; et al. UniProt: A hub for protein information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D204–D212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundir, S.; Martin, M.J.; O’Donovan, C. UniProt Tools. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moriya, Y.; Itoh, M.; Okuda, S.; Yoshizawa, A.C.; Kanehisa, M. KAAS: An automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W182–W185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajesh, R.P. Novel M-Superfamily and T-Superfamily conotoxins and contryphans from the vermivorous snail Conus figulinus. J. Pept. Sci. 2015, 21, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, R.P.; Franklin, J.B.; Badsha, I.; Arjun, P.; Jain, R.P.; Vignesh, M.S.; Kannan, R.R. proteome based de novo sequencing of novel conotoxins from marine molluscivorous cone snail Conus amadis and neurological activities of its natural venom in zebrafish model. Protein Pept. Lett. 2019, 26, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sl. No | Name | Contig No. | Mass (M + H) | Tentative Sequence | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Conopressin ba 1a | ba_contig_53 | 1023.5 | CYITNCPRG-NH2 | Conopressin |
| 2. | Conopressin ba 1b | ba_contig_53 | 1081.3 | CYITNCPRGG | |
| 3. | Conopressin ba 1c | ba_contig_53 | 1039.5 | CYITNCORG-NH2 | |
| 4. | Conopressin ba 1d | ba_contig_54 | 881.2 | CFLGNCLN | |
| 5. | ba5a | ba_contig_44 | 1016.6 | CCGSSNTGSCC-NH2 | T-Superfamily |
| 6. | ba5b | ba_contig_44 | 1103.3 | SCCGSSNTGSCC-NH2 | |
| 7. | ba14a | ba_contig_42 | 1981.6 | TLCPEHCTNGCNMDMTCI | L Superfamily |
| 8. | ba9a | ba_contig_29 | 3006.1 | VSCGgYCGDYGDCOSSCOTCTSNLLKCM | P-Superfamily |
| 9. | ba3a | ba_contig_19 | 1524.3 | TCCTACNIPPCKCCA | M-Superfamily |
| 10. | ba-2281 | ba_contig_45 | 2881.2 | SSQSTCOYCQISCCOOAYCQOSGCRGP | U superfamily |
| 11. | ba1560.9 | ba_contig_23 | 1560.9 | QNDHDVDESGHDIP | H-Superfamily LINEAR |
| 12. | ba1890.8 | ba_contig_23 | 1890.8 | QNDHDVDESGHDIPFPS | |
| 13. | ba 606.2 | ba_contig_83 | 606.2 | NSIWS | LINEAR |
| 14. | ba 818.3 | ba_contig_83 | 818.3 | DPNSIWS | LINEAR |
| 15. | ba 834.3 | ba_contig_83 | 834.3 | DONSIWS | LINEAR |
| 16. | ba 731.3 | ba_contig_83 | 731.3 | DPNSIW | LINEAR |
| 17. | ba 648.2 | ba_contig_84 | 648.2 | RSLWS | LINEAR |
| 18. | ba 745.7 | ba_contig_84 | 745.7 | PRSLWS | LINEAR |
| 19. | ba 561.1 | ba_contig_84 | 561.1 | RSLW | LINEAR |
| 20. | ba 416.9 | Not found | 416.9 | DEGP | LINEAR |
| 21. | ba 534.2 | Not found | 534.2 | FSGHS | LINEAR |
| 22. | ba 774.7 | Not found | 774.7 | KVL/IKATD | LINEAR |
| 23. | ba 558.3 | Not found | 558.3 | KVL/IKA | LINEAR |
| 24. | ba 998.2 | Not found | 998.2 | EGHDLPFPS | LINEAR |
| Sl. No | Contig No | List of Enzymes and Other Proteins |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ba_contig_85 | 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein |
| 2. | ba_contig_86 | Arginine kinase |
| 3. | ba_contig_87 | Conotoxin-specific protein disulfideisomerase (Cspdi) |
| 4. | ba_contig_88 | Cysteine-rich protein 1 |
| 5. | ba_contig_89 | Cysteine-rich venom protein (CRVP) (Substrate-specific endoprotease Tex31) |
| 6. | ba_contig_90 | Cysteine-rich venom protein Mr30 (CRVP) (Cysteine-rich secretory protein Mr30) (GlaCrisp isoform 1/2/3) (Mr30-1/2) |
| 7. | ba_contig_91 | Cytochrome b |
| 8. | ba_contig_92 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 |
| 9. | ba_contig_93 | Ferritin (EC 1.16.3.1) (Fragment) |
| 10. | ba_contig_94 | Glycoprotein hormone alpha-2 prepropeptide |
| 11. | ba_contig_95 | NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 5 (EC 1.6.5.3) |
| 12. | ba_contig_96 | Peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase (EC 1.14.17.3) |
| 13. | ba_contig_97 | Peptidyl-prolylcis-trans isomerase (PPIase) (EC 5.2.1.8) |
| 14. | ba_contig_98 | Prohormone-4 prepropeptide |
| 15. | ba_contig_99 | Protein disulfide isomerase |
| 16. | ba_contig_100 | Vitamin K-dependent gamma-glutamyl carboxylase |
| Enzymes | Functions | Possible Modified Conotoxins |
|---|---|---|
| Conotoxin-specific protein disulfide isomerase (Cspdi) | Disulfide formation | CCGSSNTGSCC-NH2 |
| Peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase (EC 1.14.17.3) | Amidation | SCCGSSNTGSCC-NH2 |
| Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase) (EC 5.2.1.8) | Cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides | SSQSTCOYCQISCCOOAYCQOSGCRGP |
| Vitamin K-dependent gamma-glutamyl carboxylase | Gamma-carboxylation of Glutamic acid | VSCGgYCGDYGDCOSSCOTCTSNLLKCM |
| Prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit alpha-2 | Hydroxylation of Proline | SSQSTCOYCQISCCOOAYCQOSGCRGP |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajaian Pushpabai, R.; Wilson Alphonse, C.R.; Mani, R.; Arun Apte, D.; Franklin, J.B. Diversity of Conopeptides and Conoenzymes from the Venom Duct of the Marine Cone Snail Conus bayani as Determined from Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analyses. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040202
Rajaian Pushpabai R, Wilson Alphonse CR, Mani R, Arun Apte D, Franklin JB. Diversity of Conopeptides and Conoenzymes from the Venom Duct of the Marine Cone Snail Conus bayani as Determined from Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analyses. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(4):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040202
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajaian Pushpabai, Rajesh, Carlton Ranjith Wilson Alphonse, Rajasekar Mani, Deepak Arun Apte, and Jayaseelan Benjamin Franklin. 2021. "Diversity of Conopeptides and Conoenzymes from the Venom Duct of the Marine Cone Snail Conus bayani as Determined from Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analyses" Marine Drugs 19, no. 4: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040202
APA StyleRajaian Pushpabai, R., Wilson Alphonse, C. R., Mani, R., Arun Apte, D., & Franklin, J. B. (2021). Diversity of Conopeptides and Conoenzymes from the Venom Duct of the Marine Cone Snail Conus bayani as Determined from Transcriptomic and Proteomic Analyses. Marine Drugs, 19(4), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040202






