Chemical and Antioxidant Characteristics of Skin-Derived Collagen Obtained by Acid-Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Bigeye Tuna (Thunnus obesus)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Quality of Fish Skin as a Source of Collagen
2.2. Extraction and Yield of Collagen
2.3. Chemical Properties of Collagen
2.3.1. Heavy Metal Content
2.3.2. Solubility
2.3.3. pH
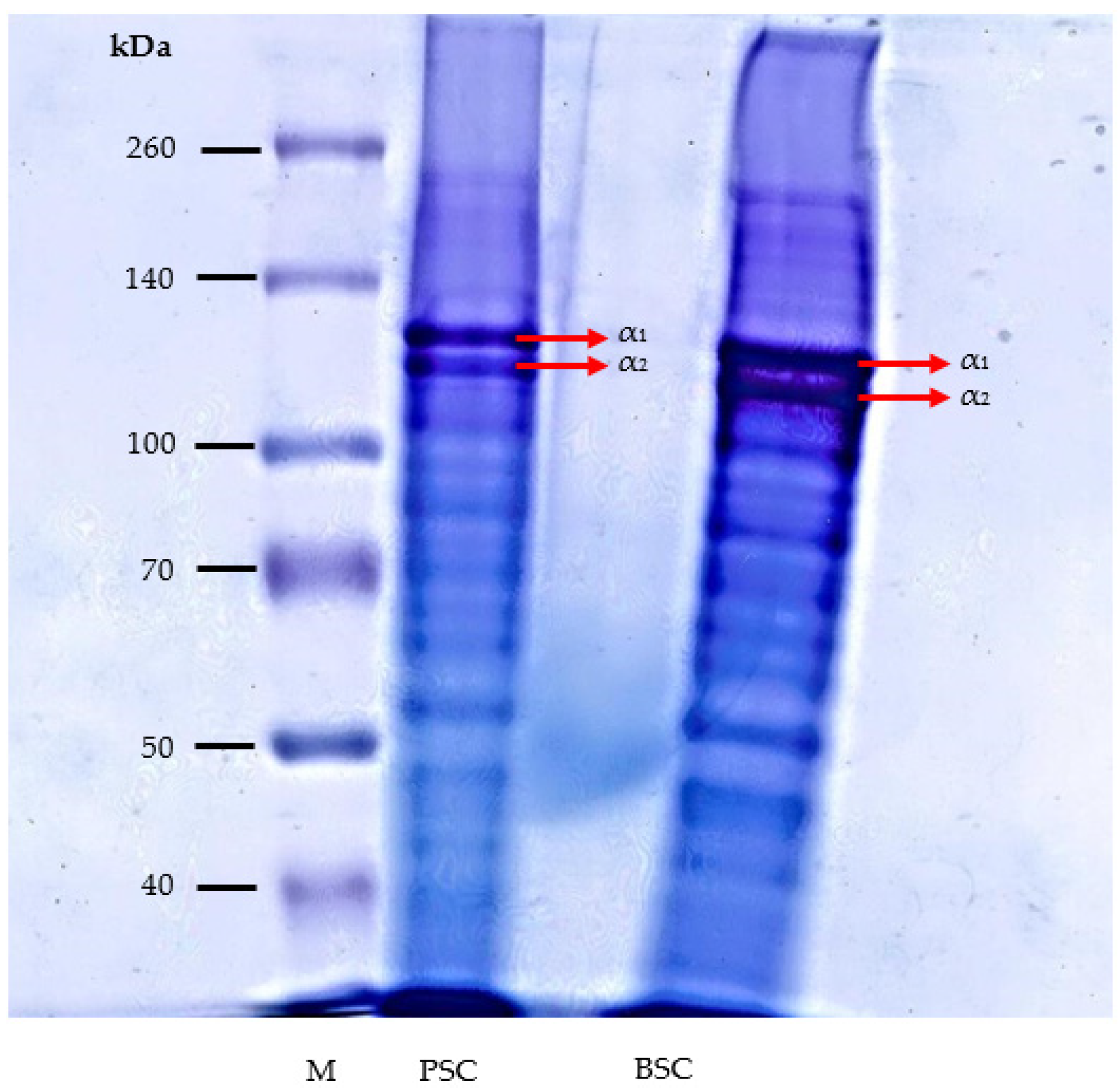
2.3.4. Protein Profile Determined by SDS-PAGE
2.3.5. Functional Group Analysis Using FTIR
2.3.6. Protein Content of Collagen
2.4. Antioxidant Activity of Collagen
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Fish Skin
3.3. Quality Determination of Fish Skin as a Source of Collagen
3.4. Extraction and Yield of Collagen
3.5. Analysis of Collagen Chemical Properties
3.5.1. Heavy Metal Content Measurement
3.5.2. Solubility Measurement
3.5.3. pH
3.5.4. Protein Pattern Analysis by SDS-PAGE
3.5.5. Functional Group Analysis Using FTIR Spectrophotometry
3.5.6. Protein Content Determination of Collagen Samples
3.6. Antioxidant Activity Tests of Collagen Samples
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krishnamoorthi, J.; Ramasamy, P.; Shanmugam, V.; Shanmugam, A. Isolation and partial characterization of collagen from outer skin of Sepia pharaonis (Ehrenberg, 1831) from Puducherry coast. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 10, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinthusamran, S.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H. Comparative study on molecular characteristics of acid soluble collagens from skin and swim bladder of seabass (Lates calcarifer). Food Chem. 2013, 138, 2435–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.M.; Dornelles, R.C.P.; Mello, R.O.; Kubota, E.H.; Mazutti, M.A.; Kempka, A.P.; Demiate, I.M. Collagen extraction process. Int. Food Res. J. 2016, 23, 913–922. [Google Scholar]
- Aberoumand, A. Comparative study between different methods of collagen extraction from fish and its properties. World Appl. Sci. J. 2012, 16, 316–319. [Google Scholar]
- Schrieber, R.; Gareis, H. Gelatine Handbook: Theory and Industrial Practice; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; ISBN 9783527315482. [Google Scholar]
- Whitford, D. Proteins: Structure and Function; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2005; ISBN 0471498939. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.K.; Mendis, E. Bioactive compounds from marine processing byproducts—A review. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewdang, O.; Benjakul, S.; Kaewmanee, T.; Kishimura, H. Characteristics of collagens from the swim bladders of yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares). Food Chem. 2014, 155, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liang, Q.; Chen, T.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Ma, H. Characterization of collagen from the skin of Amur sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii). Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 38, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Kiyose, C.; Higuchi, T.; Uchida, N.; Suzuki, H. Effect of collagen hydrolysates from salmon and trout skins on the lipid profile in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10477–10482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.R.; Shiau, C.Y.; Chen, H.H.; Huang, B.C. Isolation and characterization of acid and pepsin-solubilized collagens from the skin of balloon fish (Diodon holocanthus). Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, C.; Hong, P.; Deng, C. Characterization and comparison of collagen extracted from the skin of the Nile tilapia by fermentation and chemical pretreatment. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 128139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atef, M.; Ojagh, S.M.; Latifi, A.M.; Esmaeili, M.; Udenigwe, C.C. Biochemical and structural characterization of sturgeon fish skin collagen (Huso huso). J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, B.; Song, W.; Zhang, K.; Fan, Y.; Hou, H. Comprehensive assessment of Nile tilapia skin collagen sponges as hemostatic dressings. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, B.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, N.; Qin, S. Comprehensive Assessment of Nile Tilapia Skin (Oreochromis niloticus) Collagen Hydrogels for Wound Dressings. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Shibata, M.; Ma, Q.; Liu, F.; Lu, Q.; Shan, Q.; Hagiwara, T.; Bao, J. Characterization of fish collagen from blue shark skin and its application for chitosan- collagen composite coating to preserve red porgy (Pagrus major) meat. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, X.K.; Phan, B.V.; Dao, V.H.; Le Ho, K.H.; Nguyen, T.H.; Doan, T.T.; Nguyen, P.A. Investigation of protein patterns and antioxidant activity of collagen hydrolysates from skin of fan-bellied leatherjacket Monacanthus chinensis by various enzymes. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2019, 18, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Mahboob, S. Isolation and characterization of collagen from fish waste material—Skin, scales and fins of Catla catla and Cirrhinus mrigala. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 52, 4296–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jongjareonrak, A.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Nagai, T.; Tanaka, M. Isolation and characterisation of acid and pepsin-solubilised collagens from the skin of Brownstripe red snapper (Lutjanus vitta). Food Chem. 2005, 93, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongjareonrak, A.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Tanaka, M. Isolation and characterization of collagen from bigeye snapper (Priacanthus macracanthus) skin. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, G.K.S.; Sharma, D.; Balakrishnan, R.M.; Ettiyappan, J.B.P. Extraction, optimization and characterization of collagen from sole fish skin. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2018, 9, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardhani, F.A.K.; Safithri, M.; Tarman, K.; Husnawati, H.; Setyaningsih, I.; Meydia, M. Antioxidant activity of collagen from skin of parang-parang fish (Chirocentrus dorab) using DPPH and CUPRAC methods. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 241, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.L.; Marques, A.L.P.; Martins, E.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Cosmetic potential of Marine fish skin collagen. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, M.; Benjakul, S.; Nalinanon, S. Compositional and physicochemical characteristics of acid solubilized collagen extracted from the skin of unicorn leatherjacket (Aluterus monoceros). Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyonga, J.H.; Cole, C.G.B.; Duodu, K.G. Characterisation of acid soluble collagen from skins of young and adult Nile perch (Lates niloticus). Food Chem. 2004, 85, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Li, X.; Xin, Q.; Han, W.; Shi, C.; Guo, R.; Shi, W.; Qiao, R.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Effect of extraction methods on the preparation of electrospun/electrosprayed microstructures of tilapia skin collagen. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 128, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Preparation and Characterization of Collagens from the Skin of Northern Snakehead (Channa argus). J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iswariya, S.; Velswamy, P.; Uma, T.S. Isolation and Characterization of Biocompatible Collagen from the Skin of Puffer Fish (Lagocephalus inermis). J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 2086–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senaratne, L.S.; Park, P.J.; Kim, S.K. Isolation and characterization of collagen from brown backed toadfish (Lagocephalus gloveri) skin. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Adachi, S.; Ura, K.; Takagi, Y. Properties of collagen extracted from Amur sturgeon Acipenser schrenckii and assessment of collagen fibrils in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Tanaka, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Hatayama, H.; Zhang, X.; Ura, K.; Yunoki, S.; Takagi, Y. The effect of alkaline pretreatment on the biochemical characteristics and fibril-forming abilities of types I and II collagen extracted from bester sturgeon by-products. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Araki, Y.; Suzuki, N. Collagen of the skin of ocellate puffer fish (Takifugu rubripes). Food Chem. 2002, 78, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Li, D.; Guo, S.D. Studies on collagen from the skin of channel catfish (Ictalurus punctaus). Food Chem. 2007, 101, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Benjakul, S.; Maqsood, S.; Kishimura, H. Isolation and characterisation of collagen extracted from the skin of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus). Food Chem. 2011, 124, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalinanon, S.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Kishimura, H. Use of pepsin for collagen extraction from the skin of bigeye snapper (Priacanthus tayenus). Food Chem. 2007, 104, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.; Haq, M.; Chun, B.S. Characterization of marine derived collagen extracted from the by-products of bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Chen, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.; Li, R.; Yu, F.; Chen, Y.; Huang, F.; Yang, Z.; et al. Collagen extracted from bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus) skin by isoelectric precipitation: Physicochemical properties, proliferation, and migration activities. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Jin, H.; Yang, F.; Jin, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, S.; Yan, Z.; Cai, X.; et al. Physicochemical, antioxidant properties of giant croaker (Nibea japonica) swim bladders collagen and wound healing evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.S.; Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.K. Isolation and characterization of collagen from marine fish (Thunnus obesus). Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2013, 18, 1185–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Yamashita, E.; Taniguchi, K.; Kanamori, N.; Suzuki, N. Isolation and characterisation of collagen from the outer skin waste material of cuttlefish (Sepia lycidas). Food Chem. 2001, 72, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Suzuki, N. Preparation and partial characterization of collagen from paper nautilus (Argonauta argo, Linnaeus) outer skin. Food Chem. 2002, 76, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Suzuki, N.; Nagashima, T. Collagen from common minke whale (Balaenoptera acutorostrata) unesu. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, V. Extraction, structural and physical characterization of type I collagen from the outer skin of Sepiella inermis (Orbigny, 1848). Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 14326–14337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, A.D. Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: New York NY, USA; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1871–1873. ISBN 9780123822192. [Google Scholar]
- Rowan, A.D.; Buttle, D.J.; Barrett, A.J. Ananain: A novel cysteine proteinase found in pineapple stem. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1988, 267, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purich, D.L.; Allison, R.D. The Enzyme Reference: A Comprehensive Guide to Enzyme Nomenclature, Reactions, and Methods; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; Elsevier Science: New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 0125680414. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Gonzalez, A.I.; Díaz-Sánchez, Á.G.; De La Rosa, L.A.; Vargas-Requena, C.L.; Bustos-Jaimes, I.; Alvarez-Parrilla, E. Polyphenolic compounds and digestive enzymes: In vitro non-covalent interactions. Molecules 2017, 2, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, D.D.; Du, B.; Zhang, C.; Zaman, F.; Huang, Y. Isolation and identification of an antioxidant collagen peptide from skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) bone. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 27032–27041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nurilmala, M.; Pertiwi, R.M.; Nurhayati, T.; Fauzi, S.; Batubara, I.; Ochiai, Y. Characterization of collagen and its hydrolysate from yellowfin tuna Thunnus albacares skin and their potencies as antioxidant and antiglycation agents. Fish. Sci. 2019, 85, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.C. Fundamentals of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA; LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; ISBN 9781420069303. [Google Scholar]
- Christy, A.A.; Ozaki, Y.; Gregoriou, V.G. Modern Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; ISBN 0444500448. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, S.S. Food Analysis, 4th ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 85–104. ISBN 978-1441914774. [Google Scholar]
- Movasaghi, Z.; Rehman, S.; Rehman, I.U. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy of biological tissues. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2008, 43, 134–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of Infrared Spectra, a Practical Approach. Encycl. Anal. Chem. 2006, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, B.L.; Gao, L.Z.; Chen, H.L. Studies on bullfrog skin collagen. Food Chem. 2004, 84, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Zhang, J.; Du, X.; Yao, X.; Konno, K. Properties of collagen from skin, scale and bone of carp (Cyprinus carpio). Food Chem. 2009, 112, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pati, F.; Adhikari, B.; Dhara, S. Isolation and characterization of fish scale collagen of higher thermal stability. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3737–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Li, G. Isolation and characterisation of collagens from the skin of largefin longbarbel catfish (Mystus macropterus). Food Chem. 2009, 115, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougatef, A.; Nedjar-Arroume, N.; Manni, L.; Ravallec, R.; Barkia, A.; Guillochon, D.; Nasri, M. Purification and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) by-products proteins. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, A.; Mavi, A.; Kara, A.A. Determination of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Rumex crispus L. extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4083–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Liang, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Zhou, P. Extraction and characterisation of pepsin-solubilised collagen from fins, scales, skins, bones and swim bladders of bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis). Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bueno-Solano, C.; López-Cervantes, J.; Sánchez-Machado, D.I.; Campas-Baypoli, O.N. HPLC determination of histamine, Tyramine and Amino acids in shrimp by-products. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012, 23, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakircioglu, D.; Kurtulus, Y.B.; Ucar, G. Determination of some traces metal levels in cheese samples packaged in plastic and tin containers by ICP-OES after dry, wet and microwave digestion. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shon, J.; Eun, J.B.; Eo, J.H.; Hwang, S.J. Effect of processing conditions on functional properties of collagen powder from skate (Raja kenojei) skins. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 3, Chapter 5. [Google Scholar]
- Lowry, O.H.; Randall, R.J. Protein Measurement byt the Folin Reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksman De Torres, N.; Salazar-Aranda, R.; Pérez-López, L.A.; López-Arroyo, J.; Alanís-Garza, B.A. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of plants from northeast of Mexico. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 2011, 536139. [Google Scholar]
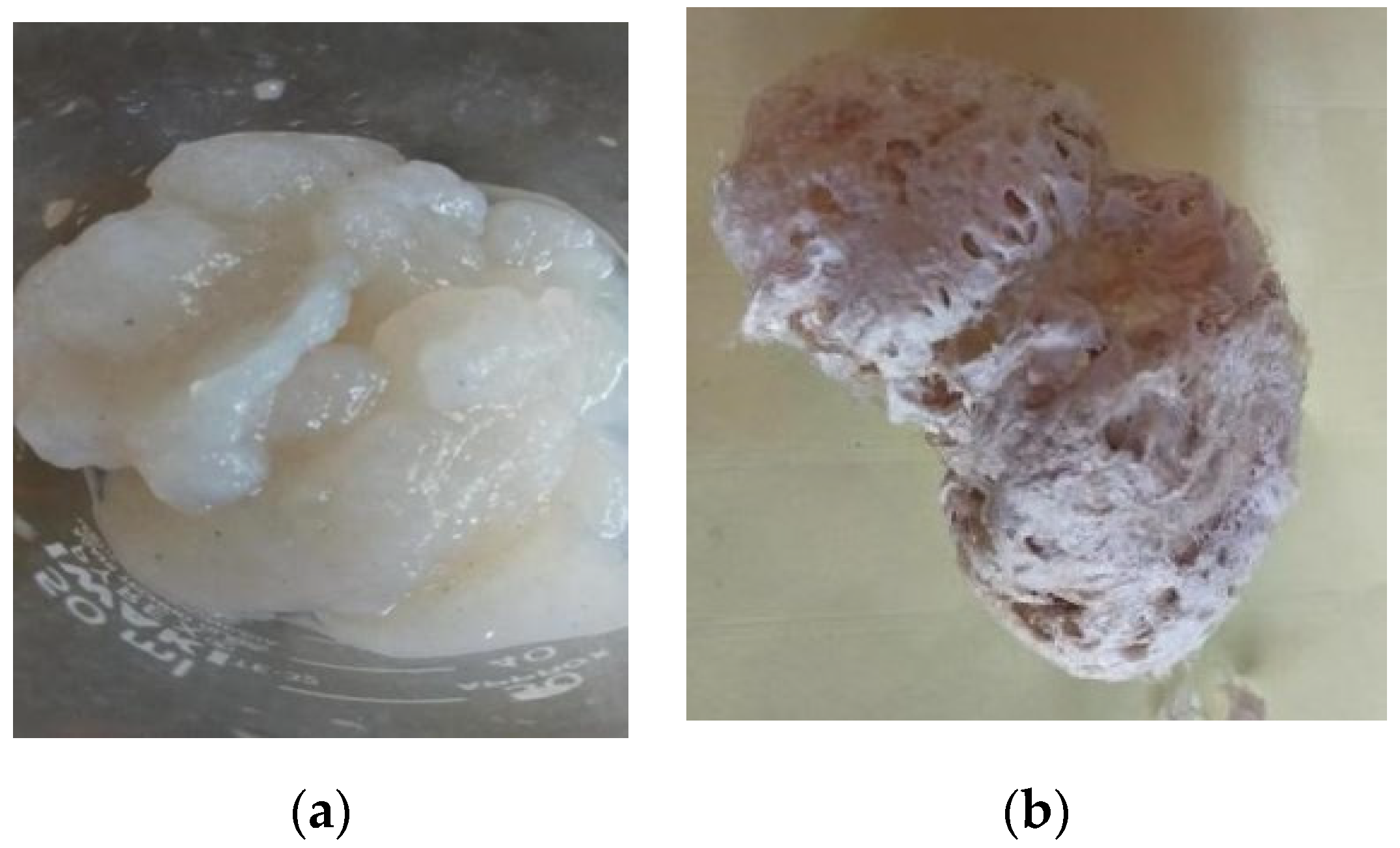

| Fish Skin (db) | Ash (%) | Carbohydrate (%) | Fat (%) | Protein (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lyophilized fish skin 1 (10 h) | 1.68 ± 0.37 | 3.35 ± 0.56 | 37.02 ± 0.61 | 57.96 ± 0.32 |
| Lyophilized fish skin 2 (14 h) | 1.95 ± 0.28 | 7.21 ± 0.37 | 25.42 ± 0.14 | 65.42 ± 0.06 |
| Parameter | Results (mg/kg) | Limit of Detection (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| As | not detected | 0.008 |
| Cd | not detected | 0.00011 |
| Co | not detected | 0.0008 |
| Cr | 0.43 ± 0.02 | - |
| Cu | 30.38 ± 0.34 | - |
| Pb | not detected | 0.009 |
| Histamine | not detected | 1.09 |
| Extracted Collagens | Yields (db) (%) |
|---|---|
| Acetate acid soluble collagen | 3.05 ± 0.82 a |
| Bromelain soluble collagen | 42.76 ± 4.72 c |
| Papain soluble collagen | 15.20 ± 6.27 b |
| Pepsin soluble collagen | 52.02 ± 0.59 c |
| Trypsin soluble collagen | 13.83 ± 1.95 b |
| Sample | Parameter | Results (mg/kg) | Limit of Detection (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bromelain-soluble collagen | Cr | Not detected | 0.04 |
| Cu | Not detected | 0.001 | |
| Pepsin-soluble collagen | Cr | Not detected | 0.04 |
| Cu | Not detected | 0.001 |
| Solvent | Solubility | |
|---|---|---|
| Bromelain-Soluble Collagen | Pepsin-Soluble Collagen | |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide | 73.48 ± 1.09 d | 76.30 ± 0.41 d |
| Distilled water | 64.30 ± 0.15 c | 63.24 ± 0.86 c |
| Ethanol | 48.56 ± 1.03 b | 48.42 ± 1.03 b |
| Methanol | 26.85 ± 0.98 a | 25.44 ± 2.44 a |
| Region | Abs. Area (cm−1) | Bigeye Tuna Skins | Others Study | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak Wave Number (cm−1) | Assign. | Peak Wave Number (cm−1) | Assign. | |||
| BSC | PSC | |||||
| Amide A | 3440–3400 [8,22] | 3272 | 3276 | The amide A band is associated with the frequency of stretching N–H. N–H stretching vibration frequency changed from a free N–H stretching vibration frequency (3440–3400 cm−1) to a lower frequency in our collagen samples (3272 and 3276 cm−1, for BSC and PSC, respectively), which indicated their involvement in the hydrogen bonding. [55,56] | 3296 (ASC), 3281 (HWM), and 3271 (SHM) [26] | NH stretch coupled with hydrogen bond |
| 3425.57 (PSC-IP) [37] | free N–H vibrations as an indication of hydrogen bonds | |||||
| 3425.58 (ASC) [22], 3440 (ASC Rohu) and 3440 (ASC Catla) [57] | NH stretching | |||||
| Amide B | 2940–2922 [22,24] | 2930 | 2930 | The amide B bands were shown at 2930 cm−1 for BSC and PSC, indicated CH2 asymmetrical stretching. | 2924.09(ASC) [22] | CH2 asymmetrical stretching |
| 2938 (ASC), 2939 (HWM), and 2936 (SHM) [26] | Asymmetrical stretch of CH2 and | |||||
| 2930.97 (PSC-IP) [37], 2923 (ASC Rohu) and 2925 (ASC Catla) [57] | CH2 asymmetrical stretch | |||||
| 2858 (ASC Rohu) and 2856 (ASC Catla) [57] | CH2 Asymmetrical stretching | |||||
| Amide I | 1690–1625 [22,56] | 1665 | 1660 | The amide I bands positions were 1665 and 1660 cm−1 (for BSC and PSC, respectively), fitting well the range of 1690–1625 cm−1 for general amide I bands position [55,56]. | 1647.21 (ASC) [22] | C=O stretching |
| 1631 (ASC), 1629 (HWM), and 1628 (SHM) [26] | C=O stretch/hydrogen bond coupled with | |||||
| 1646.26 (PSC-IP) [37] | C=O stretching vibration on the main polypeptide chain or the hydrogen bond coupled with | |||||
| 1653 (ASC Rohu) and 1643 (ASC Catla) [57] | C=O stretch/hydrogen bond coupled with | |||||
| Amide II | 1600–1550 [58] | 1545 | 1547 | The amide II bands were found at 1545 cm−1 and 1547 cm−1 (BSC and PSC, respectively). When compared to the normal absorption range of the amide II bands’ position (1600–1550 cm−1), these positions shifted to a lower frequency, indicating the presence of hydrogen bonds in the collagens [56]. | 1543.05 (ASC) [22] | NH bend CN stretch |
| 1544 (ASC), 1536 (HWM), and 1536 (SHM) [26], 1558, 1540 (ASC Rohu) and 1558, 1540 (ASC Catla) [57]. | NH bending coupled with CN stretching | |||||
| 1550.75 (PSC-IP) [37] | N–H bending vibration couples with C–N stretching vibration | |||||
| 1463 (ASC Rohu) and 1454 (ASC Catla) [57] | CH2 bend | |||||
| 1423, 1393 (ASC Rohu) and 1413, 1402 (ASC Catla) [57] | symmetrical stretching | |||||
| 1343 (ASC Rohu) and 1338 (ASC Catla) [57] | CH2 wagging | |||||
| Amide III | 1350–1220 [22] | 1385 | 1385 | The amide III bands were found at 1385 cm−1 for BSC and PSC. | 1246.02 (ASC)7 | NH bending |
| 1236 (ASC), 1236 (HWM), and 1241 (SHM) [26] | CH2 group wagging vibration in the glycine backbone proline side chains | |||||
| 1238.94 (PSC-IP) [37] | The helical arrangement in PSC-IP. | |||||
| 1240 (ASC Rohu) and 1240 (ASC Catla) [57] | NH bending coupled with CN stretching | |||||
| 1083 (ASC Rohu) and 1083 (ASC Catla) [57] | C–O stretching | |||||
| Antioxidant Activity | µmol AAE/g Protein | mg AAE/g Protein |
|---|---|---|
| Bromelain-soluble collagen | 1.03 ± 0.03 | 0.18 ± 0.00 |
| Pepsin-soluble collagen | 2.62 ± 0.03 | 0.46 ± 0.01 |
| Compounds | Absorbances (700 nm) |
|---|---|
| Bromelain-soluble collagen | 0.25 ± 0.00 |
| Pepsin-soluble collagen | 0.25 ± 0.01 |
| Parameter | |
|---|---|
| Power (kw) | 1 |
| Plasma Argon flow rate (L/min) | 15 |
| Auxiliary Argon flow rate (L/min) | 1.5 |
| Nebulizer Argon flow rate (L/min) | 0.90 |
| Pump rate (rpm) | 15 |
| Nebulizer type | Glass concentric |
| Nebulizer pressure (kPa) | 200 |
| Emission line of metals (nm): | |
| As | 188.980 |
| Cd | 214.439 |
| Co | 238.892 |
| Cr | 267.716 |
| Cu | 327.395 |
| Pb | 220.353 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Devita, L.; Nurilmala, M.; Lioe, H.N.; Suhartono, M.T. Chemical and Antioxidant Characteristics of Skin-Derived Collagen Obtained by Acid-Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Bigeye Tuna (Thunnus obesus). Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040222
Devita L, Nurilmala M, Lioe HN, Suhartono MT. Chemical and Antioxidant Characteristics of Skin-Derived Collagen Obtained by Acid-Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Bigeye Tuna (Thunnus obesus). Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(4):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040222
Chicago/Turabian StyleDevita, Liza, Mala Nurilmala, Hanifah Nuryani Lioe, and Maggy T. Suhartono. 2021. "Chemical and Antioxidant Characteristics of Skin-Derived Collagen Obtained by Acid-Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Bigeye Tuna (Thunnus obesus)" Marine Drugs 19, no. 4: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040222
APA StyleDevita, L., Nurilmala, M., Lioe, H. N., & Suhartono, M. T. (2021). Chemical and Antioxidant Characteristics of Skin-Derived Collagen Obtained by Acid-Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Bigeye Tuna (Thunnus obesus). Marine Drugs, 19(4), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040222





