Antibiofilm Activity of Phorbaketals from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp. against Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
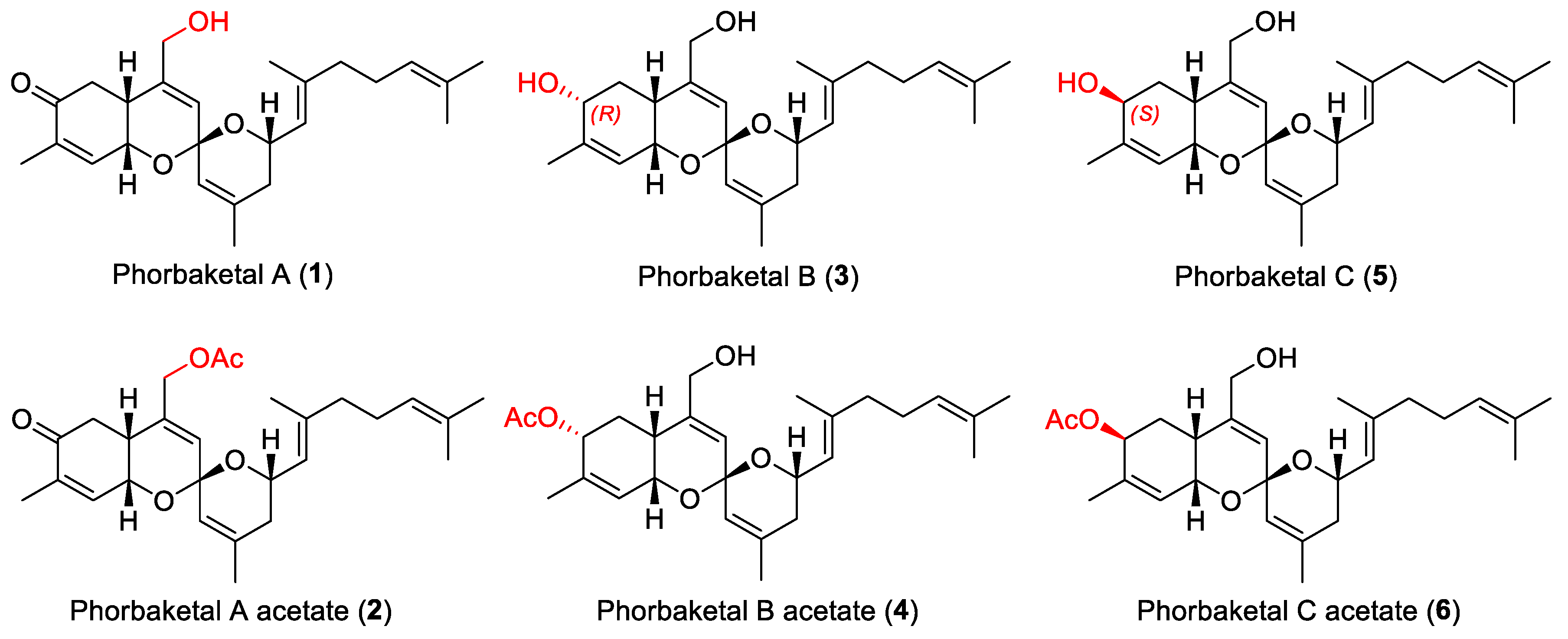
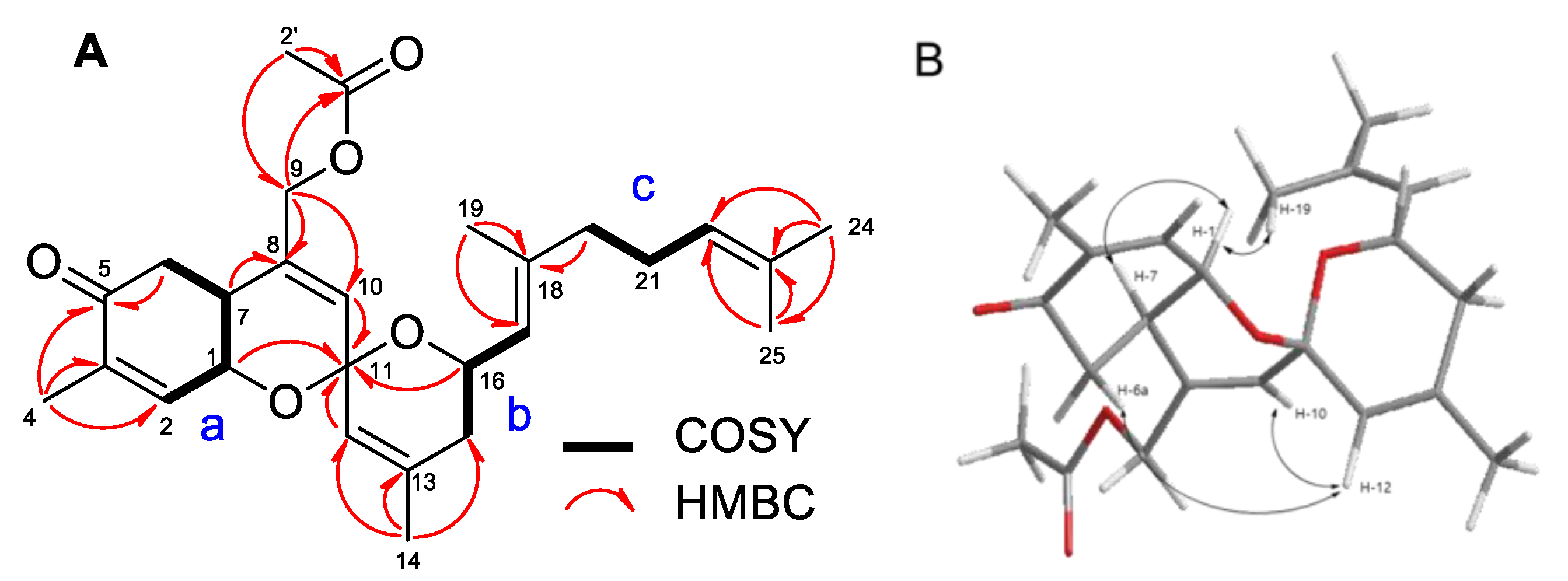
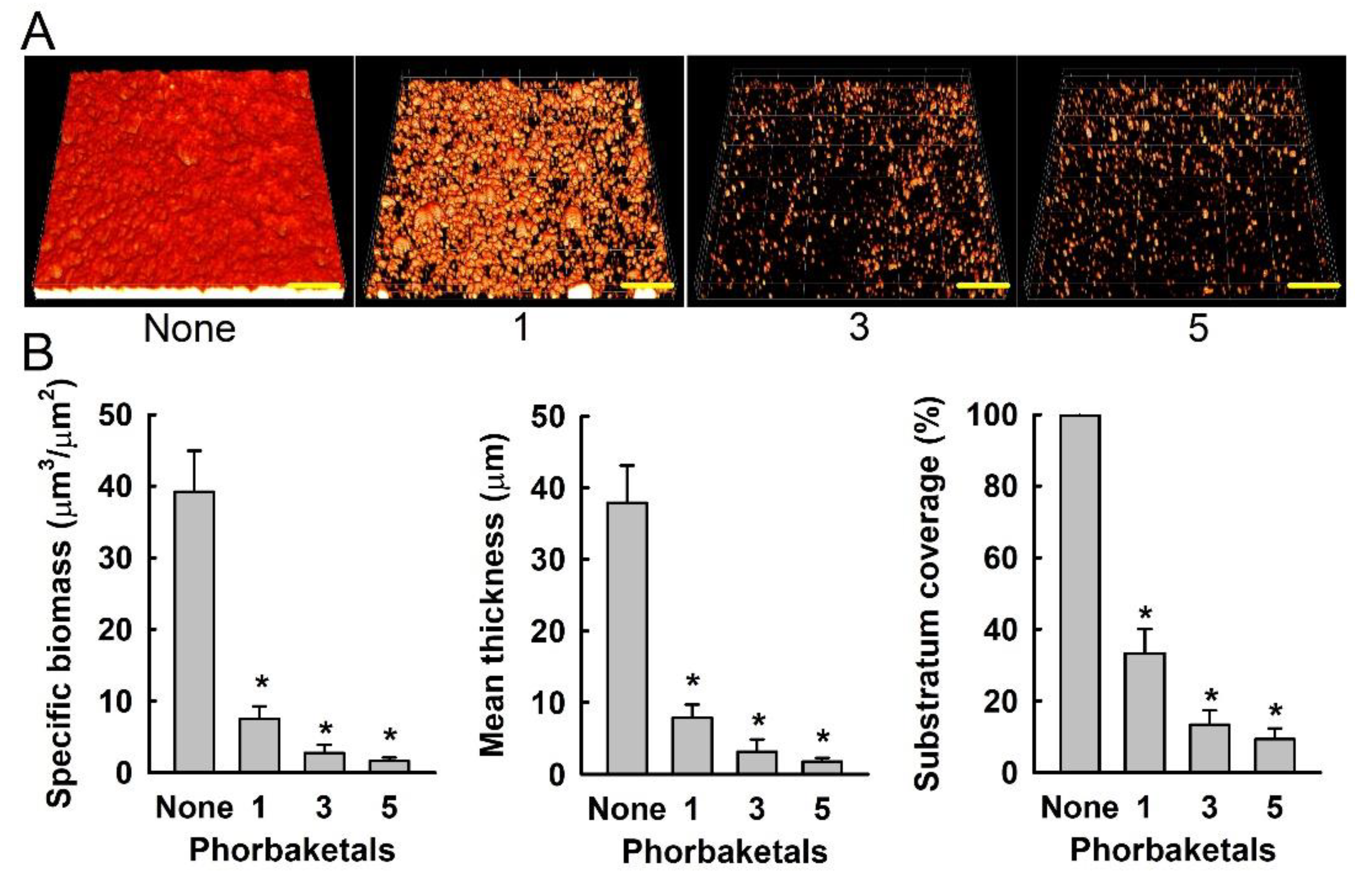
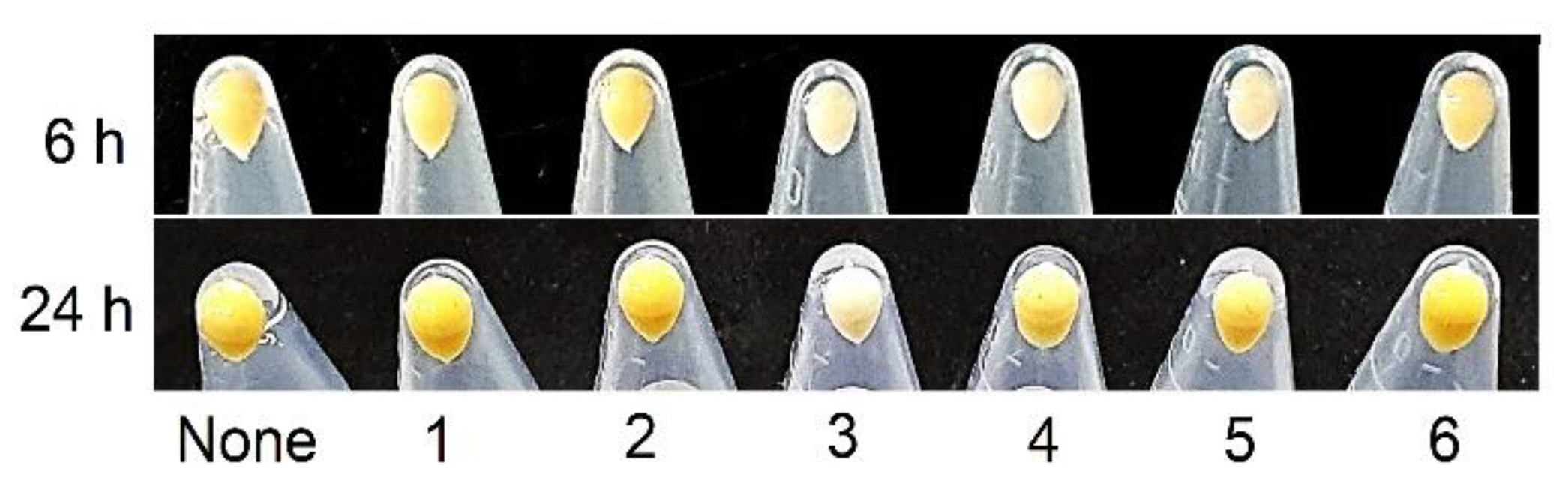
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Isolation of Phorbaketals from Phorbas sp.
3.3. Strains and Culture Conditions
3.4. Antibiofilm Assays
3.5. Confocal Laser Microscopy and COMSTAT Analysis
3.6. Staphyloxanthin Assay
3.7. Quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription (qRT-PCR) Analysis
3.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Potera, C. Forging a link between biofilms and disease. Science 1999, 283, 1837–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P.S.; Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial biofilms: A common cause of persistent infections. Science 1999, 284, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, L.R.; D’Argenio, D.A.; MacCoss, M.J.; Zhang, Z.; Jones, R.A.; Miller, S.I. Aminoglycoside antibiotics induce bacterial biofilm formation. Nature 2005, 436, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowy, F.D. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Essex, A.; Buchanan, J.T.; Datta, V.; Hoffman, H.M.; Bastian, J.F.; Fierer, J.; Nizet, V. Staphylococcus aureus golden pigment impairs neutrophil killing and promotes virulence through its antioxidant activity. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipkema, D.; Franssen, M.C.R.; Osinga, R.; Tramper, J.; Wijffels, R.H. Marine sponges as pharmacy. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 142–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschel, U.; Piel, J.; Degnan, S.M.; Taylor, M.W. Genomic insights into the marine sponge microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowe, S.D.; Richards, J.J.; Tucker, A.T.; Thompson, R.; Melander, C.; Cavanagh, J. Anti-biofilm compounds derived from marine sponges. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2010–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, J.R.; Hwang, B.S.; Sim, C.J.; Joung, S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, H.J. Phorbaketals A, B, and C, sesterterpenoids with a spiroketal of hydrobenzopyran moiety isolated from the marine sponge Phorbas sp. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5590–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.J.; Lee, K.T.; Rho, J.R.; Choi, J.H. Phorbaketal A, isolated from the marine sponge Phorbas sp., exerts its anti-inflammatory effects via NF-κB inhibition and heme oxygenase-1 activation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 7005–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, M.R.; Kim, A.R.; Hwang, J.H.; Sung, M.K.; Lee, Y.K.; Hwang, B.S.; Rho, J.R.; Hwang, E.S.; Hong, J.H. Phorbaketal A stimulates osteoblast differentiation through TAZ mediated Runx2 activation. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.; Solomon, A.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Marudhamuthu, M. Liposome encapsulated surfactant abetted copper nanoparticles alleviates biofilm mediated virulence in pathogenic Pseudomonas aeruginosa and MRSA. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morfeldt, E.; Taylor, D.; von Gabain, A.; Arvidson, S. Activation of alpha-toxin translation in Staphylococcus aureus by the trans-encoded antisense RNA, RNAIII. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 4569–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiazza, N.C.; O’Toole, G.A. Alpha-toxin is required for biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 3214–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Z.H.; Wang, H.F.; Ding, T.; Zhu, W.; Zhuang, X.Y.; Chu, W.H. Azithromycin reduces the production of α-hemolysin and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. Indian J. Microbiol. 2014, 54, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Lee, J.-H.; Ryu, S.Y.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, J. Stilbenes reduce Staphylococcus aureus hemolysis, biofilm formation, and virulence. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.S.; Lee, J.-H.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, J. Red wines and flavonoids diminish Staphylococcus aureus virulence with anti-biofilm and anti-hemolytic activities. Biofouling 2015, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldry, M.; Nielsen, A.; Bojer, M.S.; Zhao, Y.; Friberg, C.; Ifrah, D.; Heede, N.G.; Larsen, T.O.; Frokiaer, H.; Frees, D.; et al. Norlichexanthone reduces virulence gene expression and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-G.; Ryu, S.Y.; Lee, J. Calcium-chelating alizarin and other anthraquinones inhibit biofilm formation and the hemolytic activity of Staphylococcus aureus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-G.; Lee, J.-H.; Raorane, C.J.; Oh, S.T.; Park, J.G.; Lee, J. Herring oil and omega fatty acids inhibit Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation and virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Schaaf, E.; Breshears, L.M.; Wallis, H.W.; Johnson, J.R.; Tkaczyk, C.; Sellman, B.R.; Sun, J.S.; Peterson, M.L. Alpha-toxin contributes to biofilm formation among Staphylococcus aureus wound isolates. Toxins 2018, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.N.; Kang, M.S.; Chen, H.C.; Shi, X.M.; Zhou, R.; Chen, J.; Du, Y.W. The staphylococcal nuclease prevents biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus and other biofilm-forming bacteria. Sci. China Life Sci. 2011, 54, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiedrowski, M.R.; Horswill, A.R. New approaches for treating staphylococcal biofilm infections. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1241, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beenken, K.E.; Spencer, H.; Griffin, L.M.; Smeltzer, M.S. Impact of extracellular nuclease production on the biofilm phenotype of Staphylococcus aureus under in vitro and in vivo conditions. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 1634–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, E.; Choi, H.; Lee, J. Collismycin C from the micronesian marine bacterium Streptomyces sp MC025 inhibits Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, 10th ed.; Approved Standard M07-A10; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Daum, R.S. Removing the golden coat of Staphylococcus aureus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-G.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.-K.; Hwang, B.S.; Lee, J. Antibiofilm Activity of Phorbaketals from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp. against Staphylococcus aureus. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060301
Kim Y-G, Lee J-H, Lee S, Lee Y-K, Hwang BS, Lee J. Antibiofilm Activity of Phorbaketals from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp. against Staphylococcus aureus. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(6):301. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060301
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yong-Guy, Jin-Hyung Lee, Sangbum Lee, Young-Kyung Lee, Buyng Su Hwang, and Jintae Lee. 2021. "Antibiofilm Activity of Phorbaketals from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp. against Staphylococcus aureus" Marine Drugs 19, no. 6: 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060301
APA StyleKim, Y.-G., Lee, J.-H., Lee, S., Lee, Y.-K., Hwang, B. S., & Lee, J. (2021). Antibiofilm Activity of Phorbaketals from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp. against Staphylococcus aureus. Marine Drugs, 19(6), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060301






