Tetrodotoxins (TTXs) and Vibrio alginolyticus in Mussels from Central Adriatic Sea (Italy): Are They Closely Related?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Method Performance Assessment
2.2. TTXs in Mussels
2.2.1. Year 2018
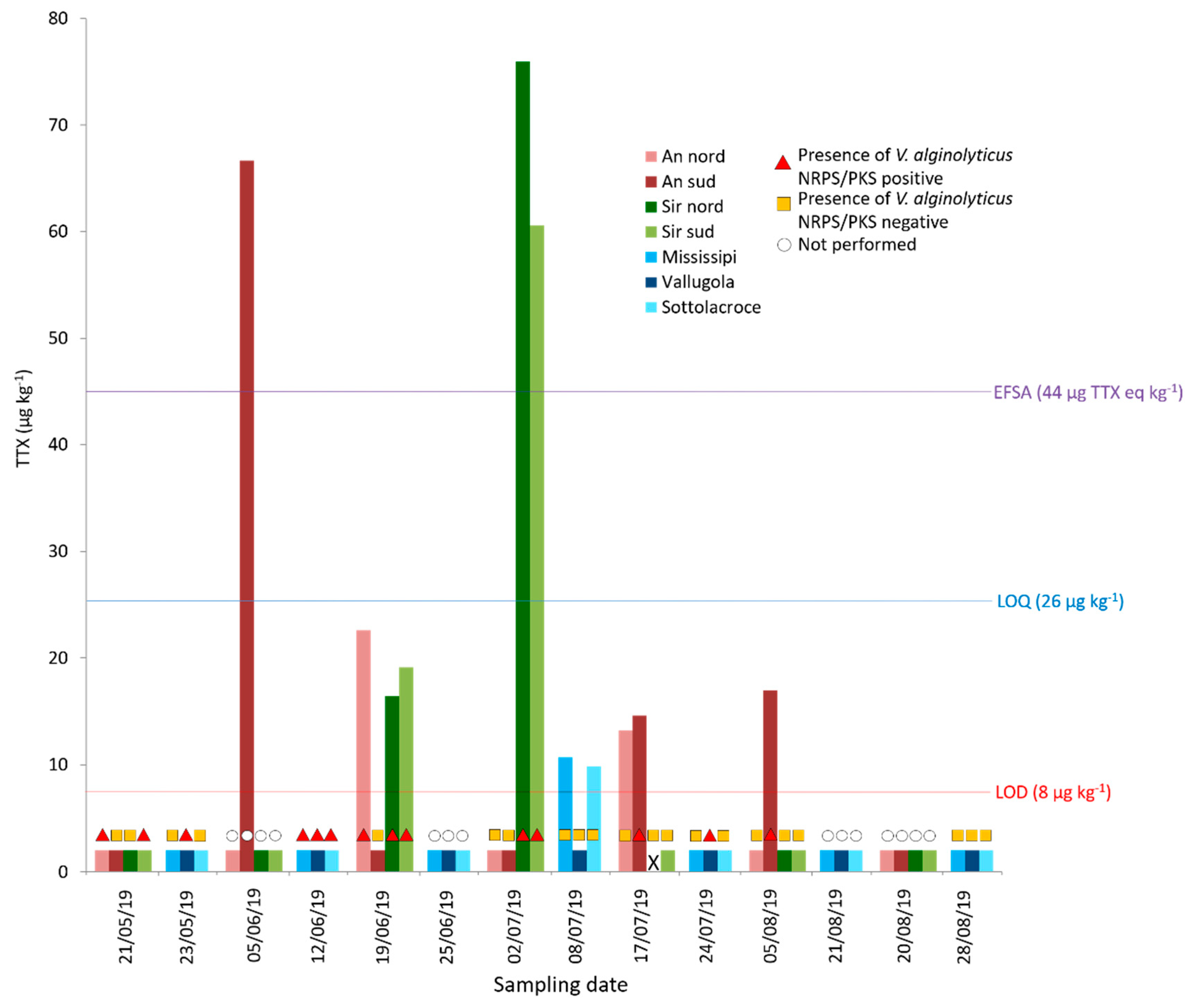
2.2.2. Year 2019
2.2.3. Distribution of TTX in Mussel Tissues
2.2.4. Uptake and Depuration Rate Estimation
2.3. Vibrio Characterization
2.3.1. Year 2018
2.3.2. Year 2019
2.3.3. TTX and NRPS/PKS-Positive Vibrio alginolyticus in Mussels Sampled in 2019
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
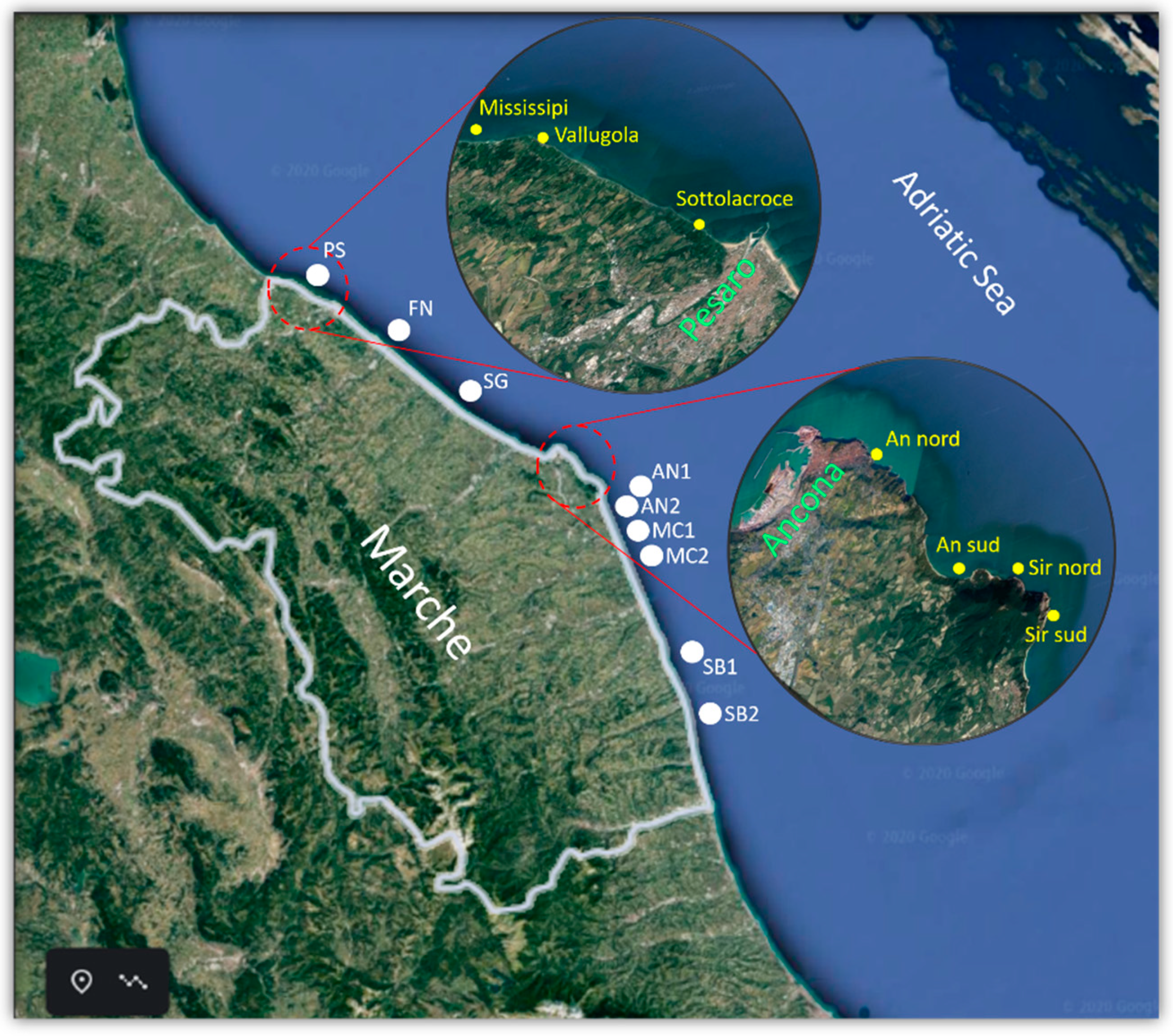
4.1. Sampling
4.2. Chemical Analysis
4.2.1. Chemicals and Standards
4.2.2. TTX Extraction from Mussels and Bacterial Pellets
- Mussels (WF, DG)
- Bacterial pellets
4.2.3. HILIC-MS/MS Analysis
4.2.4. Analytical Method Performance Assessment
4.2.5. Quality Control
4.3. Microbiological Analysis
4.3.1. Isolation of Vibrio spp. from Mussel Samples
4.3.2. Mass Culture of Bacterial Isolates
4.3.3. DNA Extraction—Operative Method
4.3.4. PCR Analysis
- gyrB and toxR species-specific genes
- NRPS and PKS biosynthesis genes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campbell, K.; Barnes, P.; Haughey, S.; Higgins, C.; Kawatsu, K.; Vasconcelos, V.; Elliott, C. Development and Single Laboratory Validation of an Optical Biosensor Assay for Tetrodotoxin Detection as a Tool to Combat Emerging Risks in European Seafood Rapid Detection in Food and Feed. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 7753–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, M.; Noguchi, T.; Maruyama, J.; Ogata, T.; Hashimoto, K. Release of Tetrodotoxin and Paralytic Shellfish Poison from Puffer Liver by RNase. J. Biochem. 1983, 93, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T. TTX Accumulation in Pufferfish. Part D: Genomics and Proteomics. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol 2006, 1, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, R.; Kalaitzis, J.A.; Neilan, B.A. On the Origins and Biosynthesis of Tetrodotoxin. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 104, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denac, H.; Mevissen, M.; Scholtysik, G. Structure, Function and Pharmacology of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2000, 362, 453–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheib, H.; McLay, I.; Guex, N.; Clare, J.J.; Blaney, F.E.; Dale, T.J.; Tate, S.N.; Robertson, G.M. Modeling the Pore Structure of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels in Closed, Open, and Fast-Inactivated Conformation Reveals Details of Site 1.Toxin and Local Anesthetic Binding. J. Mol. Model. 2006, 12, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Sugimoto, A.; Takai, A.; Yasumoto, T. Effects of Specific Modifications of Several Hydroxyls of Tetrodotoxin on Its Affinity to Rat Brain Membrane. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 289, 1688–1696. [Google Scholar]
- Bane, V.; Lehane, M.; Dikshit, M.; O’Riordan, A.; Furey, A. Tetrodotoxin: Chemistry, Toxicity, Source, Distribution and Detection. Toxins 2014, 6, 693–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noguchi, T.; Ebesu, J.S.M. Puffer Poisoning: Epidemiology and Treatment. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 2001, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsen, H.K.; Alexander, J.; Barregård, L.; Bignami, M.; Brüschweiler, B.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cottrill, B.; Dinovi, M.; Edler, L.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; et al. A Risks for Public Health Related to the Presence of Tetrodotoxin (TTX) and TTX Analogues in Marine Bivalves and Gastropods. EFSA J. 2017, 15, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, M.; Sato, S.; Sakamoto, S.; Ogata, T. Occurrence of Tetrodotoxin in Alexandrium tamarense, a Causative Dinoflagellate of Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning. Toxicon 1996, 34, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNabb, P.S.; Taylor, D.I.; Ogilvie, S.C.; Wilkinson, L.; Anderson, A.; Hamon, D.; Wood, S.A.; Peake, B.M. First Detection of Tetrodotoxin in the Bivalve Paphies australis by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry With and Without Precolumn Reaction. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNabb, P.; Selwood, A.I.; Munday, R.; Wood, S.A.; Taylor, D.I.; MacKenzie, L.A.; van Ginkel, R.; Rhodes, L.L.; Cornelisen, C.; Heasman, K.; et al. Detection of Tetrodotoxin from the Grey Side-Gilled Sea Slug—Pleurobranchaea maculata, and Associated Dog Neurotoxicosis on Beaches Adjacent to the Hauraki Gulf, Auckland, New Zealand. Toxicon 2010, 56, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, S.A.; Casas, M.; Taylor, D.I.; McNabb, P.; Salvitti, L.; Ogilvie, S.; Cary, S.C. Depuration of Tetrodotoxin and Changes in Bacterial Communities in Pleurobranchea maculata Adults and Egg Masses Maintained in Captivity. J. Chem. Ecol. 2012, 38, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, M.; Azevedo, J.; Rodriguez, P.; Alfonso, A.; Botana, L.M.; Vasconcelos, V. New Gastropod Vectors and Tetrodotoxin Potential Expansion in Temperate Waters of the Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 712–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.E.; Arakawa, O.; Noguchi, T.; Miyazawa, K.; Shida, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Tetrodotoxin and Related Substances in a Ribbon Worm Cephalothrix linearis (Nemertean). Toxicon 1990, 28, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakawa, M.; Toyoshima, T.; Shida, Y.; Noguchi, T.; Miyazawa, K. Paralytic Toxins in a Ribbon Worm Cephalothrix species (Nemertean) Adherent to Cultured Oysters in Hiroshima Bay, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. Toxicon 2000, 38, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifin, C.T. The Chemical and Evolutionary Ecology of Tetrodotoxin (TTX) Toxicity in Terrestrial Vertebrates. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Childress, J.J.; Fisher, C.R.; Brooks, J.M.; Kennicutt, M.C.; Bidigare, R.; Anderson, A.E. A Methanotrophic Marine Molluscan (Bivalvia, Mytilidae) Symbiosis: Mussels Fueled by Gas. Science 1986, 233, 1306–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, J.A.; Bright, M.; Schiemer, F. The Ecology of a Novel Symbiosis between a Marine Peritrich Ciliate and Chemoautotrophic Bacteria. Mar. Ecol. 1998, 19, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratheepa, V.; Alex, A.; Silva, M.; Vasconcelos, V. Bacterial Diversity and Tetrodotoxin Analysis in the Viscera of the Gastropods from Portuguese Coast. Toxicon 2016, 119, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, P.; Alfonso, A.; Otero, P.; Katikou, P.; Georgantelis, D.; Botana, L.M. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Method to Detect Tetrodotoxin and Its Analogues in the Puffer Fish Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) from European Waters. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magarlamov, T.Y.; Melnikova, D.I.; Chernyshev, A.V. Tetrodotoxin-Producing Bacteria: Detection, Distribution and Migration of the Toxin in Aquatic Systems. Toxins 2017, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-J.; Jeong, D.-Y.; Kim, W.-S.; Kim, H.-D.; Kim, C.-H.; Park, W.-W.; Park, Y.-H.; Kim, K.-S.; Kim, H.-M.; Kim, D.-S. A Tetrodotoxin-Producing Vibrio Strain, LM-1, from the Puffer Fish Fugu Vermicularis radiatus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 1698–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xie, L.; Xia, G.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, R. Toxicity and Distribution of Tetrodotoxin-Producing Bacteria in Puffer Fish Fugu rubripes Collected from the Bohai Sea of China. Toxicon 2005, 46, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, H.; Hamasaki, K.; Ohwada, K.; Simidu, U.; Noguchi, T.; Shida, Y.; Kogure, K. Presence of Tetrodotoxin and Tetrodotoxin-Producing Bacteria in Freshwater Sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 3934–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, A.D.; Powell, A.; Schofield, A.; Lees, D.N.; Baker-Austin, C. Detection of the Pufferfish Toxin. Tetrodotoxin in European Bivalves, England, 2013 to 2014. Eurosurveillance 2015, 20, 21009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leão, J.M.; Lozano-Leon, A.; Giráldez, J.; Vilariño, Ó.; Gago-Martínez, A. Preliminary Results on the Evaluation of the Occurrence of Tetrodotoxin Associated to Marine Vibrio Spp. in Bivalves from the Galician Rias (North-west of Spain). Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotaki, Y.; Shimizu, Y. 1-Hydroxy-5,11-Dideoxytetrodotoxin, the First N-Hydroxy and Ring-Deoxy derivative of Tetrodotoxin Found in the Newt Taricha granulosa. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, T.; Onuki, K.; Arakawa, O. Tetrodotoxin Poisoning Due to Pufferfish and Gastropods, and Their Intoxication Mechanism. ISRN Toxicol. 2011, 2011, 276939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bentur, Y.; Ashkar, J.; Lurie, Y.; Levy, Y.; Azzam, Z.S.; Litmanovich, M.; Golik, M.; Gurevych, B.; Golani, D.; Eisenman, A. Lessepsian Migration and Tetrodotoxin Poisoning Due to Lagocephalus sceleratus in the Eastern Mediterranean. Toxicon 2008, 52, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katikou, P.; Georgantelis, D.; Sinouris, N.; Petsi, A.; Fotaras, T. First Report on Toxicity Assessment of the Lessepsian Migrant Pufferfish Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) from European Waters (Aegean Sea, Greece). Toxicon 2009, 54, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, P.; Alfonso, A.; Vale, C.; Alfonso, C.; Vale, P.; Tellez, A.; Botana, L.M. First Toxicity Report of Tetrodotoxin and 5, 6,11-TrideoxyTTX in the Trumpet Shell Charonia lampas lampas in Europe. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 5622–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlamis, A.; Katikou, P.; Rodriguez, I.; Rey, V.; Alfonso, A.; Papazachariou, A.; Zacharaki, T.; Botana, A.M.; Botana, L.M. First Detection of Tetrodotoxin in Greek Shellfish by UPLC-MS/MS Potentially Linked to the Presence of the Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. Toxins 2015, 7, 1779–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerssen, A.; Bovee, T.; Klijnstra, M.D.; Poelman, M.; Portier, L.; Hoogenboom, R. First Report on the Occurrence of Tetrodotoxins in Bivalve Mollusks in The Netherlands. Toxins 2018, 10, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- EU Commission. Notification Detail: Policy Guideline on Tetrodotoxin in Live Bivalve Molluscs. Notification Number: 2016/175/NL (Netherlands). TRIS Database. 2016. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/growth/tools (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- European Union. Corrigendum to Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 Laying Down Specific Rules for the Organisation of Official Controls on Products of Animal Origin Intended for Human Consumption. Available online: http://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- Dell’Aversano, C.; Tartaglione, L.; Polito, G.; Dean, K.; Giacobbe, M.; Casabianca, S.; Capellacci, S.; Penna, A.; Turner, A.D. First Detection of Tetrodotoxin and High Levels of Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins in Shellfish from Sicily (Italy) by Three Different Analytical Methods. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordin, P.; Dall’Ara, S.; Tartaglione, L.; Antonelli, P.; Calfapietra, A.; Varriale, F.; Guiatti, D.; Milandri, A.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Arcangeli, G.; et al. First Occurrence of Tetrodotoxins in Bivalve Mollusks from Northern Adriatic Sea (Italy). Food Control 2021, 120, 107510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Fong, S.; Hungerford, J.; McNabb, P.; Boundy, M.; Harwood, T. Ultrahigh-Performance Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins and Tetrodotoxin in Mussels, Oysters, Clams, Cockles, and Scallops: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 103, 533–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hort, V.; Arnich, N.; Guérin, T.; Lavison-Bompard, G.; Nicolas, M. First Detection of Tetrodotoxin in Bivalves and Gastropods from the French Mainland Coasts. Toxins 2020, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Coates, L.; Bickerstaff, L.; Milligan, S.; Oneill, A.; Faulkner, D.; Mceneny, H.; Baker-Austin, C.; Lees, D.; et al. Detection of Tetrodotoxin Shellfish Poisoning (TSP) Toxins and Causative Factors in Bivalve Molluscs from the UK. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bacchiocchi, S.; Siracusa, M.; Ruzzi, A.; Gorbi, S.; Ercolessi, M.; Cosentino, M.; Ammazzalorso, P.; Orletti, R. Two-Year Study of Lipophilic Marine Toxin Profile in Mussels of the North-Central Adriatic Sea: First Report of Azaspiracids in Mediterranean Seafood. Toxicon 2015, 108, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, M.E.; Accoroni, S.; Mezzelani, M.; Lugarini, F.; Bacchiocchi, S.; Siracusa, M.; Tavoloni, T.; Piersanti, A.; Totti, C.; Regoli, F.; et al. Biological Effects of the Azaspiracid-Producing Dinoflagellate Azadinium dexteroporum in Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bacchiocchi, S.; Siracusa, M.; Campacci, D.; Ciriaci, M.; Dubbini, A.; Tavoloni, T.; Stramenga, A.; Gorbi, S.; Piersanti, A. Cyclic Imines (CIs) in Mussels from North-Central Adriatic Sea: First Evidence of Gymnodimine A in Italy. Toxins 2020, 12, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessy, L.; Boundy, M.J.; Smith, K.F.; Harwood, D.T.; Hawes, I.; Wood, S.A. Tetrodotoxin in Marine Bivalves and Edible Gastropods: A Mini-Review. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biessy, L.; Smith, K.F.; Wood, S.A.; Tidy, A.; van Ginkel, R.; Bowater, J.R.D.; Hawes, I. A Microencapsulation Method for Delivering Tetrodotoxin to Bivalves to Investigate Uptake and Accumulation. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biessy, L.; Smith, K.; Boundy, M.; Webb, S.; Hawes, I.; Wood, S. Distribution of Tetrodotoxin in the New Zealand Clam, Paphies Australis, Established Using Immunohistochemistry and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry. Toxins 2018, 10, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Turner, A.D.; Baker-Austin, C.; Huggett, J.F.; Ritchie, J.M. Distribution of Tetrodotoxin in Pacific Oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, F.L.; Iida, T.; Swings, J. Biodiversity of Vibrios. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 403–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbieri, E.; Falzano, L.; Fiorentini, C.; Pianetti, A.; Baffone, W.; Fabbri, A.; Matarrese, P.; Casiere, A.; Katouli, M.; Kühn, I.; et al. Occurrence, Diversity, and Pathogenicity of Halophilic Vibrio spp. and Non-O1 Vibrio cholerae from Estuarine Waters along the Italian Adriatic Coast. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 2748–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urakawa, H.; Rivera, I. The Biology of Vibrios. Aquatic Environment; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; pp. 175–189. [Google Scholar]
- Di, D.Y.W.; Lee, A.; Jang, J.; Han, D.; Hur, H.-G. Season-Specific Occurrence of Potentially Pathogenic Vibrio spp. on the Southern Coast of South Korea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bevins, C.; Salzman, N.; Bevins, C.L.; Salzman, N.H. Paneth Cells, Antimicrobial Peptides and Maintenance of Intestinal Homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EURLMB SOP-Determination of Tetrodotoxin by HILIC-MS/MS-, June 2017. Available online: https://www.aesan.gob.es/en/CRLMB/web/public_documents/seccion/crlmb_standard_operating_procedures.htmI (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- ISO 6887-3. Microbiology of the Food Chain—Preparation of Test Samples, Initial Suspension and Decimal Dilutions for Microbiological Examinations—Part 3: Specific Rules for the Preparation of Fish and Fishery Products. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/77420.html (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- ISO 21872-1:2017. Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for Determination of Vibrio spp.—Part 1: Detection of Potentially Enteropathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio vulnificus. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/74112.html (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- Hartnell, R.E.; Stockley, L.; Keay, W.; Rosec, J.-P.; Hervio-Heath, D.; Van den Berg, H.; Leoni, F.; Ottaviani, D.; Henigman, U.; Denayer, S.; et al. A Pan-European Ring Trial to Validate an International Standard for Detection of Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus in Seafoods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 288, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.-J.; Yu, R.-C.; Luo, X.; Zhou, M.-J.; Lin, X.-T. Toxin-Screening and Identification of Bacteria Isolated from Highly Toxic Marine Gastropod Nassarius semiplicatus. Toxicon 2008, 52, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, S.; Pryer, K.M.; Miao, V.P.; Palmer, J.D. Investigating Deep Phylogenetic Relationships among Cyanobacteria and Plastids by Small Subunit RRNA Sequence Analysis. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1999, 46, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, P.; Hu, C. Vibrio alginolyticus GyrB Sequence Analysis and GyrB-Targeted PCR Identification in Environmental Isolates. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2008, 82, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.B.; Okuda, J.; Matsumoto, C.; Takahashi, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Nishibuchi, M. Identification of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Strains at the Species Level by PCR Targeted to the ToxR Gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tambadou, F.; Lanneluc, I.; Sablé, S.; Klein, G.L.; Doghri, I.; Sopéna, V.; Didelot, S.; Barthélémy, C.; Thiéry, V.; Chevrot, R. Novel Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase (NRPS) Genes Sequenced from Intertidal Mudflat Bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 357, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffitt, M.C.; Neilan, B.A. On the Presence of Peptide Synthetase and Polyketide Synthase Genes in the Cyanobacterial Genus Nodularia. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 196, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bacchiocchi, S.; Campacci, D.; Siracusa, M.; Dubbini, A.; Leoni, F.; Tavoloni, T.; Accoroni, S.; Gorbi, S.; Giuliani, M.E.; Stramenga, A.; et al. Tetrodotoxins (TTXs) and Vibrio alginolyticus in Mussels from Central Adriatic Sea (Italy): Are They Closely Related? Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060304
Bacchiocchi S, Campacci D, Siracusa M, Dubbini A, Leoni F, Tavoloni T, Accoroni S, Gorbi S, Giuliani ME, Stramenga A, et al. Tetrodotoxins (TTXs) and Vibrio alginolyticus in Mussels from Central Adriatic Sea (Italy): Are They Closely Related? Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(6):304. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060304
Chicago/Turabian StyleBacchiocchi, Simone, Debora Campacci, Melania Siracusa, Alessandra Dubbini, Francesca Leoni, Tamara Tavoloni, Stefano Accoroni, Stefania Gorbi, Maria Elisa Giuliani, Arianna Stramenga, and et al. 2021. "Tetrodotoxins (TTXs) and Vibrio alginolyticus in Mussels from Central Adriatic Sea (Italy): Are They Closely Related?" Marine Drugs 19, no. 6: 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060304
APA StyleBacchiocchi, S., Campacci, D., Siracusa, M., Dubbini, A., Leoni, F., Tavoloni, T., Accoroni, S., Gorbi, S., Giuliani, M. E., Stramenga, A., & Piersanti, A. (2021). Tetrodotoxins (TTXs) and Vibrio alginolyticus in Mussels from Central Adriatic Sea (Italy): Are They Closely Related? Marine Drugs, 19(6), 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060304