Alginate-Based Micro- and Nanosystems for Targeted Cancer Therapy
Abstract
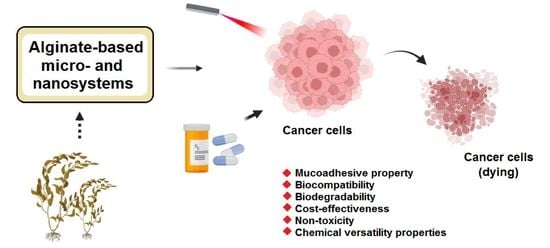
:1. Introduction
| Alginate-Based Systems | Applications | Approaches | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate and collagen-based injectable hydrogels | Anticancer and anti-metastatic effects | Photothermal therapy and immunotherapy | [23] |
| Sodium alginate conjugated plasmonic magnetic nanocomposites | Drug delivery and cancer therapy | Targeted delivery of paclitaxel against human hepatocellular carcinoma cells | [24] |
| Sodium alginate–polyvinyl alcohol–bovine serum albumin coated Fe3O4 nanomaterials | Anticancer drug delivery with pH-responsive behavior | Controlled and targeted release of anticancer drug (doxorubicin) against cancer cells | [25] |
| Alginate–polydopamine hydrogels | Anticancer drug delivery with pH-responsive behavior | Cancer chemotherapy with chemo selective approach; targeted delivery of bortezomib to cancer cells | [26] |
| Chitosan–alginate nanosystems | Drug delivery and cancer therapy | Targeted delivery of doxorubicin with controlled and sustained release behavior | [27] |
| Tin oxide–sodium alginate–polyethylene glycol–carvacrol nanocomposites | Cancer therapy (against esophagus cancer) | Increase the generation of reactive oxygen species; enhance the pro-apoptotic and reduce the antiapoptotic proteins | [28] |
| Sodium alginate/phosphate-stabilized amorphous calcium carbonate nanocarriers | Drug delivery and cancer therapy | Targeted delivery of anticancer drugs/agents (curcumin) with sustained release and concentration-dependent behavior | [29] |
| Sodium alginate hydrogels | To monitor and obstruct postoperative recurrence and metastasis (in situ) | Cancer immunotherapy | [30] |
| Sodium alginate-based micelles | Anticancer drug delivery | Prolonged and targeted delivery of curcumin with blood-compatibility and stability | [31] |
| Curcumin–casein–alginate–chitosan nanocomplexes | Cancer nutraceutical therapy | Oral nano-delivery of curcumin with improved pharmacokinetics (enhanced bioavailability and cancer therapeutic efficacy against Ehrlich carcinoma) | [32] |
| Chitosan–sodium alginate–polyethylene glycol–crocin nanocomposites | Cancer therapy | Inhibition of the esophageal cancer KYSE-150 cell growth by enhancing the production of reactive oxygen species, and apoptotic cell death | [33] |
| Alginate-coated caseinate NPs | Anticancer drug delivery | Targeted and controlled delivery of doxorubicin against Ehrlich carcinoma | [34] |
| Chitosan/sodium alginate functionalized graphene oxide-based nanocomposites | Anticancer drug delivery | Targeted delivery of doxorubicin with pH-dependent drug release behavior | [35] |
| Alginate/chitosan-based nanosystems | Drug delivery | Encapsulation of hydrophobic quercetin with enhanced sustained release | [36] |
| Sodium alginate and hydroxyapatite bi-coated iron oxide NPs | Anticancer drug delivery | pH responsive controlled release of anticancer poorly water-soluble drug molecules (curcumin and 6-gingerol) | [37] |
| Epidermal growth factor receptor conjugated fucoidan/alginates loaded hydrogels | Cancer therapy (colon cancer) | Targeted photodynamic therapy | [38] |
| Fe3O4/calcium phosphate/alginate core-shell-corona NPs | Targeted chemotherapy | Targeted drug delivery with high biocompatibility and suitable particle size, surface functionality, and drug loading/release behavior | [39] |
2. Alginate-Based Micro- and Nanosystems for Cancer Therapeutics
2.1. Targeted Anticancer Drug Delivery
2.2. Chemodynamic and Photodynamic Therapy
2.3. Photothermal Therapy
3. Challenges and Future Perspectives
4. Conclusions and Future Outlooks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chivere, V.T.; Kondiah, P.P.D.; Choonara, Y.E.; Pillay, V. Nanotechnology-Based Biopolymeric Oral Delivery Platforms for Advanced Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maity, C.; Das, N. Alginate-based smart materials and their application: Recent advances and perspectives. Top. Curr. Chem. 2022, 380, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeddi, M.K.; Mahkam, M. Magnetic nano carboxymethyl cellulose-alginate/chitosan hydrogel beads as biodegradable devices for controlled drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, R.S. Greener and sustainable chemistry. Appl. Sci. 2014, 4, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, R.S. Biomass-Derived Renewable Carbonaceous Materials for Sustainable Chemical and Environmental Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6458–6470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, G. Review on marine carbohydrate-based gold nanoparticles represented by alginate and chitosan for biomedical application. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 244, 116311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Soufi, G.J. Algae-derived materials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications: Current trends and future perspectives. Emergent Mater. 2022, 5, 631–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Important Roles of Oligo- and Polysaccharides against SARS-CoV-2: Recent Advances. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakkakula, J.R.; Gujarathi, P.; Pansare, P.; Tripathi, S. A comprehensive review on alginate-based delivery systems for the delivery of chemotherapeutic agent: Doxorubicin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 259, 117696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, M.A.J.; Alharbi, K.S.; Almalki, W.H.; Imam, S.S.; Albratty, M.; Meraya, A.M.; Alzarea, S.I.; Kazmi, I.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Afzal, O.; et al. Sodium alginate based drug delivery in management of breast cancer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 292, 119689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodero, A.; Alberti, S.; Gaggero, G.; Ferretti, M.; Botter, R.; Vicini, S.; Castellano, M. An Up-to-Date Review on Alginate Nanoparticles and Nanofibers for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2100809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, X.; Chu, Q. Bio-based nanomaterials for cancer therapy. Nano Today 2021, 38, 101134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Lee, W.W.; Han, E.J.; Ahn, G. Alginate-based nanomaterials: Fabrication techniques, properties, and applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, A.-G.; Grumezescu, A.M. Applications of Chitosan-Alginate-Based Nanoparticles—An Up-to-Date Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, R.S. Greener approach to nanomaterials and their sustainable applications. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2012, 1, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, R.S. Journey on greener pathways: From the use of alternate energy inputs and benign reaction media to sustainable applications of nano-catalysts in synthesis and environmental remediation. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 2027–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, R.S. Greener and Sustainable Trends in Synthesis of Organics and Nanomaterials. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5866–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reig-Vano, B.; Tylkowski, B.; Montané, X.; Giamberini, M. Alginate-based hydrogels for cancer therapy and research. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 170, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boontheekul, T.; Kong, H.J.; Mooney, D.J. Controlling alginate gel degradation utilizing partial oxidation and bimodal molecular weight distribution. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roquero, D.M.; Katz, E. “Smart” alginate hydrogels in biosensing, bioactuation and biocomputing: State-of-the-art and perspectives. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2022, 4, 100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Kong, H.; Tang, X.; Pan, L.; Xia, K.; Aldalbahi, A.; Li, A.; Tai, R.; et al. Sodium alginate-functionalized nanodiamonds as sustained chemotherapeutic drug-release vectors. Carbon 2016, 97, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choukaife, H.; Doolaanea, A.A.; Alfatama, M. Alginate Nanoformulation: Influence of Process and Selected Variables. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.; An, E.-K.; Zhang, W.; Kim, H.J.; Eom, Y.; Jin, J.-O. Dual-functional alginate and collagen–based injectable hydrogel for the treatment of cancer and its metastasis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, V.; Sood, A.; Kumari, S.; Kumaran, S.S.; Jain, T.K. Hydrophobically modified sodium alginate conjugated plasmonic magnetic nanocomposites for drug delivery & magnetic resonance imaging. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101470. [Google Scholar]
- Prabha, G.; Raj, V. Sodium alginate–polyvinyl alcohol–bovin serum albumin coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as anticancer drug delivery vehicle: Doxorubicin loading and in vitro release study and cytotoxicity to HepG2 and L02 cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 79, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezk, A.I.; Obiweluozor, F.O.; Choukrani, G.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Drug release and kinetic models of anticancer drug (BTZ) from a pH-responsive alginate polydopamine hydrogel: Towards cancer chemotherapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katuwavila, N.P.; Perera, A.D.L.; Samarakoon, S.R.; Soysa, P.; Karunaratne, V.; Amaratunga, G.A.J.; Karunaratne, D.N. Chitosan-alginate nanoparticle system efficiently delivers doxorubicin to MCF-7 Cells. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 3178904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Mohideen, A.P.; Seshadri, V.D.; Rengarajan, T. Biosynthesized tin oxide-sodium alginate-polyethylene glycol-carvacrol nanocomposite shows anticancer activity on esophagus squamous carcinoma cells. Process Biochem. 2022, 121, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, B.; Wang, H.; Rao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Lian, X.; Gao, X.; Niu, B.; Li, W. Preparation and characterization of sodium alginate/phosphate-stabilized amorphous calcium carbonate nanocarriers and their application in the release of curcumin. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 375712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhuang, Y.; He, T.; Wu, X.; Su, L.; Kang, J.; Chang, J.; Wang, H. Sodium alginate hydrogel-mediated cancer immunotherapy for postoperative in situ recurrence and metastasis. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 5717–5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, D.; Karabasz, A.; Bzowska, M.; Szuwarzyński, M.; Karewicz, A.; Nowakowska, M. Blood-compatible, stable micelles of sodium alginate—Curcumin bioconjugate for anti-cancer applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 113, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbialy, N.S.; Mohamed, N. Fabrication of the quaternary nanocomplex curcumin-casein-alginate-chitosan as a potential oral delivery system for cancer nutraceutical therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 70, 103226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Hirad, A.H.; Veeraraghavan, V.P.; Surapaneni, K.M.; Hussein-Al-Ali, S.H.; Natarajan, N.; Elayappan, P.K. Chitosan-sodium alginate-polyethylene glycol-crocin nanocomposite treatment inhibits esophageal cancer KYSE-150 cell growth via inducing apoptotic cell death. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbialy, N.S.; Mohamed, N. Alginate-coated caseinate nanoparticles for doxorubicin delivery: Preparation, characterisation, and in vivo assessment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 154, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.; Xie, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Y.; Xie, J. Chitosan/sodium alginate modificated graphene oxide-based nanocomposite as a carrier for drug delivery. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 17798–17805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalini, T.; Basha, S.K.; Mohamed Sadiq, A.M.; Kumari, V.S.; Kaviyarasu, K. Development and characterization of alginate/chitosan nanoparticulate system for hydrophobic drug encapsulation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 52, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manatunga, D.C.; de Silva, R.M.; de Silva, K.M.N.; de Silva, N.; Bhandari, S.; Yap, Y.K.; Costha, N.P. pH responsive controlled release of anti-cancer hydrophobic drugs from sodium alginate and hydroxyapatite bi-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugapriya, K.; Kim, H.; Kang, H.W. Epidermal growth factor receptor conjugated fucoidan/alginates loaded hydrogel for activating EGFR/AKT signaling pathways in colon cancer cells during targeted photodynamic therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-P.; Liao, Y.-T.; Liu, C.-H.; Yu, J.; Alamri, H.R.; Alothman, Z.A.; Hossain, M.S.A.; Yamauchi, Y.; Wu, K.C.-W. Trifunctional Fe3O4/CaP/Alginate Core–Shell–Corona Nanoparticles for Magnetically Guided, pH-Responsive, and Chemically Targeted Chemotherapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 2366–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimivand, M.; Tafvizi, F.; Noorbazargan, H. Synthesis and characterization of alginate nanocarrier encapsulating Artemisia ciniformis extract and evaluation of the cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction in AGS cell line. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 338–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.; Figueira, P.; Maciel, D.; Rodrigues, J.; Qu, X.; Liu, C.; Tomás, H.; Li, Y. pH-sensitive Laponite®/doxorubicin/alginate nanohybrids with improved anticancer efficacy. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawfik, S.M.; Sharipov, M.; Huy, B.T.; Gerelkhuu, Z.; Biechele-Speziale, D.; Lee, Y.-I. Naturally modified nonionic alginate functionalized upconversion nanoparticles for the highly efficient targeted pH-responsive drug delivery and enhancement of NIR-imaging. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 57, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirrahimi, M.; Beik, J.; Mirrahimi, M.; Alamzadeh, Z.; Teymouri, S.; Mahabadi, V.P.; Eslahi, N.; Tazehmahalleh, F.E.; Ghaznavi, H.; Shakeri-Zadeh, A.; et al. Triple combination of heat, drug and radiation using alginate hydrogel co-loaded with gold nanoparticles and cisplatin for locally synergistic cancer therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.-H.; Liu, C.-H.; Bastakoti, B.P.; Suzuki, N.; Chang, Y.; Yamauchi, Y.; Lin, F.-H.; Wu, K.C.-W. Functionalized magnetic iron oxide/alginate core-shell nanoparticles for targeting hyperthermia. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3315–3328. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Xie, J. Surface modification of graphene oxide nanosheets by protamine sulfate/sodium alginate for anti-cancer drug delivery application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 440, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.N.; Ferreira, L.M.B.; Miranda-Gonçalves, V.; Reis, R.M.; Seraphim, T.V.; Borges, J.C.; Baltazar, F.; Gremião, M.P.D. Alginate hydrogel improves anti-angiogenic bevacizumab activity in cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 119, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, S.; Mohamadnia, Z.; Mahdavi, A. pH-responsive hybrid magnetic polyelectrolyte complex based on alginate/BSA as efficient nanocarrier for curcumin encapsulation and delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Su, X.; Gregory, D.A.; Li, W.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, X. Magnetic Alginate/Chitosan Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Curcumin into Human Breast Cancer Cells. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Ramos-Sebastian, A.; Jung, W.S.; Kim, S.H. Fabrication and preliminary evaluation of alginate hydrogel-based magnetic springs with actively targeted heating and drug release mechanisms for cancer therapy. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 230, 109551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, G. Near-Infrared Light-, Magneto-, and pH-Responsive GO–Fe3O4/Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/alginate Nanocomposite Hydrogel Microcapsules for Controlled Drug Release. Langmuir 2021, 37, 5522–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Su, W.; Sun, X.; Li, X. Bio-responsive alginate-keratin composite nanogels with enhanced drug loading efficiency for cancer therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-F.; Ma, L.; Su, F.; Ma, X.-F.; Li, T.; Jian-Zha-Xi, W.; Zhao, G.-H.; Wu, Z.-M.; Hou, C.-l.; Yan, H.-J. pH and reduction dual-responsive feather keratin—sodium alginate nanogels with high drug loading capacity for tumor-targeting DOX delivery. Polym. Test. 2021, 103, 107375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Zheng, M.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Xie, X.; Huang, F.; Gong, R. Folate mediated self-assembled phytosterol-alginate nanoparticles for targeted intracellular anticancer drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 129, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, J.; He, L.; Cheng, X.; Yan, G.; Wang, J.; Tang, R. Hybrid pH-sensitive nanogels surface-functionalized with collagenase for enhanced tumor penetration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 525, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, B.; Sun, C.; Chen, M.; Yang, X. Microfluidic synthesis of manganese-alginate nanogels with self-supplying H2O2 capability for synergistic chemo/chemodynamic therapy and boosting anticancer immunity. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yang, J.; Zhou, L.; Hu, X.; Wang, C.; Chai, K.; Li, R.; Feng, L.; Sun, Y.; Dong, C.; et al. Dual-Responsive and ROS-Augmented Nanoplatform for Chemo/Photodynamic/Chemodynamic Combination Therapy of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Geng, Y.; Xie, X.; Shen, X.; Li, T.; Li, S.; Wu, C.; Liu, Y. Chemo-photodynamic combined gene therapy and dual-modal cancer imaging achieved by pH-responsive alginate/chitosan multilayer-modified magnetic mesoporous silica nanocomposites. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shi, G.; Zhang, J.; Niu, J.; Huang, P.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, C.; Kong, D. Redox- and light-responsive alginate nanoparticles as effective drug carriers for combinational anticancer therapy. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 3304–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; Wu, H.; Zheng, W.; Kan, D.; Cheng, R.; Yan, J.; Yu, C.; Sun, S.-K. Biocompatible Iodine–Starch–Alginate Hydrogel for Tumor Photothermal Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 3654–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirrahimi, M.; Abed, Z.; Beik, J.; Shiri, I.; Dezfuli, A.S.; Mahabadi, V.P.; Kamrava, S.K.; Ghaznavi, H.; Shakeri-Zadeh, A. A thermo-responsive alginate nanogel platform co-loaded with gold nanoparticles and cisplatin for combined cancer chemo-photothermal therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 143, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Zhang, F.; Peng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xie, J. Layer-by-layer modification of magnetic graphene oxide by chitosan and sodium alginate with enhanced dispersibility for targeted drug delivery and photothermal therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 176, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Y.; Cao, C.; Liang, Z.; Yin, Z.-Z.; Gao, J.; Cai, W.; Kong, Y. Construction of a dual-drug delivery system based on oxidized alginate and carboxymethyl chitosan for chemo-photothermal synergistic therapy of osteosarcoma. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 174, 111331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, E.; Li, S.; Song, J.; Xing, R.; Li, Z.; Yan, X. Self-assembling Collagen/Alginate hybrid hydrogels for combinatorial photothermal and immuno tumor therapy. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 577, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Shang, Z.; Liu, H.; Yuan, Z.-X. Alginate-Based Platforms for Cancer-Targeted Drug Delivery. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1487259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamecha, D.; Movsas, R.; Sano, U.; Menon, J.U. Applications of alginate microspheres in therapeutics delivery and cell culture: Past, present and future. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqosaibi, A.I. Nanocarriers for anticancer drugs: Challenges and perspectives. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 103298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Chang, J.; Kwon, N.; Moon, S.; Park, Y.; Han, K.H.; Lim, B.; Lee, J.H. Multifunctional Nanomaterial-alginate Drug Delivery and Imaging System for Cancer Therapy. BioChip J. 2019, 13, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Amin, S.S.; Hosseini, S.H. Delivery of Hydrophobic Anticancer Drugs by Hydrophobically Modified Alginate Based Magnetic Nanocarrier. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Alginate-Based Micro- and Nanosystems for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100598
Iravani S, Varma RS. Alginate-Based Micro- and Nanosystems for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(10):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100598
Chicago/Turabian StyleIravani, Siavash, and Rajender S. Varma. 2022. "Alginate-Based Micro- and Nanosystems for Targeted Cancer Therapy" Marine Drugs 20, no. 10: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100598
APA StyleIravani, S., & Varma, R. S. (2022). Alginate-Based Micro- and Nanosystems for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Marine Drugs, 20(10), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100598