The Sponge-Derived Brominated Compound Aeroplysinin-1 Impairs the Endothelial Inflammatory Response through Inhibition of the NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
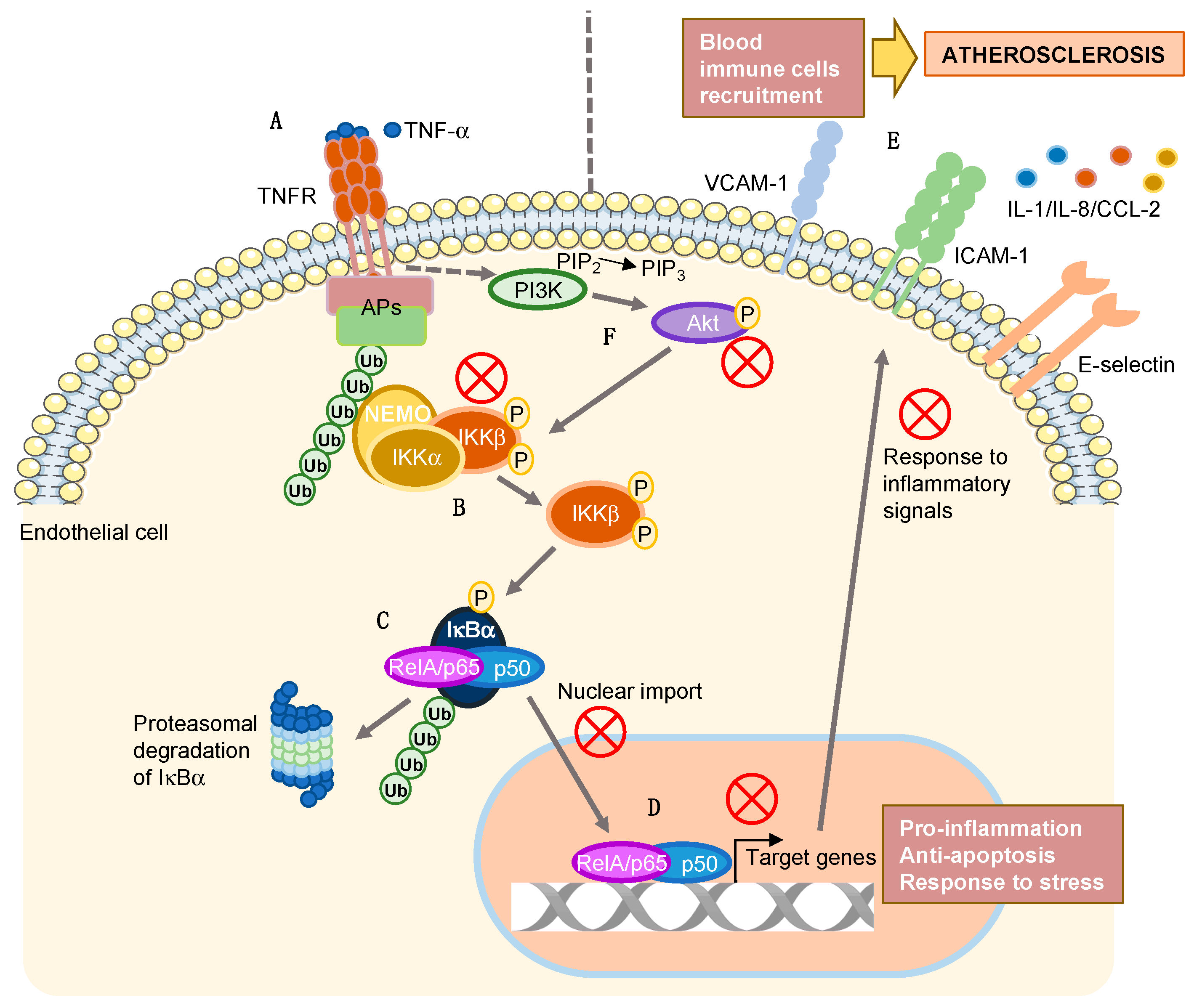
1. Introduction
2. Results
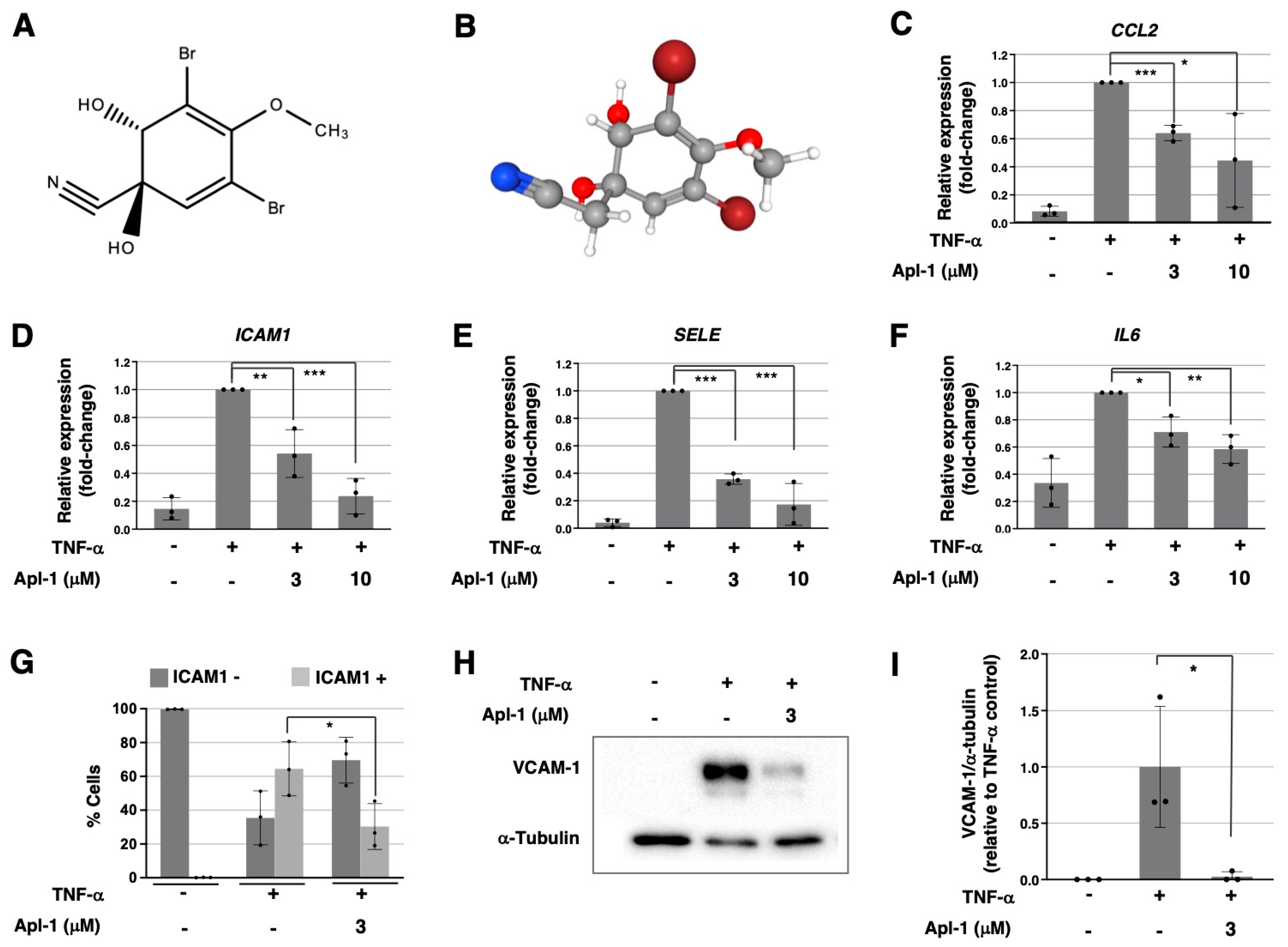
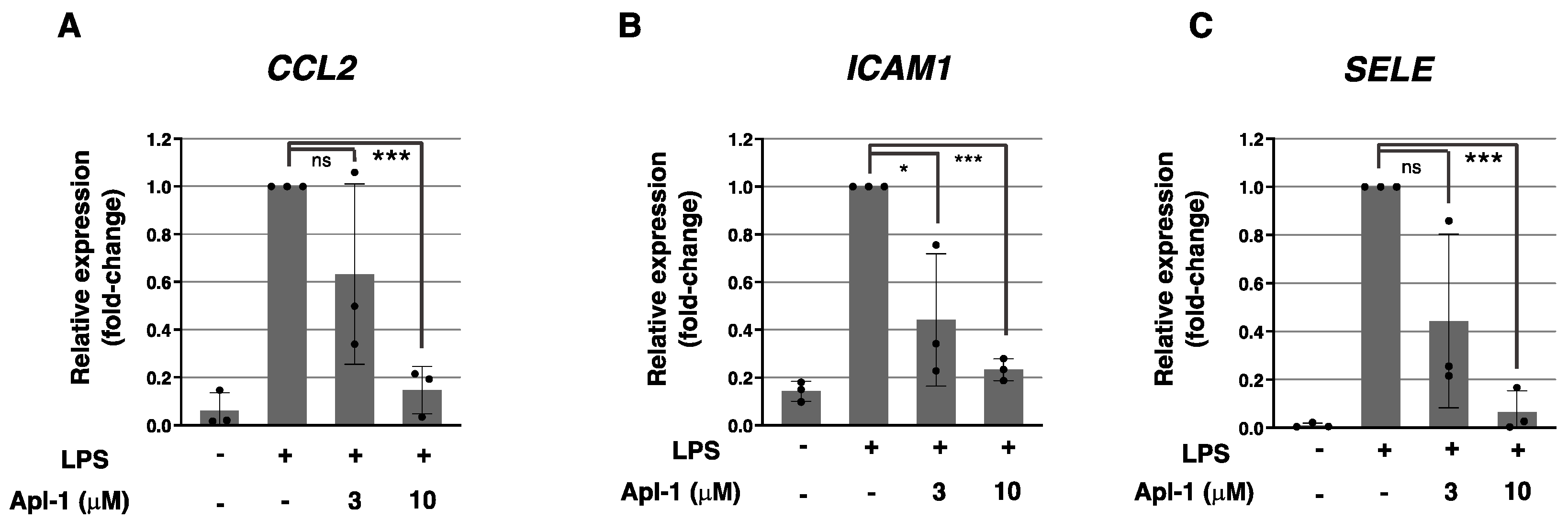
2.1. Aeroplysinin-1 Inhibits the Expression of Inflammation-Related Molecules in ECs
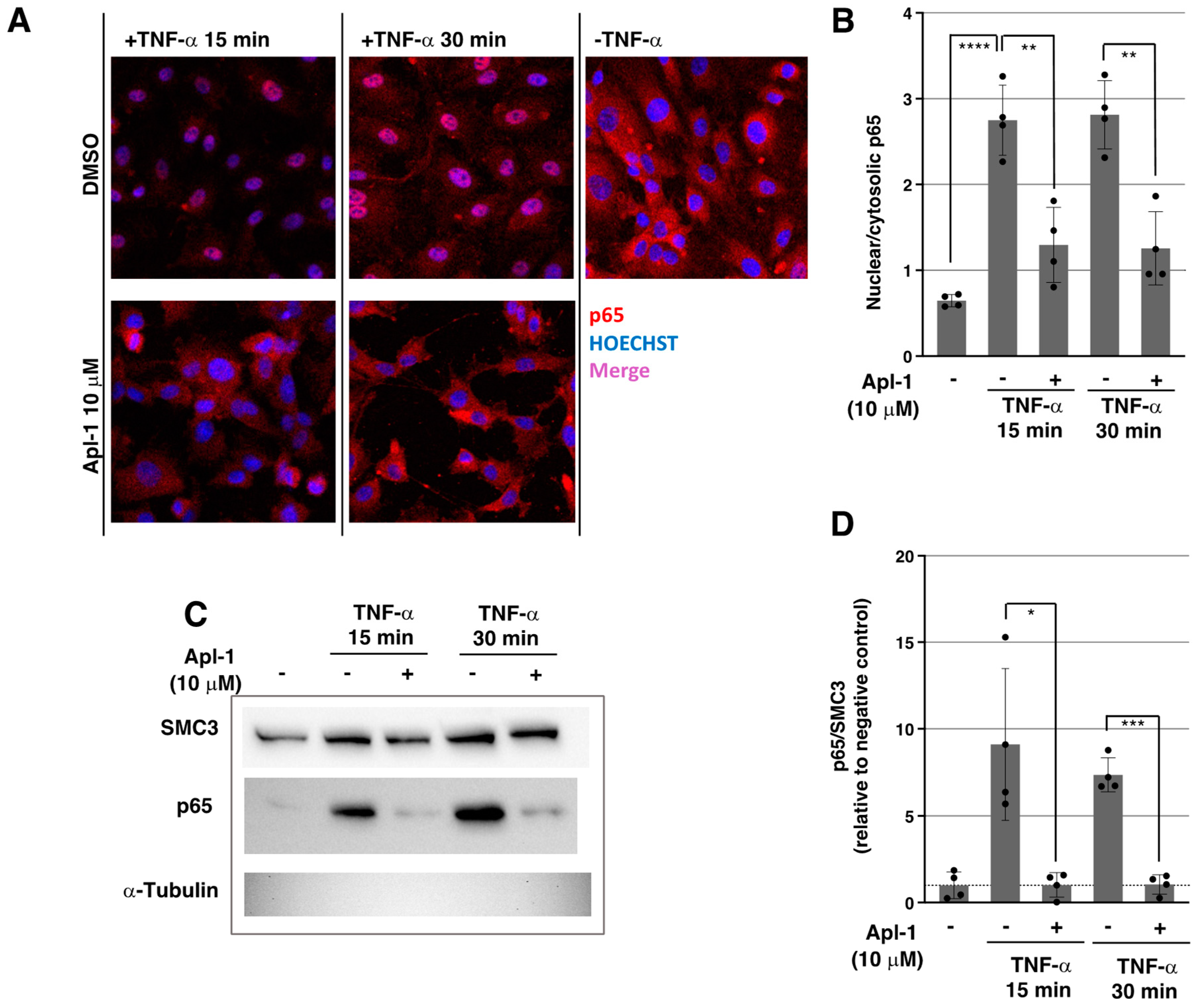
2.2. Apl-1 Impairs NF-κB Nuclear Translocation in Response to TNF-α in ECs
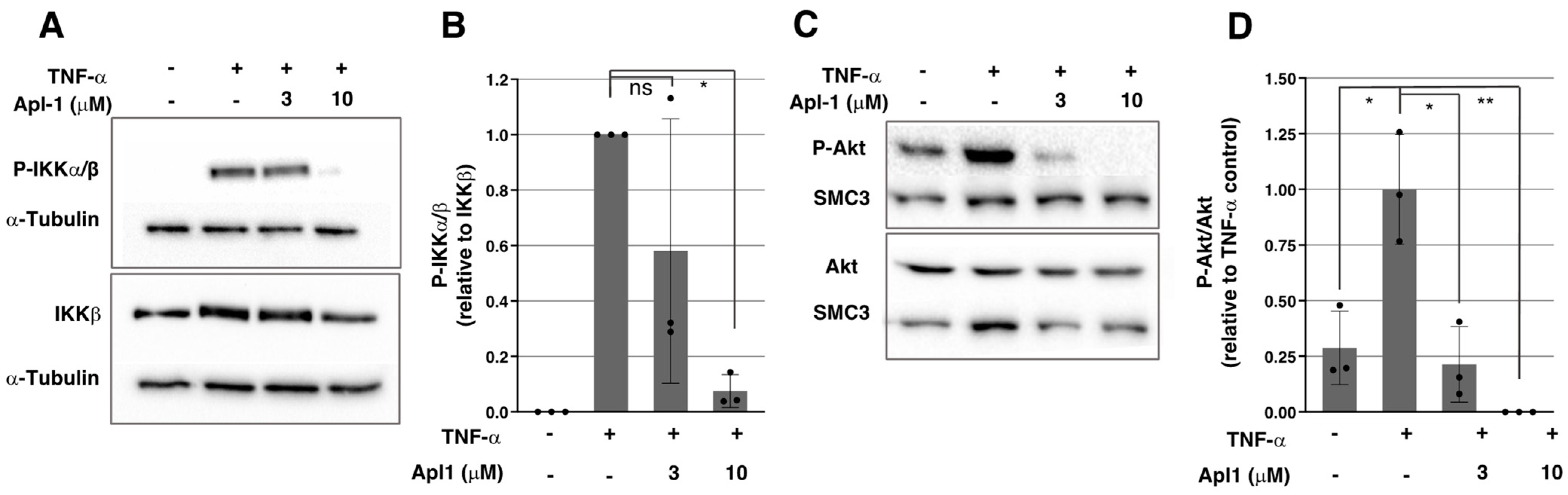
2.3. Apl-1 Inhibits IKKα/β Phosphorylation in ECs
2.4. Activation of the PI3K/Akt Pathway Is Inhibited by Apl-1 in ECs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
4.2. Gene Expression Analysis by Real-Time Quantitative PCR
4.3. Protein Detection by Western Blot
4.4. ICAM-1 Detection by Flow Cytometry
4.5. RelA/p65 Immunofluorescence in HUVECs
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mussbacher, M.; Schossleitner, K.; Kral-Pointner, J.B.; Salzmann, M.; Schrammel, A.; Schmid, J.A. More than Just a Monolayer: The Multifaceted Role of Endothelial Cells in the Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2022, 24, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; Ishigaki, Y.; Yamada, T.; Gao, J.; Imai, J.; Uno, K.; Kaneko, K.; Ogihara, T.; Shimosawa, T.; et al. Importance of Endothelial NF-κB Signalling in Vascular Remodelling and Aortic Aneurysm Formation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 97, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totoson, P.; Maguin-Gaté, K.; Prati, C.; Wendling, D.; Demougeot, C. Mechanisms of Endothelial Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Lessons from Animal Studies. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Z.; Chang, Y.; Wei, W. Endothelial Dysfunction and Inflammation: Immunity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 6813016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareus, R.; Kotsaki, E.; Xanthoulea, S.; van der Made, I.; Gijbels, M.J.J.; Kardakaris, R.; Polykratis, A.; Kollias, G.; de Winther, M.P.J.; Pasparakis, M. Endothelial Cell-Specific NF-κB Inhibition Protects Mice from Atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehnert, B.; Burkhardt, H.; Wessels, J.T.; Schröder, A.; May, M.J.; Vestweber, D.; Zwerina, J.; Warnatz, K.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Schett, G.; et al. NF-κB Inhibitor Targeted to Activated Endothelium Demonstrates a Critical Role of Endothelial NF-κB in Immune-Mediated Diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16556–16561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl, H.L. Activators and Target Genes of Rel/NF-κB Transcription Factors. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6853–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. NF-κB, the First Quarter-Century: Remarkable Progress and Outstanding Questions. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussbacher, M.; Salzmann, M.; Brostjan, C.; Hoesel, B.; Schoergenhofer, C.; Datler, H.; Hohensinner, P.; Basílio, J.; Petzelbauer, P.; Assinger, A.; et al. Cell Type Specific Roles of NF-KB Linking Inflammation and Thrombosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seigner, J.; Basilio, J.; Resch, U.; de Martin, R. CD40L and TNF Both Activate the Classical NF-κB Pathway, Which Is Not Required for the CD40L Induced Alternative Pathway in Endothelial Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Buring, J.E.; Badimon, L.; Hansson, G.K.; Deanfield, J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Tokgözoğlu, L.; Lewis, E.F. Atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, P.A.; Redmond, E.M. Vascular Endothelium—Gatekeeper of Vessel Health. Atherosclerosis 2016, 248, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. The Changing Landscape of Atherosclerosis. Nature 2021, 592, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirichenko, T.V.; Sukhorukov, V.N.; Markin, A.M.; Nikiforov, N.G.; Liu, P.Y.; Sobenin, I.A.; Tarasov, V.V.; Orekhov, A.N.; Aliev, G. Medicinal Plants as a Potential and Successful Treatment Option in the Context of Atherosclerosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Zhao, J.; Xing, M.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, H.; Ji, A.; Song, S. Current Research Landscape of Marine-Derived Anti-Atherosclerotic Substances. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, K.; Abbas, S.Q.; Shah, S.A.A.; Akhter, N.; Batool, S.; ul Hassan, S.S. Marine Sponges as a Drug Treasure. Biomol. Ther. 2016, 24, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Poveda, B.; Medina, M.Á.; Quesada, A.R. Aeroplysinin-1, A Sponge-Derived Compound with Multi-Target Biological Activity. In Encyclopedia of Marine Biotechnology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1351–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Vilas, J.A.; Martínez-Poveda, B.; Quesada, A.R.; Medina, M.A. Aeroplysinin-1, a Sponge-Derived Multi-Targeted Bioactive Marine Drug. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Nieto, S.; González-Iriarte, M.; Carmona, R.; Muñoz-Chápuli, R.; Medina, M.A.; Quesada, A.R. Antiangiogenic Activity of Aeroplysinin-1, a Brominated Compound Isolated from a Marine Sponge. FASEB J. 2001, 16, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, S.-P.; Lu, M.-C.; El-Shazly, M.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-L.; Yu, S.S.-F.; Liu, Y.-C. The Antileukemic and Anti-Prostatic Effect of Aeroplysinin-1 Is Mediated through ROS-Induced Apoptosis via NOX Activation and Inhibition of HIF-1a Activity. Life 2022, 12, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.E.; Song, G.Y.; Zhou, W.; Goh, S.H.; Na, M.K.; Oh, S. Cytotoxic Activity of Aeroplysinin-1 against Colon Cancer Cells by Promoting β-Catenin Degradation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 93, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechmann, N.; Ehrlich, H.; Eisenhofer, G.; Ehrlich, A.; Meschke, S.; Ziegler, C.G.; Bornstein, S.R. Anti-Tumorigenic and Anti-Metastatic Activity of the Sponge-Derived Marine Drugs Aeroplysinin-1 and Isofistularin-3 against Pheochromocytoma in Vitro. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Poveda, B.; García-Vilas, J.A.; Cárdenas, C.; Melgarejo, E.; Quesada, A.R.; Medina, M.A. The Brominated Compound Aeroplysinin-1 Inhibits Proliferation and the Expression of Key pro-Inflammatory Molecules in Human Endothelial and Monocyte Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Fazal, F. Blocking NF-KB: An Inflammatory Issue. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2011, 8, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The Complexity of NF-κB Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Manning, B.D.; Cantley, L.C. Targeting the PI3K-Akt Pathway in Human Cancer. Cancer Cell 2003, 4, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozes, O.N.; Mayo, L.D.; Gustin, J.A.; Pfeffer, S.R.; Pfeffer, L.M.; Donner, D.B. NF-KappaB Activation by Tumour Necrosis Factor Requires the Akt Serine-Threonine Kinase. Nature 1999, 401, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romashkova, J.A.; Makarov, S.S. NF-κB Is a Target of AKT in Anti-Apoptotic PDGF Signalling. Nature 1999, 401, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesson-Welsh, L.; Dejana, E.; McDonald, D.M. Permeability of the Endothelial Barrier: Identifying and Reconciling Controversies. Trends Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaffar, H.; Martino, N.; Garrett, J.P.; Adam, A.P. Interleukin-6 Promotes a Sustained Loss of Endothelial Barrier Function via Janus Kinase-Mediated STAT3 Phosphorylation and de Novo Protein Synthesis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2018, 314, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botts, S.R.; Fish, J.E.; Howe, K.L. Dysfunctional Vascular Endothelium as a Driver of Atherosclerosis: Emerging Insights into Pathogenesis and Treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 787541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nus, M.; Martinez-Poveda, B.; MacGrogan, D.; Chevre, R.; D’Amato, G.; Sbroggio, M.; Rodriguez, C.; Martinez-Gonzalez, J.; Andrés, V.; Hidalgo, A.; et al. Endothelial Jag1-RBPJ Signalling Promotes Inflammatory Leucocyte Recruitment and Atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 112, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goebeler, M.; Kilian, K.; Gillitzer, R.; Kunz, M.; Yoshimura, T.; Bröcker, E.B.; Rapp, U.R.; Ludwig, S. The MKK6/P38 Stress Kinase Cascade Is Critical for Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha-Induced Expression of Monocyte-Chemoattractant Protein-1 in Endothelial Cells. Blood 1999, 93, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid, L.V.; Mayo, M.W.; Reuther, J.Y.; Baldwin, A.S. Akt Stimulates the Transactivation Potential of the RelA/P65 Subunit of NF-κB through Utilization of the IκB Kinase and Activation of the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase P38. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18934–18940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Poveda, B.; Quesada, A.R.; Medina, M.A. (+)-Aeroplysinin-1 Inhibits Akt and Erk Pathway Signaling Selectively in Endothelial Cells. Integr. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2015, 2, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.B.; Rudd, D.; Smith, J.; Kotiw, M.; Mouatt, P.; Seymour, L.M.; Liu, L.; Benkendorff, K. Anti-Inflammatory Activity and Structure-Activity Relationships of Brominated Indoles from a Marine Mollusc. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCauley, E.P.; Lam, H.; Lorig-Roach, N.; Luu, J.; Lloyd, C.; Tenney, K.; Pietraszkiewicz, H.; Diaz, C.; Valeriote, F.A.; Auerbuch, V.; et al. Investigation of the Physical and Bioactive Properties of Bromo- and Iodo-Containing Sponge-Derived Compounds Possessing an Oxyphenylethanamine Core. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 3255–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virmani, R.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Burke, A.P.; Finn, A.V.; Gold, H.K.; Tulenko, T.N.; Wrenn, S.P.; Narula, J. Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression and Vulnerability to Rupture: Angiogenesis as a Source of Intraplaque Hemorrhage. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 2054–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedding, D.G.; Boyle, E.C.; Demandt, J.A.F.; Sluimer, J.C.; Dutzmann, J.; Haverich, A.; Bauersachs, J. Vasa Vasorum Angiogenesis: Key Player in the Initiation and Progression of Atherosclerosis and Potential Target for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulton, K.S.; Heller, E.; Konerding, M.A.; Flynn, E.; Palinski, W.; Folkman, J. Angiogenesis Inhibitors Endostatin or TNP-470 Reduce Intimal Neovascularization and Plaque Growth in Apolipoprotein E—Deficient Mice. Circulation 1999, 99, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, K.S.; Vakili, K.; Zurakowski, D.; Soliman, M.; Butterfield, C.; Sylvin, E.; Lo, K.-M.; Gillies, S.; Javaherian, K.; Folkman, J. Inhibition of Plaque Neovascularization Reduces Macrophage Accumulation and Progression of Advanced Atherosclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4736–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Poveda, B.; Rodríguez-Nieto, S.; García-Caballero, M.; Medina, M.Á.; Quesada, A.R. The Antiangiogenic Compound Aeroplysinin-1 Induces Apoptosis in Endothelial Cells by Activating the Mitochondrial Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2033–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Vilas, J.A.; Martínez-Poveda, B.; Quesada, A.R.; Medina, M.Á. (+)-Aeroplysinin-1 Modulates the Redox Balance of Endothelial Cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vidal, I.; Castilla, L.; Marrero, A.D.; Bravo-Ruiz, I.; Bernal, M.; Manrique, I.; R. Quesada, A.; Medina, M.Á.; Martínez-Poveda, B. The Sponge-Derived Brominated Compound Aeroplysinin-1 Impairs the Endothelial Inflammatory Response through Inhibition of the NF-κB Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100605
Vidal I, Castilla L, Marrero AD, Bravo-Ruiz I, Bernal M, Manrique I, R. Quesada A, Medina MÁ, Martínez-Poveda B. The Sponge-Derived Brominated Compound Aeroplysinin-1 Impairs the Endothelial Inflammatory Response through Inhibition of the NF-κB Pathway. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(10):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100605
Chicago/Turabian StyleVidal, Isabel, Laura Castilla, Ana Dácil Marrero, Inés Bravo-Ruiz, Manuel Bernal, Inmaculada Manrique, Ana R. Quesada, Miguel Ángel Medina, and Beatriz Martínez-Poveda. 2022. "The Sponge-Derived Brominated Compound Aeroplysinin-1 Impairs the Endothelial Inflammatory Response through Inhibition of the NF-κB Pathway" Marine Drugs 20, no. 10: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100605
APA StyleVidal, I., Castilla, L., Marrero, A. D., Bravo-Ruiz, I., Bernal, M., Manrique, I., R. Quesada, A., Medina, M. Á., & Martínez-Poveda, B. (2022). The Sponge-Derived Brominated Compound Aeroplysinin-1 Impairs the Endothelial Inflammatory Response through Inhibition of the NF-κB Pathway. Marine Drugs, 20(10), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100605






