In Silico Analysis of Tetrodotoxin Binding in Voltage-Gated Sodium Ion Channels from Toxin-Resistant Animal Lineages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
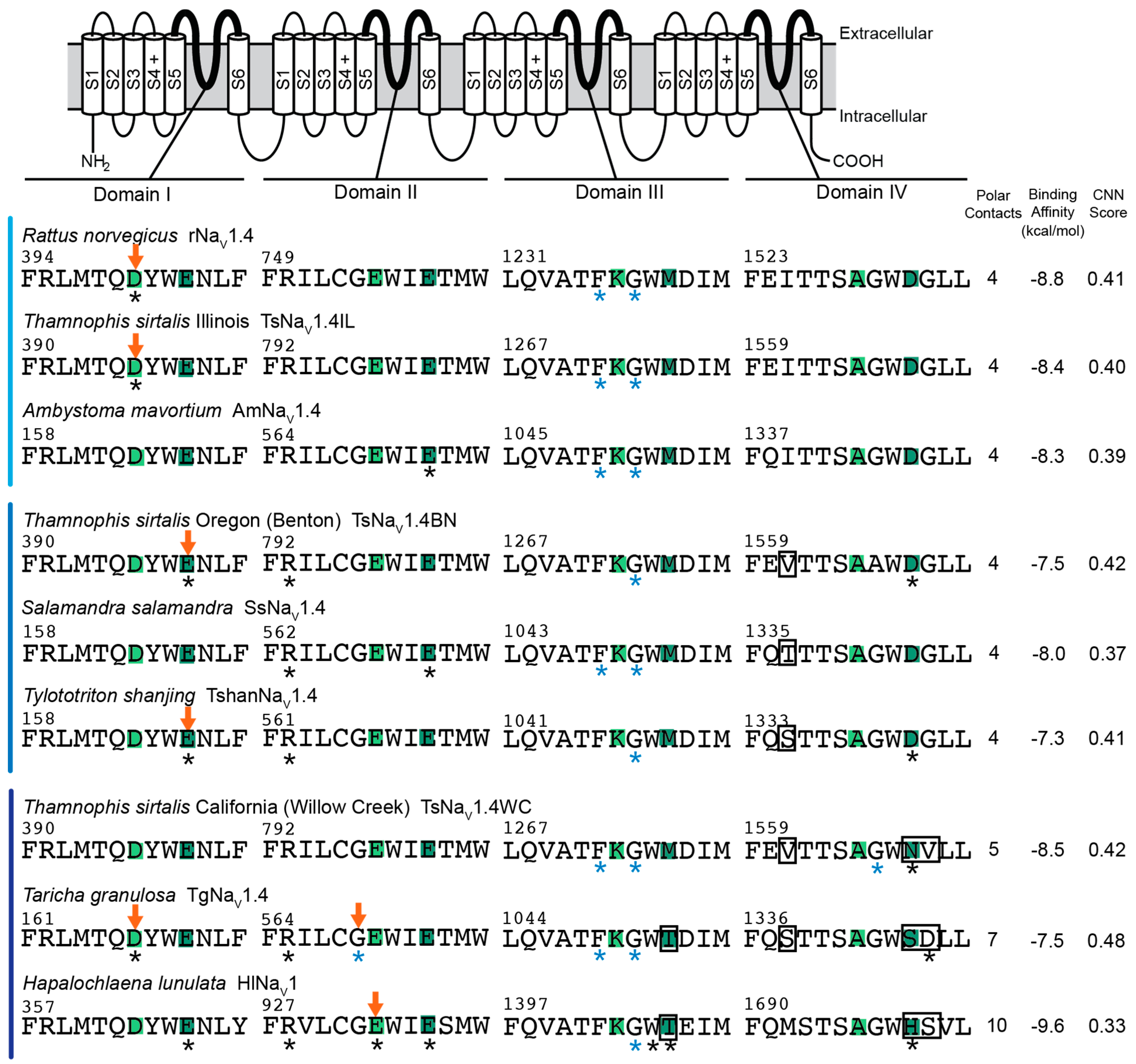
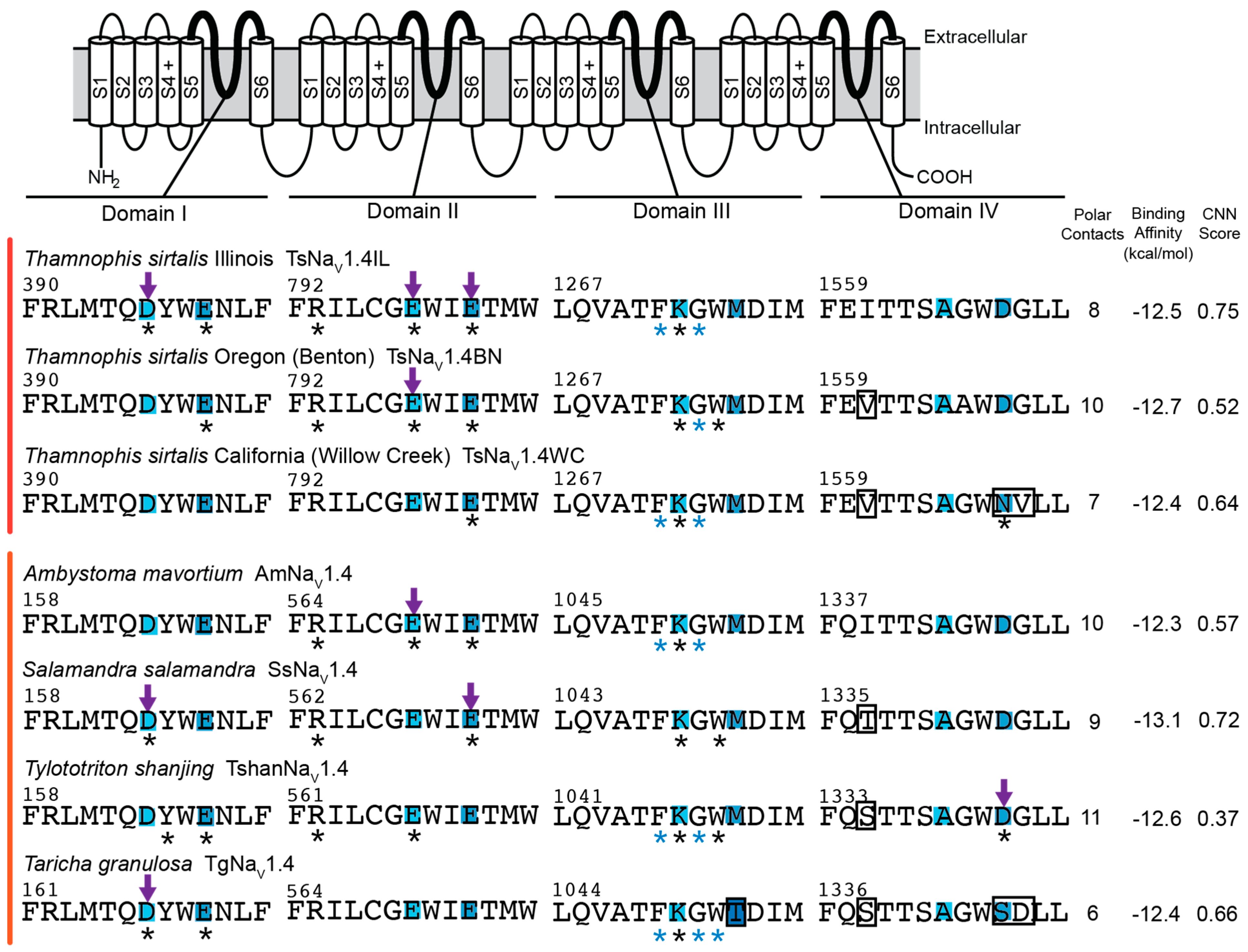
2.1. Overall Results
2.2. Polar Contact Number
2.3. Polar Contact Position Shifts
2.4. Binding Affinity and CNN Scoring of TTX Poses
3. Methods
3.1. Homology Modeling and Sampling
3.2. TTX Docking
3.3. Structure Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agrawal, A.A. Toward a Predictive Framework for Convergent Evolution: Integrating Natural History, Genetic Mechanisms, and Consequences for the Diversity of Life. Am. Nat. 2017, 190, S1–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Thiel, J.; Khan, M.A.; Wouters, R.M.; Harris, R.J.; Casewell, N.R.; Fry, B.G.; Kini, R.M.; Mackessy, S.P.; Vonk, F.J.; Wuster, W.; et al. Convergent evolution of toxin resistance in animals. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2022, 97, 1823–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fish, F.E. Secondary Evolution of Aquatic Propulsion in Higher Vertebrates: Validation and Prospect. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2016, 56, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.E. Convergence in ecomorphology and guild structure among marsupial and placental carnivores. Predat. Pouches Biol. Carniv. Marsupials 2003, 285–296. [Google Scholar]
- Dobler, S.; Dalla, S.; Wagschal, V.; Agrawal, A.A. Community-wide convergent evolution in insect adaptation to toxic cardenolides by substitutions in the Na, K-ATPase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13040–13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zakon, H.H. Convergent evolution on the molecular level. Brain Behav. Evol. 2002, 59, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, G.; Hanifin, C.; Geffeney, S.; Brodie, E.D. Chapter Four—Convergent Evolution of Tetrodotoxin-Resistant Sodium Channels in Predators and Prey. In Current Topics in Membranes; French, R.J., Noskov, S.Y., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 78, pp. 87–113. [Google Scholar]
- Gendreau, K.L.; Hornsby, A.D.; Hague, M.T.J.; McGlothlin, J.W. Gene Conversion Facilitates the Adaptive Evolution of Self-Resistance in Highly Toxic Newts. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 4077–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifin, C.T.; Gilly, W.F. Evolutionary history of a complex adaptation: Tetrodotoxin resistance in salamanders. Evolution 2015, 69, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geffeney, S.L.; Fujimoto, E.; Brodie, E.D.; Brodie, E.D.; Ruben, P.C. Evolutionary diversification of TTX-resistant sodium channels in a predator—Prey interaction. Nature 2005, 434, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlothlin, J.W.; Kobiela, M.E.; Feldman, C.R.; Castoe, T.A.; Geffeney, S.L.; Hanifin, C.T.; Toledo, G.; Vonk, F.J.; Richardson, M.K.; Brodie, E.D., Jr.; et al. Historical Contingency in a Multigene Family Facilitates Adaptive Evolution of Toxin Resistance. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffeney, S.L.; Williams, B.L.; Rosenthal, J.J.C.; Birk, M.A.; Felkins, J.; Wisell, C.M.; Curry, E.R.; Hanifin, C.T. Convergent and parallel evolution in a voltage-gated sodium channel underlies TTX-resistance in the Greater Blue-ringed Octopus: Hapalochlaena lunulata. Toxicon 2019, 170, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanifin, C.T.; Kudo, Y.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M. Chemical Ecology of the North American Newt Genera Taricha and Notophthalmus. In Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products 118; Kinghorn, A.D., Falk, H., Gibbons, S., Asakawa, Y., Liu, J.-K., Dirsch, V.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 101–130. [Google Scholar]
- Asakawa, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Umezaki, K.; Kaneko, K.; Yu, X.; Gomez-Delan, G.; Tomano, S.; Noguchi, T.; Ohtsuka, S. Toxicity and Toxin Composition of the Greater Blue-Ringed Octopus Hapalochlaena lunulata from Ishigaki Island, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. Toxins 2019, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheumack, D.D.; Howden, M.E.H.; Spence, I.; Quinn, R.J. Maculotoxin: A Neurotoxin from the Venom Glands of the Octopus Hapalochlaena maculosa Identified as Tetrodotoxin. Science 1978, 199, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.L.; Stark, M.R.; Caldwell, R.L. Microdistribution of tetrodotoxin in two species of blue-ringed octopuses (Hapalochlaena lunulata and Hapalochlaena fasciata) detected by fluorescent immunolabeling. Toxicon 2012, 60, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Mebs, D.; Flachsenberger, W. Distribution of tetrodotoxin in the body of the blue-ringed octopus (Hapalochlaena maculosa). Toxicon 2007, 49, 410–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifin, C.T.; Brodie, E.D.; Brodie, E.D. Phenotypic mismatches reveal escape from arms-race coevolution. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hague, M.T.J.; Stokes, A.N.; Feldman, C.R.; Brodie, E.D., Jr.; Brodie, E.D., 3rd. The geographic mosaic of arms race coevolution is closely matched to prey population structure. Evol. Lett. 2020, 4, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimche, J.S.; Brodie, E.D., Jr.; Stokes, A.N.; Ely, E.J.; Moniz, H.A.; Thill, V.L.; Hallas, J.M.; Pfrender, M.E.; Brodie, E.D., 3rd; Feldman, C.R. The geographic mosaic in parallel: Matching patterns of newt tetrodotoxin levels and snake resistance in multiple predator-prey pairs. J. Anim. Ecol. 2020, 89, 1645–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimche, J.S.; del Carlo, R.E.; Brodie, E.D., Jr.; McGlothlin, J.W.; Schlauch, K.; Pfrender, M.E.; Brodie, E.D., III; Leblanc, N.; Feldman, C.R. The road not taken: Evolution of tetrodotoxin resistance in the Sierra garter snake (Thamnophis couchii) by a path less travelled. Mol. Ecol. 2022, 31, 3827–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakon, H.H. Adaptive evolution of voltage-gated sodium channels: The first 800 million years. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109 (Suppl. 1), 10619–10625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noda, M.; Numa, S. Structure and Function of Sodium Channel. J. Recept. Res. 1987, 7, 467–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capes, D.L.; Arcisio-Miranda, M.; Jarecki, B.W.; French, R.J.; Chanda, B. Gating transitions in the selectivity filter region of a sodium channel are coupled to the domain IV voltage sensor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2648–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cervenka, R.; Zarrabi, T.; Lukacs, P.; Todt, H. The Outer Vestibule of the Na+ Channel–Toxin Receptor and Modulator of Permeation as Well as Gating. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1373–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Favre, I.; Moczydlowski, E.; Schild, L. On the structural basis for ionic selectivity among Na+, K+, and Ca2+ in the voltage-gated sodium channel. Biophys. J. 1996, 71, 3110–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.-J.; Favre, I.; Moczydlowski, E. Permeation of Large Tetra-Alkylammonium Cations through Mutant and Wild-Type Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels as Revealed by Relief of Block at High Voltage. J. Gen. Physiol. 2000, 115, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otagiri, T.; Kijima, K.; Osawa, M.; Ishii, K.; Makita, N.; Matoba, R.; Umetsu, K.; Hayasaka, K. Cardiac ion channel gene mutations in sudden infant death syndrome. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 64, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-M.; Favre, I.; Schild, L.; Moczydlowski, E. On the Structural Basis for Size-selective Permeation of Organic Cations through the Voltage-gated Sodium Channel: Effect of Alanine Mutations at the DEKA Locus on Selectivity, Inhibition by Ca2+ and H+, and Molecular Sieving. J. Gen. Physiol. 1997, 110, 693–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terlau, H.; Heinemann, S.H.; Stuhmer, W.; Pusch, M.; Conti, F.; Imoto, K.; Numa, S. Mapping the site of block by tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin of sodium channel II. FEBS Lett. 1991, 293, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todt, H.; Dudley, S.C.; Kyle, J.W.; French, R.J.; Fozzard, H.A. Ultra-Slow Inactivation in μ1 Na+ Channels Is Produced by a Structural Rearrangement of the Outer Vestibule. Biophys. J. 1999, 76, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vilin, Y.Y.; Fujimoto, E.; Ruben, P.C. A Single Residue Differentiates between Human Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle Na+ Channel Slow Inactivation. Biophys. J. 2001, 80, 2221–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Y.; Nomura, Y.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Z.Y.; Dong, K. Functional Expression of an Arachnid Sodium Channel Reveals Residues Responsible for Tetrodotoxin Resistance in Invertebrate Sodium Channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 33869–33875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, G.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Shang, L.; Yasumoto, T.; Dudley, S.C. Interactions of the C-11 Hydroxyl of Tetrodotoxin with the Sodium Channel Outer Vestibule. Biophys. J. 2003, 84, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahern, C.A.; Payandeh, J.; Bosmans, F.; Chanda, B. The hitchhiker’s guide to the voltage-gated sodium channel galaxy. J. Gen. Physiol 2016, 147, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cannon, S.C. Sodium Channelopathies of Skeletal Muscle. Handb Exp. Pharm. 2018, 246, 309–330. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Z. Structural Advances in Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 908867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzotti, J.L.; Fozzard, H.A.; Lipkind, G.M.; Dudley, S.C. Differences in Saxitoxin and Tetrodotoxin Binding Revealed by Mutagenesis of the Na+ Channel Outer Vestibule. Biophys. J. 1998, 75, 2647–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santarelli, V.P.; Eastwood, A.L.; Dougherty, D.A.; Horn, R.; Ahern, C.A. A Cation-π Interaction Discriminates among Sodium Channels That Are Either Sensitive or Resistant to Tetrodotoxin Block. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 8044–8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tikhonov, D.B.; Zhorov, B.S. Possible roles of exceptionally conserved residues around the selectivity filters of sodium and calcium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 2998–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, H.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Pan, X.; Wu, J.; Cristofori-Armstrong, B.; Smith, J.J.; Chin, Y.K.Y.; Lei, J.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Structural basis for the modulation of voltage-gated sodium channels by animal toxins. Science 2018, 362, 6412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, H.; Liu, D.; Wu, K.; Lei, J.; Yan, N. Structures of human Nav1.7 channel in complex with auxiliary subunits and animal toxins. Science 2019, 363, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Shen, H.; Wu, K.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Lei, J.; et al. Structure of the human voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.4 in complex with beta1. Science 2018, 362, 6412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNutt, A.T.; Francoeur, P.; Aggarwal, R.; Masuda, T.; Meli, R.; Ragoza, M.; Sunseri, J.; Koes, D.R. GNINA 1.0: Molecular docking with deep learning. J. Cheminform. 2021, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.J.; Schild, L.; Moczydlowski, E.G. Use-dependent block of the voltage-gated Na(+) channel by tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin: Effect of pore mutations that change ionic selectivity. J. Gen. Physiol. 2012, 140, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ragoza, M.; Hochuli, J.; Idrobo, E.; Sunseri, J.; Koes, D.R. Protein-Ligand Scoring with Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 942–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 2011, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrödinger, L.; DeLano, W. PyMOL. Available online: http://www.pymol.org/pymol (accessed on 20 August 2021).
- Kabsch, W.; Sander, C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: Pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers 1983, 22, 2577–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blount, Z.D.; Lenski, R.E.; Losos, J.B. Contingency and determinism in evolution: Replaying life’s tape. Science 2018, 362, eaam5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reiskind, M.O.B.; Moody, M.L.; Bolnick, D.I.; Hanifin, C.T.; Farrior, C.E. Nothing in Evolution Makes Sense Except in the Light of Biology. Bioscience 2021, 71, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geffeney, S.L.; Cordingley, J.A.; Mitchell, K.; Hanifin, C.T. In Silico Analysis of Tetrodotoxin Binding in Voltage-Gated Sodium Ion Channels from Toxin-Resistant Animal Lineages. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110723
Geffeney SL, Cordingley JA, Mitchell K, Hanifin CT. In Silico Analysis of Tetrodotoxin Binding in Voltage-Gated Sodium Ion Channels from Toxin-Resistant Animal Lineages. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(11):723. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110723
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeffeney, Shana L., Jennie Ann Cordingley, Kenyon Mitchell, and Charles T. Hanifin. 2022. "In Silico Analysis of Tetrodotoxin Binding in Voltage-Gated Sodium Ion Channels from Toxin-Resistant Animal Lineages" Marine Drugs 20, no. 11: 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110723
APA StyleGeffeney, S. L., Cordingley, J. A., Mitchell, K., & Hanifin, C. T. (2022). In Silico Analysis of Tetrodotoxin Binding in Voltage-Gated Sodium Ion Channels from Toxin-Resistant Animal Lineages. Marine Drugs, 20(11), 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110723







