New Guanidine Alkaloids Batzelladines O and P from the Marine Sponge Monanchora pulchra Induce Apoptosis and Autophagy in Prostate Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Batzelladines O and P
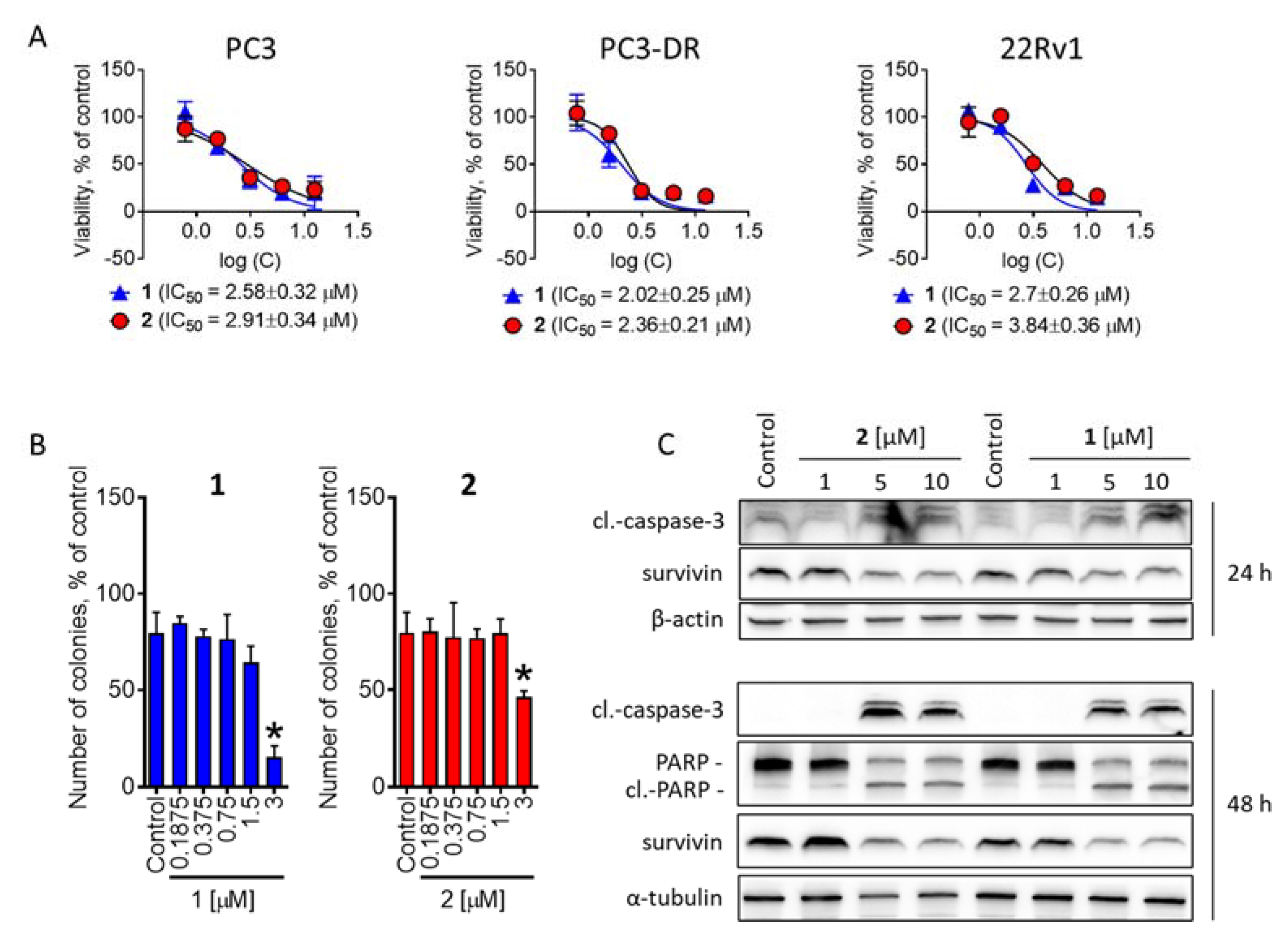
2.2. Investigation of Cytotoxic Activity in Human Prostate Cancer Cells
2.3. Batzelladines O and P Induce Cytoprotective Autophagy in Prostate Cancer Cells
2.4. Examination of the Effect on P-Glycoprotein Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Compound Characterization Data
3.5. Quantum Chemical Modeling
3.6. Reagents and Antibodies for Bioactivity Assay
3.7. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
3.8. MTT Assay
3.9. Western Blotting
3.10. Drug Combination Studies
3.11. P-Glycoprotein Activity Analysis
3.12. Data and Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berlinck, R.G.S.; Bertonha, A.F.; Takaki, M.; Rodriguez, J.P.G. The chemistry and biology of guanidine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 1264–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 122–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Moazami, Y.; Pierce, J.G. Structure, synthesis and biological properties of the pentacyclic guanidinium alkaloids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 2817–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamann, M.T.; Gul, W.; Hammond, N.L.; Yousaf, M.; Bowling, J.J.; Schinazi, R.F.; Wirtz, S.S.; Andrews, G.D.C.; Cuevas, C. Modification at the C9 position of the marine natural product isoaaptamine and the impact on HIV-1, mycobacterial, and tumor cell activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 8495–8505. [Google Scholar]
- Guzii, A.G.; Makarieva, T.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kuzmich, A.S.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Krasokhin, V.B.; Stonik, V.A. Monanchocidin: A new apoptosis-inducing polycyclic guanidine alkaloid from the marine sponge Monanchora pulchra. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4292–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Tabakmaher, K.M.; Guzii, A.G.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kuzmich, A.S.; Lee, H.-S.; Stonik, V.A. Monanchomycalins A and B, unusual guanidine alkaloids from the sponge Monanchora pulchra. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 4228–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Tabakmaher, K.M.; Guzii, A.G.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Shubina, L.K.; Kuzmich, A.S.; Lee, H.S.; Stonik, V.A. Monanchocidins B-E: Polycyclic guanidine alkaloids with potent antileukemic activities from the sponge Monanchora pulchra. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1952–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzii, A.G.; Makarieva, T.N.; Korolkova, Y.V.; Andreev, Y.A.; Mosharova, I.V.; Tabakmaher, K.M.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Ogurtsova, E.K.; Antonov, A.S.; et al. Pulchranin A, isolated from the Far-Eastern marine sponge, Monanchora pulchra: The first marine non-peptide inhibitor of TRPV-1 channels. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensemhoun, J.; Bombarda, I.; Aknin, M.; Vacelet, J.; Gaydou, E.M. Ptilomycalin D, a Polycyclic Guanidine Alkaloid from the Marine Sponge Monanchora dianchora. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 2033–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallimore, W.A.; Kelly, M.; Scheuer, P.J. Alkaloids from the sponge Monanchora unguifera. J. Nat.Prod. 2005, 68, 1420–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Tabakmakher, K.M.; Hauschild, J.; Shchekaleva, R.K.; Otte, K.; Guzii, A.G.; Makarieva, T.N.; Kudryashova, E.K.; Fedorov, S.N.; Shubina, L.K.; et al. Guanidine alkaloids from the marine sponge Monanchora pulchra show cytotoxic properties and prevent EGF-induced neoplastic transformation in vitro. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Kaune, M.; Kriegs, M.; Hauschild, J.; Busenbender, T.; Shubina, L.K.; Makarieva, T.N.; Hoffer, K.; Bokemeyer, C.; Graefen, M.; et al. Marine alkaloid monanchoxymycalin C: A new specific activator of JNK1/2 kinase with anticancer properties. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Kudryashova, E.K.; Kaune, M.; Makarieva, T.N.; Shubina, L.K.; Busenbender, T.; Denisenko, V.A.; Popov, R.S.; Hauschild, J.; Fedorov, S.N.; et al. Urupocidin C: A new marine guanidine alkaloid which selectively kills prostate cancer cells via mitochondria targeting. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Hauschild, J.; Amann, K.; Tabakmakher, K.M.; Venz, S.; Walther, R.; Guzii, A.G.; Makarieva, T.N.; Shubina, L.K.; Fedorov, S.N.; et al. Marine alkaloid monanchocidin A overcomes drug resistance by induction of autophagy and lysosomal membrane permeabilization. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17328–17341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Venz, S.; Hauschild, J.; Tabakmakher, K.M.; Otte, K.; Madanchi, R.; Walther, R.; Guzii, A.G.; Makarieva, T.N.; Shubina, L.K.; et al. Anti-migratory activity of marine alkaloid monanchocidin A—proteomics-based discovery and confirmation. Proteomics 2016, 16, 1590–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubiolo, J.A.; Lopez-Alonso, H.; Roel, M.; Vieytes, M.R.; Thomas, O.; Ternon, E.; Vega, F.V.; Botana, L.M. Mechanism of cytotoxic action of crambescidin-816 on human liver-derived tumour cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 1655–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlinck, R.G.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Bruno, I.; Riccio, R.; Ferri, S.; Spampinato, S.; Speroni, E. Polycyclic guanidine alkaloids from the marine sponge Crambe crambe and Ca++ channel blocker activity of crambescidin 816. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, V.; Vale, C.; Bondu, S.; Thomas, O.P.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Differential effects of crambescins and crambescidin 816 in voltage-gated sodium, potassium and calcium channels in neurons. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2013, 26, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Kong, D.; Matsui, K.; Kobayashi, M. Erythroid differentiation in K562 chronic myelogenous cells induced by crambescidin 800, a pentacyclic guanidine alkaloid. Anticancer Res. 2004, 24, 2325–2330. [Google Scholar]
- Sfecci, E.; Lacour, T.; Amade, P.; Mehiri, M. Polycyclic Guanidine Alkaloids from Poecilosclerida Marine Sponges. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Demerdash, A.; Atanasov, A.G.; Bishayee, A.; Abdel-Mogib, M.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Al-Mourabit, A. Batzella, Crambe and Monanchora: Highly Prolific Marine Sponge Genera Yielding Compounds with Potential Applications for Cancer and Other Therapeutic Areas. Nutrients 2018, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.H.; Sakemi, S.; Burres, N.; McCarthy, P. Isobatzellines A, B, C, and D. Cytotoxic and antifungal pyrroloquinoline alkaloids from the marine sponge Batzella sp. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 55, 4964–4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laville, R.; Thomas, O.P.; Berrué, F.; Marquez, D.; Vacelet, J.; Amade, P. Bioactive Guanidine Alkaloids from Two Caribbean Marine Sponges. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohn, L.K.; Porto, P.S.S.; Bianchi, B.R.; Santos, M.F.C.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; Arns, C.W. NOR-Batzelladine L from the sponge Monanchora sp. displays antiviral acyivity against Herpes Simplex virus type 1. Planta Med. 2012, 78, CL27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, C.; dos Santos, M.F.C.; Berlinck, R.G.S.; Ferreira, P.M.P.; Cavalcanti, B.C. Cytotoxic Batzelladine L from the Brazilian Marine Sponge Monanchora arbuscula. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, B.; Lin, X.; Yang, X.W.; Liu, Y. Marine natural products with anti-HIV activities in the last decade. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 953–973. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, A.D.; Kumar, N.V.; Kokke, W.C.; Bean, M.F.; Freyer, A.J.; Brosse, C.D.; Mai, S.; Truneh, A.; Carte, B. Novel Alkaloids from the Sponge Batzella sp.: Inhibitors of HIV gp120-Human CD4 Binding. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, H.-M.; Peng, J.; Dunbar, D.C.; Schinazi, R.F.; de Castro Andrews, A.G.; Cuevas, C.; Garcia-Fernandez, L.F.; Kelly, M.; Hamann, M.T. Batzelladine alkaloids from the caribbean sponge Monanchora unguifera and the significant activities against HIV-1 and AIDS opportunistic infectious pathogens. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 11179–11188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.F.C.; Harper, P.M.; Williams, D.E.; Mesquita, J.T.; Pinto, É.G.; da Costa-Silva, T.A.; Hajdu, E.; Ferreira, A.G.; Santos, R.A.; Murphy, P.J.; et al. Anti-parasitic Guanidine and Pyrimidine Alkaloids from the Marine Sponge Monanchora arbuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgohary, A.M.; Elfiky, A.A.; Pereira, F.; Abd El-Aziz, T.M.; Sobeh, M.; Arafa, R.K.; El-Demerdash, A. Investigating the structure-activity relationship of marine polycyclic batzelladine alkaloids as promising inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro). Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 147, 105738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shubina, L.K.; Makarieva, T.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Popov, R.S.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Grebnev, B.B.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; von Amsberg, G.; Stonik, V.A. Gracilosulfates A-G, Monosulfated Polyoxygenated Steroids from the Marine Sponge Haliclona gracilis. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Shubina, L.K.; Makarieva, T.N.; Hauschild, J.; Strewinsky, N.; Guzii, A.G.; Menshov, A.S.; Popov, R.S.; Grebnev, B.B.; Busenbender, T.; et al. New diterpenes from the marine sponge Spongionella sp. overcome drug resistance in prostate cancer by inhibition of P-glycoprotein. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Tavares, R.; Hajdu, E.; Van Soest, R.W.M. Novel Polycyclic Guanidine Alkaloids from Two Marine Sponges of the Genus Monanchora. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snider, B.B.; Chen, J. Synthesis of batzelladine E and its E isomer. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 5697–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, S.; Moore, C.M.; Chiong, E.; Beltran, H.; Bristow, R.G.; Williams, S.G. Prostate cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 1075–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, P.S. Targeting the androgen receptor in prostate cancer—A resilient foe. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1067–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampson, N.; Neuwirt, H.; Puhr, M.; Klocker, H.; Eder, I.E. In vitro model systems to study androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2013, 20, R49–R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puhr, M.; Hoefer, J.; Schäfer, G.; Erb, H.H.H.; Oh, S.J.; Klocker, H.; Heidegger, I.; Neuwirt, H.; Culig, Z. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition leads to docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer and is mediated by reduced expression of miR-200c and miR-205. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 2188–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjyrezi, A.; Xie, F.; Voznesensky, O.; Khanna, P.; Calagua, C.; Bai, Y.; Kung, J.; Wu, J.; Corey, E.; Montgomery, B.; et al. Taxane resistance in prostate cancer is mediated by decreased drug-target engagement. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 3287–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, C.; Nadiminty, N.; Lou, W.; Tummala, R.; Evans, C.P.; Gao, A.C. Inhibition of ABCB1 expression overcomes acquired docetaxel resistance in prostate cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Kaune, M.; Hauschild, J.; Kriegs, M.; Hoffer, K.; Busenbender, T.; Smirnova, P.A.; Zhidkov, M.E.; Poverennaya, E.V.; Oh-Hohenhorst, S.J.; et al. Efficacy and Mechanism of Action of Marine Alkaloid 3,10-Dibromofascaplysin in Drug-Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klionsky, D.J.; Abdel-Aziz, A.K.; Abdelfatah, S.; Abdellatif, M.; Abdoli, A.; Abel, S.; Abeliovich, H.; Abildgaard, M.H.; Abudu, Y.P.; Acevedo-Arozena, A.; et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (4th edition). Autophagy 2021, 17, 1–382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tanida, I.; Ueno, T.; Kominami, E. LC3 and Autophagy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 445, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dossou, A.S.; Basu, A. The Emerging Roles of mTORC1 in Macromanaging Autophagy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-T.; Tan, H.-L.; Shui, G.; Bauvy, C.; Huang, Q.; Wenk, M.R.; Ong, C.-N.; Codogno, P.; Shen, H.-M. Dual Role of 3-Methyladenine in Modulation of Autophagy via Different Temporal Patterns of Inhibition on Class I and III Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 10850–10861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hippert, M.M.; O’Toole, P.S.; Thorburn, A. Autophagy in cancer: Good, bad, or both? Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9349–9351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.; Karantza-Wadsworth, V.; White, E. Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Pelageev, D.N.; Hauschild, J.; Sabutskii, Y.E.; Khmelevskaya, E.A.; Krisp, C.; Kaune, M.; Venz, S.; Borisova, K.L.; Busenbender, T.; et al. Inspired by sea urchins: Warburg effect mediated selectivity of novel synthetic non-glycoside 1,4-naphthoquinone-6S-glucose conjugates in prostate cancer. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.; Wennerberg, K.; Aittokallio, T.; Tang, J. Searching for Drug Synergy in Complex Dose–Response Landscapes Using an Interaction Potency Model. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A.K.; Aittokallio, T. SynergyFinder 2.0: Visual analytics of multi-drug combination synergies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W488–W493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16 Software, Revision A.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford. CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
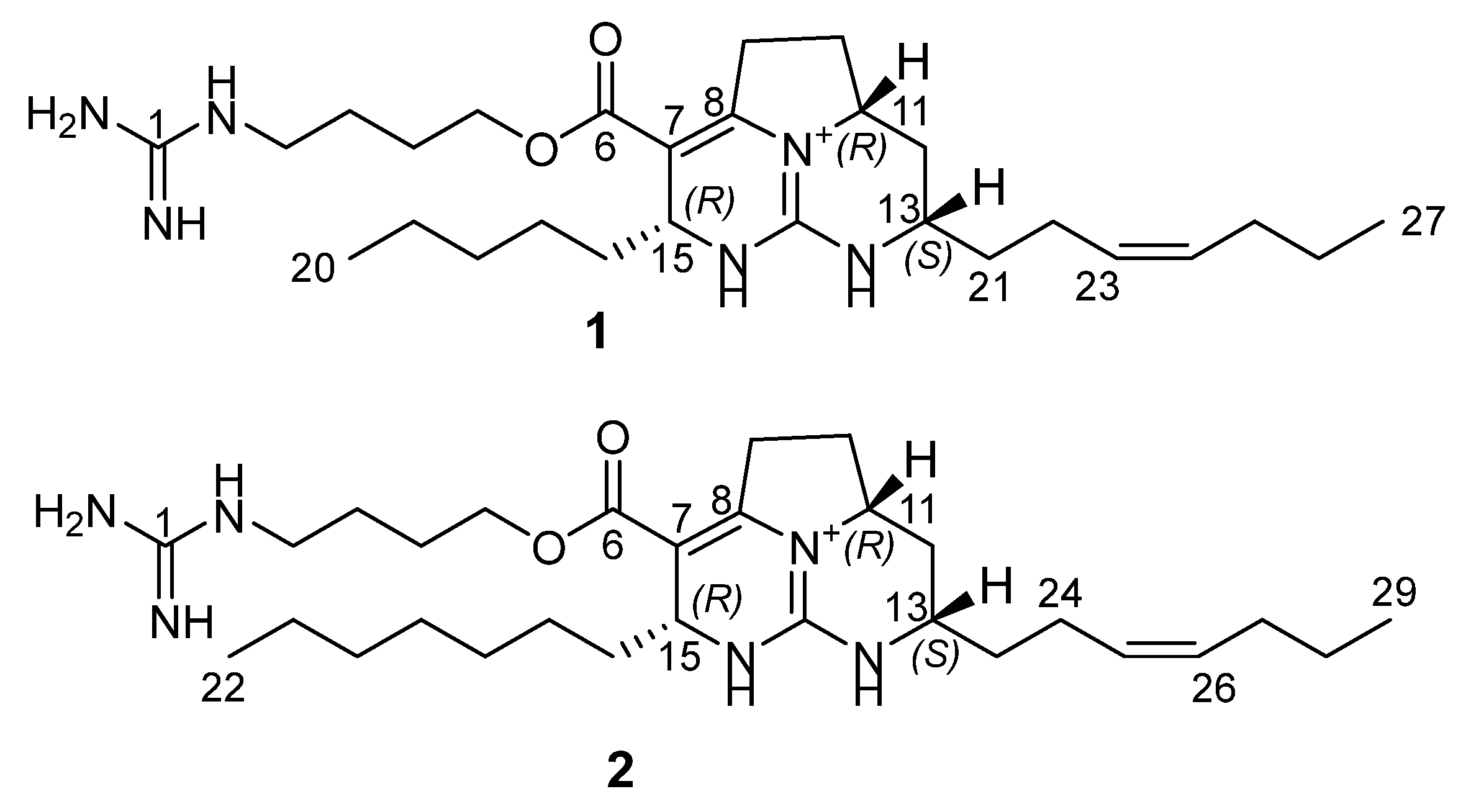
 ), HMBC (
), HMBC (  ), and ROESY (
), and ROESY (  ) correlations for 1.
) correlations for 1.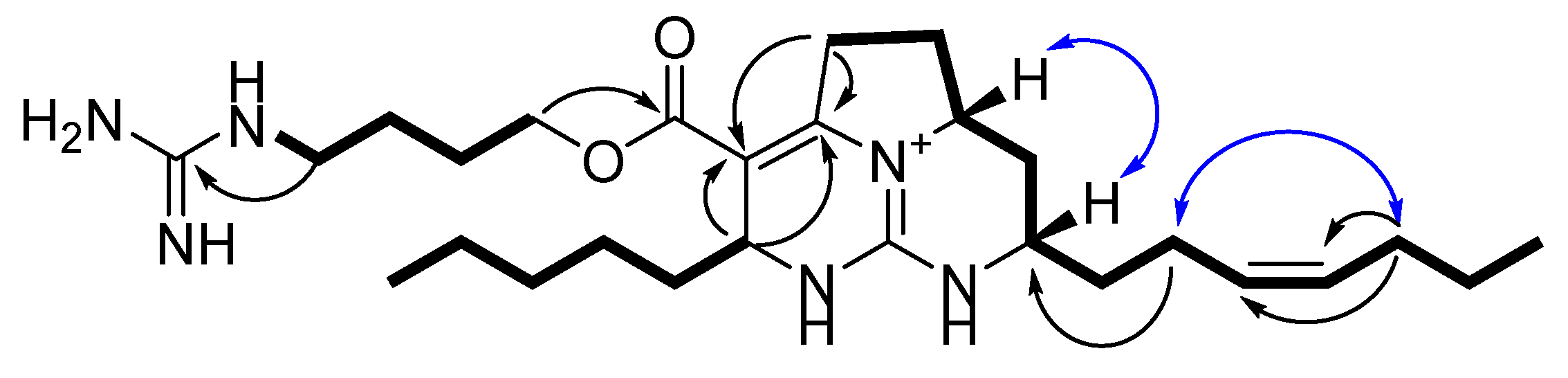



| 1 | 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| position | δH (J in Hz) | δC a type | δH (J in Hz) | δC a type |
| 1 | 158.8 | 158.8, C | ||
| 2 | 3.22, t (6.8) | 42.1, CH2 | 3.23, t (6.8) | 42.1, CH2 |
| 3 | 1.67, m | 26.6, CH2 | 1.67, m | 26.6, CH2 |
| 4 | 1.76, m | 27.1, CH2 | 1.76, m | 27.0, CH2 |
| 5 | 4.23, m | 65.2, CH2 | 4.22, m | 65.2, CH2 |
| 6 | 166.2, C | 166.2, C | ||
| 7 | 103.7, C | 103.7, C | ||
| 8 | 151.3, C | 151.4, C | ||
| 9 | 3.43, m 2.92, m | 30.8, CH2 | 3.43, m 2.92, m | 30.7, CH2 |
| 10 | 2.46, m 1.75, m | 30.3, CH2 | 2.46, m 1.74, m | 30.4, CH2 |
| 11 | 4.10,m | 58.7, CH | 4.10, m | 58.7, CH |
| 12 12 | 2.46, m 1.40, m | 34.2, CH2 | 2.44, m 1.40, m | 34.2, CH2 |
| 13 | 3.64, m | 51.9, CH | 3.63, m | 51.9, CH |
| 14 | 149.9, C | 149.9, C | ||
| 15 | 4.42, m | 51.7, CH | 4.42, m | 51.7, CH |
| 16 | 1.57, m | 37.7, CH2 | 1.57, m | 37.7, CH2 |
| 17 | 1.30, m | 24.8, CH2 | 1.30, m | 25.1, CH2 |
| 18 | 1.30, m | 32.5, CH2 | 1.30, m | 32.7, CH2 |
| 19 | 1.30, m | 23.5, CH2 | 1.30, m | 23.5, CH2 |
| 20 | 0.91, t (6.8) | 14.3, CH3 | 1.30, m | 30.3, CH2 |
| 21 | 1.75, m 1.64, m | 35.7, CH2 | 1.30, m | 30.3, CH2 |
| 22 | 2.19, m | 23.7, CH2 | 0.90, t (6.8) | 14.3, CH3 |
| 23 | 5.39, m | 129.2, CH | 1.75, m 1.64, m | 35.8, CH2 |
| 24 | 5.45, m | 132.2, CH | 2.18, m | 23.7, CH2 |
| 25 | 2.06, m | 30.4, CH2 | 5.39, m | 129.0, CH |
| 26 | 1.40, m | 23.8, CH2 | 5.45, m | 132.2, CH |
| 27 | 0.92, t (6.8) | 14.0, CH3 | 2.05, m | 30.4, CH2 |
| 28 | 1.40, m | 23.8, CH2 | ||
| 29 | 0.92, t (6.8) | 14.0, CH3 | ||
| Antibodies | Clonality | Source | Cat.-No. | Dilution | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| anti-SQSTM/p62 | pAb | rabbit | #5114 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling |
| anti-phospho-mTOR | mAb | rabbit | #5536 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling |
| anti-mTOR | mAb | rabbit | #2983 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling |
| anti-LC3B-I/II | pAb | rabbit | #2775 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling |
| anti-β-Actin-HRP | pAb | goat | sc-1616 | 1:10,000 | Santa Cruz |
| anti-α-Tubulin | mAb | mouse | T5168 | 1:5000 | Sigma-Aldrich |
| anti-LC3B-I/II | pAb | rabbit | #2775 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling |
| anti-cleaved Caspase-3 | mAb | rabbit | #9664 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling |
| anti-PARP | pAb | rabbit | #9542 | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling |
| anti-Survivin | pAb | rabbit | NB500-201 | 1:1000 | Novus |
| anti-mouse IgG-HRP | sheep | NXA931 | 1:10,000 | GE Healthcare | |
| anti-rabbit IgG-HRP | goat | #7074 | 1:5000 | Cell Signaling |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Shubina, L.K.; Makarieva, T.N.; Guzii, A.G.; Hauschild, J.; Strewinsky, N.; Berdyshev, D.V.; Kudryashova, E.K.; Menshov, A.S.; Popov, R.S.; et al. New Guanidine Alkaloids Batzelladines O and P from the Marine Sponge Monanchora pulchra Induce Apoptosis and Autophagy in Prostate Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120738
Dyshlovoy SA, Shubina LK, Makarieva TN, Guzii AG, Hauschild J, Strewinsky N, Berdyshev DV, Kudryashova EK, Menshov AS, Popov RS, et al. New Guanidine Alkaloids Batzelladines O and P from the Marine Sponge Monanchora pulchra Induce Apoptosis and Autophagy in Prostate Cancer Cells. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(12):738. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120738
Chicago/Turabian StyleDyshlovoy, Sergey A., Larisa K. Shubina, Tatyana N. Makarieva, Alla G. Guzii, Jessica Hauschild, Nadja Strewinsky, Dmitrii V. Berdyshev, Ekaterina K. Kudryashova, Alexander S. Menshov, Roman S. Popov, and et al. 2022. "New Guanidine Alkaloids Batzelladines O and P from the Marine Sponge Monanchora pulchra Induce Apoptosis and Autophagy in Prostate Cancer Cells" Marine Drugs 20, no. 12: 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120738
APA StyleDyshlovoy, S. A., Shubina, L. K., Makarieva, T. N., Guzii, A. G., Hauschild, J., Strewinsky, N., Berdyshev, D. V., Kudryashova, E. K., Menshov, A. S., Popov, R. S., Dmitrenok, P. S., Graefen, M., Bokemeyer, C., & von Amsberg, G. (2022). New Guanidine Alkaloids Batzelladines O and P from the Marine Sponge Monanchora pulchra Induce Apoptosis and Autophagy in Prostate Cancer Cells. Marine Drugs, 20(12), 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120738







