The Interplay of Mycosporine-like Amino Acids between Phytoplankton Groups and Northern Krill (Thysanoessa sp.) in a High-Latitude Fjord (Kongsfjorden, Svalbard)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chlorophyll a and Accessory Pigments of Phytoplankton
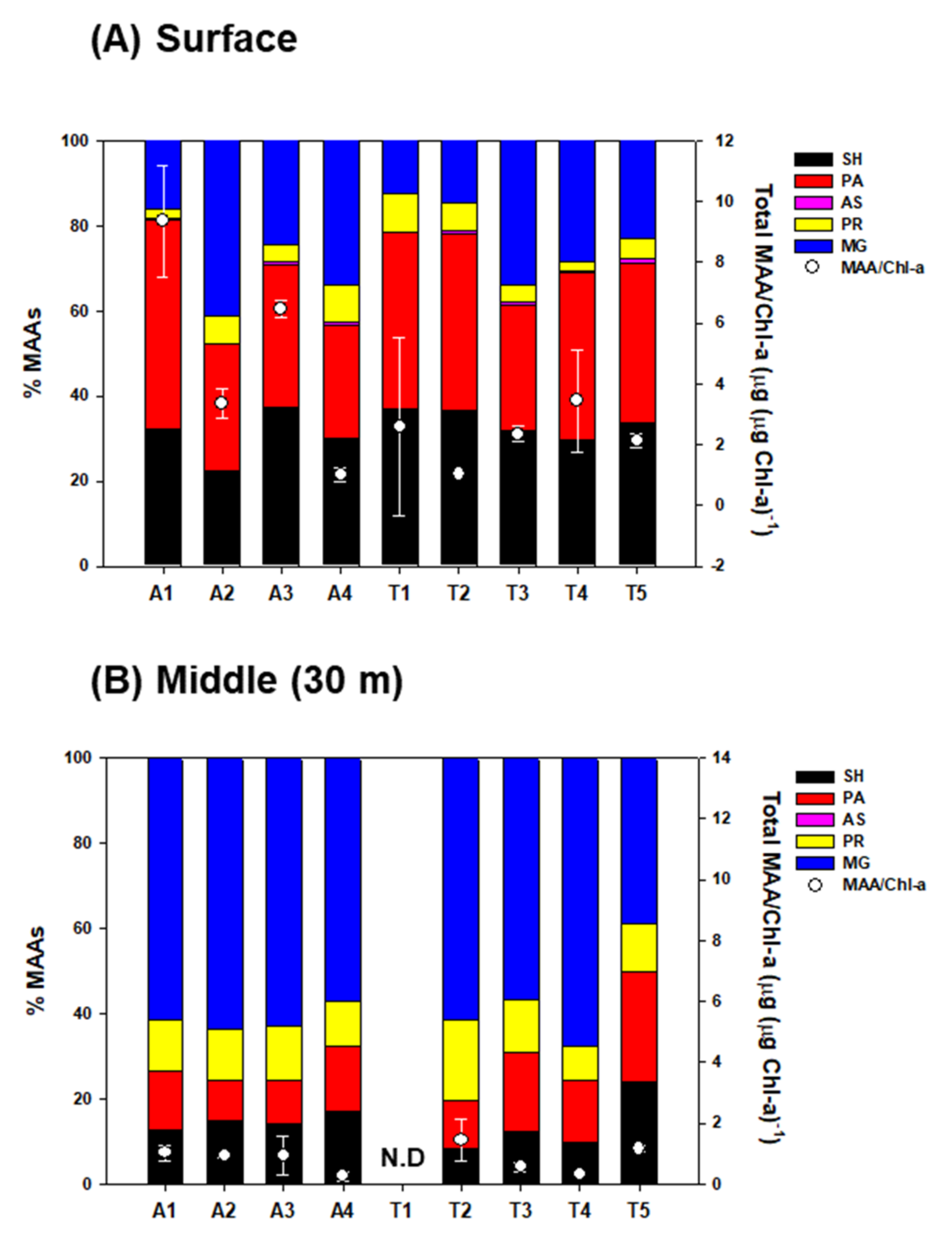
2.2. Mycosporine-like Amino Acid (MAA) Concentrations of Phytoplankton between Two Water Layers
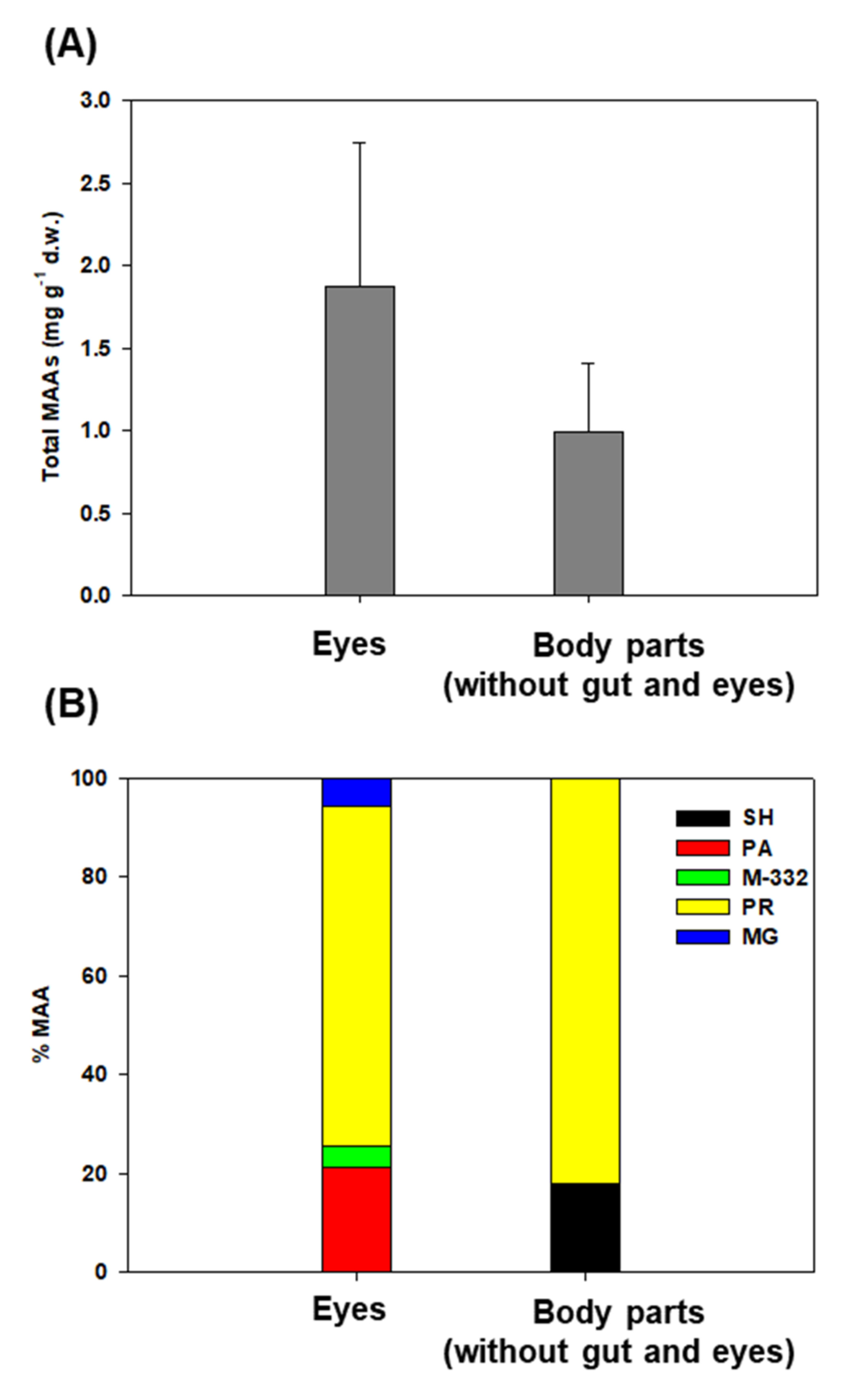
2.3. Distribution of Pigments and Mycosporine-like Amino Acids (MAAs) in Northern Krill
3. Discussion
3.1. Pigment-Based Phytoplankton Community Composition
3.2. Properties of MAA in Phytoplankton
3.3. Linkages between Phytoplankton Assemblages and Northern Krill
3.4. Bioaccumulation and Distribution of MAAs in Northern Krill
4. Materials and Methods
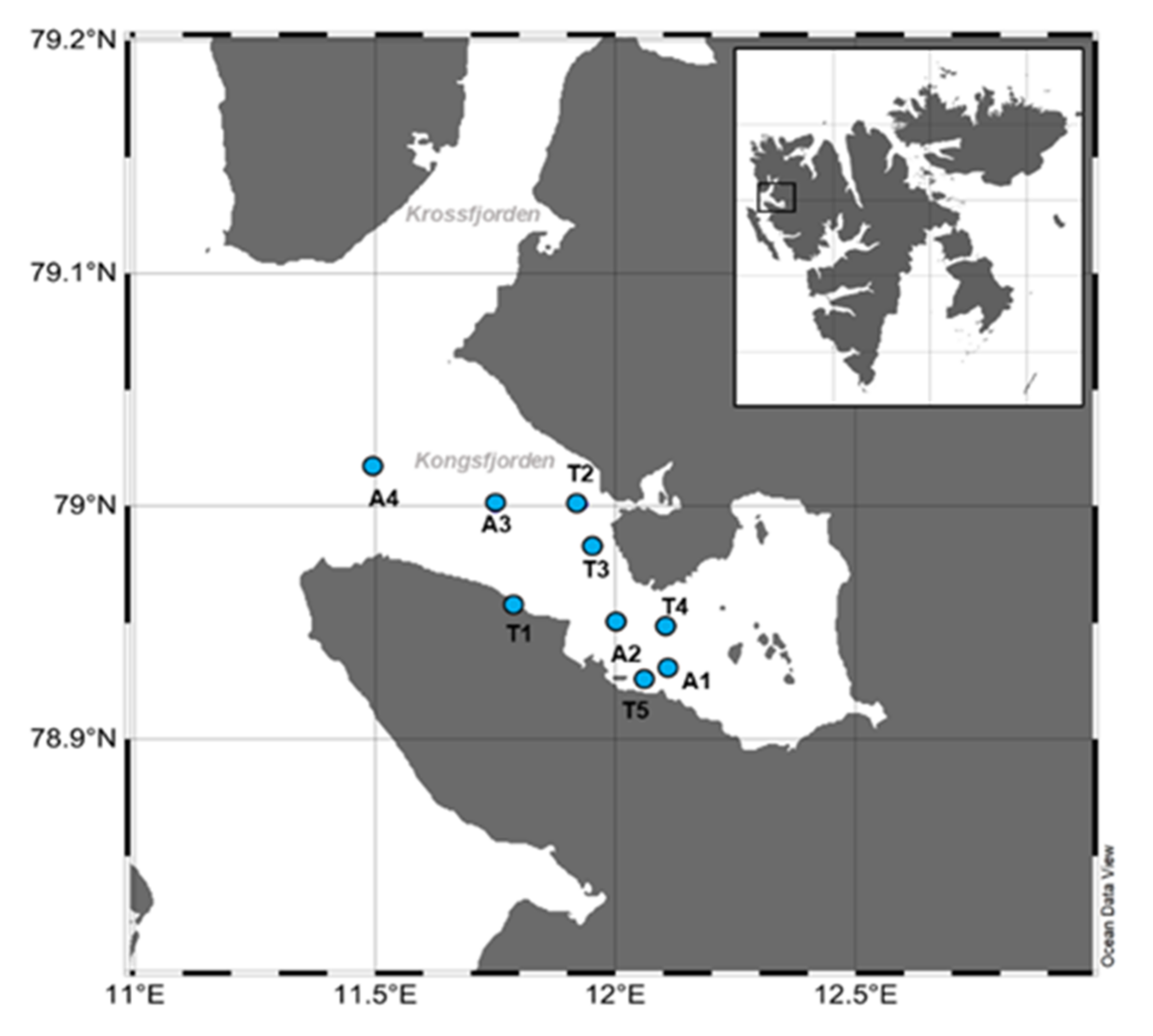
4.1. Study Area and Sampling
4.2. Pigment and MAA Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blumthaler, M.; Ambach, W. Indication of Increasing Solar Ultraviolet-B Radiation Flux in Alpine Region. Science 1990, 248, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helbling, E.W.; Chalker, B.E.; Dunlap, W.C.; Holm-Hansen, O.; Villafane, V.E. Photoacclimation of antarctic marine diatoms to solar ultraviolet radiation. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1996, 204, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wängberg, S.-Å.; Persson, A.; Karlson, B. Effects of UV-B radiation on synthesis of mycosporine-like amino acid and growth in Heterocapsa triquetra (Dinophyceae). J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 1997, 37, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.; Crutzen, P.J.; Grooβ, J.-U.; Bürhl, C.; Russell, J.M., III; Gernandt, H.; McKenna, D.S.; Tuck, A.F. Severe chemical ozone loss in the Arctic during the winter of 1995–96. Nature 1997, 389, 709–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischof, K.; Hanelt, D.; Wiencke, C. UV-radiation can affect depth zonation of Antarctic macroalgae. Mar. Biol. 1998, 131, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanelt, D.; Tüg, H.; Bischof, K.; Groß, C.; Lippert, H.; Sawall, T.; Wiencke, C. Light regime in an Arctic fjord: A study related to stratospheric ozone depletion as a basis for determination of UV effects on algal growth. Mar. Biol. 2001, 138, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, E.; Faerovig, P.J.; Hessen, D.O. UV effects on stoichiometry and PUFAs of Selenastrum capricomutum and their consequences for the grazer Daphnia magna. Freshw. Biol. 2006, 51, 2296–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohler, G.; Hagmeier, E.; Grigoleit, E.; Krause, K.D. Impact of solar UV radiation on uptake of 15N-ammonia and 15N-nitrate by marine diatoms and natural phytoplankton. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanz. 1991, 187, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karentz, D.; Cleaver, J.E.; Mitchell, D.L. Cell survival characteristics and molecular responses of Antarctic phytoplankton to ultraviolet-B radiation. J. Phycol. 1991, 27, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbling, E.W.; Villafane, V.; Ferrario, M.; Holm-Hansen, O. Impact of natural ultraviolet radiation on rates of photosynthesis and on specific marine phytoplankton species. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 80, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrenfeld, M.J.; Lean, D.R.S.; Lee, H.I.I. Ultraviolet-B radiation effects on inorganic nitrogen uptake by natural assemblages of oceanic plankton. J. Phycol. 1995, 31, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boelen, P.; de Boer, M.K.; Kraay, G.W.; Veldhuis, M.J.W.; Buma, A.G.J. UVBR-induced DNA damage in natural marine picoplankton assemblages in the tropical Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 193, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.P.; Häder, D.-P. UV-induced DNA damage and repair: A review. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2002, 1, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häder, D.-P.; Kumar, H.D.; Smith, R.C.; Worrest, R.C. Effects of solar UV radiation on aquatic ecosystems and interactions with climate change. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2007, 6, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernet, M.; Whitehead, K. Release of ultraviolet-absorbing compounds by the red-tide dinoflagellate Lingulodinium polyedra. Mar. Biol. 1996, 127, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, R.E.; Shawna, G.; Williamson, C.E.; Dee, G.; Sommaruga, R. Dietary acquisition of photoprotective compounds (mycosporine-like amino acids, carotenoids) and acclimation to ultraviolet radiation in a freshwater copepod. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Häder, D.-P.; Williamson, C.E.; Wängberg, S.-Å.; Rautio, M.; Rose, K.C.; Gao, K.; Helbling, E.W.; Sinha, R.P.; Worrest, R. Effects of UV radiation on aquatic ecosystems and interactions with other environmental factors. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015, 14, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karentz, D. Chemical defenses of marine organisms against solar radiation exposure: UV-absorbing mycosporinelike amino acids and scytonemin. In Marine Chemical Ecology; McClintock, J.B., Baker, B.J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 481–520. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead, K.; Karentz, D.; Hedges, J.I. Mycosporinelike amino acids (MAAs) in phytoplankton, a herbivorous pteropod (Limacina helicina), and its pteropod predator (Clione antarctica) in McMurdo Bay, Antarctica. Mar. Biol. 2001, 139, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Volkmann, M.; Gorbushina, A.A. A broadly applicable method for extraction and characterization of mycosporines and mycosporine-like amino acids of terrestrial, marine and freshwater origin. FEMS 2006, 255, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häder, D.-P.; Kumar, H.D.; Smith, R.C.; Worrest, R.C. Effects on aquatic ecosystems. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 1998, 46, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sommaruga, R.; Garicia-Pichel, F. UV-absorbing compounds in planktonic and benthic organisms from a high mountain lake. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1999, 144, 225–269. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, F.; Kopecky, J.; Nedbal, L. The occurrence of UV-B absorbing mycosporine-like amino acids in freshwater and terrestrial microalgae (Chlorophyta). Aquat. Bot. 1999, 63, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurion, I.; Lami, A.; Sommaruga, R. Distribution of mycosporine-like amino acids and photoprotective carotenoids among freshwater phytoplankton assemblages. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 26, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tartarotti, B.; Sommaruga, R. The effect of different methanol concentrations and temperatures on the extraction of mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) in algae and zooplankton. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2002, 154, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.P.; Singh, S.P.; Häder, D.-P. Database on mycosporines and mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) in fungi, cyanobacteria, macroalgae, phytoplankton and animals. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2007, 89, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.S.; Hwang, J.; Park, M.; Seo, H.H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.H.; Moh, S.H.; Lee, T.K. Anti-inflammation of mycosporine like amino acid (MAAs) in response to UV radiation suggest potential anti-skin aging activity. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5174–5187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oren, A.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. Mycosporines and mycosporine-like amino acids: UV protectants or multipurpose secondary metabolites? FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 269, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richa, R.; Kumari, S. Biotechnological potential of mycosporine-like amino acids and phycobiliproteins of cyanobacterial origin. Biotechnol. Bioinf. Bioeng. 2011, 1, 159–171. [Google Scholar]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Sinha, R.P. Biotechnological and industrial significance of cyanobacterial secondary metabolites. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldes, V.; Pinto, E. Mycosproine-Like Amino Acids (MAAs): Biology, Chemistry and Identification Features. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Čížková, M.; Bišová, K.; Vítová, M. Exploring Mycosporine-like Amino Acids (MAAs) as Safe and Natural Protective Agents against UV-Induced Skin Damage. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, S.J.; Dunlap, W.C.; Nicol, S.; Ritz, D. Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) acquire a UV-absorbing mycosporine-like amino acid from dietary algae. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 255, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, A.C.; Durbin, E.G.; Rynearson, T.A. Krill feeding on sediment in the Gulf of Maine (North Atlantic). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 455, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, S.J.; Ritz, D.; Nicol, S. Behavioural reactions of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba Dana) to ultraviolet and photosynthetically active radiation. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 297, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Richa; Sinha, R.P.; Singh, S.P.; Häder, D.-P. Photoprotective compounds from marine organisms. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 37, 537–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hylander, S. Mycosporine-Like Amino Acids (MAAs) in Zooplankton. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malloy, K.D.; Holman, M.A.; Mitchell, D.; Dertrich, H.W., III. Solar UVB-induced DNA damage and photoenzymatic DNA repair in antarctic zooplankton. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ormańczyk, M.R.; Głuchowska, M.; Olszewska, A.; Kwasniewski, S. Zooplankton structure in high latitude fjords with contrasting oceanography (Hornsund and Kongsfjorden, Spitsbergen). Oceanologia 2017, 59, 508–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deja, K.; Ormańczyk, M.; Dragańska-Deja, K. Plankton or benthos: Where krill belongs in Spitsbergen fjords? (Svalbard Archipelago, Arctic). Polar Biol. 2019, 41, 1415–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeffrey, S.W.; Mantoura, R.F.C.; Bjørnland, T. Data for the identification of 47 key phytoplankton pigments. In Phytoplankton Pigments in Oceanography: Guidelines to Modern Methods; Jeffrey, S.W., Mantoura, R.F.C., Wright, S.W., Eds.; Monographs on Oceanographic Methodology; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Schlüter, L.; Mohlenberg, F.; Havskum, H.; Larsen, S. The use of phytoplankton pigments for identifying and quantifying phytoplankton groups in costal areas: Testing the influence of light and nutrients on pigment/chlorophyll a ratio. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 192, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aneeshkumar, N.; Sujatha, C.H. Biomarker pigment signatures in Cochin back water system—A tropical estuary south west coast of India. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 99, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piquet, A.M.-T.; van de Poll, W.H.; Visser, R.J.W.; Wiencke, C.; Bolhuis, H.; Buma, A.G. Springtime phytoplankton dynamics in Arctic Krossfjorden and Kongsfjorden (Spitsbergen) as a function of glacier proximity. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 2263–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van de Poll, W.H.; Kulk, G.; Rozema, P.D.; Brussaard, C.P.D.; Visser, R.J.W.; Buma, A.G.J. Contrasting glacial meltwater effects on post-bloom phytoplankton on temporal and spatial scales in Kongsfjorden, Spitsbergen. Elementa 2018, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdi, N.; Tackx, M.; Traunspurger, W.; Buffan-Dubau, E. Feeding of biofilm-dwelling nematodes examined using HPLC-analysis of gut pigment contents. Hydrobiologia 2012, 680, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad Ishak, N.H.; Clementson, L.A.; Eriksen, R.S.; van den Enden, R.L.; Williams, G.D.; Swadling, K.M. Gut contents and isotopic profiles of Salpa fusiformis and Thalia democratica. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Poll, W.H.; Maat, D.S.; Fischer, P.; Rozema, P.D.; Daly, O.B.; Koppelle, S.; Visser, R.J.W.; Buma, A.G.J. Atlantic advection driven changes in glacial meltwater: Effects on phytoplankton chlorophyll-a and taxonomic composition in Kongsfjorden, Spitsbergen. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hop, H.; Pearson, T.; Hegseth, E.N.; Kovacs, K.M.; Wiencke, C.; Kwasniewski, S.; Eiane, K.; Mehlum, F.; Gulliksen, B.; Wlodarska-Kowalczuk, M.; et al. The marine ecosystem of Kongsfjorden, Svalbard. Polar Res. 2002, 21, 167–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.-N.; Park, M.-O.; Kang, S.-H.; Kim, H.-C.; Shin, K.-H. Production of mycosporine-like amino acids of in situ phytoplankton community in Kongsfjorden, Svalbard, Arctic. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2012, 114, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Joo, H.M.; Jung, J.; Lee, B.; Ha, S.-Y. In situ rates of carbon and nitrogen uptake by phytoplankton and the contribution of picophytoplankton in Kongsfjorden, Svalbard. Water 2020, 12, 2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolodkov, Y.B.; Hapter, R.; Semovsk, S.V. Phytoplankton in Kongsfjorden, Spitsbergen, July 1996. Sarsia 2000, 85, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiktor, J. Early spring microplankton development under fast ice covered fjords of Svalbard, Arctic. Oceanologia 1999, 41, 51–72. [Google Scholar]
- Millie, D.F.; Paerl, H.W.; Hurley, J.P. Microalgal Pigment Assessments Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography: A Synopsis of Organismal and Ecological Applications. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 56, 2513–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.W.; van den Enden, R.L.; Pearce, I.; Davidson, A.T.; Scott, F.J.; Westwood, K.J. Phytoplankton community structure and stocks in the Southern Ocean (30–80° E) determined by CHEMTAX analysis of HPLC pigment signatures. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2010, 57, 758–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizotte, M.P.; Sharpe, T.R.; Priscu, J.C. Phytoplankton dynamics in the stratified water column of Lake Bonney, Antarctica. I. Biomass and productivity during the winter-spring transition. Polar Biol. 1996, 16, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.-Y.; Lee, D.B.; Kang, S.-H.; Shin, K.-H. Strategy of photo-protection in phytoplankton assemblages in the Kongsfjorden, Svalbard, Arctic. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 2016, 34, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodal, H.; Falk-Petersen, S.; Hop, H.; Kristiansen, S.; Reigstad, M. Spring bloom dynamics in Kongsfjorden, Svalbard: Nutrients, phytoplankton, protozoans and primary production. Polar Biol. 2012, 35, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Payne, C.M.; Roesler, C.S. Characterizing the influence of Atlantic water intrusion on water mass formation and phytoplankton distribution in Kongsfjorden, Svalbard. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 191, 104005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-X.; Kong, F.-Z.; Geng, H.-X.; Zhang, Q.-C.; Yuan, Y.-Q.; Yu, R.-C. CHEMTAX analysis of phytoplankton assemblages revealed potential indicators for blooms of haptophyte Phaeocystis globose. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, C.A.; Airs, R.L. Distribution and Abundance of MAAs in 33 Species of Microalgae across 13 Classes. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1273–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oubelkheir, K.; Clementson, L.A.; Moore, G.F.; Tilstone, G.H. Production of mycosporine-like amino acids by phytoplankton under ultraviolet radiation exposure in the Sub-Antarctic Zone south of Tasmania. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 494, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchant, H.J.; Davidson, A. Possible Impacts of Ozone Depletion on Trophic Interactions and Biogenic Vertical Carbon Flux in the Southern Ocean; AD-P-007315/5/XAB; Geophysical Institute: Fairbanks, AK, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, A.T.; Bramich, D.; Marchant, H.J.; McMinn, A. Effects of UV-B irradiation on growth and survival of Antarctic marine diatoms. Mar. Biol. 1994, 119, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shick, J.M.; Lesser, M.P.; Dunlap, W.C.; Stochaj, W.R.; Chalker, B.E.; Won, J.W. Depth-dependent responses to solar ultraviolet radiation and oxidative stress in the zooxanthellate coral Acropora microphthalma. Mar. Biol. 1995, 122, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, W.C.; Chalker, B.E.; Bandaranayake, W.M.; Wu Won, J.J. Nature’s sunscreen from the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 1998, 20, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartarotti, B.; Laurion, I.; Sommaruga, R. Large variability in the concentration of mycosporine-like amino acids among zooplankton from lakes located across an altitude gradient. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartarotti, B.; Trattner, F.; Remias, D.; Saul, N.; Steinberg, C.E.W.; Sommaruga, R. Distribution and UV protection strategies of zooplankton in clear and glacier-fed alpine lakes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, C.; Reigstad, M.; Riser, C.W.; Mühlenbach, A.; Wassmann, P. On the trophic fate of Phaeocystis pouchetii. VII. Sterols and fatty acids reveal sedimentation of P. pouchetii-derived organic matter via krill fecal strings. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 209, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haberman, K.L.; Ross, R.M.; Quetin, L.B. Diet of the Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba Dana): II. Selective grazing in mixed phytoplankton assemblages. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2003, 283, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiørboe, T.; Saiz, E.; Tiselius, P.; Andersen, K.H. Adaptive feeding behavior and functional responses in zooplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabrol, J.; Fabre, A.; Nozais, C.; Tremblay, R.; Starr, M.; Plourde, S.; Winkler, G. Functional feeding response of Nordic and Arctic krill on natural phytoplankton and zooplankton. J. Plankton Res. 2020, 42, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk-Petersen, S.; Hagen, W.; Kattner, G.; Clarke, A.; Sargent, J.R. Lipids, trophic relationships and biodiversity in Arctic and Antarctic krill. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 57, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemer, U.; Lamare, M.D.; Peake, B.M. Temporal concentrations of sunscreen compounds (Mycosporine-like Amino Acids) in phytoplankton and in the New Zealand krill, Nyctiphanes australis G.O. Sars. J. Plankton Res. 2007, 29, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hylander, S.; Jephson, T. UV protective compounds transferred from a marine dinoflagellate to its copepod predator. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2010, 389, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P.E.; Ferraro, M.A.; Perez, A.P.; Zagarese, H.E.; Dieguez, M.C. Contrasting patterns of MAAs accumulation in two populations of the copepod Boeckella gracilipes. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2014, 13, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahon, S.; Castro Porras, V.A.; Pruski, A.M.; Charles, F. Sensitivity to UV radiation in early life stages of the Mediterranean sea urchin Sphaerechinus granularis (Lamarck). Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 1892–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.S.; Schafer, F.; Shick, J.M.; Dunlap, W.D. Ultraviolet radiation-absorbing mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) are acquired from their diet by medaka fish (Oryzias latipes) but not by SKH-1 hairless mice. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 1998, 120, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfeo, M.; Ventura, M.; Tartarotti, B.; Sommaruga, R. Body distribution and source of mycosporine-like amino acids in the cyclopoid copepod Cyclops abyssorum tatricus. J. Plankton Res. 2011, 33, 1430–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll, A.K.; Shick, J.M. Dietary accumulation of UV-absorbing mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) by the green sea urchin (Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis). Mar. Biol. 1996, 124, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartarotti, B.; Sommaruga, R. Seasonal and ontogenetic changes of mycosporine-like amino acids in planktonic organisms from an alpine lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 1530–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, I.; Yoneda, T.; Omura, Y.; Osaki, T.; Ifuku, S.; Saimoto, H.; Azuma, K.; Imagawa, T.; Tsuka, T.; Murahata, Y.; et al. Protective Effect of Chitin Urocanate Nanofibers against Ultraviolet Radiation. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 7463–7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zapata, M.; Rodriguez, F.; Garrido, J.L. Separation of chlorophylls and carotenoids from marine phytoplankton: A new HPLC method using a reversed phase C-8 column and pyridine-containing mobile phases. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2000, 195, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, J.O.; Ha, S.Y.; Choi, B.H.; Chung, M.H.; Yoon, W.D.; Lee, J.S.; Shin, K.H. Primary Productivity and Pigments Variation of Phytoplankton in the Seomjin River Estuary during Rainy Season in Summer. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 44, 303–313. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.O.; Park, J.S. HPLC method for the analysis of chlorophylls and carotenoids from marine phytoplankton. J. Korean Soc. Oceanogr. 1997, 32, 46–55. [Google Scholar]

| Station | MAAs (μg L−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH | PA | AS | PR | MG | |
| (A) Surface | |||||
| A1 | 1.349 (±0.033) | 2.029 (±0.059) | 0.023 (±0.001) | 0.094 (±0.001) | 0.662 (±0.172) |
| A2 | 0.241 (±0.018) | 0.318 (±0.018) | 0.069 (±0.011) | 0.448 (±0.098) | |
| A3 | 0.565 (±0.033) | 0.506 (±0.031) | 0.014 (±0.001) | 0.056 (±0.002) | 0.371 (±0.014) |
| A4 | 0.128 (±0.030) | 0.113 (±0.032) | 0.003 (±0.000) | 0.036 (±0.005) | 0.145 (±0.048) |
| T1 | 0.192 (±0.029) | 0.216 (±0.025) | 0.048 (±0.012) | 0.074 (±0.069) | |
| T2 | 0.226 (±0.031) | 0.254 (±0.034) | 0.006 (±0.001) | 0.039 (±0.008) | 0.090 (±0.031) |
| T3 | 0.556 (±0.175) | 0.506 (±0.101) | 0.014 (±0.002) | 0.066 (±0.017) | 0.580 (±0.109) |
| T4 | 0.406 (±0.112) | 0.527 (±0.120) | 0.014 (±0.002) | 0.028 (±0.007) | 0.533 (±0.485) |
| T5 | 0.331 (±0.063) | 0.366 (±0.047) | 0.008 (±0.001) | 0.047 (±0.011) | 0.226 (±0.048) |
| (B) Middle (30 m depth) | |||||
| A1 | 0.069 (±0.010) | 0.075 (±0.009) | 0.065 (±0.013) | 0.354 (±0.136) | |
| A2 | 0.064 (±0.006) | 0.041 (±0.005) | 0.052 (±0.017) | 0.284 (±0.085) | |
| A3 | 0.096 (±0.077) | 0.067 (±0.048) | 0.077 (±0.042) | 0.405 (±0.274) | |
| A4 | 0.041 (±0.004) | 0.036 (±0.007) | 0.028 (±0.009) | 0.180 (±0.145) | |
| T2 | 0.054 (±0.018) | 0.070 (±0.017) | 0.147 (±0.125) | 0.441 (±0.231) | |
| T3 | 0.036 (±0.011) | 0.051 (±0.009) | 0.039 (±0.018) | 0.178 (±0.098) | |
| T4 | 0.016 | 0.024 | 0.014 | 0.113 | |
| T5 | 0.102 (±0.003) | 0.109 (±0.022) | 0.047 (±0.008) | 0.167 (±0.046) | |
| Diagnostic Pigment | Abbreviation | Concentration (μg g−1 d.w.) | Phytoplankton Group(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fucoxanthin | Fuco | 0.016 ± 0.002 | Diatoms |
| 19′-hexanolyoxyfucoxanthin | 19′-Hex | 0.029 ± 0.009 | Phaeocystis sp. |
| Alloxanthin | Allo | 2.791 ± 0.333 | Cryptophytes |
| Chlorophyll a | Chl-a | 8.286 ± 1.127 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, B.K.; Park, M.-O.; Min, J.-O.; Kang, S.-H.; Shin, K.-H.; Yang, E.J.; Ha, S.-Y. The Interplay of Mycosporine-like Amino Acids between Phytoplankton Groups and Northern Krill (Thysanoessa sp.) in a High-Latitude Fjord (Kongsfjorden, Svalbard). Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040238
Kim BK, Park M-O, Min J-O, Kang S-H, Shin K-H, Yang EJ, Ha S-Y. The Interplay of Mycosporine-like Amino Acids between Phytoplankton Groups and Northern Krill (Thysanoessa sp.) in a High-Latitude Fjord (Kongsfjorden, Svalbard). Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(4):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040238
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Bo Kyung, Mi-Ok Park, Jun-Oh Min, Sung-Ho Kang, Kyung-Hoon Shin, Eun Jin Yang, and Sun-Yong Ha. 2022. "The Interplay of Mycosporine-like Amino Acids between Phytoplankton Groups and Northern Krill (Thysanoessa sp.) in a High-Latitude Fjord (Kongsfjorden, Svalbard)" Marine Drugs 20, no. 4: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040238
APA StyleKim, B. K., Park, M.-O., Min, J.-O., Kang, S.-H., Shin, K.-H., Yang, E. J., & Ha, S.-Y. (2022). The Interplay of Mycosporine-like Amino Acids between Phytoplankton Groups and Northern Krill (Thysanoessa sp.) in a High-Latitude Fjord (Kongsfjorden, Svalbard). Marine Drugs, 20(4), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040238






