Algicidal Effects of a High-Efficiency Algicidal Bacterium Shewanella Y1 on the Toxic Bloom-Causing Dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Algal Cultures
2.2. Isolation, Purification and Identification of Algicidal Bacterium
2.3. Algicidal Activity and Algicidal Mode Experiment
2.4. Algicidal Effects of Y1 Filtrate on A. pacificum
2.5. Photosynthetic Activity of A. pacificum during the Algicidal Process
2.6. ROS Levels of A. pacificum during the Algicidal Process
2.7. Lipid Peroxidation, Antioxidative Enzyme and Antioxidant of A. pacificum during the Algicidal Process
2.8. Algicidal Activity of Y1 Filtrate toward Several HABs Species
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
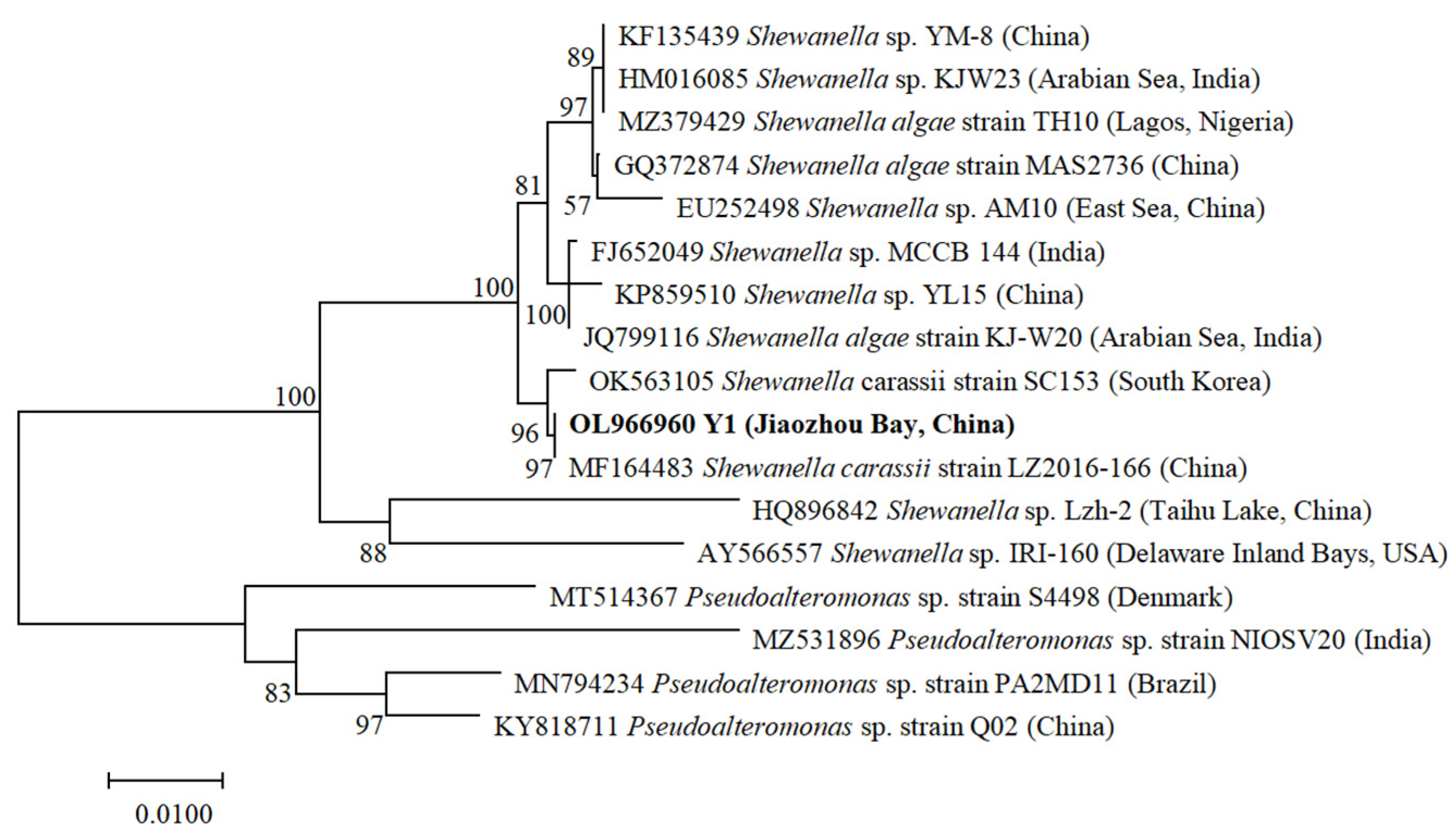
3.1. Identification of Algicidal Bacterium
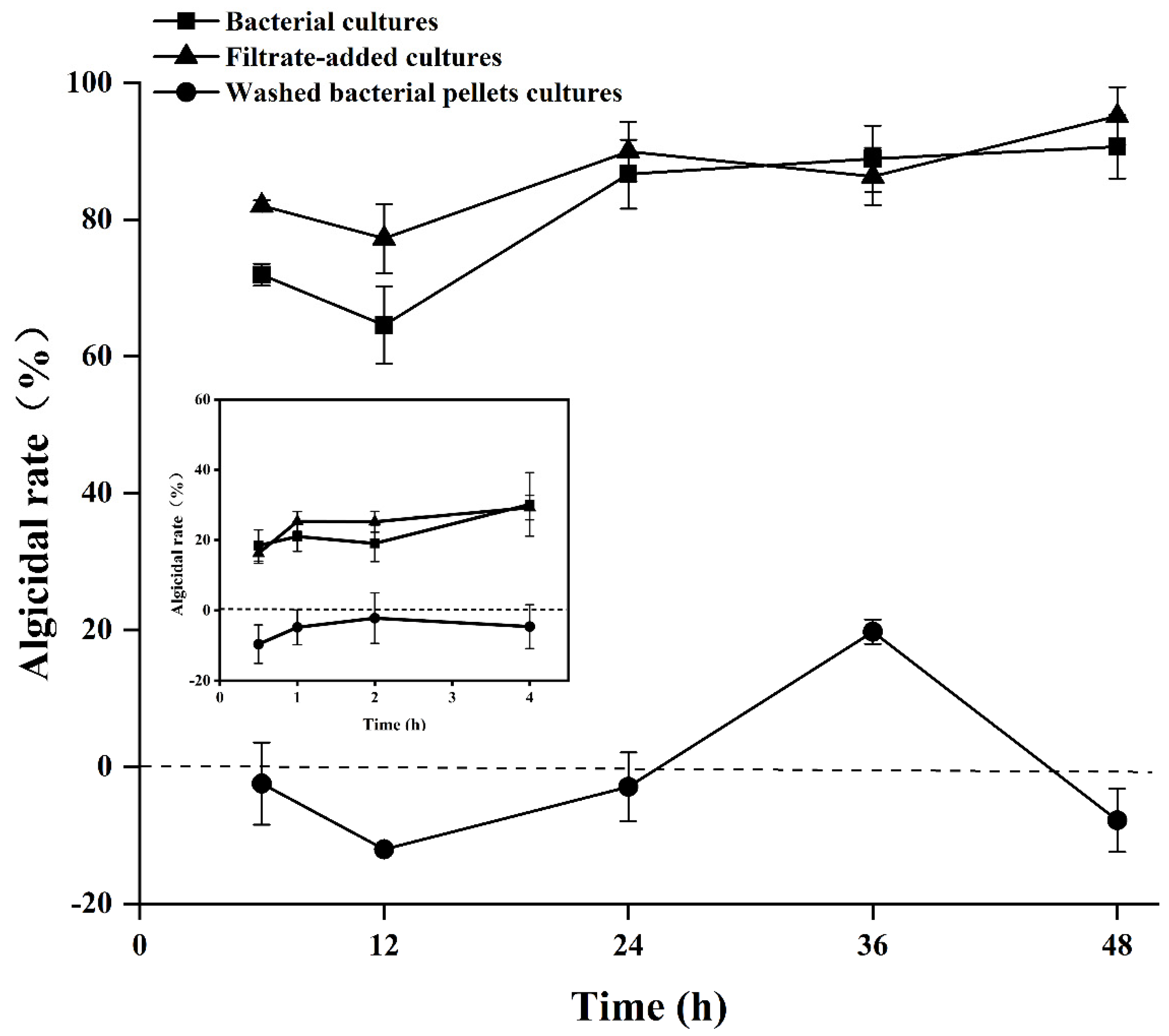
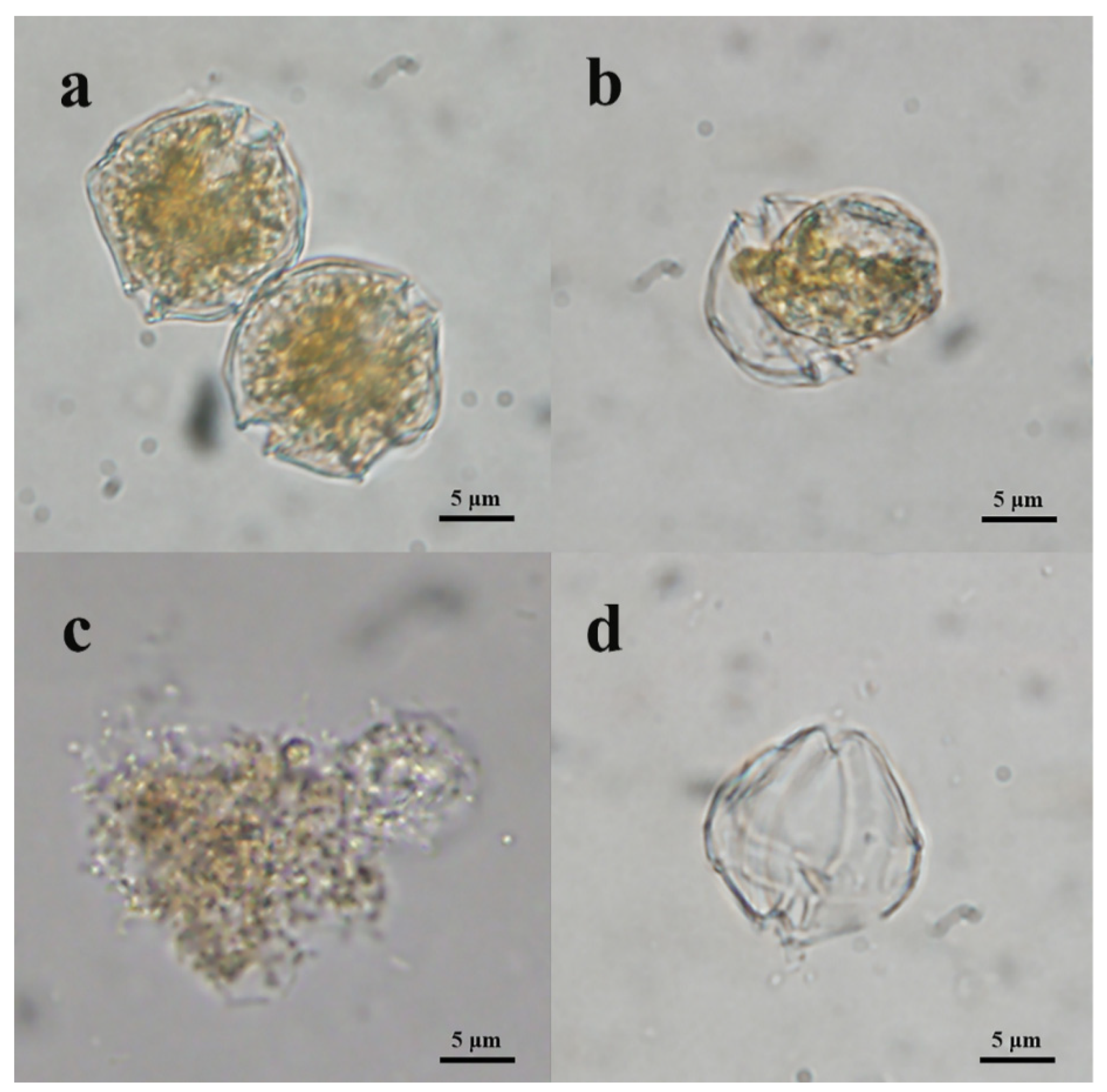
3.2. Algicidal Mode of Algicidal Strain Y1
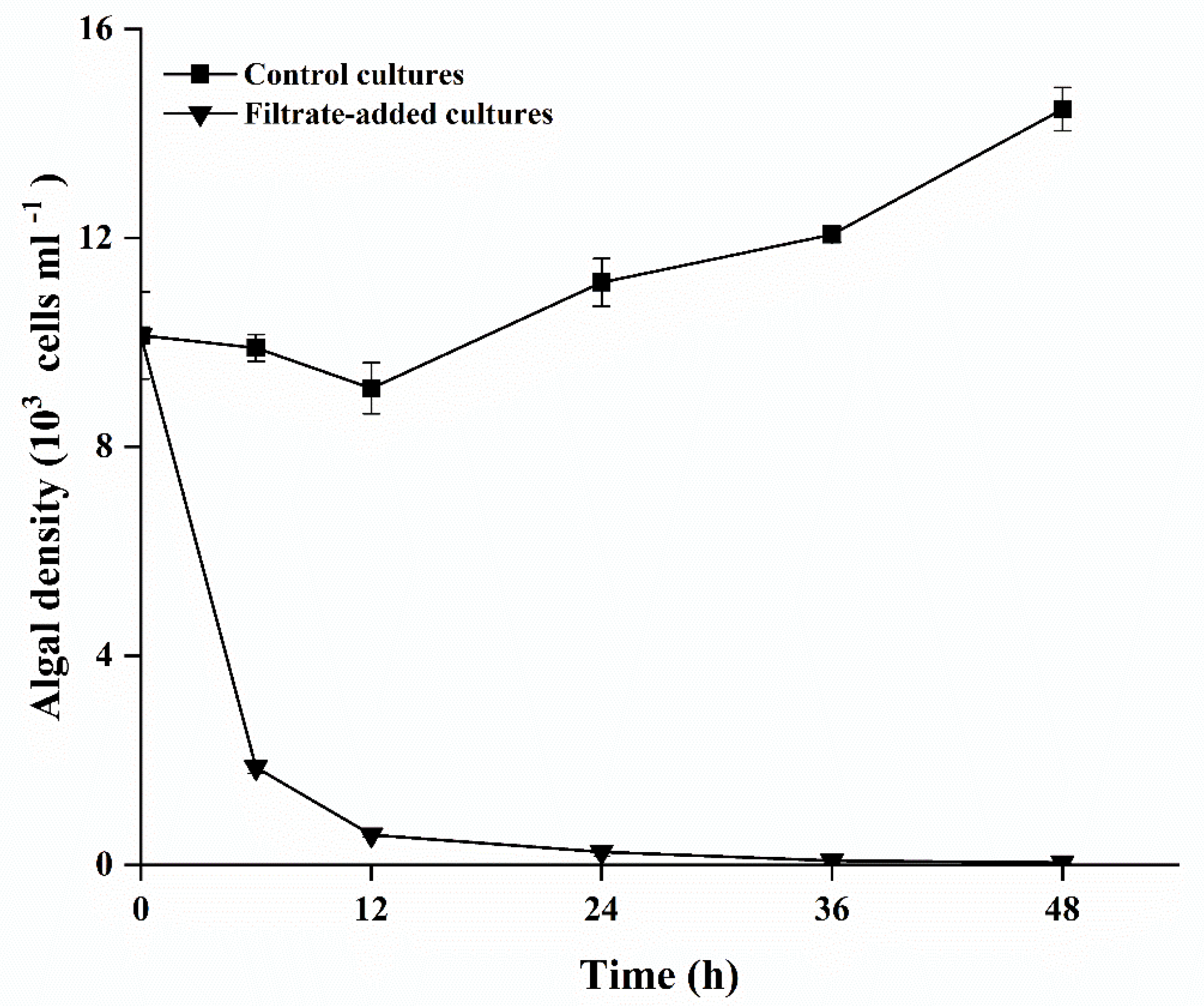
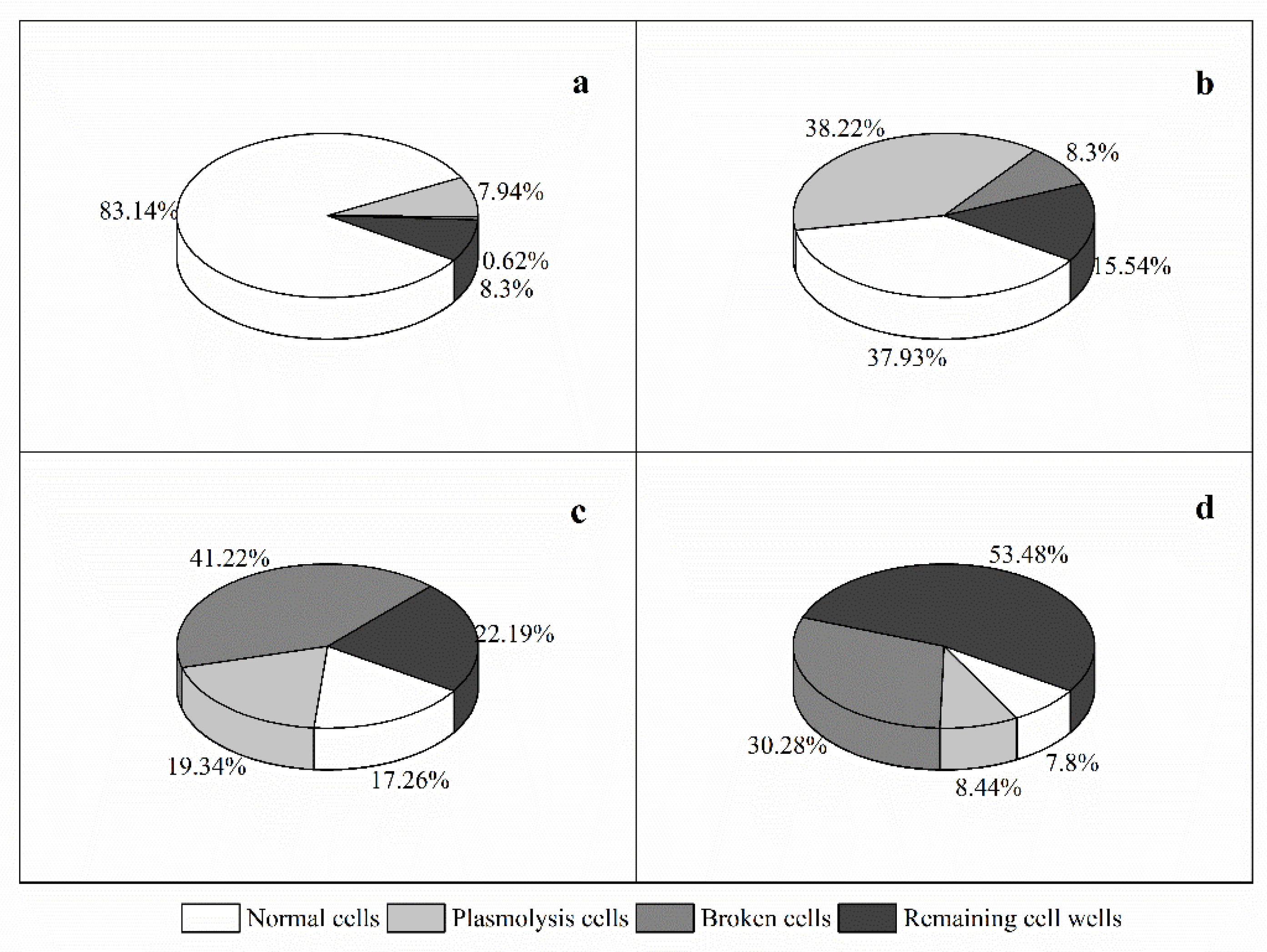
3.3. Effects of Y1 Filtrate on A. pacificum
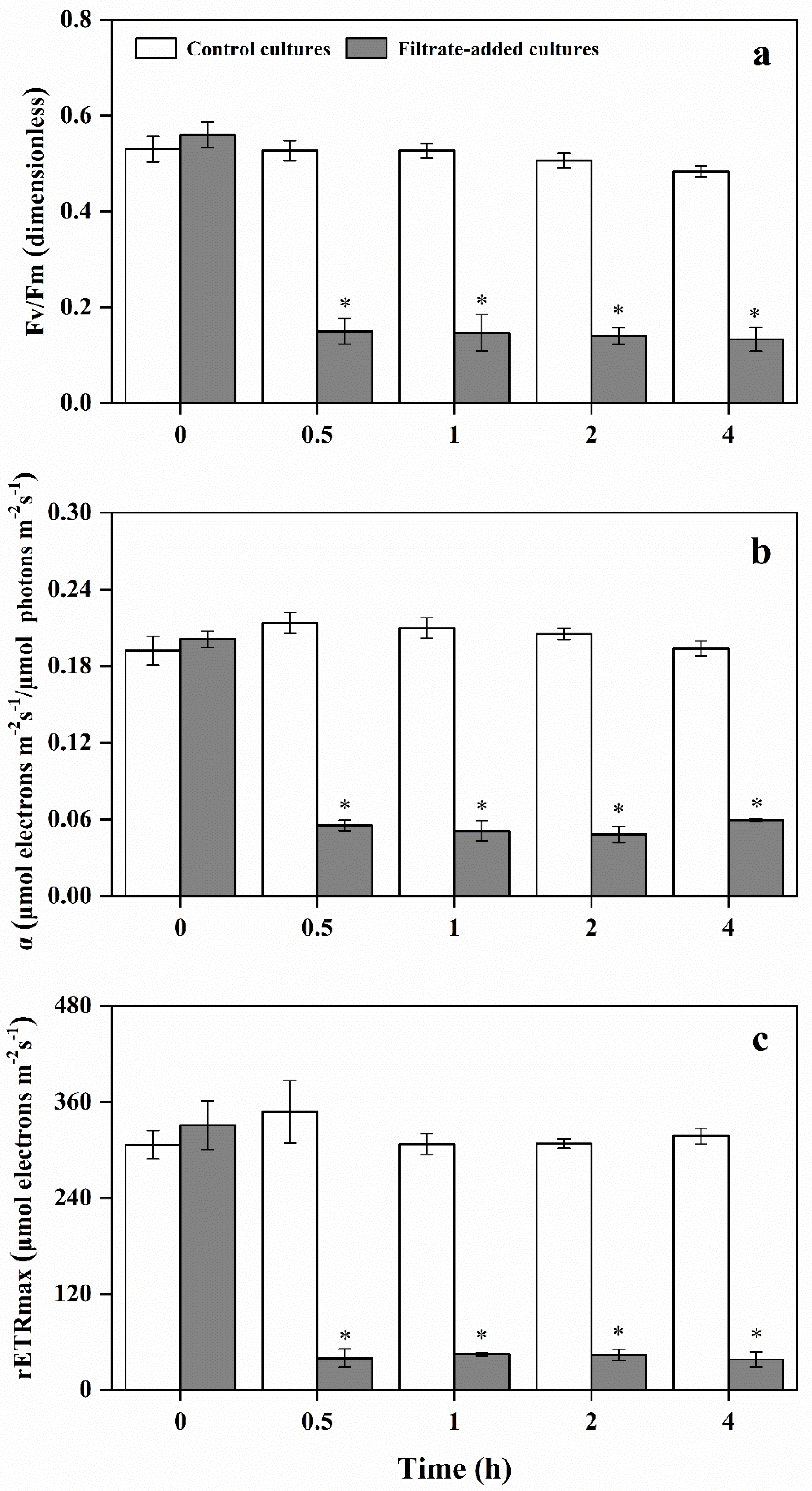
3.4. Variation of Photosynthetic Activity of A. pacificum under the Action of Y1 Filtrate
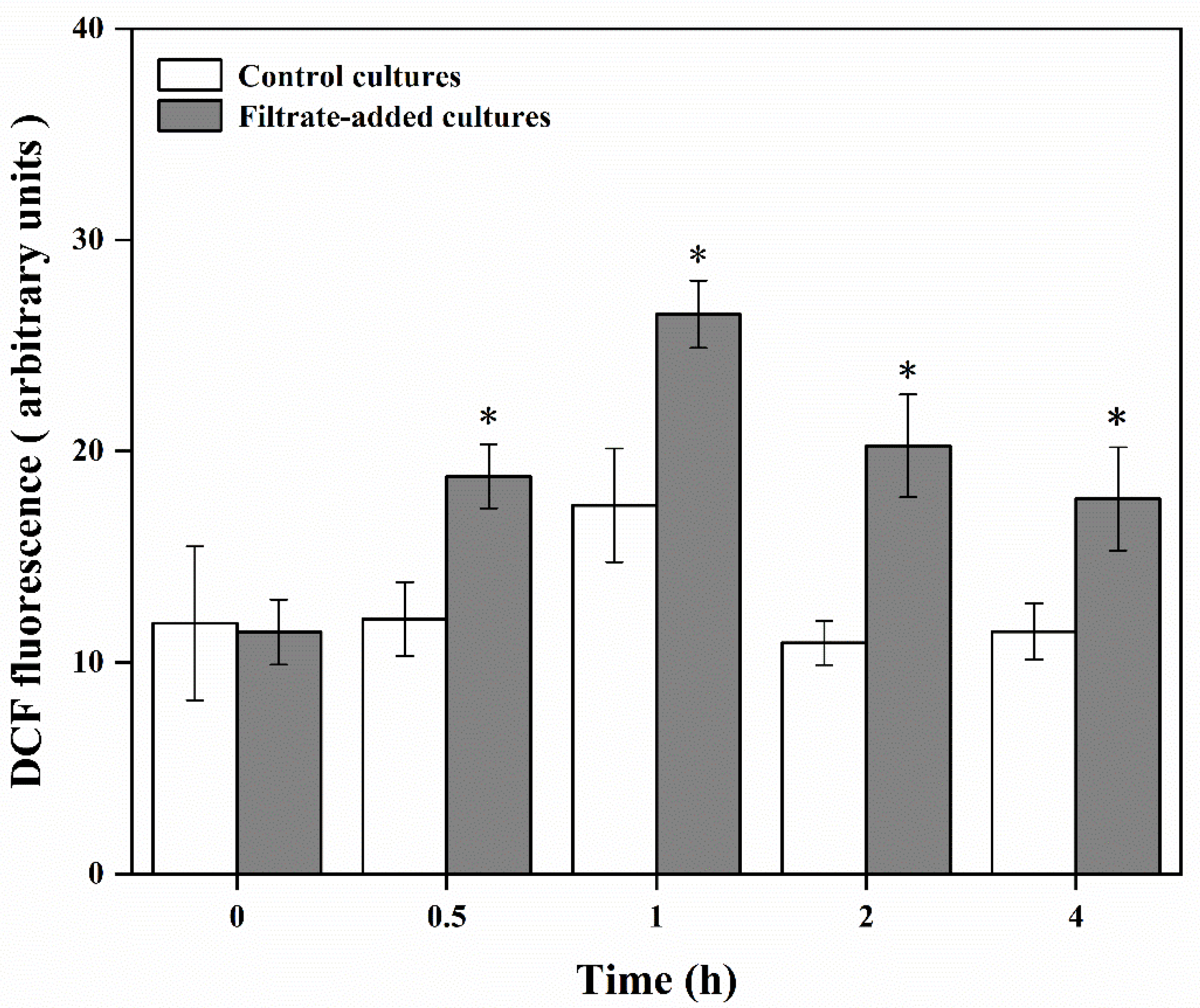
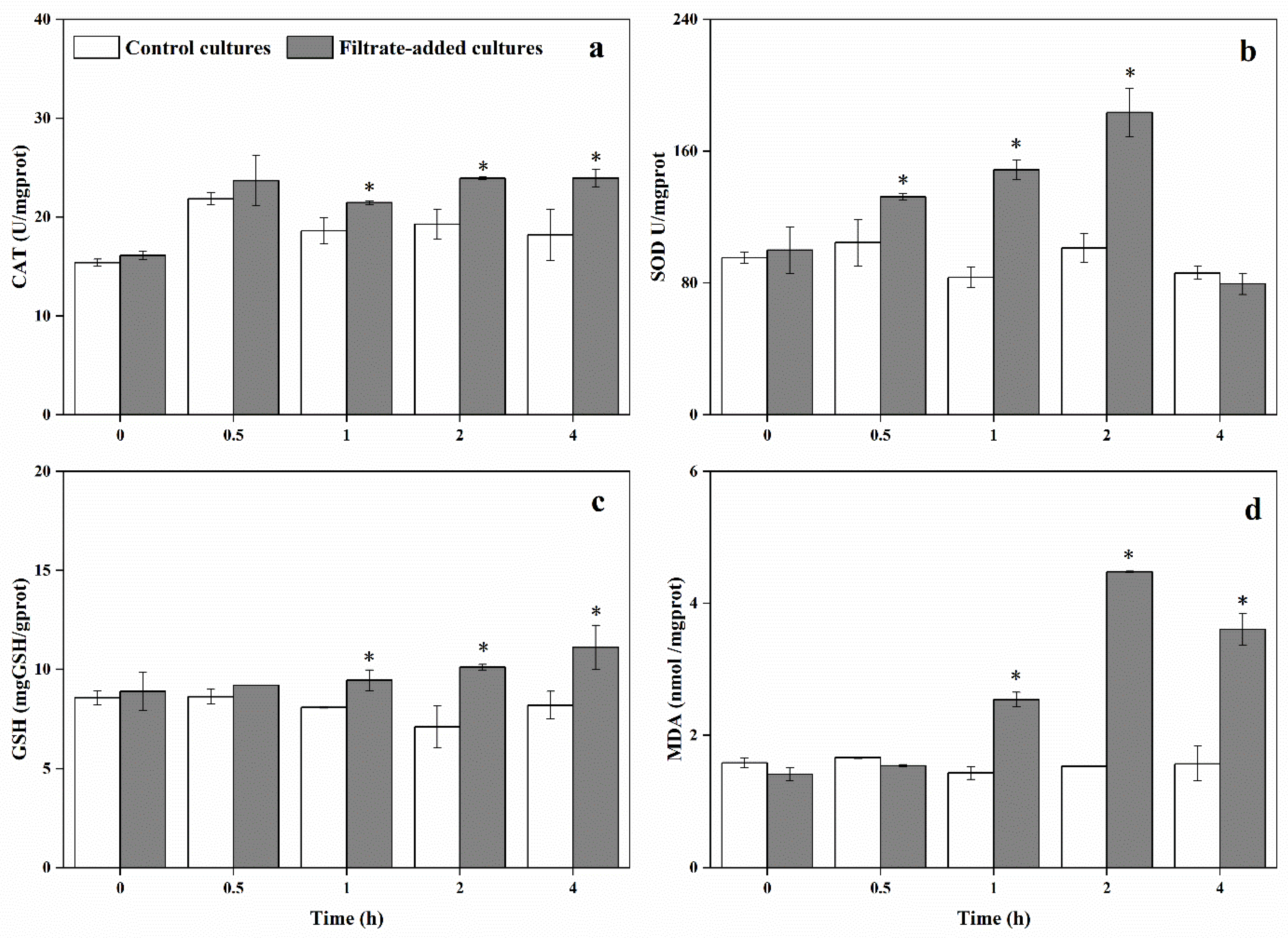
3.5. Physiological and Biochemical Responses of A. pacificum under the Action of Y1 Filtrate
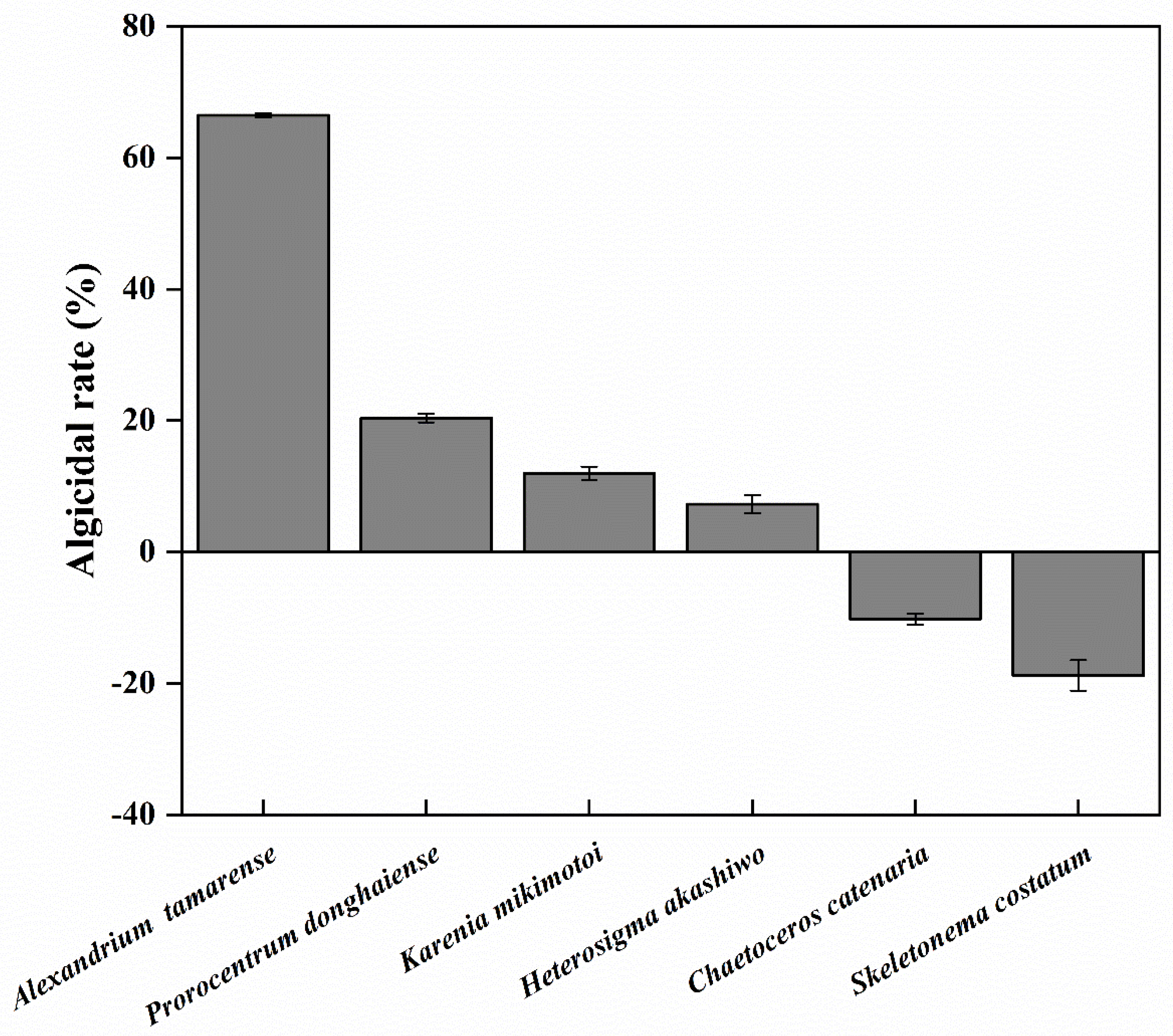
3.6. Algicidal Activity of Y1 Filtrate toward Several HABs Species
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glibert, P.M.; Al-Azri, A.; Icarus Allen, J.; Bouwman, A.F.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Burford, M.A.; Harrison, P.J.; Zhou, M. Key Questions and Recent Research Advances on Harmful Algal Blooms in Relation to Nutrients and Eutrophication. In Global Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms; Glibert, P.M., Berdalet, E., Burford, M.A., Pitcher, G.C., Zhou, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 232, pp. 229–259. ISBN 978-3-319-70069-4. [Google Scholar]
- León-Muñoz, J.; Urbina, M.A.; Garreaud, R.; Iriarte, J.L. Hydroclimatic conditions trigger record harmful algal bloom in western Patagonia (summer 2016). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anderson, D.M. Approaches to monitoring, control and management of harmful algal blooms (HABs). Ocean Coast. Manag. 2009, 52, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heisler, J.; Glibert, P.M.; Burkholder, J.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Cochlan, W.; Dennison, W.C.; Dortch, Q.; Gobler, C.J.; Heil, C.A.; Humphries, E.; et al. Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: A scientific consensus. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tillmann, U.; John, U. Toxic effects of Alexandrium spp. on heterotrophic dinoflagellates: An allelochemical defence mechanism independent of PSP-toxin content. Mar. Ecol. Prog. 2002, 230, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colin, S.P.; Dam, H.G. Effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense on the copepod Acartia hudsonica: A test of the mechanisms that reduce ingestion rates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. 2003, 248, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiyama, T. Growth and grazing responses of tintinnid ciliates feeding on the toxic dinoflagellate Heterocapsacircularisquama. Mar. Biol. 1997, 128, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucci, S. The effects of the toxic dinoflagellate Protogonyaulax tamarensis on the feeding and behaviour of bivalve molluscs. Aquat. Toxicol. 1987, 10, 9–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattenrath-Lehmann, T.K.; Gobler, C.J. Allelopathic inhibition of competing phytoplankton by North American strains of the toxic dinoflagellate, Alexandrium fundyense: Evidence from field experiments, laboratory experiments, and bloom events. Harmful Algae 2011, 11, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadji, I.; Laabir, M.; Frihi, H.; Collos, Y.; Shao, Z.J.; Berrebi, P.; Abadie, E.; Amzil, Z.; Chomérat, N.; Rolland, J.L.; et al. Unsuspected intraspecific variability in the toxin production, growth and morphology of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum R.W. Litaker (Group IV) blooming in a South Western Mediterranean marine ecosystem, Annaba Bay (Algeria). Toxicon 2020, 180, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovesi, B.; Berrebi, P.; Nagai, S.; Reynaud, N.; Wang, J.; Masseret, E. Geographic structure evidenced in the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum Litaker (A. catenella—Group IV (Whedon & Kofoid) Balech) along Japanese and Chinese coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 98, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Yu, R.; Geng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, M. Resting cysts of Alexandrium catenella and A. pacificum (Dinophyceae) in the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China: Abundance, distribution and implications for toxic algal blooms. Harmful Algae 2020, 93, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.H.; Li, Z.; Kim, E.S.; Park, J.; Lim, W.A. Which species, Alexandrium catenella (Group I) or A. pacificum (Group IV), is really responsible for past paralytic shellfish poisoning outbreaks in Jinhae-Masan Bay, Korea? Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turki, S.; Dhib, A.; Fertouna-Bellakhal, M.; Frossard, V.; Balti, N.; Kharrat, R.; Aleya, L. Harmful algal blooms (HABs) associated with phycotoxins in shellfish: What can be learned from five years of monitoring in Bizerte Lagoon (Southern Mediterranean Sea)? Ecol. Eng. 2014, 67, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Kaga, S.; Kaga, Y.; Ogata, T. Repercussions of the Great East Japan Earthquake tsunami on ellipsoidal Alexandrium cysts (Dinophyceae) in Ofunato Bay, Japan. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 135, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Alpermann, T.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Collos, Y.; Masseret, E.; Montresor, M. The globally distributed genus Alexandrium: Multifaceted roles in marine ecosystems and impacts on human health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 10–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daguer, H.; Hoff, R.B.; Molognoni, L.; Kleemann, C.R.; Felizardo, L.V. Outbreaks, toxicology, and analytical methods of marine toxins in seafood. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 24, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolah, F. Marine algal toxins: Origins, health effects, and their increased occurrence. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amin, S.A.; Green, H.D.; Hart, C.M.; Küpper, C.F.; Sunda, G.W.; Carrano, J.C. Photolysis of iron–siderophore chelates promotes bacterial–algal mutualism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17071–17076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodson, S.; Croft, M.; Deery, E.; Smith, A.; Warren, M. Algae acquire Vitamin B12 through a symbiotic relationship with bacteria. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 146, S222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Lyu, S.; An, Y.; Lu, J.; Gjermansen, C.; Schramm, A. Microalgae–bacteria symbiosis in microalgal growth and biofuel production: A review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, R.; Kim, B.; Cho, D.; Oh, H.; Kim, H. Algae–bacteria interactions: Evolution, ecology and emerging applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshihide, M.; Hiroshi, I.; Mugio, N.; Yoshikazu, S. Isolation of an Algal Morphogenesis Inducer from a Marine Bacterium. Science 2005, 307, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayali, X.; Franks, P.; Azam, F. Cultivation and Ecosystem Role of a Marine Roseobacter Clade-Affiliated Cluster Bacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2595–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, R.; Sun, P.; Zhang, J.; Esquivel-Elizondo, S.; Wu, Y. Microorganisms-based methods for harmful algal blooms control: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, S.; Zhou, W.; Yuan, W.; Wang, D. Algal cell lysis by bacteria: A review and comparison to conventional methods. Algal Res. 2020, 46, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayali, X.; Azam, F. Algicidal Bacteria in the Sea and their impact on Algal Blooms. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2010, 51, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuez, M.; González-Fernández, C.; Ballesteros, M. Algicidal microorganisms and secreted algicides: New tools to induce microalgal cell disruption. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Lei, X.; Zhang, H.; Cai, G.; Chen, Z.; Fu, L.; Xu, H.; Zheng, T. The death mechanism of the harmful algal bloom species Alexandrium tamarense induced by algicidal bacterium Deinococcus sp. Y35. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Ye, Q.; Chen, Q.; Yang, K.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Z.; Lu, S.; Shao, X.; Fan, Y.; Yao, L.; et al. Algicidal Activity of Novel Marine Bacterium Paracoccus sp. Strain Y42 against a Harmful Algal-Bloom-Causing Dinoflagellate, Prorocentrum donghaiense. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01015-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, L.; An, X.; Li, D.; Zhou, L.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, T. Isolation and alga-inhibiting characterization of Vibrio sp. BS02 against Alexandrium tamarense. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 2949–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, R. Culture of Phytoplankton for Feeding Marine Invertebrates. In Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals; Smith, W.L., Chanley, M.H., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1975; Volume 232, pp. 29–60. ISBN 978-1-4615-8714-9. [Google Scholar]
- Eyler, E. Pouring Agar Plates and Streaking or Spreading to Isolate Individual Colonies. In Methods in Enzymology; Lorsch, J., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 533, pp. 3–14. ISBN 9780124200944. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, N.; Ding, N.; Gao, P.; Han, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, L.; Fu, B.; Wang, R.; Zhou, J. Diverse algicidal bacteria associated with harmful bloom-forming Karenia mikimotoi in estuarine soil and seawater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1415–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Su, J.; Tian, Y.; Ning, X.; Hong, H.; Zheng, T. Lysis of a red-tide causing alga, Alexandrium tamarense, caused by bacteria from its phycosphere. Biol. Control 2010, 52, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.E.; Maniatis, T.E.; Fritsch, E.F. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratories: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 182–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, S.; Woese, C.R. A Definition of the Domains Archaea, Bacteria and Eucarya in Terms of Small Subunit Ribosomal RNA Characteristics. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1991, 14, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Using Maximum Likelihood, Evolutionary Distance, and Maximum Parsimony Methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parsons, T.R.; Maita, Y.; Lalli, C.M. 4.1—Determination of Chlorophylls and Total Carotenoids: Spectrophotometric Method. In A Manual of Chemical & Biological Methods for Seawater Analysis; Parsons, T.R., Maita, Y., Lalli, C.M., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1984; Volume 4, pp. 101–104. ISBN 9780080302874. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber, U.; Endo, T.; Mi, H.; Asada, K. Quenching Analysis of Chlorophyll Fluorescence by the Saturation Pulse Method: Particular Aspects Relating to the Study of Eukaryotic algae and Cyanobacteria. Plant Cell Physiol. 1995, 36, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubowski, W.; Bartosz, G. 2,7-dichlorofluorescin oxidation and reactive oxygen species: What does it measure? Cell Biol. Int. 2013, 24, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Manchanda, G. ROS generation in plants: Boon or bane? Plant Biosyst. 2009, 143, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, C.E.; Demir, E.; Coyne, K.J.; Craig Cary, S.; Kirchman, D.L.; Hutchins, D.A. A bacterium that inhibits the growth of Pfiesteria piscicida and other dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lin, S.; Liu, X.; Tan, J.; Pan, J.; Yang, H. A freshwater bacterial strain, shewanella sp. lzh-2, isolated from lake taihu and its two algicidal active substances, hexahydropyrrolo [1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione and 2,3-indolinedione. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 4737–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrzywinski, K.L.; Place, A.R.; Warner, M.E.; Coyne, K.J. Investigation of the algicidal exudate produced by Shewanella sp. IRI-160 and its effect on dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 2012, 19, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lv, J.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, S.; An, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, T. Cell death in a harmful algal bloom causing species Alexandrium tamarense upon an algicidal bacterium induction. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2014, 98, 7949–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinaga, I.; Kawai, T.; Ishida, Y. Analysis of Algicidal Ranges of the Bacteria Killing the Marine Dinoflagellate Gymnodinium mikimotoi Isolated from Tanabe Bay, Wakayama Pref., Japan. Fish. Sci. 1997, 63, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, J.Q.; Yang, X.R.; Zheng, T.L.; Tian, Y.; Jiao, N.Z.; Cai, L.Z.; Hong, H.S. Isolation and characterization of a marine algicidal bacterium against the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, W.; Yu, C.; Zheng, T. Novel insights into the algicidal bacterium DH77-1 killing the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482–483, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Guan, C.; Zhang, H.; Guo, J.; Chen, Z.; Cai, G.; Lei, X.; Zheng, W.; Tian, Y.; et al. Towards molecular, physiological, and biochemical understanding of photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress in the toxic Alexandrium tamarense induced by a marine bacterium. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2014, 98, 4637–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Yu, Z.; Fu, L.; Zheng, T. Discovery of an algicidal compound from Brevibacterium sp. BS01 and its effect on a harmful algal bloom-causing species, Alexandrium tamarense. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.S.; Son, H.; Jeong, S. Isolation of an algicide from a marine bacterium and its effects against the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella and other harmful algal bloom species. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Guo, X.; Cai, G.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, T. Novel algicidal evidence of a bacterium Bacillus sp. LP-10 killing Phaeocystis globosa, a harmful algal bloom causing species. Biol. Control 2014, 76, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-D.; Kim, J.-Y.; Park, J.-K.; Lee, C.-G. Selective Control of the Prorocentrum minimum Harmful Algal Blooms by a Novel Algal-Lytic Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis AFMB-008041. Mar. Biotechnol. 2009, 11, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Ding, G.; Lin, S.; Chen, J. Isolation of an algicidal bacterium and its effects against the harmful-algalbloom dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2018, 80, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Hu, C.; Li, H.; Hu, Z. Isolation and characterization of the marine algicidal bacterium Pseudoalteromonas S1 against the harmful alga Akashiwo sanguinea. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.O.; Kato, J.; Takiguchi, N.; Kuroda, A.; Ohtake, H. Involvement of an Extracellular Protease in Algicidal Activity of the Marine Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. Strain A28. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4334–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, P.; Zhao, L. Effects of two algicidal substances, ortho-tyrosine and urocanic acid, on the growth and physiology of Heterosoigma akashiwo. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Hu, X.; Yin, P.; Zhao, L. Photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress to the toxic Phaeocystis globosa caused by a diketopiperazine isolated from products of algicidal bacterium metabolism. J. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cai, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, K.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; et al. Algicidal Effects of Prodigiosin on the Harmful Algae Phaeocystis globosa. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pérez, M.E.; Crespo, S.D.L.A. Reactive Oxygen Species and Autophagy in Plants and Algae. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Hou, X.; Zhang, S.; Dai, X.; Zhang, X.; Igarashi, Y.; Luo, F. Algicidal effect of tryptoline against Microcystis aeruginosa: Excess reactive oxygen species production mediated by photosynthesis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Phylum | Genus | Killed Algae | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proteobacteria | Vibrio sp. | A. tamarense | [27,46] |
| A. catenella | [47] | ||
| Pseudoalteromonas sp. | A. catenella | [48] | |
| Shewanella sp. | A. pacificum | This study | |
| Bacteroidetes | Joostella sp. | A. tamarense | [49] |
| Flavobacterium sp. | A. tamarense | [50] | |
| Thermus | Deinococcus sp. | A. tamarense | [29] |
| Actinobacteria | Brevibacterium sp. | A. tamarense | [51] |
| A. catenella | [52] | ||
| Firmicules | Bacillus sp. | A. catenella | [53] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Sun, P.; Ma, S.; Chen, T. Algicidal Effects of a High-Efficiency Algicidal Bacterium Shewanella Y1 on the Toxic Bloom-Causing Dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040239
Chen X, Wang D, Wang Y, Sun P, Ma S, Chen T. Algicidal Effects of a High-Efficiency Algicidal Bacterium Shewanella Y1 on the Toxic Bloom-Causing Dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(4):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040239
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xi, Dengyu Wang, Yanqun Wang, Pengfei Sun, Shuanghui Ma, and Tiantian Chen. 2022. "Algicidal Effects of a High-Efficiency Algicidal Bacterium Shewanella Y1 on the Toxic Bloom-Causing Dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum" Marine Drugs 20, no. 4: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040239
APA StyleChen, X., Wang, D., Wang, Y., Sun, P., Ma, S., & Chen, T. (2022). Algicidal Effects of a High-Efficiency Algicidal Bacterium Shewanella Y1 on the Toxic Bloom-Causing Dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum. Marine Drugs, 20(4), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040239






