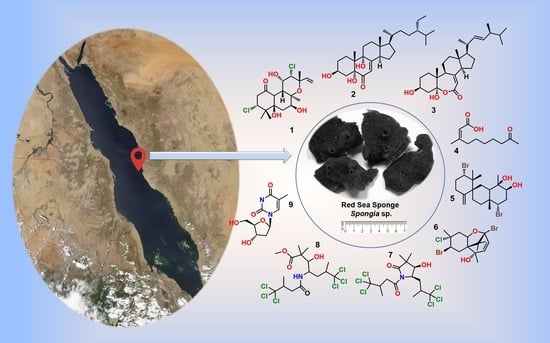
The Chemically Highly Diversified Metabolites from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Spongia sp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Separation
3.3.1. Spongianol (1)
3.3.2. 3β,5α,9α-Trihydroxy-24S-ethylcholest-7-en-6-one (2)
3.3.3. (22E,24S)-Ergosta-7,22-dien-3β,5α-diol-6,5-olide (3)
3.3.4. (Z)-3-Methyl-9-oxodec-2-enoic Acid (4)
3.4. DFT and TD-DFT Calculations
3.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.6. Antibacterial Assay
3.7. Anti-inflammatory Activity
3.7.1. Superoxide Anion Generation
3.7.2. Elastase Release
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 362–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maximo, P.; Ferreira, L.M.; Branco, P.; Lima, P.; Lourenco, A. The role of Spongia sp. in the discovery of marine lead compounds. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, Y.-Q.; Liao, X.-J.; Zhao, B.-X.; Xu, S.-H. Novel 3,4-seco-3,19-dinorspongian and 5,17-epoxy-19-norspongian diterpenes from the marine sponge Spongia sp. Org. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 3253–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.-Q.; Liao, X.-J.; Lin, J.-L.; Xu, W.; Chen, G.-D.; Zhao, B.-X.; Xu, S.-H. Spongiains A−C: Three new spongian diterpenes with ring A rearrangement from the marine sponge Spongia sp. Tetrahedron 2019, 75, 3802–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdjul, D.B.; Yamazaki, H.; Kanno, S.I.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Rotinsulu, H.; Sumilat, D.A.; Ukai, K.; Kapojos, M.M.; Namikoshi, M. Furanoterpenes, new types of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors, from two Indonesian marine sponges, Ircinia and Spongia spp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 1159–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauvais, C.; Bonneau, N.; Blond, A.; Perez, T.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L.; Zirah, S. Furanoterpene diversity and variability in the marine sponge Spongia officinalis, from untargeted LC-MS/MS metabolomic profiling to furanolactam derivatives. Metabolites 2017, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Desoky, A.H.; Kato, H.; Tsukamoto, S. Ceylonins G−I: Spongian diterpenes from the marine sponge Spongia ceylonensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 71, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Mao, Q.; Bao, M.; Mou, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhao, M.; Jiang, W.; Yu, X.; Wang, C.; Dai, L.; et al. Spongian diterpenes including one with a rearranged skeleton from the marine sponge Spongia officinalis. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1714–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Hahn, D.; Chin, J.; Won, D.H.; Ko, J.; Choi, H.; Hong, A.; Nam, S.-J.; et al. Scalalactams A−D, scalarane sesterterpenes with a γ-lactam moiety from a Korean Spongia sp. marine sponge. Molecules 2018, 23, 3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nam, S.-J.; Ko, H.; Ju, M.-K.; Hwang, H.; Chin, J.; Ham, J.; Lee, B.; Lee, J.; Won, D.-H.; Choi, H.; et al. Scalarane sesterterpenes from a marine sponge of the genus Spongia and their FXR antagonistic activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gu, B.-B.; Sun, F.; Xu, J.-R.; Jiao, W.-H.; Yu, H.-B.; Han, B.-N.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.-C.; Lin, H.-W. Sesquiterpene quinones/hydroquinones from the marine sponge Spongia pertusa Esper. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Nguyen, H.M.; Win, N.N.; Vo, H.Q.; Nguyen, H.T.; Morita, H. Three new sesquiterpene aminoquinones from a Vietnamese Spongia sp. and their biological activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 72, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.-Q.; Liao, X.-J.; Zhao, B.-X.; Xu, S.-H. (+)- and (−)-Spongiterpene, a pair of new valerenane sesquiterpene enantiomers from the marine sponge Spongia sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 35, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassia, A.; Bruno, I.; Debitus, C.; Marzocco, S.; Pinto, A.; Gomez-Paloma, L.; Riccio, R. Spongidepsin, a new cytotoxic macrolide from Spongia sp. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 6257–6260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliuolo, A.; Piccialli, V.; Sica, D. Two new 9,11-secosterols from the marine sponge Spongia officinalis. Synthesis of 9,11-seco-3b,6a,11-trihydroxy-5a-cholest-7-en-9-one. Steroids 1992, 57, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliuolo, A.; Piccialli, V.; Sica, D.; Giordano, F. New Δ8- and Δ8(14)-5α-6α-epoxysterols from the marine sponge Spongia officinalis. Steroids 1993, 58, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, G.R.; Cichacz, Z.A.; Gao, F.; Herald, C.L.; Boyd, M.R.; Schmidt, J.M.; Hooper, J.N.A. Antineoplastic agents. 257. Isolation and structure of spongistatin 1. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 1302–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, A.A.; Rae, J.; Fontaine, F.; Conte, M.M.; Khalil, Z.; Martin, S.; Parton, R.G.; Capon, R.J. Heterofibrins: Inhibitors of lipid droplet formation from a deep-water southern Australian marine sponge, Spongia (Heterofibria) sp. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 3188–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, E.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Villani, G.; Varcamonti, M.; Sayem, S.M.A.; van Soest, R.; Gavagnin, M. Bioactive terpenes from Spongia officinalis. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guella, G.; Mancini, I.; Pietra, F. C-15 acetogenins and terpenes of the dictyoceratid sponge Spongia zimocca of IL-Rogiolo: A case of seaweed-metabolite transfer to, and elaboration within, a sponge? Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B. 1992, 103, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.-H.; Cen, Y.-Z.; Zeng, L.-M.; Su, J.-Y. Isolation and structural determination of heterocyclic alkaloidal compounds. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 20, 248–250. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, C.-J.; Huang, C.-Y.; Ahmed, A.-F.; Orfali, R.-S.; Alarif, W.-M.; Huang, Y.M.; Wang, Y.-H.; Hwang, T.-L.; Sheu, J.-H. An anti-inflammatory 2,4-cyclized-3,4-secospongian diterpenoid and furanoterpene-related metabolites of a marine sponge Spongia sp. from the Red Sea. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, N.-Y.; Li, X.-M.; Li, K.; Ding, L.-P.; Gloer, J.B.; Wang, B.-G. Diterpenes, sesquiterpenes, and a C15-acetogenin from the marine red alga Laurencia mariannensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1901–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denys, R.; Coll, J.C.; Bowden, B.F. Tropical marine algae. IX. A new sesquiterpenoid metabolite from the red alga Laurencia marianensis. Aust. J. Chem. 1993, 46, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauleau, P.; Retailleau, P.; Vacelet, J.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L. New polychlorinated pyrrolidinones from the Red Sea marine sponge Lamellodysidea herbacea. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Badr, J.M.; Shaala, L.A.; Mohamed, G.A.; Bamanie, F.H. Ehrenasterol and biemnic acid; new bioactive compounds from the Red Sea sponge Biemna ehrenbergi. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 12, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescitelli, G.; Bruhn, T. Good Computational Practice in the Assignment of Absolute Configurations by TDDFT Calculations of ECD Spectra. Chirality 2016, 28, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision D.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Briand, A.; Kornprobst, J.-M.; Al-Easa, H.S.; Rizk, A.F.M.; Toupet, L. (−)-Paniculatol, a new ent-labdane bromoditerpene from Laurencia paniculata. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 3399–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Nakano, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Abe, T.; Masuda, M.; Takahashi, H.; Kobayashi, K. Brominated labdane-type diterpenoids from an Okinawan Laurencia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 801–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaoita, Y.; Amemiya, K.; Ohnuma, H.; Furumura, K.; Masaki, A.; Matsuki, T.; Kikuchi, M. Sterol constituents from five edible mushrooms. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 46, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sright, J.L.C.; McInnes, A.G.; Shimizu, S.; Smith, D.G.; Walter, J.A.; Idler, D.; Khalil, W. Identification of C-24 alkyl epimers of marine sterols by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Can. J. Chem. 1978, 56, 1898–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubinstein, I.; Goad, L.J.; Clague, A.D.H.; Mulheirn, L.J. The 220 MHz NMR spectra of phytosterols. Phytochemistry 1976, 15, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, E.; Abdel-Razik, A.F.; Zervou, M.; Christofidis, D.; Alexi, X.; Vagias, C.; Alexis, M.N.; Roussis, V. 5α,8α-Epidioxysterols from the gorgonian Eunicella cavolini and the ascidian Trididemnum inarmatum: Isolation and evaluation of their antiproliferative activity. Steroids 2009, 74, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliuolo, A.; Notaro, G.; Piccialli, V.; Sica, D. New tetrahydroxylated sterols from the marine sponge Spongia officinalis. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 1414–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Huang, Y.; Su, H.; Gao, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Qiu, M. C28 steroids from the fruiting bodies of Ganoderma resinaceum with potential anti-inflammatory activity. Phytochemistry 2019, 168, 112109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marino, S.; Palagiano, E.; Zollo, F.; Minale, L.; Iorizzi, M. A novel sulphated steroid with a 7-membered 5-oxalactone B-ring from an Antarctic starfish of the family Asteriidae. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 8625–8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-C.; Guo, Y.-W.; Song, G.-Q. Fortisterol, a novel steroid with an unusual seven-membered lactone ring B from the Chinese marine sponge Biemna fortis Topsent. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 8, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angawi, R.F.; Alarif, W.M.; Hamza, R.I.; Badria, F.A.; Ayyad, S.E.N. New cytotoxic laurene-, cuparene-, and laurokamurene-type sesquiterpenes from the red alga Laurencia obtusa. Helv. Chim. Acta 2014, 97, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.R.; Kim, I.K.; Erickson, K.L. Kahukuenes, new diterpenoids from the marine alga Laurencia majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.J.; Fenical, W.; Wing, R.M.; Radlick, P. Marine natural products. I. Pacifenol, a rare sesquiterpene containing bromine and chlorine from the red alga, Laurencia pacifica. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1971, 93, 3774–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, V.; De-Paula, J.C.; Fujii, M.; Gama, B.A.P.; Teixeira, V. Sesquiterpenes from the introduced red seaweed Laurencia caduciramulosa (Rhodomelaceae, Ceramiales). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2008, 36, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallard, M.O.; Faulkner, D.J. Chemical constituents of the digestive gland of the sea hare Aplysia californica. II. Chemical transformations. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1974, 49, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Palaniveloo, K.; Vairappan, C.S. Chemical relationship between red algae genus Laurencia and sea hare (Aplysia dactylomela Rang) in the North Borneo Island. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmely, S.; Gebreyesus, T.; Kashman, Y.; Skelton, B.W.; White, A.H.; Yosief, T. Dysidamide, a novel metabolite from a Red Sea sponge Dysidea herbacea. Aust. J. Chem. 1990, 43, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olinger, L.K.; Strangman, W.K.; McMurray, S.E.; Pawlik, J.R. Sponges with microbial symbionts transform dissolved organic matter and take up organohalides. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 665789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berumen, M.L.; Hoey, A.S.; Bass, W.H.; Bouwmeester, J.; Catania, D.; Cochran, J.E.M.; Khalil, M.T.; Miyake, S.; Mughal, M.R.; Spaet, J.L.Y.; et al. The status of coral reef ecology research in the Red Sea. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trautman, D.A.; Hinde, R.; Borowitzka, M.A. Population dynamics of an association between a coral reef sponge and a red macroalga. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 244, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubarsky, H.V.; Hubas, C.; Chocholek, M.; Larson, F.; Manz, W.; Paterson, D.M.; Gerbersdorf, S.U. The stabilisation potential of individual and mixed assemblages of natural bacteria and microalgae. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiese, J.; Thiel, V.; Nagel, K.; Staufenberger, T.; Imhoff, J.F. Diversity of antibiotic-active bacteria associated with the brown alga Laminaria saccharina from the Baltic Sea. Mar. Biotechnol. 2009, 11, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinberg, P.D.; De Nys, R. Chemical mediation of colonization of seaweed surfaces. J. Phycol. 2002, 38, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vairappan, C.S.; Suzuki, M.; Abe, T.; Masuda, M. Halogenated metabolites with antibacterial activity from the Okinawan Laurencia species. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vairappan, C.S. Potent antibacterial activity of halogenated metabolites from Malaysian red algae, Laurencia majuscula (Rhodomelaceae, Ceramiales). Biomol. Eng. 2003, 20, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-P.; Hsieh, P.-W.; Chang, Y.-J.; Chung, P.-J.; Kuo, L.-M.; Hwang, T.-L. 2-(2-Fluorobenzamido)benzoate ethyl ester (EFB-1) inhibits superoxide production by human neutrophils and attenuates hemorrhagic shock-induced organ dysfunction in rats. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 1737–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-C.; Chung, P.-J.; Ho, C.-M.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Hung, M.-F.; Huang, Y.-T.; Chang, W.-Y.; Chang, Y.-W.; Chan, K.-H.; Hwang, T.-L. Propofol inhibits superoxide production, elastase release, and chemotaxis in formyl peptide-activated human neutrophils by blocking formyl peptide receptor 1. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 6511–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwang, T.-L.; Su, Y.-C.; Chang, H.-L.; Leu, Y.-L.; Chung, P.-J.; Kuo, L.-M.; Chang, Y.-J. Suppression of superoxide anion and elastase release by C18 unsaturated fatty acids in human neutrophils. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1395–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Chang, H.-S.; Hsiao, H.-H.; Chen, Y.-F.; Kuo, Y.-P.; Yen, F.-L.; Yen, C.-H. Identification of beilschmiedia tsangii root extract as a liver cancer cell–normal keratinocyte dual-selective NRF2 regulator. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.-T.; Chen, Y.-S.; Tang, K.-W.; Lee, J.-C.; Tseng, C.-H.; Tzeng, C.-C.; Yen, C.-H.; Chen, Y.-L. Discovery of 4-anilinoquinolinylchalcone derivatives as potential NRF2 activators. Molecules 2020, 25, 3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.W.; Watkins, D.; Jin, Y.; Gong, C.; King, A.; Washington, A.Z.; Green, K.D.; Garneau-Tsodikova, S.; Oyelere, A.K.; Arya, D.P. Rapid synthesis, RNA binding, and antibacterial screening of a peptidic-aminosugar (PA) library. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 1278–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| 1 a | 2 b | 3 b | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | δH | δC | # | δH | δC | # | δH | δC |
| 1 | – | 209.2, C c | 1 | 1.52, m | 25.1, CH2 | 1 | 1.95, m | 35.9, CH2 |
| 2α | 2.64, dd (14.0, 6.0) d | 45.1, CH2 | 2.34, dt (11.0, 3.0) | 1.40, m | ||||
| 2α | 1.86, m | 30.4, CH2 | ||||||
| 2β | 3.34, t (13.0) | 2α | 1.93, m | 30.1, CH2 | 2β | 1.40, m | ||
| 3 | 4.50, dd (13.0, 6.0) | 65.9, CH | 2β | 1.51, m | 3 | 3.79, m | 67.6, CH | |
| 3 | 4.07, m | 67.2, CH | 4α | 2.25, m | 46.2. CH2 | |||
| 4 | – | 45.2, C | 4α | 2.09, dd (11.5, 1.5) | 37.2, CH2 | 4β | 2.10, m | |
| 5 | – | 104.3, C | ||||||
| 5 | – | 82.1, C | 4β | 1.77, m | 6 | – | 166.4, C | |
| 6α | 2.18, tt (15.5, 3.5) | 27.7, CH2 | 5 | – | 79.7, C | 7 | 5.70, br s | 115.3, CH |
| 6 | – | 197.7, C | 8 | – | 159.7, C | |||
| 6β | 2.05, tt (15.5, 3.5) | 7 | 5.66, br s | 119.9, CH | 9 | 2.26, m | 51.7, CH | |
| 8 | – | 164.3, C | 10 | – | 43.1, C | |||
| 7 | 3.67, t (3.5) | 75.3, CH | 9 | – | 74.6, C | 11 | 1.82, m | 25.3, CH2 |
| 8 | – | 76.2, C | 10 | – | 41.8, CH | 1.64, m | ||
| 9 | 2.72, br s e | 41.7, CH | 11 | 1.76, m | 28.8, CH2 | 12α | 2.05, m | 39.9, CH2 |
| 10 | – | 58.1, C | 1.94, m | 12β | 1.42, m | |||
| 11 | 5.32, t (2.5) | 70.9, CH | 12α | 1.72, m | 35.0, CH | 13 | – | 46.6, C |
| 12 | 4.06, d (2.5) | 68.9, CH | 12β | 1.92, m | 14 | 2.14, m | 58.1, CH | |
| 13 | – | 77.4, C | 13 | – | 45.4, C | 15α | 1.58, m | 23.1, CH2 |
| 14 | 6.78, dd (17.5, 11.5) | 139.9, CH | 14 | 2.72, dd (9.5, 4.5) | 51.7, C | 15β | 1.50, m | |
| 16 | 1.77, m | 28.0, CH2 | ||||||
| 15 | 5.21, d (11.5) | 116.7, CH2 | 15α | 1.64, m | 22.5, CH2 | 1.33, m | ||
| 5.35, d (17.5) | 15β | 1.51, m | 17 | 1.37, m | 56.3, CH | |||
| 16 | 1.49, s | 28.7, CH3 | 16 | 1.40, m | 27.7, CH2 | 18 | 0.62, s | 12.4, CH3 |
| 17 | 1.66, s | 25.9, CH3 | 2.01, m | 19 | 1.06, s | 17.8, CH3 | ||
| 18 | 1.24, s | 24.0, CH3 | 17 | 1.39, m | 56.0, CH | 20 | 2.05, m | 40.4, CH |
| 19 | 1.21, s | 20.1, CH3 | 18 | 0.61, s | 12.0, CH3 | 21 | 1.01, d (6.0) | 21.0, CH3 |
| 20 | 1.71, s | 18.9, CH3 | 19 | 1.02, s | 20.5, CH3 | 22 | 5.13, dd (15.0, 7.8) | 135.2, CH |
| 5-OH | 5.72, br s | 20 | 1.40, m | 36.4, CH | 23 | 5.21, dd (15.0, 8.4) | 132.7, CH | |
| 7-OH | 3.59, d (2.0) | 21 | 0.94, d (6.0) | 18.9, CH3 | 24 | 1.85, m | 43.1, CH | |
| 11-OH | 2.25, d (1.5) | 22 | 1.05, m | 33.7, CH2 | 25 | 1.47, m | 33.2, CH | |
| 1.39, m | 26 | 0.82, d (6.6) | 19.6, CH3 | |||||
| 23 | 1.38, m | 26.3, CH2 | 27 | 0.84, d (7.2) | 20.1, CH3 | |||
| 24 | 0.93, m | 46.0, CH | 28 | 0.92, d (7.2) | 18.0, CH3 | |||
| 25 | 1.63, m | 28.9, CH | ||||||
| 26 | 0.81, d (6.6) | 19.0, CH3 | ||||||
| 27 | 0.84, d (6.6) | 19.6, CH3 | ||||||
| 28 | 1.14, m | 23.0, CH2 | ||||||
| 1.32, m | ||||||||
| 29 | 0.85, t (7.8) | 12.3, CH3 | ||||||
| 5-OH | 3.34 br s | – | ||||||
| 9-OH | 4.12 br s | – | ||||||
| Position | 3 a (22E,24S) | 19 b (22E,24R) | 20 c (22E,24S) | 21 c (22E,24R) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-16 | 28.0 | 27.7 | 28.86 | 28.58 |
| C-24 | 43.1 | 42.8 | 43.12 | 42.90 |
| C-25 | 33.2 | 33.0 | 33.28 | 33.16 |
| C-26 | 19.6 | 19.9 | 19.69 | 20.02 |
| C-27 | 20.1 | 19.6 | 20.19 | 19.69 |
| C-28 | 18.0 | 17.6 | 18.08 | 17.68 |
| 4 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Position | δH | δC |
| 1 | - | 169.5, C a |
| 2 | 5.69, br s b | 115.3, CH |
| 3 | - | 163.5, C |
| 4 | 2.62, t (7.5) c | 33.1, CH2 |
| 5 | 1.48, quin (7.5) | 27.8, CH2 |
| 6 | 1.33, quin (7.5) | 29.0, CH2 |
| 7 | 1.60, quin (7.5) | 23.5, CH2 |
| 8 | 2.43, t (7.5) | 43.6, CH2 |
| 9 | - | 209.4, C |
| 10 | 2.14, s | 29.9, CH3 |
| 11 | 1.91, s | 25.4, CH3 |
| Compound | Superoxide Anion | Elastase Release | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (μM) a | Inh% (20 μM) | IC50 (μM) | Inh% (20 μM) | |
| 1 | >20 | 15.65 ± 7.56 | >20 | 16.31 ± 4.66 * |
| 2 | >20 | −0.04 ± 3.90 | >20 | 6.28 ± 3.04 |
| 3 | >20 | 18.10 ± 2.29 ** | >20 | 13.08 ± 2.01 ** |
| 4 | >20 | 7.81 ± 3.87 | >20 | 18.53 ± 3.57 ** |
| 5 | >20 | 3.25 ± 4.06 | >20 | 13.27 ± 3.81 * |
| 6 | >20 | 15.51 ± 7.55 | >20 | 20.00 ± 4.87 * |
| 7 | >20 | 25.24 ± 4.68 ** | 17.23 ± 2.45 | 55.96 ± 3.88 *** |
| 8 | >20 | 22.38 ± 3.95 ** | 14.60 ± 2.24 | 60.80 ± 6.49 *** |
| 9 | >20 | 15.58 ± 0.58 *** | >20 | 21.22 ± 4.71 * |
| LY294002 | 1.91 ± 0.79 | 88.71 ± 1.50 *** | 2.94 ± 0.13 | 79.50 ± 1.95 *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tai, C.-J.; Ahmed, A.F.; Chao, C.-H.; Yen, C.-H.; Hwang, T.-L.; Chang, F.-R.; Huang, Y.M.; Sheu, J.-H. The Chemically Highly Diversified Metabolites from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Spongia sp. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040241
Tai C-J, Ahmed AF, Chao C-H, Yen C-H, Hwang T-L, Chang F-R, Huang YM, Sheu J-H. The Chemically Highly Diversified Metabolites from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Spongia sp. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(4):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040241
Chicago/Turabian StyleTai, Chi-Jen, Atallah F. Ahmed, Chih-Hua Chao, Chia-Hung Yen, Tsong-Long Hwang, Fang-Rong Chang, Yusheng M. Huang, and Jyh-Horng Sheu. 2022. "The Chemically Highly Diversified Metabolites from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Spongia sp." Marine Drugs 20, no. 4: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040241
APA StyleTai, C.-J., Ahmed, A. F., Chao, C.-H., Yen, C.-H., Hwang, T.-L., Chang, F.-R., Huang, Y. M., & Sheu, J.-H. (2022). The Chemically Highly Diversified Metabolites from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Spongia sp. Marine Drugs, 20(4), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040241