Evaluation of a Thermophilic, Psychrostable, and Heavy Metal-Resistant Red Sea Brine Pool Esterase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
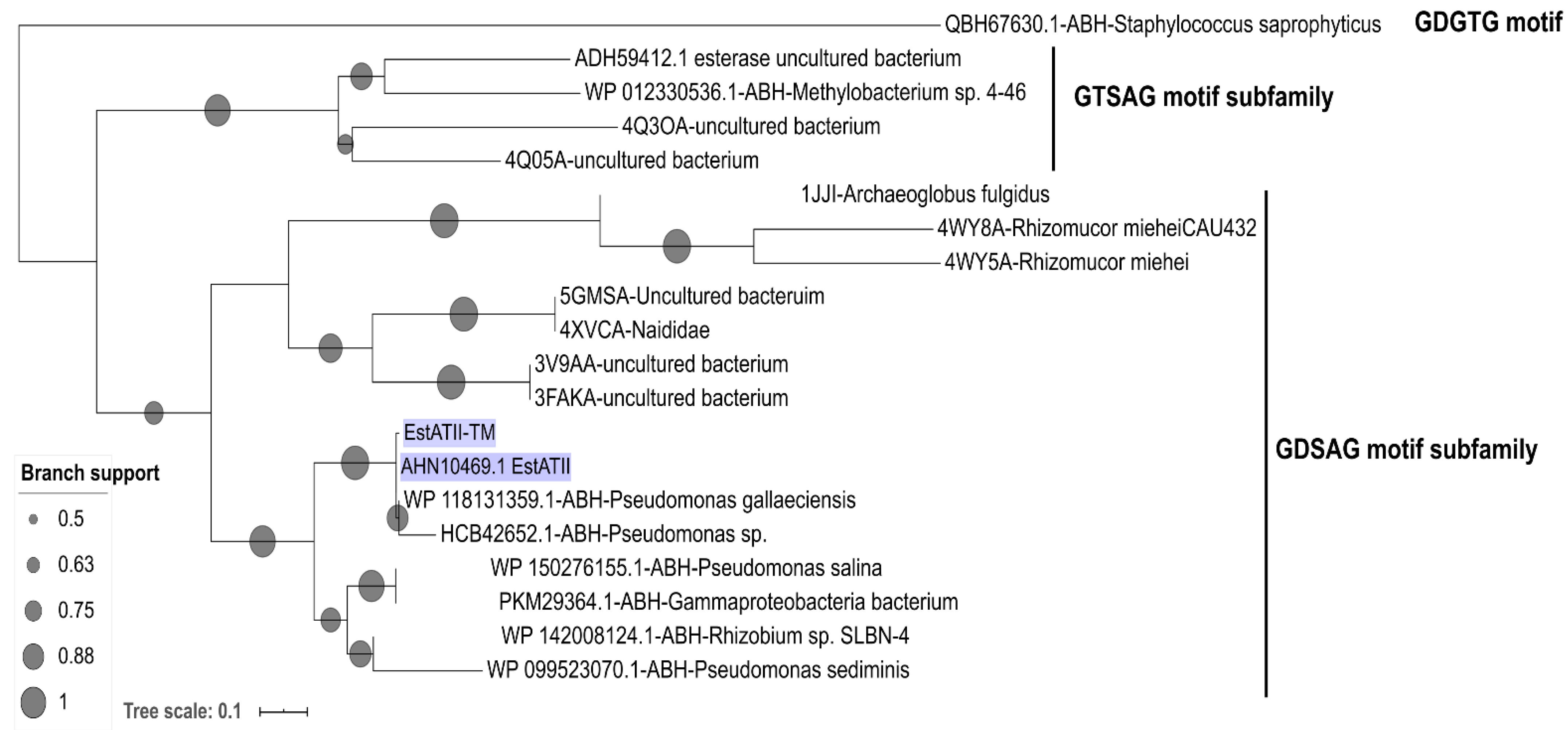
2.1. In-Silico Characterization of EstATII-TM
2.2. Characterization of EstATII-TM
2.2.1. Cloning and Expression of EstATII-TM Gene
2.2.2. Qualitative Assay of EstATII-TM Enzyme Activity
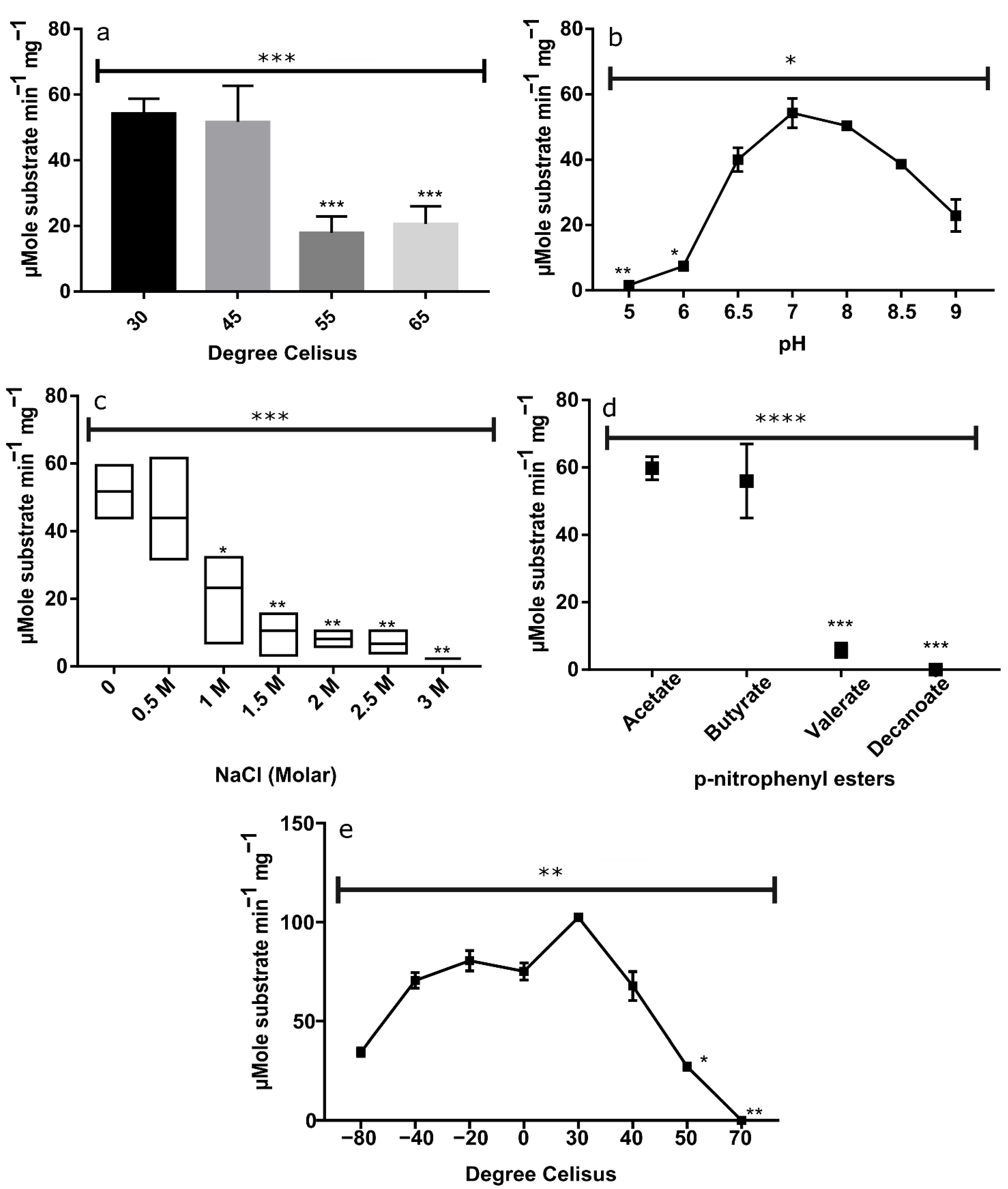
2.2.3. Thermophilicity of EstATII-TM
2.2.4. pH Effect on EstATII-TM Activity
2.2.5. Halophilicity of EstATII-TM
2.2.6. Substrate Specificity of EstATII-TM
2.2.7. Thermostability and Psychrostability of EstATII-TM
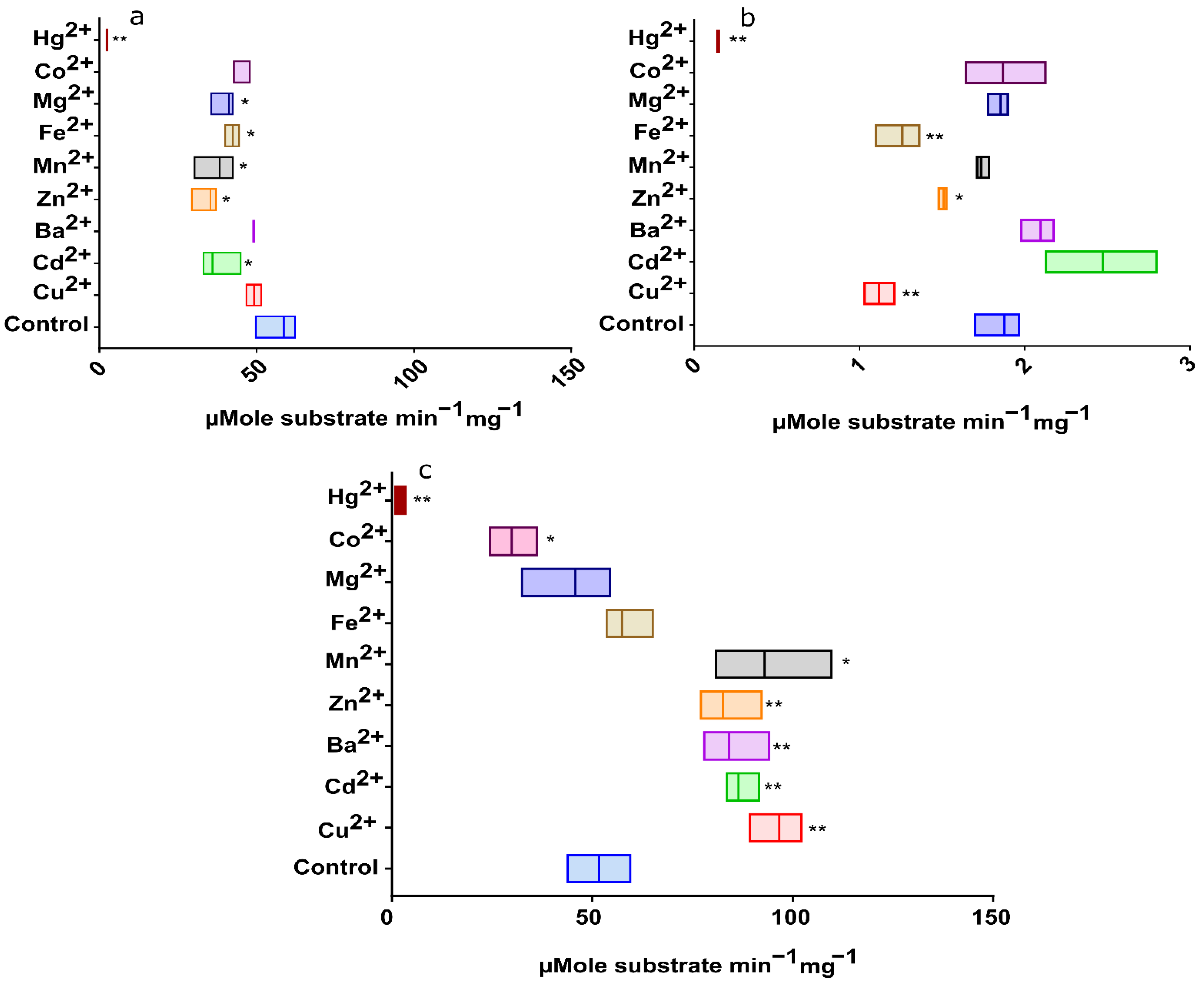
2.2.8. Effect of Heavy Metals on EstATII-TM and Two Market Esterases Activities
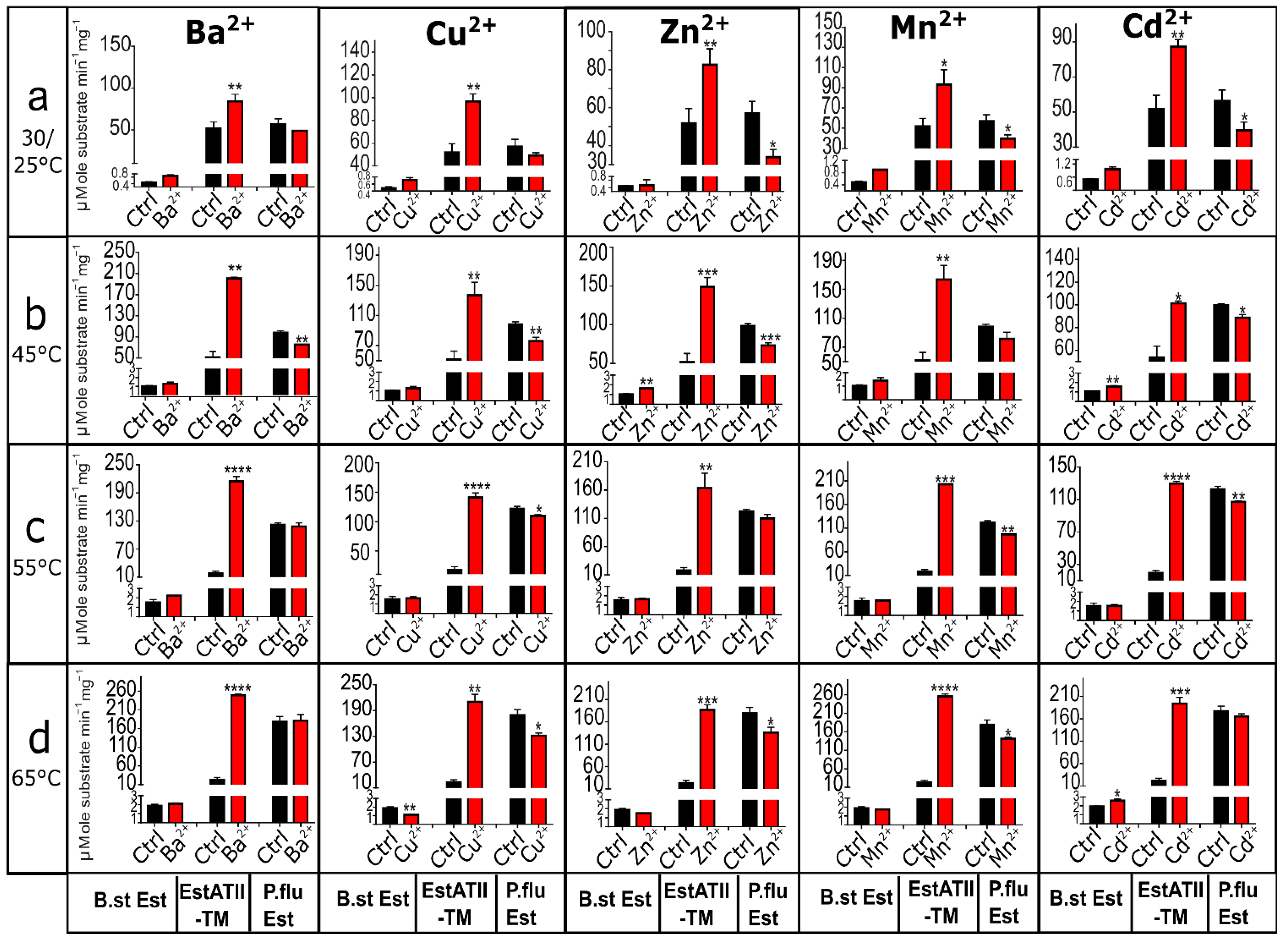
2.2.9. Effect of Heavy Metal on EstATII-TM and Two Commercial Esterases under Thermophilic Conditions
2.3. Enzyme Kinetics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Environmental DNA Isolation and Fosmid Library Construction
4.2. Cloning of the ESTAII-TM Gene
4.3. Gene Sequences and Computational Analysis
4.4. Expression and Purification of His Tagged EstATII-TM Esterase
4.5. Enzyme Characterization
4.5.1. Qualitative Assay
4.5.2. Quantitative Assay
4.5.3. Effect of Different Temperatures on Enzyme Activity and Thermostability
4.5.4. Effect of Different pH on Enzyme Activity
4.5.5. Effect of Halophilicity on Enzyme Activity
4.5.6. Enzyme Substrate Specificity
4.5.7. Effect of Metal Ions
4.5.8. Effect of Metal Ions on Two Commercial Esterases
4.5.9. Enzyme Kinetics
4.5.10. Statistical Analysis
4.5.11. Data Deposition
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antunes, A.; Ngugi, D.K.; Stingl, U. Microbiology of the Red Sea (and Other) Deep-Sea Anoxic Brine Lakes. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2011, 3, 416–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, Y.M.; Ghazy, M.A.; Sayed, A.; Ouf, A.; El-Dorry, H.; Siam, R. Isolation and Characterization of a Heavy Metal-Resistant, Thermophilic Esterase from a Red Sea Brine Pool. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sayed, A.; Ghazy, M.A.; Ferreira, A.J.S.; Setubal, J.C.; Chambergo, F.S.; Ouf, A.; Adel, M.; Dawe, A.S.; Archer, J.A.C.; Bajic, V.B.; et al. A Novel Mercuric Reductase from the Unique Deep Brine Environment of Atlantis II in the Red Sea. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sonbol, S.A.; Ferreira, A.J.S.; Siam, R. Red Sea Atlantis II Brine Pool Nitrilase with Unique Thermostability Profile and Heavy Metal Tolerance. BMC Biotechnol. 2016, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, M.; Gai, Y.; Guo, X.; Hou, Y.; Zeng, R. Properties and Applications of Extremozymes from Deep-Sea Extremophilic Microorganisms: A Mini Review. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raddadi, N.; Cherif, A.; Daffonchio, D.; Neifar, M.; Fava, F. Biotechnological Applications of Extremophiles, Extremozymes and Extremolytes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 7907–7913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Littlechild, J.A. Enzymes from Extreme Environments and Their Industrial Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madhavan, A.; Sindhu, R.; Parameswaran, B.; Sukumaran, R.K.; Pandey, A. Metagenome Analysis: A Powerful Tool for Enzyme Bioprospecting. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 183, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, T.; Gowrishankar, B.S. Production and Applications of Esterases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 67, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.S.; Kapri, A.; Goel, R. Heavy Metal Pollution: Source, Impact, and Remedies. In Biomanagement of Metal-Contaminated Soils; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Andreini, C.; Bertini, I.; Cavallaro, G.; Holliday, G.L.; Thornton, J.M. Metal Ions in Biological Catalysis: From Enzyme Databases to General Principles. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 13, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreini, C.; Bertini, I.; Cavallaro, G.; Holliday, G.L.; Thornton, J.M. Metal-MACiE: A Database of Metals Involved in Biological Catalysis. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2088–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muñoz, C.; Fermoso, F.G.; Rivas, M.; Gonzalez, J.M. Hydrolytic Enzyme Activity Enhanced by Barium Supplementation. AIMS Microbiol. 2016, 2, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Singh, B.; Adhikari, D.K.; Mukherjee, J.; Ghosh, D. A Thermoalkaliphilic Halotolerant Esterase from Rhodococcus Sp. LKE-028 (MTCC 5562): Enzyme Purification and Characterization. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaouani, A.; Neifar, M.; Hamza, A.; Chaabouni, S.; Martinez, M.J.; Gtari, M. Purification and Characterization of a Highly Thermostable Esterase from the Actinobacterium Geodermatophilus Obscurus Strain G20. J. Basic Microbiol. 2012, 52, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.H.; Oh, K.H.; Lee, M.H.; Oh, T.K.; Kim, B.H.; Yoon, J.H. A Novel Family VII Esterase with Industrial Potential from Compost Metagenomic Library. Microb. Cell Factories 2011, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chu, X.; He, H.; Guo, C.; Sun, B. Identification of Two Novel Esterases from a Marine Metagenomic Library Derived from South China Sea. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 80, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, N.A.; Knoll, M.; Abdel-Fattah, Y.R.; Schmid, R.D.; Lange, S. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of Thermostable Esterase and Lipase from Geobacillus Thermoleovorans YN Isolated from Desert Soil in Egypt. Process Biochem. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebsfänger, N.; Zocher, F.; Altenbuchner, J.; Bornscheuer, U.T. Characterization and Enantioselectivity of a Recombinant Esterase from Pseudomonas Fluorescens. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1998, 22, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-Y.; Yoo, W.; Huong Luu Le, L.T.; Kim, K.K.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.O.; Kim, T.D. Characterization and Mutation Anaylsis of a Cold-Active Bacterial Hormone-Sensitive Lipase from Salinisphaera Sp. P7-4. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 663, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel-Ruano, V.; Rivera, I.; Rajkovic, J.; Knapik, K.; Torrado, A.; Otero, J.M.; Beneventi, E.; Becerra, M.; Sánchez-Costa, M.; Hidalgo, A.; et al. Biochemical and Structural Characterization of a Novel Thermophilic Esterase EstD11 Provide Catalytic Insights for the HSL Family. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 1214–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Kang, C.H.; Won, S.M.; Oh, K.H.; Yoon, J.H. Characterization of a Novel Moderately Thermophilic Solvent-Tolerant Esterase Isolated From a Compost Metagenome Library. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, P.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Ji, P.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, B.B.; Qin, Q.L.; Su, H.N.; Zhou, B.C.; et al. Interdomain Hydrophobic Interactions Modulate the Thermostability of Microbial Esterases from the Hormone-Sensitive Lipase Family. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 11188–11198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tahir, H.M.; Rahman, R.N.Z.R.A.; Leow, A.T.C.; Ali, M.S.M. Expression, Characterisation and Homology Modelling of a Novel Hormone-Sensitive Lipase (HSL)-like Esterase from Glaciozyma Antarctica. Catalysts 2020, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayanath, G.; Mohandas, S.P.; Kachiprath, B.; Solomon, S.; Sajeevan, T.P.; Bright Singh, I.S.; Philip, R. A Novel Solvent Tolerant Esterase of GDSGG Motif Subfamily from Solar Saltern through Metagenomic Approach: Recombinant Expression and Characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 119, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gricajeva, A.; Bikutė, I.; Kalėdienė, L. Atypical Organic-Solvent Tolerant Bacterial Hormone Sensitive Lipase-like Homologue EstAG1 from Staphylococcus Saprophyticus AG1: Synthesis and Characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahinian, H.; Ali, Y.B.; Abousalham, A.; Petry, S.; Mandrich, L.; Manco, G.; Canaan, S.; Sarda, L. Substrate Specificity and Kinetic Properties of Enzymes Belonging to the Hormone-Sensitive Lipase Family: Comparison with Non-Lipolytic and Lipolytic Carboxylesterases. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2005, 1738, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoldo, J.B.; Razzera, G.; Vernal, J.; Brod, F.C.A.; Arisi, A.C.M.; Terenzi, H. Structural Stability of Staphylococcus Xylosus Lipase Is Modulated by Zn2+ Ions. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Proteins Proteom. 2011, 1814, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xin, L.; Hui-Ying, Y. Purification and Characterization of an Extracellular Esterase with Organic Solvent Tolerance from a Halotolerant Isolate, Salimicrobium Sp. LY19. BMC Biotechnol. 2013, 13, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrovskaya, L.E.; Novototskaya-Vlasova, K.A.; Gapizov, S.; Spirina, E.V.; Durdenko, E.V.; Rivkina, E.M. New Member of the Hormone-Sensitive Lipase Family from the Permafrost Microbial Community. Bioengineered 2016, 8, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinha, R.; Khare, S.K. Protective Role of Salt in Catalysis and Maintaining Structure of Halophilic Proteins against Denaturation. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Santi, C.; Tutino, M.L.; Mandrich, L.; Giuliani, M.; Parrilli, E.; del Vecchio, P.; de Pascale, D. The Hormone-Sensitive Lipase from Psychrobacter Sp. TA144: New Insight in the Structural/Functional Characterization. Biochimie 2010, 92, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balali-Mood, M.; Naseri, K.; Tahergorabi, Z.; Khazdair, M.R.; Sadeghi, M. Toxic Mechanisms of Five Heavy Metals: Mercury, Lead, Chromium, Cadmium, and Arsenic. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonsen, L.O.; Harbak, H.; Bennekou, P. Cobalt Metabolism and Toxicology—A Brief Update. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santi, C.; Durante, L.; Vecchio, P.D.; Tutino, M.L.; Parrilli, E.; de Pascale, D. Thermal Stabilization of Psychrophilic Enzymes: A Case Study of the Cold-Active Hormone-Sensitive Lipase from Psychrobacter Sp. TA144. Biotechnol. Prog. 2012, 28, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.T.H.L.; Yoo, W.; Lee, C.; Wang, Y.; Jeon, S.; Kim, K.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.D. Molecular Characterization of a Novel Cold-Active Hormone-Sensitive Lipase (HaHSL) from Halocynthiibacter Arcticus. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papaleo, E.; Invernizzi, G. Conformational Plasticity of the Calcium-Binding Pocket in the Burkholderia Glumae Lipase: Remodeling Induced by Mutation of Calcium Coordinating Residues. Biopolymers 2011, 95, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invernizzi, G.; Papaleo, E.; Grandori, R.; De Gioia, L.; Lotti, M. Relevance of Metal Ions for Lipase Stability: Structural Rearrangements Induced in the Burkholderia Glumae Lipase by Calcium Depletion. J. Struct. Biol. 2009, 168, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.Y.; Chau, V.W.; Landas, J.A. Yvonne Preparation of Calcium Competent Escherichia Coli and Heat-Shock Transformation. J. Exp. Microbiol. Immunol. (JEMI) 2017, 1, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, Scalable Generation of High-Quality Protein Multiple Sequence Alignments Using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K.H.M.B. BoxShade. Available online: https://embnet.vital-it.ch/software/BOX_form.html (accessed on 18 June 2019).
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple Sequence Alignment with High Accuracy and High Throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New Algorithms and Methods to Estimate Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies: Assessing the Performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (ITOL) v4: Recent Updates and New Developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W256–W259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGuffin, L.J.; Bryson, K.; Jones, D.T. The PSIPRED Protein Structure Prediction Server. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 404–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.F.; Cheng, C.W.; Shih, C.S.; Hwang, J.K.; Yu, C.S.; Lu, C.H. MIB: Metal Ion-Binding Site Prediction and Docking Server. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56, 2287–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smeltzer, M.S.; Hart, M.E.; Iandolo, J.J. Quantitative Spectrophotometric Assay for Staphylococcal Lipase. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 2815–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noble, M.E.M.; Cleasby, A.; Johnson, L.N.; Egmond, M.R.; Frenken, L.G.J. The Crystal Structure of Triacylglycerol Lipase from Pseudomonas Glumae Reveals a Partially Redundant Catalytic Aspartate. FEBS Lett. 1993, 331, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsunaga, A.; Koyama, N.; Nosoh, Y. Purification and Properties of Esterase from Bacillus Stearothermophilus. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1974, 160, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.A. XV.—The Correlation between Relatives on the Supposition of Mendelian Inheritance. Trans. R. Soc. Edinb. 1919, 52, 399–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of Ranks in One-Criterion Variance Analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, O.J. Multiple Comparisons Using Rank Sums. Technometrics 1964, 6, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnett, C.W. A Multiple Comparison Procedure for Comparing Several Treatments with a Control. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1955, 50, 1096–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, B.L. The Generalisation of Student’s Problems When Several Different Population Variances Are Involved. Biometrika 1947, 34, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Enzyme | Vmax (μmol∙min−1∙mg−1) | KM (μmol) | Kcat (s−1) | Kcat/KM (μmol−1 s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EstATII-TM | 37.55 (±2.84) | 0.03 (±0.01) | 4.65 × 104 (±9.27 × 103) | 1.5 × 106 |
| B. stearothermophilus | 1.58 (±0.19) | 0.02(±0.01) | 2.54 (±0.30) | 0.01 |
| P. fluorescens | 55.93 (±7.83) | 0.04 (±0.02) | 2.7 × 104 (±3.3 × 104) | 7.70 × 105 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, S.F.; Abdallah, R.Z.; Siam, R. Evaluation of a Thermophilic, Psychrostable, and Heavy Metal-Resistant Red Sea Brine Pool Esterase. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050274
Ahmed SF, Abdallah RZ, Siam R. Evaluation of a Thermophilic, Psychrostable, and Heavy Metal-Resistant Red Sea Brine Pool Esterase. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(5):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050274
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Shimaa F., Rehab Z. Abdallah, and Rania Siam. 2022. "Evaluation of a Thermophilic, Psychrostable, and Heavy Metal-Resistant Red Sea Brine Pool Esterase" Marine Drugs 20, no. 5: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050274
APA StyleAhmed, S. F., Abdallah, R. Z., & Siam, R. (2022). Evaluation of a Thermophilic, Psychrostable, and Heavy Metal-Resistant Red Sea Brine Pool Esterase. Marine Drugs, 20(5), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050274






