Inhibition of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Signaling by Soft Coral-Derived Prostaglandin A2 in RAW264.7 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
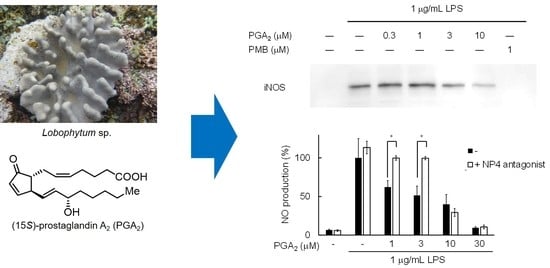
2.1. Isolation of PGA2 from the Soft Coral Lobophytum sp.
2.2. Inhibition of NO Production by PGA2 in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells
2.3. Inhibition of LPS-Induced iNOS Expression in RAW264.7 Cells by PGA2
2.4. Effects of PGA2 on the LPS-Induced Expression of IL-6 in RAW264.7 Cells
2.5. Effects of PGA2 on the Expression Levels of IκB in RAW264.7 Cells
2.6. Inhibition of LPS-Induced Degradation of IκBα by Prolonged Treatment with PGA2
2.7. Effects of L161982 on PGA2-Inhibited NO Production in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Biological Material
4.3. Extraction and Isolation of (15S)-Prostaglandin A2
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. Nitric Oxide Determination
4.6. MTT Assay
4.7. Western Blotting Analysis
4.8. IL-6 Production Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raetz, C.R.; Whitfield, C. Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 635–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chow, J.C.; Young, D.W.; Golenbock, D.T.; Christ, W.J.; Gusovsky, F. Toll-like Receptor-4 Mediates Lipopolysaccharide-induced Signal Transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 10689–10692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poltorak, A.; He, X.; Smirnova, I.; Liu, M.Y.; Huffel, C.V.; Du, X.; Birdwell, D.; Alejos, E.; Silva, M.; Galanos, C.; et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: Mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 1998, 282, 2085–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doyle, S.L.; O’Neill, L.A. Toll-like receptors: From the discovery of NFκB to new insights into transcriptional regulations in innate immunity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Zou, X.-B.; Chai, Y.-F.; Yao, Y.-M. Macrophage Polarization in Inflammatory Diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.N.; Al-Omran, A.; Parvathy, S.S. Role of nitric oxide in inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2007, 15, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.I.; Ernst, R.; Bader, M.W. LPS, TLR4 and infectious disease diversity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 3, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joh, E.-H.; Gu, W.; Kim, D.-H. Echinocystic acid ameliorates lung inflammation in mice and alveolar macrophages by inhibiting the binding of LPS to TLR4 in NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, N.; Tsuchimori, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Ii, M. TAK-242 (Resatorvid), a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of Toll-Like Receptor (TLR) 4 Signaling, Binds Selectively to TLR4 and Interferes with Interactions between TLR4 and Its Adaptor Molecules. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiu, L.C.; Wang, J.Y.; Lin, C.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Lin, L.C.; Fu, S.L. Diterpenoid Compounds Isolated from Chloranthus oldhamii Solms Exert Anti-Inflammatory Effects by Inhibiting the IKK/NF-κB Pathway. Molecules 2021, 26, 6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Q.; Fan, X.H.; Li, J.F.; Chen, J.H.; Liang, Y.; Hu, X.L.; Ma, S.M.; Hao, X.Y.; Shi, T.; Wang, Z. Discovery of a novel inhibitor of nitric oxide production with potential therapeutic effect on acute inflammation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 44, 128106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, O.; Terasaki, T.; Sano, T.; Hitomi, Y.; Miyamoto, J.; Matsuno, K. Inhibitory effects of biseokeaniamide A against lipopolysaccharide-induced signal transduction. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapleo, C.B.; Finch, M.W.; Lee, T.V.; Roberts, S.M.; Newton, R.F. Total synthesis of prostaglandin A2 involving the reaction of a heterocuprate reagent with an allyl epoxide. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1980, 2084–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaards, J.J.; Venekamp, J.C.; van Bladeren, P.J. Stereoselective conjugation of prostaglandin A2 and prostaglandin J2 with glutathione, catalyzed by the human glutathione S-transferases A1-1, A2-2, M1a-1a, and P1-1. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1997, 10, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, E.; Ramos, F.A.; Castellanos, L.; Aragon, M.; Ospina, L.F. Anti-inflammatory R-prostaglandins from Caribbean Colombian soft coral Plexaura homomalla. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, M.; Luo, G.; Wu, Z.; Chen, B.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Chen, S. Anti-Inflammatory Cembrane-Type Diterpenoids and Prostaglandins from Soft Coral Lobophytum sarcophytoides. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pahl, H.L. Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-κB transcription factors. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6853–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohmura, T.; Tian, Y.; Sarich, N.; Ke, Y.; Meliton, A.; Shah, A.S.; Andreasson, K.; Birukov, K.G.; Birukova, A.A. Regulation of lung endothelial permeability and inflammatory responses by prostaglandin A2: Role of EP4 receptor. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 1622–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, K.; Fujiwara, M.; Fukushima, M.; Narumiya, S. Metabolic dehydration of prostaglandin E2 and cellular uptake of the dehydration product: Correlation with prostaglandin E2-induced growth inhibition. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986, 139, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitomi, M.; Shu, J.; Strom, D.; Hiebert, S.W.; Harter, M.L.; Stacey, D.W. Prostaglandin A2 blocks the activation of G1 phase cyclin-dependent kinase without altering mitogen-activated protein kinase stimulation. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 9376–9383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Costanzo, F.; Di Dato, V.; Ianora, A.; Romano, G. Prostaglandins in Marine Organisms: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerhart, D.J. Prostaglandin A2: An agent of chemical defense in the Caribbean gorgonian Plexaura homomalla. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1984, 19, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storer, P.D.; Xu, J.; Chavis, J.A.; Drew, P.D. Cyclopentenone prostaglandins PGA2 and 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-PGJ2 suppress activation of murine microglia and astrocytes: Implications for multiple sclerosis. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 80, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bryson, T.D.; Ross, J.; Peterson, E.; Harding, P. Prostaglandin E2 and an EP4 receptor agonist inhibit LPS-Induced monocyte chemotactic protein 5 production and secretion in mouse cardiac fibroblasts via Akt and NF-κB signaling. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2019, 144, 106349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajima, T.; Murata, T.; Aritake, K.; Urade, Y.; Michishita, M.; Matsuoka, T.; Narumiya, S.; Ozaki, H.; Hori, M. EP2 and EP4 receptors on muscularis resident macrophages mediate LPS-induced intestinal dysmotility via iNOS upregulation through cAMP/ERK signals. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G524–G534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, A.; Elia, G.; Santoro, M.G. Inhibition of nuclear factor κB by prostaglandin A1: An effect associated with heat shock transcription factor activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Straus, D.S.; Pascual, G.; Li, M.; Welch, J.S.; Ricote, M.; Hsiang, C.H.; Sengchanthalangsy, L.L.; Ghosh, G.; Glass, C.K. 15-Deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2 inhibits multiple steps in the NF-κB signaling pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4844–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cernuda-Morollón, E.; Pineda-Molina, E.; Cañada, F.J.; Pérez-Sala, D. 15-Deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2 inhibition of NF-κB-DNA binding through covalent modification of the p50 subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 35530–35536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.S.; Tsai, H.L.; Chau, L.Y. Induction of heme oxygenase-1 expression in murine macrophages is essential for the anti-inflammatory effect of low dose 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 19325–19330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vodovotz, Y. Modified microassay for serum nitrite and nitrate. Biotechniques 1996, 20, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ohno, O.; Mizuno, E.; Miyamoto, J.; Hoshina, T.; Sano, T.; Matsuno, K. Inhibition of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Signaling by Soft Coral-Derived Prostaglandin A2 in RAW264.7 Cells. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050316
Ohno O, Mizuno E, Miyamoto J, Hoshina T, Sano T, Matsuno K. Inhibition of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Signaling by Soft Coral-Derived Prostaglandin A2 in RAW264.7 Cells. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(5):316. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050316
Chicago/Turabian StyleOhno, Osamu, Eika Mizuno, Junichiro Miyamoto, Tomoyuki Hoshina, Takuya Sano, and Kenji Matsuno. 2022. "Inhibition of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Signaling by Soft Coral-Derived Prostaglandin A2 in RAW264.7 Cells" Marine Drugs 20, no. 5: 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050316
APA StyleOhno, O., Mizuno, E., Miyamoto, J., Hoshina, T., Sano, T., & Matsuno, K. (2022). Inhibition of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Signaling by Soft Coral-Derived Prostaglandin A2 in RAW264.7 Cells. Marine Drugs, 20(5), 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20050316