Comparative Study on the Performance of Three Detection Methods for the Quantification of Pacific Ciguatoxins in French Polynesian Strains of Gambierdiscus polynesiensis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Binding Affinity of CTX3C and Gambierdiscus polynesiensis Extracts Using the fRBA
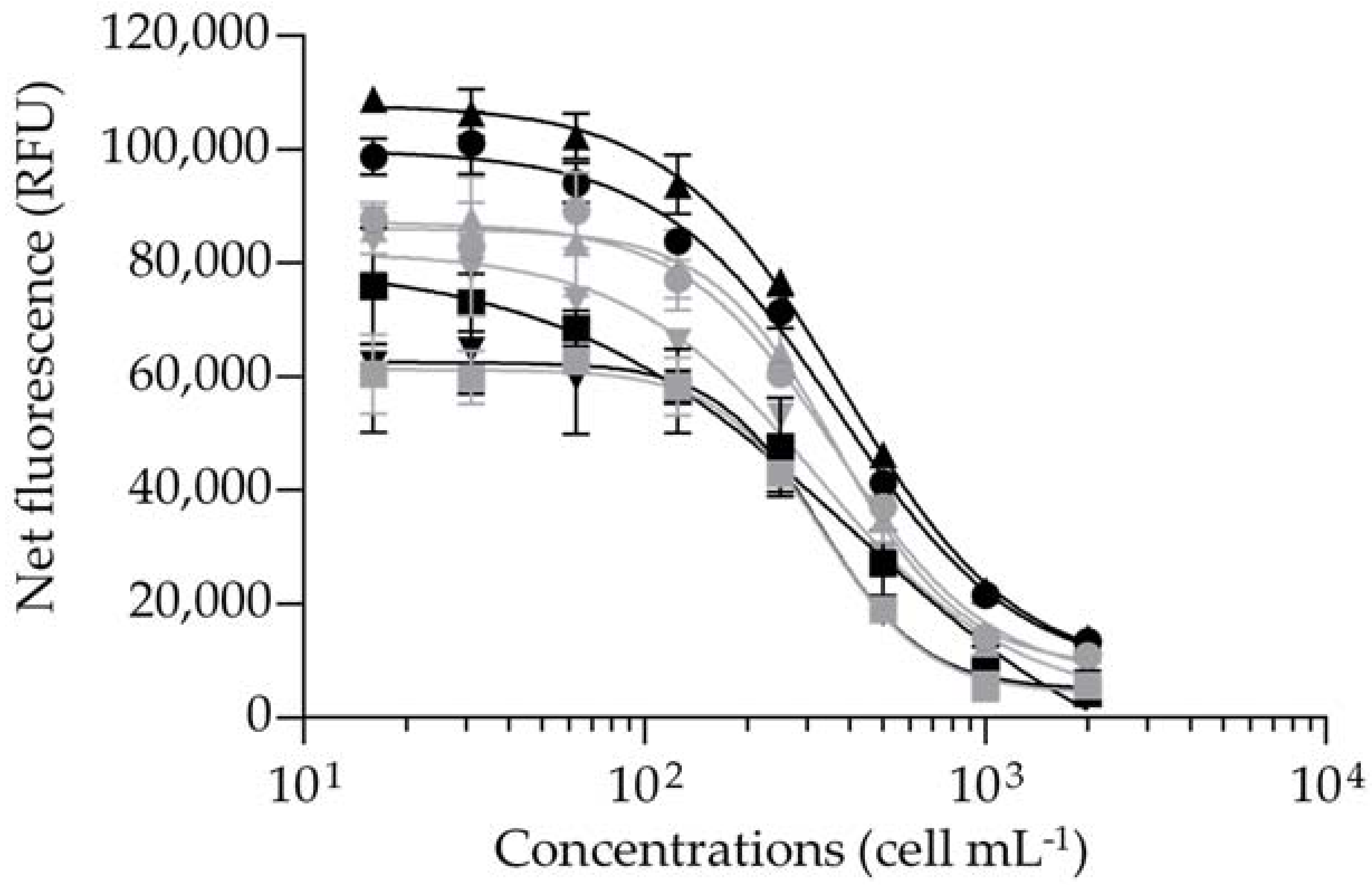
2.1.1. Solvent Effect, Incubation Parameters, and Matrix Effects
2.1.2. Efficiency of the fRBA When Applied to CTX3C and Gambierdiscus polynesiensis Samples
2.2. Cytotoxic Activity of CTX3C and Gambierdiscus polynesiensis on N2a cells Using the CBA-N2a
2.3. Detection and Quantification of CTX3C and Gambierdiscus polynesiensis Using LC-MS/MS
2.4. Comparison of the Performance of the Three Detection Methods
2.5. Practical Considerations for Algal-Based Ciguatera Risk Monitoring Programs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Gambierdiscus Isolates
3.2. Reagents and Chemicals
3.3. In Vitro Cultures
3.4. Cells Harvest and Toxin Extraction
3.5. Fluorescent Receptor Binding Assay (fRBA)
3.5.1. Reagents
3.5.2. The fRBA Reaction
3.5.3. Solvent Effect
3.5.4. Incubation Parameters
3.5.5. Matrix Effects
3.5.6. Repeatability of fRBA
3.6. Neuroblastoma Cell-Based Assay (CBA-N2a)
3.7. Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
3.8. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adachi, R.; Fukuyo, Y. The Thecal Structure of a Marine Toxic Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus gen. et sp. nov. Collected in a Ciguatera-endemic Area. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish 1979, 45, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faust, M.A. Observation of sand-dwelling toxic dinoflagellates (Dinophyceae) from widely differing sites, including two new species1. J. Phycol. 1995, 31, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinain, M.; Faust, M.A.; Pauillac, S. Morphology and molecular analyses of three toxic species of Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae): G. pacificus, sp. nov., G. australes, sp. nov., and G. polynesiensis, sp. nov. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 1282–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litaker, R.W.; Vandersea, M.W.; Faust, M.A.; Kibler, S.R.; Chinain, M.; Holmes, M.J.; Holland, W.C.; Tester, P.A. Taxonomy of Gambierdiscus including four new species, Gambierdiscus caribaeus, Gambierdiscus carolinianus, Gambierdiscus carpenteri and Gambierdiscus ruetzleri (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae). Phycologia 2009, 48, 344–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, S.; Rodríguez, F.; Caillaud, A.; Diogène, J.; Raho, N.; Zapata, M. Gambierdiscus excentricus sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), a benthic toxic dinoflagellate from the Canary Islands (NE Atlantic Ocean). Harmful Algae 2011, 11, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fraga, S.; Rodriguez, F. Genus Gambierdiscus in the Canary Islands (NE Atlantic Ocean) with Description of Gambierdiscus silvae sp. nov., a New Potentially Toxic Epiphytic Benthic Dinoflagellate. Protist 2014, 165, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, S.; Rodríguez, F.; Riobó, P.; Bravo, I. Gambierdiscus balechii sp. nov (Dinophyceae), a new benthic toxic dinoflagellate from the Celebes Sea (SW Pacific Ocean). Harmful Algae 2016, 58, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.F.; Verma, A.; Curley, B.G.; Harwood, D.T.; Murray, S.; Kohli, G.S.; Solomona, D.; Rongo, T.; Munday, R.; et al. A new species of Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae) from the south-west Pacific: Gambierdiscus honu sp. nov. Harmful Algae 2017, 65, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretzschmar, A.L.; Verma, A.; Harwood, D.T.; Hoppenrath, M.; Murray, S. Characterization of Gambierdiscus lapillus sp. nov. (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae): A new toxic dinoflagellate from the Great Barrier Reef (Australia). J. Phycol. 2017, 53, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H.; Jeong, H.J.; Yoo, Y.D. Gambierdiscus jejuensis sp. nov., an epiphytic dinoflagellate from the waters of Jeju Island, Korea, effect of temperature on the growth, and its global distribution. Harmful Algae 2018, 80, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.F.; Rhodes, L.; Verma, A.; Curley, B.G.; Harwood, D.T.; Kohli, G.S.; Solomona, D.; Rongo, T.; Munday, R.; Murray, S.A. A new Gambierdiscus species (Dinophyceae) from Rarotonga, Cook Islands: Gambierdiscus cheloniae sp. nov. Harmful Algae 2016, 60, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretzschmar, A.L.; Larsson, M.E.; Hoppenrath, M.; Doblin, M.A.; Murray, S.A. Characterisation of Two Toxic Gambierdiscus spp. (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae) from the Great Barrier Reef (Australia): G. lewisii sp. nov. and G. holmesii sp. nov. Protist 2019, 170, 125699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, M.J. Gambierdiscus yasumotoi sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), a toxic benthic dinoflagellate from Southeastern Asia. J. Phycol. 1998, 34, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, F.; Qiu, D.; Lopes, R.M.; Lin, S. Fukuyoa paulensis gen. et sp. nov., a New Genus for the Globular Species of the Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Park, J.S.; Kang, N.S.; Chomérat, N.; Mertens, K.N.; Gu, H.; Lee, K.-W.; Kim, K.H.; Baek, S.H.; Shin, K.; et al. A new potentially toxic dinoflagellate Fukuyoa koreansis sp. nov. (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae) from Korean coastal waters: Morphology, phylogeny, and effects of temperature and salinity on growth. Harmful Algae 2021, 109, 102107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasumoto, T.; Igarashi, T.; Legrand, A.-M.; Cruchet, P.; Chinain, M.; Fujita, T.; Naoki, H. Structural Elucidation of Ciguatoxin Congeners by Fast-Atom Bombardment Tandem Mass Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4988–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinain, M.; Darius, H.T.; Ung, A.; Cruchet, P.; Wang, Z.; Ponton, D.; Laurent, D.; Pauillac, S. Growth and toxin production in the ciguatera-causing dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus polynesiensis (Dinophyceae) in culture. Toxicon 2010, 56, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Inafuku, Y.; Hirama, M.; Yasumoto, T. Detailed LC-MS/MS Analysis of Ciguatoxins Revealing Distinct Regional and Species Characteristics in Fish and Causative Alga from the Pacific. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8886–8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roué, M.; Darius, H.T.; Picot, S.; Ung, A.; Viallon, J.; Gaertner-Mazouni, N.; Sibat, M.; Amzil, Z.; Chinain, M. Evidence of the bioaccumulation of ciguatoxins in giant clams (Tridacna maxima) exposed to Gambierdiscus spp. cells. Harmful Algae 2016, 57, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roué, M.; Darius, H.T.; Ung, A.; Viallon, J.; Sibat, M.; Hess, P.; Amzil, Z.; Chinain, M. Tissue Distribution and Elimination of Ciguatoxins in Tridacna maxima (Tridacnidae, Bivalvia) Fed Gambierdiscus polynesiensis. Toxins 2018, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sibat, M.; Herrenknecht, C.; Darius, H.T.; Roué, M.; Chinain, M.; Hess, P. Detection of pacific ciguatoxins using liquid chromatography coupled to either low or high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1571, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, S.; Sibat, M.; Viallon, J.; Darius, H.T.; Hess, P.; Chinain, M. Intraspecific Variability in the Toxin Production and Toxin Profiles of In Vitro Cultures of Gambierdiscus polynesiensis (Dinophyceae) from French Polynesia. Toxins 2019, 11, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Longo, S.; Sibat, M.; Darius, H.T.; Hess, P.; Chinain, M. Effects of pH and Nutrients (Nitrogen) on Growth and Toxin Profile of the Ciguatera-Causing Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus polynesiensis (Dinophyceae). Toxins 2020, 12, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yon, T.; Sibat, M.; Réveillon, D.; Bertrand, S.; Chinain, M.; Hess, P. Deeper insight into Gambierdiscus polynesiensis toxin production relies on specific optimization of high-performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry. Talanta 2021, 232, 122400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Gillespie, N.C. Toxicity of Australian and French Polynesian strains of Gambierdiscus toxicus (Dinophyceae) grown in culture: Characterization of a new type of maitotoxin. Toxicon 1990, 28, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Iwashita, T.; Yokoyama, A.; Sasaki, M.; Yasumoto, T. Partial structures of maitotoxin, the most potent marine toxin from the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 6594–6596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Sasaki, M.; Yokoyama, A.; Iwashita, T.; Gusovsky, F.; Daly, J.W.; Yasumoto, T. Partial structures and binding studies of maitotoxin, the most potent marine toxin. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1992, 85, 470–473. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, M.; Naoki, H.; Iwashita, T.; Matsunaga, S.; Sasaki, M.; Yokoyama, A.; Yasumoto, T. Structure of maitotoxin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 2060–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Naoki, H.; Matsunaga, S.; Satake, M.; Yasumoto, T. Structure and Partial Stereochemical Assignments for Maitotoxin, the Most Toxic and Largest Natural Non-Biopolymer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 7098–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Lewis, R.J. Purification and characterisation of large and small maitotoxins from cultured Gambierdiscus toxicus. Nat. Toxins 1994, 2, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Ishida, S.; Yasumoto, T.; Murata, M.; Utsumi, H.; Hinomoto, T. Structural Confirmation of Maitotoxin Based on Complete 13C NMR Assignments and the Three-Dimensional PFG NOESY-HMQC Spectrum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 7019–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; Harwood, T.; Smith, K.; Argyle, P.; Munday, R. Production of ciguatoxin and maitotoxin by strains of Gambierdiscus australes, G. pacificus and G. polynesiensis (Dinophyceae) isolated from Rarotonga, Cook Islands. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisapia, F.; Sibat, M.; Herrenknecht, C.; Lhaute, K.; Gaiani, G.; Ferron, P.-J.; Fessard, V.; Fraga, S.; Nascimento, S.M.; Litaker, R.W.; et al. Maitotoxin-4, a Novel MTX Analog Produced by Gambierdiscus excentricus. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, E.P.; Deeds, J.R.; Stutts, W.L.; Ridge, C.D.; Dickey, R.W.; White, K.D.; Williamson, R.T.; Martin, G.E. Elucidation and partial NMR assignment of monosulfated maitotoxins from the Caribbean. Toxicon 2019, 164, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisapia, F.; Sibat, M.; Watanabe, R.; Roullier, C.; Suzuki, T.; Hess, P.; Herrenknecht, C. Characterization of maitotoxin-4 (MTX4) using electrospray positive mode ionization high-resolution mass spectrometry and UV spectroscopy. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 34, e8859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estevez, P.; Castro, D.; Leão-Martins, J.M.; Sibat, M.; Tudó, A.; Dickey, R.; Diogene, J.; Hess, P.; Gago-Martinez, A. Toxicity Screening of a Gambierdiscus australes Strain from the Western Mediterranean Sea and Identification of a Novel Maitotoxin Analogue. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, H.; Murata, M.; Torigoe, K.; Satake, M.; Yasumoto, T. Gambieric acids, new potent antifungal substances with unprecedented polyether structures from a marine dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 5448–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H.; Torigoe, K.; Satake, M.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T.; Hirota, H. Gambieric acids: Unprecedented potent antifungal substances isolated from cultures of a marine dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 1102–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T. Gambierol: A new toxic polyether compound isolated from the marine dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagide, E.; Louzao, M.C.; Espiña, B.; Ares, I.R.; Vieytes, M.R.; Sasaki, M.; Fuwa, H.; Tsukano, C.; Konno, Y.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; et al. Comparative Cytotoxicity of Gambierol versus Other Marine Neurotoxins. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Uchida, H.; Suzuki, T.; Matsushima, R.; Nagae, M.; Toyohara, Y.; Satake, M.; Oshima, Y.; Inoue, A.; Yasumoto, T. Gambieroxide, a novel epoxy polyether compound from the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus GTP2 strain. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 10299–10303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, I.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Alfonso, C.; Calabro, K.; Alonso, E.; Sánchez, J.A.; Alfonso, A.; Thomas, O.P.; Botana, L.M. Gambierone, a Ladder-Shaped Polyether from the Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus belizeanus. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 2392–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boente-Juncal, A.; Álvarez, M.; Antelo, Á.; Rodríguez, I.; Calabro, K.; Vale, C.; Thomas, O.P.; Botana, L.M. Structure Elucidation and Biological Evaluation of Maitotoxin-3, a Homologue of gambierone, from Gambierdiscus belizeanus. Toxins 2019, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murray, J.S.; Selwood, A.I.; Harwood, D.T.; van Ginkel, R.; Puddick, J.; Rhodes, L.L.; Rise, F.; Wilkins, A.L. 44-Methylgambierone, a new gambierone analogue isolated from Gambierdiscus australes. Tetrahedron Lett. 2019, 60, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, P.; Sibat, M.; Leão-Martins, J.M.; Tudó, A.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Aligizaki, K.; Diogène, J.; Gago-Martinez, A.; Hess, P. Use of Mass Spectrometry to Determine the Diversity of Toxins Produced by Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa Species from Balearic Islands and Crete (Mediterranean Sea) and the Canary Islands (Northeast Atlantic). Toxins 2020, 12, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibiriçá, C.E.J.D.A.; Sibat, M.; Fernandes, L.F.; Bilien, G.; Chomérat, N.; Hess, P.; Mafra, L.L., Jr. Diversity and Toxicity of the Genus Coolia Meunier in Brazil, and Detection of 44-methyl Gambierone in Coolia tropicalis. Toxins 2020, 12, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yon, T.; Sibat, M.; Robert, E.; Lhaute, K.; Holland, W.C.; Litaker, R.W.; Bertrand, S.; Hess, P.; Réveillon, D. Sulfo-Gambierones, Two New Analogs of Gambierone Produced by Gambierdiscus excentricus. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.S.; Finch, S.C.; Puddick, J.; Rhodes, L.L.; Harwood, D.T.; van Ginkel, R.; Prinsep, M.R. Acute Toxicity of Gambierone and Quantitative Analysis of Gambierones Produced by Cohabitating Benthic Dinoflagellates. Toxins 2021, 13, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudge, E.M.; Robertson, A.; Leynse, A.K.; McCarron, P.; Miles, C.O. Selective extraction of gambierone and related metabolites in Gambierdiscus silvae using m-aminophenylboronic acid–agarose gel and liquid chromatography–high-resolution mass spectrometric detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2022, 1188, 123014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malto, Z.B.L.; Benico, G.A.; Batucan, J.D.; Cruz, J.D.; Romero, M.L.J.; Azanza, R.V.; Salvador-Reyes, L.A. Global Mass Spectrometric Analysis Reveals Chemical Diversity of Secondary Metabolites and 44-Methylgambierone Production in Philippine Gambierdiscus Strains. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 767024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.M.; Roué, M.; Darius, H.T. Ciguatera-causing dinoflagellates in the genera Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa: Distribution, ecophysiology and toxicology. In Ciguatera-Poisoning Causing Dinoflagellates; Subba Rao, D.V., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 405–457. Available online: https://www.novapublishers.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/978-1-53617-888-3.pdf (accessed on 22 October 2020).
- Holland, W.C.; Litaker, R.W.; Tomas, C.R.; Kibler, S.R.; Place, A.R.; Davenport, E.D.; Tester, P.A. Differences in the toxicity of six Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae) species measured using an in vitro human erythrocyte lysis assay. Toxicon 2013, 65, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, G.S.; Papiol, G.G.; Rhodes, L.L.; Harwood, D.T.; Selwood, A.; Jerrett, A.; Murray, S.A.; Neilan, B.A. A feeding study to probe the uptake of Maitotoxin by snapper (Pagrus auratus). Harmful Algae 2014, 37, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Hirama, M.; Satake, M.; Sugiyama, K.; Yasumoto, T. Inhibition of brevetoxin binding to the voltage-gated sodium channel by gambierol and gambieric acid-A. Toxicon 2003, 41, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepage, K.T.; Rainier, J.D.; Johnson, H.W.B.; Baden, D.G.; Murray, T.F. Gambierol Acts as a Functional Antagonist of Neurotoxin Site 5 on Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels in Cerebellar Granule Neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 323, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlumberger, S.; Ouanounou, G.; Girard, E.; Sasaki, M.; Fuwa, H.; Louzao, M.C.; Botana, L.M.; Benoit, E.; Molgó, J. The marine polyether gambierol enhances muscle contraction and blocks a transient K+ current in skeletal muscle cells. Toxicon 2010, 56, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, S.; Vale, C.; Alonso, E.; Fuwa, H.; Sasaki, M.; Konno, Y.; Goto, T.; Suga, Y.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Effect of Gambierol and Its Tetracyclic and Heptacyclic Analogues in Cultured Cerebellar Neurons: A Structure–Activity Relationships Study. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopljar, I.; Labro, A.J.; de Block, T.; Rainier, J.D.; Tytgat, J.; Snyders, D.J. The ladder-shaped polyether toxin gambierol anchors the gating machinery of Kv3.1 channels in the resting state. J. Gen. Physiol. 2013, 141, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Z.; Cui, Y.; Busse, E.; Mehrotra, S.; Rainier, J.D.; Murray, T.F. Gambierol inhibition of voltage-gated potassium channels augments spontaneous Ca2+ oscillations in cerebrocortical neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2014, 350, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubiolo, J.A.; Vale, C.; Martín, V.; Fuwa, H.; Sasaki, M.; Botana, L.M. Potassium currents inhibition by gambierol analogs prevents human T lymphocyte activation. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molgó, J.; Schlumberger, S.; Sasaki, M.; Fuwa, H.; Louzao, M.C.; Botana, L.M.; Servent, D.; Benoit, E. Gambierol Potently Increases Evoked Quantal Transmitter Release and Reverses Pre- and Post-Synaptic Blockade at Vertebrate Neuromuscular Junctions. Neuroscience 2020, 439, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Theemsche, K.M.; Van De Sande, D.V.; Snyders, D.J.; Labro, A.J. Hydrophobic Drug/Toxin Binding Sites in Voltage-Dependent K+ and Na+ Channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randall, J.E. A review of ciguatera, tropical fish poisoning, with a tentative explanation of its cause. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1958, 8, 236–267. [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto, T. Chemistry, etiology, and food chain dynamics of marine toxins. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2005, 81, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.M.I.; Darius, H.T.; Quod, J.-P.; Tester, P.A. Ciguatera poisonings: A global review of occurrences and trends. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliño, L.; Costa, P.R. Differential toxin profiles of ciguatoxins in marine organisms: Chemistry, fate and global distribution. Toxicon 2018, 150, 124–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasinszki, T.; Lako, J.; Dennis, T.E. Advances in Detecting Ciguatoxins in Fish. Toxins 2020, 12, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehara, T.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Yasumoto, T. Biooxidation of Ciguatoxins Leads to Species-Specific Toxin Profiles. Toxins 2017, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission. Global Ciguatera Strategy 2015–2019, IPHAB-XII. Available online: https://oceanexpert.org/document/15111 (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Caillaud, A.; De la Iglesia, P.; Darius, H.T.; Pauillac, S.; Aligizaki, K.; Fraga, S.; Chinain, M.; Diogène, J. Update on Methodologies Available for Ciguatoxin Determination: Perspectives to Confront the Onset of Ciguatera Fish Poisoning in Europe. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1838–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand-Clement, M. A study of toxin production by Gambierdiscus toxicus in culture. Toxicon 1986, 24, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Poli, M.A.; Gillespie, N.C. Strain dependent production of ciguatoxin precursors (gambiertoxins) by Gambierdiscus toxicus (Dinophyceae) in culture. Toxicon 1991, 29, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Sellin, M.; Street, R. The origin of ciguatera in Platypus Bay, Australia. Mem. Qld. Mus. 1994, 34, 505–512. [Google Scholar]
- Chinain, M.; Germain, M.; Sako, Y.; Pauillac, S.; Legrand, A.-M. Intraspecific variation in the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus (Dinophyceae). I. isozyme analysis. J. Phycol. 1997, 33, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinain, M.; Germain, M.; Deparis, X.; Pauillac, S.; Legrand, A.-M. Seasonal abundance and toxicity of the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus spp. (Dinophyceae), the causative agent of ciguatera in Tahiti, French Polynesia. Mar. Biol. 1999, 135, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.L.; Smith, K.F.; Munday, R.; Selwood, A.I.; McNabb, P.S.; Holland, P.T.; Bottein, M.-Y. Toxic dinoflagellates (Dinophyceae) from Rarotonga, Cook Islands. Toxicon 2010, 56, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.; Harwood, T.; Selwood, A.; Argyle, P.; Bedford, C.; Munday, R. Gambierdiscus and Ostreopsis from New Zealand, the Kermadec Islands and the Cook Islands and the risk of ciguatera fish poisoning in New Zealand. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Harmful Algae, Wellington, New Zealand, 27–31 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Laza-Martínez, A.; David, H.; Riobó, P.; Miguel, I.; Orive, E. Characterization of a Strain of Fukuyoa paulensis (Dinophyceae) from the Western Mediterranean Sea. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2016, 63, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munday, R.; Murray, S.; Rhodes, L.L.; Larsson, M.E.; Harwood, D.T. Ciguatoxins and Maitotoxins in Extracts of Sixteen Gambierdiscus Isolates and One Fukuyoa Isolate from the South Pacific and Their Toxicity to Mice by Intraperitoneal and Oral Administration. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolas, J.; Hendriksen, P.J.M.; Gerssen, A.; Bovee, T.F.H.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M. Marine neurotoxins: State of the art, bottlenecks, and perspectives for mode of action based methods of detection in seafood. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombet, A.; Bidard, J.-N.; Lazdunski, M. Ciguatoxin and brevetoxins share a common receptor site on the neuronal voltage-dependent Na+channel. FEBS Lett. 1987, 219, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gawley, R.E.; Rein, K.S.; Kinoshita, M.; Baden, D.G. Binding of brevetoxins and ciguatoxin to the voltage-sensitive sodium channel and conformational analysis of brevetoxin B. Toxicon 1992, 30, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechraoui, M.-Y.; Naar, J.; Pauillac, S.; Legrand, A.-M. Ciguatoxins and brevetoxins, neurotoxic polyether compounds active on sodium channels. Toxicon 1999, 37, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darius, H.T.; Ponton, D.; Revel, T.; Cruchet, P.; Ung, A.; Fouc, M.T.; Chinain, M. Ciguatera risk assessment in two toxic sites of French Polynesia using the receptor-binding assay. Toxicon 2007, 50, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinain, M.; Darius, H.T.; Ung, A.; Fouc, M.T.; Revel, T.; Cruchet, P.; Pauillac, S.; Laurent, D. Ciguatera risk management in French Polynesia: The case study of Raivavae Island (Australes Archipelago). Toxicon 2010, 56, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clausing, R.J.; Losen, B.; Oberhaensli, F.R.; Darius, H.T.; Sibat, M.; Hess, P.; Swarzenski, P.W.; Chinain, M.; Dechraoui Bottein, M.-Y. Experimental evidence of dietary ciguatoxin accumulation in an herbivorous coral reef fish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 200, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Díaz-Asencio, L.; Clausing, R.J.; Vandersea, M.; Chamero-Lago, D.; Gómez-Batista, M.; Hernández-Albernas, J.I.; Chomérat, N.; Rojas-Abrahantes, G.; Litaker, R.W.; Tester, P.; et al. Ciguatoxin Occurrence in Food-Web Components of a Cuban Coral Reef Ecosystem: Risk-Assessment Implications. Toxins 2019, 11, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díaz-Asencio, L.; Vandersea, M.; Chomérat, N.; Fraga, S.; Clausing, R.J.; Litaker, R.W.; Chamero-Lago, D.; Gómez-Batista, M.; Moreira-González, A.; Tester, P.; et al. Morphology, toxicity and molecular characterization of Gambierdiscus spp. towards risk assessment of ciguatera in south central Cuba. Harmful Algae 2019, 86, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.M.i.; Ung, A.; Cruchet, P.; Revel, T.; Viallon, J.; Sibat, M.; Varney, P.; Laurent, V.; Hess, P.; et al. Evidence for the Range Expansion of Ciguatera in French Polynesia: A Revisit of the 2009 Mass-Poisoning Outbreak in Rapa Island (Australes Archipelago). Toxins 2020, 12, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lartigue, J.; Jester, E.L.E.; Dickey, R.W.; Villareal, T.A. Nitrogen source effects on the growth and toxicity of two strains of the ciguatera-causing dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowiez, R.; Darius, H.T.; Cruchet, P.; Rossi, F.; Caillaud, A.; Laurent, D.; Chinain, M. Evaluation of seafood toxicity in the Australes archipelago (French Polynesia) using the neuroblastoma cell-based assay. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 567–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catania, D.; Richlen, M.L.; Mak, Y.L.; Morton, S.L.; Laban, E.H.; Xu, Y.; Anderson, D.M.; Chan, L.L.; Berumen, M.L. The prevalence of benthic dinoflagellates associated with ciguatera fish poisoning in the central Red Sea. Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Mak, Y.L.; Lu, C.-K.; Mei, H.-H.; Wu, J.J.; Lee, W.H.; Chan, L.L.; Lim, P.T.; Mustapa, N.I.; Lim, H.C.; et al. Taxonomic assignment of the benthic toxigenic dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus sp. type 6 as Gambierdiscus balechii (Dinophyceae), including its distribution and ciguatoxicity. Harmful Algae 2017, 67, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litaker, R.W.; Holland, W.C.; Hardison, D.R.; Pisapia, F.; Hess, P.; Kibler, S.R.; Tester, P.A. Ciguatoxicity of Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa species from the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisapia, F.; Holland, W.C.; Hardison, D.R.; Litaker, R.W.; Fraga, S.; Nishimura, T.; Adachi, M.; Nguyen-Ngoc, L.; Séchet, V.; Amzil, Z.; et al. Toxicity screening of 13 Gambierdiscus strains using neuro-2a and erythrocyte lysis bioassays. Harmful Algae 2017, 63, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darius, H.T.; Roué, M.; Sibat, M.; Viallon, J.; Gatti, C.M.i.; Vandersea, M.W.; Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W.; Amzil, Z.; Hess, P.; et al. Tectus niloticus (Tegulidae, Gastropod) as a Novel Vector of Ciguatera Poisoning: Detection of Pacific Ciguatoxins in Toxic Samples from Nuku Hiva Island (French Polynesia). Toxins 2018, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darius, H.T.; Roué, M.; Sibat, M.; Viallon, J.; Gatti, C.M.I.; Vandersea, M.W.; Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W.; Amzil, Z.; Hess, P.; et al. Toxicological Investigations on the Sea Urchin Tripneustes gratilla (Toxopneustidae, Echinoid) from Anaho Bay (Nuku Hiva, French Polynesia): Evidence for the Presence of Pacific Ciguatoxins. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reverté, L.; Toldrà, A.; Andree, K.B.; Fraga, S.; De Falco, G.; Campàs, M.; Diogène, J. Assessment of cytotoxicity in ten strains of Gambierdiscus australes from Macaronesian Islands by neuro-2a cell-based assays. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2447–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudó, À.; Toldrà, A.; Rey, M.; Todolí, I.; Andree, K.B.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Campàs, M.; Sureda, F.X.; Diogène, J. Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa as potential indicators of ciguatera risk in the Balearic Islands. Harmful Algae 2020, 99, 101913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudó, À.; Gaiani, G.; Rey Varela, M.; Tsumuraya, T.; Andree, K.B.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Campàs, M.; Diogène, J. Further Advance of Gambierdiscus Species in the Canary Islands, with the First Report of Gambierdiscus belizeanus. Toxins 2020, 12, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liefer, J.D.; Richlen, M.L.; Smith, T.B.; DeBose, J.L.; Xu, Y.; Anderson, D.M.; Robertson, A. Asynchrony of Gambierdiscus spp. Abundance and Toxicity in the U.S. Virgin Islands: Implications for Monitoring and Management of Ciguatera. Toxins 2021, 13, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; He, X.; Lee, W.H.; Chan, L.L.; Lu, D.; Wang, P.; Tao, X.; Li, H.; Yu, K. Ciguatoxin-Producing Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus in the Beibu Gulf: First Report of Toxic Gambierdiscus in Chinese Waters. Toxins 2021, 13, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeder, K.; Erler, K.; Kibler, S.; Tester, P.; Van The, H.; Nguyen-Ngoc, L.; Gerdts, G.; Luckas, B. Characteristic profiles of Ciguatera toxins in different strains of Gambierdiscus spp. Toxicon 2010, 56, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; Papiol, G.G.; Smith, K.; Harwood, T. Gambierdiscus cf. yasumotoi (Dinophyceae) isolated from New Zealand’s sub-tropical northern coastal waters. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2014, 48, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhodes, L.L.; Smith, K.F.; Verma, A.; Murray, S.; Harwood, D.T.; Trnski, T. The dinoflagellate genera Gambierdiscus and Ostreopsis from subtropical Raoul Island and North Meyer Island, Kermadec Islands. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2017, 51, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.; Smith, K.F.; Murray, S.; Harwood, D.T.; Trnski, T.; Munday, R. The epiphytic genus Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae) in the Kermadec Islands and Zealandia regions of the southwestern Pacific and the associated risk of ciguatera fish poisoning. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsson, M.E.; Laczka, O.F.; Harwood, D.T.; Lewis, R.J.; Himaya, S.W.A.; Murray, S.A.; Doblin, M.A. Toxicology of Gambierdiscus spp. (Dinophyceae) from Tropical and Temperate Australian Waters. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murray, J.S.; Boundy, M.J.; Selwood, A.I.; Harwood, D.T. Development of an LC–MS/MS method to simultaneously monitor maitotoxins and selected ciguatoxins in algal cultures and P-CTX-1B in fish. Harmful Algae 2018, 80, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roué, M.; Smith, K.F.; Sibat, M.; Viallon, J.; Henry, K.; Ung, A.; Biessy, L.; Hess, P.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M. Assessment of Ciguatera and Other Phycotoxin-Related Risks in Anaho Bay (Nuku Hiva Island, French Polynesia): Molecular, Toxicological, and Chemical Analyses of Passive Samplers. Toxins 2020, 12, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations & World Health Organization. Report of the Expert Meeting on Ciguatera Poisoning: Rome, 19–23 November 2018; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/332640 (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Tsumuraya, T.; Sato, T.; Hirama, M.; Fujii, I. Highly Sensitive and Practical Fluorescent Sandwich ELISA for Ciguatoxins. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7318–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardo, S.; Gaiani, G.; Tsumuraya, T.; Hirama, M.; Turquet, J.; Sagristà, N.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Flores, C.; Caixach, J.; Diogène, J.; et al. Addressing the Analytical Challenges for the Detection of Ciguatoxins Using an Electrochemical Biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 4858–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiani, G.; Leonardo, S.; Tudó, À.; Toldrà, A.; Rey, M.; Andree, K.B.; Tsumuraya, T.; Hirama, M.; Diogène, J.; O’Sullivan, C.K.; et al. Rapid detection of ciguatoxins in Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa with immunosensing tools. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 204, 111004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiani, G.; Cucchi, F.; Toldrà, A.; Andree, K.B.; Rey, M.; Tsumuraya, T.; O’Sullivan, C.K.; Diogène, J.; Campàs, M. Electrochemical biosensor for the dual detection of Gambierdiscus australes and Gambierdiscus excentricus in field samples. First report of G. excentricus in the Balearic Islands. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viallon, J.; Chinain, M.; Darius, H.T. Revisiting the Neuroblastoma Cell-Based Assay (CBA-N2a) for the Improved Detection of Marine Toxins Active on Voltage Gated Sodium Channels (VGSCs). Toxins 2020, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCall, J.R.; Jacocks, H.M.; Baden, D.G.; Bourdelais, A.J. Development of a competitive fluorescence-based synaptosome binding assay for brevetoxins. Harmful Algae 2012, 19, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poli, M.A.; Mende, T.J.; Baden, D.G. Brevetoxins, unique activators of voltage-sensitive sodium channels, bind to specific sites in rat brain synaptosomes. Mol. Pharmacol. 1986, 30, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Sellin, M.; Poli, M.A.; Norton, R.S.; MacLeod, J.K.; Sheil, M.M. Purification and characterization of ciguatoxins from moray eel (Lycodontis javanicus, Muraenidae). Toxicon 1991, 29, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, B.; Hurbungs, M.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Multiple ciguatoxins present in Indian Ocean reef fish. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, B.; Hurbungs, M.; Vernoux, J.P.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Isolation and characterisation of Indian Ocean ciguatoxin. Toxicon 2002, 40, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechraoui, M.-Y.B.; Ramsdell, J.S. Type B brevetoxins show tissue selectivity for voltage-gated sodium channels: Comparison of brain, skeletal muscle and cardiac sodium channels. Toxicon 2003, 41, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechraoui, M.-Y.B.; Tiedeken, J.A.; Persad, R.; Wang, Z.; Granade, H.R.; Dickey, R.W.; Ramsdell, J.S. Use of two detection methods to discriminate ciguatoxins from brevetoxins: Application to great barracuda from Florida Keys. Toxicon 2005, 46, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechraoui, M.-Y.B.; Wacksman, J.J.; Ramsdell, J.S. Species selective resistance of cardiac muscle voltage gated sodium channels: Characterization of brevetoxin and ciguatoxin binding sites in rats and fish. Toxicon 2006, 48, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darius, H.T.; Drescher, O.; Ponton, D.; Pawlowiez, R.; Laurent, D.; Dewailly, E.; Chinain, M. Use of folk tests to detect ciguateric fish: A scientific evaluation of their effectiveness in Raivavae Island (Australes, French Polynesia). Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 550–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottein, M.-Y.D.; Clausing, R.J. Receptor-Binding Assay for the Analysis of Marine Toxins: Detection and mode of action. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2017, 78, 277–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Asencio, L.; Clausing, R.J.; Rañada, M.L.; Alonso-Hernández, C.M.; Dechraoui Bottein, M.-Y. A radioligand receptor binding assay for ciguatoxin monitoring in environmental samples: Method development and determination of quality control criteria. J. Environ. Radioact. 2018, 192, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darius, H.T.; Revel, T.; Cruchet, P.; Viallon, J.; Gatti, C.M.I.; Sibat, M.; Hess, P.; Chinain, M. Deep-Water Fish Are Potential Vectors of Ciguatera Poisoning in the Gambier Islands, French Polynesia. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruberu, S.R.; Liu, Y.-G.; Wong, C.T.; Perera, S.K.; Langlois, G.W.; Doucette, G.J.; Powell, C.L. Receptor Binding Assay for Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins: Optimization and Interlaboratory Comparison. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Usup, G.; Leaw, C.-P.; Cheah, M.-Y.; Ahmad, A.; Ng, B.-K. Analysis of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxin congeners by a sodium channel receptor binding assay. Toxicon 2004, 44, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dolah, F.M.; Leighfield, T.A.; Doucette, G.J.; Bean, L.; Niedzwiadek, B.; Rawn, D.F.K. Single-laboratory validation of the microplate receptor binding assay for paralytic shellfish toxins in shellfish. J. AOAC Int. 2009, 92, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dolah, F.M.; Fire, S.E.; Leighfield, T.A.; Mikulski, C.M.; Doucette, G.J. Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Shellfish by Receptor Binding Assay: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 795–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Broadwater, M.; Van Dolah, F. Use of the receptor binding assay for determination of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in bivalve molluscs from Great Britain and the assessment of method performance in oysters. Toxicon 2018, 148, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Tarnovius, S.; Hatfield, R.G.; Teixeira-Alves, M.; Broadwater, M.; Van Dolah, F.; Garcia-Mendoza, E.; Medina, D.; Salhi, M.; Goya, A.B.; et al. Application of Six Detection Methods for Analysis of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Shellfish from Four Regions within Latin America. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdelais, A.J.; Campbell, S.; Jacocks, H.; Naar, J.; Wright, J.L.C.; Carsi, J.; Baden, D.G. Brevenal Is a Natural Inhibitor of Brevetoxin Action in Sodium Channel Receptor Binding Assays. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2004, 24, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourdelais, A.J.; Jacocks, H.M.; Wright, J.L.C.; Bigwarfe, P.M.; Baden, D.G. A New Polyether Ladder Compound Produced by the Dinoflagellate Karenia brevis. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hardison, D.R.; Holland, W.C.; McCall, J.R.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Baden, D.G.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Tester, P.A.; Shea, D.; Flores Quintana, H.A.; et al. Fluorescent Receptor Binding Assay for Detecting Ciguatoxins in Fish. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottein Dechraoui, M.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Ramsdell, J.S. Optimization of ciguatoxin extraction method from blood for Pacific ciguatoxin (P-CTX-1). Toxicon 2007, 49, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledreux, A.; Brand, H.; Chinain, M.; Bottein, M.-Y.D.; Ramsdell, J.S. Dynamics of ciguatoxins from Gambierdiscus polynesiensis in the benthic herbivore Mugil cephalus: Trophic transfer implications. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler, C.R.; Bodi, D.; Tartaglione, L.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Preiss-Weigert, A. Improving in vitro ciguatoxin and brevetoxin detection: Selecting neuroblastoma (Neuro-2a) cells with lower sensitivity to ouabain and veratridine (OV-LS). Harmful Algae 2021, 103, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roué, M.; Darius, H.T.; Picot, S.; Ung, A.; Viallon, J.; Gaertner-Mazouni, N.; Sibat, M.; Amzil, Z.; Chinain, M. Corrigendum to “Evidence of the bioaccumulation of ciguatoxins in giant clams (Tridacna maxima) exposed to Gambierdiscus spp. cells” [Harmful Algae 57 (2016) 78–87]. Harmful Algae 2017, 63, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vial, J.; Jardy, A. Experimental Comparison of the Different Approaches To Estimate LOD and LOQ of an HPLC Method. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 2672–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twiner, M.J.; Dechraoui, M.-Y.B.; Wang, Z.; Mikulski, C.M.; Henry, M.S.; Pierce, R.H.; Doucette, G.J. Extraction and analysis of lipophilic brevetoxins from the red tide dinoflagellate Karenia brevis. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 369, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardison, D.R.; Holland, W.C.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Tester, P.A.; Shea, D.; Bogdanoff, A.K.; Morris, J.A., Jr.; Quintana, H.A.F.; Loeffler, C.R.; et al. Investigation of ciguatoxins in invasive lionfish from the greater Caribbean region: Implications for fishery development. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCall, J.R.; Holland, W.C.; Keeler, D.M.; Hardison, D.R.; Litaker, R.W. Improved Accuracy of Saxitoxin Measurement Using an Optimized Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Toxins 2019, 11, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mattei, C.; Dechraoui, M.-Y.; Molgó, J.; Meunier, F.A.; Legrand, A.-M.; Benoit, E. Neurotoxins targetting receptor site 5 of voltage-dependent sodium channels increase the nodal volume of myelinated axons. J. Neurosci. Res. 1999, 55, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Mak, Y.L.; Murphy, M.B.; Lam, J.C.W.; Chan, W.H.; Wang, M.; Chan, L.L.; Lam, P.K.S. Validation of an accelerated solvent extraction liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for Pacific ciguatoxin-1 in fish flesh and comparison with the mouse neuroblastoma assay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 3165–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.R.; Estévez, P.; Soliño, L.; Castro, D.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Timoteo, V.; Leao-Martins, J.M.; Santos, C.; Gouveia, N.; Diogène, J.; et al. An Update on Ciguatoxins and CTX-like Toxicity in Fish from Different Trophic Levels of the Selvagens Islands (NE Atlantic, Madeira, Portugal). Toxins 2021, 13, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tester, P.A.; Kibler, S.R.; Holland, W.C.; Usup, G.; Vandersea, M.W.; Leaw, C.P.; Teen, L.P.; Larsen, J.; Mohammad-Noor, N.; Faust, M.A.; et al. Sampling harmful benthic dinoflagellates: Comparison of artificial and natural substrate methods. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, J.R.; Jacocks, H.M.; Niven, S.C.; A Poli, M.; Baden, D.G.; Bourdelais, A.J. Development and Utilization of a Fluorescence-Based Receptor-Binding Assay for the Site 5 Voltage-Sensitive Sodium Channel Ligands Brevetoxin and Ciguatoxin. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Scientific Opinion on marine biotoxins in shellfish—Emerging toxins: Ciguatoxin group. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, I.; Vieytes, M.R.; Alfonso, A. Analytical challenges for regulated marine toxins. Detection methods. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 18, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledreux, A.; Sérandour, A.-L.; Morin, B.; Derick, S.; Lanceleur, R.; Hamlaoui, S.; Furger, C.; Biré, R.; Krys, S.; Fessard, V.; et al. Collaborative study for the detection of toxic compounds in shellfish extracts using cell-based assays. Part II: Application to shellfish extracts spiked with lipophilic marine toxins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1995–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sérandour, A.-L.; Ledreux, A.; Morin, B.; Derick, S.; Augier, E.; Lanceleur, R.; Hamlaoui, S.; Moukha, S.; Furger, C.; Biré, R.; et al. Collaborative study for the detection of toxic compounds in shellfish extracts using cell-based assays. Part I: Screening strategy and pre-validation study with lipophilic marine toxins. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Fong, S.Y.T.; Hungerford, J.; McNabb, P.S.; Boundy, M.J.; Harwood, D.T.; Collaborators. Ultrahigh-Performance Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins and Tetrodotoxin in Mussels, Oysters, Clams, Cockles, and Scallops: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 533–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Toxin and Matrix | Parameters 1 | fRBA | rRBA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| References | This Study | [136] | [87,88,126] | [91] | [84] | |
| CTX3C | LOD = EC80 (ng mL−1) | 1.10 ± 0.08 | ND 2 | 0.90 ± 0.19 3 | ND | ND |
| LOQ = EC50 (ng mL−1) | 2.10 ± 0.16 | 0.66 ± 0.16 | 1.92 ± 0.38 3 | 0.62 ± 0.13 | 0.62 ± 0.16 | |
| EC20 (ng mL−1) | 4.06 ± 0.59 | ND | 4.17 ± 1.12 3 | ND | ND | |
| Gambierdiscus | MCE (cell mL−1) | 16,000 | ND | 7500 | ND | ND |
| LOD (fg CTX3C eq cell−1) | 68.53 ± 5.25 | ND | 250 | ND | 15.5 | |
| LOQ (fg CTX3C eq cell−1) | 131.32 ± 9.94 | ND | ND | ND | <310–330 | |
| Strain Name 1 | ID# | EC50 2 (cell mL−1) | Coefficient of Variation (CV %) 3 | CTX Content 2 (pg CTX3C eq cell−1) | Coefficient of Variation (CV %) 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RG92 | RG92-a | 1188 ± 563 | 51 | 2.04 ± 1.40 | 69 |
| RG92-b | 1926 ± 237 | 12 | 1.10 ± 0.15 | 14 | |
| RG92-c | 1314 ± 101 | 8 | 1.64 ± 0.17 | 10 | |
| RIK7 | RIK7-a | 482 ± 41 | 9 | 4.36 ± 0.14 | 3 |
| RIK7-b | 467 ± 64 | 14 | 4.54 ± 0.48 | 11 | |
| RIK7-c | 747 ± 36 | 5 | 2.88 ± 0.23 | 8 | |
| RIK7-d | 1006 ± 57 | 6 | 2.14 ± 0.13 | 6 | |
| RIK7-e | 448 ± 26 | 6 | 4.70 ± 0.18 | 4 | |
| RIK7-f | 1143 ± 89 | 8 | 1.89 ± 0.31 | 16 | |
| RIK7-g | 387 ± 14 | 4 | 5.56 ± 0.64 | 11 | |
| RIK7-h | 405 ± 20 | 5 | 5.19 ± 0.21 | 4 | |
| RIK7-i | 794 ± 85 | 11 | 2.74 ± 0.50 | 18 | |
| RIK7-j | 368 ± 24 | 6 | 5.87 ± 0.76 | 13 | |
| RIK7-k | 561 ± 47 | 8 | 3.76 ± 0.53 | 14 | |
| RIK7-l | 415 ± 51 | 12 | 5.07 ± 0.49 | 10 | |
| RAI1 | RAI1-a | 439 ± 43 | 10 | 4.90 ± 0.10 | 2 |
| RAI1-b | 439 ± 33 | 8 | 4.92 ± 0.66 | 13 | |
| RAI1-c | 377 ± 28 | 7 | 5.73 ± 0.73 | 13 | |
| RAI1-d | 442 ± 30 | 7 | 4.88 ± 0.50 | 10 | |
| RAI1-e | 376 ± 30 | 8 | 5.60 ± 0.35 | 6 | |
| RAI1-f | 466 ± 230 | 49 | 5.53 ± 2.12 | 38 | |
| RAI1-g | 579 ± 33 | 6 | 3.63 ± 0.45 | 12 | |
| RAI1-h | 360 ± 14 | 4 | 5.87 ± 0.73 | 13 | |
| NHA4 | NHA4-a | 267 ± 12 | 5 | 8.05 ± 0.40 | 5 |
| NHA4-b | 255 ± 16 | 6 | 8.27 ± 0.68 | 8 | |
| NHA4-c | 270 ± 15 | 6 | 7.97 ± 0.76 | 10 | |
| NHA4-d | 272 ± 19 | 7 | 7.72 ± 0.17 | 2 | |
| NHA4-e | 279 ± 15 | 5 | 7.53 ± 0.35 | 5 | |
| NHA4-f | 279 ± 8 | 3 | 7.70 ± 0.46 | 6 | |
| NHA4-g | 263 ± 11 | 4 | 8.01 ± 0.65 | 8 |
| OV Treatment | CTX3C 1 | Gambierdiscus Matrix 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O/V (µM) | LOD = EC80 (pg mL−1) | LOQ = EC50 (pg mL−1) | MCE (cell mL−1) | LOD (fg CTX3C eq cell−1) | LOQ (fg CTX3C eq cell−1) | References |
| 76.2/7.62 | ND 2 | ND | ND | 0.17 | 0.34 | [22] |
| 80/8 | ND | 3.10 ± 0.76 | ND | 0.17 | ND | [19,140] |
| (80/8–90/9) | ND | 1.91 ± 0.22 | ND | ND | ND | [89] |
| 90/9 | 0.63 ± 0.05 | 1.50 ± 0.23 | 1904 | 0.33 ± 0.03 | 0.79 ± 0.12 | This study |
| 100/10 | ND | ND | ND | ND | 8.7 × 10−4–4.7 × 10−2 | [93] 3 |
| ND | ND | ND | ND | 6.74–7.27 × 10−7 | [92] 3 | |
| 0.2 | ND | ND | ND | ND | [94] | |
| ND | 1.44 ± 0.70 | ND | 0.17 | ND | [96] | |
| ND | 1.73 ± 0.41 | ND | ND | ND | [115] | |
| ND | 1.84 ± 0.31 | ND | ND | N−D | [109] | |
| ND | 3.52 ± 0.27 | ND | ND | ND | [139] | |
| 250/25 | ND | 1.66 ± 0.16 | ND | ND | ND | [136] |
| ND | 1.66 ± 0.16 | ND | ND | ND | [95] | |
| 500/50 | ND | 0.91 ± 0.13 | ND | ND | ND | [138] |
| ND | 1.30 ± 0.06 | ND | ND | ND | [91] | |
| ND | 0.57 ± 0.11 | ND | ND | ND | [137] | |
| Strain Name 1 | ID# | EC50 2 (cell mL−1) | Coefficient of Variation (CV %) 3 | CTX Content 2 (pg CTX3C eq cell−1) | Coefficient of Variation (CV %) 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RG92 | RG92-a | 2.28 ± 0.54 | 24% | 0.68 ± 0.09 | 14 |
| RG92-b | 2.08 ± 0.46 | 23% | 0.68 ± 0.03 | 4 | |
| RG92-c | 2.15 ± 0.50 | 22% | 0.75 ± 0.10 | 14 | |
| RIK7 | RIK7-a | 0.73 ± 0.18 | 25% | 2.03 ± 0.12 | 6 |
| RIK7-b | 0.67 ± 0.10 | 15% | 2.19 ± 0.30 | 14 | |
| RIK7-c | 0.76 ± 0.09 | 12% | 2.03 ± 0.35 | 17 | |
| RIK7-d | 1.45 ± 0.39 | 27% | 1.10 ± 0.35 | 22 | |
| RIK7-e | 0.59 ± 0.13 | 23% | 2.53 ± 0.54 | 21 | |
| RIK7-f | 0.72 ± 0.09 | 12% | 2.14 ± 0.17 | 8 | |
| RIK7-g | 0.66 ± 0.13 | 20% | 2.34 ± 0.32 | 14 | |
| RIK7-h | 0.45 ± 0.14 | 30% | 3.39 ± 0.91 | 27 | |
| RIK7-i | 1.96 ± 0.31 | 16% | 0.79 ± 0.08 | 10 | |
| RIK7-j | 0.46 ± 0.08 | 17% | 3.33 ± 0.43 | 13 | |
| RIK7-k | 0.64 ± 0.16 | 25% | 2.32 ± 0.36 | 16 | |
| RIK7-l | 0.45 ± 0.13 | 29% | 3.31 ± 0.33 | 10 | |
| RAI1 | RAI1-a | 0.65 ± 0.17 | 26% | 2.44 ± 0.48 | 20 |
| RAI1-b | 0.60 ± 0.11 | 18% | 2.57 ± 0.31 | 12 | |
| RAI1-c | 0.65 ± 0.10 | 15% | 2.38 ± 0.41 | 22 | |
| RAI1-d | 0.43 ± 0.07 | 16% | 3.55 ± 0.16 | 5 | |
| RAI1-e | 0.50 ± 0.14 | 28% | 3.00 ± 0.24 | 8 | |
| RAI1-f | 0.55 ± 0.09 | 17% | 2.70 ± 0.35 | 13 | |
| RAI1-g | 0.64 ± 0.13 | 20% | 2.31 ± 0.16 | 7 | |
| RAI1-h | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 14% | 4.72 ± 0.31 | 7 | |
| NHA4 | NHA4-a | 0.31 ± 0.06 | 19% | 5.04 ± 0.63 | 13 |
| NHA4-b | 0.21 ± 0.06 | 27% | 6.93 ± 0.66 | 10 | |
| NHA4-c | 0.28 ± 0.06 | 20% | 5.75 ± 0.92 | 16 | |
| NHA4-d | 0.36 ± 0.14 | 38% | 4.21 ± 0.73 | 17 | |
| NHA4-e | 0.33 ± 0.05 | 16% | 4.45 ± 0.86 | 19 | |
| NHA4-f | 0.40 ± 0.06 | 16% | 3.90 ± 0.49 | 13 | |
| NHA4-g | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 29% | 9.72 ± 1.64 | 17 |
| CTX3C 1 | Gambierdiscus1 | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOD (ng mL−1) | LOQ (ng mL−1) | MCE (cell mL−1) | LOD (fg CTX3C eq cell−1) | LOQ (fg CTX3C eq cell−1) | |
| 2 | 6 | 100,000 | 20 | 60 | This study |
| 5 | 10 | ND 2 | ND | ND | [23] |
| 2 | 6 | ND | ND | ND | [109] |
| ND | 40 | ND | ND | [20–80] | [22] |
| 1 | ND | ND | ND | ND | [8,106] |
| 60 | ND | ND | ND | ND | [19] |
| 1–2 | ND | ND | ND | ND | [104] |
| ND | ND | ND | 0.005 | ND | [76] |
| Strain Name 1 | ID# | CTX3B 2 | CTX3C | CTX4A | CTX4B | M-Seco-CTX3C | 2OH-CTX3C | 3OH-CTX3C | CTX3C Isomers 4 | Total CTX Content 2 (pg CTX3C eq cell−1) | Coefficient of Variation (CV %) 5 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (6.90) | 2 (7.25) | 3 (7.70) | 4 (9.80) | 5 (10.10) | |||||||||||
| RG92 | RG92-a | 0.35 ± 0.01 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | <LOD 3 | 0.09 ± 0.00 | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 1.03 ± 0.10 | 10% |
| RG92-b | 0.41 ± 0.04 | 0.42 ± 0.11 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOQ 3 | <LOQ | 0.05 ± 0.03 | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 1.01 ± 0.14 | 14% | |
| RG92-c | 0.43 ± 0.01 | 0.47 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.04 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | <LOD | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 1.24 ± 0.06 | 5% | |
| RIK7 | RIK7-a | 1.33 ± 0.17 | 0.96 ± 0.13 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 0.11 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 0.09 ± 0.00 | 2.76 ± 0.31 | 11% |
| RIK7-b | 1.51 ± 0.02 | 1.12 ± 0.11 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | <LOD | 0.11 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.05 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 3.18 ± 0.18 | 6% | |
| RIK7-c | 0.98 ± 0.07 | 0.80 ± 0.04 | 0.10 ± 0.09 | 0.24 ± 0.07 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 2.27 ± 0.20 | 9% | |
| RIK7-d | 0.98 ± 0.06 | 0.56 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.04 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOQ | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | <LOD | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 1.81 ± 0.16 | 9% | |
| RIK7-e | 2.81 ± 0.21 | 1.42 ± 0.22 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.23 ± 0.07 | <LOD | <LOD | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 4.90 ± 0.48 | 10% | |
| RIK7-f | 1.37 ± 0.06 | 0.98 ± 0.06 | 0.15 ± 0.08 | 0.26 ± 0.07 | <LOD | 0.05 ± 0.00 | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 0.08 ± 0.05 | 3.08 ± 0.07 | 2% | |
| RIK7-g | 1.75 ± 0.03 | 1.31 ± 0.08 | 0.20 ± 0.12 | 0.43 ± 0.15 | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.00 | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 4.11 ± 0.16 | 4% | |
| RIK7-h | 3.16 ± 0.25 | 1.58 ± 0.17 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.18 ± 0.06 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOQ | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 5.25 ± 0.49 | 9% | |
| RIK7-i | 0.92 ± 0.03 | 0.57 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.06 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 1.87 ± 0.10 | 6% | |
| RIK7-j | 3.07 ± 0.08 | 1.71 ± 0.21 | 0.10 ± 0.04 | 0.17 ± 0.04 | <LOD | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 5.41 ± 0.24 | 4% | |
| RIK7-k | 1.96 ± 0.08 | 1.23 ± 0.17 | 0.19 ± 0.04 | 0.30 ± 0.09 | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.03 | <LOD | <LOQ | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 3.82 ± 0.35 | 9% | |
| RIK7-l | 3.26 ± 0.10 | 1.65 ± 0.09 | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.22 ± 0.06 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | <LOD | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 5.56 ± 0.12 | 2% | |
| RAI1 | RAI1-a | 1.81 ± 0.02 | 1.29 ± 0.04 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.17 ± 0.05 | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.00 | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 3.84 ± 0.01 | 0% |
| RAI1-b | 1.43 ± 0.04 | 1.10 ± 0.07 | 0.12 ± 0.05 | 0.19 ± 0.05 | <LOD | 0.10 ± 0.00 | <LOD | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 3.33 ± 0.05 | 2% | |
| RAI1-c | 1.46 ± 0.08 | 1.32 ± 0.01 | 0.20 ± 0.14 | 0.42 ± 0.13 | <LOD | 0.09 ± 0.00 | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 3.87 ± 0.28 | 7% | |
| RAI1-d | 2.73 ± 0.03 | 1.75 ± 0.17 | 0.12 ± 0.05 | 0.27 ± 0.08 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 5.12 ± 0.16 | 3% | |
| RAI1-e | 2.91 ± 0.18 | 2.12 ± 0.35 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.05 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | <LOQ | 0.08 ± 0.05 | 5.60 ± 0.52 | 9% | |
| RAI1-f | 1.40 ± 0.02 | 0.92 ± 0.06 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOQ | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 2.60 ± 0.14 | 6% | |
| RAI1-g | 1.76 ± 0.08 | 1.22 ± 0.11 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 0.23 ± 0.07 | <LOD | 0.05 ± 0.03 | <LOQ | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 3.61 ± 0.27 | 7% | |
| RAI1-h | 3.28 ± 0.15 | 1.91 ± 0.15 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.22 ± 0.06 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.08 ± 0.05 | 5.91 ± 0.32 | 5% | |
| NHA4 | NHA4-a | 3.74 ± 0.14 | 2.37 ± 0.10 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | <LOD | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 6.84 ± 0.21 | 3% |
| NHA4-b | 4.12 ± 0.19 | 2.44 ± 0.33 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.12 ± 0.04 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | <LOQ | 0.07 ± 0.00 | <LOQ | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 7.14 ± 0.51 | 7% | |
| NHA4-c | 4.31 ± 0.14 | 2.14 ± 0.16 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 7.25 ± 0.10 | 1% | |
| NHA4-d | 3.27 ± 0.10 | 2.53 ± 0.17 | 0.10 ± 0.02 | 0.18 ± 0.05 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | <LOD | <LOQ | 0.13 ± 0.07 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.08 ± 0.05 | 6.68 ± 0.19 | 3% | |
| NHA4-e | 4.32 ± 0.19 | 2.72 ± 0.50 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | <LOD | <LOQ | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 7.76 ± 0.70 | 9% | |
| NHA4-f | 3.66 ± 0.11 | 2.17 ± 0.07 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.04 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 6.74 ± 0.10 | 1% | |
| NHA4-g | 4.87 ± 0.18 | 2.67 ± 0.25 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.04 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | <LOD | 0.05 ± 0.03 | <LOQ | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 0.18 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | 8.25 ± 0.45 | 6% | |
| Method | Min | Max | Median | Mean | Standard Deviation of Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fRBA | 1.10 | 8.27 | 5.002 | 4.996 | 2.11 |
| CBA-N2a | 0.68 | 9.72 | 2.553 | 3.103 | 1.94 |
| LC-MS/MS | 1.01 | 8.25 | 3.990 | 4.395 | 2.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Darius, H.T.; Revel, T.; Viallon, J.; Sibat, M.; Cruchet, P.; Longo, S.; Hardison, D.R.; Holland, W.C.; Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W.; et al. Comparative Study on the Performance of Three Detection Methods for the Quantification of Pacific Ciguatoxins in French Polynesian Strains of Gambierdiscus polynesiensis. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060348
Darius HT, Revel T, Viallon J, Sibat M, Cruchet P, Longo S, Hardison DR, Holland WC, Tester PA, Litaker RW, et al. Comparative Study on the Performance of Three Detection Methods for the Quantification of Pacific Ciguatoxins in French Polynesian Strains of Gambierdiscus polynesiensis. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(6):348. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060348
Chicago/Turabian StyleDarius, Hélène Taiana, Taina Revel, Jérôme Viallon, Manoëlla Sibat, Philippe Cruchet, Sébastien Longo, Donnie Ransom Hardison, William C. Holland, Patricia A. Tester, R. Wayne Litaker, and et al. 2022. "Comparative Study on the Performance of Three Detection Methods for the Quantification of Pacific Ciguatoxins in French Polynesian Strains of Gambierdiscus polynesiensis" Marine Drugs 20, no. 6: 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060348
APA StyleDarius, H. T., Revel, T., Viallon, J., Sibat, M., Cruchet, P., Longo, S., Hardison, D. R., Holland, W. C., Tester, P. A., Litaker, R. W., McCall, J. R., Hess, P., & Chinain, M. (2022). Comparative Study on the Performance of Three Detection Methods for the Quantification of Pacific Ciguatoxins in French Polynesian Strains of Gambierdiscus polynesiensis. Marine Drugs, 20(6), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060348









