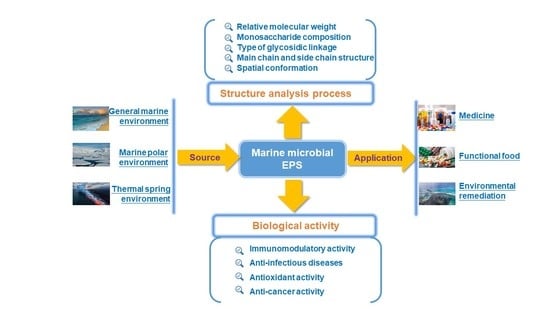
Exopolysaccharides from Marine Microbes: Source, Structure and Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Source of Marine EPS
2.1. EPS Produced by General Marine Environmental Microorganisms
2.2. EPS Produced by Polar Microorganisms
2.3. EPS from Marine Hot Spring Microorganisms
3. The Structural Characteristics of Marine EPS
3.1. Structural Characterization Methods of Marine Microbial EPS
3.2. Examples of Marine Microbial EPS in the Last Decade
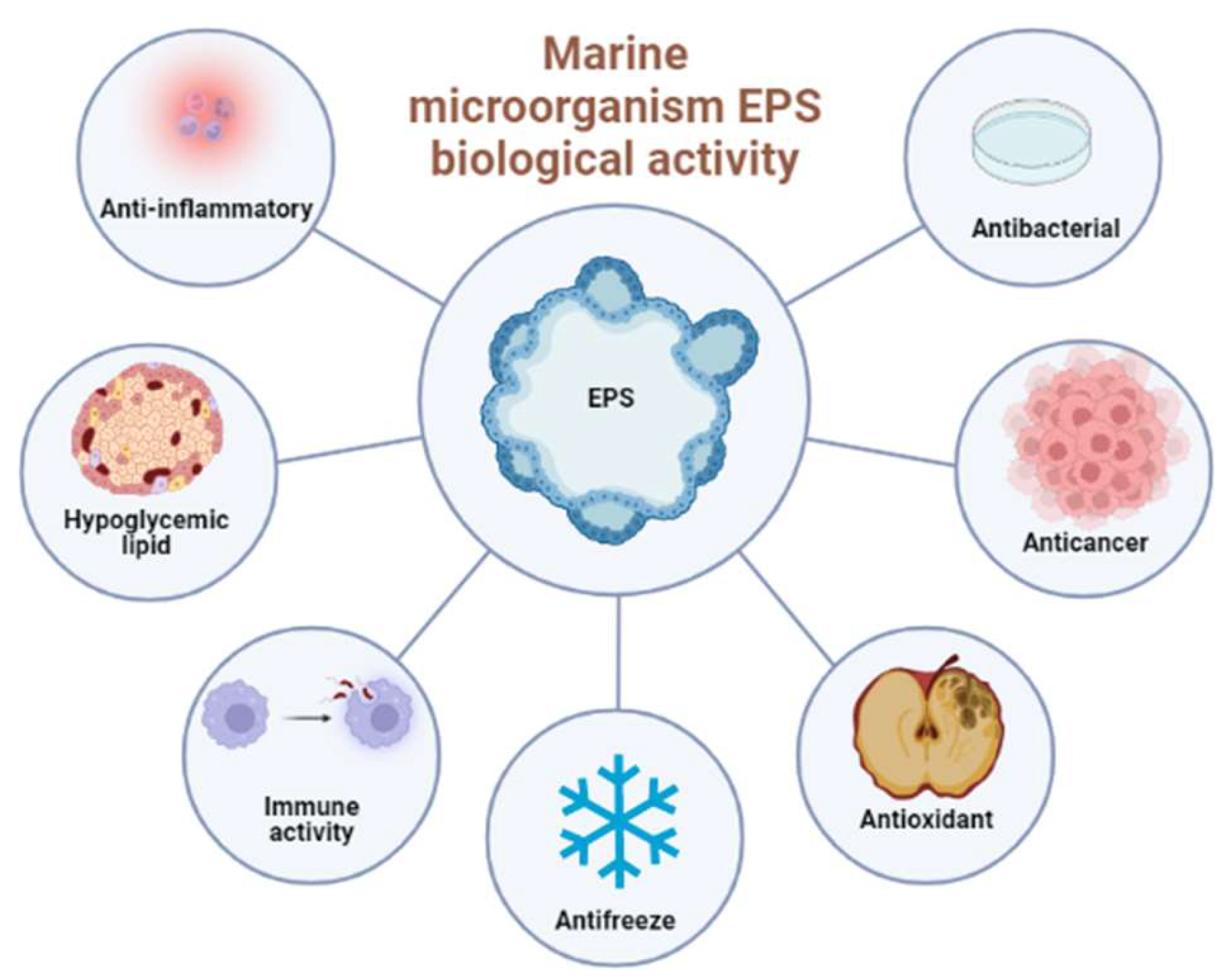
4. The Biological Activities of Marine EPS
4.1. Antioxidant Activity
4.2. Anti-Cancer Activity
4.3. Anti-Infectious Diseases
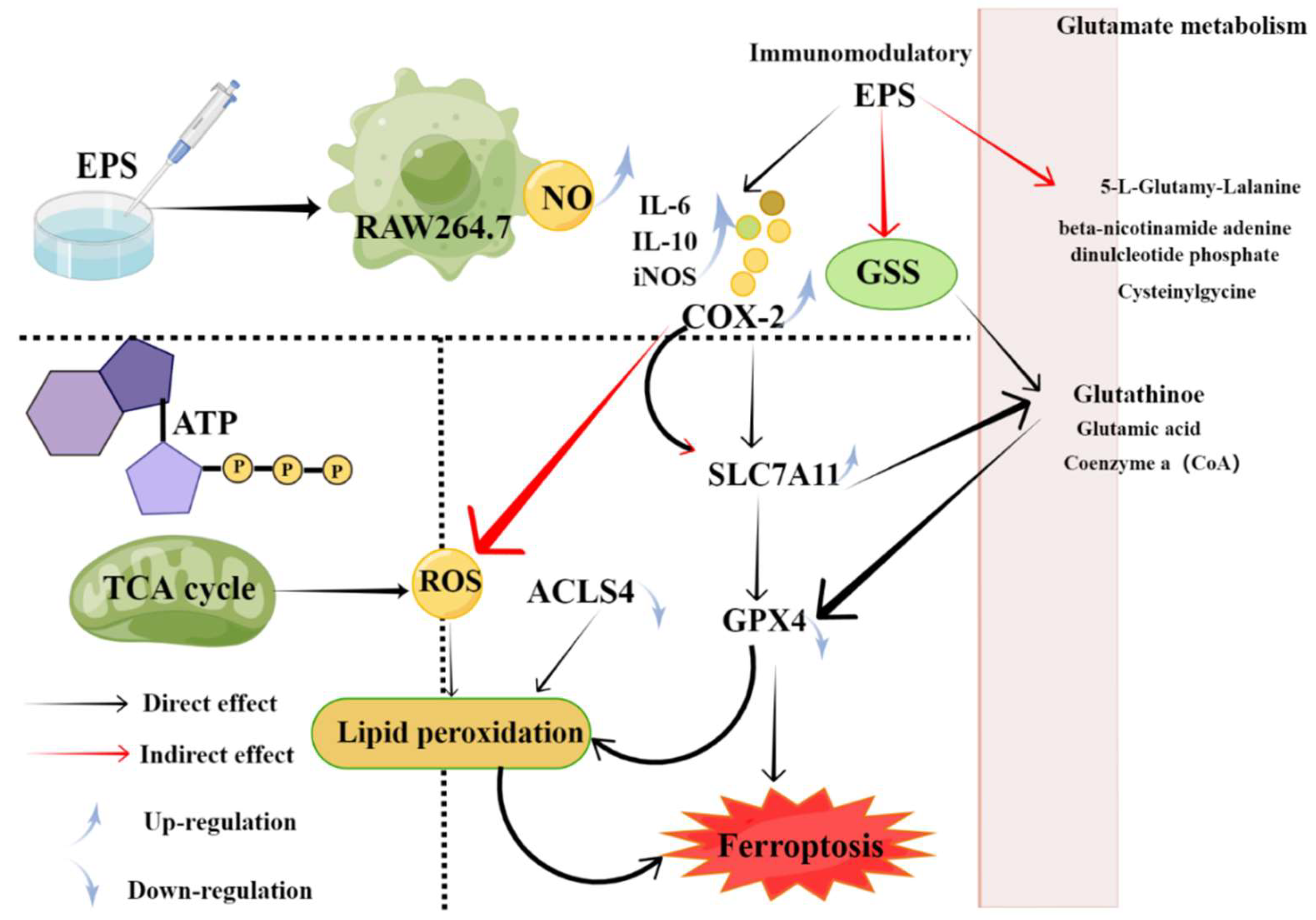
4.4. Immunomodulatory Activity
5. Environmental Remediation
5.1. Biological Restoration
5.2. Oil pollution Remediation
5.3. Carbon Sequestration
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López-Ortega, M.A.; Chavarría-Hernández, N.; del Rocio Lopez-Cuellar, M.; Rodríguez-Hernández, A.I. A review of extracellular polysaccharides from extreme niches: An emerging natural source for the biotechnology. From the adverse to diverse! Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzma, M.; Clack, B.; Edwards, J.; Tylingo, R.; Samaszko, J.; Madaj, J. Structure and properties of the exopolysaccharides produced by Pseudomonas mutabilis T6 and P. mutabilis ATCC 31014. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 348, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan-Lu, W.; Tzu-Huang, H.; Tzu-Wen, L.; Chun-Yong, F.; San-Lang, W. Production and characterization of exopolysaccharides and antioxidant from Paenibacillus sp. TKU023. New Biotechnol. 2011, 28, 559–565. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, D.N.; Reis, R.L.; Silva, T.H. Marine origin materials on biomaterials and advanced therapies to cartilage tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 6718–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decho, A.W.; Gutierrez, T. Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPSs) in Ocean Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravella, S.R.; Quiñones, T.S.; Retter, A.; Heiermann, M.; Amon, T.; Hobbs, P.J. Extracellular polysaccharide (EPS) production by a novel strain of yeast-like fungus Aureobasidium pullulans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wei, Z.; Li, S.; Xiao, R.; Xu, Q.; Ran, Y.; Ding, W. Plant secondary metabolite, daphnetin reduces extracellular polysaccharides production and virulence factors of Ralstonia solanacearum. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2021, 179, 104948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.S.; Mody, K.; Jha, B. Bacterial exopolysaccharides—A perception. J. Basic Microbiol. 2007, 47, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, C.A.M.; Guezennec, J.; Bowman, J.P. Bacterial exopolysaccharides from extreme marine environments with special consideration of the Southern Ocean, sea ice, and deep-sea hydrothermal vents: A review. Mar. Biotechnol. 2005, 7, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Katzen, F.; Pühler, A.; Ielpi, L. Xanthan gum biosynthesis and application: A biochemical /genetic perspective. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 50, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Du, G.; Chen, J. Microbial production of hyaluronic acid: Current state, challenges, and perspectives. Microb. Cell Factories 2011, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, A.; Anzelmo, G.; Nicolaus, B. Bacterial Exopolysaccharides from Extreme Marine Habitats: Production, Characterization and Biological Activities. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1779–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, M.; Jayaraman, G. Structural features of microbial exopolysaccharides in relation to their antioxidant activity. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcelos, M.C.S.; Vespermann, K.A.C.; Pelissari, F.M.; Molina, G. Current status of biotechnological production and applications of microbial exopolysaccharides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1475–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guezennec, J. Deep-sea hydrothermal vents: A new source of innovative bacterial exopolysaccharides of biotechnological interest. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot. 2002, 29, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornmann, H.; Duboc, P.; Marison, I.; von Stockar, U. Influence of nutritional factors on the nature, yield, and composition of exopolysaccharides produced by Gluconacetobacter xylinus I-2281. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2003, 69, 6091–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Zeev, E.; Rahav, E. Microbial metabolism of transparent exopolymer particles during the summer months along a eutrophic estuary system. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, Y.; Chennaoui, M.; Sylla, A.; Mountadar, M.; Rihani, M.; Assobhei, O. Characterization, structure, and function of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial biofilm in biological wastewater treatment systems: A review. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 16220–16237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaus, B.; Kambourova, M.; Oner, E.T. Exopolysaccharides from extremophiles: From fundamentals to biotechnology. Environ Technol 2010, 31, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivasagan, P.; Kim, S.K. Extracellular Polysaccharides Produced by Marine Bacteria. In Marine Medicinal Foods Implications and Applications, Macro and Microalgae; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 72, pp. 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Casillo, A.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Corsaro, M.M. Exopolysaccharides from Marine and Marine Extremophilic Bacteria: Structures, Properties, Ecological Roles and Applications. Mar. Drugs. 2018, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Sarkar, S.; Govil, T.; González-Faune, P.; Cabrera-Barjas, G.; Bandopadhyay, R.; Salem, D.R.; Sani, R.K. Extremophilic Exopolysaccharides: Biotechnologies and Wastewater Remediation. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 721365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acuna, N.; Ortega-Morales, B.O.; Valadez-Gonzalez, A. Biofilm colonization dynamics and its influence on the corrosion resistance of austenitic UNSS31603 stainless steel exposed to Gulf of Mexico seawater. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drira, M.; Elleuch, J.; Ben Hlima, H.; Hentati, F.; Gardarin, C.; Rihouey, C.; Le Cerf, D.; Michaud, P.; Abdelkafi, S.; Fendri, I. Optimization of Exopolysaccharides Production by Porphyridium sordidum and Their Potential to In-duce Defense Responses in Arabidopsis thaliana against Fusarium oxysporum. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, J. Recent insights in microbial exopolysaccharide biosynthesis and engineering strategies. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 53, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casillo, A.; Parrilli, E.; Sannino, F.; Mitchell, D.E.; Gibson, M.I.; Marino, G.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Cosconati, S.; Novellino, E.; et al. Structure activity relationship of the exopolysaccharide from a psychrophilic bacterium: A strategy for cryoprotection. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radchenkova, N.; Vassilev, S.; Martinov, M.; Kuncheva, M.; Panchev, I.; Vlaev, S.; Kambourova, M. Optimiza-tion of the aeration and agitation speed of Aeribacillus palidus 418 exopolysaccharide production and the emulsifying properties of the product. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccamo, M.T.; Gugliandolo, C.; Zammuto, V.; Magazu, S. Thermal properties of an exopolysaccharide produced by a marine thermotolerant Bacillus licheniformis by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 145, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccamo, M.T.; Zammuto, V.; Gugliandolo, C.; Madeleine-Perdrillat, C.; Spano, A.; Magazu, S. Thermal restraint of a bacterial exopolysaccharide of shallow vent origin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Peng, B.; Tian, Y. Structural characterization and functional evaluation of a novel exopolysaccharide from the moderate halophile Gracilibacillus sp. SCU50. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 154, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radchenkova, N.; Vassilev, S.; Panchev, I.; Anzelmo, G.; Tomova, I.; Nicolaus, B.; Kuncheva, M.; Petrov, K.; Kambourova, M. Production and Properties of Two Novel Exopolysaccharides Synthesized by a Thermophilic Bacterium Aeribacillus pallidus 418. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2013, 171, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Costaouëc, T.; Cérantola, S.; Ropartz, D.; Ratiskol, J.; Sinquin, C.; Colliec-Jouault, S.; Boisset, C. Structural data on a bacterial exopolysaccharide produced by a deep-sea Alteromonas macleodii strain. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erginer, M.; Akcay, A.; Coskunkan, B.; Morova, T.; Rende, D.; Bucak, S.; Baysal, N.; Ozisik, R.; Eroglu, M.S.; Agirbasli, M.; et al. Sulfated levan from Halomonas smyrnensis as a bioactive, heparin-mimetic glycan for cardiac tissue engineering applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 149, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahana, T.G.; Rekha, P.D. A novel exopolysaccharide from marine bacterium Pantoea sp. YU16-S3 accelerates cutaneous wound healing through Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 238, 116191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, C.B.; Behrenfeld, M.J.; Randerson, J.T.; Falkowski, P. Primary Production of the Biosphere: Integrating Terrestrial and Oceanic Components. Science 1998, 281, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rougeaux, H.; Guezennec, J.; Carlson, R.W.; Kervarec, N.; Pichon, R.; Talaga, P. Structural determination of the exopolysaccharide of Pseudoalteromonas strain HYD 721 isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent. Carbohydr. Res. 1999, 315, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliandolo, C.; Maugeri, T.L. Temporal variations in heterotrophic mesophilic bacteria from a marine shallow hydrothermal vent off the Island of Vulcano (Eolian Islands, Italy). Microb. Ecol. 1998, 36, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouault, S.C.; Chevolot, L.; Helley, D.; Ratiskol, J.; Bros, A.; Sinquin, C.; Roger, O.; Fischer, A.M. Characterization, chemical modifications and in vitro anticoagulant properties of an exopolysaccharide produced by Alteromonas infernus. BBA-Gen Subjects 2001, 1528, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchetta, P.; Lagarde, N.; Guezennec, J. A new bone-healing material: A hyaluronic acid like bacterial exopolysaccharide. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2003, 72, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.; Abu-Jdayil, B.; Olaimat, A.; Esposito, G.; Itsaranuwat, P.; Osaili, T.; Obaid, R.; Kizhakkayil, J.; Liu, S.Q. Physicochemical, bioactive and rheological properties of an exopolysaccharide produced by a probiotic Pediococcus pentosaceus M41. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, M.; Uthaya, C.J.; Thangavel, M.; Annadurai, V.; Rajendran, R.; Gurusamy, A. Optimization, compositional analysis, and characterization of exopolysaccharides produced by multimetal resistant Bacillus cereus KMS3-1. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Gnanakan, A.; Lakshmana, S.S.; Meivelu, M.; Jeganathan, A. Structural characterization and anti-cancer activity of extracellular polysaccharides from ascidian symbiotic bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 190, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavita, K.; Singh, V.K.; Mishra, A.; Jha, B. Characterization and anti-biofilm activity of extracellular polymeric substances from Oceanobacillus iheyensis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca, C.; Lehmann, M.; Torres, C.A.; Baptista, S.; Gaudêncio, S.P.; Freitas, F.; Reis, M.A. Exopolysaccharide production by a marine Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain isolated from Madeira Archipelago ocean sediments. New Biotechnol. 2016, 33, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; Geng, L.; Wang, Q.; Yue, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, N.; Wang, X.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Q. Purification, characterization and immunostimulatory activity of a novel exopolysaccharide from Bacillus sp. H5. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cai, R.; Zhang, W.; Fu, Y.; Jiao, N. A Novel Exopolysaccharide with Metal Adsorption Capacity Produced by a Marine Bacterium Alteromonas sp. JL2810. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanya, B.E.; Prabhu, A.; Rekha, P.D. Extraction and characterization of an exopolysaccharide from a marine bacterium. Int. Microbiol. 2022, 25, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almutairi, M.H.; Helal, M.M. Biological and microbiological activities of isolated Enterobacter sp. ACD2 exopolysaccharides from Tabuk region of Saudi Arabia. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2020, 33, 101328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, G.; Jin, W.; Xiu, P.; Sun, C. Antibiofilm and Anti-Infection of a Marine Bacterial Exopolysaccharide Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sran, K.S.; Bisht, B.; Mayilraj, S.; Choudhury, A.R. Structural characterization and antioxidant potential of a novel anionic exopolysaccharide produced by marine Microbacterium aurantiacum FSW-25. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selim, S.; Almuhayawi, M.S.; Alharbi, M.T.; Nagshabandi, M.K.; Alanazi, A.; Warrad, M.; Hagagy, N.; Ghareeb, A.; Ali, A.S. In Vitro Assessment of Antistaphylococci, Antitumor, Immunological and Structural Characterization of Acidic Bioactive Exopolysaccharides from Marine Bacillus cereus Isolated from Saudi Arabia. Metabolites 2022, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Li, J.B.; Han, F.; Duan, G.F.; Lu, X.Z.; Gu, Y.C.; Yu, W.G. Antibiofilm Activity of an Exopolysaccharide from Marine Bacterium Vibrio sp QY101. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, J.; Selvakumar, S.; Sathishkumar, R.; Moovendhan, M.; Ananthan, G.; Maruthiah, T.; Palavesam, A. In vitro antioxidant activities of an exopolysaccharide from a salt pan bacterium Halolactibacillus miurensis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 155, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Peng, B.; Tian, Y. Preparation, characterization and functional properties of a novel exopolysaccharide produced by the halophilic strain Halomonas saliphila LCB169T. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, G.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, P.G.; Zhang, Y. Structural characterization and ecological roles of a novel exopolysaccharide from the deep-sea psychrotolerant bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. SM9913. Microbiology 2007, 153, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrión, O.; Delgado, L.; Mercade, E. New emulsifying and cryoprotective exopolysaccharide from Antarctic Pseudomonas sp. ID1. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, P.; Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Hertkorn, N.; Gonsior, M.; Sajjad, W.; Chen, F. A Glacier Bacterium Produces High Yield of Cryoprotective Exopolysaccharide. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, C.; Rizzo, C.; Mangano, S.; Poli, A.; Di Donato, P.; Nicolaus, B.; Finore, I.; Di Marco, G.; Michaud, L.; Giudice, A.L. Isolation, characterization and optimization of EPSs produced by a cold-adapted Marinobacter isolate from Antarctic seawater. Antarct. Sci. 2019, 31, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-B.; Chen, X.-L.; He, H.-L.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Xie, B.-B.; Yu, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhou, B.-C.; Zhang, Y.Z. Structure and Ecological Roles of a Novel Exopolysaccharide from the Arctic Sea Ice Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. Strain SM20310. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wei, M.; Zhang, J.; Yue, Y.; Wu, N.; Geng, L.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J. Structural characteristics and immune-enhancing activity of an extracellular polysaccharide produced by marine Halomonas sp. 2E1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.K.; Gauri, S.S.; Dey, S. Sphingobactan, a new alpha-mannan exopolysaccharide from Arctic Sphingobacterium sp. IITKGP-BTPF3 capable of biological response modification. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 60, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Qian, W.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, K. Exopolysaccharide of Antarctic bacterium Pseudoaltermonas sp. S-5 induces apoptosis in K562 cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.L.; Zhao, F.; Shi, M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhou, B.C.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Chen, X.L. Characterization and Biotechnological Potential Analysis of a New Exopolysaccharide from the Arctic Marine Bacterium Polaribacter sp. SM1127. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.L.; Zhao, F.; Chen, X.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Song, X.Y.; Sun, C.Y.; Yang, J. Promotion of Wound Healing and Prevention of Frostbite Injury in Rat Skin by Exopolysaccharide from the Arctic Marine Bacterium Polaribacter sp. SM1127. Mar. Drugs. 2020, 18, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sran, K.S.; Sundharam, S.S.; Krishnamurthi, S.; Choudhury, A.R. Production, characterization and bioemulsifying activity of a novel thermostable exopolysaccharide produced by a marine strain of Rhodobacter johrii CDR-SL 7Cii. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 127, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zykwinska, A.; Berre, L.T.; Sinquin, C.; Ropartz, D.; Rogniaux, H.; Colliec-Jouault, S.; Delbarre-Ladrat, C. Enzymatic depolymerization of the GY785 exopolysaccharide produced by the deep-sea hydrothermal bacterium Alteromonas infernus: Structural study and enzyme activity assessment. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 188, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, O.; Kervarec, N.; Ratiskol, J.; Colliec-Jouault, S.; Chevolot, L. Structural studies of the main exopolysaccharide produced by the deep-sea bacterium Alteromonas infernus. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, D. Advances in Physicochemical Properties of Biopolymers; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Cao, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Liang, X. Structural Characterization and Biosorption of Exopolysaccharides from Anoxybacillus sp. R4-33 Isolated from Radioactive Radon Hot Spring. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 2732–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Pastor, M.; Ferreira, A.S.; Moppert, X.; Nunes, C.; Coimbra, M.A.; Reis, R.L.; Guezennec, J.; Novoa Carballal, R. Structure, rheology, and copper complexation of a hyaluronan-like exopolysaccharide from Vibrio. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 114999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaborieau, M.; Castignolles, P. Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) of branched polymers and polysaccharides. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Pang, X.; Wang, P.G.; Chen, M. Isolation and characterization of an antioxidant exopolysaccharide produced by Bacillus sp. S-1 from Sichuan Pickles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 204, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Yin, J.-Y.; Nie, S.-P.; Xie, M.-Y. Applications of infrared spectroscopy in polysaccharide structural analysis: Progress, challenge and perspective. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Yang, J.; Luo, L.; Zhang, X.; Deng, S.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Bekhit, A.E.A.; Xu, B.; Huang, R. Ferroptosis Related Immunomodulatory Effect of a Novel Extracellular Polysaccharides from Marine Fungus Aureobasidium melanogenum. Mar. Drugs. 2022, 20, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota, R.; Vidal, R.; Pandeirada, C.; Flores, C.; Adessi, A.; De Philippis, R.; Nunes, C.; Coimbra, M.A.; Tamagnini, P. Cyanoflan: A cyanobacterial sulfated carbohydrate polymer with emulsifying properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 229, 115525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ba-akdah, M.A.; Satheesh, S. Characterization and antifouling activity analysis of extracellular polymeric substances produced by an epibiotic bacterial strain Kocuria flava associated with the green macroalga Ulva lactuca. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2021, 40, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carillo, S.; Casillo, A.; Pieretti, G.; Parrilli, E.; Sannino, F.; Bayer-Giraldi, M.; Cosconati, S.; Novellino, E.; Ewert, M.; Deming, J.W.; et al. A Unique Capsular Polysaccharide Structure from the Psychrophilic Marine Bacterium Colwellia psychrerythraea 34H That Mimics Antifreeze (Glyco)proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasman, G.D. Circular dichroism and the conformational analysis of biomolecules; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zayed, A.; Mansour, M.K.; Sedeek, M.S.; Habib, M.H.; Ulber, R.; Farag, M.A. Rediscovering bacterial exopolysaccharides of terrestrial and marine origins: Novel insights on their distribution, biosynthesis, biotechnological production, and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 597–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidi, M.; Kozani, P.S.; Kozani, P.S.; Pierre, G.; Michaud, P.; Delattre, C. Marine Bacteria versus Microalgae: Who Is the Best for Biotechnological Production of Bioactive Compounds with Antioxidant Properties and Other Biological Applications? Mar. Drugs. 2020, 18, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraj, V.; Skillman, L.; Li, D.; Ho, G. Review—Bacteria and their extracellular polymeric substances causing biofouling on seawater reverse osmosis desalination membranes. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chunyan, W.; Wenjun, M.; Zhengqian, C.; Weiming, Z.; Yanli, C.; Chunqi, Z.; Na, L.; Mengxia, Y.; Xue, L.; Tiantian, G. Purification, structural characterization and antioxidant property of an extracellular polysaccharide from Aspergillus terreus. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Mao, W.-J.; Tao, H.-W.; Zhu, W.-M.; Yan, M.-X.; Liu, X.; Guo, T.-T.; Guo, T. Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Extracellular Polysaccharide with Antioxidant Activity, from the Mangrove-Associated Fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Mar. Biotechnol. 2015, 17, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Mao, W.-J.; Yan, M.-X.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.-Y.; Xia, Z.; Xiao, B.; Cao, S.-J.; Yang, B.-Q.; Li, J. Purification, Chemical Characterization, and Bioactivity of an Extracellular Polysaccharide Produced by the Marine Sponge Endogenous Fungus Alternaria sp. SP-32. Mar. Biotechnol. 2016, 18, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Mao, W.; Gao, Y.; Teng, X.; Zhu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Yan, M.; et al. Structural elucidation of an extracellular polysaccharide produced by the marine fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 93, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Mao, W.; Yang, Y.; Teng, X.; Zhu, W.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.; Hou, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Structure and antioxidant activity of an extracellular polysaccharide from coral-associated fungus, Aspergillus versicolor LCJ-5-4. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Mao, W.; Chen, C.; Kong, X.; Gu, Q.; Li, N.; Liu, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Xiao, B. Structural elucidation of the exopolysaccharide produced by the mangrove fungus Penicillium solitum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, K.; Cong, P.; Liu, Y.; Cui, H.; Xue, C. Structure characterization and antitumor activity of the extracellular polysaccharide from the marine fungus Hansfordia sinuosae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 190, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, M.F.D.; de Morais, R.M.S.C.; de Morais, A.M.M.B. Bioactivity and Applications of Sulphated Polysaccharides from Marine Microalgae. Mar. Drugs. 2013, 11, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroche, C. Exopolysaccharides from Microalgae and Cyanobacteria: Diversity of Strains, Production Strategies, and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esqueda, A.B.; Gardarin, C.; Laroche, C. Exploring the Diversity of Red Microalgae for Exopolysaccharide Production. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavian, Z.; Safavi, M.; Azizmohseni, F.; Hadizadeh, M.; Mirdamadi, S. Characterization, antioxidant and anticoagulant properties of exopolysaccharide from marine microalgae. AMB Express 2022, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.H.; Abou-ElWaf, G.S.; Shaaban-De, S.A.; Hassan, N.I. Characterization and Antioxidant Activity of Exopolysaccharide Secreted by Nostoc carneum. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 11, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Riofrío, G.; García-Márquez, J.; Casas-Arrojo, V.; Uribe-Tapia, E.; Abdala-Díaz, R. Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Effects on Tumor Cells of Exopolysaccharides from Tetraselmis suecica (Kylin) Butcher Grown Under Autotrophic and Heterotrophic Conditions. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargouch, N.; Elleuch, F.; Karkouch, I.; Tabbene, O.; Pichon, C.; Gardarin, C.; Rihouey, C.; Picton, L.; Abdelkafi, S.; Fendri, I.; et al. Potential of Exopolysaccharide from Porphyridium marinum to Contend with Bacterial Proliferation, Biofilm Formation, and Breast Cancer. Mar. Drugs. 2021, 19, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaignard, C.; Macao, V.; Gardarin, C.; Rihouey, C.; Picton, L.; Michaud, P.; Laroche, C. The red microalga Flintiella sanguinaria as a new exopolysaccharide producer. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2803–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafana, A. Characterization and optimization of production of exopolysaccharide from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhliariková, I.; Matulová, M.; Capek, P. Structural features of the bioactive cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. exopolysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2284–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhliariková, I.; Šutovská, M.; Barboríková, J.; Molitorisová, M.; Kim, H.J.; Park, Y.I.; Matulová, M.; Lukavský, J.; Hromadková, Z.; Capek, P. Structural characteristics and biological effects of exopolysaccharide produced by cyanobacterium Nostoc sp. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 160, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gongi, W.; Cordeiro, N.; Pinchetti, J.L.G.; Ben Ouada, H. Functional, rheological, and antioxidant properties of extracellular polymeric substances produced by a thermophilic cyanobacterium Leptolyngbya sp. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Li, H.; Dong, F.K.; Yan, F.; Cheng, M.; Li, W.Z.; Chang, Q.; Song, T.Z.; Liu, A.Y.; Song, B. Therapeutic Effect of Calcipotriol Pickering Nanoemulsions Prepared by Exopolysaccharides Produced by Bacillus halotolerans FYS Strain on Psoriasis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 10371–10384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besednova, N.N.; Smolina, T.P.; Andryukov, B.G.; Kuznetsova, T.A.; Mikhailov, V.V.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. Exopolysaccharides of Marine Bacteria: Prospects for Use in Medicine. Antibiot. Khimiote. 2018, 63, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.W.M.; Ibrahim, H.A.H. Production, Characterization and Valuable Applications of Exopolysaccharides from Marine Bacillus subtilis SH1. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.H.; Pan, T.M.; Wu, Y.J.; Chang, S.J.; Chang, M.S.; Hu, C.Y. Exopolysaccharide activities from probi-otic bifidobacterium: Immunomodulatory effects (on J774A.1 macrophages) and antimicrobial properties. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 144, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, M.-Y.; Ko, W.-C.; Lin, L.-Y. Hypolipidemic and Antioxidant Activity of Enoki Mushrooms (Flammulina velutipes). BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ding, F.; Xiao, L.; Shi, R.; Wang, H.; Han, W.; Huang, Z. Food-Derived Antioxidant Polysaccharides and Their Pharmacological Potential in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Nutrients 2017, 9, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Wu, C.; Liu, D.; Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liao, B.; He, H.; Li, H. Overview of Antioxidant Peptides Derived from Marine Resources: The Sources, Characteristic, Purification, and Evaluation Methods. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 1815–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Rhodes, C.J.; Moncol, J.; Izakovic, M.; Mazur, M. Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxida-tive stress-induced cancer. Chem. Biol. Interact 2006, 160, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, A.; Das, I.; Chandhok, D.; Saha, T. Redox regulation in cancer A double-edged sword with therapeu-tic potential. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2010, 3, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.T.; Beal, M.F. The oxidative damage theory of aging. Clin. Neurosci. Res. 2003, 2, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.D.; Ksiazek, K.; Menezes, R. Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Ageing. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Pop, A. The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squillaci, G.; Finamore, R.; Diana, P.; Restaino, O.F.; Schiraldi, C.; Arbucci, S.; Ionata, E.; La Cara, F.; Morana, A. Production and properties of an exopolysaccharide synthesized by the extreme halophilic archaeon Haloterrigena turkmenica. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2016, 100, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Yang, X.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Cao, M.; Ragauskas, A.; Thies, M.; Ding, J.; Zheng, Y. Investigation of composition, structure and bioactivity of extracellular polymeric substances from original and stress-induced strains of Thraustochytrium striatum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.-L.; Liu, S.-B.; Qiao, L.-P.; Chen, X.-L.; Pang, X.; Shi, M.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Qin, Q.-L.; Zhou, B.-C.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; et al. A novel exopolysaccharide from deep-sea bacterium Zunongwangia profunda SM-A87: Low-cost fermentation, moisture retention, and antioxidant activities. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 7437–7445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; You, W.; Huang, J.; Yu, Y.; Chen, W. Isolation and antioxidant property of the extracellular polysaccharide from Rhodella reticulata. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 26, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeber, F.; Holeiter, M.; Hampel, M.; Hinderer, S.; Schenke-Layland, K. Skin tissue engineering—In vivo and in vitro applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 352–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, S.; Chou, C.F.; Dinda, A.K.; Potdar, P.D.; Mishra, N.C. Surface modification of nanofibrous poly-caprolactone/gelatin composite scaffold by collagen type I grafting for skin tissue engineering. Mat. Sci. Eng. C Mater. 2014, 34, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Ning, K.; Ling, B.; Chen, X.; Cheng, H.; Lu, B.; Gao, Z.; Xu, J. Multiple Injections of Autologous Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Accelerate the Burn Wound Healing Process and Promote Blood Vessel Regeneration in a Rat Model. Stem Cells Dev. 2019, 28, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruk, G.; Roxo, M.; De Lise, F.; Mensitieri, F.; Notomista, E.; Wink, M.; Izzo, V.; Monti, D.M. The marine Gram-negative bacterium Novosphingobium sp. PP1Y as a potential source of novel metabolites with antioxidant activity. Biotechnol. Lett. 2018, 41, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, S.N.; Ermakova, S.P.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Stonik, V.A. Anticancer and Cancer Preventive Properties of Marine Polysaccharides: Some Results and Prospects. Mar. Drugs. 2013, 11, 4876–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, I.; Kim, S.-K. Immense Essence of Excellence: Marine Microbial Bioactive Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2673–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho, C.C.C.R.; Fernandes, P. Production of Metabolites as Bacterial Responses to the Marine Environment. Mar. Drugs. 2010, 8, 705–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satpute, S.K.; Banat, I.M.; Dhakephalkar, P.K.; Banpurkar, A.G.; Chopade, B.A. Biosurfactants, bioemulsifiers and exopolysaccharides from marine microorganisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 436–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aullybux, A.A.; Puchooa, D.; Bahorun, T.; Jeewon, R.; Wen, X.S.; Matin, P. Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activities of Exopolysaccharides from Alcaligenes faecalis Species Isolated from the Marine Environment of Mauritius. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 1462–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, R.; Shan, Y.; Sun, C. Marine bacterial exopolysaccharide EPS11 inhibits migration and invasion of liver cancer cells by directly targeting collagen I. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, X.; Wu, R.; Wu, J. Purification, characterization and antitumor activity of an exopolysaccharide produced by Bacillus velezensis SN-1. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Yamori, T.; Naitoh, M.; Okutani, K. Structural Revision of Sulfated Polysaccharide B-1 Isolated from a Marine Pseudomonas Species and Its Cytotoxic Activity Against Human Cancer Cell Lines. Mar. Biotechnol. 2003, 5, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahya, S.M.M.; Abdelnasser, S.M.; Hamed, A.R.; El Sayed, O.H.; Asker, M.S. Newly isolated marine bacterial exopolysaccharides enhance antitumor activity in HepG2 cells via affecting key apoptotic factors and activating toll like receptors. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 6231–6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyanagi, S.; Tanigawa, N.; Nakagawa, H.; Soeda, S.; Shimeno, H. Oversulfation of fucoidan enhances its anti-angiogenic and antitumor activities. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 65, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisuwan, W.; Jantanasakulwong, K.; Wangtueai, S.; Phimolsiripol, Y.; Chaiyaso, T.; Techapun, C.; Phongthai, S.; You, S.; Regenstein, J.M.; Seesuriyachan, P. Microbial exopolysaccharides for immune enhancement: Fermentation, modifications and bioactivities. Food Bio. Sci. 2020, 35, 100564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Cui, Y.; De Agostini, A.; Zhang, L. Chapter Eighteen—Biological mechanisms of glycan and glycosaminoglycan based nutraceuticals. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2019, 163, 445–469. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rubini, D.; Varthan, P.V.; Jayasankari, S.; Vedahari, B.N.; Nithyanand, P. Suppressing the phenotypic virulence factors of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli using marine polysaccharide. Microb Pathog. 2020, 141, 103973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huleihel, M.; Ishanu, V.; Tal, J.; Arad, S. Antiviral effect of red microalgal polysaccharides on Herpes simplex and Varicella zoster viruses. J. Appl. Phycol. 2001, 13, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huheihel, M.; Ishanu, V.; Tal, J.; Arad, S. Activity of Porphyridium sp. polysaccharide against herpes simplex viruses in vitro and in vivo. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2001, 50, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burston, M.; Ranasinghe, K.; Gardi, A.; Parezanović, V.; Ajaj, R.; Sabatini, R. Design principles and digital control of advanced distributed propulsion systems. Energy 2021, 241, 122788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.R.; Wala, S.M. Inflammation, Allergy and Asthma, Complex Immune Origin Diseases: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Agents. Recent Patents Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2013, 7, 62–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, A.; Maugeri, T.L.; Pavone, B.; Iannello, D.; Gugliandolo, C.; Bisignano, G. Antiviral and immunoregulatory effect of a novel exopolysaccharide from a marine thermotolerant Bacillus licheniformis. Int. Immunopharma. Col. 2006, 6, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Banerjee, A.; Halder, U.; Biswas, R.; Bandopadhyay, R. Degradation of Synthetic Azo Dyes of Textile Industry: A Sustainable Approach Using Microbial Enzymes. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, G.; Cao, J.; Huang, T.; Chen, K. Macrophage immunomodulatory activity of extracellular polysaccharide (PEP) of Antarctic bacterium Pseudoaltermonas sp.S-5. Int Immunopharmacol 2012, 12, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktan, F. iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production and its regulation. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujak, M.; Frangogiannis, N.G. The role of IL-1 in the pathogenesis of heart disease. Arch. Immunol. Et Ther. Exp. 2009, 57, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Z.; Gauldie, J.; Cox, G.; Baumann, H.; Jordana, M.; Lei, X.F.; Achong, M.K. IL-6 is an antiinflammatory cytokine required for controlling local or systemic acute inflammatory responses. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanAntwerp, D.J.; Martin, S.J.; Kafri, T.; Green, D.R.; Verma, I.M. Suppression of TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis by NF-kappa B. Science 1996, 274, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ding, R.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, R.; Gao, X.-D. Immunomodulatory Effects of Polysaccharide from Marine Fungus Phoma herbarumYS4108 on T Cells and Dendritic Cells. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafiuddin, A.; Fulazzaky, M.A. Decolorization kinetics and mass transfer mechanisms of Remazol Brilliant Blue R dye mediated by different fungi. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 29, e00573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, I.W. Biofilm exopolysaccharides: A strong and sticky framework. Microbiology 2001, 147, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Shen, B.; Meng, F.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. Coagulation enhancement of exopolysaccharide secreted by an Antarctic sea-ice bacterium on dye wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 76, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-F.; Li, X.-Y. Influences of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the characteristics of activated sludge under non-steady-state conditions. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, P.; Shukla, A.; Goswami, D.; Gaur, S.; Patel, B.; Saraf, M. Comprehensive depiction of novel heavy metal tolerant and EPS producing bioluminescent Vibrio alginolyticus PBR1 and V. rotiferianus PBL1 confined from marine organisms. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 238, 126526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lin, P.; Zhang, S.; Sun, L.; Xing, W.; Schwehr, K.A.; Chin, W.-C.; Wade, T.L.; Knap, A.H.; Hatcher, P.G.; et al. The interplay of extracellular polymeric substances and oil/Corexit to affect the petroleum incorporation into sinking marine oil snow in four mesocosms. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwabuchi, N.; Sunairi, M.; Urai, M.; Itoh, C.; Anzai, H.; Nakajima, M.; Harayama, S. Extracellular polysaccharides of Rhodococcus rhodochrous S-2 stimulate the degradation of aromatic components in crude oil by indigenous marine bacteria. Appl. Env. Microb 2002, 68, 2337–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepi, M.; Ro, A.C.; Liut, G.; Baldi, F. An antarctic psychrotrophic bacterium Halomonas sp. ANT-3b, growing on n-hexadecane, produces a new emulsyfying glycolipid. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2005, 53, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilori, M.O.; Amobi, C.J.; Odocha, A.C. Factors affecting biosurfactant production by oil degrading Aeromonas spp. isolated from a tropical environment. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.H.; Pearson, H.C.; Saba, G.K.; Olsen, E.M. Integral functions of marine vertebrates in the ocean carbon cycle and climate change mitigation. One Earth 2021, 4, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, F.; AlNadhari, S.; Al-Homaidan, A.A. Marine microorganisms as an untapped source of bioactive compounds. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 28, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimeno, J.; Faircloth, G.; Sousa-Faro, J.F.; Scheuer, P.; Rinehart, K. New Marine Derived Anticancer Therapeutics—A Journey from the Sea to Clinical Trials. Mar. Drugs. 2004, 2, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, T.; Sailakshmi, G.; Gnanamani, A.; Raja, S.T.K.; Thiruselvi, T.; Gowri, V.M.; Selvaraj, N.V.; Ramesh, G.; Mandal, A. Preparation and characterization of a thermostable and biodegradable biopolymers using natural cross-linker. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 48, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnosti, C. Microbial Extracellular Enzymes and the Marine Carbon Cycle. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2011, 3, 401–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, J.G.; Carpenter, S.D.; Deming, J.W. Production of cryoprotectant extracellular polysaccharide substances (EPS) by the marine psychrophilic bacterium Colwellia psychrerythraea strain 34H under extreme conditions. This article is one of a selection of papers in the Special Issue on Polar and Alpine Microbiology. Can. J. Microbiol. 2009, 55, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Mergelov, N.; Dolgikh, A.; Shorkunov, I.; Zazovskaya, E.; Soina, V.; Yakushev, A.; Fedorov-Davydov, D.; Pryakhin, S.; Dobryansky, A. Hypolithic communities shape soils and organic matter reservoirs in the ice-free landscapes of East Antarctica. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, A.; Krolikowski, M.; Fretwell, P.; Convey, P.; Peck, L.S.; Mendelova, M.; Smith, A.G.; Davey, M.P. Re-mote sensing reveals Antarctic green snow algae as important terrestrial carbon sink. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anesio, A.M.; Sattler, B.; Foreman, C.; Telling, J.; Hodson, A.; Tranter, M.; Psenner, R. Carbon fluxes through bacterial communities on glacier surfaces. Ann. Glaciol. 2010, 51, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anesio, A.M.; Hodson, A.J.; Fritz, A.; Psenner, R.; Sattler, B. High microbial activity on glaciers: Importance to the global carbon cycle. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Source | Name | Preparation Method | Monosaccharides Composition | Mw (Da) | Bioactivity | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pantoea sp. YU16-S3 | EPS-S3 | Ethanol precipitation extraction and purification by Sephacryl S500-HR column | Glc, Gal, GalNAc, GalN (1.9:1:0.4:0.02) | 1.75 × 105 | Promotion of Wound Healing | [34] |
| Pediococcus pentosaceus M41 | EPS-M41 | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by ultra-filtration | Ara, Man, Glc, Gal (1.2:1.8:15.1:1.0) | 6.8 × 105 | Antioxidant, Anticancer | [40] |
| Bacillus cereus KMS3-1 | EPS | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by dialysis | Man, Glc, Xyl, Rha (73.51:17.87:2.18:6.49) | Waste-water treatment | [41] | |
| Oceanobacillus iheyensis | EPS | Ethanol precipitation and purification by dialysis | Man, Glc, Ara (47.78:29.71:22.46) | 2.14 × 106 | Anti-biofilm | [43] |
| Bacillus thuringiensis RSK CAS4 | EPS | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by Sepharose 4-LB Fast Flow column | Fuc, Gal, Xyl, Glc, Rha, Man (43.8:20:17.8:7.2:7.1:4.1) | Antioxidant, Anticancer | [42] | |
| Pseudoalteromonas, MD12-642 | EPS | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by ultra-filtration | GalA, GlcA, Rha, GlcN (41–42:25–26:16–22:12–16) | >1.0 × 106 | [44] | |
| Bacillus sp. H5 | EPS5SH | Aqueous extraction and purification by GPC | Man, GlcN, Glc, Gal (1.00:0.02:0.07:0.02) | 8.9 × 104 | Immunomodulatory activity | [45] |
| Alteromonas sp. JL2810 | EPS | Ethanol precipitation extraction and purification by DEAE column | GalA, Man, Rha (1:1:1) | >1.67 × 105 | [46] | |
| Pseudoalteromonas sp. YU16-DR3A | EPS-DR3A | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by dialysis | Fuc, Erythrotetrose, Glc, Rib (6.7:1.0:1.5:1.0) | 2 × 104 | Antioxidant | [47] |
| Enterobacter sp. ACD2 | EPS | Culture centrifugal extraction | Glc, Gal, Fuc, GlcA (25:25:40:10) | Antibacterial | [48] | |
| P. stutzeri 273 | EPS273 | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by GPC | GlcN, Rha, Glc (35.4:28.6:27.2) | 1.9 × 105 | Antibiofilm, Anti-Infection | [49] |
| Microbacterim FSW-25 | EPS Mi25 | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by dialysis | Glc, Man, Fuc, GlcA | 7.0 × 106 | Antioxidant | [50] |
| Bacillus cereus | EPSR3 | Culture centrifugal extraction | Glc, GalA, Arb (2.0: 0.8: 1.0) | Antioxidant, Antitumor, Anti-inflammatory activities | [51] | |
| Vibrio sp. QY101 | A101 | Ethanol precipitation extraction and purification by GPC | GlcA, GalA, Rha, GlcN (21.47:23.05:23.90:12.15) | 5.46 × 103 | Antibacterial | [52] |
| Halolactibacillus miurensis | EPS | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by Sepharose 4-LB Fast Flow column | Gal, Glc (61.87:25.17) | Antioxidant | [53] | |
| Halomonas saliphila LCB169T | hsEPS | Ethanol precipitation, anion-exchange and gel-filtration chromatography | Man, Glc, Ara, Xyl, Gal, Fuc (81.22:15.83:1.47:0.59:0.55:0.35) | 5.133 × 104 | Emulsifying activity | [54] |
| C.psychrerythraea 34H | EPS | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by QFF column | QuiN, GalA (1:2) | Antifreeze | [26] | |
| Issachenkonii | SM20310 | Ethanol precipitation extraction and purification by DEAE column | Rha, Xyl, Man, Gal, Glc, GalNAc, GlcNAc (2.1:0.9:71.7:9.0:10.7:1.5:4.0) | >2.0 × 106 | Anti-freeze | [55] |
| Halomonas sp. 2E1 | EPS2E1 | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by DEAE column and Sephadex G75 column | Man, Glc (3.76:1) | 4.7 × 104 | Immunomodulatory activity | [56] |
| Sphingobacterium sp. IITKGP-BTPF3 | Sphingobatan | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by DEAE column | Man | >2 × 106 | Immunomodulatory activity | [57] |
| Pseudoaltermonas sp. | PEP | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by dialysis and GPC | Glc, Gal, Man (4.8:50.9:44.3) | 3.97 × 105 | Anticancer | [58] |
| Polaribacter sp. | SM1127 EPS | Ethanol precipitation extraction and purification by Sepharose column | Rha, Fuc, GlcA, Man, Gal, Glc, GlcNAc (0.8:7.4:21.4:23.4:17.3:1.6:28.0) | 2.2 × 105 | Promotion of Wound Healing, Prevention of Frostbite Injury, Antioxidant | [59,60] |
| Aeribacillus pallidus 418 | EPS1, EPS2 | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by Sepharose DEAE CL-6B column | Man, Glc, GalN, GlcN, Gal, Rib (69.3:11.2:6.3:5.4:4.7:2.9); Man, Gal, Glc, GalN, GlcN, Rib, Ara (33.9:17.9:15.5:11.7:8.1:5.3:4.9) | 7 × 105; >1 × 106 | [31] | |
| Rhodobacter johrii CDR-SL 7Cii | EPS RH-7 | Ethanol precipitation and purification by dialysis | Glc, GlcA, Rha, Gal (3:1.5:0.25:0.25) | 2 × 106 | Emulsifying activity | [61] |
| Alteromonas ininus | GY785 | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by ultra-filtration | Rha, Fuc, Man, Gal, Glc, GalA, GlcA (0.2:0.1:0.4: 3.6:4.7:1.0:2.0) | 2.0 × 106 | [62,63] |
| Source | Name | Preparation Method | Monosaccharides Composition | Mw (Da) | Bioactivity | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aureobasidium melanogenum SCAU-266 | AUM-1 | Alcohol precipitation and further purified through DEAE-column | Glc, Man, Gal (97.30:1.9:0.08) | 6.0 × 103 | Immunomodulatory activity | [74] |
| Aspergillus Terreus | YSS | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by QFF column | Glc, Man (8.6:1.0) | 1.86 × 104 | Antioxidant | [82] |
| Fusarium oxysporum | Fw-1 | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by QFF column | Gal, Glc, Man (1.33:1.33:1.00) | 6.12 × 104 | Antioxidant | [83] |
| Alternaria sp. | AS2-1 | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by QFF column | Man, Glc, Gal (1.00:0.67:0.35) | 2.74 × 104 | Anticancer, Antioxidant | [84] |
| Aspergillus versicolor | AWP | Culture centrifugal extractionand purification by QFF column | Glc, Man (8.6:1.0) | 5 × 107 | [85] | |
| Aspergillus versicolor | LCJ-5-4 | Culture centrifugal extractionand purification by QFF column | Glc, Man (1.7:1.0) | 7 × 103 | Antioxidant | [86] |
| Penicillium solitum | GW-12 | Ethanol precipitation, anion-exchange and size exclusion chromatography | Man | 1.13 × 104 | [87] | |
| Hansfordia sinuosae | HPA | Ethanol precipitation, anion-exchange and size exclusion chromatography | Man, Gal, Glc, (96.1, 3.3, and 0.60) | 2.25 × 104 | Anticancer | [88] |
| Source | Name | Preparation Method | Monosaccharides Composition | Mw (Da) | Bioactivity | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porphyridium sordidum | EPS | Cold aqueous centrifugal extraction and purification by dialysis | Fuc, Rha, Ara, Gal, Glc, Xyl, GlcA (1.93:0.36:0.36:48.28: 19.01:28.2:0.76) | Antibacterial | [24] | |
| Porphyridium marinum | EPS-0C, EPS-2C, EPS-5C | Culture centrifugal extraction, ultra-filtration and High-Pressure Homogenizer | Xyl, Gal, Glc, Fuc, Ara, GlcA (44–47:25–29:19–20:1:1–2:4–5) | 1.4 × 106 5.5 × 105 5.5 × 105 | Antibacterial, Anti-biofilm, Anticancer | [95] |
| Flintiella sanguinaria | EPS | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by ultra-filtration | Xyl, Gal, GlcA, Rha, Glc, Ara (47:21:14:10:6:2) | 1.5 × 106 | [96] | |
| Cyanothece sp. CCY 0110 | Cyanoflan | Cold aqueous extraction and purification by dialysis | Man, Glc, uronic acid, Gal, Xyl, Rha, Fuc, Ara (20:20:18:10:9:9:8:6) | >1 × 106 | [75] | |
| Chlamydonas reinhardtii | EPS | Culture centrifugal extraction | GalA, Rib, Rha, Ara, Gal, Glc, Xyl | 2.25 × 105 | Antioxidant | [97] |
| Nostoc carneum | EPS | Culture centrifugal extraction | Xyl, Glc (4.3:2.1) | Antioxidant | [93] | |
| Nostoc sp. | EPS | Culture centrifugal extraction and purification by DEAE column | Uronic acid, Rha, Fuc, Ara, Xyl, Man, Gal, Glc (25.0:0.2:0.8:18.6:15.3:19.1:1.3:19.7) | 2.37 × 105 | Antitussive, Immunomodulatory activity | [98,99] |
| Tetraselmis suecica | EPS | Cold aqueous extractionand purification by dialysis | Ara, Rib, Man, GalA, Gal, Glc, GlcA (5.23:0.83:6.64:0.1:25.27:35.46:21.47) | Antioxidant, Anticancer | [94] | |
| Leptolyngbya sp. | EPS | Culture centrifugal extraction | Man, Ara, Glc, Rha, uronic acid (35:24:15:2:8) | Antioxidant | [100] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, M.; Zheng, C.; Wu, W.; Yu, G.; Wang, P. Exopolysaccharides from Marine Microbes: Source, Structure and Application. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080512
Qi M, Zheng C, Wu W, Yu G, Wang P. Exopolysaccharides from Marine Microbes: Source, Structure and Application. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(8):512. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080512
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Mingxing, Caijuan Zheng, Wenhui Wu, Guangli Yu, and Peipei Wang. 2022. "Exopolysaccharides from Marine Microbes: Source, Structure and Application" Marine Drugs 20, no. 8: 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080512
APA StyleQi, M., Zheng, C., Wu, W., Yu, G., & Wang, P. (2022). Exopolysaccharides from Marine Microbes: Source, Structure and Application. Marine Drugs, 20(8), 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080512