Carrageenophyte Kappaphycus malesianus Inhibits Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation via Suppression of AKT/NF-κB and ERK Signaling Pathways
Abstract
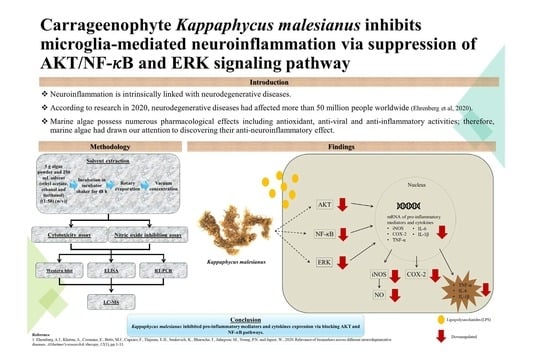
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of K. malesianus Extracts on the Viability of BV2 Microglia
2.2. Effect of K. malesianus Extracts on NO Production in LPS-Stimulated BV2 Microglia
2.3. Effects of K. malesianus Methanol Extract on iNOS and COX-2 Protein Expression in LPS-Stimulated BV2 Microglia
2.4. Effect of K. malesianus Methanol Extract on Proinflammatory Cytokines Expression in LPS-Stimulated BV2 Microglia
2.5. Effect of K. malesianus Methanol Extract on Proinflammatory Mediators in LPS-Stimulated BV2 Microglia Using RT-PCR
2.6. Effect of K. malesianus Methanol Extract on the AKT and ERK Signaling Pathway in LPS-Stimulated BV2 Microglia
2.7. Effect of K. malesianus Methanol Extract on the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in LPS-Stimulated BV2 Microglia
2.8. Proposed Bioactive Compounds Present in K. malesianus Methanol Extract
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Seaweed Collection and Extract Preparation
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2yl)-2,5-diphenyl Tetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Measurement of Nitric Oxide
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.7. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.8. Separation and Analysis of Major Compound(s) Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M. Age Structure. 2019. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/age-structure#citation (accessed on 29 April 2020).
- Feigin, V.L.; Nichols, E.; Alam, T.; Bannick, M.S.; Beghi, E.; Blake, N.; Culpepper, W.J.; Dorsey, E.R.; Elbaz, A.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephenson, J.; Nutma, E.; van der Valk, P.; Amor, S. Inflammation in CNS neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology 2018, 154, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Surguchov, A.; Bernal, L.; Surguchev, A.A. Phytochemicals as regulators of genes involved in synucleinopathies. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauss-Wegrzyniak, B.; Dobrzanski, P.; Stoehr, J.D.; Wenk, G.L. Chronic neuroinflammation in rats reproduces components of the neurobiology of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 1998, 780, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, L.R.; Maier, S.F.; Goehler, L.E. Immune activation: The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in inflammation, illness responses and pathological pain states. Pain 1995, 63, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, E.; Mychasiuk, R.; Hibbs, M.L.; Semple, B.D. Dysregulated phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling in microglia: Shaping chronic neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamian, E.S. AKT/GSK3 signaling pathway and schizophrenia. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Risso, G.; Blaustein, M.; Pozzi, B.; Mammi, P.; Srebrow, A. Akt/PKB: One kinase, many modifications. Biochem. J. 2015, 468, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Na, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, L. Roles of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways in neurodegenerative diseases and tumours. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baeuerle, P.A.; Henkel, T. Function and activation of NF-kappaB in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994, 12, 141–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Acquisto, F.; Iuvone, T.; Rombolà, L.; Sautebin, L.; Di Rosa, M.; Carnuccio, R. Involvement of NF-KB in the regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 protein expression in LPS-stimulated J774 macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1997, 418, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, Z.; Lu, P.; Wang, K.; Zhao, X.; Li, Q.; Wen, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, R.; Wei, H.; Lv, Y.; et al. Dexmedetomidine inhibits neuroinflammation by altering microglial M1/M2 polarization through MAPK/ERK pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrhman, A.M.; Ashour, M.; Al-Zahaby, M.A.; Sharawy, Z.Z.; Nazmi, H.; Zaki, M.A.; Ahmed, N.H.; Ahmed, S.R.; El-Haroun, E.; Van Doan, H.; et al. Effect of polysaccharides derived from brown macroalgae Sargassum dentifolium on growth performance, serum biochemical, digestive histology and enzyme activity of hybrid red tilapia. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 25, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, M.; Mabrouk, M.M.; Abo-Taleb, H.A.; Sharawy, Z.Z.; Ayoub, H.F.; Van Doan, H.; Davies, S.J.; El-Haroun, E.; Goda, A.M.A. A liquid seaweed extract (TAM®) improves aqueous rearing environment, diversity of zooplankton community, whilst enhancing growth and immune response of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, challenged by Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquaculture 2021, 543, 736915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, S.; Vinosha, M.; Marudhupandi, T.; Rajasekar, P.; Prabhu, N.M. Isolation of fucoidan from Sargassum polycystum brown algae: Structural characterization, in vitro antioxidant and anticancer activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shenody, R.A.; Ashour, M.; Ghobara, M.M.E. Evaluating the chemical composition and antioxidant activity of three Egyptian seaweeds: Dictyota dichotoma, Turbinaria decurrens, and Laurencia obtusa. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2019, 22, e2018203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elshobary, M.E.; El-Shenody, R.A.; Ashour, M.; Zabed, H.M.; Qi, X. Antimicrobial and antioxidant characterization of bioactive components from Chlorococcum minutum. Food Biosci. 2020, 35, 100567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, I.W.F.; Rodrigues, J.A.G.; Quinderé, A.L.G.; Silva, J.D.; de Freitas Marciel, G.; Ribeiro, N.A.; Vanderlei, E.D.; Ribeiro, K.A.; Chaves, H.V.; Pereira, K.M.; et al. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory actions on bradykinin route of a polysulfated fraction from alga Ulva lactuca. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berri, M.; Slugocki, C.; Olivier, M.; Helloin, E.; Jacques, I.; Salmon, H.; Demais, H.; Le Goff, M.; Collen, P.N. Marine-sulfated polysaccharides extract of Ulva armoricana green algae exhibits an antimicrobial activity and stimulates cytokine expression by intestinal epithelial cells. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 2999–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Abid, M.; Hussain, F. Antifungal activity of aqueous and methanolic extracts of some seaweeds against common soil-borne plant pathogenic fungi. Pak. J. Bot. 2017, 49, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Sornsiri, J.; Srisook, K.; Pornngam, P.; Sootanan, P. Prediction of biochemical mechanism of anti-inflammation explained from two marine-derived bioactive compounds. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2018, 52, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Mascuch, S.J.; Villa, F.A.; Byrum, T.; Teasdale, M.E.; Smith, J.E.; Preskitt, L.B.; Rowley, D.C.; Gerwick, L.; Gerwick, W.H. Honaucins A-C, potent inhibitors of inflammation and bacterial quorum sensing: Synthetic derivatives and structure-activity relationships. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motoyama, K.; Tanida, Y.; Hata, K.; Hayashi, T.; Hashim, I.I.; Higashi, T.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Irie, T.; Kaneko, S.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of novel polysaccharide sacran extracted from cyanobacterium Aphanothece sacrum in various inflammatory animal models. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, J.; Lim, P.E.; Phang, S.M.; Rahiman, A.; Nikmatullah, A.; Sunarpi, H.; Hurtado, A.Q. Kappaphycus malesianus sp. nov.: A new species of Kappaphycus (Gigartinales, Rhodophyta) from Southeast Asia. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganayaki, P.; Susmitha, S.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Study on metabolic compounds of Kappaphycus alvarezii and its in vitro analysis of anti-inflammatory activity. Int. J. Curr. Res. Acad. Rev. 2014, 2, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Tirtawijaya, G.; Haque, M.N.; Choi, J.S.; Moon, I.S.; Meinita, M.D.; Choi, J.S.; Hong, Y.K. Spinogenesis and synaptogenesis effects of the red seaweed Kappaphycus alvarezii and its isolated cholesterol on hippocampal neuron cultures. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 24, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Song, H.; Wang, L.; Jing, H. Characterization of key aroma-active compounds in black garlic by sensory-directed flavor analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7926–7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demange, L.; Dugave, C. Synthesis of phosphinic alanyl-proline surrogates Alaψ(PO2R-CH) Pro as potential inhibitors of the human cyclophilin hCyp-18. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 6295–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.S.; Yang, L.H.; Ye, J.L.; Huang, T.; Ruan, Y.P.; Fu, J.; Huang, P.Q. Diastereoselective synthesis and bioactivity of long-chain anti-2-amino-3-alkanols. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 5480–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, C.; Crews, P. Novel marine sponge amino acids, 10.1 xestoaminols from Xestospongia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira-Dorta, G.; Martín, V.S.; Padrón, J.M. Synthesis and antiproliferative activity of glutamic acid-based dipeptides. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takao, K.I.; Nigawara, Y.; Nishino, E.; Takagi, I.; Maeda, K.; Tadano, K.I.; Ogawa, S. Stereoselective total syntheses of (−)-desoxoprosopinine and (−)-desoxoprosophylline: Palladium(O)-catalyzed intramolecular N-alkylation for the key piperidine ring formation. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 5681–5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayanwuyi, L.O.; Yaro, A.H.; Abodunde, O.M. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of the methanol stem bark extract of Prosopis africana. Pharm. Biol. 2010, 48, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konishi, T.; Satsu, H.; Hatsugai, Y.; Aizawa, K.; Inakuma, T.; Nagata, S.; Sakuda, S.H.; Nagasawa, H.; Shimizu, M. Inhibitory effect of a bitter melon extract on the P-glycoprotein activity in intestinal Caco-2 cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 143, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.C.; Liaw, C.C.; Lin, M.K.; Chen, C.J.; Chao, C.L.; Chao, C.H.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chiu, Y.P.; Peng, Y.S.; Huang, H.C. Anti-influenza virus activity and chemical components from the parasitic plant Cuscuta japonica choisy on Dimocarpus longans Lour. Molecules 2020, 25, 4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, B.; Reichek, N.; Willenbrock, R.; Zannad, F.; Phillips, R.A.; Roniker, B.; Kleiman, J.; Krause, S.; Burns, D.; Williams, G.H. Effects of eplerenone, enalapril, and eplerenone/enalapril in patients with essential hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy: The 4E-left ventricular hypertrophy study. Circulation 2003, 108, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, B.; Remme, W.; Zannad, F.; Neaton, J.; Martinez, F.; Roniker, B.; Bittman, R.; Hurley, S.; Kleiman, J.; Gatlin, M. Eplerenone, a selective aldosterone blocker, in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.J. Eplerenone: Cardiovascular protection. Circulation 2003, 107, 2512–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, J.; Shimada, M.; Liu, W.; Hu, D.; Matsumori, A. Anti-inflammatory effects of eplerenone on viral myocarditis. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2009, 11, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grodowska, K.; Parczewski, A. Organic solvents in the pharmaceutical industry. Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica. Drug Res. 2010, 67, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, B.; Anwar, F.; Ashraf, M. Effect of extraction solvent/technique on the antioxidant activity of selected medicinal plant extracts. Molecules 2009, 14, 2167–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschel, W.; Sánchez-Rabaneda, F.; Diekmann, W.; Plescher, A.; Gartzía, I.; Jiménez, D.; Lameula-Raventos, R.; Buxaderas, S.; Codina, C. An industrial approach in the search of natural antioxidants from vegetable and fruit wastes. Food Chem. 2006, 97, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Robinson, N.A.; Warner, R.D.; Barrow, C.J.; Dunshea, F.R.; Suleria, H.A. LC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS characterization of seaweed phenolics and their antioxidant potential. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tiller, C.; Shen, J.; Wang, C.; Girouard, G.S.; Dennis, D.; Barrow, C.J.; Miao, M.; Ewart, H.S. Antidiabetic properties of polysaccharide- and polyphenolic-enriched fractions from the brown seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 85, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yahfoufi, N.; Alsadi, N.; Jambi, M.; Matar, C. The immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory role of polyphenols. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagarani, N.; Kumaraguru, A.K. Chemical characterization, temperature stability, and enzymatic studies on edible marine algae Kappaphycus alvarezii (Doty). J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2012, 21, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasooriya, R.G.P.T.; Kang, C.H.; Park, S.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Moon, D.O.; Kim, G.Y. Methanol extract of Polyopes lancifolius inhibits the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated BV2 microglia cells via downregulation of the NF-κB pathway. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 11, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wijesinghe, W.A.J.P.; Kang, M.C.; Lee, W.W.; Lee, H.S.; Kamada, T.; Vairappan, C.S.; Jeon, Y.J. 5β-Hydroxypalisadin B isolated from red alga Laurencia snackeyi attenuates inflammatory response in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Algae 2014, 29, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, E.J.; Moon, J.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, N.H.; Hyun, C.G. Anti-inflammatory effect of Petalonia binghamiae in LPS-induced macrophages is mediated by suppression of iNOS and COX-2. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2010, 12, 754–758. [Google Scholar]
- Sumayya, S.; Lubaina, A.; Murugan, K. Suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators via the inhibition of the NF-κB in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophage cells by purified terpenoid extract from Hypnea musciformis (Wulfen) J V Lamouroux. J. Adv. Sci. Res. 2020, 11, 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, S.; O’Gorman, D.M.; Nolan, Y.M. Evidence that the marine-derived multi-mineral aquamin has anti-inflammatory effects on cortical glial-enriched cultures. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 765–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbalace, M.C.; Malaguti, M.; Giusti, L.; Lucacchini, A.; Hrelia, S.; Angeloni, C. Anti-inflammatory activities of marine algae in neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, B.C.; Paik, J.H.; Kim, S.P.; Shin, D.H.; Song, D.K.; Park, J.G.; Suh, M.H.; Park, J.W.; Suh, S.I. Catalase induced expression of inflammatory mediators via activation of NF-κB, PI3K/AKT, p70S6K, and JNKs in BV2 microglia. Cell. Signal. 2005, 17, 25–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lee, W.W.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Cha, S.-H.; Jeon, Y.J. Dieckol, an algae-derived phenolic compound, suppresses airborne particulate matter-induced skin aging by inhibiting the expressions of pro-inflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases through regulating NF-κB, AP-1, and MAPKs signaling pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 146, 111823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.K.; Sung, S.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, S.G. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-inducible nitric oxide synthase, TNF-a and COX-2 expression by sauchinone effects on I-kBα, C/EBP and AP-1 activation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, H. Black garlic: Processing, composition change, and bioactivity. eFood 2020, 1, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V.; Kauloorkar, S.V.; Pradeep, K. Stereoselective approach to 2,6-disubstituted piperidin-3-ol: Synthesis of (–)-deoxoprosopinine and (+)-deoxoprosophylline. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 2014, 4897–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmita, A.O.; Ling, A.P.K.; Voon, K.G.L.; Koh, R.Y.; Wong, Y.P. Madecassoside activates anti-neuroinflammatory mechanisms by inhibiting lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 3033–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, T.; Sun, H.; Cheng, K.W.; Chen, F. Fucoxanthinol from the diatom Nitzschia laevis ameliorates neuroinflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV-2 microglia. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, B.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, Y.R.; Choi, J.J.; Yang, C.; Jang, I.S.; Lee, M.Y. Antineuroinflammatory and neuroprotective effects of Gyejibokryeong-Hwan in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglia. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 7585896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Kim, Y.T. Erythronium japonicum alleviates inflammatory pain by inhibiting MAPK activation and by suppressing NF-kB activation via ERK/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| No | Compound Name | Formula | Chemical Structure | m/z | Mass | Bioactivity | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 2,6-Nonadien-1-ol | C9H16O |  | 158.154 | 140.1201 | Key aroma-active compound that contributes fresh flavors to black garlic | [29] |
| 2. | Alanyl-Proline | C8H14N2O3 |  | 187.1075 | 186.1003 | Inhibitor of human cyclophilin hCyp-18 | [30] |
| 3. | Xestoaminol C | C14H31NO |  | 230.2478 | 229.2405 | Antitumor activity, antimicrobial activity and antiparasitic activity | [31,32] |
| 4. | Glutamyl-Proline | C10H16N2O5 |  | 245.1133 | 244.1059 | Antitumor activity | [33] |
| 5. | Prosopinine | C16H33NO3 |  | 288.2535 | 287.2463 | Anaesthetic activity; antibiotic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity | [34,35] |
| 6. | 1-Monopalmitin | C19H38O4 |  | 331.284 | 330.2768 | Antitumor activity, antiviral activity | [36,37] |
| 7. | Eplerenone | C24H30O6 |  | 415.2124 | 414.2048 | Reduced mortality and morbidity in patients with acute myocardial infarction; reduced blood pressure; antiinflammatory activity | [38,39,40,41] |
| mRNA Species | Primer Sequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| iNOS | 5′-TTGCCACGGACGAGACGGATAGG-3′ 5′-GGGCACATGCAAGGAAGGGAACTC-3′ | [60] |
| COX-2 | 5′-TGCTGGTGGAAAAACCTCGT-3′ 5′-GGTGCTCGGCTTCCAGTATT-3′ | [60] |
| TNF-α | 5′-GAAAAGCAAGCAGCCAACCA-3′ 5′-CGGATCATGCTTTCTGTGCTC-3′ | [61] |
| IL-1β | 5′-GCTGAAAGCTCTCCACCTCA-3′ 5′-AGGCCACAGGTATTTTGTCG-3′ | [62] |
| IL-6 | 5′-GAGGATACCACTCCCAACAGACC-3′ 5′-AAGTGCATCATCGTTGTTCATACA-3′ | [62] |
| GAPDH | 5′-GGAGCGAGACCCCACTAACAT-3′ 5′-GTGAGTTGTCATATTTCTCGTGG-3′ | [63] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, N.J.-Y.; Ngu, E.-L.; Pang, J.-R.; Wong, K.-H.; Ardianto, C.; Ming, L.C.; Lim, S.-H.; Walvekar, S.G.; Anwar, A.; Yow, Y.-Y. Carrageenophyte Kappaphycus malesianus Inhibits Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation via Suppression of AKT/NF-κB and ERK Signaling Pathways. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080534
Lai NJ-Y, Ngu E-L, Pang J-R, Wong K-H, Ardianto C, Ming LC, Lim S-H, Walvekar SG, Anwar A, Yow Y-Y. Carrageenophyte Kappaphycus malesianus Inhibits Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation via Suppression of AKT/NF-κB and ERK Signaling Pathways. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(8):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080534
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Nicole Jean-Yean, Ee-Ling Ngu, Jun-Rui Pang, Kah-Hui Wong, Chrismawan Ardianto, Long Chiau Ming, Siew-Huah Lim, Shweta Gangasa Walvekar, Ayaz Anwar, and Yoon-Yen Yow. 2022. "Carrageenophyte Kappaphycus malesianus Inhibits Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation via Suppression of AKT/NF-κB and ERK Signaling Pathways" Marine Drugs 20, no. 8: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080534
APA StyleLai, N. J.-Y., Ngu, E.-L., Pang, J.-R., Wong, K.-H., Ardianto, C., Ming, L. C., Lim, S.-H., Walvekar, S. G., Anwar, A., & Yow, Y.-Y. (2022). Carrageenophyte Kappaphycus malesianus Inhibits Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation via Suppression of AKT/NF-κB and ERK Signaling Pathways. Marine Drugs, 20(8), 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080534