Mutable Collagenous Tissue Isolated from Echinoderms Leads to the Production of a Dermal Template That Is Biocompatible and Effective for Wound Healing in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
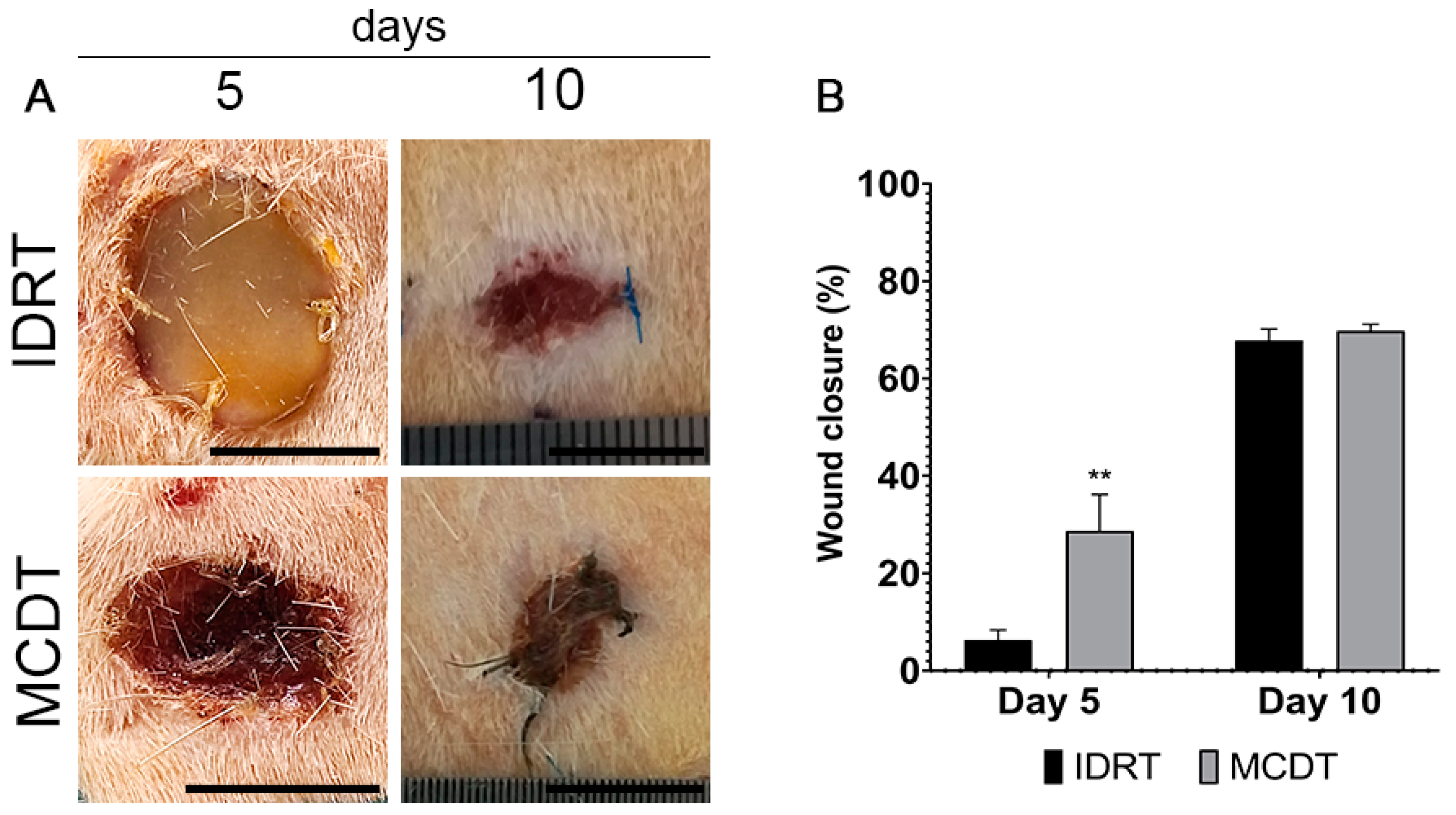
2.1. Clinical Follow-Up
2.2. Histological Analysis
2.3. Gene Expression Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Model and Ethical Statement
4.2. Sea Urchin Collagen Extraction, Production of 3D Scaffolds
4.3. Surgical Procedure and Clinical Follow-Up
4.4. Histological Analysis
4.5. Gene Expression Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borena, B.M.; Martens, A.; Broeckx, S.Y.; Meyer, E.; Chiers, K.; Duchateau, L.; Spaas, J.H. Regenerative Skin Wound Healing in Mammals: State-of-the-Art on Growth Factor and Stem Cell Based Treatments. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorg, H.; Tilkorn, D.J.; Hager, S.; Hauser, J.; Mirastschijski, U. Skin Wound Healing: An Update on the Current Knowledge and Concepts. Eur. Surg. Res. 2017, 58, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theoret, C. Tissue Engineering in Wound Repair: The Three “r”s—Repair, Replace, Regenerate. Vet. Surg. 2009, 38, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggs, J.; Jennings, J.L.F.; Friend, E.J.; Halfacree, Z.; Nelissen, P.; Holmes, M.A.; Demetriou, J.L. Outcome of Full-Thickness Skin Grafts Used to Close Skin Defects Involving the Distal Aspects of the Limbs in Cats and Dogs: 52 Cases (2005–2012). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2015, 247, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badis, D.; Omar, B. The Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma on the Skin Wound Healing Process: A Comparative Experimental Study in Sheep. Vet. World 2018, 11, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.C.; Paggiaro, A.O.; Isaac, C.; Teixeira Neto, N.; Santos, G.B. dos Substitutos Cutâneos: Conceitos Atuais e Proposta de Classificação. Rev. Bras. Cir. Plast. 2011, 26, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuono, C.B.; Langdon, R.; Birchall, N.; Barttelbort, S.; McGuire, J. Composite Autologous-Allogeneic Skin Replacement: Development and Clinical Application. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1987, 80, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramani, M.; Kumar, T.R.; Babu, M. Skin Substitutes: A Review. Burns 2001, 27, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansbrough, J.F.; Morgan, J.; Greenleaf, G.; Underwood, J. Development of a Temporary Living Skin Replacement Composed of Human Neonatal Fibroblasts Cultured in Biobrane, a Synthetic Dressing Material. Surgery 1994, 115, 633–644. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, I.; Currie, L.; Martin, R. A Guide to Biological Skin Substitutes. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 2002, 55, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, L.A.; De Caigny, P.; Guay, N.A.; Lineaweaver, W.C.; Shokrollahi, K. The Evidence Base for the Acellular Dermal Matrix AlloDerm: A Systematic Review. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2013, 70, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wester, J.L.; Pittman, A.L.; Lindau, R.H.; Wax, M.K. AlloDerm with Split-Thickness Skin Graft for Coverage of the Forearm Free Flap Donor Site. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2014, 150, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fourman, M.S.; Phillips, B.T.; Fritz, J.R.; Conkling, N.; McClain, S.A.; Simon, M.; Dagum, A.B. Laser-Assisted Indocyanine Green Dye Angiography Accurately Predicts the Split-Thickness Graft Timing of Integra Artificial Dermis. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2014, 73, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notodihardjo, S.C.; Morimoto, N.; Munisso, M.C.; Le, T.M.; Mitsui, T.; Kakudo, N.; Kusumoto, K. A Comparison of the Wound Healing Process after the Application of Three Dermal Substitutes with or without Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Impregnation in Diabetic Mice. JPRAS 2020, 73, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervelli, V.; Brinci, L.; Spallone, D.; Tati, E.; Palla, L.; Lucarini, L.; De Angelis, B. The Use of MatriDerm® and Skin Grafting in Post-Traumatic Wounds. Int. Wound J. 2011, 8, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.H.; Yun, I.S.; Lew, D.H.; Roh, T.S.; Lee, W.J. The Use of Matriderm and Autologous Skin Graft in the Treatment of Full Thickness Skin Defects. Arch. Plast. Surg. 2014, 41, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.H.; Moreira-Silva, J.; Marques, A.L.P.; Domingues, A.; Bayon, Y.; Reis, R.L. Marine Origin Collagens and Its Potential Applications. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5881–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizur Rahman, M. Collagen of Extracellular Matrix from Marine Invertebrates and Its Medical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melotti, L.; Martinello, T.; Perazzi, A.; Iacopetti, I.; Ferrario, C.; Sugni, M.; Sacchetto, R.; Patruno, M. A Prototype Skin Substitute, Made of Recycled Marine Collagen, Improves the Skin Regeneration of Sheep. Animals 2021, 11, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, D.L.; Yannas, I.V. Recent Advances in Tissue Synthesis in Vivo by Use of Collagen-Glycosaminoglycan Copolymers. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Benedetto, C.; Barbaglio, A.; Martinello, T.; Alongi, V.; Fassini, D.; Cullorà, E.; Patruno, M.; Bonasoro, F.; Barbosa, M.A.; Carnevali, M.D.C.; et al. Production, Characterization and Biocompatibility of Marine Collagen Matrices from an Alternative and Sustainable Source: The Sea Urchin Paracentrotus Lividus. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4912–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrario, C.; Leggio, L.; Leone, R.; Di Benedetto, C.; Guidetti, L.; Coccè, V.; Ascagni, M.; Bonasoro, F.; La Porta, C.A.M.; Candia Carnevali, M.D.; et al. Marine-Derived Collagen Biomaterials from Echinoderm Connective Tissues. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricarico, S.; Barbaglio, A.; Burlini, N.; Del Giacco, L.; Ghilardi, A.; Sugni, M.; Di Benedetto, C.; Bonasoro, F.; Wilkie, I.C.; Daniela Candia Carnevali, M. New Insights into the Mutable Collagenous Tissue of Paracentrotus Lividus: Preliminary Results. Zoosymposia 2010, 7, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkie, I.C.; Sugni, M.; Gupta, H.S.; Carnevali, M.D.C.; Elphick, M.R. The Mutable Collagenous Tissue of Echinoderms: From Biology to Biomedical Applications. In Soft Matter for Biomedical Applications; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2021; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkie, I.C. Mutable Collagenous Tissue: Overview and Biotechnological Perspective. Prog. Mol. Subcell. Biol. 2005, 39, 221–250. [Google Scholar]
- Bonasoro, F.; Carnevali, M.D.C.; Wilkie, I.C. The Peristomial Membrane of Regular Sea-Urchins: Functional Morphology of the Epidermis and Coelomic Lining in Paracentrotus Lividus (Lamarck). Bolletino Zool. 1995, 62, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.; Rusconi, F.; Pulaj, A.; Macchi, R.; Landini, P.; Paroni, M.; Colombo, G.; Martinello, T.; Melotti, L.; Gomiero, C.; et al. From Food Waste to Innovative Biomaterial: Sea Urchin-Derived Collagen for Applications in Skin Regenerative Medicine. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chocarro-Wrona, C.; López-Ruiz, E.; Perán, M.; Gálvez-Martín, P.; Marchal, J.A. Therapeutic Strategies for Skin Regeneration Based on Biomedical Substitutes. JEADV 2019, 33, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brem, H.; Tomic-Canic, M. Cellular and Molecular Basis of Wound Healing in Diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramió-Lluch, L.; Cerrato, S.; Brazis, P.; Rabanal, R.M.; Fondevila, D.; Puigdemont, A. Proof of Concept of a New Autologous Skin Substitute for the Treatment of Deep Wounds in Dogs. Vet. J. 2017, 230, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaasi, A.; Lima-Neto, J.F.; Matiello-Filho, J.A.; Calejo, M.H.S.; Jardini, A.L.; Kharmandayan, P. Regenerative Collagen Biomembrane: Interim Results of a Phase i Veterinary Clinical Trial for Skin Repair [Version 1; Referees: 2 Approved, 1 Approved with Reservations]. F1000Res 2018, 7, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunyaratavej, P.; Wang, H.-L. Collagen Membranes: A Review. J. Periodontol. 2001, 72, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneault, A.; Prawitt, J.; Fabien Soulé, V.; Coxam, V.; Wittrant, Y. Biological Effect of Hydrolyzed Collagen on Bone Metabolism. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1922–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juher, T.F.; Pérez, E.B. An Overview of the Beneficial Effects of Hydrolysed Collagen Intake on Joint and Bone Health and on Skin Ageing. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 32, 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Fassini, D.; Wilkie, I.C.; Pozzolini, M.; Ferrario, C.; Sugni, M.; Rocha, M.S.; Giovine, M.; Bonasoro, F.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Diverse and Productive Source of Biopolymer Inspiration: Marine Collagens. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 1815–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monavarian, M.; Kader, S.; Moeinzadeh, S.; Jabbari, E. Regenerative Scar-Free Skin Wound Healing. Tissue Eng. Part. B. Rev. 2019, 25, 294–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.; Kosaric, N.; Bonham, C.A.; Gurtner, G.C. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 665–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.H.; Huang, B.S.; Horng, H.C.; Yeh, C.C.; Chen, Y.J. Wound Healing. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2018, 81, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosique, R.G.; Rosique, M.J.; Farina Junior, J.A. Curbing Inflammation in Skin Wound Healing: A Review. Int. J. Inflam. 2015, 2015, 316235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke, N.B.; Ward, K.R.; Witten, T.M.; Bonchev, D.G.; Diegelmann, R.F. Impaired Wound Healing. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borish, L.C.; Steinke, J.W. 2. Cytokines and Chemokines. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, S460–S475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehrel, B. Platelet Receptors for Collagens. Platelets 1995, 6, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farndale, R.W. Collagen-Induced Platelet Activation. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2006, 36, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonmez, O.; Sonmez, M. Role of Platelets in Immune System and Inflammation. Porto Biomed. J. 2017, 2, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ollivier, V.; Syvannarath, V.; Gros, A.; Butt, A.; Loyau, S.; Jandrot-Perrus, M.; Ho-Tin-Noé, B. Collagen Can Selectively Trigger a Platelet Secretory Phenotype via Glycoprotein VI. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.; Vavken, P.; Kevy, S.; Jacobson, M.; Zurakowski, D.; Murray, M.M. Platelet Activation by Collagen Provides Sustained Release of Anabolic Cytokines. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Jain, R.K. Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Applications of Angiogenesis. Nature 2011, 473, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landén, N.X.; Li, D.; Ståhle, M. Transition from Inflammation to Proliferation: A Critical Step during Wound Healing. CMLS 2016, 73, 3861–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.A.; Araujo, T.A.; Avanzi, I.R.; Parisi, J.R.; de Andrade, A.L.M.; Rennó, A.C.M. Collagen from Marine Sources and Skin Wound Healing in Animal Experimental Studies: A Systematic Review. Mar. Biotechnol. 2021, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbialy, Z.I.; Atiba, A.; Abdelnaby, A.; Al-Hawary, I.I.; Elsheshtawy, A.; El-Serehy, H.A.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Fadl, S.E.; Assar, D.H. Collagen Extract Obtained from Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus L.) Skin Accelerates Wound Healing in Rat Model via up Regulating VEGF, BFGF, and α-SMA Genes Expression. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Chen, B.; Yan, X.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Hou, X.; Dai, J. Promotion of Diabetic Wound Healing by Collagen Scaffold with Collagen-Binding Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in a Diabetic Rat Model. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2014, 8, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Van Den Diepstraten, C.; D’Souza, S.J.; Chan, B.M.C.; Pickering, J.G. Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Orchestrate the Assembly of Type I Collagen via Alpha2beta1 Integrin, RhoA, and Fibronectin Polymerization. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiano, R.D.; Michaels, V.J.; Dobryansky, M.; Levine, J.P.; Gurtner, G.C. Quantitative and Reproducible Murine Model of Excisional Wound Healing. Wound Repair. Regen. 2004, 12, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, J.M. Animal Models for Wound Repair. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1998, 290 (Suppl. 1), S1–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, W.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, G.; He, J.; Li, Q. A Novel Model for Cutaneous Wound Healing and Scarring in the Rat. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 143, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häkkinen, L.; Larjava, H.; Koivisto, L. Granulation Tissue Formation and Remodeling. Endod. Top. 2011, 24, 94–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurtner, G.C.; Werner, S.; Barrandon, Y.; Longaker, M.T. Wound Repair and Regeneration. Nature 2008, 453, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| GAPDH | FW: 5′-CCATTCTTCCACCTTTGATGCT-3′ RW: 5′-TGTTGCTGTAGCCATATTCATTGT-3′ |
| β-ACT | FW: 5′-CCGTAAAGACCTCTATGCCA-3′ RW: 5′-AAGAAAGGGTGTAAAACGCA-3′ |
| IL-1β | FW: 5′-GACAAGCAACGACAAAATCCC-3′ RW: 5′-TGGGTATTGTTTGGGATCCAC-3′ |
| TGF-β1 | FW: 5′-CCCCTGGAAAGGGCTCAACAC-3′ RW: 5′-TCCAACCCAGGTCCTTCCTAAAGTC-3′ |
| TNF-α | FW: 5′-AGCCTCTTCTCATTCCTGCTC-3′ RW: 5′-GTTTGCTACGACGTGGGCTAC-3′ |
| COL1A1 | FW: 5′-ATCAGCCCAAACCCCAAGGAGA-3′ RW: 5′-CGCAGGAAGGTCAGCTGGATAG-3′ |
| COL3A1 | FW: 5′-TGATGGGATCCAATGAGGGAGA-3′ RW: 5′-GAGTCTCATGGCCTTGCGTGTTT-3′ |
| PDGFb | FW: 5′-TGGAGTCGAGTCGGAAAGCT-3′ RW: 5′-GAAGTTGGCATTGGTGCGAT-3′ |
| VEGF | FW: 5′-ATCATGCGGATCAAACCTCACC-3′ RW: 5′-GGTCTGCATTCACATCTGCTATGC-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carolo, A.; Melotti, L.; Zivelonghi, G.; Sacchetto, R.; Akyürek, E.E.; Martinello, T.; Venerando, A.; Iacopetti, I.; Sugni, M.; Martinelli, G.; et al. Mutable Collagenous Tissue Isolated from Echinoderms Leads to the Production of a Dermal Template That Is Biocompatible and Effective for Wound Healing in Rats. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21100506
Carolo A, Melotti L, Zivelonghi G, Sacchetto R, Akyürek EE, Martinello T, Venerando A, Iacopetti I, Sugni M, Martinelli G, et al. Mutable Collagenous Tissue Isolated from Echinoderms Leads to the Production of a Dermal Template That Is Biocompatible and Effective for Wound Healing in Rats. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(10):506. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21100506
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarolo, Anna, Luca Melotti, Giulia Zivelonghi, Roberta Sacchetto, Eylem Emek Akyürek, Tiziana Martinello, Andrea Venerando, Ilaria Iacopetti, Michela Sugni, Giordana Martinelli, and et al. 2023. "Mutable Collagenous Tissue Isolated from Echinoderms Leads to the Production of a Dermal Template That Is Biocompatible and Effective for Wound Healing in Rats" Marine Drugs 21, no. 10: 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21100506










